Phospholipid Influence on Drug Delivery Systems
JUL 16, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Phospholipid-Based DDS Background and Objectives
Phospholipid-based drug delivery systems (DDS) have emerged as a pivotal technology in the pharmaceutical industry, revolutionizing the way drugs are administered and absorbed by the body. The evolution of this field can be traced back to the 1960s when researchers first recognized the potential of liposomes as drug carriers. Since then, the development of phospholipid-based DDS has progressed rapidly, driven by advancements in nanotechnology, biochemistry, and materials science.
The primary objective of phospholipid-based DDS is to enhance the therapeutic efficacy of drugs while minimizing their side effects. This is achieved by improving drug solubility, stability, and bioavailability, as well as by enabling targeted delivery to specific tissues or cells. Phospholipids, being the main components of biological membranes, offer unique advantages in drug delivery due to their biocompatibility, biodegradability, and amphiphilic nature.
The technological trajectory of phospholipid-based DDS has been marked by several key milestones. These include the development of various types of liposomes (conventional, stealth, and targeted), the creation of solid lipid nanoparticles (SLNs), and the advent of nanostructured lipid carriers (NLCs). Each of these innovations has contributed to expanding the range of drugs that can be effectively delivered and the routes of administration available.
Current research in this field is focused on overcoming remaining challenges, such as improving the stability of phospholipid-based formulations, enhancing their targeting capabilities, and developing novel methods for controlled release. Additionally, there is a growing interest in combining phospholipid-based DDS with other technologies, such as stimuli-responsive materials and gene delivery systems, to create more sophisticated and effective drug delivery platforms.
The global market for phospholipid-based DDS is projected to grow significantly in the coming years, driven by the increasing prevalence of chronic diseases, the rise of personalized medicine, and the growing demand for targeted therapies. This trend is further supported by the pharmaceutical industry's shift towards biologics and other complex molecules that often require advanced delivery systems to maintain their efficacy.
As we look to the future, the continued evolution of phospholipid-based DDS is expected to play a crucial role in addressing unmet medical needs and improving patient outcomes. The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning in formulation design, coupled with advances in manufacturing technologies, promises to accelerate the development of more efficient and tailored drug delivery systems. These advancements will not only enhance the effectiveness of existing drugs but also enable the successful delivery of emerging therapeutic modalities, such as RNA-based therapies and cell-free DNA vaccines.
The primary objective of phospholipid-based DDS is to enhance the therapeutic efficacy of drugs while minimizing their side effects. This is achieved by improving drug solubility, stability, and bioavailability, as well as by enabling targeted delivery to specific tissues or cells. Phospholipids, being the main components of biological membranes, offer unique advantages in drug delivery due to their biocompatibility, biodegradability, and amphiphilic nature.
The technological trajectory of phospholipid-based DDS has been marked by several key milestones. These include the development of various types of liposomes (conventional, stealth, and targeted), the creation of solid lipid nanoparticles (SLNs), and the advent of nanostructured lipid carriers (NLCs). Each of these innovations has contributed to expanding the range of drugs that can be effectively delivered and the routes of administration available.
Current research in this field is focused on overcoming remaining challenges, such as improving the stability of phospholipid-based formulations, enhancing their targeting capabilities, and developing novel methods for controlled release. Additionally, there is a growing interest in combining phospholipid-based DDS with other technologies, such as stimuli-responsive materials and gene delivery systems, to create more sophisticated and effective drug delivery platforms.
The global market for phospholipid-based DDS is projected to grow significantly in the coming years, driven by the increasing prevalence of chronic diseases, the rise of personalized medicine, and the growing demand for targeted therapies. This trend is further supported by the pharmaceutical industry's shift towards biologics and other complex molecules that often require advanced delivery systems to maintain their efficacy.
As we look to the future, the continued evolution of phospholipid-based DDS is expected to play a crucial role in addressing unmet medical needs and improving patient outcomes. The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning in formulation design, coupled with advances in manufacturing technologies, promises to accelerate the development of more efficient and tailored drug delivery systems. These advancements will not only enhance the effectiveness of existing drugs but also enable the successful delivery of emerging therapeutic modalities, such as RNA-based therapies and cell-free DNA vaccines.
Market Analysis for Phospholipid-Enhanced Drug Delivery
The phospholipid-enhanced drug delivery market has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by the increasing demand for targeted and efficient drug delivery systems. This market segment is expected to continue its upward trajectory due to several key factors.
Firstly, the pharmaceutical industry's focus on developing more effective and less toxic treatments has led to increased interest in phospholipid-based drug delivery systems. These systems offer improved bioavailability, enhanced drug stability, and reduced side effects, making them attractive for both new drug formulations and reformulations of existing drugs.
The global market for phospholipid-enhanced drug delivery systems is diverse, with applications spanning across various therapeutic areas. Oncology remains a primary focus, as phospholipid-based nanocarriers have shown promise in delivering cancer drugs more effectively to tumor sites. Other significant areas include cardiovascular diseases, neurological disorders, and infectious diseases.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the market, owing to their advanced healthcare infrastructure and high R&D investments. However, the Asia-Pacific region is emerging as a rapidly growing market, driven by increasing healthcare expenditure, rising prevalence of chronic diseases, and growing awareness of advanced drug delivery technologies.
The market is characterized by intense competition among key players, including major pharmaceutical companies and specialized drug delivery technology firms. These companies are investing heavily in research and development to create innovative phospholipid-based formulations and expand their product portfolios.
One of the key trends shaping the market is the growing adoption of liposomal drug delivery systems. Liposomes, composed of phospholipid bilayers, have gained traction due to their ability to encapsulate both hydrophilic and hydrophobic drugs, improving their therapeutic index.
Another significant trend is the increasing focus on personalized medicine. Phospholipid-enhanced drug delivery systems are being explored for their potential in tailoring treatments to individual patient profiles, potentially revolutionizing therapeutic approaches across various diseases.
Despite the promising outlook, the market faces challenges such as high development costs, complex regulatory pathways, and manufacturing scalability issues. However, ongoing technological advancements and collaborations between pharmaceutical companies and drug delivery specialists are expected to address these challenges and drive further market growth.
Firstly, the pharmaceutical industry's focus on developing more effective and less toxic treatments has led to increased interest in phospholipid-based drug delivery systems. These systems offer improved bioavailability, enhanced drug stability, and reduced side effects, making them attractive for both new drug formulations and reformulations of existing drugs.
The global market for phospholipid-enhanced drug delivery systems is diverse, with applications spanning across various therapeutic areas. Oncology remains a primary focus, as phospholipid-based nanocarriers have shown promise in delivering cancer drugs more effectively to tumor sites. Other significant areas include cardiovascular diseases, neurological disorders, and infectious diseases.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the market, owing to their advanced healthcare infrastructure and high R&D investments. However, the Asia-Pacific region is emerging as a rapidly growing market, driven by increasing healthcare expenditure, rising prevalence of chronic diseases, and growing awareness of advanced drug delivery technologies.
The market is characterized by intense competition among key players, including major pharmaceutical companies and specialized drug delivery technology firms. These companies are investing heavily in research and development to create innovative phospholipid-based formulations and expand their product portfolios.
One of the key trends shaping the market is the growing adoption of liposomal drug delivery systems. Liposomes, composed of phospholipid bilayers, have gained traction due to their ability to encapsulate both hydrophilic and hydrophobic drugs, improving their therapeutic index.
Another significant trend is the increasing focus on personalized medicine. Phospholipid-enhanced drug delivery systems are being explored for their potential in tailoring treatments to individual patient profiles, potentially revolutionizing therapeutic approaches across various diseases.
Despite the promising outlook, the market faces challenges such as high development costs, complex regulatory pathways, and manufacturing scalability issues. However, ongoing technological advancements and collaborations between pharmaceutical companies and drug delivery specialists are expected to address these challenges and drive further market growth.
Current Challenges in Phospholipid-Based DDS
Phospholipid-based drug delivery systems (DDS) have shown immense potential in enhancing therapeutic efficacy and reducing side effects of various drugs. However, several challenges persist in their development and application. One of the primary obstacles is the stability of phospholipid formulations. These systems are prone to physical and chemical degradation, which can significantly impact their shelf life and efficacy. Oxidation and hydrolysis of phospholipids can lead to the formation of lysolipids and free fatty acids, altering the structure and properties of the delivery system.
Another critical challenge is the control of drug release kinetics. While phospholipids offer excellent biocompatibility and can encapsulate a wide range of drugs, achieving precise control over the release profile remains difficult. Factors such as lipid composition, drug-lipid interactions, and environmental conditions can all influence the release rate, making it challenging to design systems with predictable and consistent drug delivery.
The scalability of phospholipid-based DDS production is also a significant hurdle. Many laboratory-scale preparation methods, such as thin-film hydration or ethanol injection, are not easily translatable to industrial-scale manufacturing. This gap between bench and production scales often results in inconsistencies in product quality and performance, hindering the commercialization of these promising delivery systems.
Furthermore, the complexity of biological barriers presents ongoing challenges for phospholipid-based DDS. While these systems can improve the solubility and bioavailability of drugs, they still face obstacles in overcoming physiological barriers such as the blood-brain barrier, mucosal surfaces, and cellular uptake mechanisms. Enhancing the targeting efficiency and tissue penetration of these delivery systems remains an active area of research.
The regulatory landscape for phospholipid-based DDS adds another layer of complexity. As novel formulations and applications emerge, regulatory agencies are continually adapting their guidelines. This evolving regulatory environment can lead to uncertainties in the approval process, potentially delaying the introduction of innovative phospholipid-based therapies to the market.
Lastly, the cost-effectiveness of phospholipid-based DDS remains a concern. While these systems offer numerous advantages, the expenses associated with their development, production, and quality control can be substantial. Balancing the enhanced therapeutic benefits with economic viability is crucial for the widespread adoption of these delivery systems in clinical practice.
Another critical challenge is the control of drug release kinetics. While phospholipids offer excellent biocompatibility and can encapsulate a wide range of drugs, achieving precise control over the release profile remains difficult. Factors such as lipid composition, drug-lipid interactions, and environmental conditions can all influence the release rate, making it challenging to design systems with predictable and consistent drug delivery.
The scalability of phospholipid-based DDS production is also a significant hurdle. Many laboratory-scale preparation methods, such as thin-film hydration or ethanol injection, are not easily translatable to industrial-scale manufacturing. This gap between bench and production scales often results in inconsistencies in product quality and performance, hindering the commercialization of these promising delivery systems.
Furthermore, the complexity of biological barriers presents ongoing challenges for phospholipid-based DDS. While these systems can improve the solubility and bioavailability of drugs, they still face obstacles in overcoming physiological barriers such as the blood-brain barrier, mucosal surfaces, and cellular uptake mechanisms. Enhancing the targeting efficiency and tissue penetration of these delivery systems remains an active area of research.
The regulatory landscape for phospholipid-based DDS adds another layer of complexity. As novel formulations and applications emerge, regulatory agencies are continually adapting their guidelines. This evolving regulatory environment can lead to uncertainties in the approval process, potentially delaying the introduction of innovative phospholipid-based therapies to the market.
Lastly, the cost-effectiveness of phospholipid-based DDS remains a concern. While these systems offer numerous advantages, the expenses associated with their development, production, and quality control can be substantial. Balancing the enhanced therapeutic benefits with economic viability is crucial for the widespread adoption of these delivery systems in clinical practice.
Existing Phospholipid-Based DDS Solutions
01 Liposomal drug delivery systems
Phospholipids are used to create liposomes, which are spherical vesicles that can encapsulate drugs. These liposomal systems enhance drug delivery by improving bioavailability, targeting specific tissues, and controlling drug release. The phospholipid bilayer structure of liposomes mimics cell membranes, allowing for better cellular uptake and reduced toxicity.- Liposomal drug delivery systems: Phospholipids are used to create liposomes, which are spherical vesicles that can encapsulate drugs. These liposomal systems enhance drug delivery by improving bioavailability, targeting specific tissues, and controlling drug release. The phospholipid bilayer structure of liposomes mimics cell membranes, allowing for better cellular uptake and reduced toxicity.
- Nanoparticle-based phospholipid formulations: Phospholipids are utilized in the development of nanoparticle-based drug delivery systems. These nanoformulations can improve drug solubility, stability, and targeted delivery. The small size of nanoparticles allows for enhanced penetration through biological barriers and increased cellular uptake, leading to improved therapeutic efficacy.
- Phospholipid-based gene delivery vectors: Phospholipids are employed in the design of gene delivery vectors, particularly for nucleic acid therapeutics. These systems can protect genetic material from degradation and facilitate its entry into target cells. The cationic nature of some phospholipid formulations allows for efficient complexation with negatively charged nucleic acids, enhancing transfection efficiency.
- Phospholipid-drug conjugates: Drugs are chemically conjugated to phospholipids to create novel delivery systems. These conjugates can alter the pharmacokinetics and biodistribution of drugs, potentially improving their therapeutic index. The phospholipid moiety can enhance drug solubility, membrane permeability, and targeting to specific tissues or cellular compartments.
- Phospholipid-based transdermal drug delivery: Phospholipids are utilized in transdermal drug delivery systems to enhance skin penetration and drug absorption. These formulations can include vesicular systems, microemulsions, or lipid-based nanocarriers that interact with the skin's lipid barrier. The use of phospholipids in transdermal delivery can improve drug bioavailability and provide sustained release profiles.
02 Nanoparticle-based phospholipid formulations
Phospholipids are utilized in the development of nanoparticle-based drug delivery systems. These nanoformulations can improve drug solubility, stability, and targeted delivery. The small size of nanoparticles allows for enhanced penetration through biological barriers and increased cellular uptake, leading to improved therapeutic efficacy.Expand Specific Solutions03 Phospholipid-based gene delivery vectors
Phospholipids are employed in the design of gene delivery vectors, particularly for nucleic acid therapeutics. These systems can protect genetic material from degradation and facilitate its entry into target cells. The cationic nature of some phospholipids allows for complexation with negatively charged nucleic acids, enhancing transfection efficiency.Expand Specific Solutions04 Phospholipid-drug conjugates
The development of phospholipid-drug conjugates involves covalently linking drugs to phospholipid molecules. This approach can enhance drug solubility, improve pharmacokinetics, and allow for targeted delivery. The conjugates can form self-assembling nanostructures or be incorporated into larger delivery systems for optimized therapeutic outcomes.Expand Specific Solutions05 Stimuli-responsive phospholipid delivery systems
Phospholipids are used to create stimuli-responsive drug delivery systems that can release their payload in response to specific environmental triggers such as pH, temperature, or enzymatic activity. These smart delivery systems allow for precise control over drug release at the target site, potentially reducing side effects and improving therapeutic efficacy.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Phospholipid-Based DDS Industry
The phospholipid influence on drug delivery systems market is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demand for targeted and controlled drug release technologies. The global market size is projected to expand significantly, fueled by advancements in nanotechnology and personalized medicine. Technologically, the field is rapidly evolving, with companies like NOF Corp., Taiwan Liposome Co., and Sapreme Technologies BV leading innovation in lipid-based formulations and nanoparticle delivery systems. Established pharmaceutical giants such as Novartis and Santen Pharmaceutical are also investing heavily in this area, indicating its growing importance. Academic institutions like Fudan University and research organizations like CNRS are contributing to fundamental research, further accelerating technological maturity in this field.
NOF Corp.
Technical Solution: NOF Corp. has established itself as a leading supplier of specialized phospholipids and lipid-based excipients for drug delivery applications. The company has developed a range of high-purity synthetic phospholipids, including PEGylated phospholipids, which are crucial components in many advanced drug delivery systems[13]. NOF's phospholipid products are widely used in the formulation of liposomes, lipid nanoparticles, and other lipid-based drug carriers. Their technology focuses on optimizing phospholipid structures to enhance drug encapsulation efficiency, improve stability, and control drug release kinetics[15]. NOF has also developed novel phospholipid conjugates that enable the creation of targeted drug delivery systems with improved pharmacokinetics and biodistribution profiles[17].
Strengths: Extensive expertise in phospholipid synthesis and modification, broad product portfolio, and strong partnerships with pharmaceutical companies. Weaknesses: Primarily focused on supplying materials rather than developing complete drug delivery systems.
Taiwan Liposome Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Taiwan Liposome Co., Ltd. has pioneered the development of proprietary NanoX platform technology, which utilizes specific phospholipid compositions to create stable and efficient drug delivery systems[2]. Their approach focuses on optimizing the lipid bilayer structure to enhance drug loading capacity and improve pharmacokinetics. The company has successfully applied this technology to develop a range of products, including long-acting injectables and targeted cancer therapies[4]. TLC's phospholipid-based formulations have demonstrated improved drug solubility, prolonged circulation time, and enhanced tissue penetration compared to conventional formulations[6].
Strengths: Specialized expertise in liposomal drug delivery, proprietary technology platform, and a growing portfolio of products in clinical development. Weaknesses: Limited global market presence compared to larger pharmaceutical companies.
Core Innovations in Phospholipid-DDS Integration
Drug Delivery System Containing Phospholipid and Cholesterol
PatentActiveUS20200289652A1
Innovation
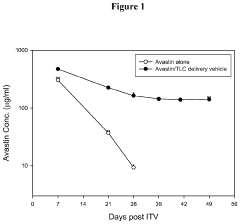
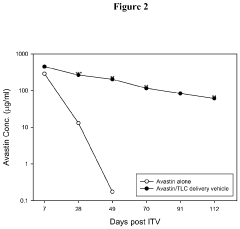
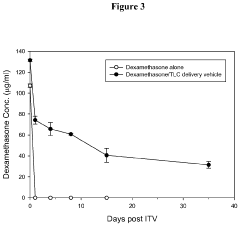
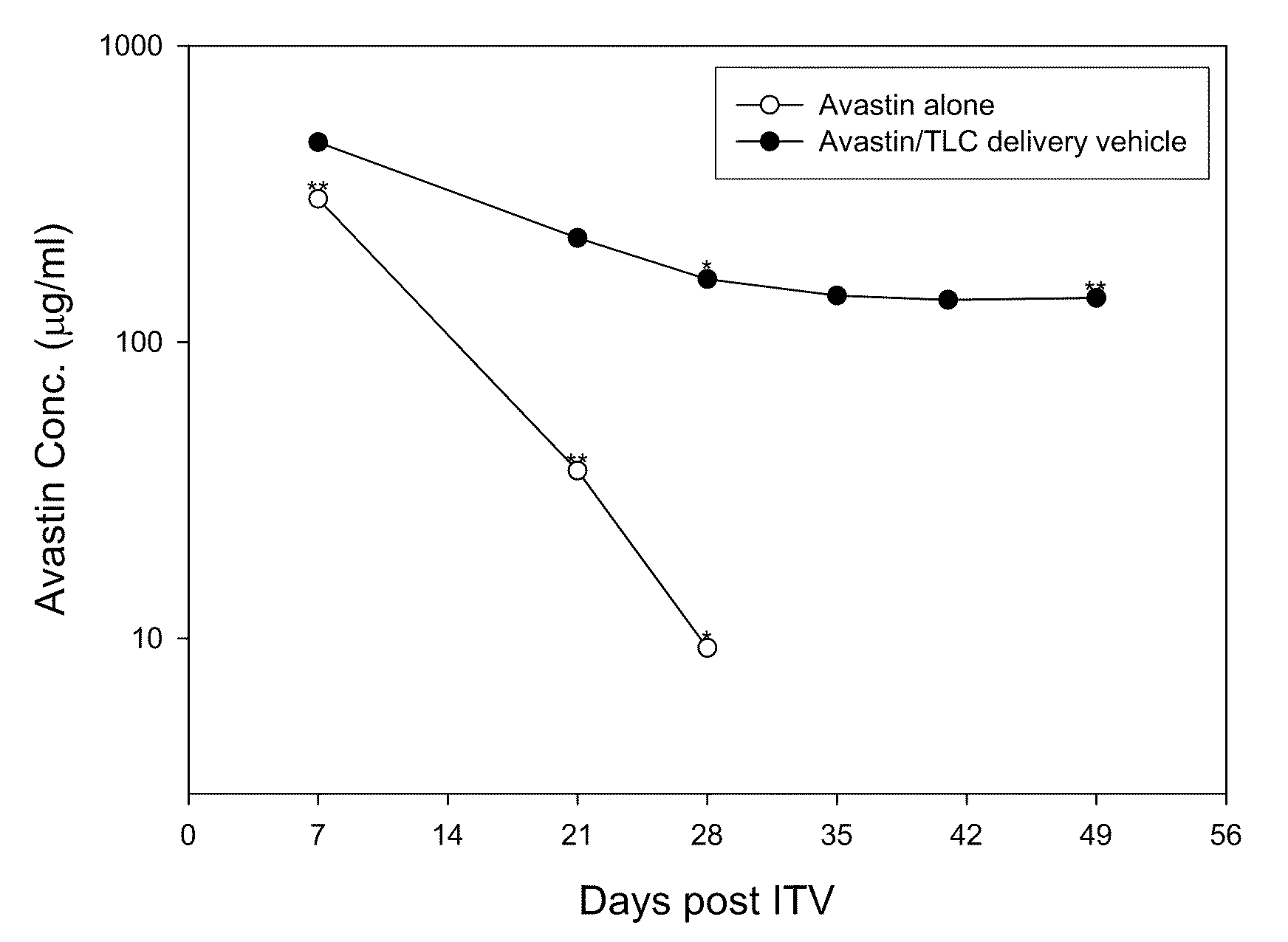
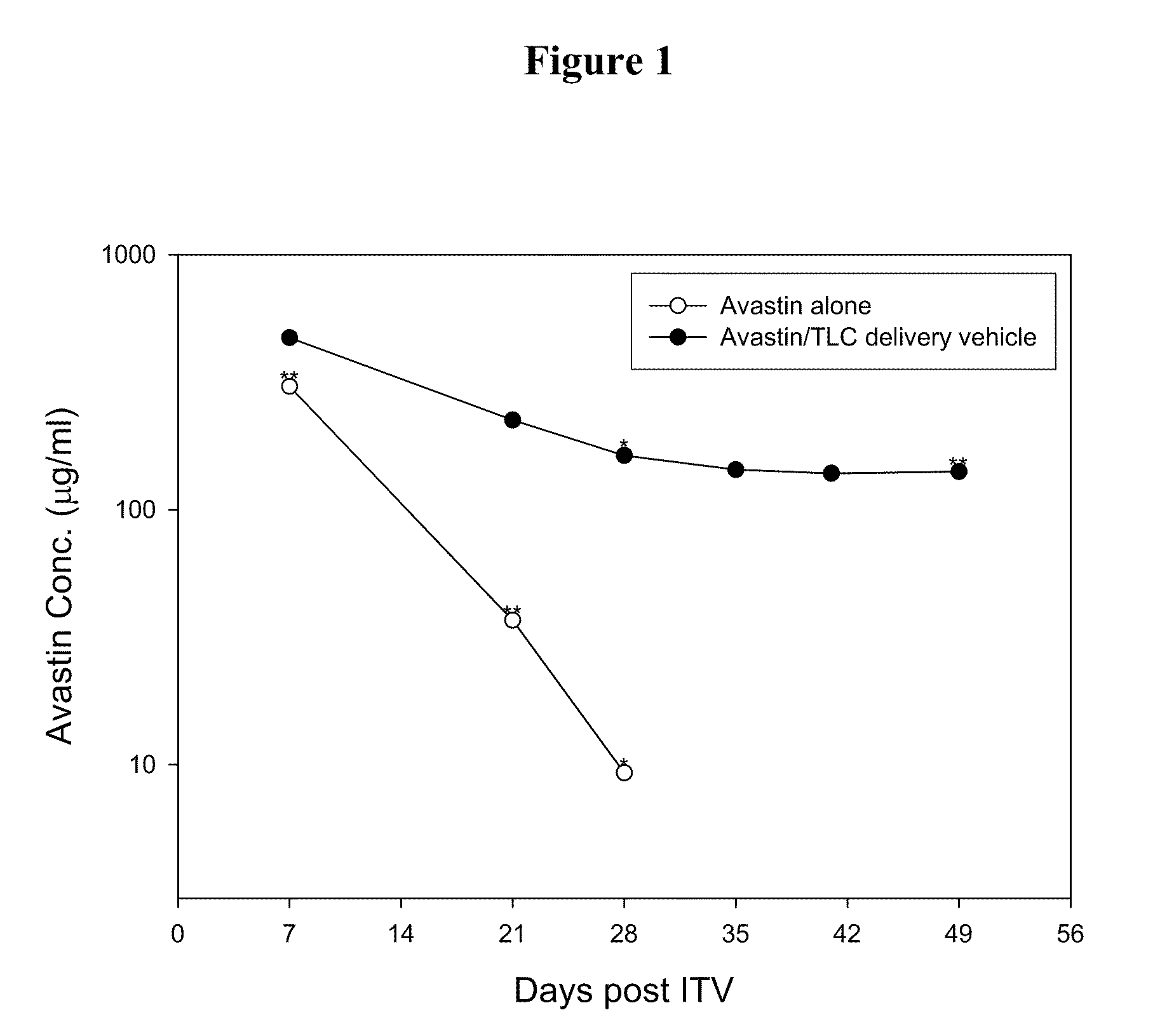
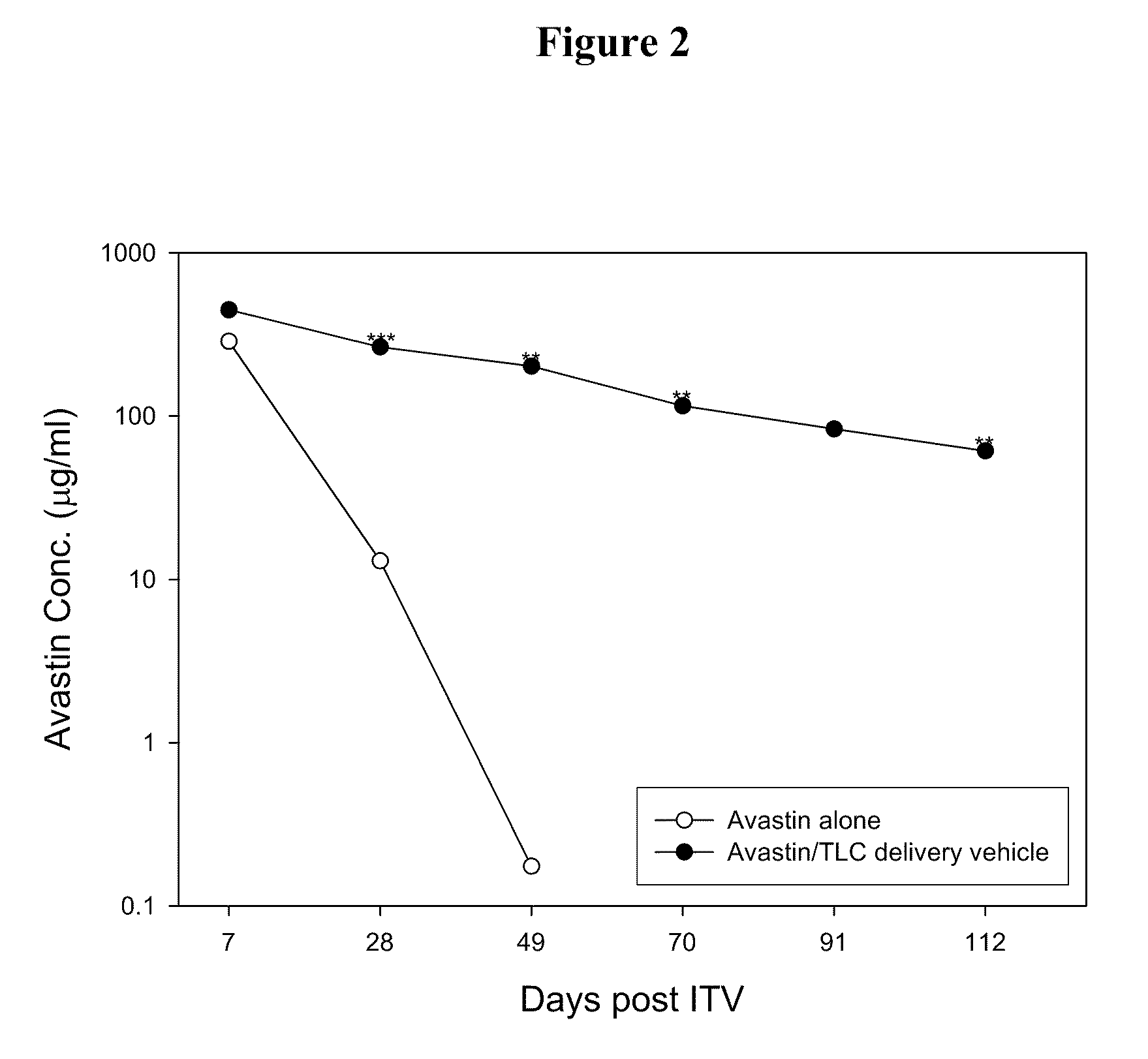
- A drug delivery system containing phospholipid and cholesterol, which prolongs the lifetime of therapeutic agents like Avastin in the eyes, allowing for reduced frequency of intravitreal injections by maintaining effective concentrations over a longer period.
Ophthalmic Drug Delivery System Containing Phospholipid and Cholesterol
PatentActiveUS20110033468A1
Innovation
- A drug delivery system containing phospholipid and cholesterol, which prolongs the lifetime of therapeutic agents like Avastin in the eyes, allowing for reduced frequency of intravitreal injections by maintaining effective concentrations through a combination of phospholipids such as DOPC, DOPG, and cholesterol, with the therapeutic agent in a non-associated form.
Regulatory Landscape for Phospholipid-Based DDS
The regulatory landscape for phospholipid-based drug delivery systems (DDS) is complex and evolving, reflecting the increasing importance of these systems in pharmaceutical development. Regulatory agencies worldwide, including the FDA in the United States and the EMA in Europe, have established specific guidelines and requirements for the development, manufacturing, and approval of phospholipid-based DDS.
In the United States, the FDA has implemented a comprehensive regulatory framework for liposomal drug products, which are a prominent example of phospholipid-based DDS. This framework includes guidance on the characterization of liposomal drug products, stability testing, and bioequivalence studies for generic versions. The agency emphasizes the importance of understanding the critical quality attributes of these systems and their impact on drug performance.
European regulators have also developed specific guidelines for liposomal products, focusing on quality, safety, and efficacy aspects. The EMA's "Reflection paper on the data requirements for intravenous liposomal products developed with reference to an innovator liposomal product" provides detailed recommendations for the development of generic liposomal formulations.
Regulatory bodies in other regions, such as Japan's PMDA and China's NMPA, have also recognized the unique characteristics of phospholipid-based DDS and are developing tailored regulatory approaches. These agencies often collaborate with their international counterparts to harmonize regulatory standards and facilitate global drug development.
A key regulatory consideration for phospholipid-based DDS is the classification of the delivery system itself. Depending on the jurisdiction, these systems may be classified as drug-device combinations, nanomedicines, or complex drug products. This classification can significantly impact the regulatory pathway and requirements for approval.
Manufacturing and quality control of phospholipid-based DDS are subject to stringent regulatory oversight. Regulatory agencies require robust analytical methods for characterizing the physicochemical properties of these systems, including particle size distribution, drug encapsulation efficiency, and lipid composition. Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) guidelines specific to liposomal and other phospholipid-based formulations have been developed to ensure consistent product quality.
As the field of phospholipid-based DDS continues to advance, regulatory agencies are adapting their approaches to keep pace with technological innovations. This includes the development of new guidance documents, the establishment of expert working groups, and increased collaboration with academic and industry stakeholders to address emerging regulatory challenges.
In the United States, the FDA has implemented a comprehensive regulatory framework for liposomal drug products, which are a prominent example of phospholipid-based DDS. This framework includes guidance on the characterization of liposomal drug products, stability testing, and bioequivalence studies for generic versions. The agency emphasizes the importance of understanding the critical quality attributes of these systems and their impact on drug performance.
European regulators have also developed specific guidelines for liposomal products, focusing on quality, safety, and efficacy aspects. The EMA's "Reflection paper on the data requirements for intravenous liposomal products developed with reference to an innovator liposomal product" provides detailed recommendations for the development of generic liposomal formulations.
Regulatory bodies in other regions, such as Japan's PMDA and China's NMPA, have also recognized the unique characteristics of phospholipid-based DDS and are developing tailored regulatory approaches. These agencies often collaborate with their international counterparts to harmonize regulatory standards and facilitate global drug development.
A key regulatory consideration for phospholipid-based DDS is the classification of the delivery system itself. Depending on the jurisdiction, these systems may be classified as drug-device combinations, nanomedicines, or complex drug products. This classification can significantly impact the regulatory pathway and requirements for approval.
Manufacturing and quality control of phospholipid-based DDS are subject to stringent regulatory oversight. Regulatory agencies require robust analytical methods for characterizing the physicochemical properties of these systems, including particle size distribution, drug encapsulation efficiency, and lipid composition. Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) guidelines specific to liposomal and other phospholipid-based formulations have been developed to ensure consistent product quality.
As the field of phospholipid-based DDS continues to advance, regulatory agencies are adapting their approaches to keep pace with technological innovations. This includes the development of new guidance documents, the establishment of expert working groups, and increased collaboration with academic and industry stakeholders to address emerging regulatory challenges.
Biocompatibility and Safety Considerations
Biocompatibility and safety considerations are paramount in the development of phospholipid-based drug delivery systems. These systems, while offering numerous advantages in drug delivery, must be thoroughly evaluated for their potential interactions with biological systems to ensure patient safety and efficacy.
Phospholipids, being naturally occurring components of cell membranes, generally exhibit good biocompatibility. However, their incorporation into drug delivery systems can alter their behavior and interactions with biological tissues. It is crucial to assess the potential for immune responses, inflammation, or toxicity that may arise from these modified structures.
One key aspect of biocompatibility is the interaction between phospholipid-based delivery systems and blood components. These systems must be designed to minimize unwanted interactions with proteins, platelets, and other blood cells to prevent thrombosis or hemolysis. Additionally, the potential for complement activation, which could lead to hypersensitivity reactions, must be carefully evaluated.
The biodegradability of phospholipid-based systems is another important safety consideration. While phospholipids are generally biodegradable, the rate and products of degradation must be thoroughly investigated to ensure they do not accumulate in tissues or organs, potentially causing long-term toxicity.
The stability of phospholipid-based drug delivery systems in physiological conditions is crucial for both safety and efficacy. Premature degradation or structural changes could lead to uncontrolled drug release, potentially causing toxicity or reducing therapeutic efficacy. Conversely, excessive stability might impair drug release or lead to accumulation of the delivery system in the body.
Potential interactions between phospholipids and the encapsulated drugs must also be considered. Some drugs may alter the structure or properties of the phospholipid system, potentially affecting its safety profile or drug release characteristics. Conversely, phospholipids might influence drug stability or activity, necessitating comprehensive compatibility studies.
Long-term safety studies are essential to identify any potential chronic toxicity or cumulative effects of repeated administration of phospholipid-based drug delivery systems. This includes evaluating their potential impact on organ function, metabolism, and the potential for carcinogenicity or teratogenicity.
Regulatory considerations play a significant role in the development of phospholipid-based drug delivery systems. Adherence to guidelines set by regulatory bodies such as the FDA and EMA is crucial for ensuring the safety and efficacy of these systems. This includes conducting appropriate preclinical and clinical studies to demonstrate their safety profile.
In conclusion, while phospholipid-based drug delivery systems offer promising advantages, their development must be guided by rigorous biocompatibility and safety assessments. These considerations are integral to the successful translation of these systems from laboratory research to clinical applications, ensuring both patient safety and therapeutic efficacy.
Phospholipids, being naturally occurring components of cell membranes, generally exhibit good biocompatibility. However, their incorporation into drug delivery systems can alter their behavior and interactions with biological tissues. It is crucial to assess the potential for immune responses, inflammation, or toxicity that may arise from these modified structures.
One key aspect of biocompatibility is the interaction between phospholipid-based delivery systems and blood components. These systems must be designed to minimize unwanted interactions with proteins, platelets, and other blood cells to prevent thrombosis or hemolysis. Additionally, the potential for complement activation, which could lead to hypersensitivity reactions, must be carefully evaluated.
The biodegradability of phospholipid-based systems is another important safety consideration. While phospholipids are generally biodegradable, the rate and products of degradation must be thoroughly investigated to ensure they do not accumulate in tissues or organs, potentially causing long-term toxicity.
The stability of phospholipid-based drug delivery systems in physiological conditions is crucial for both safety and efficacy. Premature degradation or structural changes could lead to uncontrolled drug release, potentially causing toxicity or reducing therapeutic efficacy. Conversely, excessive stability might impair drug release or lead to accumulation of the delivery system in the body.
Potential interactions between phospholipids and the encapsulated drugs must also be considered. Some drugs may alter the structure or properties of the phospholipid system, potentially affecting its safety profile or drug release characteristics. Conversely, phospholipids might influence drug stability or activity, necessitating comprehensive compatibility studies.
Long-term safety studies are essential to identify any potential chronic toxicity or cumulative effects of repeated administration of phospholipid-based drug delivery systems. This includes evaluating their potential impact on organ function, metabolism, and the potential for carcinogenicity or teratogenicity.
Regulatory considerations play a significant role in the development of phospholipid-based drug delivery systems. Adherence to guidelines set by regulatory bodies such as the FDA and EMA is crucial for ensuring the safety and efficacy of these systems. This includes conducting appropriate preclinical and clinical studies to demonstrate their safety profile.
In conclusion, while phospholipid-based drug delivery systems offer promising advantages, their development must be guided by rigorous biocompatibility and safety assessments. These considerations are integral to the successful translation of these systems from laboratory research to clinical applications, ensuring both patient safety and therapeutic efficacy.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!