Impact of Sodium Percarbonate on Metallurgical Acid Neutralization
JUL 22, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Sodium Percarbonate in Acid Neutralization: Background and Objectives
Sodium percarbonate, a compound of sodium carbonate and hydrogen peroxide, has emerged as a significant player in the field of metallurgical acid neutralization. This technology has evolved from traditional acid neutralization methods, which often relied on lime or caustic soda. The development of sodium percarbonate as an alternative neutralizing agent represents a key milestone in the ongoing efforts to improve efficiency and reduce environmental impact in metallurgical processes.
The evolution of acid neutralization techniques in metallurgy has been driven by the need for more effective and environmentally friendly solutions. Early methods often resulted in large volumes of waste and were energy-intensive. The introduction of sodium percarbonate addresses many of these historical challenges, offering a more balanced approach to acid neutralization.
The primary objective of utilizing sodium percarbonate in metallurgical acid neutralization is to achieve efficient pH control while simultaneously introducing beneficial oxidizing properties. This dual-action capability sets sodium percarbonate apart from traditional neutralizing agents. By neutralizing acids and oxidizing certain metal ions, it potentially simplifies downstream processing and improves overall metal recovery rates.
Another critical goal is to minimize the environmental footprint of metallurgical operations. Sodium percarbonate breaks down into harmless byproducts, reducing the long-term environmental impact associated with acid neutralization processes. This aligns with the growing global emphasis on sustainable industrial practices and stricter environmental regulations in the metallurgical sector.
The technology also aims to enhance operational efficiency. By potentially reducing the volume of neutralizing agents required and simplifying waste management, sodium percarbonate could lead to significant cost savings and process streamlining in metallurgical operations. This economic incentive drives further research and development in this area.
As the metallurgical industry continues to seek innovative solutions for acid management, the role of sodium percarbonate is expected to expand. Future technological objectives include optimizing the application methods of sodium percarbonate, exploring its potential in treating complex acid mixtures, and developing synergistic combinations with other neutralizing agents to further enhance its effectiveness.
The evolution of acid neutralization techniques in metallurgy has been driven by the need for more effective and environmentally friendly solutions. Early methods often resulted in large volumes of waste and were energy-intensive. The introduction of sodium percarbonate addresses many of these historical challenges, offering a more balanced approach to acid neutralization.
The primary objective of utilizing sodium percarbonate in metallurgical acid neutralization is to achieve efficient pH control while simultaneously introducing beneficial oxidizing properties. This dual-action capability sets sodium percarbonate apart from traditional neutralizing agents. By neutralizing acids and oxidizing certain metal ions, it potentially simplifies downstream processing and improves overall metal recovery rates.
Another critical goal is to minimize the environmental footprint of metallurgical operations. Sodium percarbonate breaks down into harmless byproducts, reducing the long-term environmental impact associated with acid neutralization processes. This aligns with the growing global emphasis on sustainable industrial practices and stricter environmental regulations in the metallurgical sector.
The technology also aims to enhance operational efficiency. By potentially reducing the volume of neutralizing agents required and simplifying waste management, sodium percarbonate could lead to significant cost savings and process streamlining in metallurgical operations. This economic incentive drives further research and development in this area.
As the metallurgical industry continues to seek innovative solutions for acid management, the role of sodium percarbonate is expected to expand. Future technological objectives include optimizing the application methods of sodium percarbonate, exploring its potential in treating complex acid mixtures, and developing synergistic combinations with other neutralizing agents to further enhance its effectiveness.
Market Analysis for Metallurgical Acid Treatment Solutions
The market for metallurgical acid treatment solutions has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing environmental regulations and the need for more efficient and cost-effective acid neutralization processes in the mining and metallurgical industries. The global market size for acid neutralization solutions in metallurgy is projected to reach several billion dollars by 2025, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 5% during the forecast period.
The demand for acid treatment solutions is primarily fueled by the expansion of mining activities, particularly in developing countries, and the growing emphasis on sustainable practices in the metallurgical industry. As governments worldwide implement stricter environmental regulations, companies are compelled to adopt more effective acid neutralization techniques to minimize their environmental footprint and comply with regulatory standards.
Sodium percarbonate has emerged as a promising alternative to traditional acid neutralization agents in the metallurgical industry. Its ability to release hydrogen peroxide and sodium carbonate upon dissolution makes it an effective oxidizing and neutralizing agent for various acidic solutions. The market for sodium percarbonate in metallurgical applications is expected to grow at a faster rate than the overall acid treatment solutions market, with some industry analysts predicting a CAGR of 7-8% over the next five years.
Key factors driving the adoption of sodium percarbonate in acid neutralization processes include its high oxygen content, which enhances oxidation reactions, and its ability to generate alkaline conditions for effective neutralization. Additionally, sodium percarbonate is considered more environmentally friendly compared to some traditional neutralizing agents, aligning with the industry's shift towards greener technologies.
The market for metallurgical acid treatment solutions is highly competitive, with several major players dominating the global landscape. These companies are investing heavily in research and development to improve the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of their acid neutralization products, including sodium percarbonate-based solutions. The Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the highest growth in demand for acid treatment solutions, driven by rapid industrialization and increasing mining activities in countries like China, India, and Australia.
Despite the positive market outlook, challenges such as fluctuating raw material prices and the need for significant capital investments in new acid treatment technologies may hinder market growth to some extent. However, the ongoing development of innovative acid neutralization techniques and the increasing focus on circular economy principles in the metallurgical industry are expected to create new opportunities for market expansion in the coming years.
The demand for acid treatment solutions is primarily fueled by the expansion of mining activities, particularly in developing countries, and the growing emphasis on sustainable practices in the metallurgical industry. As governments worldwide implement stricter environmental regulations, companies are compelled to adopt more effective acid neutralization techniques to minimize their environmental footprint and comply with regulatory standards.
Sodium percarbonate has emerged as a promising alternative to traditional acid neutralization agents in the metallurgical industry. Its ability to release hydrogen peroxide and sodium carbonate upon dissolution makes it an effective oxidizing and neutralizing agent for various acidic solutions. The market for sodium percarbonate in metallurgical applications is expected to grow at a faster rate than the overall acid treatment solutions market, with some industry analysts predicting a CAGR of 7-8% over the next five years.
Key factors driving the adoption of sodium percarbonate in acid neutralization processes include its high oxygen content, which enhances oxidation reactions, and its ability to generate alkaline conditions for effective neutralization. Additionally, sodium percarbonate is considered more environmentally friendly compared to some traditional neutralizing agents, aligning with the industry's shift towards greener technologies.
The market for metallurgical acid treatment solutions is highly competitive, with several major players dominating the global landscape. These companies are investing heavily in research and development to improve the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of their acid neutralization products, including sodium percarbonate-based solutions. The Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the highest growth in demand for acid treatment solutions, driven by rapid industrialization and increasing mining activities in countries like China, India, and Australia.
Despite the positive market outlook, challenges such as fluctuating raw material prices and the need for significant capital investments in new acid treatment technologies may hinder market growth to some extent. However, the ongoing development of innovative acid neutralization techniques and the increasing focus on circular economy principles in the metallurgical industry are expected to create new opportunities for market expansion in the coming years.
Current Challenges in Metallurgical Acid Neutralization
Metallurgical acid neutralization is a critical process in various industrial applications, particularly in mining and metal processing. However, this process faces several significant challenges that impact its efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and environmental sustainability. One of the primary issues is the high consumption of neutralizing agents, which leads to increased operational costs and potential environmental concerns.
The traditional neutralization methods often require large quantities of lime or other alkaline substances, resulting in substantial chemical expenses and the generation of voluminous sludge. This sludge, rich in metal hydroxides, poses disposal challenges and potential environmental risks if not managed properly. Moreover, the effectiveness of conventional neutralization techniques can be compromised when dealing with complex acid mixtures or highly concentrated acidic solutions.
Another pressing challenge is the variability in acid composition and concentration across different metallurgical processes. This inconsistency makes it difficult to develop a standardized neutralization approach, often necessitating process-specific solutions. The presence of various metal ions in the acidic solutions further complicates the neutralization process, as different metals precipitate at different pH levels, requiring careful control of reaction conditions.
The energy intensity of acid neutralization processes also presents a significant hurdle. Many neutralization reactions are exothermic, requiring sophisticated cooling systems to maintain optimal reaction conditions. This not only increases the complexity of the process but also contributes to higher energy consumption and associated costs.
Furthermore, the recovery of valuable metals from acidic solutions during neutralization remains a challenge. Conventional methods often result in the loss of potentially recoverable metals, which are precipitated along with other waste products. This represents both an economic loss and a missed opportunity for resource recovery.
The environmental impact of acid neutralization processes is another area of concern. The release of carbon dioxide during the reaction of carbonates with acids contributes to greenhouse gas emissions. Additionally, the potential for incomplete neutralization or over-neutralization can lead to the discharge of either acidic or alkaline effluents, both of which can have detrimental effects on aquatic ecosystems.
In light of these challenges, there is a growing need for innovative approaches to metallurgical acid neutralization. The exploration of alternative neutralizing agents, such as sodium percarbonate, offers potential solutions to some of these issues. However, the integration of new technologies and materials into existing industrial processes presents its own set of challenges, including scalability, process compatibility, and regulatory compliance.
The traditional neutralization methods often require large quantities of lime or other alkaline substances, resulting in substantial chemical expenses and the generation of voluminous sludge. This sludge, rich in metal hydroxides, poses disposal challenges and potential environmental risks if not managed properly. Moreover, the effectiveness of conventional neutralization techniques can be compromised when dealing with complex acid mixtures or highly concentrated acidic solutions.
Another pressing challenge is the variability in acid composition and concentration across different metallurgical processes. This inconsistency makes it difficult to develop a standardized neutralization approach, often necessitating process-specific solutions. The presence of various metal ions in the acidic solutions further complicates the neutralization process, as different metals precipitate at different pH levels, requiring careful control of reaction conditions.
The energy intensity of acid neutralization processes also presents a significant hurdle. Many neutralization reactions are exothermic, requiring sophisticated cooling systems to maintain optimal reaction conditions. This not only increases the complexity of the process but also contributes to higher energy consumption and associated costs.
Furthermore, the recovery of valuable metals from acidic solutions during neutralization remains a challenge. Conventional methods often result in the loss of potentially recoverable metals, which are precipitated along with other waste products. This represents both an economic loss and a missed opportunity for resource recovery.
The environmental impact of acid neutralization processes is another area of concern. The release of carbon dioxide during the reaction of carbonates with acids contributes to greenhouse gas emissions. Additionally, the potential for incomplete neutralization or over-neutralization can lead to the discharge of either acidic or alkaline effluents, both of which can have detrimental effects on aquatic ecosystems.
In light of these challenges, there is a growing need for innovative approaches to metallurgical acid neutralization. The exploration of alternative neutralizing agents, such as sodium percarbonate, offers potential solutions to some of these issues. However, the integration of new technologies and materials into existing industrial processes presents its own set of challenges, including scalability, process compatibility, and regulatory compliance.
Existing Sodium Percarbonate-based Neutralization Methods
01 Acid neutralization using sodium percarbonate
Sodium percarbonate is used as an effective agent for neutralizing acids. When dissolved in water, it releases hydrogen peroxide and sodium carbonate, which react with acids to neutralize them. This process is particularly useful in various industrial and environmental applications where acid neutralization is required.- Acid neutralization mechanism of sodium percarbonate: Sodium percarbonate acts as an effective acid neutralizing agent due to its ability to release hydrogen peroxide and sodium carbonate when dissolved in water. The sodium carbonate component reacts with acids to form neutral salts, while the hydrogen peroxide can further decompose to oxygen and water, contributing to the neutralization process.
- Formulation of cleaning compositions with sodium percarbonate: Sodium percarbonate is incorporated into cleaning compositions to provide both bleaching and acid neutralization properties. These formulations often include additional components such as surfactants, enzymes, and other stabilizers to enhance cleaning efficacy while maintaining the acid neutralizing capability of sodium percarbonate.
- Stabilization of sodium percarbonate for improved acid neutralization: Various methods are employed to stabilize sodium percarbonate, enhancing its acid neutralization effectiveness and storage stability. These techniques include coating the particles, adding stabilizing agents, or controlling moisture content to prevent premature decomposition and ensure consistent acid neutralization performance.
- Application of sodium percarbonate in textile treatment: Sodium percarbonate is utilized in textile treatment processes for its acid neutralization properties. It helps neutralize acidic residues from dyeing or bleaching processes, improving fabric quality and reducing the risk of fabric degradation due to residual acidity.
- Environmental applications of sodium percarbonate for acid neutralization: Sodium percarbonate finds use in environmental applications for neutralizing acidic pollutants. Its ability to release oxygen during decomposition makes it particularly effective in treating acidic water bodies or soil, helping to restore pH balance while also providing beneficial oxygenation effects.
02 Formulation of cleaning compositions with sodium percarbonate
Sodium percarbonate is incorporated into cleaning compositions to provide both bleaching and acid-neutralizing properties. These formulations are used in laundry detergents, dishwashing products, and other household cleaners. The dual action of sodium percarbonate helps in removing stains and neutralizing acidic residues.Expand Specific Solutions03 Stabilization of sodium percarbonate for improved acid neutralization
Various methods are employed to stabilize sodium percarbonate, enhancing its effectiveness in acid neutralization. These include coating the particles, adding stabilizing agents, or modifying the crystal structure. Stabilized sodium percarbonate exhibits improved storage stability and maintains its acid-neutralizing capacity over longer periods.Expand Specific Solutions04 Use of sodium percarbonate in wastewater treatment
Sodium percarbonate is utilized in wastewater treatment processes for acid neutralization and oxidation of contaminants. It helps in adjusting the pH of acidic wastewater streams while simultaneously providing oxygen through the release of hydrogen peroxide, aiding in the breakdown of organic pollutants.Expand Specific Solutions05 Combination of sodium percarbonate with other neutralizing agents
Sodium percarbonate is often combined with other neutralizing agents to enhance its acid-neutralizing capabilities. These combinations can provide synergistic effects, improving the overall efficiency of acid neutralization in various applications, such as soil treatment, industrial processes, and consumer products.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players in Metallurgical Waste Treatment
The competitive landscape for the impact of sodium percarbonate on metallurgical acid neutralization is in a growth phase, with increasing market size and technological advancements. The global market for this application is expanding due to rising environmental concerns and stricter regulations in the metallurgical industry. Key players like Henkel AG & Co. KGaA, Evonik Operations GmbH, and Kemira Oyj are investing in research and development to improve the efficiency and sustainability of acid neutralization processes. The technology is reaching maturity, with companies such as Solvay Interox GmbH & Co. KG and Degussa AG offering advanced solutions. However, there is still room for innovation, particularly in optimizing sodium percarbonate's performance and reducing costs in large-scale industrial applications.
Evonik Operations GmbH
Technical Solution: Evonik has developed an innovative approach to metallurgical acid neutralization using sodium percarbonate. Their process involves a controlled release mechanism that optimizes the reaction between sodium percarbonate and acidic waste streams. This method ensures a gradual pH increase, preventing sudden spikes that could lead to metal precipitation. Evonik's technology incorporates a proprietary catalyst that enhances the decomposition of sodium percarbonate, resulting in more efficient oxygen generation and improved neutralization kinetics[1]. The company has also implemented a real-time monitoring system that adjusts the sodium percarbonate dosage based on the incoming acid concentration, ensuring optimal neutralization while minimizing chemical consumption[3].
Strengths: Precise pH control, improved neutralization efficiency, and reduced chemical usage. Weaknesses: Potentially higher initial implementation costs and the need for specialized equipment.
Solvay Interox GmbH & Co. KG
Technical Solution: Solvay Interox has pioneered a sodium percarbonate-based acid neutralization system specifically tailored for metallurgical applications. Their approach utilizes a high-purity, stabilized form of sodium percarbonate that resists premature decomposition in harsh industrial environments. The company's technology incorporates a multi-stage reaction process, where sodium percarbonate is introduced at strategic points in the acid stream, allowing for optimal neutralization and oxygen generation[2]. Solvay's system also includes a proprietary mixing technology that ensures uniform distribution of sodium percarbonate, maximizing its contact with acidic species and improving overall neutralization efficiency[4]. Additionally, they have developed a waste heat recovery system that captures the exothermic energy released during the neutralization process, contributing to improved energy efficiency in metallurgical operations[5].
Strengths: High-purity reagent, efficient mixing technology, and energy recovery capabilities. Weaknesses: May require significant modifications to existing neutralization systems and potential higher operational costs.
Innovative Research on Sodium Percarbonate Efficiency
Process for detoxifying cyanides containing aqueous solutions
PatentInactiveEP0595789A1
Innovation
- The process uses alkali metal percarbonate as a peroxide compound at pH 8 to 12 and temperatures up to 80 °C, with at least one equivalent per cyanide, allowing for effective detoxification of cyanide solutions containing heavy metals like copper, cadmium, nickel, and manganese by oxidizing cyanides to cyanates and hydrolyzing them, reducing the need for excessive hydrogen peroxide and improving economic efficiency.
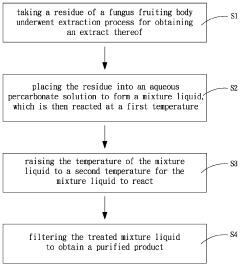
Purification method of fungal cell wall composition
PatentActiveUS20230310529A1
Innovation
- An aqueous percarbonate solution is used for decolorization and digestion, replacing the two-stage treatment with sodium hydroxide and hypochlorite or hydrogen peroxide, allowing for simultaneous decolorization and decomposition at controlled temperatures, reducing waste burden and increasing recovery rates.
Environmental Impact Assessment of Neutralization Processes
The environmental impact assessment of neutralization processes involving sodium percarbonate in metallurgical acid neutralization is a critical aspect of evaluating the overall sustainability and ecological footprint of this treatment method. Sodium percarbonate, a compound of sodium carbonate and hydrogen peroxide, offers several advantages in acid neutralization, but its use also raises important environmental considerations.
One of the primary environmental benefits of using sodium percarbonate for acid neutralization is its potential to reduce the overall chemical consumption compared to traditional neutralization agents. This reduction in chemical usage can lead to decreased transportation requirements and associated carbon emissions. Additionally, sodium percarbonate breaks down into environmentally benign components - sodium carbonate, water, and oxygen - which minimizes the risk of introducing harmful residues into the ecosystem.
However, the production of sodium percarbonate itself requires energy and resources, which must be factored into the overall environmental impact assessment. The manufacturing process typically involves the reaction of sodium carbonate with hydrogen peroxide, both of which have their own environmental footprints. The energy consumption and emissions associated with the production of these precursors should be carefully evaluated to provide a comprehensive understanding of the environmental implications.
The use of sodium percarbonate in acid neutralization can also affect the quality of treated effluents. While it generally results in a lower total dissolved solids (TDS) content compared to some other neutralization agents, the release of oxygen during the decomposition of sodium percarbonate may impact the dissolved oxygen levels in receiving water bodies. This could have both positive and negative effects on aquatic ecosystems, depending on the specific conditions and existing oxygen levels.
Another important consideration is the potential for sodium accumulation in soil and water systems. Although sodium is a naturally occurring element, excessive concentrations can lead to soil degradation and negatively impact plant growth. Long-term monitoring of sodium levels in areas where sodium percarbonate is used for acid neutralization is essential to prevent adverse effects on local ecosystems.
The assessment should also consider the life cycle impacts of sodium percarbonate usage, including packaging, transportation, and disposal of any residual materials. Comparing these impacts to those of alternative neutralization methods is crucial for making informed decisions about the most environmentally sustainable approach.
In conclusion, while sodium percarbonate offers several environmental advantages in metallurgical acid neutralization, a comprehensive assessment must consider the full spectrum of impacts, from production to end-use and beyond. This holistic approach ensures that the environmental benefits are accurately weighed against potential drawbacks, enabling informed decision-making in industrial processes.
One of the primary environmental benefits of using sodium percarbonate for acid neutralization is its potential to reduce the overall chemical consumption compared to traditional neutralization agents. This reduction in chemical usage can lead to decreased transportation requirements and associated carbon emissions. Additionally, sodium percarbonate breaks down into environmentally benign components - sodium carbonate, water, and oxygen - which minimizes the risk of introducing harmful residues into the ecosystem.
However, the production of sodium percarbonate itself requires energy and resources, which must be factored into the overall environmental impact assessment. The manufacturing process typically involves the reaction of sodium carbonate with hydrogen peroxide, both of which have their own environmental footprints. The energy consumption and emissions associated with the production of these precursors should be carefully evaluated to provide a comprehensive understanding of the environmental implications.
The use of sodium percarbonate in acid neutralization can also affect the quality of treated effluents. While it generally results in a lower total dissolved solids (TDS) content compared to some other neutralization agents, the release of oxygen during the decomposition of sodium percarbonate may impact the dissolved oxygen levels in receiving water bodies. This could have both positive and negative effects on aquatic ecosystems, depending on the specific conditions and existing oxygen levels.
Another important consideration is the potential for sodium accumulation in soil and water systems. Although sodium is a naturally occurring element, excessive concentrations can lead to soil degradation and negatively impact plant growth. Long-term monitoring of sodium levels in areas where sodium percarbonate is used for acid neutralization is essential to prevent adverse effects on local ecosystems.
The assessment should also consider the life cycle impacts of sodium percarbonate usage, including packaging, transportation, and disposal of any residual materials. Comparing these impacts to those of alternative neutralization methods is crucial for making informed decisions about the most environmentally sustainable approach.
In conclusion, while sodium percarbonate offers several environmental advantages in metallurgical acid neutralization, a comprehensive assessment must consider the full spectrum of impacts, from production to end-use and beyond. This holistic approach ensures that the environmental benefits are accurately weighed against potential drawbacks, enabling informed decision-making in industrial processes.
Regulatory Framework for Industrial Waste Treatment
The regulatory framework for industrial waste treatment, particularly in the context of metallurgical acid neutralization using sodium percarbonate, is a complex and evolving landscape. Governments worldwide have implemented stringent regulations to mitigate the environmental impact of industrial waste and protect public health.
At the international level, organizations such as the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) and the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) have established guidelines for hazardous waste management. These guidelines often serve as a foundation for national and regional regulations, promoting consistency in waste treatment practices across borders.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) oversees industrial waste treatment through the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA). This comprehensive legislation governs the generation, transportation, treatment, storage, and disposal of hazardous waste. The RCRA specifically addresses the neutralization of acidic waste streams, requiring facilities to meet specific pH levels before discharge.
The European Union has implemented the Industrial Emissions Directive (IED), which sets strict standards for pollution prevention and control. This directive applies to various industrial activities, including metallurgical processes, and mandates the use of Best Available Techniques (BAT) for waste treatment. The use of sodium percarbonate in acid neutralization must comply with these BAT standards.
Many countries have adopted a tiered regulatory approach, with federal or national laws providing overarching guidelines, while state or regional authorities enforce more specific regulations. This approach allows for tailored implementation based on local environmental conditions and industrial activities.
Regulatory bodies often require industrial facilities to obtain permits for waste treatment processes. These permits typically specify treatment methods, monitoring requirements, and discharge limits. The use of sodium percarbonate in metallurgical acid neutralization would need to be explicitly approved and documented in such permits.
Compliance monitoring and reporting are crucial components of the regulatory framework. Facilities must regularly test and report on the effectiveness of their waste treatment processes, including pH levels, heavy metal concentrations, and other relevant parameters. Failure to meet regulatory standards can result in significant fines, legal action, or facility closure.
As environmental concerns grow, regulations are becoming increasingly stringent. Many jurisdictions are moving towards a "zero discharge" policy, requiring industries to implement closed-loop systems or advanced treatment technologies. This trend may impact the use of sodium percarbonate and other neutralization agents, pushing for more sustainable and efficient treatment methods.
At the international level, organizations such as the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) and the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) have established guidelines for hazardous waste management. These guidelines often serve as a foundation for national and regional regulations, promoting consistency in waste treatment practices across borders.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) oversees industrial waste treatment through the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA). This comprehensive legislation governs the generation, transportation, treatment, storage, and disposal of hazardous waste. The RCRA specifically addresses the neutralization of acidic waste streams, requiring facilities to meet specific pH levels before discharge.
The European Union has implemented the Industrial Emissions Directive (IED), which sets strict standards for pollution prevention and control. This directive applies to various industrial activities, including metallurgical processes, and mandates the use of Best Available Techniques (BAT) for waste treatment. The use of sodium percarbonate in acid neutralization must comply with these BAT standards.
Many countries have adopted a tiered regulatory approach, with federal or national laws providing overarching guidelines, while state or regional authorities enforce more specific regulations. This approach allows for tailored implementation based on local environmental conditions and industrial activities.
Regulatory bodies often require industrial facilities to obtain permits for waste treatment processes. These permits typically specify treatment methods, monitoring requirements, and discharge limits. The use of sodium percarbonate in metallurgical acid neutralization would need to be explicitly approved and documented in such permits.
Compliance monitoring and reporting are crucial components of the regulatory framework. Facilities must regularly test and report on the effectiveness of their waste treatment processes, including pH levels, heavy metal concentrations, and other relevant parameters. Failure to meet regulatory standards can result in significant fines, legal action, or facility closure.
As environmental concerns grow, regulations are becoming increasingly stringent. Many jurisdictions are moving towards a "zero discharge" policy, requiring industries to implement closed-loop systems or advanced treatment technologies. This trend may impact the use of sodium percarbonate and other neutralization agents, pushing for more sustainable and efficient treatment methods.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!