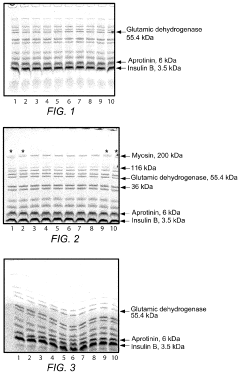
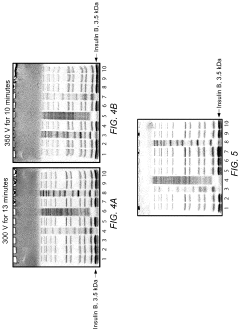
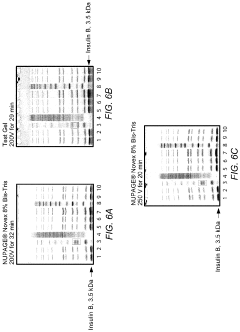
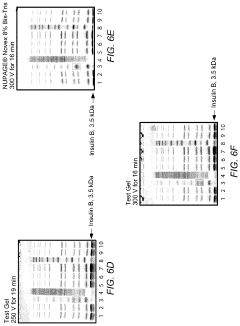
How to Minimize System Noise in Gel Electrophoresis Output?
JUL 1, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Gel Electrophoresis Noise Reduction Objectives
Gel electrophoresis is a fundamental technique in molecular biology, widely used for separating and analyzing DNA, RNA, and proteins. However, system noise can significantly impact the quality and reliability of results. The primary objective of noise reduction in gel electrophoresis output is to enhance the signal-to-noise ratio, thereby improving the accuracy and reproducibility of experimental data.
One key goal is to minimize background interference, which can obscure faint bands and lead to misinterpretation of results. This involves optimizing various parameters such as gel composition, buffer conditions, and staining techniques to reduce non-specific signals and enhance the contrast between bands and background.
Another critical objective is to eliminate artifacts that can be mistaken for genuine bands. These artifacts may arise from contamination, uneven gel polymerization, or inconsistent electric field distribution. By addressing these issues, researchers aim to produce cleaner, more reliable electrophoresis patterns.
Improving the resolution of closely spaced bands is also a paramount concern. This objective focuses on enhancing the system's ability to distinguish between fragments of similar size or charge, which is crucial for applications such as DNA sequencing and protein isoform analysis.
Reducing edge effects and improving lane-to-lane consistency are additional targets for noise reduction. These goals are particularly important in comparative studies where multiple samples are analyzed simultaneously, ensuring that variations observed are due to genuine sample differences rather than system inconsistencies.
Quantitative accuracy is another key objective, especially for applications involving densitometry or fluorescence-based quantification. Minimizing system noise is essential for obtaining reliable quantitative data, enabling more precise measurements of band intensity and relative abundance of molecular species.
Enhancing the detection of low-abundance molecules is a critical goal, particularly in sensitive applications such as trace DNA analysis or protein biomarker detection. By reducing system noise, researchers aim to lower the detection threshold and improve the ability to visualize and quantify minor components in complex mixtures.
Lastly, increasing the dynamic range of detection is an important objective. This involves optimizing the system to accurately represent both high and low intensity signals simultaneously, allowing for more comprehensive analysis of samples with wide concentration ranges of analytes.
One key goal is to minimize background interference, which can obscure faint bands and lead to misinterpretation of results. This involves optimizing various parameters such as gel composition, buffer conditions, and staining techniques to reduce non-specific signals and enhance the contrast between bands and background.
Another critical objective is to eliminate artifacts that can be mistaken for genuine bands. These artifacts may arise from contamination, uneven gel polymerization, or inconsistent electric field distribution. By addressing these issues, researchers aim to produce cleaner, more reliable electrophoresis patterns.
Improving the resolution of closely spaced bands is also a paramount concern. This objective focuses on enhancing the system's ability to distinguish between fragments of similar size or charge, which is crucial for applications such as DNA sequencing and protein isoform analysis.
Reducing edge effects and improving lane-to-lane consistency are additional targets for noise reduction. These goals are particularly important in comparative studies where multiple samples are analyzed simultaneously, ensuring that variations observed are due to genuine sample differences rather than system inconsistencies.
Quantitative accuracy is another key objective, especially for applications involving densitometry or fluorescence-based quantification. Minimizing system noise is essential for obtaining reliable quantitative data, enabling more precise measurements of band intensity and relative abundance of molecular species.
Enhancing the detection of low-abundance molecules is a critical goal, particularly in sensitive applications such as trace DNA analysis or protein biomarker detection. By reducing system noise, researchers aim to lower the detection threshold and improve the ability to visualize and quantify minor components in complex mixtures.
Lastly, increasing the dynamic range of detection is an important objective. This involves optimizing the system to accurately represent both high and low intensity signals simultaneously, allowing for more comprehensive analysis of samples with wide concentration ranges of analytes.
Market Demand for High-Resolution Gel Electrophoresis
The demand for high-resolution gel electrophoresis has been steadily increasing across various sectors of the life sciences industry. This growth is primarily driven by the need for more precise and reliable separation of biomolecules in research, diagnostics, and quality control applications. The global market for gel electrophoresis equipment and consumables is expected to expand significantly in the coming years, with a particular emphasis on systems that can deliver high-resolution results with minimal noise.
In the research sector, academic and pharmaceutical laboratories are increasingly focusing on the analysis of complex biological samples, including proteins, nucleic acids, and their fragments. This trend has created a strong demand for gel electrophoresis systems that can provide clear, high-resolution separation of these molecules, even when dealing with samples containing closely related species or low-abundance targets.
The clinical diagnostics field is another major driver of market demand for high-resolution gel electrophoresis. As personalized medicine and molecular diagnostics continue to advance, there is a growing need for accurate and sensitive methods to detect genetic variations, biomarkers, and disease-associated proteins. High-resolution gel electrophoresis systems that can minimize system noise are crucial for developing reliable diagnostic tests and monitoring disease progression.
In the biopharmaceutical industry, the production of biologics and biosimilars requires stringent quality control measures. High-resolution gel electrophoresis plays a vital role in assessing the purity, stability, and integrity of protein-based drugs throughout the manufacturing process. The ability to detect minor impurities or structural changes with minimal interference from system noise is essential for ensuring product safety and efficacy.
The food and beverage industry is also contributing to the market demand for high-resolution gel electrophoresis. With increasing regulatory requirements and consumer awareness, there is a growing need for accurate methods to detect food adulterants, allergens, and genetically modified organisms. High-resolution gel electrophoresis systems with low noise levels are valuable tools for food safety testing and quality assurance.
Environmental monitoring and forensic applications represent emerging markets for high-resolution gel electrophoresis. These fields require sensitive and reliable methods for detecting and analyzing trace amounts of DNA or proteins in complex environmental or forensic samples. The ability to minimize system noise is crucial for obtaining accurate results in these challenging applications.
As the demand for high-resolution gel electrophoresis continues to grow, manufacturers are focusing on developing innovative systems that can deliver superior performance with minimal noise. This includes advancements in hardware design, improved detection technologies, and sophisticated software for data analysis and noise reduction. The market is likely to see increased competition among established players and new entrants, driving further innovation and improvements in system performance.
In the research sector, academic and pharmaceutical laboratories are increasingly focusing on the analysis of complex biological samples, including proteins, nucleic acids, and their fragments. This trend has created a strong demand for gel electrophoresis systems that can provide clear, high-resolution separation of these molecules, even when dealing with samples containing closely related species or low-abundance targets.
The clinical diagnostics field is another major driver of market demand for high-resolution gel electrophoresis. As personalized medicine and molecular diagnostics continue to advance, there is a growing need for accurate and sensitive methods to detect genetic variations, biomarkers, and disease-associated proteins. High-resolution gel electrophoresis systems that can minimize system noise are crucial for developing reliable diagnostic tests and monitoring disease progression.
In the biopharmaceutical industry, the production of biologics and biosimilars requires stringent quality control measures. High-resolution gel electrophoresis plays a vital role in assessing the purity, stability, and integrity of protein-based drugs throughout the manufacturing process. The ability to detect minor impurities or structural changes with minimal interference from system noise is essential for ensuring product safety and efficacy.
The food and beverage industry is also contributing to the market demand for high-resolution gel electrophoresis. With increasing regulatory requirements and consumer awareness, there is a growing need for accurate methods to detect food adulterants, allergens, and genetically modified organisms. High-resolution gel electrophoresis systems with low noise levels are valuable tools for food safety testing and quality assurance.
Environmental monitoring and forensic applications represent emerging markets for high-resolution gel electrophoresis. These fields require sensitive and reliable methods for detecting and analyzing trace amounts of DNA or proteins in complex environmental or forensic samples. The ability to minimize system noise is crucial for obtaining accurate results in these challenging applications.
As the demand for high-resolution gel electrophoresis continues to grow, manufacturers are focusing on developing innovative systems that can deliver superior performance with minimal noise. This includes advancements in hardware design, improved detection technologies, and sophisticated software for data analysis and noise reduction. The market is likely to see increased competition among established players and new entrants, driving further innovation and improvements in system performance.
Current Challenges in Gel Electrophoresis Signal-to-Noise Ratio
Gel electrophoresis is a fundamental technique in molecular biology, yet it faces significant challenges in maintaining a high signal-to-noise ratio. The primary issue stems from various sources of system noise that can obscure or distort the output, leading to difficulties in data interpretation and reduced reliability of results.
One of the most prominent challenges is background noise, which manifests as a uniform or non-uniform haze across the gel. This noise can result from impurities in the gel matrix, buffer contamination, or suboptimal imaging conditions. It reduces contrast and makes it harder to distinguish faint bands, particularly in cases where target molecules are present in low concentrations.
Another significant challenge is the presence of non-specific bands or smears. These artifacts can arise from partial digestion of DNA, contamination with genomic DNA, or non-specific binding of fluorescent dyes. Such noise not only complicates the interpretation of results but can also lead to false positives or negatives in molecular weight determinations.
Electrical noise poses a substantial challenge, especially in automated gel electrophoresis systems. Fluctuations in current or voltage during the run can cause band distortions or uneven migration, compromising the accuracy of size estimations. This type of noise is particularly problematic when working with high-sensitivity detection methods or when analyzing complex mixtures of biomolecules.
The inherent limitations of detection systems also contribute to the signal-to-noise ratio challenges. CCD cameras or fluorescence scanners used for gel imaging have finite sensitivity and dynamic range. This can result in either oversaturation of strong signals or failure to detect weak signals, both of which distort the true representation of the sample composition.
Sample-related issues further compound the noise problem. Overloading of wells can lead to streaking and poor resolution, while insufficient sample loading may result in bands that are too faint to distinguish from background noise. Achieving the optimal balance is crucial but can be challenging, especially when working with samples of varying concentrations or complex mixtures.
Environmental factors such as temperature fluctuations and vibrations during the electrophoresis run can introduce additional noise. These factors can cause band broadening or irregular migration patterns, reducing the overall resolution and making it difficult to accurately interpret the results.
Addressing these challenges requires a multifaceted approach, combining improvements in gel preparation techniques, optimized running conditions, advanced imaging technologies, and sophisticated data analysis algorithms. The development of noise reduction strategies is an active area of research, with potential solutions ranging from novel gel formulations to machine learning-based image processing techniques.
One of the most prominent challenges is background noise, which manifests as a uniform or non-uniform haze across the gel. This noise can result from impurities in the gel matrix, buffer contamination, or suboptimal imaging conditions. It reduces contrast and makes it harder to distinguish faint bands, particularly in cases where target molecules are present in low concentrations.
Another significant challenge is the presence of non-specific bands or smears. These artifacts can arise from partial digestion of DNA, contamination with genomic DNA, or non-specific binding of fluorescent dyes. Such noise not only complicates the interpretation of results but can also lead to false positives or negatives in molecular weight determinations.
Electrical noise poses a substantial challenge, especially in automated gel electrophoresis systems. Fluctuations in current or voltage during the run can cause band distortions or uneven migration, compromising the accuracy of size estimations. This type of noise is particularly problematic when working with high-sensitivity detection methods or when analyzing complex mixtures of biomolecules.
The inherent limitations of detection systems also contribute to the signal-to-noise ratio challenges. CCD cameras or fluorescence scanners used for gel imaging have finite sensitivity and dynamic range. This can result in either oversaturation of strong signals or failure to detect weak signals, both of which distort the true representation of the sample composition.
Sample-related issues further compound the noise problem. Overloading of wells can lead to streaking and poor resolution, while insufficient sample loading may result in bands that are too faint to distinguish from background noise. Achieving the optimal balance is crucial but can be challenging, especially when working with samples of varying concentrations or complex mixtures.
Environmental factors such as temperature fluctuations and vibrations during the electrophoresis run can introduce additional noise. These factors can cause band broadening or irregular migration patterns, reducing the overall resolution and making it difficult to accurately interpret the results.
Addressing these challenges requires a multifaceted approach, combining improvements in gel preparation techniques, optimized running conditions, advanced imaging technologies, and sophisticated data analysis algorithms. The development of noise reduction strategies is an active area of research, with potential solutions ranging from novel gel formulations to machine learning-based image processing techniques.
Existing Noise Minimization Strategies for Gel Electrophoresis
01 Noise reduction in power supply
Implementing noise reduction techniques in the power supply of gel electrophoresis systems can significantly improve signal quality. This may involve using low-noise power supplies, incorporating noise filters, or employing voltage stabilization circuits to minimize electrical interference during the electrophoresis process.- Noise reduction in power supply: Implementing noise reduction techniques in the power supply of gel electrophoresis systems can significantly improve the overall performance and accuracy of the system. This may involve using filters, voltage regulators, or specialized circuit designs to minimize electrical noise and ensure a stable power source for the electrophoresis process.
- Shielding and grounding techniques: Proper shielding and grounding of the gel electrophoresis system components can help reduce electromagnetic interference and minimize noise. This may include using Faraday cages, conductive materials for enclosures, and implementing effective grounding strategies to prevent unwanted electrical signals from affecting the system's performance.
- Improved electrode design: Optimizing the design of electrodes used in gel electrophoresis systems can help reduce noise and improve signal quality. This may involve using materials with better conductivity, modifying electrode shapes or configurations, or implementing novel electrode designs to minimize electrical interference and enhance the overall system performance.
- Signal processing and filtering: Implementing advanced signal processing techniques and filtering methods can help reduce noise in gel electrophoresis systems. This may include using digital filters, noise cancellation algorithms, or specialized software to enhance signal quality and minimize the impact of electrical noise on the final results.
- Temperature control and stabilization: Maintaining stable temperature conditions during gel electrophoresis can help reduce noise caused by thermal fluctuations. This may involve implementing precise temperature control systems, using heat sinks or cooling mechanisms, or designing thermally stable components to minimize temperature-related noise and improve overall system performance.
02 Shielding and grounding techniques
Proper shielding and grounding of the gel electrophoresis system components can help reduce electromagnetic interference and minimize noise. This may include using Faraday cages, conductive enclosures, or strategic placement of grounding points to isolate sensitive components from external electromagnetic sources.Expand Specific Solutions03 Optimized electrode design
Improving electrode design and placement can help reduce noise in gel electrophoresis systems. This may involve using materials with low electrical resistance, optimizing electrode geometry, or implementing novel electrode configurations to minimize signal distortion and improve overall system performance.Expand Specific Solutions04 Signal processing and filtering
Implementing advanced signal processing and filtering techniques can help reduce noise in gel electrophoresis systems. This may include using digital filters, signal amplification, or noise cancellation algorithms to improve the signal-to-noise ratio and enhance the clarity of electrophoresis results.Expand Specific Solutions05 Temperature control and stabilization
Maintaining stable temperature conditions during gel electrophoresis can help reduce noise caused by thermal fluctuations. This may involve implementing precise temperature control systems, using heat sinks, or incorporating thermal insulation to minimize temperature-induced variations in electrophoresis results.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Electrophoresis Equipment and Reagents
The gel electrophoresis market is in a mature stage, with a global size estimated at over $1 billion. The technology is well-established, with ongoing innovations focused on improving resolution and reducing system noise. Key players like Life Technologies Corp. and Dionex Corp. are driving advancements in noise reduction through enhanced buffer systems and electrode designs. Other companies such as Hitachi Ltd. and Tecan Trading AG are contributing to the field with improved imaging and analysis software. The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of large, diversified life science companies and specialized instrumentation firms, all striving to enhance the accuracy and reliability of gel electrophoresis results.
Life Technologies Corp.
Technical Solution: Life Technologies Corp. has developed a multi-faceted approach to minimize system noise in gel electrophoresis. Their strategy includes the use of high-quality, ultra-pure reagents to reduce background noise caused by contaminants[1]. They have also implemented advanced imaging systems with cooled CCD cameras to reduce thermal noise during gel visualization[2]. Life Technologies has introduced automated gel loading systems that ensure consistent sample application, minimizing variability that can contribute to noise[3]. Furthermore, they have developed specialized buffer formulations that help maintain stable pH and ionic conditions throughout the run, reducing noise from fluctuations in the electrophoresis environment[4].
Strengths: Comprehensive approach addressing multiple sources of noise, from sample preparation to imaging. Weaknesses: May be more expensive due to the use of specialized reagents and equipment.
Tecan Trading AG
Technical Solution: Tecan Trading AG has focused on automation and precision liquid handling to minimize system noise in gel electrophoresis. Their approach includes the development of high-precision robotic systems for sample preparation and gel loading, which significantly reduce human error and variability[1]. Tecan has also introduced microfluidic-based electrophoresis systems that minimize sample volumes and reduce diffusion-related noise[2]. Their systems incorporate advanced software algorithms for data analysis and noise filtering, improving the signal-to-noise ratio in the final output[3]. Additionally, Tecan has developed specialized consumables, such as optimized gel cassettes, that are designed to reduce background noise and improve overall system performance[4].
Strengths: High level of automation and precision, reducing human-induced variability. Weaknesses: May have a steeper learning curve for users transitioning from manual methods.
Innovative Approaches to Enhance Signal Quality
System for rapid high-resolution GEL electrophoresis
PatentActiveUS20190391113A1
Innovation
- The development of electrophoretic systems and formulations that allow for higher field strengths up to 50% more than conventional systems, using a discontinuous buffer system with specific gel amine and ampholyte buffers, and a pH range of 5.5 to 7.5, enabling faster separation of proteins within 30 minutes or less, even at higher voltages.
Gel electrophoresis device
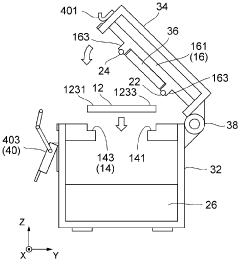
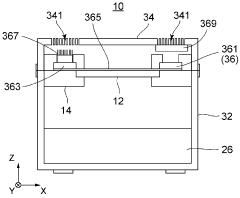
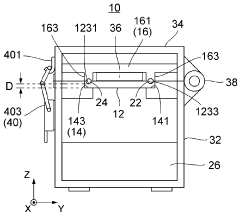
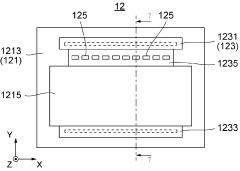
PatentWO2024122250A1
Innovation
- A gel electrophoresis device design that presses electrodes directly onto the gel cassette to form a uniform electric field without additional buffers, using a gel cassette without integrated electrodes, which reduces costs and environmental impact by eliminating the need for additional buffer solutions and addressing surface irregularities.
Standardization of Noise Reduction Protocols
Standardization of noise reduction protocols in gel electrophoresis is crucial for ensuring consistent and reliable results across different laboratories and experiments. The development of standardized protocols involves a systematic approach to identify, quantify, and mitigate various sources of noise in the electrophoresis system.
One of the primary steps in standardization is the establishment of a comprehensive checklist for equipment maintenance and calibration. This includes regular inspection and cleaning of electrophoresis chambers, power supplies, and imaging systems. Standardized procedures for electrode maintenance, buffer preparation, and gel casting are also essential components of noise reduction protocols.
The optimization of sample preparation techniques is another critical aspect of standardization. This involves developing guidelines for consistent sample loading, including recommendations for sample volume, concentration, and buffer composition. Standardized protocols should also address the use of internal standards and markers to facilitate accurate band identification and quantification.
Electrophoresis running conditions play a significant role in noise reduction. Standardized protocols should specify optimal voltage settings, running times, and buffer compositions for different gel types and applications. Temperature control during electrophoresis is also crucial, and standardized methods for maintaining consistent temperature throughout the run should be established.
Imaging and data analysis procedures are equally important in noise reduction efforts. Standardized protocols should outline best practices for image acquisition, including exposure times, filter settings, and background correction methods. Guidelines for image processing and quantification software usage should also be included to ensure consistent data interpretation across different laboratories.
Quality control measures are integral to standardized noise reduction protocols. This includes the implementation of regular system performance checks using standard samples or DNA ladders. Establishing acceptance criteria for background noise levels, signal-to-noise ratios, and band resolution can help maintain consistent performance across different experiments and laboratories.
Interlaboratory validation studies are essential for refining and validating standardized protocols. These studies involve multiple laboratories performing the same experiments using the proposed standardized methods. The results are then compared and analyzed to identify any remaining sources of variability and to further refine the protocols.
Documentation and training are crucial components of protocol standardization. Detailed standard operating procedures (SOPs) should be developed and regularly updated to reflect the latest best practices in noise reduction. Comprehensive training programs for laboratory personnel should be implemented to ensure consistent application of these standardized protocols across different research groups and institutions.
One of the primary steps in standardization is the establishment of a comprehensive checklist for equipment maintenance and calibration. This includes regular inspection and cleaning of electrophoresis chambers, power supplies, and imaging systems. Standardized procedures for electrode maintenance, buffer preparation, and gel casting are also essential components of noise reduction protocols.
The optimization of sample preparation techniques is another critical aspect of standardization. This involves developing guidelines for consistent sample loading, including recommendations for sample volume, concentration, and buffer composition. Standardized protocols should also address the use of internal standards and markers to facilitate accurate band identification and quantification.
Electrophoresis running conditions play a significant role in noise reduction. Standardized protocols should specify optimal voltage settings, running times, and buffer compositions for different gel types and applications. Temperature control during electrophoresis is also crucial, and standardized methods for maintaining consistent temperature throughout the run should be established.
Imaging and data analysis procedures are equally important in noise reduction efforts. Standardized protocols should outline best practices for image acquisition, including exposure times, filter settings, and background correction methods. Guidelines for image processing and quantification software usage should also be included to ensure consistent data interpretation across different laboratories.
Quality control measures are integral to standardized noise reduction protocols. This includes the implementation of regular system performance checks using standard samples or DNA ladders. Establishing acceptance criteria for background noise levels, signal-to-noise ratios, and band resolution can help maintain consistent performance across different experiments and laboratories.
Interlaboratory validation studies are essential for refining and validating standardized protocols. These studies involve multiple laboratories performing the same experiments using the proposed standardized methods. The results are then compared and analyzed to identify any remaining sources of variability and to further refine the protocols.
Documentation and training are crucial components of protocol standardization. Detailed standard operating procedures (SOPs) should be developed and regularly updated to reflect the latest best practices in noise reduction. Comprehensive training programs for laboratory personnel should be implemented to ensure consistent application of these standardized protocols across different research groups and institutions.
Environmental Factors Affecting Electrophoresis Noise
Environmental factors play a crucial role in the quality and reliability of gel electrophoresis output. Temperature fluctuations can significantly impact the migration rate of DNA fragments, leading to inconsistent results. Maintaining a stable temperature throughout the electrophoresis process is essential for minimizing system noise. Variations in ambient temperature can affect buffer viscosity and electrical conductivity, altering the movement of molecules through the gel matrix.
Humidity levels in the laboratory environment can also contribute to system noise. High humidity may cause gel swelling or uneven drying, resulting in distorted band patterns. Conversely, low humidity can lead to rapid gel dehydration, affecting the overall separation quality. Implementing proper humidity control measures, such as using dehumidifiers or conducting experiments in climate-controlled rooms, can help mitigate these issues.
Electromagnetic interference from nearby electronic equipment can introduce noise into the electrophoresis system. Power supplies, centrifuges, and other laboratory instruments may generate electromagnetic fields that interfere with the electric field applied during electrophoresis. Shielding the electrophoresis apparatus or relocating potential sources of interference can minimize this type of noise.
Vibrations from laboratory equipment or external sources can cause disturbances in the gel matrix, leading to band smearing or irregular migration patterns. Placing the electrophoresis apparatus on vibration-dampening surfaces or in isolated areas can help reduce this environmental factor's impact on system noise.
Air quality and particulate matter in the laboratory environment can also affect electrophoresis results. Dust particles or airborne contaminants may settle on the gel surface, interfering with DNA migration or introducing artifacts in the final output. Conducting electrophoresis in clean, well-ventilated spaces and using dust covers when appropriate can minimize this source of noise.
Lighting conditions in the laboratory can impact the visualization and analysis of electrophoresis results. Excessive ambient light or inconsistent illumination may lead to difficulties in accurately interpreting band patterns or detecting faint signals. Implementing proper lighting control, such as using light-tight imaging systems or conducting analysis in darkened rooms, can enhance the signal-to-noise ratio in gel electrophoresis output.
Humidity levels in the laboratory environment can also contribute to system noise. High humidity may cause gel swelling or uneven drying, resulting in distorted band patterns. Conversely, low humidity can lead to rapid gel dehydration, affecting the overall separation quality. Implementing proper humidity control measures, such as using dehumidifiers or conducting experiments in climate-controlled rooms, can help mitigate these issues.
Electromagnetic interference from nearby electronic equipment can introduce noise into the electrophoresis system. Power supplies, centrifuges, and other laboratory instruments may generate electromagnetic fields that interfere with the electric field applied during electrophoresis. Shielding the electrophoresis apparatus or relocating potential sources of interference can minimize this type of noise.
Vibrations from laboratory equipment or external sources can cause disturbances in the gel matrix, leading to band smearing or irregular migration patterns. Placing the electrophoresis apparatus on vibration-dampening surfaces or in isolated areas can help reduce this environmental factor's impact on system noise.
Air quality and particulate matter in the laboratory environment can also affect electrophoresis results. Dust particles or airborne contaminants may settle on the gel surface, interfering with DNA migration or introducing artifacts in the final output. Conducting electrophoresis in clean, well-ventilated spaces and using dust covers when appropriate can minimize this source of noise.
Lighting conditions in the laboratory can impact the visualization and analysis of electrophoresis results. Excessive ambient light or inconsistent illumination may lead to difficulties in accurately interpreting band patterns or detecting faint signals. Implementing proper lighting control, such as using light-tight imaging systems or conducting analysis in darkened rooms, can enhance the signal-to-noise ratio in gel electrophoresis output.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!