PMMA's Influence on Touch-Sensitive Technology
AUG 7, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
PMMA in Touch Tech: Background and Objectives
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), commonly known as acrylic or plexiglass, has emerged as a crucial material in the development of touch-sensitive technology. The evolution of PMMA's role in this field can be traced back to the early 2000s when touchscreens began to gain prominence in consumer electronics. Initially, PMMA was primarily used as a protective cover for display screens, but its potential for enhancing touch sensitivity was soon recognized.
The journey of PMMA in touch technology has been marked by continuous improvements in its optical and mechanical properties. As touchscreens became more prevalent in smartphones, tablets, and other devices, the demand for materials that could provide both durability and responsiveness increased. PMMA's unique combination of transparency, scratch resistance, and flexibility made it an ideal candidate for touch-sensitive applications.
Over the years, researchers and engineers have focused on modifying PMMA to enhance its touch-sensitive properties. This has involved exploring various formulations and manufacturing techniques to improve its conductivity, reduce optical interference, and increase its overall performance in touch-based interfaces. The goal has been to create PMMA variants that can offer superior touch sensitivity while maintaining the material's inherent advantages.
One of the key objectives in the development of PMMA for touch-sensitive technology has been to improve its compatibility with different sensing mechanisms. This includes capacitive sensing, which is widely used in modern touchscreens, as well as emerging technologies like force-sensitive touch and multi-touch capabilities. Researchers have been working on creating PMMA composites that can effectively transmit electrical signals while maintaining optical clarity.
Another important aspect of PMMA's evolution in touch technology has been the focus on enhancing its durability and longevity. As touch-sensitive devices became more ubiquitous and subjected to frequent use, the need for materials that could withstand repeated interactions without degradation became paramount. This led to the development of PMMA formulations with improved scratch resistance, impact strength, and chemical resistance.
The current technological landscape presents both challenges and opportunities for PMMA in touch-sensitive applications. The ongoing trend towards flexible and foldable displays has pushed researchers to explore new ways of incorporating PMMA into these advanced form factors. Additionally, the growing interest in sustainable and eco-friendly materials has prompted investigations into bio-based alternatives to traditional PMMA formulations.
Looking ahead, the objectives for PMMA in touch technology are centered around further enhancing its performance, expanding its applicability, and addressing emerging market needs. This includes developing ultra-thin PMMA films for next-generation touchscreens, improving its compatibility with various sensing technologies, and exploring novel surface treatments to enhance touch sensitivity and user experience.
The journey of PMMA in touch technology has been marked by continuous improvements in its optical and mechanical properties. As touchscreens became more prevalent in smartphones, tablets, and other devices, the demand for materials that could provide both durability and responsiveness increased. PMMA's unique combination of transparency, scratch resistance, and flexibility made it an ideal candidate for touch-sensitive applications.
Over the years, researchers and engineers have focused on modifying PMMA to enhance its touch-sensitive properties. This has involved exploring various formulations and manufacturing techniques to improve its conductivity, reduce optical interference, and increase its overall performance in touch-based interfaces. The goal has been to create PMMA variants that can offer superior touch sensitivity while maintaining the material's inherent advantages.
One of the key objectives in the development of PMMA for touch-sensitive technology has been to improve its compatibility with different sensing mechanisms. This includes capacitive sensing, which is widely used in modern touchscreens, as well as emerging technologies like force-sensitive touch and multi-touch capabilities. Researchers have been working on creating PMMA composites that can effectively transmit electrical signals while maintaining optical clarity.
Another important aspect of PMMA's evolution in touch technology has been the focus on enhancing its durability and longevity. As touch-sensitive devices became more ubiquitous and subjected to frequent use, the need for materials that could withstand repeated interactions without degradation became paramount. This led to the development of PMMA formulations with improved scratch resistance, impact strength, and chemical resistance.
The current technological landscape presents both challenges and opportunities for PMMA in touch-sensitive applications. The ongoing trend towards flexible and foldable displays has pushed researchers to explore new ways of incorporating PMMA into these advanced form factors. Additionally, the growing interest in sustainable and eco-friendly materials has prompted investigations into bio-based alternatives to traditional PMMA formulations.
Looking ahead, the objectives for PMMA in touch technology are centered around further enhancing its performance, expanding its applicability, and addressing emerging market needs. This includes developing ultra-thin PMMA films for next-generation touchscreens, improving its compatibility with various sensing technologies, and exploring novel surface treatments to enhance touch sensitivity and user experience.
Market Analysis for PMMA-Enhanced Touch Devices
The market for PMMA-enhanced touch devices has shown significant growth in recent years, driven by the increasing demand for durable and responsive touch-sensitive technology across various industries. PMMA (Polymethyl methacrylate), also known as acrylic glass, has emerged as a key material in enhancing the performance and longevity of touch-sensitive devices.
The global touch screen market, which heavily relies on PMMA technology, was valued at $70.2 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $139.7 billion by 2028, growing at a CAGR of 8.6% during the forecast period. This growth is primarily attributed to the widespread adoption of touch-enabled devices in consumer electronics, automotive, healthcare, and retail sectors.
In the consumer electronics segment, PMMA-enhanced touch devices have gained substantial traction, particularly in smartphones, tablets, and laptops. The material's optical clarity, scratch resistance, and durability have made it a preferred choice for manufacturers looking to improve the user experience and device longevity. The smartphone market alone accounts for over 40% of the touch screen market share, with PMMA playing a crucial role in screen protection and touch sensitivity.
The automotive industry has also witnessed a surge in demand for PMMA-enhanced touch devices, driven by the increasing integration of infotainment systems and digital dashboards in modern vehicles. The automotive touch screen market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 11.5% from 2021 to 2026, with PMMA-based solutions at the forefront of this expansion.
In the healthcare sector, PMMA-enhanced touch devices have found applications in medical equipment, patient monitoring systems, and diagnostic tools. The material's antimicrobial properties and ease of sterilization make it particularly suitable for healthcare environments. The medical touch screen market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 7.8% from 2021 to 2028, with PMMA-based solutions playing a significant role in this growth.
The retail and hospitality industries have also embraced PMMA-enhanced touch devices for point-of-sale systems, self-service kiosks, and interactive displays. These sectors value PMMA's durability and resistance to wear, which is crucial for high-traffic environments. The market for touch-based kiosks is expected to grow at a CAGR of 9.5% from 2021 to 2026, with PMMA-enhanced solutions contributing significantly to this expansion.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific dominates the PMMA-enhanced touch device market, accounting for over 40% of the global market share. This is primarily due to the presence of major electronics manufacturers in countries like China, Japan, and South Korea. North America and Europe follow closely, driven by technological advancements and increasing adoption in automotive and healthcare sectors.
The global touch screen market, which heavily relies on PMMA technology, was valued at $70.2 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $139.7 billion by 2028, growing at a CAGR of 8.6% during the forecast period. This growth is primarily attributed to the widespread adoption of touch-enabled devices in consumer electronics, automotive, healthcare, and retail sectors.
In the consumer electronics segment, PMMA-enhanced touch devices have gained substantial traction, particularly in smartphones, tablets, and laptops. The material's optical clarity, scratch resistance, and durability have made it a preferred choice for manufacturers looking to improve the user experience and device longevity. The smartphone market alone accounts for over 40% of the touch screen market share, with PMMA playing a crucial role in screen protection and touch sensitivity.
The automotive industry has also witnessed a surge in demand for PMMA-enhanced touch devices, driven by the increasing integration of infotainment systems and digital dashboards in modern vehicles. The automotive touch screen market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 11.5% from 2021 to 2026, with PMMA-based solutions at the forefront of this expansion.
In the healthcare sector, PMMA-enhanced touch devices have found applications in medical equipment, patient monitoring systems, and diagnostic tools. The material's antimicrobial properties and ease of sterilization make it particularly suitable for healthcare environments. The medical touch screen market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 7.8% from 2021 to 2028, with PMMA-based solutions playing a significant role in this growth.
The retail and hospitality industries have also embraced PMMA-enhanced touch devices for point-of-sale systems, self-service kiosks, and interactive displays. These sectors value PMMA's durability and resistance to wear, which is crucial for high-traffic environments. The market for touch-based kiosks is expected to grow at a CAGR of 9.5% from 2021 to 2026, with PMMA-enhanced solutions contributing significantly to this expansion.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific dominates the PMMA-enhanced touch device market, accounting for over 40% of the global market share. This is primarily due to the presence of major electronics manufacturers in countries like China, Japan, and South Korea. North America and Europe follow closely, driven by technological advancements and increasing adoption in automotive and healthcare sectors.
PMMA Integration Challenges in Touch Sensors
The integration of PMMA (Polymethyl Methacrylate) into touch-sensitive technology presents several significant challenges that require careful consideration and innovative solutions. One of the primary obstacles is the material's inherent electrical insulation properties, which can interfere with the capacitive sensing mechanisms commonly used in touch screens. This necessitates the development of specialized conductive coatings or additives that can be seamlessly incorporated into PMMA without compromising its optical clarity or mechanical strength.
Another challenge lies in the thermal expansion characteristics of PMMA. Touch sensors often operate in environments with varying temperatures, and the differential expansion between PMMA and other components in the touch system can lead to stress, deformation, or even delamination of layers. Engineers must devise strategies to mitigate these thermal effects, such as implementing flexible bonding techniques or incorporating expansion joints in the sensor design.
The surface properties of PMMA also pose integration difficulties. While PMMA offers excellent optical transparency, its surface can be prone to scratching and wear over time, potentially degrading touch sensitivity and visual quality. Developing durable, scratch-resistant coatings that maintain the material's transparency and do not interfere with touch functionality is a critical area of research.
Manufacturing processes present additional hurdles. PMMA's relatively low heat resistance compared to other materials used in touch sensors can limit the range of assembly and bonding techniques available. This constraint requires the development of low-temperature processing methods or the use of specialized adhesives that can effectively bond PMMA to other sensor components without causing thermal damage or distortion.
Furthermore, the integration of PMMA into flexible or curved touch sensors introduces complexities in terms of maintaining uniform sensitivity and preventing optical distortions. Researchers must explore methods to create thin, flexible PMMA films or develop composite materials that combine PMMA's desirable optical properties with the necessary flexibility for curved displays.
Lastly, the long-term stability and reliability of PMMA in touch sensor applications remain areas of concern. Environmental factors such as UV exposure, humidity, and chemical interactions can potentially degrade PMMA over time, affecting both its optical and mechanical properties. Developing effective protective measures and conducting extensive durability testing are essential steps in addressing these long-term performance issues.
Another challenge lies in the thermal expansion characteristics of PMMA. Touch sensors often operate in environments with varying temperatures, and the differential expansion between PMMA and other components in the touch system can lead to stress, deformation, or even delamination of layers. Engineers must devise strategies to mitigate these thermal effects, such as implementing flexible bonding techniques or incorporating expansion joints in the sensor design.
The surface properties of PMMA also pose integration difficulties. While PMMA offers excellent optical transparency, its surface can be prone to scratching and wear over time, potentially degrading touch sensitivity and visual quality. Developing durable, scratch-resistant coatings that maintain the material's transparency and do not interfere with touch functionality is a critical area of research.
Manufacturing processes present additional hurdles. PMMA's relatively low heat resistance compared to other materials used in touch sensors can limit the range of assembly and bonding techniques available. This constraint requires the development of low-temperature processing methods or the use of specialized adhesives that can effectively bond PMMA to other sensor components without causing thermal damage or distortion.
Furthermore, the integration of PMMA into flexible or curved touch sensors introduces complexities in terms of maintaining uniform sensitivity and preventing optical distortions. Researchers must explore methods to create thin, flexible PMMA films or develop composite materials that combine PMMA's desirable optical properties with the necessary flexibility for curved displays.
Lastly, the long-term stability and reliability of PMMA in touch sensor applications remain areas of concern. Environmental factors such as UV exposure, humidity, and chemical interactions can potentially degrade PMMA over time, affecting both its optical and mechanical properties. Developing effective protective measures and conducting extensive durability testing are essential steps in addressing these long-term performance issues.
Current PMMA-Based Touch Solutions
01 PMMA-based touch-sensitive materials
PMMA is used as a base material for touch-sensitive applications due to its optical clarity and durability. It can be modified or combined with other materials to enhance its touch sensitivity, making it suitable for various touch screen and sensor applications.- PMMA-based touch-sensitive materials: PMMA is used as a base material for touch-sensitive applications due to its optical clarity and durability. It can be modified or combined with other materials to enhance touch sensitivity, making it suitable for various touch screen and sensor applications.
- Surface treatment techniques for PMMA touch sensitivity: Various surface treatment methods are applied to PMMA to improve its touch sensitivity. These techniques may include plasma treatment, chemical etching, or coating with conductive materials to enhance the material's responsiveness to touch inputs.
- PMMA composites for enhanced touch sensitivity: PMMA is combined with other materials such as conductive polymers or nanoparticles to create composites with improved touch sensitivity. These composites maintain the optical properties of PMMA while enhancing its electrical conductivity and touch responsiveness.
- PMMA-based flexible touch sensors: Flexible touch sensors incorporating PMMA are developed for applications in wearable devices and curved displays. These sensors combine the optical clarity of PMMA with flexibility and touch sensitivity, enabling new form factors for touch-enabled devices.
- Integration of PMMA in multi-layer touch structures: PMMA is used as a key component in multi-layer touch structures, often serving as a protective or optical layer. These structures combine different materials and technologies to achieve optimal touch sensitivity, durability, and optical performance in touch screen devices.
02 Surface treatment techniques for PMMA touch sensitivity
Various surface treatment methods are applied to PMMA to improve its touch sensitivity. These may include coating with conductive materials, etching, or applying specific patterns to enhance touch responsiveness while maintaining optical properties.Expand Specific Solutions03 Integration of PMMA in multi-layer touch-sensitive structures
PMMA is often used in multi-layer structures for touch-sensitive devices. It can serve as a protective outer layer, a substrate for conductive layers, or an intermediate layer in complex touch screen assemblies, contributing to both functionality and durability.Expand Specific Solutions04 PMMA composites for enhanced touch sensitivity
Researchers have developed PMMA-based composites by incorporating various additives or nanoparticles. These composites aim to improve touch sensitivity, durability, and other desirable properties while maintaining the optical clarity of PMMA.Expand Specific Solutions05 Manufacturing processes for PMMA touch-sensitive components
Specialized manufacturing processes have been developed for producing PMMA-based touch-sensitive components. These may include injection molding, extrusion, or other techniques optimized to maintain optical quality and enhance touch sensitivity in the final product.Expand Specific Solutions
Key PMMA and Touch Tech Industry Players
The PMMA touch-sensitive technology market is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demand for advanced user interfaces in consumer electronics and automotive applications. The global market size is projected to reach several billion dollars by 2025, with a compound annual growth rate of over 10%. Technologically, PMMA-based touch sensors are maturing but still have room for innovation in areas like flexibility, durability, and optical performance. Key players like DuPont, Kingfa, and Truly Opto-Electronics are investing heavily in R&D to improve PMMA formulations and manufacturing processes. Emerging companies such as Cambridge Mechatronics and Nanchang O-Film are also contributing novel approaches, intensifying competition in this dynamic field.
DuPont de Nemours, Inc.
Technical Solution: DuPont has developed advanced PMMA formulations specifically tailored for touch-sensitive technology applications. Their proprietary PMMA blends offer enhanced optical clarity and durability, crucial for touchscreen devices. DuPont's PMMA solutions incorporate nano-additives that improve scratch resistance and reduce glare, addressing key challenges in touch-sensitive displays[1]. The company has also introduced PMMA variants with improved impact resistance, making them suitable for rugged touch-enabled devices used in industrial settings[2]. DuPont's research focuses on optimizing PMMA's light transmission properties, achieving up to 92% light transmittance in the visible spectrum, which is essential for vibrant and responsive touchscreens[3].
Strengths: Industry-leading optical clarity and durability, advanced nano-additive technology, and tailored solutions for various touch-sensitive applications. Weaknesses: Potentially higher cost compared to standard PMMA formulations, and limited flexibility in extreme temperature conditions.
Truly Opto-Electronics (Shanwei) Ltd.
Technical Solution: Truly Opto-Electronics has developed a unique PMMA-based optical film technology for touch-sensitive displays. Their approach involves creating ultra-thin PMMA layers with precisely controlled refractive indices, enabling enhanced touch sensitivity and reduced parallax error in touchscreens[4]. The company's PMMA films incorporate conductive nanoparticles, allowing for the creation of transparent, flexible touch sensors that can be integrated into curved displays[5]. Truly Opto-Electronics has also pioneered a PMMA coating process that significantly reduces surface reflections, improving outdoor readability of touch devices by up to 40% compared to standard anti-glare treatments[6].
Strengths: Innovative PMMA-based optical films, expertise in flexible touch sensors, and advanced anti-reflection technology. Weaknesses: Potential scalability challenges for mass production, and higher production costs for specialized PMMA formulations.
PMMA Innovations for Touch Sensitivity
Sensitive ELISA for disease diagnosis on surface modified poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA) microfluidic microplates
PatentActiveUS11014088B2
Innovation
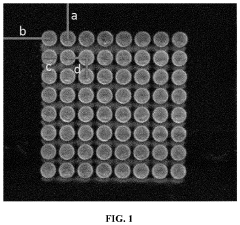
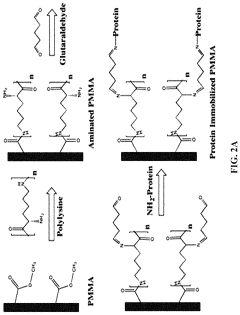
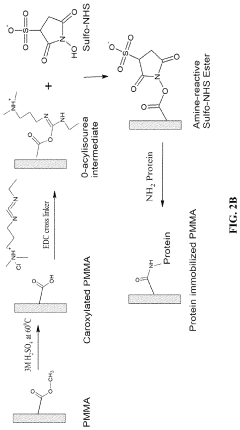
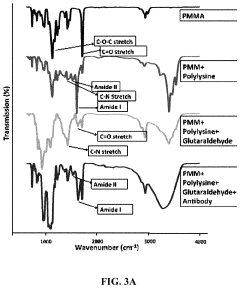
- A poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA) microfluidic microplate with a surface modified using poly-lysine or carboxylation for covalent binding of proteins, allowing for rapid and ultrasensitive detection of disease biomarkers with reduced reagent consumption and no need for expensive equipment, achieving detection limits 10-fold more sensitive than commercial ELISA kits.
Method for producing an impact-resistant polymethylmethacrylate, and corresponding polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA)
PatentInactiveEP1470169A1
Innovation
- A process involving dissolving impact modifiers in methyl methacrylate (MMA) or polymerized MMA, followed by polymerization in a chamber, using a formulation with stabilizers and additives, to produce a cast plastic molding with enhanced impact strength without interpenetrating networks or complicated isolation steps.
Environmental Impact of PMMA in Touch Devices
The environmental impact of PMMA (Polymethyl methacrylate) in touch devices is a crucial consideration as the technology becomes increasingly prevalent in consumer electronics. PMMA, commonly known as acrylic or plexiglass, is widely used in touch-sensitive displays due to its optical clarity, durability, and cost-effectiveness.
One of the primary environmental concerns associated with PMMA in touch devices is its production process. The manufacturing of PMMA involves the polymerization of methyl methacrylate, which requires significant energy input and can result in the emission of volatile organic compounds (VOCs). These emissions contribute to air pollution and can have adverse effects on both human health and the environment.
Additionally, the disposal of PMMA-containing touch devices presents challenges. While PMMA is theoretically recyclable, the complex nature of modern touch screens, which often incorporate multiple layers and materials, makes recycling difficult and energy-intensive. As a result, many touch devices end up in landfills, where PMMA can take hundreds of years to decompose.
The use of PMMA in touch devices also raises concerns about resource depletion. The production of PMMA relies on petroleum-based raw materials, contributing to the consumption of non-renewable resources. As the demand for touch-sensitive technology grows, so does the pressure on these finite resources.
However, it's important to note that PMMA offers some environmental benefits compared to alternative materials. Its durability and resistance to scratching and impact mean that devices using PMMA screens may have longer lifespans, potentially reducing electronic waste. Furthermore, PMMA's lightweight nature can contribute to reduced energy consumption in transportation and device operation.
Efforts are being made to mitigate the environmental impact of PMMA in touch devices. Research is ongoing into bio-based alternatives that could reduce reliance on petroleum-derived materials. Additionally, advancements in recycling technologies are being developed to better handle the complex composition of modern touch screens.
The industry is also exploring ways to improve the energy efficiency of PMMA production and to reduce VOC emissions during manufacturing. Some companies are implementing closed-loop production systems to minimize waste and maximize resource utilization.
As consumer awareness of environmental issues grows, there is increasing pressure on manufacturers to consider the entire lifecycle of their products, including the environmental impact of materials like PMMA. This has led to initiatives focused on eco-design principles, which aim to create touch devices that are more easily recyclable and have a reduced environmental footprint.
One of the primary environmental concerns associated with PMMA in touch devices is its production process. The manufacturing of PMMA involves the polymerization of methyl methacrylate, which requires significant energy input and can result in the emission of volatile organic compounds (VOCs). These emissions contribute to air pollution and can have adverse effects on both human health and the environment.
Additionally, the disposal of PMMA-containing touch devices presents challenges. While PMMA is theoretically recyclable, the complex nature of modern touch screens, which often incorporate multiple layers and materials, makes recycling difficult and energy-intensive. As a result, many touch devices end up in landfills, where PMMA can take hundreds of years to decompose.
The use of PMMA in touch devices also raises concerns about resource depletion. The production of PMMA relies on petroleum-based raw materials, contributing to the consumption of non-renewable resources. As the demand for touch-sensitive technology grows, so does the pressure on these finite resources.
However, it's important to note that PMMA offers some environmental benefits compared to alternative materials. Its durability and resistance to scratching and impact mean that devices using PMMA screens may have longer lifespans, potentially reducing electronic waste. Furthermore, PMMA's lightweight nature can contribute to reduced energy consumption in transportation and device operation.
Efforts are being made to mitigate the environmental impact of PMMA in touch devices. Research is ongoing into bio-based alternatives that could reduce reliance on petroleum-derived materials. Additionally, advancements in recycling technologies are being developed to better handle the complex composition of modern touch screens.
The industry is also exploring ways to improve the energy efficiency of PMMA production and to reduce VOC emissions during manufacturing. Some companies are implementing closed-loop production systems to minimize waste and maximize resource utilization.
As consumer awareness of environmental issues grows, there is increasing pressure on manufacturers to consider the entire lifecycle of their products, including the environmental impact of materials like PMMA. This has led to initiatives focused on eco-design principles, which aim to create touch devices that are more easily recyclable and have a reduced environmental footprint.
PMMA Touch Tech Manufacturing Processes
The manufacturing processes for PMMA-based touch-sensitive technology involve several key steps that ensure the production of high-quality, responsive touch screens. The process begins with the preparation of PMMA (Polymethyl methacrylate) sheets, which are typically manufactured through extrusion or casting methods. These sheets are then cut to the desired size and shape for the specific touch screen application.
One of the critical stages in the manufacturing process is the application of conductive coatings to the PMMA surface. This is often achieved through techniques such as sputtering or vapor deposition, where a thin layer of conductive material, such as indium tin oxide (ITO), is applied to the PMMA substrate. The precision of this step is crucial for ensuring uniform conductivity across the entire surface of the touch screen.
Following the conductive coating application, a patterning process is employed to create the touch-sensitive grid or matrix. This is typically accomplished using photolithography techniques, where a photoresist is applied to the coated PMMA surface, exposed to UV light through a mask, and then developed to create the desired electrode pattern. Etching processes are then used to remove the excess conductive material, leaving behind the precise touch-sensitive circuitry.
The next phase involves the integration of the touch sensor components. This includes attaching the controller chips, connecting the electrodes to the circuitry, and implementing any necessary shielding to prevent electromagnetic interference. The assembly process must be carried out in a clean environment to avoid contamination that could affect the performance of the touch screen.
To enhance the durability and functionality of the PMMA touch screen, additional layers may be applied. These can include anti-glare coatings, scratch-resistant layers, and oleophobic treatments to reduce fingerprint smudges. The application of these layers requires precise control over temperature, humidity, and curing conditions to ensure proper adhesion and performance.
The final stages of manufacturing involve rigorous testing and quality control measures. Each touch screen undergoes a series of tests to verify its responsiveness, accuracy, and durability. This includes multi-touch functionality tests, environmental stress tests, and longevity assessments to ensure the product meets the required specifications and industry standards.
Throughout the entire manufacturing process, strict adherence to cleanliness and precision is maintained. The use of automated systems and robotics in many stages helps to ensure consistency and reduce the risk of human error. Additionally, advanced process control systems are employed to monitor and adjust manufacturing parameters in real-time, maintaining optimal conditions for PMMA touch screen production.
One of the critical stages in the manufacturing process is the application of conductive coatings to the PMMA surface. This is often achieved through techniques such as sputtering or vapor deposition, where a thin layer of conductive material, such as indium tin oxide (ITO), is applied to the PMMA substrate. The precision of this step is crucial for ensuring uniform conductivity across the entire surface of the touch screen.
Following the conductive coating application, a patterning process is employed to create the touch-sensitive grid or matrix. This is typically accomplished using photolithography techniques, where a photoresist is applied to the coated PMMA surface, exposed to UV light through a mask, and then developed to create the desired electrode pattern. Etching processes are then used to remove the excess conductive material, leaving behind the precise touch-sensitive circuitry.
The next phase involves the integration of the touch sensor components. This includes attaching the controller chips, connecting the electrodes to the circuitry, and implementing any necessary shielding to prevent electromagnetic interference. The assembly process must be carried out in a clean environment to avoid contamination that could affect the performance of the touch screen.
To enhance the durability and functionality of the PMMA touch screen, additional layers may be applied. These can include anti-glare coatings, scratch-resistant layers, and oleophobic treatments to reduce fingerprint smudges. The application of these layers requires precise control over temperature, humidity, and curing conditions to ensure proper adhesion and performance.
The final stages of manufacturing involve rigorous testing and quality control measures. Each touch screen undergoes a series of tests to verify its responsiveness, accuracy, and durability. This includes multi-touch functionality tests, environmental stress tests, and longevity assessments to ensure the product meets the required specifications and industry standards.
Throughout the entire manufacturing process, strict adherence to cleanliness and precision is maintained. The use of automated systems and robotics in many stages helps to ensure consistency and reduce the risk of human error. Additionally, advanced process control systems are employed to monitor and adjust manufacturing parameters in real-time, maintaining optimal conditions for PMMA touch screen production.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!