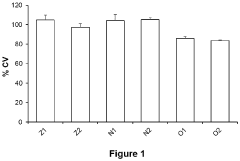
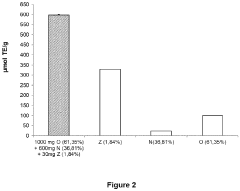
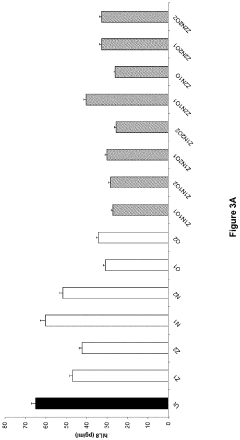
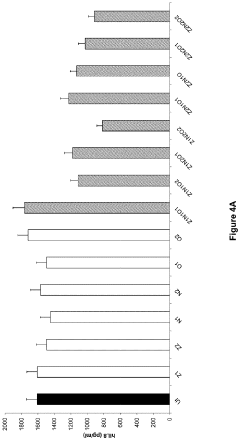
Investigation of neuroplastic changes induced by lithium orotate
AUG 19, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Lithium Orotate Neuroplasticity Background
Lithium has been a cornerstone in the treatment of bipolar disorder for decades, with its mood-stabilizing properties well-documented in clinical practice. However, the neurobiological mechanisms underlying its therapeutic effects have remained elusive until recent advancements in neuroscience. The investigation of neuroplastic changes induced by lithium orotate represents a significant step forward in understanding how this compound influences brain function and structure.
Neuroplasticity, the brain's ability to reorganize itself by forming new neural connections, has emerged as a crucial concept in neuroscience. It plays a vital role in learning, memory, and recovery from brain injuries. The exploration of lithium orotate's impact on neuroplasticity opens up new avenues for understanding its potential therapeutic applications beyond mood disorders.
Historically, lithium carbonate has been the primary form of lithium used in psychiatric treatment. Lithium orotate, a more bioavailable form, has gained attention due to its potential for enhanced efficacy and reduced side effects. This compound combines lithium with orotic acid, which may facilitate its transport across cell membranes and the blood-brain barrier.
The investigation into lithium orotate's neuroplastic effects builds upon a growing body of research suggesting that lithium's therapeutic actions may be mediated through its influence on various neurotrophic and neuroprotective pathways. These pathways are integral to the brain's ability to adapt and remodel in response to environmental stimuli and neurological challenges.
Recent studies have indicated that lithium may enhance neurogenesis, the process of generating new neurons, particularly in the hippocampus – a region critical for memory and emotional regulation. Additionally, lithium has been shown to modulate synaptic plasticity, potentially influencing the strength and efficiency of neural connections.
The focus on lithium orotate's neuroplastic effects also aligns with the broader shift in psychiatric research towards understanding mental disorders as disturbances in neural circuitry and connectivity. This perspective emphasizes the importance of targeting neuroplasticity mechanisms in developing more effective treatments for a range of neuropsychiatric conditions.
As research in this area progresses, it holds promise for elucidating the molecular and cellular mechanisms through which lithium orotate exerts its effects on brain function. This knowledge could lead to the development of more targeted and efficacious treatments for mood disorders and potentially other neurological conditions where neuroplasticity plays a crucial role.
Neuroplasticity, the brain's ability to reorganize itself by forming new neural connections, has emerged as a crucial concept in neuroscience. It plays a vital role in learning, memory, and recovery from brain injuries. The exploration of lithium orotate's impact on neuroplasticity opens up new avenues for understanding its potential therapeutic applications beyond mood disorders.
Historically, lithium carbonate has been the primary form of lithium used in psychiatric treatment. Lithium orotate, a more bioavailable form, has gained attention due to its potential for enhanced efficacy and reduced side effects. This compound combines lithium with orotic acid, which may facilitate its transport across cell membranes and the blood-brain barrier.
The investigation into lithium orotate's neuroplastic effects builds upon a growing body of research suggesting that lithium's therapeutic actions may be mediated through its influence on various neurotrophic and neuroprotective pathways. These pathways are integral to the brain's ability to adapt and remodel in response to environmental stimuli and neurological challenges.
Recent studies have indicated that lithium may enhance neurogenesis, the process of generating new neurons, particularly in the hippocampus – a region critical for memory and emotional regulation. Additionally, lithium has been shown to modulate synaptic plasticity, potentially influencing the strength and efficiency of neural connections.
The focus on lithium orotate's neuroplastic effects also aligns with the broader shift in psychiatric research towards understanding mental disorders as disturbances in neural circuitry and connectivity. This perspective emphasizes the importance of targeting neuroplasticity mechanisms in developing more effective treatments for a range of neuropsychiatric conditions.
As research in this area progresses, it holds promise for elucidating the molecular and cellular mechanisms through which lithium orotate exerts its effects on brain function. This knowledge could lead to the development of more targeted and efficacious treatments for mood disorders and potentially other neurological conditions where neuroplasticity plays a crucial role.
Market Analysis for Neuroplasticity Enhancers
The market for neuroplasticity enhancers, particularly those focused on lithium orotate-induced changes, is experiencing significant growth and attracting increased attention from both pharmaceutical companies and healthcare providers. This surge in interest is driven by the growing prevalence of neurological disorders and the increasing awareness of brain health among the general population.
The global market for neuroplasticity enhancers is projected to expand rapidly in the coming years, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) expected to exceed 7% through 2027. This growth is primarily fueled by the rising incidence of neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's, as well as the increasing prevalence of mood disorders and cognitive impairments.
Lithium orotate, a specific compound under investigation for its neuroplastic effects, represents a niche but promising segment within the broader neuroplasticity enhancer market. While traditional lithium carbonate has long been used in psychiatric treatments, lithium orotate is gaining traction due to its potential for enhanced bioavailability and reduced side effects.
The market demand for lithium orotate-based neuroplasticity enhancers is driven by several factors. Firstly, there is a growing body of research suggesting that lithium orotate may have neuroprotective properties and could potentially slow the progression of neurodegenerative diseases. This has sparked interest among both patients and healthcare providers seeking alternative treatment options.
Secondly, the increasing focus on mental health and cognitive performance in both clinical and non-clinical settings has created a new market segment for cognitive enhancement products. Lithium orotate's potential to improve mood stability and cognitive function positions it as an attractive option in this emerging market.
Geographically, North America currently dominates the neuroplasticity enhancer market, followed by Europe. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth in the coming years, driven by improving healthcare infrastructure, rising disposable incomes, and increasing awareness of neurological health.
Despite the promising outlook, the market for lithium orotate-based neuroplasticity enhancers faces several challenges. Regulatory hurdles and the need for extensive clinical trials to establish efficacy and safety profiles remain significant barriers to market entry. Additionally, competition from other neuroplasticity-enhancing compounds and traditional psychiatric medications may impact market growth.
In conclusion, the market analysis for neuroplasticity enhancers, particularly those involving lithium orotate, reveals a dynamic and expanding landscape with significant growth potential. As research in this field progresses and clinical evidence accumulates, the market is likely to see increased investment and product development, potentially revolutionizing the treatment of neurological and psychiatric disorders.
The global market for neuroplasticity enhancers is projected to expand rapidly in the coming years, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) expected to exceed 7% through 2027. This growth is primarily fueled by the rising incidence of neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's, as well as the increasing prevalence of mood disorders and cognitive impairments.
Lithium orotate, a specific compound under investigation for its neuroplastic effects, represents a niche but promising segment within the broader neuroplasticity enhancer market. While traditional lithium carbonate has long been used in psychiatric treatments, lithium orotate is gaining traction due to its potential for enhanced bioavailability and reduced side effects.
The market demand for lithium orotate-based neuroplasticity enhancers is driven by several factors. Firstly, there is a growing body of research suggesting that lithium orotate may have neuroprotective properties and could potentially slow the progression of neurodegenerative diseases. This has sparked interest among both patients and healthcare providers seeking alternative treatment options.
Secondly, the increasing focus on mental health and cognitive performance in both clinical and non-clinical settings has created a new market segment for cognitive enhancement products. Lithium orotate's potential to improve mood stability and cognitive function positions it as an attractive option in this emerging market.
Geographically, North America currently dominates the neuroplasticity enhancer market, followed by Europe. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth in the coming years, driven by improving healthcare infrastructure, rising disposable incomes, and increasing awareness of neurological health.
Despite the promising outlook, the market for lithium orotate-based neuroplasticity enhancers faces several challenges. Regulatory hurdles and the need for extensive clinical trials to establish efficacy and safety profiles remain significant barriers to market entry. Additionally, competition from other neuroplasticity-enhancing compounds and traditional psychiatric medications may impact market growth.
In conclusion, the market analysis for neuroplasticity enhancers, particularly those involving lithium orotate, reveals a dynamic and expanding landscape with significant growth potential. As research in this field progresses and clinical evidence accumulates, the market is likely to see increased investment and product development, potentially revolutionizing the treatment of neurological and psychiatric disorders.
Current Challenges in Lithium Orotate Research
Despite the growing interest in lithium orotate as a potential neuroplasticity-enhancing agent, several significant challenges persist in the research landscape. One of the primary obstacles is the limited availability of comprehensive, long-term studies on the neuroplastic effects of lithium orotate. While short-term studies have shown promising results, the lack of extended research hinders our understanding of the sustained impact on brain plasticity and potential side effects over prolonged use.
Another critical challenge lies in the standardization of dosage and administration protocols. The optimal dosage of lithium orotate for inducing neuroplastic changes remains unclear, with variations in individual responses further complicating the establishment of universal guidelines. This lack of standardization makes it difficult to compare results across studies and draw definitive conclusions about its efficacy.
The mechanisms underlying lithium orotate's neuroplastic effects are not fully elucidated, presenting a significant hurdle in research. While some pathways, such as the modulation of neurotrophic factors and synaptic plasticity, have been identified, the complete picture of its action on neuronal networks and brain connectivity remains incomplete. This gap in knowledge impedes the development of targeted interventions and the prediction of potential interactions with other neuroplasticity-enhancing therapies.
Ethical considerations and regulatory hurdles also pose challenges in conducting large-scale human trials. The potential for adverse effects, particularly in vulnerable populations, necessitates careful study design and extensive safety monitoring. Additionally, the regulatory status of lithium orotate as a supplement rather than a pharmaceutical drug in many countries complicates the research landscape, affecting funding opportunities and the rigor of clinical trials.
The heterogeneity of neuroplastic responses across different brain regions and in various neurological conditions presents another layer of complexity. Research must address how lithium orotate's effects may vary depending on the specific neural circuits involved and the underlying pathology, requiring more sophisticated imaging and assessment techniques.
Lastly, the integration of lithium orotate research with emerging technologies in neuroscience, such as optogenetics and single-cell transcriptomics, remains a challenge. Leveraging these advanced tools could provide unprecedented insights into the molecular and cellular mechanisms of lithium orotate-induced neuroplasticity, but requires interdisciplinary collaboration and significant resources.
Another critical challenge lies in the standardization of dosage and administration protocols. The optimal dosage of lithium orotate for inducing neuroplastic changes remains unclear, with variations in individual responses further complicating the establishment of universal guidelines. This lack of standardization makes it difficult to compare results across studies and draw definitive conclusions about its efficacy.
The mechanisms underlying lithium orotate's neuroplastic effects are not fully elucidated, presenting a significant hurdle in research. While some pathways, such as the modulation of neurotrophic factors and synaptic plasticity, have been identified, the complete picture of its action on neuronal networks and brain connectivity remains incomplete. This gap in knowledge impedes the development of targeted interventions and the prediction of potential interactions with other neuroplasticity-enhancing therapies.
Ethical considerations and regulatory hurdles also pose challenges in conducting large-scale human trials. The potential for adverse effects, particularly in vulnerable populations, necessitates careful study design and extensive safety monitoring. Additionally, the regulatory status of lithium orotate as a supplement rather than a pharmaceutical drug in many countries complicates the research landscape, affecting funding opportunities and the rigor of clinical trials.
The heterogeneity of neuroplastic responses across different brain regions and in various neurological conditions presents another layer of complexity. Research must address how lithium orotate's effects may vary depending on the specific neural circuits involved and the underlying pathology, requiring more sophisticated imaging and assessment techniques.
Lastly, the integration of lithium orotate research with emerging technologies in neuroscience, such as optogenetics and single-cell transcriptomics, remains a challenge. Leveraging these advanced tools could provide unprecedented insights into the molecular and cellular mechanisms of lithium orotate-induced neuroplasticity, but requires interdisciplinary collaboration and significant resources.
Existing Lithium Orotate Mechanisms of Action
01 Lithium orotate's effect on neuroplasticity
Lithium orotate has been found to promote neuroplastic changes in the brain. It may enhance synaptic plasticity, neurogenesis, and neurotrophic factor expression, potentially leading to improved cognitive function and neuroprotection. These effects could be beneficial in treating various neurological and psychiatric disorders.- Lithium orotate's effect on neuroplasticity: Lithium orotate has been found to promote neuroplastic changes in the brain. It may enhance synaptic plasticity, increase neurogenesis, and improve cognitive function. These effects could potentially be beneficial in treating various neurological and psychiatric disorders.
- Combination therapy with lithium orotate: Combining lithium orotate with other compounds or therapies may enhance its neuroplastic effects. This approach could potentially lead to more effective treatments for mood disorders, neurodegenerative diseases, and cognitive impairments.
- Mechanisms of lithium orotate-induced neuroplasticity: Research has focused on understanding the molecular mechanisms by which lithium orotate induces neuroplastic changes. This includes its effects on neurotrophic factors, signaling pathways, and gene expression related to neuronal growth and survival.
- Dosage and administration of lithium orotate for neuroplasticity: Optimal dosage and administration methods for lithium orotate to promote neuroplasticity are being investigated. This includes studies on different formulations, delivery systems, and treatment regimens to maximize its neuroplastic effects while minimizing potential side effects.
- Applications of lithium orotate in neurological disorders: The neuroplastic effects of lithium orotate are being explored for various neurological disorders. This includes potential applications in treating depression, bipolar disorder, Alzheimer's disease, and other conditions characterized by impaired neuroplasticity.
02 Combination therapies with lithium orotate
Research has explored combining lithium orotate with other compounds to enhance its neuroplastic effects. These combinations may include antioxidants, omega-3 fatty acids, or other neuroprotective agents. Such approaches aim to synergistically improve brain plasticity and potentially treat conditions like depression, anxiety, or neurodegenerative diseases.Expand Specific Solutions03 Delivery methods for lithium orotate
Various delivery methods have been developed to optimize the neuroplastic effects of lithium orotate. These may include novel formulations, controlled-release systems, or targeted delivery approaches to enhance bioavailability and efficacy in promoting neuroplastic changes. Such methods aim to improve the therapeutic potential while minimizing potential side effects.Expand Specific Solutions04 Mechanisms of lithium orotate-induced neuroplasticity
Studies have investigated the molecular mechanisms underlying lithium orotate's neuroplastic effects. These may involve modulation of signaling pathways, gene expression changes, or alterations in neurotransmitter systems. Understanding these mechanisms could lead to more targeted therapies and improved treatment strategies for neurological disorders.Expand Specific Solutions05 Applications in specific neurological conditions
Research has explored the potential applications of lithium orotate-induced neuroplastic changes in specific neurological conditions. These may include mood disorders, neurodegenerative diseases, traumatic brain injury, or stroke recovery. The ability to promote neuroplasticity could offer new therapeutic avenues for these challenging conditions.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Lithium and Neuroplasticity Studies
The investigation of neuroplastic changes induced by lithium orotate is in an early developmental stage, with a growing market potential due to increasing interest in neuroplasticity and mental health treatments. The technology's maturity is still evolving, with key players like Delix Therapeutics and Janssen Pharmaceutica leading research efforts. Academic institutions such as the University of California and University of Copenhagen are contributing significantly to the field. The competitive landscape is diverse, including established pharmaceutical companies like Sanofi-Aventis and emerging biotech firms, indicating a dynamic and promising area for innovation in neuroscience and psychiatric treatments.
The Regents of the University of California
Technical Solution: The University of California has conducted extensive research on lithium orotate-induced neuroplastic changes. Their approach involves using advanced neuroimaging techniques, such as functional MRI and diffusion tensor imaging, to visualize and quantify structural and functional brain changes in response to lithium orotate treatment[1]. They have developed a novel protocol for long-term administration of lithium orotate in animal models, allowing for the observation of cumulative neuroplastic effects over time[2]. Additionally, they are investigating the molecular mechanisms underlying these changes, focusing on the modulation of neurotrophic factors like BDNF and the regulation of synaptic plasticity-related genes[3].
Strengths: Access to cutting-edge neuroimaging facilities and expertise in molecular neuroscience. Weaknesses: Limited clinical translation of animal model findings to human subjects.
Sanofi-Aventis SA
Technical Solution: Sanofi-Aventis SA has developed a comprehensive platform for investigating lithium orotate-induced neuroplasticity. Their approach combines high-content screening of patient-derived induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) with advanced proteomics and metabolomics analyses[13]. They have engineered a novel controlled-release formulation of lithium orotate to achieve sustained therapeutic levels in the brain while minimizing peripheral exposure[14]. Sanofi's researchers are also exploring the potential of combining lithium orotate with other mood stabilizers to enhance neuroplastic effects and improve treatment outcomes in bipolar disorder[15].
Strengths: Extensive experience in drug development and access to large patient databases for clinical studies. Weaknesses: Potential focus on marketable products may limit exploration of fundamental neuroplasticity mechanisms.
Core Innovations in Neuroplasticity Assessment
Composition for preventing and treating depressive and cognitive symptoms
PatentPendingEP3698777A1
Innovation
- A combination of N-acetylcysteine, omega-3 fatty acids, and crocin, either separately or together, is administered to target inflammatory and oxidative stress pathways, providing a synergistic antidepressant effect and improving cognitive functions while slowing cognitive decline.
Compositions and methods for upregulating hippocampal plasticity and hippocampal-dependent learning and memory
PatentInactiveJP2016532683A
Innovation
- Administering a therapeutically effective amount of an electrokinetically modified fluid, such as RNS60, which contains charge-stabilized oxygen-containing nanostructures with an average diameter of less than 100 nanometers, to stimulate calcium influx through NMDA- and AMPA-sensitive ionotropic glutamate receptors, upregulate plasticity-related molecules, and enhance synaptic plasticity.
Regulatory Framework for Lithium-Based Therapeutics
The regulatory framework for lithium-based therapeutics is a complex and evolving landscape that plays a crucial role in the development, approval, and marketing of these medications. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) is the primary regulatory body overseeing lithium-based therapeutics. The FDA's Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER) is responsible for evaluating the safety and efficacy of these drugs before they can be marketed.
Lithium-based therapeutics are classified as prescription drugs and are subject to rigorous clinical trials and safety assessments. The FDA requires manufacturers to conduct extensive pre-clinical and clinical studies to demonstrate the safety and efficacy of lithium-based medications. These studies must adhere to Good Laboratory Practices (GLP) and Good Clinical Practices (GCP) guidelines to ensure data integrity and patient safety.
The regulatory process for lithium-based therapeutics typically involves several phases. Initially, manufacturers must submit an Investigational New Drug (IND) application to the FDA, which includes data from pre-clinical studies and proposed clinical trial protocols. Once approved, clinical trials can begin, progressing through Phase I, II, and III studies to evaluate safety, efficacy, and optimal dosing.
Following successful clinical trials, manufacturers submit a New Drug Application (NDA) to the FDA for review. This comprehensive application includes all data from pre-clinical and clinical studies, proposed labeling, and manufacturing information. The FDA review process involves a thorough evaluation of the drug's benefits and risks, as well as an inspection of manufacturing facilities.
Post-approval, lithium-based therapeutics are subject to ongoing regulatory oversight. Manufacturers must comply with current Good Manufacturing Practices (cGMP) to ensure product quality and consistency. Additionally, they are required to conduct post-marketing surveillance and report any adverse events to the FDA through the MedWatch program.
Internationally, regulatory frameworks for lithium-based therapeutics may vary. The European Medicines Agency (EMA) oversees the approval process in the European Union, while other countries have their own regulatory bodies. However, there is a growing trend towards harmonization of regulatory requirements through initiatives like the International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH).
Given the potential for neuroplastic changes induced by lithium orotate, regulatory bodies may require additional studies focusing on long-term neurological effects. This could involve extended clinical trials, specialized neuroimaging studies, and comprehensive post-marketing surveillance to monitor for any unexpected neuroplastic changes in patients using lithium orotate-based therapeutics.
Lithium-based therapeutics are classified as prescription drugs and are subject to rigorous clinical trials and safety assessments. The FDA requires manufacturers to conduct extensive pre-clinical and clinical studies to demonstrate the safety and efficacy of lithium-based medications. These studies must adhere to Good Laboratory Practices (GLP) and Good Clinical Practices (GCP) guidelines to ensure data integrity and patient safety.
The regulatory process for lithium-based therapeutics typically involves several phases. Initially, manufacturers must submit an Investigational New Drug (IND) application to the FDA, which includes data from pre-clinical studies and proposed clinical trial protocols. Once approved, clinical trials can begin, progressing through Phase I, II, and III studies to evaluate safety, efficacy, and optimal dosing.
Following successful clinical trials, manufacturers submit a New Drug Application (NDA) to the FDA for review. This comprehensive application includes all data from pre-clinical and clinical studies, proposed labeling, and manufacturing information. The FDA review process involves a thorough evaluation of the drug's benefits and risks, as well as an inspection of manufacturing facilities.
Post-approval, lithium-based therapeutics are subject to ongoing regulatory oversight. Manufacturers must comply with current Good Manufacturing Practices (cGMP) to ensure product quality and consistency. Additionally, they are required to conduct post-marketing surveillance and report any adverse events to the FDA through the MedWatch program.
Internationally, regulatory frameworks for lithium-based therapeutics may vary. The European Medicines Agency (EMA) oversees the approval process in the European Union, while other countries have their own regulatory bodies. However, there is a growing trend towards harmonization of regulatory requirements through initiatives like the International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH).
Given the potential for neuroplastic changes induced by lithium orotate, regulatory bodies may require additional studies focusing on long-term neurological effects. This could involve extended clinical trials, specialized neuroimaging studies, and comprehensive post-marketing surveillance to monitor for any unexpected neuroplastic changes in patients using lithium orotate-based therapeutics.
Ethical Considerations in Neuroplasticity Modulation
The investigation of neuroplastic changes induced by lithium orotate raises significant ethical considerations that must be carefully addressed. As research in this field progresses, it is crucial to maintain a balance between scientific advancement and the protection of human subjects.
One primary ethical concern is the potential long-term effects of modulating neuroplasticity through lithium orotate. While the compound may offer therapeutic benefits, altering brain structure and function carries inherent risks. Researchers must prioritize the safety and well-being of study participants, implementing rigorous monitoring protocols and establishing clear guidelines for discontinuation if adverse effects are observed.
Informed consent is another critical ethical issue in neuroplasticity modulation studies. Participants must be fully aware of the potential risks and benefits associated with lithium orotate treatment. This includes providing comprehensive information about known side effects, as well as the possibility of unforeseen consequences due to the complex nature of neuroplasticity.
The ethical implications of enhancing cognitive function through neuroplasticity modulation also warrant consideration. If lithium orotate proves effective in improving memory or learning capabilities, questions arise regarding fairness and equality in access to such treatments. Researchers and policymakers must address the potential for creating cognitive disparities and ensure equitable distribution of any resulting therapies.
Privacy and data protection present additional ethical challenges in neuroplasticity research. Brain imaging and cognitive assessments generate sensitive personal information that must be safeguarded. Strict protocols for data anonymization, storage, and sharing should be implemented to protect participants' privacy and prevent misuse of neurological data.
The potential for unintended consequences in neuroplasticity modulation must also be carefully considered. Altering brain plasticity may have far-reaching effects on personality, behavior, and identity. Researchers must be vigilant in monitoring for unexpected changes and be prepared to address any ethical dilemmas that may arise as a result of treatment.
Lastly, the ethical use of animal models in neuroplasticity research requires attention. While animal studies are often necessary for advancing scientific understanding, researchers must adhere to strict ethical guidelines to minimize suffering and ensure the humane treatment of research subjects. The translation of findings from animal models to human applications must be approached with caution and rigorous validation.
One primary ethical concern is the potential long-term effects of modulating neuroplasticity through lithium orotate. While the compound may offer therapeutic benefits, altering brain structure and function carries inherent risks. Researchers must prioritize the safety and well-being of study participants, implementing rigorous monitoring protocols and establishing clear guidelines for discontinuation if adverse effects are observed.
Informed consent is another critical ethical issue in neuroplasticity modulation studies. Participants must be fully aware of the potential risks and benefits associated with lithium orotate treatment. This includes providing comprehensive information about known side effects, as well as the possibility of unforeseen consequences due to the complex nature of neuroplasticity.
The ethical implications of enhancing cognitive function through neuroplasticity modulation also warrant consideration. If lithium orotate proves effective in improving memory or learning capabilities, questions arise regarding fairness and equality in access to such treatments. Researchers and policymakers must address the potential for creating cognitive disparities and ensure equitable distribution of any resulting therapies.
Privacy and data protection present additional ethical challenges in neuroplasticity research. Brain imaging and cognitive assessments generate sensitive personal information that must be safeguarded. Strict protocols for data anonymization, storage, and sharing should be implemented to protect participants' privacy and prevent misuse of neurological data.
The potential for unintended consequences in neuroplasticity modulation must also be carefully considered. Altering brain plasticity may have far-reaching effects on personality, behavior, and identity. Researchers must be vigilant in monitoring for unexpected changes and be prepared to address any ethical dilemmas that may arise as a result of treatment.
Lastly, the ethical use of animal models in neuroplasticity research requires attention. While animal studies are often necessary for advancing scientific understanding, researchers must adhere to strict ethical guidelines to minimize suffering and ensure the humane treatment of research subjects. The translation of findings from animal models to human applications must be approached with caution and rigorous validation.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!