Impact of Sodium Percarbonate on Textile Brightness Retention
JUL 22, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Sodium Percarbonate Textile Brightening Background
Sodium percarbonate, a compound of sodium carbonate and hydrogen peroxide, has emerged as a significant player in the textile industry, particularly in the realm of brightness retention. This adduct, with its chemical formula 2Na2CO3·3H2O2, has gained prominence due to its dual functionality as both a cleaning agent and a bleaching compound.
The journey of sodium percarbonate in textile applications began in the mid-20th century, coinciding with the growing demand for more effective and environmentally friendly laundry detergents. Its development was driven by the need to find alternatives to chlorine-based bleaches, which were known for their harsh effects on fabrics and potential environmental concerns.
As the textile industry evolved, so did the requirements for maintaining fabric appearance, particularly in terms of brightness and whiteness. Sodium percarbonate emerged as a solution to address these needs, offering a stable, solid form of hydrogen peroxide that could be easily incorporated into detergent formulations.
The compound's ability to release active oxygen when dissolved in water made it particularly effective in removing stains and brightening fabrics. This characteristic set it apart from traditional bleaching agents, as it could achieve similar results at lower temperatures, thus reducing energy consumption and minimizing fabric damage.
Over the years, research into sodium percarbonate's effects on textiles has intensified. Studies have focused on its impact on various fiber types, its efficacy in different washing conditions, and its long-term effects on fabric integrity. The compound's role in maintaining textile brightness has been of particular interest, as it addresses a key consumer concern in the laundry and textile care sectors.
The evolution of sodium percarbonate usage in textiles has also been influenced by broader trends in the industry, such as the shift towards more sustainable and eco-friendly products. Its biodegradability and the fact that it breaks down into harmless substances (water, oxygen, and sodium carbonate) have aligned well with these environmental considerations.
As we delve deeper into the impact of sodium percarbonate on textile brightness retention, it is crucial to understand this historical context and the technological advancements that have shaped its current role in the industry. This background sets the stage for a comprehensive analysis of its effectiveness, limitations, and potential future developments in maintaining the visual appeal of textiles.
The journey of sodium percarbonate in textile applications began in the mid-20th century, coinciding with the growing demand for more effective and environmentally friendly laundry detergents. Its development was driven by the need to find alternatives to chlorine-based bleaches, which were known for their harsh effects on fabrics and potential environmental concerns.
As the textile industry evolved, so did the requirements for maintaining fabric appearance, particularly in terms of brightness and whiteness. Sodium percarbonate emerged as a solution to address these needs, offering a stable, solid form of hydrogen peroxide that could be easily incorporated into detergent formulations.
The compound's ability to release active oxygen when dissolved in water made it particularly effective in removing stains and brightening fabrics. This characteristic set it apart from traditional bleaching agents, as it could achieve similar results at lower temperatures, thus reducing energy consumption and minimizing fabric damage.
Over the years, research into sodium percarbonate's effects on textiles has intensified. Studies have focused on its impact on various fiber types, its efficacy in different washing conditions, and its long-term effects on fabric integrity. The compound's role in maintaining textile brightness has been of particular interest, as it addresses a key consumer concern in the laundry and textile care sectors.
The evolution of sodium percarbonate usage in textiles has also been influenced by broader trends in the industry, such as the shift towards more sustainable and eco-friendly products. Its biodegradability and the fact that it breaks down into harmless substances (water, oxygen, and sodium carbonate) have aligned well with these environmental considerations.
As we delve deeper into the impact of sodium percarbonate on textile brightness retention, it is crucial to understand this historical context and the technological advancements that have shaped its current role in the industry. This background sets the stage for a comprehensive analysis of its effectiveness, limitations, and potential future developments in maintaining the visual appeal of textiles.
Market Analysis for Brightening Agents
The market for brightening agents in the textile industry has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing consumer demand for vibrant and long-lasting colors in clothing and home textiles. This trend is particularly evident in the fashion and sportswear sectors, where bright and eye-catching colors are often key selling points.
The global market for textile brightening agents was valued at approximately $900 million in 2020 and is projected to reach $1.2 billion by 2025, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.8%. This growth is primarily attributed to the rising disposable income in developing countries, leading to increased spending on high-quality textiles and garments.
Asia-Pacific dominates the market, accounting for over 40% of the global share, with China and India being the major contributors. The region's strong textile manufacturing base and growing consumer markets are key factors driving this dominance. North America and Europe follow, with a combined market share of around 35%.
The market is segmented based on product type, with optical brightening agents (OBAs) holding the largest share. OBAs are widely used due to their ability to enhance the whiteness and brightness of textiles effectively. Other segments include fluorescent brightening agents and various chemical brighteners.
In terms of application, the detergent industry remains the largest consumer of brightening agents, followed by the textile industry. The increasing use of brightening agents in paper and plastic industries is also contributing to market growth.
Key market players include Archroma, Huntsman Corporation, Clariant AG, and BASF SE, among others. These companies are focusing on research and development to introduce innovative products that offer improved performance and sustainability.
The market is witnessing a shift towards eco-friendly and sustainable brightening agents due to growing environmental concerns and stringent regulations. This trend is driving investments in bio-based and biodegradable brightening agents, which are expected to gain significant market share in the coming years.
Challenges facing the market include volatile raw material prices and increasing competition from low-cost manufacturers in developing countries. Additionally, the COVID-19 pandemic has temporarily disrupted supply chains and reduced demand in certain sectors, although the market is expected to recover as global economic activities normalize.
The global market for textile brightening agents was valued at approximately $900 million in 2020 and is projected to reach $1.2 billion by 2025, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.8%. This growth is primarily attributed to the rising disposable income in developing countries, leading to increased spending on high-quality textiles and garments.
Asia-Pacific dominates the market, accounting for over 40% of the global share, with China and India being the major contributors. The region's strong textile manufacturing base and growing consumer markets are key factors driving this dominance. North America and Europe follow, with a combined market share of around 35%.
The market is segmented based on product type, with optical brightening agents (OBAs) holding the largest share. OBAs are widely used due to their ability to enhance the whiteness and brightness of textiles effectively. Other segments include fluorescent brightening agents and various chemical brighteners.
In terms of application, the detergent industry remains the largest consumer of brightening agents, followed by the textile industry. The increasing use of brightening agents in paper and plastic industries is also contributing to market growth.
Key market players include Archroma, Huntsman Corporation, Clariant AG, and BASF SE, among others. These companies are focusing on research and development to introduce innovative products that offer improved performance and sustainability.
The market is witnessing a shift towards eco-friendly and sustainable brightening agents due to growing environmental concerns and stringent regulations. This trend is driving investments in bio-based and biodegradable brightening agents, which are expected to gain significant market share in the coming years.
Challenges facing the market include volatile raw material prices and increasing competition from low-cost manufacturers in developing countries. Additionally, the COVID-19 pandemic has temporarily disrupted supply chains and reduced demand in certain sectors, although the market is expected to recover as global economic activities normalize.
Current Challenges in Textile Brightness Retention
Textile brightness retention remains a significant challenge in the textile industry, with various factors contributing to the gradual loss of fabric brightness over time. One of the primary issues is the accumulation of soil and stains on textile fibers, which can dull the appearance of fabrics and reduce their overall brightness. This problem is particularly prevalent in white and light-colored textiles, where even minor discoloration can be noticeable.
The use of traditional laundry detergents and bleaching agents often proves insufficient in maintaining long-term brightness, as these products may not effectively remove all types of stains or prevent the redeposition of soil during the washing process. Additionally, repeated washing cycles can lead to fiber damage and color fading, further compromising the fabric's brightness.
Another significant challenge is the interaction between textile fibers and various environmental factors. Exposure to sunlight, air pollution, and certain chemicals can cause photochemical reactions that alter the fabric's color and brightness. This is especially problematic for textiles used in outdoor applications or those frequently exposed to harsh environmental conditions.
The presence of hard water in many regions poses an additional obstacle to brightness retention. Mineral deposits from hard water can accumulate on fabric fibers, creating a dull film that reduces the textile's reflective properties and overall brightness. This issue is compounded by the fact that many conventional laundry products are less effective in hard water conditions.
Furthermore, the increasing demand for eco-friendly and sustainable textile care solutions has limited the use of certain highly effective but environmentally harmful brightening agents. This has created a need for alternative solutions that can maintain fabric brightness without compromising environmental standards or fabric integrity.
The textile industry also faces challenges related to the diverse range of fabric types and blends in use today. Different fibers and fabric constructions respond differently to brightening treatments, making it difficult to develop a one-size-fits-all solution for brightness retention. This diversity necessitates the development of specialized treatments and care instructions for various textile types.
In the context of sodium percarbonate's impact on textile brightness retention, there are specific challenges to consider. While sodium percarbonate is known for its bleaching and stain-removing properties, its effectiveness can vary depending on water temperature, fabric type, and the nature of the stains. Ensuring consistent performance across different washing conditions and fabric compositions remains a significant hurdle.
Moreover, the potential for fabric damage from repeated use of sodium percarbonate-based products is a concern. Balancing the bleaching action with fabric care to prevent weakening or discoloration of fibers over time is crucial. This challenge is particularly relevant for delicate or colored fabrics that may be more susceptible to damage from oxidizing agents.
The use of traditional laundry detergents and bleaching agents often proves insufficient in maintaining long-term brightness, as these products may not effectively remove all types of stains or prevent the redeposition of soil during the washing process. Additionally, repeated washing cycles can lead to fiber damage and color fading, further compromising the fabric's brightness.
Another significant challenge is the interaction between textile fibers and various environmental factors. Exposure to sunlight, air pollution, and certain chemicals can cause photochemical reactions that alter the fabric's color and brightness. This is especially problematic for textiles used in outdoor applications or those frequently exposed to harsh environmental conditions.
The presence of hard water in many regions poses an additional obstacle to brightness retention. Mineral deposits from hard water can accumulate on fabric fibers, creating a dull film that reduces the textile's reflective properties and overall brightness. This issue is compounded by the fact that many conventional laundry products are less effective in hard water conditions.
Furthermore, the increasing demand for eco-friendly and sustainable textile care solutions has limited the use of certain highly effective but environmentally harmful brightening agents. This has created a need for alternative solutions that can maintain fabric brightness without compromising environmental standards or fabric integrity.
The textile industry also faces challenges related to the diverse range of fabric types and blends in use today. Different fibers and fabric constructions respond differently to brightening treatments, making it difficult to develop a one-size-fits-all solution for brightness retention. This diversity necessitates the development of specialized treatments and care instructions for various textile types.
In the context of sodium percarbonate's impact on textile brightness retention, there are specific challenges to consider. While sodium percarbonate is known for its bleaching and stain-removing properties, its effectiveness can vary depending on water temperature, fabric type, and the nature of the stains. Ensuring consistent performance across different washing conditions and fabric compositions remains a significant hurdle.
Moreover, the potential for fabric damage from repeated use of sodium percarbonate-based products is a concern. Balancing the bleaching action with fabric care to prevent weakening or discoloration of fibers over time is crucial. This challenge is particularly relevant for delicate or colored fabrics that may be more susceptible to damage from oxidizing agents.
Sodium Percarbonate-based Brightening Solutions
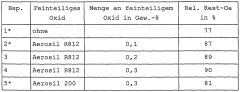
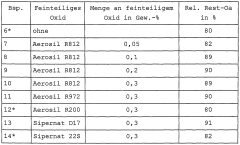
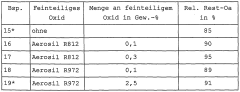
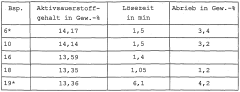
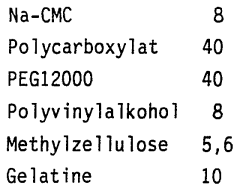
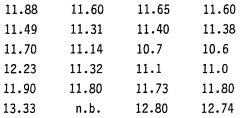
01 Stabilization of sodium percarbonate
Various methods are employed to stabilize sodium percarbonate, enhancing its brightness retention. These include coating the particles with inorganic or organic compounds, adding stabilizing agents, and controlling the particle size distribution. Such stabilization techniques improve the shelf life and effectiveness of sodium percarbonate in cleaning and bleaching applications.- Stabilization of sodium percarbonate: Various methods are employed to stabilize sodium percarbonate, enhancing its brightness retention. These include coating the particles with inorganic or organic compounds, adding stabilizing agents, and controlling the particle size distribution. Such stabilization techniques improve the shelf life and effectiveness of sodium percarbonate in cleaning and bleaching applications.
- Formulation with other bleaching agents: Sodium percarbonate is often combined with other bleaching agents to enhance its brightness retention properties. These formulations may include additional peroxide compounds, activators, or catalysts that work synergistically with sodium percarbonate to improve overall bleaching performance and maintain brightness over time.
- Surface modification techniques: Surface modification of sodium percarbonate particles is used to improve brightness retention. This can involve treatments such as silicate coatings, polymer encapsulation, or the addition of surfactants. These modifications help protect the particles from moisture and premature decomposition, thereby maintaining their bleaching efficacy.
- Incorporation of optical brighteners: Optical brighteners are often incorporated into sodium percarbonate formulations to enhance perceived brightness. These compounds absorb UV light and emit visible blue light, creating a whitening effect that complements the bleaching action of sodium percarbonate. This combination helps maintain brightness even after repeated use.
- pH control and buffering systems: Controlling the pH and incorporating buffering systems in sodium percarbonate formulations can significantly impact brightness retention. Optimal pH conditions are maintained to ensure the stability of the percarbonate and its bleaching effectiveness. Buffering agents help prevent rapid pH changes that could lead to decreased performance or premature decomposition.
02 Incorporation of additives for brightness enhancement
Additives such as optical brighteners, fluorescent whitening agents, and other synergistic compounds are incorporated into sodium percarbonate formulations. These additives work in conjunction with sodium percarbonate to enhance the perceived brightness and whiteness of treated materials, contributing to improved brightness retention over time.Expand Specific Solutions03 Controlled release mechanisms
Developing controlled release mechanisms for sodium percarbonate helps maintain its brightness-enhancing effects over extended periods. This can involve encapsulation techniques, matrix systems, or other delivery methods that gradually release the active components, ensuring sustained brightness retention in various applications.Expand Specific Solutions04 Synergistic formulations with other bleaching agents
Combining sodium percarbonate with other bleaching agents or activators creates synergistic formulations that enhance overall brightness retention. These combinations can improve the efficacy of the bleaching process, leading to better and longer-lasting brightness in treated materials.Expand Specific Solutions05 Process optimization for improved brightness retention
Optimizing manufacturing processes and application methods for sodium percarbonate-based products can significantly impact brightness retention. This includes controlling factors such as temperature, pH, and reaction conditions during production, as well as developing optimal usage protocols for end-users to maximize the brightness-enhancing effects of sodium percarbonate.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Textile Chemical Industry
The impact of sodium percarbonate on textile brightness retention is a niche but growing area within the textile industry. The market is in its early growth stage, with increasing demand for eco-friendly bleaching agents driving expansion. The global sodium percarbonate market size is projected to reach several billion dollars by 2025, with a significant portion attributed to textile applications. Technologically, the field is moderately mature, with ongoing innovations focused on improving efficiency and sustainability. Key players like Solvay SA, Evonik Operations GmbH, and Henkel AG & Co. KGaA are leading research and development efforts, while companies such as Zhejiang Jinke Daily Chemical Co. Ltd. and Shandong Tianli Energy Co., Ltd. are emerging as significant contributors in the Asian market.
Solvay SA
Technical Solution: Solvay SA has developed an advanced sodium percarbonate formulation for textile brightness retention. Their technology involves a stabilized sodium percarbonate particle with a protective coating, which enhances its stability and effectiveness in laundry applications. This formulation releases active oxygen gradually, providing prolonged bleaching action and improved fabric care. Solvay's sodium percarbonate is designed to work effectively at lower temperatures, reducing energy consumption during washing cycles[1][3]. The company has also implemented a proprietary manufacturing process that ensures consistent particle size distribution, leading to better dissolution and performance in various detergent formulations[2].
Strengths: Improved stability, energy-efficient, and enhanced fabric care. Weaknesses: Potentially higher production costs and may require specialized handling during manufacturing and transportation.
Evonik Operations GmbH
Technical Solution: Evonik has innovated in the field of sodium percarbonate for textile brightness retention by developing a unique encapsulation technology. Their product features a core-shell structure where the sodium percarbonate core is surrounded by a protective layer of inorganic materials. This encapsulation significantly improves the stability of the percarbonate in detergent formulations, extending its shelf life and maintaining its effectiveness over time[4]. Evonik's technology also incorporates trace amounts of transition metal compounds, which act as catalysts to enhance the bleaching efficiency at lower temperatures. This allows for effective stain removal and brightness retention while reducing energy consumption during washing[5].
Strengths: Enhanced stability, improved bleaching efficiency, and energy-saving potential. Weaknesses: Complex manufacturing process and potential for higher production costs.
Innovations in Percarbonate Brightening Mechanisms
Sodium percarbonate particles with improved storage stability
PatentWO2004058932A1
Innovation
- Sodium percarbonate particles coated with 0.01 to 1% by weight of a hydrophobic, finely divided oxide such as hydrophobic silica, aluminum, or titanium oxide, which improves storage stability and handling without dust formation or caking, and ensures easy dispersion in water.
Long-shelf-life encapsulated particulate sodium percarbonate and process for producing it
PatentWO1992017400A1
Innovation
- Encapsulating sodium percarbonate particles with a multi-layered protective shell composed of water-soluble polymer compounds with a glass transition temperature above the operating temperature, ensuring a minimum dry mass of 7-8% by weight, to prevent agglomeration and enhance storage stability.
Environmental Impact of Brightening Agents
The use of brightening agents in textile processing has raised significant environmental concerns due to their potential impact on ecosystems and human health. Sodium percarbonate, a common brightening agent, is no exception to this scrutiny. When released into aquatic environments, these chemicals can disrupt natural ecosystems by altering pH levels and introducing excess oxygen, potentially harming aquatic life.
Furthermore, the production and disposal of sodium percarbonate contribute to environmental issues. The manufacturing process requires energy and resources, leading to carbon emissions and resource depletion. Improper disposal of textile wastewater containing brightening agents can contaminate soil and water sources, affecting both terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems.
However, sodium percarbonate offers some environmental advantages compared to traditional chlorine-based bleaches. It breaks down into harmless substances - water, oxygen, and sodium carbonate - which are generally less harmful to the environment. This decomposition process also makes it more biodegradable than many other brightening agents.
Despite these benefits, the cumulative effect of widespread use remains a concern. The increased oxygen levels resulting from sodium percarbonate breakdown can lead to algal blooms in water bodies, disrupting aquatic ecosystems. Additionally, the sodium content may contribute to soil salinization if repeatedly introduced into terrestrial environments.
Efforts to mitigate these environmental impacts include developing more eco-friendly brightening agents, improving wastewater treatment processes, and implementing stricter regulations on chemical usage and disposal in the textile industry. Some manufacturers are exploring alternatives such as enzyme-based brighteners or mechanical brightening techniques to reduce reliance on chemical agents.
The textile industry is also investigating closed-loop systems that recycle water and chemicals, minimizing environmental discharge. Advanced oxidation processes and membrane filtration technologies are being employed to treat wastewater more effectively, removing residual brightening agents before release into the environment.
In conclusion, while sodium percarbonate offers some environmental advantages over traditional brightening agents, its widespread use still poses potential risks to ecosystems. Balancing the need for effective textile brightness retention with environmental protection remains a challenge for the industry, driving ongoing research into more sustainable brightening solutions.
Furthermore, the production and disposal of sodium percarbonate contribute to environmental issues. The manufacturing process requires energy and resources, leading to carbon emissions and resource depletion. Improper disposal of textile wastewater containing brightening agents can contaminate soil and water sources, affecting both terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems.
However, sodium percarbonate offers some environmental advantages compared to traditional chlorine-based bleaches. It breaks down into harmless substances - water, oxygen, and sodium carbonate - which are generally less harmful to the environment. This decomposition process also makes it more biodegradable than many other brightening agents.
Despite these benefits, the cumulative effect of widespread use remains a concern. The increased oxygen levels resulting from sodium percarbonate breakdown can lead to algal blooms in water bodies, disrupting aquatic ecosystems. Additionally, the sodium content may contribute to soil salinization if repeatedly introduced into terrestrial environments.
Efforts to mitigate these environmental impacts include developing more eco-friendly brightening agents, improving wastewater treatment processes, and implementing stricter regulations on chemical usage and disposal in the textile industry. Some manufacturers are exploring alternatives such as enzyme-based brighteners or mechanical brightening techniques to reduce reliance on chemical agents.
The textile industry is also investigating closed-loop systems that recycle water and chemicals, minimizing environmental discharge. Advanced oxidation processes and membrane filtration technologies are being employed to treat wastewater more effectively, removing residual brightening agents before release into the environment.
In conclusion, while sodium percarbonate offers some environmental advantages over traditional brightening agents, its widespread use still poses potential risks to ecosystems. Balancing the need for effective textile brightness retention with environmental protection remains a challenge for the industry, driving ongoing research into more sustainable brightening solutions.
Consumer Trends in Textile Care Products
Consumer trends in textile care products have been evolving rapidly in recent years, driven by increasing awareness of environmental issues, health concerns, and a desire for convenience. One significant trend is the growing demand for eco-friendly and sustainable laundry solutions. Consumers are increasingly seeking products that minimize environmental impact, such as biodegradable detergents and packaging made from recycled materials. This shift has led to the rise of concentrated formulas and refillable packaging options, reducing plastic waste and transportation emissions.
Another notable trend is the preference for multi-functional products that offer time and space-saving benefits. Consumers are gravitating towards all-in-one solutions that combine cleaning, softening, and fabric protection properties. This trend has spurred innovation in laundry pods and sheets, which provide pre-measured doses and eliminate the need for multiple products.
Health-conscious consumers are driving demand for hypoallergenic and fragrance-free options. There is a growing market for products that are gentle on sensitive skin and free from harsh chemicals. This has led to the development of plant-based and natural ingredient formulations, appealing to those seeking alternatives to traditional synthetic detergents.
The rise of smart home technology has also influenced the textile care industry. Consumers are showing interest in connected appliances and IoT-enabled laundry products that offer personalized washing recommendations, remote monitoring, and automatic detergent dispensing. This trend aligns with the broader desire for convenience and efficiency in household chores.
In response to the fast fashion phenomenon and increased awareness of textile waste, there is a growing interest in products that extend the life of clothing. Consumers are seeking solutions that maintain fabric quality, prevent color fading, and reduce wear and tear. This has led to the development of specialized fabric care products and treatments designed to preserve garments over time.
The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated the trend towards hygiene-focused products. Consumers are now more conscious of the need for thorough cleaning and disinfection of textiles. This has resulted in increased demand for laundry detergents and additives with antibacterial and antiviral properties, as well as products that can effectively clean at lower temperatures to save energy.
Lastly, there is a growing market for customized and personalized laundry solutions. Consumers are seeking products tailored to specific fabric types, colors, or personal preferences. This trend has led to the emergence of subscription-based services offering personalized detergent blends and the development of modular laundry systems that allow users to customize their washing experience.
Another notable trend is the preference for multi-functional products that offer time and space-saving benefits. Consumers are gravitating towards all-in-one solutions that combine cleaning, softening, and fabric protection properties. This trend has spurred innovation in laundry pods and sheets, which provide pre-measured doses and eliminate the need for multiple products.
Health-conscious consumers are driving demand for hypoallergenic and fragrance-free options. There is a growing market for products that are gentle on sensitive skin and free from harsh chemicals. This has led to the development of plant-based and natural ingredient formulations, appealing to those seeking alternatives to traditional synthetic detergents.
The rise of smart home technology has also influenced the textile care industry. Consumers are showing interest in connected appliances and IoT-enabled laundry products that offer personalized washing recommendations, remote monitoring, and automatic detergent dispensing. This trend aligns with the broader desire for convenience and efficiency in household chores.
In response to the fast fashion phenomenon and increased awareness of textile waste, there is a growing interest in products that extend the life of clothing. Consumers are seeking solutions that maintain fabric quality, prevent color fading, and reduce wear and tear. This has led to the development of specialized fabric care products and treatments designed to preserve garments over time.
The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated the trend towards hygiene-focused products. Consumers are now more conscious of the need for thorough cleaning and disinfection of textiles. This has resulted in increased demand for laundry detergents and additives with antibacterial and antiviral properties, as well as products that can effectively clean at lower temperatures to save energy.
Lastly, there is a growing market for customized and personalized laundry solutions. Consumers are seeking products tailored to specific fabric types, colors, or personal preferences. This trend has led to the emergence of subscription-based services offering personalized detergent blends and the development of modular laundry systems that allow users to customize their washing experience.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!