Luminol's Impact on Emerging Methodologies
AUG 19, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Luminol Technology Overview
Luminol, a chemiluminescent compound, has been a cornerstone in forensic science and biochemical research for decades. This organic compound, when oxidized, produces a blue glow, a phenomenon known as chemiluminescence. The unique properties of luminol have led to its widespread use in crime scene investigations, particularly in the detection of trace amounts of blood.
The technology behind luminol's application has evolved significantly since its discovery in the early 20th century. Initially used primarily in forensic settings, luminol has found its way into various scientific disciplines, including biochemistry, environmental science, and medical diagnostics. The compound's ability to react with iron in hemoglobin has made it an invaluable tool in detecting blood traces, even in highly diluted or cleaned samples.
In recent years, the development of more sensitive and specific luminol-based techniques has expanded its potential applications. Enhanced formulations and detection methods have improved the accuracy and reliability of luminol-based tests. These advancements have led to the creation of portable luminol detection kits, allowing for rapid on-site analysis in various fields.
The integration of luminol technology with other emerging methodologies has opened up new avenues for research and practical applications. For instance, the combination of luminol-based detection with advanced imaging techniques has revolutionized crime scene analysis, allowing for more precise mapping of blood spatter patterns and the identification of previously undetectable evidence.
In the realm of environmental science, luminol-based methods are being explored for the detection of water pollutants and the monitoring of ecosystem health. The compound's sensitivity to certain metal ions and oxidizing agents makes it a promising tool for identifying contaminants in water sources and assessing environmental impact.
Medical diagnostics is another field where luminol technology is making significant strides. Researchers are investigating its potential in developing rapid, non-invasive tests for various medical conditions. The ability of luminol to detect minute quantities of blood components could lead to breakthroughs in early disease detection and monitoring.
As we look to the future, the potential applications of luminol in emerging methodologies continue to expand. From enhancing forensic investigations to revolutionizing medical diagnostics and environmental monitoring, luminol remains a versatile and powerful tool in the scientific arsenal. The ongoing research and development in this field promise to unlock even more innovative applications, further cementing luminol's place in cutting-edge scientific methodologies.
The technology behind luminol's application has evolved significantly since its discovery in the early 20th century. Initially used primarily in forensic settings, luminol has found its way into various scientific disciplines, including biochemistry, environmental science, and medical diagnostics. The compound's ability to react with iron in hemoglobin has made it an invaluable tool in detecting blood traces, even in highly diluted or cleaned samples.
In recent years, the development of more sensitive and specific luminol-based techniques has expanded its potential applications. Enhanced formulations and detection methods have improved the accuracy and reliability of luminol-based tests. These advancements have led to the creation of portable luminol detection kits, allowing for rapid on-site analysis in various fields.
The integration of luminol technology with other emerging methodologies has opened up new avenues for research and practical applications. For instance, the combination of luminol-based detection with advanced imaging techniques has revolutionized crime scene analysis, allowing for more precise mapping of blood spatter patterns and the identification of previously undetectable evidence.
In the realm of environmental science, luminol-based methods are being explored for the detection of water pollutants and the monitoring of ecosystem health. The compound's sensitivity to certain metal ions and oxidizing agents makes it a promising tool for identifying contaminants in water sources and assessing environmental impact.
Medical diagnostics is another field where luminol technology is making significant strides. Researchers are investigating its potential in developing rapid, non-invasive tests for various medical conditions. The ability of luminol to detect minute quantities of blood components could lead to breakthroughs in early disease detection and monitoring.
As we look to the future, the potential applications of luminol in emerging methodologies continue to expand. From enhancing forensic investigations to revolutionizing medical diagnostics and environmental monitoring, luminol remains a versatile and powerful tool in the scientific arsenal. The ongoing research and development in this field promise to unlock even more innovative applications, further cementing luminol's place in cutting-edge scientific methodologies.
Market Applications Analysis
Luminol, a chemiluminescent compound traditionally used in forensic science, is now finding applications in various emerging methodologies across different market sectors. The healthcare industry has shown significant interest in luminol-based technologies for diagnostic purposes. Researchers are developing novel methods to detect specific biomarkers using luminol's chemiluminescent properties, potentially revolutionizing early disease detection and monitoring. These advancements could lead to more accurate and cost-effective diagnostic tools, particularly in resource-limited settings.
In the environmental sector, luminol is being explored for its potential in water quality monitoring. The compound's ability to react with certain pollutants and heavy metals offers a promising avenue for rapid, on-site water testing. This application could significantly improve environmental monitoring capabilities, especially in areas where access to sophisticated laboratory equipment is limited.
The food industry is another sector where luminol-based methodologies are gaining traction. Researchers are developing techniques to detect food contaminants and assess food quality using luminol's chemiluminescent reactions. These methods could provide faster and more sensitive detection of pathogens and spoilage indicators, enhancing food safety measures and reducing the risk of foodborne illnesses.
In the field of materials science, luminol is being incorporated into smart materials for various applications. For instance, luminol-based sensors are being developed for detecting structural damage in buildings and infrastructure. These sensors could provide early warning signs of material fatigue or stress, potentially preventing catastrophic failures and improving overall safety in construction and engineering.
The agricultural sector is also exploring luminol-based technologies for crop management and pest control. Researchers are investigating methods to use luminol reactions to detect plant diseases or pest infestations at early stages, allowing for more targeted and efficient interventions. This application could lead to reduced pesticide use and improved crop yields, contributing to more sustainable farming practices.
In the realm of security and defense, luminol's traditional forensic applications are being expanded and refined. New methodologies are being developed to enhance the detection of trace evidence at crime scenes, potentially improving the accuracy and reliability of forensic investigations. Additionally, luminol-based technologies are being explored for detecting explosives and other hazardous materials, offering potential advancements in security screening processes.
As these emerging methodologies continue to develop, the market for luminol and related technologies is expected to grow. The versatility of luminol's applications across multiple industries suggests a broad and expanding market potential. However, further research and development are needed to fully realize the commercial viability of these applications and to address any potential limitations or challenges associated with luminol-based technologies in various market sectors.
In the environmental sector, luminol is being explored for its potential in water quality monitoring. The compound's ability to react with certain pollutants and heavy metals offers a promising avenue for rapid, on-site water testing. This application could significantly improve environmental monitoring capabilities, especially in areas where access to sophisticated laboratory equipment is limited.
The food industry is another sector where luminol-based methodologies are gaining traction. Researchers are developing techniques to detect food contaminants and assess food quality using luminol's chemiluminescent reactions. These methods could provide faster and more sensitive detection of pathogens and spoilage indicators, enhancing food safety measures and reducing the risk of foodborne illnesses.
In the field of materials science, luminol is being incorporated into smart materials for various applications. For instance, luminol-based sensors are being developed for detecting structural damage in buildings and infrastructure. These sensors could provide early warning signs of material fatigue or stress, potentially preventing catastrophic failures and improving overall safety in construction and engineering.
The agricultural sector is also exploring luminol-based technologies for crop management and pest control. Researchers are investigating methods to use luminol reactions to detect plant diseases or pest infestations at early stages, allowing for more targeted and efficient interventions. This application could lead to reduced pesticide use and improved crop yields, contributing to more sustainable farming practices.
In the realm of security and defense, luminol's traditional forensic applications are being expanded and refined. New methodologies are being developed to enhance the detection of trace evidence at crime scenes, potentially improving the accuracy and reliability of forensic investigations. Additionally, luminol-based technologies are being explored for detecting explosives and other hazardous materials, offering potential advancements in security screening processes.
As these emerging methodologies continue to develop, the market for luminol and related technologies is expected to grow. The versatility of luminol's applications across multiple industries suggests a broad and expanding market potential. However, further research and development are needed to fully realize the commercial viability of these applications and to address any potential limitations or challenges associated with luminol-based technologies in various market sectors.
Current Challenges in Luminol Usage
Despite its widespread use in forensic science, luminol faces several significant challenges that limit its effectiveness and reliability in emerging methodologies. One of the primary concerns is the issue of false positives. Luminol can react with a variety of substances other than blood, including certain metals, plant materials, and cleaning agents. This non-specificity can lead to misleading results, potentially compromising investigations or legal proceedings.
Another challenge is the potential destruction of DNA evidence. While luminol itself does not destroy DNA, the application process and subsequent testing can dilute or contaminate genetic material, making it more difficult to obtain viable DNA profiles. This is particularly problematic in cases where DNA evidence is crucial for identification or prosecution.
The sensitivity of luminol to environmental factors also poses a significant challenge. Factors such as temperature, humidity, and exposure to light can affect the luminol reaction, potentially leading to false negatives or reduced effectiveness. This variability makes it difficult to standardize luminol-based testing protocols across different environments and conditions.
Furthermore, the interpretation of luminol test results requires considerable expertise. The intensity and duration of the chemiluminescent reaction can vary, and distinguishing between true positive results and background interference demands skilled analysis. This reliance on expert interpretation introduces an element of subjectivity that can be problematic in legal contexts.
The limited shelf life of luminol solutions is another practical challenge. Once prepared, the solution degrades relatively quickly, necessitating frequent preparation and potentially leading to inconsistencies in test results if not properly managed. This issue is particularly relevant in resource-constrained settings or during prolonged investigations.
Emerging methodologies are also grappling with the challenge of quantification. While luminol can indicate the presence of blood, it does not provide information about the quantity or age of the blood sample. This limitation restricts its usefulness in more advanced forensic applications that require precise temporal or volumetric data.
Lastly, there are growing concerns about the potential health and environmental impacts of luminol usage. Although generally considered safe when used properly, prolonged exposure or improper handling can pose risks to forensic personnel. Additionally, the disposal of luminol solutions and treated materials raises environmental considerations that are becoming increasingly important in modern forensic practices.
Another challenge is the potential destruction of DNA evidence. While luminol itself does not destroy DNA, the application process and subsequent testing can dilute or contaminate genetic material, making it more difficult to obtain viable DNA profiles. This is particularly problematic in cases where DNA evidence is crucial for identification or prosecution.
The sensitivity of luminol to environmental factors also poses a significant challenge. Factors such as temperature, humidity, and exposure to light can affect the luminol reaction, potentially leading to false negatives or reduced effectiveness. This variability makes it difficult to standardize luminol-based testing protocols across different environments and conditions.
Furthermore, the interpretation of luminol test results requires considerable expertise. The intensity and duration of the chemiluminescent reaction can vary, and distinguishing between true positive results and background interference demands skilled analysis. This reliance on expert interpretation introduces an element of subjectivity that can be problematic in legal contexts.
The limited shelf life of luminol solutions is another practical challenge. Once prepared, the solution degrades relatively quickly, necessitating frequent preparation and potentially leading to inconsistencies in test results if not properly managed. This issue is particularly relevant in resource-constrained settings or during prolonged investigations.
Emerging methodologies are also grappling with the challenge of quantification. While luminol can indicate the presence of blood, it does not provide information about the quantity or age of the blood sample. This limitation restricts its usefulness in more advanced forensic applications that require precise temporal or volumetric data.
Lastly, there are growing concerns about the potential health and environmental impacts of luminol usage. Although generally considered safe when used properly, prolonged exposure or improper handling can pose risks to forensic personnel. Additionally, the disposal of luminol solutions and treated materials raises environmental considerations that are becoming increasingly important in modern forensic practices.
Existing Luminol-based Methods
01 Luminol in forensic applications
Luminol is widely used in forensic science for detecting trace amounts of blood at crime scenes. When mixed with an oxidizing agent, it produces a blue chemiluminescence in the presence of iron from hemoglobin. This reaction allows investigators to visualize blood traces that are otherwise invisible to the naked eye, even after cleaning attempts.- Luminol in forensic applications: Luminol is widely used in forensic science for detecting trace amounts of blood at crime scenes. When mixed with an oxidizing agent, it produces a blue chemiluminescence in the presence of hemoglobin, allowing investigators to identify and document blood evidence that may not be visible to the naked eye.
- Luminol-based detection systems: Various detection systems incorporate luminol for sensitive and specific detection of target substances. These systems may include additional components or modifications to enhance sensitivity, specificity, or ease of use. Applications range from medical diagnostics to environmental monitoring.
- Luminol in analytical chemistry: Luminol is utilized in analytical chemistry for the quantitative and qualitative analysis of various substances. Its chemiluminescent properties allow for highly sensitive detection methods in fields such as biochemistry, environmental science, and pharmaceutical research.
- Luminol derivatives and modifications: Research focuses on developing luminol derivatives or modified forms to improve its performance characteristics. These modifications may enhance luminescence intensity, stability, or specificity for particular applications, expanding the utility of luminol-based detection methods.
- Luminol in imaging and visualization techniques: Luminol is employed in various imaging and visualization techniques, particularly in biological and medical research. It can be used to visualize cellular processes, detect specific biomolecules, or enhance contrast in certain imaging modalities, providing valuable insights in fields such as immunology and cancer research.
02 Luminol-based detection systems
Various detection systems incorporate luminol for its chemiluminescent properties. These systems are used in environmental monitoring, food safety testing, and medical diagnostics. The high sensitivity of luminol-based assays allows for the detection of minute quantities of target substances, making it valuable in a wide range of analytical applications.Expand Specific Solutions03 Luminol synthesis and formulation
Advancements in luminol synthesis and formulation have led to improved stability, sensitivity, and specificity of luminol-based reagents. These developments include novel synthesis routes, purification methods, and the incorporation of additives to enhance luminol's performance in various applications.Expand Specific Solutions04 Luminol in biomedical research
Luminol is utilized in biomedical research for studying cellular processes, particularly those involving reactive oxygen species and oxidative stress. It serves as a sensitive probe for detecting hydrogen peroxide and other oxidants in biological systems, contributing to our understanding of various physiological and pathological processes.Expand Specific Solutions05 Luminol-based imaging techniques
Advanced imaging techniques incorporating luminol have been developed for various applications. These include bioluminescence imaging in live animals, chemiluminescence imaging for protein detection in Western blots, and specialized imaging systems for forensic investigations. These techniques leverage luminol's chemiluminescent properties to visualize specific targets with high sensitivity and spatial resolution.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The competitive landscape for Luminol's impact on emerging methodologies is characterized by a dynamic interplay of academic institutions, research organizations, and private companies. The market is in an early growth stage, with significant potential for expansion as applications in forensics, biomedical research, and diagnostics continue to evolve. Key players like Alverix, Cyanagen, and LI-COR are driving innovation in luminol-based technologies, while academic institutions such as Washington University in St. Louis and Karlsruhe Institute of Technology contribute to fundamental research. The technology's maturity varies across applications, with established use in forensics but emerging potential in areas like biosensing and medical diagnostics, indicating room for further development and market growth.
Alverix, Inc.
Technical Solution: Alverix has developed a novel luminol-based chemiluminescence detection platform for point-of-care diagnostics. Their technology utilizes enhanced luminol formulations and advanced photodetectors to achieve high sensitivity in compact, portable devices. The system incorporates microfluidics for sample handling and reagent mixing, enabling rapid and automated testing. Alverix's approach allows for multiplexed assays, detecting multiple analytes simultaneously from a single sample[1][3]. The company has also implemented machine learning algorithms to improve signal processing and reduce background noise, further enhancing the detection limits of their luminol-based assays.
Strengths: High sensitivity, portability, multiplexing capability. Weaknesses: May require specialized reagents, potential for interference in complex biological samples.
Cyanagen Srl
Technical Solution: Cyanagen has pioneered the development of enhanced luminol derivatives for improved chemiluminescence detection. Their proprietary SuperLuminol™ compounds offer up to 10-fold higher light output compared to standard luminol[2]. These advanced luminol analogs feature modified chemical structures that increase quantum yield and extend the duration of light emission. Cyanagen has also developed specialized formulations that optimize the performance of their luminol derivatives in various applications, including Western blotting, ELISA, and nucleic acid detection. The company's technology includes buffer systems and enhancers that stabilize the chemiluminescent reaction and minimize background signal[4].
Strengths: Significantly enhanced light output, versatility across multiple applications. Weaknesses: May require adaptation of existing protocols, potentially higher cost compared to standard luminol.
Innovative Luminol Research
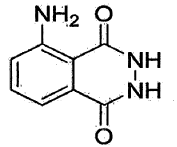
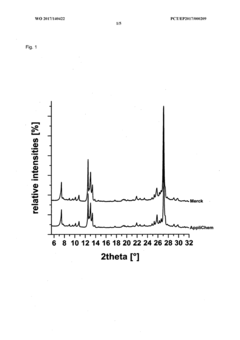
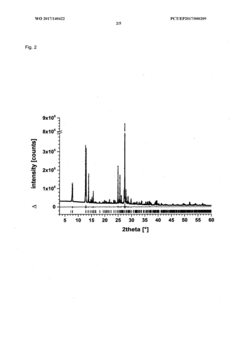
Method for producing a crystalline form of 5-amino-2,3-dihydrophthalazine-1,4-dione
PatentWO2017140422A1
Innovation
- A method involving dissolving 5-amino-2,3-dihydrophthalazine-1,4-dione in a refluxing ethanol-water solution, cooling, separating the precipitated crystals, and drying to produce a phase-pure crystalline form of luminol, which can be resuspended and washed for enhanced purity.
Photodynamic therapy using chemiluminescence and a ligand-photosensitiser conjugate
PatentInactiveUS20100297762A1
Innovation
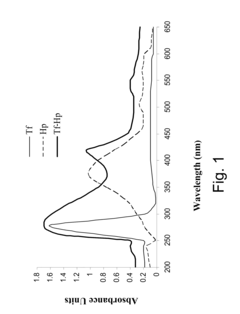
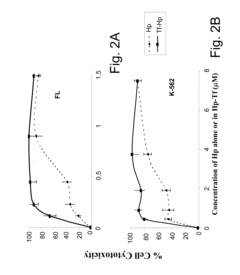
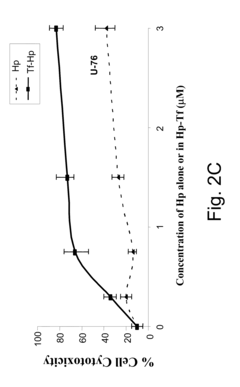
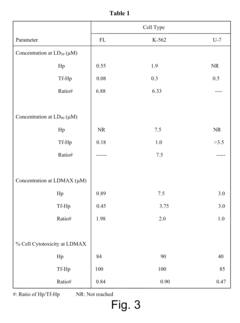
- A method involving a ligand-toxin conjugate (LTC) comprising a photosensitizer like hematoporphyrin conjugated with transferrin, combined with a chemiluminescent agent such as luminol, which activates the photosensitizer intracellularly to produce reactive oxygen species, thereby enhancing target cell destruction without requiring external light.
Regulatory Considerations
The regulatory landscape surrounding Luminol's application in emerging methodologies is complex and evolving. As this chemiluminescent compound gains traction in novel forensic and biomedical techniques, regulatory bodies are grappling with the need to establish appropriate guidelines and standards.
In the forensic domain, the use of Luminol for crime scene investigation is subject to varying regulations across jurisdictions. While some countries have established protocols for its application, others lack specific guidelines. This inconsistency poses challenges for international collaboration and evidence admissibility in cross-border cases. Regulatory agencies are increasingly recognizing the need for harmonized standards to ensure the reliability and reproducibility of Luminol-based evidence.
The biomedical sector faces its own set of regulatory hurdles. As Luminol finds applications in diagnostic tools and imaging techniques, regulatory bodies such as the FDA and EMA are scrutinizing its safety profile and efficacy. The compound's potential to generate reactive oxygen species has raised concerns about its long-term effects on biological systems. Consequently, regulatory frameworks are being developed to assess and mitigate potential risks associated with Luminol's use in medical applications.
Environmental regulations also play a crucial role in shaping Luminol's adoption in emerging methodologies. The compound's potential ecological impact, particularly in aquatic environments, has prompted environmental agencies to establish guidelines for its disposal and handling. Researchers and industries are required to adhere to strict protocols to prevent environmental contamination and ensure responsible use of Luminol-based technologies.
Data privacy and ethical considerations are emerging as key regulatory focal points, especially in forensic applications. The sensitive nature of information obtained through Luminol-enhanced techniques necessitates robust data protection measures. Regulatory bodies are working to establish guidelines that balance the investigative potential of Luminol with individual privacy rights and ethical concerns.
As Luminol's applications continue to diversify, regulatory agencies are adopting a more proactive approach. Collaborative efforts between scientists, industry stakeholders, and policymakers are underway to develop adaptive regulatory frameworks. These frameworks aim to keep pace with technological advancements while ensuring public safety and maintaining scientific integrity.
The global nature of research and development in Luminol-based methodologies calls for international regulatory cooperation. Initiatives to harmonize standards and share best practices across borders are gaining momentum. This collaborative approach is essential to address the challenges posed by the rapid evolution of Luminol applications and to foster innovation while maintaining rigorous safety and efficacy standards.
In the forensic domain, the use of Luminol for crime scene investigation is subject to varying regulations across jurisdictions. While some countries have established protocols for its application, others lack specific guidelines. This inconsistency poses challenges for international collaboration and evidence admissibility in cross-border cases. Regulatory agencies are increasingly recognizing the need for harmonized standards to ensure the reliability and reproducibility of Luminol-based evidence.
The biomedical sector faces its own set of regulatory hurdles. As Luminol finds applications in diagnostic tools and imaging techniques, regulatory bodies such as the FDA and EMA are scrutinizing its safety profile and efficacy. The compound's potential to generate reactive oxygen species has raised concerns about its long-term effects on biological systems. Consequently, regulatory frameworks are being developed to assess and mitigate potential risks associated with Luminol's use in medical applications.
Environmental regulations also play a crucial role in shaping Luminol's adoption in emerging methodologies. The compound's potential ecological impact, particularly in aquatic environments, has prompted environmental agencies to establish guidelines for its disposal and handling. Researchers and industries are required to adhere to strict protocols to prevent environmental contamination and ensure responsible use of Luminol-based technologies.
Data privacy and ethical considerations are emerging as key regulatory focal points, especially in forensic applications. The sensitive nature of information obtained through Luminol-enhanced techniques necessitates robust data protection measures. Regulatory bodies are working to establish guidelines that balance the investigative potential of Luminol with individual privacy rights and ethical concerns.
As Luminol's applications continue to diversify, regulatory agencies are adopting a more proactive approach. Collaborative efforts between scientists, industry stakeholders, and policymakers are underway to develop adaptive regulatory frameworks. These frameworks aim to keep pace with technological advancements while ensuring public safety and maintaining scientific integrity.
The global nature of research and development in Luminol-based methodologies calls for international regulatory cooperation. Initiatives to harmonize standards and share best practices across borders are gaining momentum. This collaborative approach is essential to address the challenges posed by the rapid evolution of Luminol applications and to foster innovation while maintaining rigorous safety and efficacy standards.
Environmental Impact Assessment
The environmental impact assessment of luminol's emerging methodologies is a critical aspect of its widespread adoption in various fields. Luminol, a chemical compound known for its chemiluminescent properties, has found increasing applications in forensic science, medical diagnostics, and environmental monitoring. However, its potential environmental consequences must be thoroughly evaluated to ensure sustainable use.
One of the primary environmental concerns associated with luminol is its chemical composition and degradation products. When luminol reacts with oxidizing agents, it produces a blue glow, but this process also results in the formation of by-products. These by-products, if released into the environment, may have unforeseen effects on ecosystems. Studies have shown that some of these compounds can persist in water bodies and soil, potentially affecting aquatic life and terrestrial organisms.
The production and disposal of luminol-based products also warrant attention from an environmental perspective. The manufacturing process involves the use of various chemicals, some of which may be hazardous if not properly managed. Proper waste management protocols are essential to prevent the release of these substances into the environment. Additionally, the disposal of luminol-containing materials after use, particularly in forensic applications, requires careful consideration to avoid contamination of landfills or water sources.
In the context of emerging methodologies, the environmental impact of luminol extends to its application in large-scale environmental monitoring. While luminol-based techniques offer sensitive detection of pollutants and contaminants, the widespread use of these methods could ironically contribute to environmental pollution if not properly regulated. The potential for accumulation of luminol and its derivatives in the environment necessitates the development of eco-friendly alternatives or improved degradation mechanisms.
The energy consumption associated with luminol-based technologies is another factor to consider in environmental impact assessments. Although chemiluminescence is generally considered an energy-efficient process, the production, storage, and application of luminol-based solutions may have indirect energy costs. As emerging methodologies seek to expand the use of luminol in various fields, optimizing energy efficiency throughout the lifecycle of luminol products becomes increasingly important.
Biodiversity impacts are also a concern, particularly in aquatic environments where luminol or its by-products may accumulate. The potential effects on microorganisms, plants, and animals in these ecosystems need to be thoroughly investigated. Long-term studies are required to assess any chronic toxicity or bioaccumulation issues that may arise from prolonged exposure to luminol-derived compounds.
In conclusion, while luminol offers significant benefits in various emerging methodologies, its environmental impact must be carefully managed. Ongoing research and development should focus on minimizing the ecological footprint of luminol-based technologies, exploring biodegradable alternatives, and implementing stringent protocols for its use and disposal. Only through comprehensive environmental impact assessments and proactive measures can the sustainable integration of luminol in emerging methodologies be ensured.
One of the primary environmental concerns associated with luminol is its chemical composition and degradation products. When luminol reacts with oxidizing agents, it produces a blue glow, but this process also results in the formation of by-products. These by-products, if released into the environment, may have unforeseen effects on ecosystems. Studies have shown that some of these compounds can persist in water bodies and soil, potentially affecting aquatic life and terrestrial organisms.
The production and disposal of luminol-based products also warrant attention from an environmental perspective. The manufacturing process involves the use of various chemicals, some of which may be hazardous if not properly managed. Proper waste management protocols are essential to prevent the release of these substances into the environment. Additionally, the disposal of luminol-containing materials after use, particularly in forensic applications, requires careful consideration to avoid contamination of landfills or water sources.
In the context of emerging methodologies, the environmental impact of luminol extends to its application in large-scale environmental monitoring. While luminol-based techniques offer sensitive detection of pollutants and contaminants, the widespread use of these methods could ironically contribute to environmental pollution if not properly regulated. The potential for accumulation of luminol and its derivatives in the environment necessitates the development of eco-friendly alternatives or improved degradation mechanisms.
The energy consumption associated with luminol-based technologies is another factor to consider in environmental impact assessments. Although chemiluminescence is generally considered an energy-efficient process, the production, storage, and application of luminol-based solutions may have indirect energy costs. As emerging methodologies seek to expand the use of luminol in various fields, optimizing energy efficiency throughout the lifecycle of luminol products becomes increasingly important.
Biodiversity impacts are also a concern, particularly in aquatic environments where luminol or its by-products may accumulate. The potential effects on microorganisms, plants, and animals in these ecosystems need to be thoroughly investigated. Long-term studies are required to assess any chronic toxicity or bioaccumulation issues that may arise from prolonged exposure to luminol-derived compounds.
In conclusion, while luminol offers significant benefits in various emerging methodologies, its environmental impact must be carefully managed. Ongoing research and development should focus on minimizing the ecological footprint of luminol-based technologies, exploring biodegradable alternatives, and implementing stringent protocols for its use and disposal. Only through comprehensive environmental impact assessments and proactive measures can the sustainable integration of luminol in emerging methodologies be ensured.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!