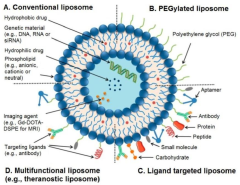
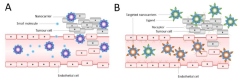
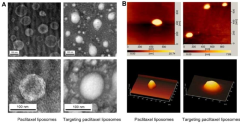
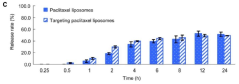
Phospholipid Composition Effects on Liposome Formation
JUL 16, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Liposome Formation Background and Objectives
Liposomes have been a subject of intense research and development since their discovery in the 1960s. These microscopic vesicles, composed of one or more phospholipid bilayers enclosing an aqueous core, have revolutionized drug delivery systems and have found applications in various fields, including pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and food technology. The formation of liposomes is a complex process influenced by numerous factors, with phospholipid composition being a critical determinant of their structure, stability, and functionality.
The primary objective of this research is to elucidate the intricate relationship between phospholipid composition and liposome formation. This investigation aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of how different types, ratios, and combinations of phospholipids affect the physical and chemical properties of liposomes. By exploring this relationship, we seek to optimize liposome formulations for specific applications and enhance their overall performance in various biological and industrial contexts.
The evolution of liposome technology has been marked by significant milestones in understanding lipid self-assembly, membrane biophysics, and colloidal science. Early research focused on basic liposome preparation methods and characterization techniques. As the field progressed, attention shifted towards manipulating liposome properties through careful selection and modification of lipid components. This led to the development of more sophisticated liposome systems, including long-circulating, targeted, and stimuli-responsive liposomes.
Current trends in liposome research emphasize the fine-tuning of phospholipid compositions to achieve desired characteristics such as improved stability, controlled release kinetics, and enhanced cellular uptake. The advent of synthetic and modified phospholipids has expanded the toolkit available to researchers, allowing for greater control over liposome properties. Additionally, the integration of computational modeling and high-throughput screening techniques has accelerated the process of optimizing phospholipid formulations for specific applications.
The technological goals of this research extend beyond merely understanding the effects of phospholipid composition on liposome formation. We aim to develop predictive models that can guide the rational design of liposome formulations, reducing the reliance on empirical trial-and-error approaches. Furthermore, we seek to establish standardized protocols for liposome preparation that account for the complex interplay between different phospholipids and environmental factors.
Ultimately, this research endeavors to bridge the gap between fundamental lipid science and practical applications of liposomes. By elucidating the principles governing phospholipid-based liposome formation, we aim to enable the development of more effective drug delivery systems, advanced diagnostic tools, and innovative biomimetic materials. The insights gained from this study will contribute to the broader field of nanomedicine and potentially open new avenues for personalized therapies and targeted treatments.
The primary objective of this research is to elucidate the intricate relationship between phospholipid composition and liposome formation. This investigation aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of how different types, ratios, and combinations of phospholipids affect the physical and chemical properties of liposomes. By exploring this relationship, we seek to optimize liposome formulations for specific applications and enhance their overall performance in various biological and industrial contexts.
The evolution of liposome technology has been marked by significant milestones in understanding lipid self-assembly, membrane biophysics, and colloidal science. Early research focused on basic liposome preparation methods and characterization techniques. As the field progressed, attention shifted towards manipulating liposome properties through careful selection and modification of lipid components. This led to the development of more sophisticated liposome systems, including long-circulating, targeted, and stimuli-responsive liposomes.
Current trends in liposome research emphasize the fine-tuning of phospholipid compositions to achieve desired characteristics such as improved stability, controlled release kinetics, and enhanced cellular uptake. The advent of synthetic and modified phospholipids has expanded the toolkit available to researchers, allowing for greater control over liposome properties. Additionally, the integration of computational modeling and high-throughput screening techniques has accelerated the process of optimizing phospholipid formulations for specific applications.
The technological goals of this research extend beyond merely understanding the effects of phospholipid composition on liposome formation. We aim to develop predictive models that can guide the rational design of liposome formulations, reducing the reliance on empirical trial-and-error approaches. Furthermore, we seek to establish standardized protocols for liposome preparation that account for the complex interplay between different phospholipids and environmental factors.
Ultimately, this research endeavors to bridge the gap between fundamental lipid science and practical applications of liposomes. By elucidating the principles governing phospholipid-based liposome formation, we aim to enable the development of more effective drug delivery systems, advanced diagnostic tools, and innovative biomimetic materials. The insights gained from this study will contribute to the broader field of nanomedicine and potentially open new avenues for personalized therapies and targeted treatments.
Market Analysis for Liposomal Drug Delivery
The liposomal drug delivery market has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by the increasing demand for targeted and efficient drug delivery systems. This market segment is expected to continue its upward trajectory due to several key factors. Firstly, the rising prevalence of chronic diseases, such as cancer and cardiovascular disorders, has created a substantial need for advanced drug delivery technologies that can improve therapeutic outcomes and reduce side effects.
Liposomal drug delivery systems offer numerous advantages over conventional drug formulations, including enhanced drug solubility, improved bioavailability, and prolonged circulation time. These benefits have led to increased adoption across various therapeutic areas, particularly in oncology and infectious diseases. The market has also been bolstered by the growing focus on personalized medicine, as liposomes can be tailored to specific patient needs and disease characteristics.
The pharmaceutical industry's ongoing shift towards biologics and large molecule drugs has further fueled the demand for liposomal delivery systems. These complex therapeutics often require specialized delivery mechanisms to maintain their stability and efficacy, making liposomes an attractive option for drug developers. Additionally, the increasing investment in research and development activities by both pharmaceutical companies and academic institutions has accelerated innovation in liposomal technologies, expanding their potential applications.
From a geographical perspective, North America currently dominates the liposomal drug delivery market, followed by Europe and Asia-Pacific. However, emerging economies in Asia and Latin America are expected to witness rapid growth in the coming years, driven by improving healthcare infrastructure and rising healthcare expenditure. The market landscape is characterized by a mix of established pharmaceutical giants and specialized biotechnology firms, with ongoing collaborations and partnerships shaping the competitive dynamics.
Despite the positive outlook, the liposomal drug delivery market faces certain challenges. These include the high cost of development and manufacturing, regulatory hurdles, and the need for specialized expertise in formulation and scale-up processes. Nevertheless, the market is poised for continued expansion, with technological advancements in areas such as remote loading techniques, surface modification, and targeted delivery expected to unlock new opportunities and drive further adoption of liposomal drug delivery systems across various therapeutic areas.
Liposomal drug delivery systems offer numerous advantages over conventional drug formulations, including enhanced drug solubility, improved bioavailability, and prolonged circulation time. These benefits have led to increased adoption across various therapeutic areas, particularly in oncology and infectious diseases. The market has also been bolstered by the growing focus on personalized medicine, as liposomes can be tailored to specific patient needs and disease characteristics.
The pharmaceutical industry's ongoing shift towards biologics and large molecule drugs has further fueled the demand for liposomal delivery systems. These complex therapeutics often require specialized delivery mechanisms to maintain their stability and efficacy, making liposomes an attractive option for drug developers. Additionally, the increasing investment in research and development activities by both pharmaceutical companies and academic institutions has accelerated innovation in liposomal technologies, expanding their potential applications.
From a geographical perspective, North America currently dominates the liposomal drug delivery market, followed by Europe and Asia-Pacific. However, emerging economies in Asia and Latin America are expected to witness rapid growth in the coming years, driven by improving healthcare infrastructure and rising healthcare expenditure. The market landscape is characterized by a mix of established pharmaceutical giants and specialized biotechnology firms, with ongoing collaborations and partnerships shaping the competitive dynamics.
Despite the positive outlook, the liposomal drug delivery market faces certain challenges. These include the high cost of development and manufacturing, regulatory hurdles, and the need for specialized expertise in formulation and scale-up processes. Nevertheless, the market is poised for continued expansion, with technological advancements in areas such as remote loading techniques, surface modification, and targeted delivery expected to unlock new opportunities and drive further adoption of liposomal drug delivery systems across various therapeutic areas.
Current Challenges in Phospholipid-based Liposomes
Despite significant advancements in liposome technology, several challenges persist in the development and optimization of phospholipid-based liposomes. One of the primary obstacles is achieving consistent and reproducible liposome formation across different batches. The complex interplay between various phospholipids and their composition significantly impacts the physicochemical properties of the resulting liposomes, making it difficult to maintain uniformity in size, shape, and encapsulation efficiency.
Another major challenge lies in controlling the stability of liposomes. Phospholipid-based liposomes are prone to aggregation, fusion, and leakage of encapsulated contents over time. This instability can lead to reduced shelf life and compromised therapeutic efficacy, particularly in drug delivery applications. Researchers are continuously striving to develop strategies to enhance liposome stability without compromising their functional properties.
The selection of appropriate phospholipid compositions for specific applications remains a complex task. Different phospholipids exhibit varying degrees of biocompatibility, biodegradability, and interactions with biological systems. Optimizing the phospholipid composition to achieve desired properties such as controlled release, targeted delivery, or enhanced cellular uptake requires extensive experimentation and fine-tuning.
Scale-up and manufacturing of liposomes present additional challenges. Transitioning from laboratory-scale production to industrial-scale manufacturing while maintaining consistent quality and performance is a significant hurdle. The complexity of liposome formulations and the sensitivity of the preparation process to various parameters make it challenging to establish robust and reproducible large-scale production methods.
Furthermore, the characterization and quality control of liposomes pose ongoing challenges. Accurate determination of size distribution, lamellarity, and encapsulation efficiency requires sophisticated analytical techniques. Developing standardized methods for liposome characterization across different research groups and industries is crucial for ensuring consistency and comparability of results.
Regulatory considerations also present challenges in the development of phospholipid-based liposomes for therapeutic applications. Meeting stringent regulatory requirements for safety, efficacy, and quality control adds complexity to the development process. Demonstrating long-term stability, batch-to-batch consistency, and in vivo performance of liposomal formulations are critical aspects that require extensive validation and documentation.
Addressing these challenges requires interdisciplinary approaches combining expertise in lipid chemistry, biophysics, pharmaceutical sciences, and nanotechnology. Continued research efforts are needed to develop innovative strategies for overcoming these obstacles and unlocking the full potential of phospholipid-based liposomes in various applications, ranging from drug delivery to diagnostics and beyond.
Another major challenge lies in controlling the stability of liposomes. Phospholipid-based liposomes are prone to aggregation, fusion, and leakage of encapsulated contents over time. This instability can lead to reduced shelf life and compromised therapeutic efficacy, particularly in drug delivery applications. Researchers are continuously striving to develop strategies to enhance liposome stability without compromising their functional properties.
The selection of appropriate phospholipid compositions for specific applications remains a complex task. Different phospholipids exhibit varying degrees of biocompatibility, biodegradability, and interactions with biological systems. Optimizing the phospholipid composition to achieve desired properties such as controlled release, targeted delivery, or enhanced cellular uptake requires extensive experimentation and fine-tuning.
Scale-up and manufacturing of liposomes present additional challenges. Transitioning from laboratory-scale production to industrial-scale manufacturing while maintaining consistent quality and performance is a significant hurdle. The complexity of liposome formulations and the sensitivity of the preparation process to various parameters make it challenging to establish robust and reproducible large-scale production methods.
Furthermore, the characterization and quality control of liposomes pose ongoing challenges. Accurate determination of size distribution, lamellarity, and encapsulation efficiency requires sophisticated analytical techniques. Developing standardized methods for liposome characterization across different research groups and industries is crucial for ensuring consistency and comparability of results.
Regulatory considerations also present challenges in the development of phospholipid-based liposomes for therapeutic applications. Meeting stringent regulatory requirements for safety, efficacy, and quality control adds complexity to the development process. Demonstrating long-term stability, batch-to-batch consistency, and in vivo performance of liposomal formulations are critical aspects that require extensive validation and documentation.
Addressing these challenges requires interdisciplinary approaches combining expertise in lipid chemistry, biophysics, pharmaceutical sciences, and nanotechnology. Continued research efforts are needed to develop innovative strategies for overcoming these obstacles and unlocking the full potential of phospholipid-based liposomes in various applications, ranging from drug delivery to diagnostics and beyond.
Existing Phospholipid Composition Strategies
01 Preparation methods for liposome formation
Various methods are used to form liposomes, including thin-film hydration, reverse-phase evaporation, and ethanol injection. These techniques involve the formation of lipid bilayers that encapsulate aqueous solutions, creating vesicles of different sizes and lamellarity. The choice of method depends on the desired liposome characteristics and the intended application.- Preparation methods for liposomes: Various techniques are used to form liposomes, including thin-film hydration, reverse-phase evaporation, and ethanol injection. These methods involve the formation of lipid bilayers that encapsulate aqueous compartments, creating vesicles of different sizes and lamellarity. The choice of method depends on the desired liposome characteristics and the intended application.
- Lipid composition and membrane properties: The selection of lipids and their ratios greatly influences liposome formation and properties. Phospholipids, cholesterol, and other membrane components are carefully chosen to control membrane fluidity, stability, and permeability. Tailoring the lipid composition allows for the creation of liposomes with specific characteristics suitable for various applications in drug delivery and cosmetics.
- Size control and homogenization techniques: Controlling liposome size is crucial for their intended applications. Techniques such as extrusion, sonication, and microfluidization are employed to achieve desired size distributions. These methods help in producing uniform liposome populations with specific size ranges, which is important for drug delivery efficiency and product stability.
- Functionalization and surface modification: Liposomes can be functionalized or surface-modified to enhance their properties and targeting capabilities. This includes the incorporation of targeting ligands, PEGylation for improved circulation time, and the addition of charged molecules for electrostatic stabilization. These modifications can improve the efficacy and specificity of liposome-based formulations.
- Encapsulation efficiency and drug loading: Optimizing the encapsulation efficiency and drug loading capacity of liposomes is essential for their effectiveness as drug delivery systems. Various strategies are employed to maximize the amount of active ingredients that can be incorporated into liposomes, including pH gradient methods, remote loading techniques, and the use of complexing agents. These approaches aim to improve the therapeutic potential of liposomal formulations.
02 Lipid composition and membrane properties
The selection of lipids and their ratios significantly influence liposome properties such as stability, size, and permeability. Commonly used lipids include phosphatidylcholine, cholesterol, and PEGylated lipids. The lipid composition affects the phase transition temperature, fluidity, and surface charge of the liposomal membrane, which in turn impacts drug encapsulation efficiency and release kinetics.Expand Specific Solutions03 Size control and homogenization techniques
Controlling liposome size is crucial for their application in drug delivery and other fields. Techniques such as extrusion, sonication, and microfluidization are employed to achieve desired size distributions. These methods help in producing uniform liposome populations with specific size ranges, which is important for optimizing their pharmacokinetic properties and cellular uptake.Expand Specific Solutions04 Functionalization and targeting of liposomes
Liposomes can be functionalized with various ligands, antibodies, or other targeting moieties to enhance their specificity for certain tissues or cell types. This modification allows for targeted drug delivery, improving therapeutic efficacy while reducing side effects. Surface modification techniques include covalent attachment, electrostatic interactions, or incorporation of specialized lipids during liposome formation.Expand Specific Solutions05 Stability and storage of liposomal formulations
Ensuring the long-term stability of liposomal formulations is critical for their practical use. Strategies to enhance stability include lyophilization, the use of cryoprotectants, and optimizing storage conditions. These approaches help maintain the integrity of liposomes, prevent aggregation, and preserve the encapsulated cargo during storage and transportation.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Liposomal Technology
The research on phospholipid composition effects on liposome formation is in a mature stage of development, with a significant market size and established technological foundations. The field is characterized by a mix of academic institutions, pharmaceutical companies, and specialized biotech firms, indicating a diverse and competitive landscape. Key players include universities like The University of California and Tianjin University, alongside major pharmaceutical corporations such as Pfizer and FUJIFILM. The presence of specialized companies like Esperion LUV Development and Neopharma suggests a high level of technical expertise and niche focus within the industry. The involvement of both academic and commercial entities points to ongoing research and development efforts, as well as potential for commercial applications in drug delivery and other biomedical fields.
The Regents of the University of California
Technical Solution: The University of California has conducted extensive research on phospholipid composition effects on liposome formation. They have developed a novel approach using microfluidic devices to precisely control the lipid composition and size distribution of liposomes[1]. Their method allows for the rapid screening of different phospholipid combinations and their impact on liposome stability and drug encapsulation efficiency. The researchers have also investigated the role of cholesterol in modulating membrane fluidity and permeability[2]. Additionally, they have explored the use of pH-sensitive phospholipids to create stimuli-responsive liposomes for targeted drug delivery[3]. Their work has significantly contributed to understanding how phospholipid composition influences liposome characteristics and functionality.
Strengths: Advanced microfluidic technology for precise liposome formation; Comprehensive understanding of lipid-cholesterol interactions. Weaknesses: Potential scalability issues for large-scale production; Complexity in translating research findings to clinical applications.
FUJIFILM Corp.
Technical Solution: FUJIFILM has leveraged its expertise in nanotechnology and materials science to advance research on phospholipid composition effects on liposome formation. They have developed a unique liposome production method called "Hydrogenated Soybean Phosphatidylcholine (HSPC) Technology" that allows for the creation of highly stable liposomes with improved drug encapsulation efficiency[7]. FUJIFILM's research has focused on optimizing the ratio of HSPC to other phospholipids and cholesterol to enhance liposome stability and drug release profiles. They have also investigated the use of pH-sensitive phospholipids to create stimuli-responsive liposomes for targeted drug delivery in cancer treatment[8]. Additionally, FUJIFILM has explored the incorporation of antioxidants into the phospholipid bilayer to improve the shelf-life of liposomal formulations.
Strengths: Strong expertise in materials science and nanotechnology; Innovative liposome production techniques. Weaknesses: Limited experience in pharmaceutical development compared to established drug companies; Potential challenges in regulatory approval processes.
Innovative Approaches in Lipid Bilayer Engineering
Deep learning based technique to analyse the impact of liposomal formulations in delivering antifungal and antibacterial drugs
PatentPendingIN202211067529A
Innovation
- The use of liposomal formulations with specific lipid compositions, such as a 70:30 molar ratio of phospholipids to cholesterol, combined with surface modifications like PEGylation and targeting ligands, along with thermosensitive and magnetic liposomes, enhances stability and controlled release of chemotherapeutic agents, allowing for targeted delivery to cancer tissues.
Regulatory Considerations for Liposomal Drugs
The regulatory landscape for liposomal drugs is complex and evolving, reflecting the unique characteristics and challenges associated with these advanced drug delivery systems. Regulatory agencies, such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Medicines Agency (EMA), have developed specific guidelines to address the development, manufacturing, and approval of liposomal formulations.
One of the primary regulatory considerations for liposomal drugs is the demonstration of quality, safety, and efficacy. Manufacturers must provide comprehensive data on the physicochemical properties of the liposomes, including size distribution, zeta potential, and encapsulation efficiency. These parameters are critical in determining the drug's pharmacokinetics and biodistribution, which can significantly impact its therapeutic efficacy and safety profile.
The stability of liposomal formulations is another key regulatory concern. Developers must demonstrate the long-term stability of their products under various storage conditions, as well as the stability of the drug-loaded liposomes in biological fluids. This includes assessing potential drug leakage, changes in particle size, and chemical degradation of both the encapsulated drug and the lipid components.
Regulatory agencies also place significant emphasis on the manufacturing process for liposomal drugs. Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) guidelines must be strictly adhered to, with particular attention paid to the reproducibility and scalability of the production process. This includes validation of critical steps such as lipid mixing, drug loading, and sterilization procedures.
The choice of excipients, particularly the phospholipid composition, is subject to regulatory scrutiny. Manufacturers must justify the selection of lipids based on their impact on drug release, stability, and safety. Novel or non-traditional lipid components may require additional safety data and toxicological studies.
Pharmacokinetic and biodistribution studies are essential components of the regulatory submission for liposomal drugs. These studies must demonstrate how the liposomal formulation alters the drug's behavior in vivo compared to its conventional form. This includes assessing the impact of the phospholipid composition on drug release kinetics and tissue distribution.
Immunogenicity and complement activation are specific safety concerns for liposomal formulations that regulators closely monitor. Developers must provide data on the potential for their products to elicit immune responses or activate the complement system, which could lead to hypersensitivity reactions or altered pharmacokinetics upon repeated administration.
One of the primary regulatory considerations for liposomal drugs is the demonstration of quality, safety, and efficacy. Manufacturers must provide comprehensive data on the physicochemical properties of the liposomes, including size distribution, zeta potential, and encapsulation efficiency. These parameters are critical in determining the drug's pharmacokinetics and biodistribution, which can significantly impact its therapeutic efficacy and safety profile.
The stability of liposomal formulations is another key regulatory concern. Developers must demonstrate the long-term stability of their products under various storage conditions, as well as the stability of the drug-loaded liposomes in biological fluids. This includes assessing potential drug leakage, changes in particle size, and chemical degradation of both the encapsulated drug and the lipid components.
Regulatory agencies also place significant emphasis on the manufacturing process for liposomal drugs. Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) guidelines must be strictly adhered to, with particular attention paid to the reproducibility and scalability of the production process. This includes validation of critical steps such as lipid mixing, drug loading, and sterilization procedures.
The choice of excipients, particularly the phospholipid composition, is subject to regulatory scrutiny. Manufacturers must justify the selection of lipids based on their impact on drug release, stability, and safety. Novel or non-traditional lipid components may require additional safety data and toxicological studies.
Pharmacokinetic and biodistribution studies are essential components of the regulatory submission for liposomal drugs. These studies must demonstrate how the liposomal formulation alters the drug's behavior in vivo compared to its conventional form. This includes assessing the impact of the phospholipid composition on drug release kinetics and tissue distribution.
Immunogenicity and complement activation are specific safety concerns for liposomal formulations that regulators closely monitor. Developers must provide data on the potential for their products to elicit immune responses or activate the complement system, which could lead to hypersensitivity reactions or altered pharmacokinetics upon repeated administration.
Scalability and Manufacturing Processes
The scalability and manufacturing processes of liposomes are critical factors in their commercial viability and widespread application. As research on phospholipid composition effects on liposome formation progresses, it becomes increasingly important to consider how these findings can be translated into large-scale production.
Traditional methods of liposome preparation, such as thin-film hydration and reverse-phase evaporation, often face challenges when scaled up. These challenges include maintaining consistent size distribution, encapsulation efficiency, and stability across larger batch sizes. To address these issues, several innovative approaches have been developed.
Microfluidic techniques have emerged as a promising solution for scalable liposome production. These methods allow for precise control over lipid mixing and hydration, resulting in more uniform liposome populations. Microfluidic devices can be designed to operate in parallel, enabling higher throughput without compromising quality.
Continuous flow processes represent another avenue for scaling up liposome production. These systems can produce liposomes in a continuous manner, potentially increasing output while maintaining consistent quality. Continuous flow reactors can be designed to incorporate multiple steps, such as lipid mixing, hydration, and size refinement, in a single integrated process.
The impact of phospholipid composition on manufacturing processes cannot be overstated. Different phospholipid combinations may require adjustments in production parameters, such as temperature, pressure, and mixing ratios. Understanding these relationships is crucial for optimizing large-scale manufacturing protocols.
Advances in process analytical technology (PAT) have greatly enhanced the ability to monitor and control liposome production in real-time. Techniques such as dynamic light scattering and Raman spectroscopy can provide instant feedback on liposome size, polydispersity, and composition during the manufacturing process.
Quality control and reproducibility remain significant challenges in scaling up liposome production. Implementing robust quality management systems and standardized operating procedures is essential for ensuring consistent product quality across batches and production sites.
As the field progresses, there is a growing need for specialized equipment designed specifically for large-scale liposome production. This includes custom-designed mixers, extruders, and purification systems that can handle the unique requirements of liposome formulations while maintaining scalability.
Traditional methods of liposome preparation, such as thin-film hydration and reverse-phase evaporation, often face challenges when scaled up. These challenges include maintaining consistent size distribution, encapsulation efficiency, and stability across larger batch sizes. To address these issues, several innovative approaches have been developed.
Microfluidic techniques have emerged as a promising solution for scalable liposome production. These methods allow for precise control over lipid mixing and hydration, resulting in more uniform liposome populations. Microfluidic devices can be designed to operate in parallel, enabling higher throughput without compromising quality.
Continuous flow processes represent another avenue for scaling up liposome production. These systems can produce liposomes in a continuous manner, potentially increasing output while maintaining consistent quality. Continuous flow reactors can be designed to incorporate multiple steps, such as lipid mixing, hydration, and size refinement, in a single integrated process.
The impact of phospholipid composition on manufacturing processes cannot be overstated. Different phospholipid combinations may require adjustments in production parameters, such as temperature, pressure, and mixing ratios. Understanding these relationships is crucial for optimizing large-scale manufacturing protocols.
Advances in process analytical technology (PAT) have greatly enhanced the ability to monitor and control liposome production in real-time. Techniques such as dynamic light scattering and Raman spectroscopy can provide instant feedback on liposome size, polydispersity, and composition during the manufacturing process.
Quality control and reproducibility remain significant challenges in scaling up liposome production. Implementing robust quality management systems and standardized operating procedures is essential for ensuring consistent product quality across batches and production sites.
As the field progresses, there is a growing need for specialized equipment designed specifically for large-scale liposome production. This includes custom-designed mixers, extruders, and purification systems that can handle the unique requirements of liposome formulations while maintaining scalability.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!