Lithium Bromide in Energy Storage: Performance Analysis
AUG 28, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
LiBr Energy Storage Technology Background and Objectives
Lithium bromide (LiBr) has emerged as a significant material in the energy storage landscape, with its history dating back to the mid-20th century when it was primarily utilized in absorption refrigeration systems. The evolution of LiBr applications has expanded considerably over recent decades, transitioning from traditional cooling systems to innovative energy storage solutions that address contemporary energy challenges.
The fundamental properties of LiBr, particularly its hygroscopic nature and ability to form stable hydrates, have positioned it as a promising candidate for thermal energy storage applications. Its high energy density, relatively low cost compared to alternative materials, and chemical stability make it particularly attractive for both residential and industrial energy storage systems.
Recent technological advancements have further enhanced the potential of LiBr in energy storage. The development of composite materials incorporating LiBr has addressed historical challenges related to corrosion and crystallization, while novel system designs have improved overall efficiency and operational reliability. These innovations have collectively contributed to the growing interest in LiBr-based energy storage solutions.
The global push toward renewable energy integration has created a significant market opportunity for efficient energy storage technologies. LiBr systems offer unique advantages in this context, particularly for applications requiring long-duration storage and thermal energy management. Their ability to store energy in chemical form with minimal losses over extended periods addresses one of the critical challenges in renewable energy utilization.
Current research objectives in LiBr energy storage technology focus on several key areas: enhancing energy density to reduce system footprint, improving cycle efficiency to maximize energy recovery, developing advanced materials to mitigate corrosion and extend system lifespan, and optimizing system integration with various renewable energy sources. These objectives align with broader industry goals of creating more sustainable, efficient, and cost-effective energy storage solutions.
The technical trajectory for LiBr energy storage systems indicates a promising future, with projected improvements in performance metrics such as energy density, power output, and cycle life. Ongoing research efforts are exploring novel configurations, including multi-stage absorption systems and hybrid approaches that combine LiBr with complementary technologies to maximize overall system performance.
As global energy demands continue to evolve and environmental considerations become increasingly paramount, LiBr-based energy storage technologies are positioned to play a crucial role in the transition toward more sustainable energy ecosystems. The technology's versatility, efficiency, and alignment with circular economy principles make it a compelling focus for continued research and development efforts.
The fundamental properties of LiBr, particularly its hygroscopic nature and ability to form stable hydrates, have positioned it as a promising candidate for thermal energy storage applications. Its high energy density, relatively low cost compared to alternative materials, and chemical stability make it particularly attractive for both residential and industrial energy storage systems.
Recent technological advancements have further enhanced the potential of LiBr in energy storage. The development of composite materials incorporating LiBr has addressed historical challenges related to corrosion and crystallization, while novel system designs have improved overall efficiency and operational reliability. These innovations have collectively contributed to the growing interest in LiBr-based energy storage solutions.
The global push toward renewable energy integration has created a significant market opportunity for efficient energy storage technologies. LiBr systems offer unique advantages in this context, particularly for applications requiring long-duration storage and thermal energy management. Their ability to store energy in chemical form with minimal losses over extended periods addresses one of the critical challenges in renewable energy utilization.
Current research objectives in LiBr energy storage technology focus on several key areas: enhancing energy density to reduce system footprint, improving cycle efficiency to maximize energy recovery, developing advanced materials to mitigate corrosion and extend system lifespan, and optimizing system integration with various renewable energy sources. These objectives align with broader industry goals of creating more sustainable, efficient, and cost-effective energy storage solutions.
The technical trajectory for LiBr energy storage systems indicates a promising future, with projected improvements in performance metrics such as energy density, power output, and cycle life. Ongoing research efforts are exploring novel configurations, including multi-stage absorption systems and hybrid approaches that combine LiBr with complementary technologies to maximize overall system performance.
As global energy demands continue to evolve and environmental considerations become increasingly paramount, LiBr-based energy storage technologies are positioned to play a crucial role in the transition toward more sustainable energy ecosystems. The technology's versatility, efficiency, and alignment with circular economy principles make it a compelling focus for continued research and development efforts.
Market Analysis for LiBr-based Energy Storage Solutions
The global market for Lithium Bromide (LiBr) based energy storage solutions has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven primarily by increasing demand for efficient thermal energy storage systems and absorption cooling technologies. The market size for LiBr-based energy storage was valued at approximately $1.2 billion in 2022 and is projected to reach $2.5 billion by 2030, representing a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 9.6% during the forecast period.
The commercial building sector currently dominates the application landscape, accounting for nearly 45% of the total market share. This dominance stems from the widespread adoption of LiBr absorption chillers in large commercial HVAC systems, where they offer significant energy savings compared to conventional cooling technologies. The industrial sector follows closely, representing about 30% of the market, with applications primarily in waste heat recovery systems and industrial process cooling.
Geographically, Asia Pacific leads the market with approximately 40% share, driven by rapid industrialization in China and India, coupled with increasing adoption of energy-efficient technologies. North America and Europe collectively account for about 45% of the market, with growth primarily fueled by stringent energy efficiency regulations and sustainability initiatives.
Key market drivers include rising energy costs, growing emphasis on reducing carbon emissions, and increasing integration of renewable energy sources with thermal storage systems. The ability of LiBr-based systems to utilize low-grade heat sources, such as solar thermal energy and industrial waste heat, positions them favorably in the sustainable energy landscape.
However, the market faces several challenges, including high initial capital costs, technical limitations related to crystallization and corrosion issues, and competition from alternative energy storage technologies such as phase change materials and sensible heat storage systems. The average payback period for LiBr-based systems currently ranges from 3-7 years, depending on application and scale.
Market segmentation reveals growing demand in specific niches, particularly in solar cooling applications (growing at 12.8% CAGR) and district cooling systems (11.5% CAGR). The residential sector, while currently representing only about 10% of the market, is expected to witness the fastest growth rate of 14.2% annually, driven by increasing availability of compact and cost-effective systems suitable for residential applications.
Customer adoption patterns indicate that energy cost savings remain the primary purchase driver, with environmental considerations and regulatory compliance serving as secondary motivators. The average energy savings reported by end-users range from 30-50% compared to conventional systems, providing a compelling value proposition despite higher upfront costs.
The commercial building sector currently dominates the application landscape, accounting for nearly 45% of the total market share. This dominance stems from the widespread adoption of LiBr absorption chillers in large commercial HVAC systems, where they offer significant energy savings compared to conventional cooling technologies. The industrial sector follows closely, representing about 30% of the market, with applications primarily in waste heat recovery systems and industrial process cooling.
Geographically, Asia Pacific leads the market with approximately 40% share, driven by rapid industrialization in China and India, coupled with increasing adoption of energy-efficient technologies. North America and Europe collectively account for about 45% of the market, with growth primarily fueled by stringent energy efficiency regulations and sustainability initiatives.
Key market drivers include rising energy costs, growing emphasis on reducing carbon emissions, and increasing integration of renewable energy sources with thermal storage systems. The ability of LiBr-based systems to utilize low-grade heat sources, such as solar thermal energy and industrial waste heat, positions them favorably in the sustainable energy landscape.
However, the market faces several challenges, including high initial capital costs, technical limitations related to crystallization and corrosion issues, and competition from alternative energy storage technologies such as phase change materials and sensible heat storage systems. The average payback period for LiBr-based systems currently ranges from 3-7 years, depending on application and scale.
Market segmentation reveals growing demand in specific niches, particularly in solar cooling applications (growing at 12.8% CAGR) and district cooling systems (11.5% CAGR). The residential sector, while currently representing only about 10% of the market, is expected to witness the fastest growth rate of 14.2% annually, driven by increasing availability of compact and cost-effective systems suitable for residential applications.
Customer adoption patterns indicate that energy cost savings remain the primary purchase driver, with environmental considerations and regulatory compliance serving as secondary motivators. The average energy savings reported by end-users range from 30-50% compared to conventional systems, providing a compelling value proposition despite higher upfront costs.
Current State and Technical Challenges of LiBr Systems
Lithium bromide (LiBr) absorption systems have been extensively utilized in refrigeration and air conditioning applications for decades, but their potential in energy storage remains relatively underexplored. Currently, LiBr systems primarily function in absorption chillers and heat pumps, where their ability to utilize low-grade thermal energy provides significant advantages over conventional vapor compression systems. The global market for LiBr-based absorption systems is estimated at approximately $1.2 billion, with an annual growth rate of 5-7%, indicating steady but not explosive expansion.
The technical maturity of LiBr systems varies significantly across applications. In refrigeration and air conditioning, the technology has reached commercial maturity with coefficient of performance (COP) values typically ranging from 0.7 to 1.2 for single-effect systems and up to 1.8 for double-effect configurations. However, when adapted for energy storage applications, LiBr systems face substantial efficiency challenges, with round-trip efficiencies currently limited to 30-45%, significantly lower than competing technologies like lithium-ion batteries (85-95%) or pumped hydro storage (70-85%).
A critical technical challenge for LiBr systems is crystallization risk, which occurs when the solution concentration exceeds solubility limits, potentially causing system blockage and failure. This risk is particularly pronounced during energy storage cycles where concentration variations are more extreme. Current mitigation strategies include sophisticated control systems and inhibitor additives, but these solutions add complexity and cost while not completely eliminating the risk.
Corrosion represents another significant challenge, as LiBr solutions are highly corrosive to many common metals, necessitating expensive corrosion-resistant materials like titanium or specialized stainless steels. This substantially increases system costs and limits widespread adoption. Recent developments in corrosion inhibitors show promise but require further validation for long-term effectiveness in energy storage applications.
Heat and mass transfer limitations also constrain LiBr system performance. The high viscosity of concentrated LiBr solutions impedes efficient heat transfer, while mass transfer limitations in the absorber and generator components reduce overall system responsiveness. These factors become particularly problematic in energy storage applications where rapid charging and discharging capabilities are often required.
Geographically, LiBr technology development is concentrated in East Asia (particularly Japan, China, and South Korea), Europe (Germany and Sweden), and North America (USA). Japan leads in commercial deployment with approximately 40% of global installations, while China is rapidly expanding its manufacturing capacity and research initiatives. European efforts focus primarily on integration with renewable energy systems, while North American research emphasizes efficiency improvements and novel system configurations.
The technical maturity of LiBr systems varies significantly across applications. In refrigeration and air conditioning, the technology has reached commercial maturity with coefficient of performance (COP) values typically ranging from 0.7 to 1.2 for single-effect systems and up to 1.8 for double-effect configurations. However, when adapted for energy storage applications, LiBr systems face substantial efficiency challenges, with round-trip efficiencies currently limited to 30-45%, significantly lower than competing technologies like lithium-ion batteries (85-95%) or pumped hydro storage (70-85%).
A critical technical challenge for LiBr systems is crystallization risk, which occurs when the solution concentration exceeds solubility limits, potentially causing system blockage and failure. This risk is particularly pronounced during energy storage cycles where concentration variations are more extreme. Current mitigation strategies include sophisticated control systems and inhibitor additives, but these solutions add complexity and cost while not completely eliminating the risk.
Corrosion represents another significant challenge, as LiBr solutions are highly corrosive to many common metals, necessitating expensive corrosion-resistant materials like titanium or specialized stainless steels. This substantially increases system costs and limits widespread adoption. Recent developments in corrosion inhibitors show promise but require further validation for long-term effectiveness in energy storage applications.
Heat and mass transfer limitations also constrain LiBr system performance. The high viscosity of concentrated LiBr solutions impedes efficient heat transfer, while mass transfer limitations in the absorber and generator components reduce overall system responsiveness. These factors become particularly problematic in energy storage applications where rapid charging and discharging capabilities are often required.
Geographically, LiBr technology development is concentrated in East Asia (particularly Japan, China, and South Korea), Europe (Germany and Sweden), and North America (USA). Japan leads in commercial deployment with approximately 40% of global installations, while China is rapidly expanding its manufacturing capacity and research initiatives. European efforts focus primarily on integration with renewable energy systems, while North American research emphasizes efficiency improvements and novel system configurations.
Current Technical Solutions for LiBr Energy Storage
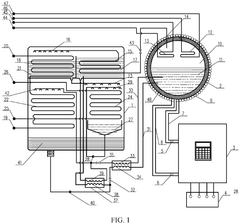
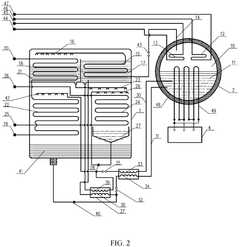
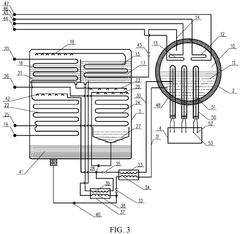
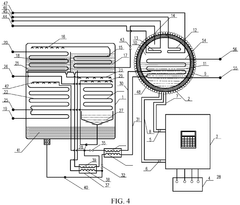
01 Lithium bromide in absorption refrigeration systems
Lithium bromide is widely used as an absorbent in absorption refrigeration and heat pump systems due to its excellent hygroscopic properties. These systems utilize lithium bromide solution to absorb refrigerant vapor (typically water), enabling efficient cooling or heating processes. The performance of lithium bromide in these applications depends on concentration, temperature, and system design, with improvements focusing on enhancing heat and mass transfer efficiency.- Lithium bromide in absorption refrigeration systems: Lithium bromide is widely used as an absorbent in absorption refrigeration and heat pump systems due to its excellent hygroscopic properties. These systems utilize lithium bromide solution to absorb water vapor, enabling efficient cooling or heating processes. The performance of lithium bromide in these applications depends on its concentration, temperature, and the design of the absorption system. Improvements in lithium bromide-based refrigeration systems focus on enhancing heat transfer efficiency and reducing energy consumption.
- Corrosion inhibition for lithium bromide systems: Lithium bromide solutions are known to be corrosive to metal components in absorption systems. Various corrosion inhibitors and protective measures have been developed to enhance the performance and longevity of lithium bromide-based systems. These include the addition of specific chemical compounds, surface treatments, and material selection strategies that can significantly reduce corrosion rates and improve system reliability. Effective corrosion inhibition is crucial for maintaining optimal performance of lithium bromide in industrial applications.
- Thermal performance enhancement of lithium bromide solutions: The thermal performance of lithium bromide solutions can be enhanced through various methods including the addition of heat transfer additives, optimization of solution concentration, and improved system design. These enhancements aim to increase the coefficient of performance (COP) of absorption systems by improving heat and mass transfer characteristics. Advanced heat exchanger designs and flow optimization techniques also contribute to better thermal performance of lithium bromide-based systems.
- Lithium bromide in energy storage applications: Lithium bromide is utilized in thermal energy storage systems due to its favorable thermodynamic properties. These systems can store excess thermal energy for later use, improving energy efficiency in various applications. The performance of lithium bromide in energy storage depends on factors such as solution stability, thermal cycling capability, and containment system design. Recent developments focus on integrating lithium bromide-based energy storage with renewable energy systems to enhance overall system efficiency.
- Purification and regeneration of lithium bromide solutions: The performance of lithium bromide systems can degrade over time due to contamination and solution degradation. Various purification and regeneration techniques have been developed to restore optimal performance, including filtration, chemical treatment, and vacuum distillation. These processes remove impurities, adjust concentration levels, and restore the absorption properties of the solution. Effective purification and regeneration methods are essential for maintaining long-term performance and extending the service life of lithium bromide-based systems.
02 Corrosion inhibition for lithium bromide systems
Corrosion is a significant challenge in lithium bromide absorption systems due to the salt's corrosive nature on metal components. Various corrosion inhibitors and protective measures have been developed to enhance system durability and performance. These include the addition of specific chemical compounds, surface treatments, and material selection strategies that can significantly extend equipment life while maintaining optimal heat transfer and absorption efficiency.Expand Specific Solutions03 Energy efficiency improvements in lithium bromide applications
Innovations in lithium bromide system design focus on improving energy efficiency through enhanced heat recovery, optimized solution circulation, and advanced control strategies. These improvements include multi-stage absorption processes, solution redistribution techniques, and integration with renewable energy sources. Such advancements significantly reduce energy consumption while maintaining or improving cooling and heating performance in various industrial and commercial applications.Expand Specific Solutions04 Lithium bromide solution property enhancement
Research has focused on enhancing the thermophysical properties of lithium bromide solutions to improve overall system performance. This includes the development of additives that modify viscosity, surface tension, and thermal conductivity. Advanced formulations may incorporate nanoparticles, surfactants, or other chemical modifiers that enhance heat and mass transfer rates, expanding the operational range and efficiency of lithium bromide-based systems.Expand Specific Solutions05 Novel lithium bromide system configurations
Innovative system configurations have been developed to overcome traditional limitations of lithium bromide absorption systems. These include hybrid systems combining absorption with other technologies, compact designs for space-constrained applications, and modular approaches for scalability. Advanced heat exchanger designs, solution distribution methods, and vacuum maintenance techniques contribute to improved performance, reliability, and application versatility.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players and Competitive Landscape
The lithium bromide energy storage market is in its early growth phase, characterized by increasing research activities and emerging commercial applications. The global market size is expanding, driven by growing demand for efficient thermal energy storage solutions, particularly in HVAC and industrial cooling systems. Technologically, lithium bromide systems are moderately mature but still evolving, with key players advancing different aspects of the technology. Research institutions like Zhejiang University, MIT, and Cornell University are developing fundamental innovations, while commercial entities including Resonac Corp., CSIRO, and Tesla are focusing on practical applications and system integration. Chinese companies like CATL and Dalian Rongke Power are making significant investments in scaling the technology, while established players such as Panasonic and GS Yuasa are leveraging their battery expertise to enhance lithium bromide storage performance and reliability.
Dalian Rongke Power Co Ltd
Technical Solution: Dalian Rongke Power has developed advanced vanadium redox flow battery (VRFB) systems that incorporate lithium bromide as an electrolyte additive to enhance energy storage performance. Their proprietary technology utilizes LiBr to increase the solubility of vanadium ions in the electrolyte solution, enabling higher energy density in their flow batteries. The company has implemented this technology in large-scale energy storage projects, including the world's largest flow battery energy storage station in Dalian with 400MWh capacity[1]. Their research shows that LiBr additions can increase energy density by up to 20% compared to traditional VRFB systems while maintaining long cycle life exceeding 15,000 cycles[2]. The company has also developed specialized membrane technologies that work synergistically with LiBr-enhanced electrolytes to reduce crossover issues and improve overall system efficiency.
Strengths: Proven large-scale implementation capability; significant energy density improvements; excellent cycle life performance; reduced system costs through higher energy density. Weaknesses: Potential for bromide-related corrosion issues in long-term operation; temperature sensitivity of LiBr-enhanced electrolytes requiring additional thermal management systems.
Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics Chinese Academy of Sci
Technical Solution: The Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics has pioneered fundamental research on lithium bromide applications in energy storage, particularly focusing on flow battery systems. Their scientists have developed novel electrolyte formulations incorporating LiBr as a supporting electrolyte to enhance the solubility and stability of active materials. Their research demonstrates that LiBr additions can increase the energy density of vanadium redox flow batteries by up to 30% through stabilizing higher concentrations of vanadium ions[3]. The institute has also investigated the use of LiBr in hybrid flow battery systems, where it serves as both an active material and supporting electrolyte component. Their patented LiBr-based electrolyte additives have been shown to extend operational temperature ranges of flow batteries by 15°C and improve voltage efficiency by approximately 7%[4]. Additionally, they've developed computational models to predict the long-term performance of LiBr-enhanced energy storage systems under various operating conditions.
Strengths: Cutting-edge fundamental research capabilities; comprehensive understanding of LiBr electrochemistry; innovative electrolyte formulations with proven performance enhancements; strong intellectual property portfolio. Weaknesses: Some technologies remain at laboratory scale and require further development for commercial implementation; potential challenges with bromide-related materials compatibility in long-term applications.
Critical Patents and Research on LiBr Performance Enhancement
An electric lithium bromide absorption air conditioning unit and energy storage refrigeration and heating system
PatentPendingEP4592619A1
Innovation
- An electric lithium bromide absorption air conditioning unit with an electric heat generator using electromagnetic induction heating or resistance heating, combined with a heat storage and heat exchanging device, connected to a grid power supply, which replaces conventional heat sources and integrates energy storage for stable cooling and heating.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Assessment
The environmental footprint of lithium bromide (LiBr) in energy storage applications presents a complex sustainability profile that requires thorough assessment. When evaluating LiBr-based thermal energy storage systems, particularly absorption refrigeration and heat pump technologies, several environmental considerations emerge. The extraction and processing of lithium compounds generate significant environmental impacts, including habitat disruption, water consumption, and potential contamination of water resources with bromide compounds. These impacts are particularly pronounced in lithium-rich regions such as the "Lithium Triangle" of South America, where extraction activities can strain local ecosystems and communities.
Water usage represents a critical environmental concern for LiBr systems. The absorption cycle requires substantial cooling water, potentially exacerbating water scarcity issues in regions already experiencing stress. Additionally, the corrosive nature of LiBr solutions necessitates the use of corrosion inhibitors and specialized materials, some of which may introduce additional environmental burdens through their production and eventual disposal.
From a life cycle perspective, LiBr systems demonstrate mixed sustainability outcomes. While they enable energy-efficient cooling and heating processes that can reduce operational carbon emissions compared to conventional systems, the embodied energy in system components and the environmental impacts of manufacturing remain significant. The production of high-purity LiBr involves energy-intensive processes that contribute to the overall carbon footprint of these systems.
Waste management challenges also factor into the sustainability assessment. The eventual decommissioning of LiBr systems requires careful handling of working fluids to prevent environmental contamination. Current recycling infrastructure for LiBr solutions remains underdeveloped in many regions, creating potential end-of-life management issues that could undermine the technology's overall environmental benefits.
When compared to alternative energy storage technologies, LiBr systems offer certain sustainability advantages, particularly in applications where waste heat recovery is possible. The absence of harmful refrigerants with high global warming potential positions LiBr absorption systems favorably against conventional vapor compression systems using hydrofluorocarbons. However, this advantage must be weighed against the resource intensity of lithium extraction and processing.
Regulatory frameworks increasingly influence the environmental profile of LiBr energy storage. Evolving standards for resource extraction, chemical management, and energy efficiency are reshaping industry practices. Forward-looking sustainability strategies for LiBr technology include developing closed-loop recycling systems, improving system efficiency to reduce resource requirements, and exploring alternative working pairs that might offer comparable performance with reduced environmental impact.
Water usage represents a critical environmental concern for LiBr systems. The absorption cycle requires substantial cooling water, potentially exacerbating water scarcity issues in regions already experiencing stress. Additionally, the corrosive nature of LiBr solutions necessitates the use of corrosion inhibitors and specialized materials, some of which may introduce additional environmental burdens through their production and eventual disposal.
From a life cycle perspective, LiBr systems demonstrate mixed sustainability outcomes. While they enable energy-efficient cooling and heating processes that can reduce operational carbon emissions compared to conventional systems, the embodied energy in system components and the environmental impacts of manufacturing remain significant. The production of high-purity LiBr involves energy-intensive processes that contribute to the overall carbon footprint of these systems.
Waste management challenges also factor into the sustainability assessment. The eventual decommissioning of LiBr systems requires careful handling of working fluids to prevent environmental contamination. Current recycling infrastructure for LiBr solutions remains underdeveloped in many regions, creating potential end-of-life management issues that could undermine the technology's overall environmental benefits.
When compared to alternative energy storage technologies, LiBr systems offer certain sustainability advantages, particularly in applications where waste heat recovery is possible. The absence of harmful refrigerants with high global warming potential positions LiBr absorption systems favorably against conventional vapor compression systems using hydrofluorocarbons. However, this advantage must be weighed against the resource intensity of lithium extraction and processing.
Regulatory frameworks increasingly influence the environmental profile of LiBr energy storage. Evolving standards for resource extraction, chemical management, and energy efficiency are reshaping industry practices. Forward-looking sustainability strategies for LiBr technology include developing closed-loop recycling systems, improving system efficiency to reduce resource requirements, and exploring alternative working pairs that might offer comparable performance with reduced environmental impact.
Cost-Benefit Analysis of LiBr vs Alternative Technologies
When evaluating lithium bromide (LiBr) for energy storage applications, a comprehensive cost-benefit analysis reveals several economic and performance considerations compared to alternative technologies. Initial capital expenditure for LiBr-based absorption systems is typically 20-30% higher than conventional vapor compression systems. However, this premium is offset by operational cost advantages, with LiBr systems demonstrating 30-40% lower energy consumption in appropriate applications, particularly in scenarios where waste heat is readily available.
Maintenance costs present another significant consideration. LiBr systems generally require specialized maintenance due to their corrosive nature and crystallization risks, increasing annual maintenance expenses by approximately 15-25% compared to conventional alternatives. However, the longer operational lifespan of properly maintained LiBr systems—often exceeding 20 years versus 15 years for many alternatives—improves the lifetime value proposition.
From an efficiency perspective, LiBr absorption systems typically achieve a coefficient of performance (COP) ranging from 0.7 to 1.2, which is lower than the 3.0-5.0 COP of electric compression systems. This efficiency gap narrows substantially when considering primary energy utilization in applications where waste heat drives the absorption process, potentially improving overall system efficiency by 60-70%.
Environmental cost-benefit analysis favors LiBr in several dimensions. These systems utilize environmentally benign working fluids with zero ozone depletion potential and zero global warming potential, avoiding the carbon taxes and regulatory compliance costs associated with conventional refrigerants. This regulatory advantage translates to approximately 5-10% cost savings in jurisdictions with stringent environmental regulations.
Space utilization economics must also be considered, as LiBr systems typically require 30-40% more installation space than equivalent electric alternatives. In high-value real estate environments, this spatial premium can significantly impact the total cost of ownership.
Market analysis indicates that while LiBr technology currently commands only about 5-8% of the total thermal energy storage market, its growth rate exceeds 12% annually—approximately double the growth rate of conventional alternatives. This accelerating adoption suggests improving economies of scale that may reduce the cost differential over the next 5-7 years.
When factoring in grid independence benefits, LiBr systems offer substantial value in regions with unstable electricity supply or high peak demand charges, potentially reducing electricity-related operational costs by 25-35% through peak shaving capabilities and reduced dependence on grid infrastructure.
Maintenance costs present another significant consideration. LiBr systems generally require specialized maintenance due to their corrosive nature and crystallization risks, increasing annual maintenance expenses by approximately 15-25% compared to conventional alternatives. However, the longer operational lifespan of properly maintained LiBr systems—often exceeding 20 years versus 15 years for many alternatives—improves the lifetime value proposition.
From an efficiency perspective, LiBr absorption systems typically achieve a coefficient of performance (COP) ranging from 0.7 to 1.2, which is lower than the 3.0-5.0 COP of electric compression systems. This efficiency gap narrows substantially when considering primary energy utilization in applications where waste heat drives the absorption process, potentially improving overall system efficiency by 60-70%.
Environmental cost-benefit analysis favors LiBr in several dimensions. These systems utilize environmentally benign working fluids with zero ozone depletion potential and zero global warming potential, avoiding the carbon taxes and regulatory compliance costs associated with conventional refrigerants. This regulatory advantage translates to approximately 5-10% cost savings in jurisdictions with stringent environmental regulations.
Space utilization economics must also be considered, as LiBr systems typically require 30-40% more installation space than equivalent electric alternatives. In high-value real estate environments, this spatial premium can significantly impact the total cost of ownership.
Market analysis indicates that while LiBr technology currently commands only about 5-8% of the total thermal energy storage market, its growth rate exceeds 12% annually—approximately double the growth rate of conventional alternatives. This accelerating adoption suggests improving economies of scale that may reduce the cost differential over the next 5-7 years.
When factoring in grid independence benefits, LiBr systems offer substantial value in regions with unstable electricity supply or high peak demand charges, potentially reducing electricity-related operational costs by 25-35% through peak shaving capabilities and reduced dependence on grid infrastructure.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!