How to Integrate Phospholipid Research in Academic Curriculum?
JUL 16, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Phospholipid Research Background and Objectives
Phospholipid research has emerged as a critical field in biochemistry and molecular biology, with far-reaching implications for various scientific disciplines. The study of phospholipids, essential components of cell membranes, has evolved significantly over the past decades, revealing their crucial roles in cellular processes, signaling pathways, and disease mechanisms. As our understanding of these complex molecules deepens, there is a growing need to integrate this knowledge into academic curricula to prepare the next generation of scientists and researchers.
The primary objective of integrating phospholipid research into academic curricula is to provide students with a comprehensive understanding of these vital biomolecules and their significance in biological systems. This integration aims to bridge the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical applications, fostering a deeper appreciation for the interdisciplinary nature of phospholipid research. By incorporating cutting-edge discoveries and methodologies, academic institutions can ensure that students are well-equipped to contribute to this rapidly advancing field.
The evolution of phospholipid research has been marked by several key milestones. From the initial discovery of phospholipids in the late 19th century to the elucidation of their structure and function in the mid-20th century, the field has continuously expanded. Recent advancements in analytical techniques, such as mass spectrometry and high-resolution microscopy, have revolutionized our ability to study phospholipids at the molecular level, opening new avenues for research and applications.
Current trends in phospholipid research focus on understanding the dynamic nature of lipid membranes, the role of phospholipids in cell signaling, and their involvement in various pathological conditions. The field is also exploring the potential of phospholipids in drug delivery systems, biomarker discovery, and the development of novel therapeutic strategies. These trends highlight the importance of integrating up-to-date research findings into academic curricula to maintain relevance and foster innovation.
The integration of phospholipid research into academic programs presents both opportunities and challenges. On one hand, it offers the potential to enhance students' critical thinking skills, promote interdisciplinary collaboration, and prepare them for careers in cutting-edge research and biotechnology. On the other hand, it requires careful curriculum design, access to advanced laboratory equipment, and continuous updating of course materials to reflect the latest scientific developments.
To achieve the goal of effective integration, academic institutions must consider a multi-faceted approach. This may include developing specialized courses focused on phospholipid biochemistry and biophysics, incorporating research modules into existing laboratory classes, and encouraging student participation in ongoing research projects. Additionally, fostering partnerships with industry and research institutions can provide students with valuable exposure to real-world applications of phospholipid research.
The primary objective of integrating phospholipid research into academic curricula is to provide students with a comprehensive understanding of these vital biomolecules and their significance in biological systems. This integration aims to bridge the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical applications, fostering a deeper appreciation for the interdisciplinary nature of phospholipid research. By incorporating cutting-edge discoveries and methodologies, academic institutions can ensure that students are well-equipped to contribute to this rapidly advancing field.
The evolution of phospholipid research has been marked by several key milestones. From the initial discovery of phospholipids in the late 19th century to the elucidation of their structure and function in the mid-20th century, the field has continuously expanded. Recent advancements in analytical techniques, such as mass spectrometry and high-resolution microscopy, have revolutionized our ability to study phospholipids at the molecular level, opening new avenues for research and applications.
Current trends in phospholipid research focus on understanding the dynamic nature of lipid membranes, the role of phospholipids in cell signaling, and their involvement in various pathological conditions. The field is also exploring the potential of phospholipids in drug delivery systems, biomarker discovery, and the development of novel therapeutic strategies. These trends highlight the importance of integrating up-to-date research findings into academic curricula to maintain relevance and foster innovation.
The integration of phospholipid research into academic programs presents both opportunities and challenges. On one hand, it offers the potential to enhance students' critical thinking skills, promote interdisciplinary collaboration, and prepare them for careers in cutting-edge research and biotechnology. On the other hand, it requires careful curriculum design, access to advanced laboratory equipment, and continuous updating of course materials to reflect the latest scientific developments.
To achieve the goal of effective integration, academic institutions must consider a multi-faceted approach. This may include developing specialized courses focused on phospholipid biochemistry and biophysics, incorporating research modules into existing laboratory classes, and encouraging student participation in ongoing research projects. Additionally, fostering partnerships with industry and research institutions can provide students with valuable exposure to real-world applications of phospholipid research.
Educational Market Demand Analysis
The integration of phospholipid research into academic curricula has become increasingly important due to the growing demand for specialized knowledge in this field. The educational market for phospholipid-related courses and programs is experiencing significant growth, driven by advancements in biotechnology, pharmaceutical research, and medical sciences. Universities and research institutions are recognizing the need to equip students with a deep understanding of phospholipid structures, functions, and applications.
The demand for phospholipid education is particularly strong in the life sciences and biomedical engineering sectors. As the pharmaceutical industry continues to develop novel drug delivery systems and personalized medicine approaches, the need for professionals with expertise in phospholipid research has surged. This trend is reflected in the increasing number of job postings requiring knowledge of lipid biochemistry and membrane biology.
Furthermore, the food and nutrition industry has shown a growing interest in phospholipid research, particularly in the development of functional foods and nutraceuticals. This has created additional demand for educational programs that cover the role of phospholipids in nutrition and health. As a result, universities are expanding their course offerings to include specialized modules on lipid metabolism and membrane biophysics.
The biotechnology sector is another key driver of demand for phospholipid education. With the rise of liposome-based technologies and the development of artificial cell membranes, companies are actively seeking graduates with a strong foundation in phospholipid research. This has led to an increase in industry-academia collaborations, with many universities partnering with biotech firms to develop targeted educational programs.
In response to this market demand, educational institutions are adapting their curricula to include more comprehensive coverage of phospholipid research. This includes the introduction of advanced laboratory techniques, computational modeling of lipid membranes, and the integration of cutting-edge research findings into course materials. Some universities have even established dedicated research centers focused on lipid science, further emphasizing the importance of this field in academic and industrial settings.
The global nature of phospholipid research has also contributed to the demand for international educational programs. Many universities are now offering exchange programs and collaborative research opportunities, allowing students to gain exposure to diverse research environments and methodologies. This global perspective is highly valued by employers in the pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries, who are increasingly operating on an international scale.
As the educational market for phospholipid research continues to expand, there is a growing need for qualified instructors and updated teaching resources. Publishers are responding by producing specialized textbooks and online learning materials focused on lipid biochemistry and membrane science. Additionally, professional organizations are offering workshops and certification programs to support continuing education in this rapidly evolving field.
The demand for phospholipid education is particularly strong in the life sciences and biomedical engineering sectors. As the pharmaceutical industry continues to develop novel drug delivery systems and personalized medicine approaches, the need for professionals with expertise in phospholipid research has surged. This trend is reflected in the increasing number of job postings requiring knowledge of lipid biochemistry and membrane biology.
Furthermore, the food and nutrition industry has shown a growing interest in phospholipid research, particularly in the development of functional foods and nutraceuticals. This has created additional demand for educational programs that cover the role of phospholipids in nutrition and health. As a result, universities are expanding their course offerings to include specialized modules on lipid metabolism and membrane biophysics.
The biotechnology sector is another key driver of demand for phospholipid education. With the rise of liposome-based technologies and the development of artificial cell membranes, companies are actively seeking graduates with a strong foundation in phospholipid research. This has led to an increase in industry-academia collaborations, with many universities partnering with biotech firms to develop targeted educational programs.
In response to this market demand, educational institutions are adapting their curricula to include more comprehensive coverage of phospholipid research. This includes the introduction of advanced laboratory techniques, computational modeling of lipid membranes, and the integration of cutting-edge research findings into course materials. Some universities have even established dedicated research centers focused on lipid science, further emphasizing the importance of this field in academic and industrial settings.
The global nature of phospholipid research has also contributed to the demand for international educational programs. Many universities are now offering exchange programs and collaborative research opportunities, allowing students to gain exposure to diverse research environments and methodologies. This global perspective is highly valued by employers in the pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries, who are increasingly operating on an international scale.
As the educational market for phospholipid research continues to expand, there is a growing need for qualified instructors and updated teaching resources. Publishers are responding by producing specialized textbooks and online learning materials focused on lipid biochemistry and membrane science. Additionally, professional organizations are offering workshops and certification programs to support continuing education in this rapidly evolving field.
Current State of Phospholipid Education
Phospholipid education in academic curricula is currently undergoing significant changes to meet the growing demand for expertise in this field. Traditional biochemistry and cell biology courses often touch upon phospholipids as part of broader topics, but dedicated courses focusing solely on phospholipid research are still relatively rare. Many universities are recognizing the need to expand their offerings in this area, given the increasing importance of phospholipids in various scientific and industrial applications.
The current state of phospholipid education varies widely across institutions. Some leading research universities have begun to incorporate specialized modules or elective courses on phospholipid biochemistry and biophysics into their graduate programs. These courses typically cover topics such as phospholipid structure, metabolism, and function in cellular membranes. However, at the undergraduate level, comprehensive coverage of phospholipids remains limited, often confined to brief mentions within broader biochemistry or cell biology courses.
In recent years, there has been a growing trend towards interdisciplinary approaches in phospholipid education. This reflects the diverse applications of phospholipid research across fields such as medicine, nutrition, nanotechnology, and materials science. Some institutions have started to offer cross-departmental courses that bring together students from biology, chemistry, and engineering backgrounds to study phospholipids from multiple perspectives.
Laboratory components in phospholipid education are becoming increasingly sophisticated. Advanced analytical techniques such as mass spectrometry, nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, and various microscopy methods are being introduced to students to provide hands-on experience with state-of-the-art phospholipid research tools. This practical training is crucial for preparing students for careers in both academia and industry.
Online resources and digital learning platforms are playing a growing role in phospholipid education. Several universities and research institutions have developed open-access courses and webinars focusing on phospholipid research, making this specialized knowledge more accessible to a global audience. These resources often include interactive simulations and virtual laboratory experiences, complementing traditional classroom instruction.
Despite these advancements, challenges remain in integrating phospholipid research into academic curricula. The rapid pace of discoveries in this field makes it difficult for textbooks and course materials to stay current. Additionally, the interdisciplinary nature of phospholipid research can make it challenging to fit comprehensively into traditional departmental structures. There is also a need for more trained educators specializing in phospholipid science to develop and teach these courses effectively.
The current state of phospholipid education varies widely across institutions. Some leading research universities have begun to incorporate specialized modules or elective courses on phospholipid biochemistry and biophysics into their graduate programs. These courses typically cover topics such as phospholipid structure, metabolism, and function in cellular membranes. However, at the undergraduate level, comprehensive coverage of phospholipids remains limited, often confined to brief mentions within broader biochemistry or cell biology courses.
In recent years, there has been a growing trend towards interdisciplinary approaches in phospholipid education. This reflects the diverse applications of phospholipid research across fields such as medicine, nutrition, nanotechnology, and materials science. Some institutions have started to offer cross-departmental courses that bring together students from biology, chemistry, and engineering backgrounds to study phospholipids from multiple perspectives.
Laboratory components in phospholipid education are becoming increasingly sophisticated. Advanced analytical techniques such as mass spectrometry, nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, and various microscopy methods are being introduced to students to provide hands-on experience with state-of-the-art phospholipid research tools. This practical training is crucial for preparing students for careers in both academia and industry.
Online resources and digital learning platforms are playing a growing role in phospholipid education. Several universities and research institutions have developed open-access courses and webinars focusing on phospholipid research, making this specialized knowledge more accessible to a global audience. These resources often include interactive simulations and virtual laboratory experiences, complementing traditional classroom instruction.
Despite these advancements, challenges remain in integrating phospholipid research into academic curricula. The rapid pace of discoveries in this field makes it difficult for textbooks and course materials to stay current. Additionally, the interdisciplinary nature of phospholipid research can make it challenging to fit comprehensively into traditional departmental structures. There is also a need for more trained educators specializing in phospholipid science to develop and teach these courses effectively.
Existing Curriculum Integration Approaches
01 Phospholipid-based drug delivery systems
Phospholipids are used to create various drug delivery systems, including liposomes and nanoparticles. These systems can improve drug solubility, stability, and targeted delivery, enhancing therapeutic efficacy and reducing side effects. The amphiphilic nature of phospholipids allows them to encapsulate both hydrophilic and hydrophobic drugs.- Phospholipid-based drug delivery systems: Phospholipids are used to create various drug delivery systems, including liposomes and nanoparticles. These systems can improve drug solubility, stability, and targeted delivery, enhancing therapeutic efficacy and reducing side effects. The amphiphilic nature of phospholipids allows them to form bilayer structures that can encapsulate both hydrophilic and hydrophobic drugs.
- Phospholipid synthesis and modification: Various methods for synthesizing and modifying phospholipids are developed to create novel compounds with specific properties. These techniques include enzymatic synthesis, chemical modifications, and the use of recombinant DNA technology. Modified phospholipids can have improved stability, functionality, or targeting capabilities for use in pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and food industries.
- Phospholipid applications in cosmetics: Phospholipids are widely used in cosmetic formulations due to their emulsifying, moisturizing, and skin-friendly properties. They can form lamellar structures similar to the skin's natural lipid barrier, helping to improve skin hydration, elasticity, and overall appearance. Phospholipids are incorporated into various skincare products, including creams, lotions, and anti-aging formulations.
- Phospholipid extraction and purification: Various techniques are employed to extract and purify phospholipids from natural sources such as egg yolk, soybeans, and microorganisms. These methods include solvent extraction, chromatography, and membrane separation. The purification process is crucial for obtaining high-quality phospholipids suitable for use in pharmaceuticals, nutraceuticals, and other industries.
- Phospholipid-based functional foods and nutraceuticals: Phospholipids are utilized in the development of functional foods and nutraceuticals due to their potential health benefits. They are incorporated into various food products to improve nutritional value, texture, and stability. Phospholipids, particularly those rich in omega-3 fatty acids, are studied for their potential roles in supporting cardiovascular health, cognitive function, and overall well-being.
02 Phospholipid synthesis and modification
Research focuses on developing new methods for synthesizing and modifying phospholipids. This includes creating novel phospholipid structures, improving existing synthesis processes, and developing enzymatic approaches for phospholipid modification. These advancements can lead to phospholipids with enhanced properties for various applications in pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and food industries.Expand Specific Solutions03 Phospholipid applications in cosmetics and skincare
Phospholipids are utilized in cosmetic and skincare formulations due to their emulsifying properties and skin-friendly nature. They can improve product stability, enhance skin penetration of active ingredients, and provide moisturizing effects. Phospholipids are also used in anti-aging products and as carriers for other cosmetic ingredients.Expand Specific Solutions04 Phospholipid extraction and purification techniques
Various methods are developed for extracting and purifying phospholipids from natural sources such as egg yolk, soybeans, and microorganisms. These techniques aim to improve yield, purity, and cost-effectiveness of phospholipid production. Advanced separation and purification methods, including chromatography and membrane technologies, are employed to obtain high-quality phospholipids for different applications.Expand Specific Solutions05 Phospholipid-based biomaterials and tissue engineering
Phospholipids are used in the development of biomaterials for tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. They can be incorporated into scaffolds, hydrogels, and other biomaterials to improve biocompatibility, cell adhesion, and tissue regeneration. Phospholipid-based materials are also explored for their potential in wound healing and drug-eluting implants.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Academic Institutions and Research Centers
The integration of phospholipid research into academic curricula is gaining momentum as the field matures. The market for phospholipid-related education and research is expanding, driven by growing applications in pharmaceuticals, nutrition, and biotechnology. While the technology is well-established, ongoing innovations in lipidomics and membrane biology continue to push the boundaries. Leading institutions like Jiangnan University, University of Michigan, and South China University of Technology are at the forefront, developing comprehensive programs that blend theoretical knowledge with practical applications. The involvement of industry players such as Aker Biomarine and Life Technologies Corp. further enhances the relevance and real-world applicability of academic phospholipid research.
Jiangnan University
Technical Solution: Jiangnan University has developed a comprehensive approach to integrating phospholipid research into their academic curriculum. Their method involves a multi-tiered strategy that combines theoretical knowledge with practical laboratory experience. The university has established dedicated courses on lipid biochemistry and membrane biology, focusing on the structure, function, and metabolism of phospholipids[1]. They have also implemented advanced analytical techniques such as lipidomics and mass spectrometry into their laboratory practicals, allowing students to gain hands-on experience in phospholipid analysis[2]. Furthermore, Jiangnan University has fostered collaborations with industry partners to provide students with real-world applications of phospholipid research, including internships and joint research projects[3]. This approach ensures that students not only understand the fundamental concepts but also appreciate the practical implications of phospholipid research in various fields such as nutrition, pharmaceuticals, and biotechnology.
Strengths: Comprehensive curriculum covering both theory and practice, state-of-the-art analytical techniques, strong industry collaborations. Weaknesses: May require significant resources and specialized equipment, potentially limiting accessibility to all students.
The Regents of the University of Michigan
Technical Solution: The University of Michigan has implemented an innovative approach to integrating phospholipid research into their academic curriculum. They have developed a cross-disciplinary program that combines elements from biochemistry, biophysics, and bioengineering[1]. The curriculum includes specialized courses on membrane biophysics and lipid-protein interactions, providing students with a deep understanding of phospholipid structure and function[2]. The university has also established advanced research facilities equipped with cutting-edge technologies such as cryo-electron microscopy and atomic force microscopy, allowing students to visualize and manipulate phospholipid membranes at the molecular level[3]. Additionally, the University of Michigan has incorporated computational modeling and simulation techniques into their curriculum, enabling students to predict and analyze phospholipid behavior in complex biological systems[4]. To ensure practical relevance, the university regularly organizes workshops and seminars featuring leading experts in phospholipid research from both academia and industry.
Strengths: Interdisciplinary approach, access to advanced research facilities, incorporation of computational techniques. Weaknesses: High level of complexity may be challenging for some students, potentially requiring strong prerequisites in multiple scientific disciplines.
Core Phospholipid Research Methodologies
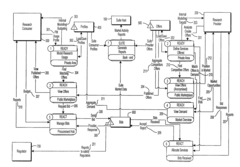
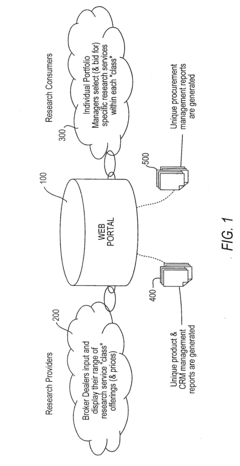
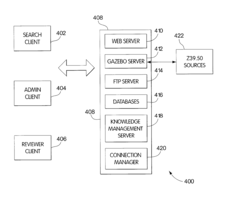
Method and electronic platform for enabling and hosting a market for research, and a taxonomy method for specifying research
PatentInactiveUS20080313091A1
Innovation
- A web-based electronic marketplace platform that classifies and prices investment research products based on a taxonomy, allowing providers to offer a range of prices and fund managers to negotiate and consolidate purchases, enhancing the quality of research procurement negotiations.
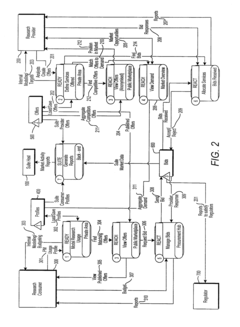
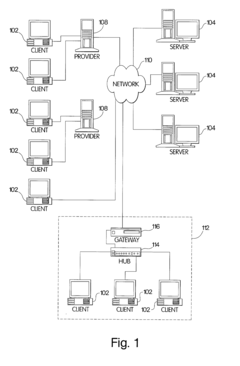
Collaborative research systems
PatentInactiveUS20020165856A1
Innovation
- A collaborative research system that enables structured and refined searches across various data sources, with variable access control for viewing and editing throughout iterative research stages, deployable in client/server or stand-alone configurations, allowing for network publication of organized search results.
Interdisciplinary Applications of Phospholipid Research
Phospholipid research has far-reaching applications across multiple scientific disciplines, making it an ideal subject for interdisciplinary studies in academic curricula. The integration of phospholipid research can bridge gaps between traditional academic boundaries, fostering collaboration and innovation across various fields.
In the realm of biomedical sciences, phospholipid research plays a crucial role in understanding cell membrane structure and function. This knowledge is fundamental to drug delivery systems, where liposomal formulations are used to enhance the efficacy and reduce the side effects of therapeutic agents. By incorporating phospholipid research into pharmaceutical studies, students can gain insights into advanced drug delivery mechanisms and personalized medicine approaches.
The field of nanotechnology also benefits significantly from phospholipid research. Lipid-based nanoparticles are increasingly used in various applications, from targeted drug delivery to biosensors. Integrating this research into engineering and materials science curricula can inspire the development of novel nanomaterials with enhanced properties and functionalities.
In environmental sciences, phospholipids serve as biomarkers for microbial activity and ecosystem health. Studying phospholipid profiles in soil and water samples can provide valuable information about microbial communities and their responses to environmental changes. This application highlights the importance of incorporating phospholipid research into environmental studies and ecology programs.
The food industry is another sector where phospholipid research finds extensive applications. Emulsifiers derived from phospholipids are widely used in food processing to improve texture, stability, and shelf life of various products. Integrating this research into food science and technology curricula can enhance students' understanding of food formulation and preservation techniques.
In the field of biophysics, phospholipid research is essential for studying membrane dynamics and protein-lipid interactions. Advanced techniques such as nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy and molecular dynamics simulations are employed to investigate these phenomena. Incorporating these methods into physics and computational biology curricula can provide students with powerful tools for exploring complex biological systems.
Lastly, the emerging field of synthetic biology heavily relies on phospholipid research for the creation of artificial cells and organelles. By integrating this research into biotechnology programs, students can explore the frontiers of cellular engineering and contribute to the development of novel biosynthetic systems.
In the realm of biomedical sciences, phospholipid research plays a crucial role in understanding cell membrane structure and function. This knowledge is fundamental to drug delivery systems, where liposomal formulations are used to enhance the efficacy and reduce the side effects of therapeutic agents. By incorporating phospholipid research into pharmaceutical studies, students can gain insights into advanced drug delivery mechanisms and personalized medicine approaches.
The field of nanotechnology also benefits significantly from phospholipid research. Lipid-based nanoparticles are increasingly used in various applications, from targeted drug delivery to biosensors. Integrating this research into engineering and materials science curricula can inspire the development of novel nanomaterials with enhanced properties and functionalities.
In environmental sciences, phospholipids serve as biomarkers for microbial activity and ecosystem health. Studying phospholipid profiles in soil and water samples can provide valuable information about microbial communities and their responses to environmental changes. This application highlights the importance of incorporating phospholipid research into environmental studies and ecology programs.
The food industry is another sector where phospholipid research finds extensive applications. Emulsifiers derived from phospholipids are widely used in food processing to improve texture, stability, and shelf life of various products. Integrating this research into food science and technology curricula can enhance students' understanding of food formulation and preservation techniques.
In the field of biophysics, phospholipid research is essential for studying membrane dynamics and protein-lipid interactions. Advanced techniques such as nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy and molecular dynamics simulations are employed to investigate these phenomena. Incorporating these methods into physics and computational biology curricula can provide students with powerful tools for exploring complex biological systems.
Lastly, the emerging field of synthetic biology heavily relies on phospholipid research for the creation of artificial cells and organelles. By integrating this research into biotechnology programs, students can explore the frontiers of cellular engineering and contribute to the development of novel biosynthetic systems.
Ethical Considerations in Lipid Research Education
Integrating phospholipid research into academic curricula necessitates careful consideration of ethical implications. The use of animal models and human subjects in lipid research raises significant ethical concerns that must be addressed in educational settings. Students should be taught to critically evaluate the necessity of animal testing and explore alternative methods where possible. When animal models are deemed essential, researchers must adhere to strict ethical guidelines to minimize suffering and ensure humane treatment.
Human subject research in lipid studies requires rigorous informed consent procedures and protection of participant privacy. Students should be trained in the ethical collection, storage, and use of human biological samples, emphasizing the importance of confidentiality and data protection. The curriculum should also cover the ethical implications of genetic testing related to lipid disorders, including issues of genetic privacy and potential discrimination.
Environmental ethics is another crucial aspect of lipid research education. The sourcing of lipids from natural resources, such as marine organisms, raises questions about sustainability and ecosystem impact. Students should be taught to consider the environmental consequences of their research and explore eco-friendly alternatives in lipid synthesis and extraction.
The ethical use of research funding and potential conflicts of interest in lipid studies should be addressed. Students need to understand the importance of transparency in reporting funding sources and any financial interests that may influence research outcomes. This includes discussing the ethical implications of industry-sponsored research and the need for maintaining scientific integrity.
Ethical considerations in the application of lipid research findings are equally important. Students should be educated on the responsible communication of research results to the public, avoiding sensationalism and ensuring accurate representation of data. The curriculum should also cover the ethical implications of developing lipid-based pharmaceuticals or nutraceuticals, including issues of equitable access and fair pricing.
Lastly, the ethical dimensions of emerging technologies in lipid research, such as gene editing and nanotechnology, should be explored. Students need to understand the potential risks and benefits of these technologies, as well as the ethical frameworks guiding their development and application. By integrating these ethical considerations into the academic curriculum, institutions can ensure that future lipid researchers are equipped to navigate the complex ethical landscape of their field.
Human subject research in lipid studies requires rigorous informed consent procedures and protection of participant privacy. Students should be trained in the ethical collection, storage, and use of human biological samples, emphasizing the importance of confidentiality and data protection. The curriculum should also cover the ethical implications of genetic testing related to lipid disorders, including issues of genetic privacy and potential discrimination.
Environmental ethics is another crucial aspect of lipid research education. The sourcing of lipids from natural resources, such as marine organisms, raises questions about sustainability and ecosystem impact. Students should be taught to consider the environmental consequences of their research and explore eco-friendly alternatives in lipid synthesis and extraction.
The ethical use of research funding and potential conflicts of interest in lipid studies should be addressed. Students need to understand the importance of transparency in reporting funding sources and any financial interests that may influence research outcomes. This includes discussing the ethical implications of industry-sponsored research and the need for maintaining scientific integrity.
Ethical considerations in the application of lipid research findings are equally important. Students should be educated on the responsible communication of research results to the public, avoiding sensationalism and ensuring accurate representation of data. The curriculum should also cover the ethical implications of developing lipid-based pharmaceuticals or nutraceuticals, including issues of equitable access and fair pricing.
Lastly, the ethical dimensions of emerging technologies in lipid research, such as gene editing and nanotechnology, should be explored. Students need to understand the potential risks and benefits of these technologies, as well as the ethical frameworks guiding their development and application. By integrating these ethical considerations into the academic curriculum, institutions can ensure that future lipid researchers are equipped to navigate the complex ethical landscape of their field.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!