How to Improve Transparency in Cellophane Films?
JUL 9, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Cellophane Transparency Evolution and Objectives
Cellophane films have undergone significant evolution since their inception in the early 20th century. Initially developed as a moisture-proof packaging material, cellophane has continuously improved in terms of transparency, strength, and versatility. The journey towards enhanced transparency began with the basic cellulose-based film, which offered moderate clarity but was limited by its inherent yellowish tint and susceptibility to moisture.
As market demands for clearer packaging materials grew, researchers focused on refining the production process and introducing additives to enhance transparency. The 1950s and 1960s saw the development of improved manufacturing techniques, including better purification methods for cellulose and the introduction of plasticizers, which significantly boosted the film's clarity. These advancements led to a new generation of cellophane with markedly improved optical properties.
The late 20th century brought about further innovations, with the integration of nanotechnology and advanced polymer science. These developments allowed for the creation of ultra-thin, highly transparent cellophane films that maintained excellent barrier properties. The focus shifted towards achieving optical clarity comparable to that of synthetic polymers while retaining cellophane's biodegradability and eco-friendly characteristics.
Current objectives in cellophane transparency improvement are multifaceted. Primarily, there is a drive to achieve near-perfect optical clarity without compromising the material's inherent biodegradability. This involves refining the cellulose structure at the molecular level to minimize light scattering and absorption. Additionally, researchers aim to develop coatings and treatments that can enhance transparency while simultaneously improving moisture resistance and mechanical strength.
Another key objective is to maintain transparency across a wider range of environmental conditions. This includes developing cellophane films that remain clear under varying humidity levels and temperatures, addressing a long-standing challenge in the material's application. Furthermore, there is a growing emphasis on creating cellophane films with selective transparency, allowing certain wavelengths of light to pass while blocking others, which could have significant implications for food preservation and packaging design.
The pursuit of improved transparency in cellophane films is also closely tied to sustainability goals. As such, current research is focused on achieving these optical improvements using eco-friendly processes and materials. This includes exploring bio-based additives and green chemistry approaches to enhance clarity without introducing harmful substances or increasing the environmental footprint of production.
As market demands for clearer packaging materials grew, researchers focused on refining the production process and introducing additives to enhance transparency. The 1950s and 1960s saw the development of improved manufacturing techniques, including better purification methods for cellulose and the introduction of plasticizers, which significantly boosted the film's clarity. These advancements led to a new generation of cellophane with markedly improved optical properties.
The late 20th century brought about further innovations, with the integration of nanotechnology and advanced polymer science. These developments allowed for the creation of ultra-thin, highly transparent cellophane films that maintained excellent barrier properties. The focus shifted towards achieving optical clarity comparable to that of synthetic polymers while retaining cellophane's biodegradability and eco-friendly characteristics.
Current objectives in cellophane transparency improvement are multifaceted. Primarily, there is a drive to achieve near-perfect optical clarity without compromising the material's inherent biodegradability. This involves refining the cellulose structure at the molecular level to minimize light scattering and absorption. Additionally, researchers aim to develop coatings and treatments that can enhance transparency while simultaneously improving moisture resistance and mechanical strength.
Another key objective is to maintain transparency across a wider range of environmental conditions. This includes developing cellophane films that remain clear under varying humidity levels and temperatures, addressing a long-standing challenge in the material's application. Furthermore, there is a growing emphasis on creating cellophane films with selective transparency, allowing certain wavelengths of light to pass while blocking others, which could have significant implications for food preservation and packaging design.
The pursuit of improved transparency in cellophane films is also closely tied to sustainability goals. As such, current research is focused on achieving these optical improvements using eco-friendly processes and materials. This includes exploring bio-based additives and green chemistry approaches to enhance clarity without introducing harmful substances or increasing the environmental footprint of production.
Market Demand for High-Transparency Packaging
The demand for high-transparency packaging has been steadily increasing across various industries, driven by consumer preferences and evolving market trends. In the food and beverage sector, transparent packaging allows consumers to visually inspect products before purchase, enhancing trust and perceived quality. This trend has led to a significant rise in the use of cellophane films, particularly in applications where product visibility is crucial.
The global market for transparent packaging materials, including cellophane films, has shown robust growth in recent years. Manufacturers of consumer goods, especially in the premium and organic product segments, are increasingly adopting transparent packaging to showcase the quality and freshness of their offerings. This shift has created a substantial market opportunity for improved cellophane films with enhanced transparency.
In the cosmetics and personal care industry, high-transparency packaging has become a key differentiator. Brands are leveraging clear packaging to highlight the color, texture, and purity of their products, aligning with the clean beauty movement. This trend has fueled demand for cellophane films that can provide exceptional clarity without compromising on protective properties.
The electronics industry has also contributed to the growing demand for high-transparency packaging. As consumer electronics become more visually appealing, manufacturers are opting for packaging that allows potential buyers to see the product without opening the box. This has created a niche market for ultra-clear cellophane films that can protect delicate electronic components while maintaining perfect visibility.
Environmental concerns have further shaped the market demand for high-transparency packaging. Consumers are increasingly seeking sustainable packaging solutions, and cellophane films, being biodegradable, have gained favor over synthetic alternatives. However, this has also raised the bar for manufacturers to develop cellophane films that combine superior transparency with enhanced eco-friendly characteristics.
The pharmaceutical sector presents another significant growth area for high-transparency cellophane films. With stringent regulations on drug packaging and a need for tamper-evident solutions, there is a growing demand for cellophane films that offer both clarity and security features. This has spurred innovation in multi-layer cellophane films that can meet the complex requirements of pharmaceutical packaging.
As e-commerce continues to expand, the demand for high-transparency packaging in the logistics and shipping industry has also increased. Online retailers are seeking packaging solutions that can withstand the rigors of shipping while allowing easy visual inspection of contents upon delivery. This has created a new market segment for durable, high-clarity cellophane films suitable for e-commerce applications.
The global market for transparent packaging materials, including cellophane films, has shown robust growth in recent years. Manufacturers of consumer goods, especially in the premium and organic product segments, are increasingly adopting transparent packaging to showcase the quality and freshness of their offerings. This shift has created a substantial market opportunity for improved cellophane films with enhanced transparency.
In the cosmetics and personal care industry, high-transparency packaging has become a key differentiator. Brands are leveraging clear packaging to highlight the color, texture, and purity of their products, aligning with the clean beauty movement. This trend has fueled demand for cellophane films that can provide exceptional clarity without compromising on protective properties.
The electronics industry has also contributed to the growing demand for high-transparency packaging. As consumer electronics become more visually appealing, manufacturers are opting for packaging that allows potential buyers to see the product without opening the box. This has created a niche market for ultra-clear cellophane films that can protect delicate electronic components while maintaining perfect visibility.
Environmental concerns have further shaped the market demand for high-transparency packaging. Consumers are increasingly seeking sustainable packaging solutions, and cellophane films, being biodegradable, have gained favor over synthetic alternatives. However, this has also raised the bar for manufacturers to develop cellophane films that combine superior transparency with enhanced eco-friendly characteristics.
The pharmaceutical sector presents another significant growth area for high-transparency cellophane films. With stringent regulations on drug packaging and a need for tamper-evident solutions, there is a growing demand for cellophane films that offer both clarity and security features. This has spurred innovation in multi-layer cellophane films that can meet the complex requirements of pharmaceutical packaging.
As e-commerce continues to expand, the demand for high-transparency packaging in the logistics and shipping industry has also increased. Online retailers are seeking packaging solutions that can withstand the rigors of shipping while allowing easy visual inspection of contents upon delivery. This has created a new market segment for durable, high-clarity cellophane films suitable for e-commerce applications.
Current Challenges in Cellophane Film Transparency
Despite significant advancements in cellophane film production, several challenges persist in achieving optimal transparency. One of the primary issues is the inherent molecular structure of cellulose, which can lead to light scattering and reduced clarity. The presence of crystalline regions within the cellulose matrix can cause optical interference, resulting in a slightly hazy appearance.
Another challenge lies in the film formation process. During manufacturing, uneven distribution of cellulose molecules or the presence of micro-voids can create optical imperfections. These imperfections scatter light, reducing the overall transparency of the film. Additionally, the thickness of the film plays a crucial role in its transparency, with thicker films generally exhibiting lower light transmission.
Surface roughness is another factor affecting transparency. Even minor irregularities on the film surface can cause light diffraction and reflection, diminishing the film's clarity. Achieving and maintaining a smooth surface throughout the production process remains a significant challenge.
The presence of additives, while necessary for certain functional properties, can also impact transparency. Plasticizers, stabilizers, and other additives may introduce optical heterogeneity, leading to reduced light transmission. Balancing the need for these additives with the desire for high transparency is an ongoing challenge for manufacturers.
Environmental factors pose additional challenges to cellophane film transparency. Moisture absorption can cause swelling and structural changes in the cellulose matrix, affecting its optical properties. Temperature fluctuations during production and storage can also lead to thermal stress, potentially causing optical distortions in the film.
The degradation of cellophane over time presents another hurdle. Exposure to UV light, heat, and certain chemicals can cause yellowing or other color changes, reducing the film's transparency. Developing cellophane formulations that maintain their optical properties over extended periods remains a significant challenge.
Lastly, achieving consistent transparency across large production batches is difficult. Variations in raw materials, processing conditions, and environmental factors can lead to inconsistencies in film quality and transparency from one batch to another. Maintaining tight control over these variables to ensure uniform transparency is an ongoing challenge for manufacturers in the cellophane industry.
Another challenge lies in the film formation process. During manufacturing, uneven distribution of cellulose molecules or the presence of micro-voids can create optical imperfections. These imperfections scatter light, reducing the overall transparency of the film. Additionally, the thickness of the film plays a crucial role in its transparency, with thicker films generally exhibiting lower light transmission.
Surface roughness is another factor affecting transparency. Even minor irregularities on the film surface can cause light diffraction and reflection, diminishing the film's clarity. Achieving and maintaining a smooth surface throughout the production process remains a significant challenge.
The presence of additives, while necessary for certain functional properties, can also impact transparency. Plasticizers, stabilizers, and other additives may introduce optical heterogeneity, leading to reduced light transmission. Balancing the need for these additives with the desire for high transparency is an ongoing challenge for manufacturers.
Environmental factors pose additional challenges to cellophane film transparency. Moisture absorption can cause swelling and structural changes in the cellulose matrix, affecting its optical properties. Temperature fluctuations during production and storage can also lead to thermal stress, potentially causing optical distortions in the film.
The degradation of cellophane over time presents another hurdle. Exposure to UV light, heat, and certain chemicals can cause yellowing or other color changes, reducing the film's transparency. Developing cellophane formulations that maintain their optical properties over extended periods remains a significant challenge.
Lastly, achieving consistent transparency across large production batches is difficult. Variations in raw materials, processing conditions, and environmental factors can lead to inconsistencies in film quality and transparency from one batch to another. Maintaining tight control over these variables to ensure uniform transparency is an ongoing challenge for manufacturers in the cellophane industry.
Existing Transparency Enhancement Techniques
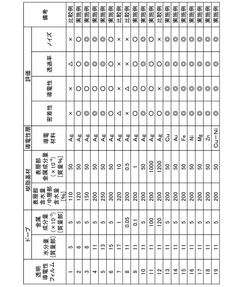
01 Improving transparency through chemical modifications
Chemical modifications to cellophane films can enhance their transparency. This includes treatments to reduce crystallinity, modify the cellulose structure, or incorporate additives that improve light transmission. These methods can result in clearer, more transparent films suitable for various applications.- Improving transparency of cellophane films: Various methods are employed to enhance the transparency of cellophane films. These include modifying the film composition, adjusting processing parameters, and applying surface treatments. Improved transparency is achieved through careful control of crystallinity, reduction of haze-causing particles, and optimization of film thickness.
- Biodegradable transparent cellophane films: Development of biodegradable cellophane films with high transparency is a focus area. These films are created using renewable resources and environmentally friendly processes. The formulations often include natural polymers and additives that maintain transparency while ensuring biodegradability.
- Nanocomposite cellophane films for improved optical properties: Incorporation of nanoparticles or nanocomposites into cellophane films can significantly enhance their optical properties, including transparency. These nanocomposites can reduce light scattering, improve clarity, and provide additional functionalities such as UV protection without compromising transparency.
- Surface modification techniques for cellophane transparency: Various surface modification techniques are applied to cellophane films to improve their transparency. These include plasma treatment, chemical etching, and application of anti-reflective coatings. Such treatments can reduce surface roughness and minimize light scattering, resulting in enhanced transparency.
- Transparent cellophane films for packaging applications: Development of highly transparent cellophane films specifically for packaging applications is an important area of research. These films combine excellent optical clarity with other desirable properties such as barrier protection, printability, and sealability. The focus is on creating versatile packaging materials that maintain product visibility while ensuring protection.
02 Surface treatments for enhanced transparency
Various surface treatments can be applied to cellophane films to increase their transparency. These may include coating with specific materials, polishing techniques, or plasma treatments. Such processes can reduce surface roughness and minimize light scattering, resulting in improved optical clarity.Expand Specific Solutions03 Nanocomposite cellophane films for improved transparency
Incorporating nanoparticles or nanostructures into cellophane films can enhance their transparency. These nanocomposites can modify the film's optical properties, reducing haze and increasing light transmission. The careful selection and dispersion of nanoparticles are crucial for achieving optimal transparency.Expand Specific Solutions04 Controlling film thickness for optimal transparency
The thickness of cellophane films plays a crucial role in their transparency. Optimizing the film thickness through precise manufacturing processes can lead to improved light transmission. This may involve adjusting production parameters or developing new techniques for creating ultra-thin, highly transparent films.Expand Specific Solutions05 Blending cellulose with other polymers for transparency
Blending cellulose with other compatible polymers can result in cellophane films with enhanced transparency. This approach allows for the combination of desirable properties from different materials, potentially leading to films with improved optical clarity while maintaining other essential characteristics.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Transparent Film Industry
The cellophane film transparency improvement market is in a mature stage, with established players and steady demand. The global market size for cellophane films is estimated to be around $600 million, growing moderately. Technologically, the field is well-developed but continues to evolve, with companies like FUJIFILM Corp., Toyobo Co., Ltd., and Nitto Denko Corp. leading innovation. These firms are focusing on enhancing optical properties, reducing haze, and improving moisture resistance to increase transparency. Emerging players such as Toray Plastics and BOE Technology Group are also contributing to advancements, particularly in areas like nano-coatings and surface treatments to further improve film clarity and performance.
FUJIFILM Corp.
Technical Solution: FUJIFILM Corp. has developed advanced technologies to improve transparency in cellophane films. Their approach involves utilizing nano-scale control of film structure and surface modification techniques. By optimizing the molecular orientation and reducing light scattering within the film, they have achieved significant improvements in transparency[1]. FUJIFILM's process includes a proprietary coating technology that enhances the film's surface smoothness, further reducing light reflection and improving overall clarity[2]. Additionally, they have implemented a multi-layer film structure that allows for precise control of refractive indices, minimizing internal reflections and maximizing light transmission[3].
Strengths: High-quality optical properties, advanced nano-scale control, and multi-layer film expertise. Weaknesses: Potentially higher production costs and complexity in manufacturing process.
Dow Global Technologies LLC
Technical Solution: Dow Global Technologies LLC has developed innovative solutions for improving transparency in cellophane films through their advanced polymer science. Their approach focuses on modifying the cellulose structure at a molecular level to reduce crystallinity and enhance amorphous regions, resulting in improved light transmission[4]. Dow's technology incorporates specialized additives that act as nucleating agents, controlling the crystallization process and minimizing light scattering centers within the film[5]. Furthermore, they have implemented a unique extrusion process that optimizes film orientation, reducing birefringence and enhancing overall optical clarity[6]. Dow's films also feature a proprietary surface treatment that reduces micro-roughness, further improving transparency and reducing haze[7].
Strengths: Extensive polymer expertise, innovative molecular-level modifications, and advanced extrusion techniques. Weaknesses: Potential limitations in biodegradability compared to traditional cellophane.
Innovative Approaches to Cellophane Clarity
Transparent film, and transparent film for agricultural use
PatentWO2018181569A1
Innovation
- A transparent film comprising a cellulose ester film with a protective layer having a thickness of 5 to 50 μm, UV transmittance of 50% or less, and moisture permeability of 400g/m²/24h or more, where the protective layer contains acrylic resin, methacrylic resin, cellulose polymer, and an ultraviolet absorber, enhancing both moisture permeability and light resistance.
Transparent conductive film and method for producing transparent conductive film
PatentWO2016170957A1
Innovation
- A transparent conductive film with a cycloolefin resin base material having a specific range of metal components (1×10^-6 ~ 1×10^-3% by mass) and controlled water content (120 to 300% of the middle layer's water content per unit volume) is developed, using a solution casting method and inkjet process to form a metal conductive layer, enhancing adhesion and conductivity.
Environmental Impact of Transparent Films
The environmental impact of transparent films, particularly cellophane, is a critical consideration in the quest to improve their transparency. As the demand for packaging materials continues to grow, the ecological footprint of these films becomes increasingly significant.
Cellophane, despite its biodegradable nature, still poses environmental challenges. The production process of cellophane involves the use of chemicals and energy-intensive methods, contributing to carbon emissions and potential water pollution. While the film itself may decompose naturally, the additives and coatings used to enhance its properties can persist in the environment, potentially harming ecosystems.
Improving transparency in cellophane films often requires additional processing or the incorporation of synthetic materials, which can further exacerbate environmental concerns. For instance, some methods to enhance clarity may involve the use of petroleum-based additives or nanoparticles, which can complicate recycling efforts and increase the overall environmental impact of the product.
The disposal of transparent films also presents challenges. While cellophane is biodegradable, it may not decompose efficiently in landfill conditions. Improper disposal can lead to the accumulation of these materials in natural environments, contributing to litter and potentially harming wildlife.
However, advancements in eco-friendly production methods and materials offer promising solutions. Research into plant-based alternatives and bio-engineered polymers could lead to more environmentally benign transparent films. These innovations aim to maintain or improve transparency while reducing the ecological footprint of production and disposal.
Recycling and circular economy principles are increasingly being applied to the lifecycle of transparent films. Developing more efficient recycling processes for cellophane and similar materials can help mitigate their environmental impact. Additionally, designing films for easier recyclability without compromising transparency is an area of active research.
The push for improved transparency in cellophane films must be balanced with environmental considerations. This balance involves optimizing production processes to reduce energy consumption and chemical use, exploring bio-based alternatives, and enhancing end-of-life management strategies. As industries and consumers become more environmentally conscious, the development of transparent films that offer both high performance and minimal ecological impact will likely drive innovation in this field.
Cellophane, despite its biodegradable nature, still poses environmental challenges. The production process of cellophane involves the use of chemicals and energy-intensive methods, contributing to carbon emissions and potential water pollution. While the film itself may decompose naturally, the additives and coatings used to enhance its properties can persist in the environment, potentially harming ecosystems.
Improving transparency in cellophane films often requires additional processing or the incorporation of synthetic materials, which can further exacerbate environmental concerns. For instance, some methods to enhance clarity may involve the use of petroleum-based additives or nanoparticles, which can complicate recycling efforts and increase the overall environmental impact of the product.
The disposal of transparent films also presents challenges. While cellophane is biodegradable, it may not decompose efficiently in landfill conditions. Improper disposal can lead to the accumulation of these materials in natural environments, contributing to litter and potentially harming wildlife.
However, advancements in eco-friendly production methods and materials offer promising solutions. Research into plant-based alternatives and bio-engineered polymers could lead to more environmentally benign transparent films. These innovations aim to maintain or improve transparency while reducing the ecological footprint of production and disposal.
Recycling and circular economy principles are increasingly being applied to the lifecycle of transparent films. Developing more efficient recycling processes for cellophane and similar materials can help mitigate their environmental impact. Additionally, designing films for easier recyclability without compromising transparency is an area of active research.
The push for improved transparency in cellophane films must be balanced with environmental considerations. This balance involves optimizing production processes to reduce energy consumption and chemical use, exploring bio-based alternatives, and enhancing end-of-life management strategies. As industries and consumers become more environmentally conscious, the development of transparent films that offer both high performance and minimal ecological impact will likely drive innovation in this field.
Regulatory Standards for Food-Contact Films
Regulatory standards for food-contact films play a crucial role in ensuring the safety and quality of cellophane films used in food packaging. These standards are established and enforced by various regulatory bodies worldwide, with the primary goal of protecting consumer health and maintaining product integrity.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) is responsible for regulating food-contact materials, including cellophane films. The FDA's regulations are outlined in the Code of Federal Regulations (CFR), specifically in 21 CFR 177.1200 for cellophane. These regulations stipulate the permissible raw materials, additives, and manufacturing processes for cellophane films intended for food contact.
The European Union has its own set of regulations for food-contact materials, governed by the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). The EU's Framework Regulation (EC) No 1935/2004 provides the general principles for all food-contact materials, while specific measures for plastic materials are detailed in Regulation (EU) No 10/2011. These regulations establish migration limits for substances that may transfer from the packaging to food.
In Japan, the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare (MHLW) oversees the regulation of food-contact materials. The Japanese Food Sanitation Law and its associated positive lists define the requirements for food packaging materials, including cellophane films.
Transparency in cellophane films is a key factor in meeting regulatory standards. Improved transparency can enhance visual inspection capabilities, allowing for easier detection of contaminants or defects in the packaging. This aligns with the regulatory focus on food safety and quality control.
Regulatory bodies often require manufacturers to demonstrate compliance through testing and documentation. For cellophane films, this may include migration tests to ensure that any substances transferred from the film to the food are within acceptable limits. Transparency improvements must not compromise these migration properties or introduce new substances that could pose risks to consumer health.
As sustainability becomes an increasingly important consideration, regulatory standards are evolving to address environmental concerns. This includes requirements for recyclability, biodegradability, and the use of sustainable raw materials in cellophane film production. Manufacturers seeking to improve transparency must also consider these emerging regulatory trends to ensure long-term compliance.
Harmonization efforts between different regulatory bodies are ongoing, aiming to streamline compliance processes for global manufacturers. The Global Food Safety Initiative (GFSI) is one such effort that promotes the convergence of food safety standards worldwide, including those related to packaging materials like cellophane films.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) is responsible for regulating food-contact materials, including cellophane films. The FDA's regulations are outlined in the Code of Federal Regulations (CFR), specifically in 21 CFR 177.1200 for cellophane. These regulations stipulate the permissible raw materials, additives, and manufacturing processes for cellophane films intended for food contact.
The European Union has its own set of regulations for food-contact materials, governed by the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). The EU's Framework Regulation (EC) No 1935/2004 provides the general principles for all food-contact materials, while specific measures for plastic materials are detailed in Regulation (EU) No 10/2011. These regulations establish migration limits for substances that may transfer from the packaging to food.
In Japan, the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare (MHLW) oversees the regulation of food-contact materials. The Japanese Food Sanitation Law and its associated positive lists define the requirements for food packaging materials, including cellophane films.
Transparency in cellophane films is a key factor in meeting regulatory standards. Improved transparency can enhance visual inspection capabilities, allowing for easier detection of contaminants or defects in the packaging. This aligns with the regulatory focus on food safety and quality control.
Regulatory bodies often require manufacturers to demonstrate compliance through testing and documentation. For cellophane films, this may include migration tests to ensure that any substances transferred from the film to the food are within acceptable limits. Transparency improvements must not compromise these migration properties or introduce new substances that could pose risks to consumer health.
As sustainability becomes an increasingly important consideration, regulatory standards are evolving to address environmental concerns. This includes requirements for recyclability, biodegradability, and the use of sustainable raw materials in cellophane film production. Manufacturers seeking to improve transparency must also consider these emerging regulatory trends to ensure long-term compliance.
Harmonization efforts between different regulatory bodies are ongoing, aiming to streamline compliance processes for global manufacturers. The Global Food Safety Initiative (GFSI) is one such effort that promotes the convergence of food safety standards worldwide, including those related to packaging materials like cellophane films.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!