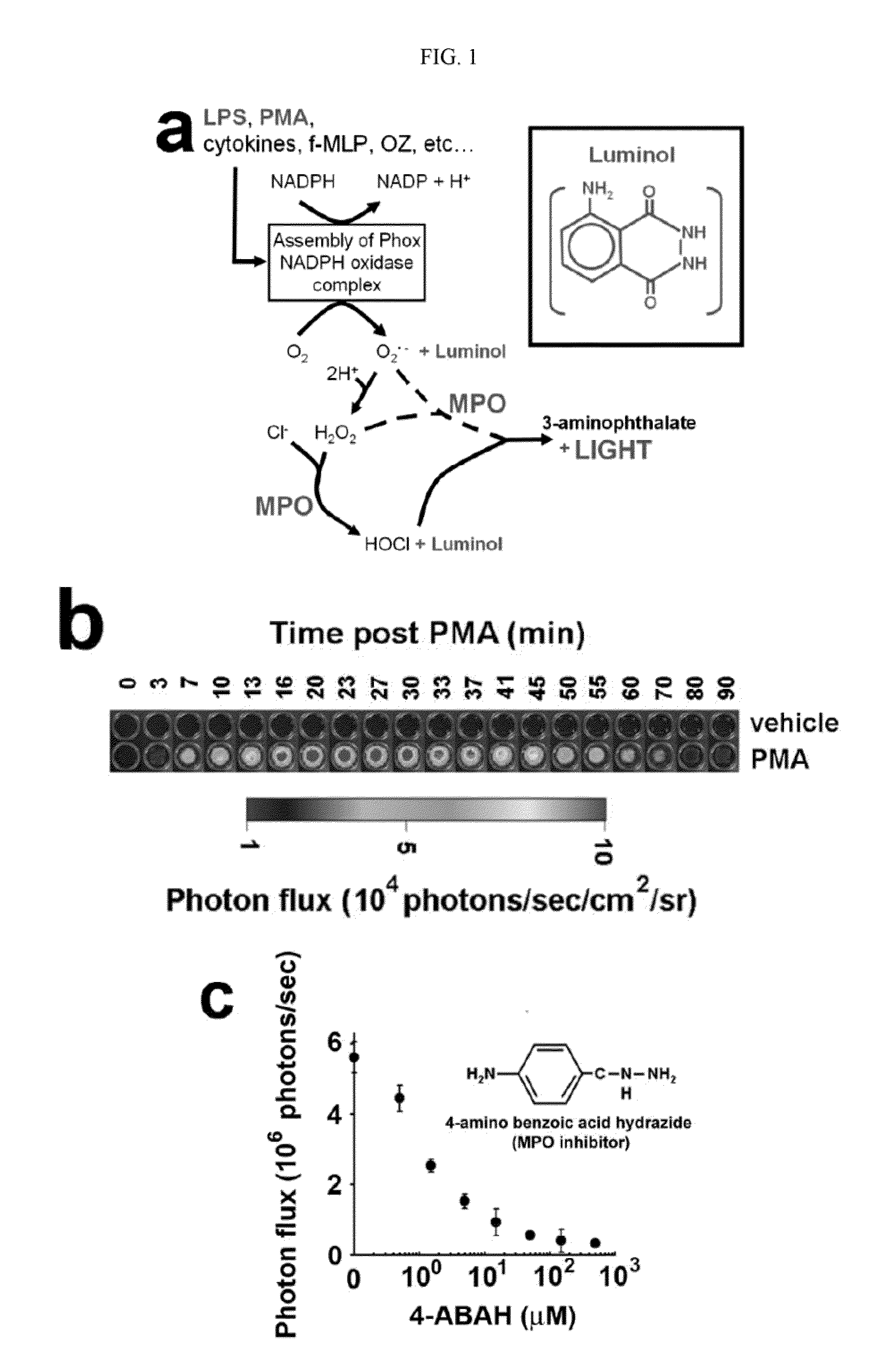
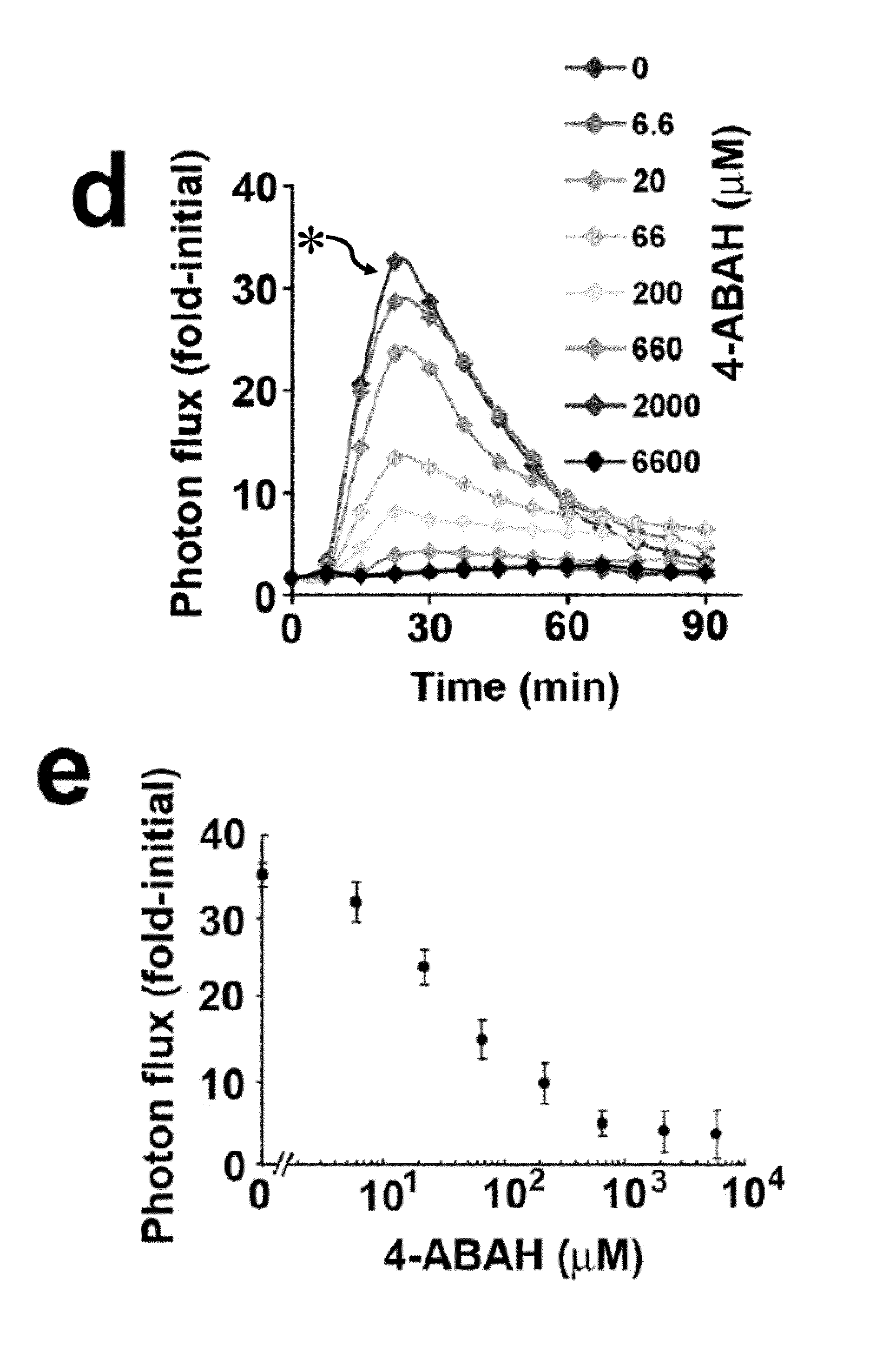
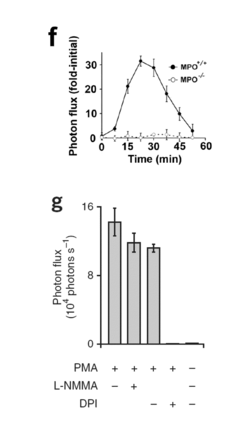
How to Optimize Luminol's Use in Emerging Technologies?
AUG 19, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Luminol Tech Evolution
Luminol, a chemiluminescent compound, has undergone significant technological evolution since its discovery in the late 19th century. Initially used primarily in forensic science for blood detection, luminol's applications have expanded dramatically over the years, driven by advancements in chemistry, biotechnology, and materials science.
In the 1930s, researchers began to explore luminol's potential beyond forensics, leading to its use in analytical chemistry for trace metal detection. This period marked the beginning of luminol's diversification into scientific and industrial applications. The 1950s and 1960s saw further refinement of luminol-based techniques, with improvements in sensitivity and specificity.
The 1970s brought a breakthrough in luminol technology with the development of enhanced chemiluminescence (ECL) systems. These systems combined luminol with other compounds to amplify light emission, greatly expanding its utility in biochemical assays and medical diagnostics. This innovation paved the way for luminol's integration into immunoassays and DNA detection methods in the 1980s and 1990s.
The turn of the millennium heralded a new era for luminol technology. Nanotechnology advancements led to the creation of luminol-based nanoparticles and nanocomposites, offering unprecedented control over light emission properties. These developments opened up possibilities in fields such as biosensing, environmental monitoring, and advanced imaging techniques.
Recent years have seen a focus on optimizing luminol's performance through molecular engineering and formulation improvements. Researchers have explored ways to enhance luminol's stability, increase its light output, and tailor its emission spectrum for specific applications. This has resulted in the development of luminol derivatives and hybrid systems that offer superior performance in targeted applications.
The integration of luminol with emerging technologies has been a key trend in its recent evolution. For instance, the combination of luminol-based systems with microfluidic devices has enabled the development of portable, high-sensitivity diagnostic tools. Similarly, the incorporation of luminol into smart materials and responsive systems has opened up new possibilities in areas such as drug delivery and environmental remediation.
Looking forward, the optimization of luminol's use in emerging technologies is likely to focus on several key areas. These include enhancing its compatibility with advanced materials and nanosystems, improving its performance under diverse environmental conditions, and developing novel activation mechanisms for more precise control over light emission. Additionally, efforts to reduce the environmental impact of luminol-based systems and improve their sustainability are expected to gain prominence, aligning with global trends towards greener technologies.
In the 1930s, researchers began to explore luminol's potential beyond forensics, leading to its use in analytical chemistry for trace metal detection. This period marked the beginning of luminol's diversification into scientific and industrial applications. The 1950s and 1960s saw further refinement of luminol-based techniques, with improvements in sensitivity and specificity.
The 1970s brought a breakthrough in luminol technology with the development of enhanced chemiluminescence (ECL) systems. These systems combined luminol with other compounds to amplify light emission, greatly expanding its utility in biochemical assays and medical diagnostics. This innovation paved the way for luminol's integration into immunoassays and DNA detection methods in the 1980s and 1990s.
The turn of the millennium heralded a new era for luminol technology. Nanotechnology advancements led to the creation of luminol-based nanoparticles and nanocomposites, offering unprecedented control over light emission properties. These developments opened up possibilities in fields such as biosensing, environmental monitoring, and advanced imaging techniques.
Recent years have seen a focus on optimizing luminol's performance through molecular engineering and formulation improvements. Researchers have explored ways to enhance luminol's stability, increase its light output, and tailor its emission spectrum for specific applications. This has resulted in the development of luminol derivatives and hybrid systems that offer superior performance in targeted applications.
The integration of luminol with emerging technologies has been a key trend in its recent evolution. For instance, the combination of luminol-based systems with microfluidic devices has enabled the development of portable, high-sensitivity diagnostic tools. Similarly, the incorporation of luminol into smart materials and responsive systems has opened up new possibilities in areas such as drug delivery and environmental remediation.
Looking forward, the optimization of luminol's use in emerging technologies is likely to focus on several key areas. These include enhancing its compatibility with advanced materials and nanosystems, improving its performance under diverse environmental conditions, and developing novel activation mechanisms for more precise control over light emission. Additionally, efforts to reduce the environmental impact of luminol-based systems and improve their sustainability are expected to gain prominence, aligning with global trends towards greener technologies.
Market Demand Analysis
The market demand for luminol in emerging technologies is experiencing significant growth, driven by its unique chemiluminescent properties and versatile applications. Luminol's ability to produce a bright blue light when oxidized has made it a valuable tool in various fields, including forensic science, medical diagnostics, and environmental monitoring.
In the forensic science sector, luminol remains a crucial component in crime scene investigation kits. The increasing focus on advanced forensic techniques and the rising number of criminal investigations worldwide are fueling the demand for luminol-based products. Law enforcement agencies and forensic laboratories are continuously seeking improved formulations and application methods to enhance the sensitivity and reliability of luminol in detecting trace amounts of blood.
The medical diagnostics industry represents another significant market for luminol. Its use in chemiluminescent immunoassays for detecting various biomarkers has gained traction due to the growing emphasis on early disease detection and personalized medicine. The increasing prevalence of chronic diseases and the need for rapid, accurate diagnostic tools are driving the adoption of luminol-based testing methods in clinical laboratories and point-of-care settings.
Environmental monitoring applications are also contributing to the expanding market for luminol. Its ability to detect and quantify pollutants, such as heavy metals and organic compounds in water and soil samples, has made it an essential tool for environmental scientists and regulatory agencies. The growing concerns over water quality and soil contamination have led to increased investments in environmental testing technologies, further boosting the demand for luminol-based solutions.
The pharmaceutical and biotechnology sectors are exploring novel applications of luminol in drug discovery and development processes. Its use in high-throughput screening assays and as a chemiluminescent label for biomolecules has opened up new avenues for research and development. This trend is expected to create additional market opportunities for luminol suppliers and technology developers.
As emerging technologies continue to evolve, the demand for luminol is likely to expand into new areas. For instance, the development of advanced biosensors and microfluidic devices incorporating luminol-based detection systems shows promise for applications in food safety testing, agricultural monitoring, and industrial quality control.
The global market for luminol and related chemiluminescent technologies is projected to grow steadily in the coming years. Factors such as increasing R&D investments, technological advancements in detection methods, and the expansion of application areas are expected to drive this growth. However, market players must address challenges such as the need for improved stability, sensitivity, and specificity of luminol-based assays to fully capitalize on these opportunities and meet the evolving demands of various industries.
In the forensic science sector, luminol remains a crucial component in crime scene investigation kits. The increasing focus on advanced forensic techniques and the rising number of criminal investigations worldwide are fueling the demand for luminol-based products. Law enforcement agencies and forensic laboratories are continuously seeking improved formulations and application methods to enhance the sensitivity and reliability of luminol in detecting trace amounts of blood.
The medical diagnostics industry represents another significant market for luminol. Its use in chemiluminescent immunoassays for detecting various biomarkers has gained traction due to the growing emphasis on early disease detection and personalized medicine. The increasing prevalence of chronic diseases and the need for rapid, accurate diagnostic tools are driving the adoption of luminol-based testing methods in clinical laboratories and point-of-care settings.
Environmental monitoring applications are also contributing to the expanding market for luminol. Its ability to detect and quantify pollutants, such as heavy metals and organic compounds in water and soil samples, has made it an essential tool for environmental scientists and regulatory agencies. The growing concerns over water quality and soil contamination have led to increased investments in environmental testing technologies, further boosting the demand for luminol-based solutions.
The pharmaceutical and biotechnology sectors are exploring novel applications of luminol in drug discovery and development processes. Its use in high-throughput screening assays and as a chemiluminescent label for biomolecules has opened up new avenues for research and development. This trend is expected to create additional market opportunities for luminol suppliers and technology developers.
As emerging technologies continue to evolve, the demand for luminol is likely to expand into new areas. For instance, the development of advanced biosensors and microfluidic devices incorporating luminol-based detection systems shows promise for applications in food safety testing, agricultural monitoring, and industrial quality control.
The global market for luminol and related chemiluminescent technologies is projected to grow steadily in the coming years. Factors such as increasing R&D investments, technological advancements in detection methods, and the expansion of application areas are expected to drive this growth. However, market players must address challenges such as the need for improved stability, sensitivity, and specificity of luminol-based assays to fully capitalize on these opportunities and meet the evolving demands of various industries.
Current Challenges
Luminol, a chemiluminescent compound, has shown great potential in various emerging technologies. However, its optimization and widespread adoption face several significant challenges. One of the primary obstacles is the limited stability of luminol in different environmental conditions. The compound's luminescence can be affected by factors such as pH, temperature, and the presence of interfering substances, which can lead to inconsistent results in practical applications.
Another challenge lies in the relatively low quantum yield of luminol chemiluminescence. While the compound produces a visible blue light, the intensity and duration of the emission are often insufficient for certain advanced applications, particularly in fields requiring high sensitivity or prolonged detection periods. This limitation hinders its use in areas such as advanced biosensing and long-term environmental monitoring.
The selectivity of luminol-based detection systems also presents a significant hurdle. In complex matrices, such as biological samples or environmental specimens, the presence of other compounds can interfere with the luminol reaction, leading to false positives or reduced sensitivity. Enhancing the specificity of luminol-based assays without compromising their simplicity and cost-effectiveness remains a key challenge for researchers and developers.
Furthermore, the integration of luminol into emerging technologies faces scalability issues. While luminol works well in laboratory settings, translating these applications to large-scale industrial processes or miniaturized portable devices presents numerous engineering challenges. These include maintaining reagent stability, ensuring consistent mixing and reaction conditions, and developing robust, user-friendly interfaces for non-specialist operators.
The environmental impact of luminol and its reaction products is another area of concern. As the use of luminol in various technologies increases, there is a growing need to assess and mitigate any potential ecological effects. This includes developing more environmentally friendly synthesis methods for luminol and finding ways to safely dispose of or recycle the compound after use.
Lastly, the regulatory landscape surrounding the use of luminol in new technologies presents a complex challenge. As luminol finds applications in sensitive areas such as forensics, medical diagnostics, and environmental monitoring, navigating the regulatory requirements for approval and standardization becomes increasingly important. Ensuring compliance with diverse international standards while maintaining the cost-effectiveness and accessibility of luminol-based technologies is a significant hurdle for innovators in this field.
Another challenge lies in the relatively low quantum yield of luminol chemiluminescence. While the compound produces a visible blue light, the intensity and duration of the emission are often insufficient for certain advanced applications, particularly in fields requiring high sensitivity or prolonged detection periods. This limitation hinders its use in areas such as advanced biosensing and long-term environmental monitoring.
The selectivity of luminol-based detection systems also presents a significant hurdle. In complex matrices, such as biological samples or environmental specimens, the presence of other compounds can interfere with the luminol reaction, leading to false positives or reduced sensitivity. Enhancing the specificity of luminol-based assays without compromising their simplicity and cost-effectiveness remains a key challenge for researchers and developers.
Furthermore, the integration of luminol into emerging technologies faces scalability issues. While luminol works well in laboratory settings, translating these applications to large-scale industrial processes or miniaturized portable devices presents numerous engineering challenges. These include maintaining reagent stability, ensuring consistent mixing and reaction conditions, and developing robust, user-friendly interfaces for non-specialist operators.
The environmental impact of luminol and its reaction products is another area of concern. As the use of luminol in various technologies increases, there is a growing need to assess and mitigate any potential ecological effects. This includes developing more environmentally friendly synthesis methods for luminol and finding ways to safely dispose of or recycle the compound after use.
Lastly, the regulatory landscape surrounding the use of luminol in new technologies presents a complex challenge. As luminol finds applications in sensitive areas such as forensics, medical diagnostics, and environmental monitoring, navigating the regulatory requirements for approval and standardization becomes increasingly important. Ensuring compliance with diverse international standards while maintaining the cost-effectiveness and accessibility of luminol-based technologies is a significant hurdle for innovators in this field.
Existing Optimization Methods
01 Chemical composition optimization
Improving the chemical composition of luminol solutions to enhance its chemiluminescent properties. This involves adjusting the concentrations of luminol and other reagents, as well as incorporating additives to increase light intensity and duration.- Chemical modifications to enhance luminol performance: Various chemical modifications can be made to the luminol molecule to enhance its performance in chemiluminescence reactions. These modifications may include altering functional groups, adding substituents, or creating derivatives to improve factors such as quantum yield, reaction kinetics, and stability.
- Optimization of reaction conditions for luminol-based assays: The efficiency of luminol-based assays can be improved by optimizing reaction conditions such as pH, temperature, catalyst concentration, and buffer composition. These adjustments can lead to increased sensitivity, reproducibility, and signal-to-noise ratio in various analytical applications.
- Development of novel luminol-based detection systems: Innovative detection systems incorporating luminol are being developed to enhance sensitivity and specificity in various fields, including forensics, environmental monitoring, and medical diagnostics. These systems may involve new instrumentation, microfluidic devices, or integration with other analytical techniques.
- Formulation of enhanced luminol reagents: Advanced formulations of luminol reagents are being developed to improve stability, shelf-life, and ease of use. These formulations may include additives, stabilizers, or encapsulation techniques to enhance the overall performance and practicality of luminol-based detection methods.
- Integration of luminol with nanomaterials for enhanced detection: Combining luminol with various nanomaterials, such as nanoparticles, quantum dots, or nanocomposites, can lead to significant improvements in sensitivity and selectivity of chemiluminescence assays. This approach exploits the unique properties of nanomaterials to amplify signals and create novel detection platforms.
02 Detection method enhancement
Developing advanced detection methods using optimized luminol formulations. This includes improving sensitivity, specificity, and reliability of luminol-based assays for various applications such as forensic investigations and medical diagnostics.Expand Specific Solutions03 Luminol synthesis optimization
Refining the synthesis process of luminol to improve yield, purity, and cost-effectiveness. This involves exploring new synthetic routes, catalysts, and reaction conditions to produce high-quality luminol more efficiently.Expand Specific Solutions04 Application-specific formulations
Developing tailored luminol formulations for specific applications such as crime scene investigation, environmental monitoring, and biomedical research. These formulations are optimized for particular conditions and requirements of each application.Expand Specific Solutions05 Instrumentation and measurement optimization
Improving the design and functionality of instruments used for luminol-based detection. This includes enhancing sensitivity, reducing background noise, and developing more user-friendly devices for various applications.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The optimization of luminol in emerging technologies is at a pivotal stage, with the market showing significant growth potential. The industry is transitioning from research to early commercialization, driven by advancements in biomedical imaging, forensics, and analytical chemistry. Key players like LG Electronics, Samsung, and Konica Minolta are leveraging their expertise in display technologies to explore luminol applications. Academic institutions such as Washington University in St. Louis and Kyushu University are contributing to fundamental research. The technology's maturity varies across applications, with established use in forensics but emerging potential in areas like biosensors and OLED displays, indicating a dynamic and evolving competitive landscape.
Merck Patent GmbH
Technical Solution: Merck Patent GmbH has developed innovative luminol-based chemiluminescence systems for emerging technologies. Their approach involves synthesizing novel luminol derivatives with enhanced stability and quantum yield[1]. These compounds are incorporated into microfluidic devices for ultra-sensitive bioanalytical applications[2]. The company has also explored the use of luminol in advanced imaging techniques, such as bioluminescence resonance energy transfer (BRET) systems, for real-time monitoring of cellular processes[3]. Additionally, Merck has invested in developing luminol-based sensors for environmental monitoring, particularly for detecting trace amounts of heavy metals in water sources[4].
Strengths: High sensitivity and specificity in bioanalytical applications, versatility in imaging techniques. Weaknesses: Potential for interference from other compounds in complex matrices, limited shelf-life of some luminol derivatives.
Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Samsung Electronics has focused on integrating luminol-based technologies into consumer electronics and smart devices. They have developed luminol-enhanced OLED displays with improved brightness and energy efficiency[5]. The company has also explored the use of luminol in novel biometric authentication systems, utilizing its chemiluminescent properties for secure and tamper-evident user identification[6]. Samsung's research extends to incorporating luminol-based sensors in smart home devices for air and water quality monitoring[7]. Furthermore, they have patented a method for using luminol in self-cleaning surfaces for electronic devices, leveraging its oxidative properties to break down organic contaminants[8].
Strengths: Integration with existing consumer electronics, potential for mass-market applications. Weaknesses: Challenges in long-term stability of luminol-based components in consumer devices, potential cost implications for mass production.
Innovative Luminol Research
Bioluminescence imaging of myeloperoxidase activity in vivo, methods, compositions and apparatuses therefor
PatentInactiveUS20110250145A1
Innovation
- The development of methods for non-invasive imaging of MPO activity using luminogenic-optical probes that emit light upon contact with oxidizing agents, allowing for the visualization of MPO activity in vivo, particularly through bioluminescence imaging (BLI) techniques.
Environmental Impact Assessment
The environmental impact of luminol's use in emerging technologies is a critical consideration that requires thorough assessment. Luminol, a chemiluminescent compound widely used in forensic science and biomedical research, has potential applications in various emerging fields. However, its increased utilization may pose environmental risks that need to be carefully evaluated and mitigated.
One primary concern is the potential for luminol to contaminate water systems. When used in large quantities or disposed of improperly, luminol and its byproducts could enter aquatic ecosystems, potentially affecting water quality and aquatic life. Studies have shown that luminol can be toxic to certain aquatic organisms at high concentrations, highlighting the need for proper waste management and disposal protocols in industries utilizing this compound.
Air pollution is another environmental aspect to consider. While luminol itself is not highly volatile, the production processes and associated chemicals used in its manufacture may contribute to air quality issues if not properly controlled. Emissions from industrial facilities producing or using luminol should be monitored and regulated to minimize their impact on local air quality and comply with environmental standards.
The production of luminol also raises concerns about resource consumption and energy use. As demand for luminol increases with its adoption in emerging technologies, there may be a corresponding increase in the extraction of raw materials and energy consumption for its synthesis. This could contribute to broader environmental issues such as habitat destruction, greenhouse gas emissions, and depletion of non-renewable resources.
Biodegradability and persistence in the environment are crucial factors to assess. While luminol can break down under certain conditions, its environmental fate and the potential for bioaccumulation in food chains are not fully understood. Long-term studies are needed to evaluate the compound's behavior in various environmental compartments and its potential impacts on ecosystems over time.
To mitigate these environmental concerns, several strategies can be implemented. Developing more efficient and environmentally friendly production methods for luminol could reduce its ecological footprint. Additionally, exploring green chemistry principles to design less toxic alternatives or modify luminol's structure to enhance its biodegradability could significantly improve its environmental profile.
Implementing strict waste management protocols and encouraging recycling and reuse of luminol in industrial applications can minimize its release into the environment. Furthermore, establishing comprehensive guidelines for the handling, use, and disposal of luminol across different industries can ensure consistent environmental protection practices.
One primary concern is the potential for luminol to contaminate water systems. When used in large quantities or disposed of improperly, luminol and its byproducts could enter aquatic ecosystems, potentially affecting water quality and aquatic life. Studies have shown that luminol can be toxic to certain aquatic organisms at high concentrations, highlighting the need for proper waste management and disposal protocols in industries utilizing this compound.
Air pollution is another environmental aspect to consider. While luminol itself is not highly volatile, the production processes and associated chemicals used in its manufacture may contribute to air quality issues if not properly controlled. Emissions from industrial facilities producing or using luminol should be monitored and regulated to minimize their impact on local air quality and comply with environmental standards.
The production of luminol also raises concerns about resource consumption and energy use. As demand for luminol increases with its adoption in emerging technologies, there may be a corresponding increase in the extraction of raw materials and energy consumption for its synthesis. This could contribute to broader environmental issues such as habitat destruction, greenhouse gas emissions, and depletion of non-renewable resources.
Biodegradability and persistence in the environment are crucial factors to assess. While luminol can break down under certain conditions, its environmental fate and the potential for bioaccumulation in food chains are not fully understood. Long-term studies are needed to evaluate the compound's behavior in various environmental compartments and its potential impacts on ecosystems over time.
To mitigate these environmental concerns, several strategies can be implemented. Developing more efficient and environmentally friendly production methods for luminol could reduce its ecological footprint. Additionally, exploring green chemistry principles to design less toxic alternatives or modify luminol's structure to enhance its biodegradability could significantly improve its environmental profile.
Implementing strict waste management protocols and encouraging recycling and reuse of luminol in industrial applications can minimize its release into the environment. Furthermore, establishing comprehensive guidelines for the handling, use, and disposal of luminol across different industries can ensure consistent environmental protection practices.
Regulatory Compliance Landscape
The regulatory landscape surrounding luminol's use in emerging technologies is complex and evolving. As luminol finds applications beyond traditional forensic science, regulatory bodies are adapting to ensure its safe and ethical use. In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) oversees the use of luminol in environmental applications, such as detecting water contamination. The agency has established guidelines for its use and disposal, considering potential ecological impacts.
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulates luminol's use in medical and diagnostic technologies. As new applications emerge, such as cancer detection methods, the FDA is developing specific protocols for clinical trials and approval processes. These regulations aim to balance innovation with patient safety and efficacy standards.
In the European Union, the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) plays a crucial role in regulating luminol under the REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) framework. This comprehensive approach ensures that luminol's production, import, and use comply with stringent safety and environmental standards across EU member states.
For industrial applications, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) in the U.S. has established workplace safety guidelines for handling luminol. These regulations cover exposure limits, protective equipment requirements, and proper storage and handling procedures.
As luminol-based technologies expand into new sectors like agriculture and food safety, regulatory bodies such as the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) are developing specific guidelines. These regulations focus on ensuring that luminol use does not compromise food safety or introduce harmful residues into the food chain.
Internationally, the harmonization of regulations is an ongoing challenge. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) is working on developing global standards for luminol use in various applications, aiming to facilitate international trade and ensure consistent safety measures worldwide.
Emerging technologies utilizing luminol in nanotechnology and biosensors are pushing regulatory boundaries. Agencies like the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) are actively researching to establish appropriate regulatory frameworks for these cutting-edge applications, balancing innovation with potential risks.
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulates luminol's use in medical and diagnostic technologies. As new applications emerge, such as cancer detection methods, the FDA is developing specific protocols for clinical trials and approval processes. These regulations aim to balance innovation with patient safety and efficacy standards.
In the European Union, the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) plays a crucial role in regulating luminol under the REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) framework. This comprehensive approach ensures that luminol's production, import, and use comply with stringent safety and environmental standards across EU member states.
For industrial applications, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) in the U.S. has established workplace safety guidelines for handling luminol. These regulations cover exposure limits, protective equipment requirements, and proper storage and handling procedures.
As luminol-based technologies expand into new sectors like agriculture and food safety, regulatory bodies such as the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) are developing specific guidelines. These regulations focus on ensuring that luminol use does not compromise food safety or introduce harmful residues into the food chain.
Internationally, the harmonization of regulations is an ongoing challenge. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) is working on developing global standards for luminol use in various applications, aiming to facilitate international trade and ensure consistent safety measures worldwide.
Emerging technologies utilizing luminol in nanotechnology and biosensors are pushing regulatory boundaries. Agencies like the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) are actively researching to establish appropriate regulatory frameworks for these cutting-edge applications, balancing innovation with potential risks.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!