Research on sealing processes for enhanced anodized aluminum durability
OCT 11, 202510 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Anodized Aluminum Sealing Technology Background and Objectives
Anodized aluminum has been widely utilized across various industries since its commercial development in the early 20th century. The anodization process, which creates a protective oxide layer on aluminum surfaces, significantly enhances corrosion resistance, wear resistance, and aesthetic appeal. However, the inherent porosity of this oxide layer necessitates sealing processes to achieve optimal durability and performance characteristics.
The evolution of sealing technologies for anodized aluminum has progressed through several distinct phases. Traditional hot water sealing, developed in the 1930s, represented the first systematic approach to closing the porous structure. This was followed by the introduction of nickel acetate sealing in the 1950s, which offered improved corrosion protection. The 1970s and 1980s witnessed the development of cold sealing processes using nickel fluoride, providing energy efficiency advantages over hot sealing methods.
Recent technological advancements have focused on environmentally friendly alternatives to address concerns regarding heavy metal content in traditional sealing solutions. This shift aligns with global sustainability initiatives and increasingly stringent environmental regulations in manufacturing processes.
Current research objectives in anodized aluminum sealing technology center on several key areas. Primary among these is the development of sealing processes that enhance long-term durability while minimizing environmental impact. This includes exploration of novel sealing agents derived from sustainable sources and processes that reduce energy consumption and waste generation.
Another critical objective involves improving sealing efficiency to reduce processing time and energy requirements without compromising performance characteristics. This encompasses optimization of sealing parameters such as temperature, pH, and concentration of sealing agents to achieve maximum pore closure with minimal resource utilization.
Additionally, research aims to develop specialized sealing technologies tailored for emerging high-performance applications in aerospace, automotive, and electronic industries. These applications often demand exceptional corrosion resistance under extreme conditions, necessitating advanced sealing solutions that exceed conventional performance metrics.
The integration of nanotechnology into sealing processes represents another frontier, with investigations into nano-scale sealing agents that can penetrate and seal pores more effectively than traditional methods. This approach shows promise for creating more uniform and complete sealing of the anodic oxide layer.
Understanding the fundamental mechanisms of the sealing process at the molecular level remains an ongoing research focus, as this knowledge can inform the development of next-generation sealing technologies with enhanced performance characteristics and sustainability profiles.
The evolution of sealing technologies for anodized aluminum has progressed through several distinct phases. Traditional hot water sealing, developed in the 1930s, represented the first systematic approach to closing the porous structure. This was followed by the introduction of nickel acetate sealing in the 1950s, which offered improved corrosion protection. The 1970s and 1980s witnessed the development of cold sealing processes using nickel fluoride, providing energy efficiency advantages over hot sealing methods.
Recent technological advancements have focused on environmentally friendly alternatives to address concerns regarding heavy metal content in traditional sealing solutions. This shift aligns with global sustainability initiatives and increasingly stringent environmental regulations in manufacturing processes.
Current research objectives in anodized aluminum sealing technology center on several key areas. Primary among these is the development of sealing processes that enhance long-term durability while minimizing environmental impact. This includes exploration of novel sealing agents derived from sustainable sources and processes that reduce energy consumption and waste generation.
Another critical objective involves improving sealing efficiency to reduce processing time and energy requirements without compromising performance characteristics. This encompasses optimization of sealing parameters such as temperature, pH, and concentration of sealing agents to achieve maximum pore closure with minimal resource utilization.
Additionally, research aims to develop specialized sealing technologies tailored for emerging high-performance applications in aerospace, automotive, and electronic industries. These applications often demand exceptional corrosion resistance under extreme conditions, necessitating advanced sealing solutions that exceed conventional performance metrics.
The integration of nanotechnology into sealing processes represents another frontier, with investigations into nano-scale sealing agents that can penetrate and seal pores more effectively than traditional methods. This approach shows promise for creating more uniform and complete sealing of the anodic oxide layer.
Understanding the fundamental mechanisms of the sealing process at the molecular level remains an ongoing research focus, as this knowledge can inform the development of next-generation sealing technologies with enhanced performance characteristics and sustainability profiles.
Market Analysis of Durable Anodized Aluminum Products
The global market for durable anodized aluminum products has experienced significant growth over the past decade, driven primarily by increasing applications in construction, automotive, aerospace, and consumer electronics sectors. The market size for anodized aluminum products was valued at approximately $8.2 billion in 2022, with projections indicating a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.3% through 2028. Enhanced durability through advanced sealing processes represents a critical value-added segment within this broader market.
Construction remains the largest application segment, accounting for nearly 40% of the total market share. The demand for corrosion-resistant, aesthetically pleasing, and long-lasting aluminum facades, window frames, and structural components continues to drive innovation in sealing technologies. Particularly in coastal and high-pollution urban environments, where traditional anodized surfaces face accelerated degradation, premium sealed products command price premiums of 15-25%.
The automotive industry represents the fastest-growing segment, with a CAGR of 8.7%, as manufacturers increasingly substitute steel components with lightweight, durable aluminum parts to improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions. Enhanced sealing processes that provide superior wear resistance and corrosion protection are especially valued in this sector, where exposure to road salts and environmental contaminants presents significant challenges.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific dominates the market with a 42% share, led by China's massive construction boom and manufacturing capabilities. North America and Europe follow with 28% and 23% market shares respectively, with these regions particularly focused on high-performance sealing technologies that extend product lifecycles and reduce maintenance requirements.
Consumer willingness to pay for superior durability has created distinct market tiers. Standard anodized products occupy the economy segment, while products featuring advanced sealing processes command premium positioning. Market research indicates that products with documented extended lifespans of 15+ years can command price premiums of up to 35% compared to standard offerings.
Environmental regulations are increasingly shaping market dynamics, with restrictions on hexavalent chromium and other hazardous substances driving research into environmentally friendly sealing alternatives. Products utilizing green sealing technologies are growing at nearly twice the rate of conventional solutions, reflecting shifting consumer and regulatory priorities.
The competitive landscape features both integrated aluminum manufacturers who have developed proprietary sealing technologies and specialized surface treatment companies focusing exclusively on high-performance finishing processes. This bifurcation has created opportunities for technology licensing and strategic partnerships throughout the value chain.
Construction remains the largest application segment, accounting for nearly 40% of the total market share. The demand for corrosion-resistant, aesthetically pleasing, and long-lasting aluminum facades, window frames, and structural components continues to drive innovation in sealing technologies. Particularly in coastal and high-pollution urban environments, where traditional anodized surfaces face accelerated degradation, premium sealed products command price premiums of 15-25%.
The automotive industry represents the fastest-growing segment, with a CAGR of 8.7%, as manufacturers increasingly substitute steel components with lightweight, durable aluminum parts to improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions. Enhanced sealing processes that provide superior wear resistance and corrosion protection are especially valued in this sector, where exposure to road salts and environmental contaminants presents significant challenges.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific dominates the market with a 42% share, led by China's massive construction boom and manufacturing capabilities. North America and Europe follow with 28% and 23% market shares respectively, with these regions particularly focused on high-performance sealing technologies that extend product lifecycles and reduce maintenance requirements.
Consumer willingness to pay for superior durability has created distinct market tiers. Standard anodized products occupy the economy segment, while products featuring advanced sealing processes command premium positioning. Market research indicates that products with documented extended lifespans of 15+ years can command price premiums of up to 35% compared to standard offerings.
Environmental regulations are increasingly shaping market dynamics, with restrictions on hexavalent chromium and other hazardous substances driving research into environmentally friendly sealing alternatives. Products utilizing green sealing technologies are growing at nearly twice the rate of conventional solutions, reflecting shifting consumer and regulatory priorities.
The competitive landscape features both integrated aluminum manufacturers who have developed proprietary sealing technologies and specialized surface treatment companies focusing exclusively on high-performance finishing processes. This bifurcation has created opportunities for technology licensing and strategic partnerships throughout the value chain.
Current Sealing Techniques and Technical Barriers
Anodized aluminum sealing represents a critical post-treatment process that significantly enhances the durability and corrosion resistance of anodized aluminum surfaces. Currently, several established sealing techniques dominate the industrial landscape, each with distinct advantages and limitations that influence their application across various sectors.
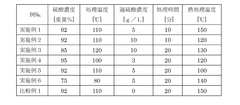
Hot water sealing remains the most traditional and widely implemented technique, operating at temperatures between 95-100°C for 2-3 minutes per micrometer of coating thickness. This method facilitates the hydration of aluminum oxide to form boehmite (AlO(OH)), effectively closing the porous structure. While cost-effective and environmentally friendly, hot water sealing suffers from high energy consumption, extended processing times, and potential for smudge formation that can compromise aesthetic qualities.
Nickel acetate sealing (mid-temperature sealing) operates at 82-88°C and incorporates nickel salts that precipitate within the pores, forming a more robust barrier against environmental factors. This technique offers improved corrosion resistance compared to hot water sealing while requiring less energy. However, environmental concerns regarding nickel compounds and increasingly stringent regulations are limiting its application in certain markets.
Cold sealing technologies, including those based on nickel fluoride or organic compounds, function at room temperature (20-30°C) and have gained popularity due to their energy efficiency and reduced processing times. Despite these advantages, cold sealing typically delivers lower durability metrics compared to hot sealing methods and often requires proprietary chemical formulations that increase operational costs.
Two-step sealing processes combining different techniques have emerged as promising alternatives, offering enhanced performance characteristics. However, these approaches introduce additional complexity to production lines and increase processing times, creating implementation barriers for high-volume manufacturing environments.
The technical barriers limiting advancement in aluminum sealing technologies are multifaceted. Foremost among these is the fundamental trade-off between sealing quality and processing efficiency. Higher quality sealing typically demands longer processing times and elevated temperatures, directly conflicting with industry demands for faster production cycles and reduced energy consumption.
Another significant challenge involves the development of environmentally sustainable sealing solutions that maintain performance standards while eliminating hazardous substances. The industry faces increasing regulatory pressure to phase out chromium, nickel, and other potentially harmful compounds traditionally used in sealing formulations.
Uniformity of sealing across complex geometries presents another persistent technical barrier, particularly for components with intricate designs or varying thicknesses. Current technologies often produce inconsistent results across different surface areas, leading to variability in durability performance and aesthetic qualities.
Hot water sealing remains the most traditional and widely implemented technique, operating at temperatures between 95-100°C for 2-3 minutes per micrometer of coating thickness. This method facilitates the hydration of aluminum oxide to form boehmite (AlO(OH)), effectively closing the porous structure. While cost-effective and environmentally friendly, hot water sealing suffers from high energy consumption, extended processing times, and potential for smudge formation that can compromise aesthetic qualities.
Nickel acetate sealing (mid-temperature sealing) operates at 82-88°C and incorporates nickel salts that precipitate within the pores, forming a more robust barrier against environmental factors. This technique offers improved corrosion resistance compared to hot water sealing while requiring less energy. However, environmental concerns regarding nickel compounds and increasingly stringent regulations are limiting its application in certain markets.
Cold sealing technologies, including those based on nickel fluoride or organic compounds, function at room temperature (20-30°C) and have gained popularity due to their energy efficiency and reduced processing times. Despite these advantages, cold sealing typically delivers lower durability metrics compared to hot sealing methods and often requires proprietary chemical formulations that increase operational costs.
Two-step sealing processes combining different techniques have emerged as promising alternatives, offering enhanced performance characteristics. However, these approaches introduce additional complexity to production lines and increase processing times, creating implementation barriers for high-volume manufacturing environments.
The technical barriers limiting advancement in aluminum sealing technologies are multifaceted. Foremost among these is the fundamental trade-off between sealing quality and processing efficiency. Higher quality sealing typically demands longer processing times and elevated temperatures, directly conflicting with industry demands for faster production cycles and reduced energy consumption.
Another significant challenge involves the development of environmentally sustainable sealing solutions that maintain performance standards while eliminating hazardous substances. The industry faces increasing regulatory pressure to phase out chromium, nickel, and other potentially harmful compounds traditionally used in sealing formulations.
Uniformity of sealing across complex geometries presents another persistent technical barrier, particularly for components with intricate designs or varying thicknesses. Current technologies often produce inconsistent results across different surface areas, leading to variability in durability performance and aesthetic qualities.
Comparative Analysis of Modern Sealing Processes
01 Hot water sealing methods for anodized aluminum
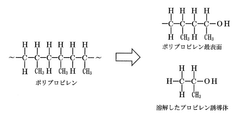
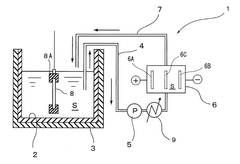
Hot water sealing is a traditional method for sealing anodized aluminum surfaces. This process involves immersing the anodized aluminum in hot water, typically at temperatures near boiling point (90-100°C), which causes the aluminum oxide pores to hydrate and expand, effectively sealing the surface. This method creates aluminum oxide monohydrate (boehmite) that fills the pores, providing good corrosion resistance and durability. The quality of sealing depends on water temperature, immersion time, and water purity, with longer immersion times generally resulting in better sealing quality and improved durability.- Hot water sealing processes for anodized aluminum: Hot water sealing is a traditional method for sealing anodized aluminum surfaces. This process involves immersing the anodized aluminum in hot water, typically at temperatures near boiling point (90-100°C). During this process, the aluminum oxide layer hydrates, forming aluminum hydroxide which fills the pores of the anodic coating. This transformation increases the volume of the coating, effectively sealing the pores and enhancing the durability and corrosion resistance of the anodized surface. The quality of hot water sealing can be improved by controlling parameters such as water temperature, immersion time, and water purity.
- Chemical sealing methods using metal salts: Chemical sealing methods involve the use of metal salt solutions to enhance the durability of anodized aluminum. These processes typically use nickel acetate, nickel fluoride, cobalt acetate, or other metal salts that react with the anodic oxide layer to form insoluble compounds within the pores. This chemical reaction creates a more robust seal than traditional hot water methods, providing superior corrosion resistance and wear properties. The effectiveness of chemical sealing depends on factors such as solution concentration, pH level, temperature, and immersion time. These methods are particularly valuable for applications requiring enhanced durability and resistance to harsh environmental conditions.
- Cold sealing technologies for improved efficiency: Cold sealing technologies have been developed as energy-efficient alternatives to traditional hot sealing methods. These processes operate at room temperature or slightly above (20-30°C), significantly reducing energy consumption. Cold sealing typically involves specialized chemical formulations containing fluorides, silicates, or polymer-based compounds that react with the anodic layer to form stable compounds within the pores. While requiring longer processing times than hot sealing methods, cold sealing can provide comparable durability and corrosion resistance when properly executed. These technologies are particularly valuable for large components where hot sealing would be impractical or energy-intensive.
- Two-step and hybrid sealing processes: Two-step and hybrid sealing processes combine multiple sealing technologies to maximize the durability of anodized aluminum. These methods typically involve a primary sealing step using one technique (such as hot water or chemical sealing) followed by a secondary treatment with a different method. Common combinations include hot water sealing followed by a nickel acetate treatment, or chemical pre-sealing followed by hydrothermal post-treatment. These multi-stage approaches create more comprehensive pore closure and can significantly enhance properties such as corrosion resistance, color stability, and wear resistance compared to single-method sealing processes. The synergistic effects of combined treatments provide superior long-term performance in demanding applications.
- Advanced sealing additives and performance enhancers: Advanced additives and performance enhancers have been developed to improve the durability of sealed anodized aluminum. These include corrosion inhibitors, surfactants, pH buffers, and nanoparticles that can be incorporated into sealing solutions to enhance their effectiveness. Certain organic compounds and polymers can also be used to create hydrophobic or oleophobic surface properties while maintaining the integrity of the seal. These additives can significantly improve the resistance to weathering, UV degradation, and chemical attack. The incorporation of these performance enhancers allows for customized sealing solutions tailored to specific environmental challenges and application requirements, extending the service life of anodized aluminum components.
02 Chemical sealing processes using metal salts
Chemical sealing processes involve the use of metal salt solutions to seal anodized aluminum surfaces. Common metal salts used include nickel acetate, nickel fluoride, cobalt acetate, and various chromates. These solutions react with the aluminum oxide layer to form insoluble compounds that plug the pores of the anodized surface. Chemical sealing typically operates at lower temperatures (50-85°C) than hot water sealing, making it more energy-efficient. The metal salt sealing methods provide enhanced corrosion resistance, color stability, and improved wear resistance compared to traditional hot water sealing, resulting in superior long-term durability of the anodized surface.Expand Specific Solutions03 Cold sealing technologies and polymer-based sealants
Cold sealing technologies operate at room temperature or slightly above (20-30°C), offering energy efficiency advantages over hot sealing methods. These processes often utilize polymer-based sealants, silicates, or specialized organic compounds that penetrate and seal the pores of anodized aluminum. Polymer-based sealants form a protective layer that enhances corrosion resistance and provides additional protection against environmental factors. These methods are particularly valuable for temperature-sensitive components or large parts where hot sealing might be impractical. Cold sealing technologies can provide excellent durability with proper application, though they may require longer processing times to achieve optimal sealing quality.Expand Specific Solutions04 Two-step and multi-step sealing processes
Two-step and multi-step sealing processes combine different sealing methods to enhance the durability of anodized aluminum. These processes typically involve a primary sealing step using one method (such as metal salt sealing) followed by secondary treatments (such as hot water or polymer sealing). The combination of different sealing mechanisms provides superior pore closure and creates multiple barriers against environmental degradation. Multi-step processes can address specific performance requirements by leveraging the advantages of each sealing method while minimizing their individual limitations. These combined approaches often result in exceptional corrosion resistance, wear resistance, and overall durability of the anodized aluminum surface, making them suitable for demanding applications.Expand Specific Solutions05 Advanced sealing additives and process enhancements
Advanced sealing processes incorporate specialized additives and process enhancements to improve the durability of anodized aluminum. These include surfactants, pH modifiers, anti-smudge compounds, and nano-materials that enhance pore penetration and sealing efficiency. Process enhancements such as ultrasonic assistance, controlled atmosphere, and precise temperature ramping can significantly improve sealing quality. Some advanced processes utilize environmentally friendly alternatives to traditional heavy metal-based sealants, addressing sustainability concerns while maintaining or improving performance. These innovations in sealing technology result in anodized surfaces with superior weathering resistance, color stability, and mechanical durability, extending the service life of aluminum components in demanding environments.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Manufacturers and Research Institutions in Anodizing Industry
The anodized aluminum sealing technology market is currently in a growth phase, with increasing demand for durable protective finishes across automotive, aerospace, and consumer electronics sectors. The market size is expanding due to rising applications in industries requiring corrosion-resistant and aesthetically appealing aluminum surfaces. Technologically, the field shows moderate maturity with ongoing innovation. Leading players include Henkel AG, offering comprehensive sealing solutions; Apple, which has pioneered proprietary anodizing techniques for consumer electronics; Safran Landing Systems, developing specialized aerospace applications; and Wuhan Fengfan Electrochemical, focusing on advanced electrochemical additives. Research institutions like Naval Research Laboratory and Beijing University of Chemical Technology are driving fundamental advancements, while specialized manufacturers such as Vapor Tech and WKW Engineering are developing application-specific sealing technologies for enhanced durability.
Henkel AG & Co. KGaA
Technical Solution: Henkel has developed advanced sealing technologies for anodized aluminum that focus on environmentally friendly solutions. Their BONDERITE® sealing processes utilize nickel-free formulations that comply with strict environmental regulations while providing superior corrosion resistance. The technology employs a combination of organic and inorganic compounds that penetrate and seal the porous anodic oxide layer through controlled hydration reactions. Henkel's process operates at lower temperatures (85-95°C) compared to traditional hot water sealing (95-100°C), reducing energy consumption while achieving comparable or superior performance. Their two-step sealing system first applies a specialized primer that penetrates deep into the pores, followed by a polymer-based topcoat that creates an impermeable barrier against environmental contaminants[1][3].
Strengths: Environmentally compliant formulations eliminate heavy metals while maintaining high performance; reduced energy consumption through lower processing temperatures; excellent corrosion resistance even in harsh environments. Weaknesses: May require more precise process control than traditional methods; potentially higher initial chemical costs compared to simple hot water sealing.
Apple, Inc.
Technical Solution: Apple has developed proprietary sealing technologies for anodized aluminum specifically designed for consumer electronics applications where aesthetics, durability, and environmental resistance are critical. Their process employs a multi-stage approach that begins with precision-controlled anodizing followed by a specialized sealing system that maintains color consistency while enhancing durability. The technology utilizes a combination of hydrothermal and organic sealing methods, with proprietary additives that promote complete pore closure while maintaining surface appearance. Apple's process incorporates strict quality control measures, including real-time monitoring of sealing bath parameters and automated adjustment systems. Their research has yielded sealing methods that provide exceptional resistance to fingerprints, oils, and daily wear while maintaining the premium aesthetic qualities of their products. The company has also pioneered recycled aluminum processing techniques that maintain sealing performance while reducing environmental impact through closed-loop manufacturing systems[8][10].
Strengths: Exceptional aesthetic quality control combined with practical durability; specialized for consumer electronics applications; integrated with sustainable manufacturing practices. Weaknesses: Highly proprietary processes may not be broadly applicable to other industries; optimized for specific aluminum alloys used in their products.
Key Patents and Innovations in Anodized Aluminum Sealing
Sealing treatment method for anodized surface of aluminum or aluminum alloy
PatentWO2020217694A1
Innovation
- A method involving a sealing solution prepared by dissolving a resin in sulfuric acid with an added oxidizing agent, where the anodized aluminum or aluminum alloy is immersed, allowing monomer or oligomer derivatives with hydrophilic groups to penetrate and seal the pores, followed by heat treatment to enhance durability.
Process for the manufacture of sealed anodized aluminum components
PatentInactiveUS9187839B2
Innovation
- A two-step process involving a first solution with an anion capable of reacting with a cation to form a water-insoluble precipitate, followed by a second solution with a cation to seal the anodic pores, reducing porosity and enhancing corrosion resistance without damaging the oxide layer.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability of Sealing Processes
The environmental impact of sealing processes for anodized aluminum has become increasingly significant as industries strive for more sustainable manufacturing practices. Traditional hot water sealing, while effective, consumes substantial energy due to the requirement of maintaining water at near-boiling temperatures for extended periods. This process typically requires 15-20 kWh of energy per cubic meter of treated aluminum, contributing significantly to the carbon footprint of anodized products.
Cold sealing alternatives, particularly nickel-based processes, present their own environmental challenges. Nickel compounds are classified as carcinogenic and pose risks to aquatic ecosystems when discharged in wastewater. Studies indicate that even at concentrations as low as 0.1 mg/L, nickel can adversely affect aquatic organisms, necessitating costly wastewater treatment systems.
Recent advancements in mid-temperature sealing technologies have demonstrated promising environmental benefits. These processes operate at 60-80°C, reducing energy consumption by approximately 40% compared to traditional hot water sealing while maintaining comparable durability performance. Additionally, the incorporation of biodegradable additives in these systems has shown potential for reducing the environmental persistence of chemical agents.
Water consumption represents another critical environmental consideration. Conventional sealing processes require 10-15 liters of water per square meter of anodized surface. Closed-loop water recycling systems have emerged as an effective solution, capable of reducing freshwater consumption by up to 80% while simultaneously minimizing wastewater discharge. Several manufacturers have reported significant cost savings following implementation of these systems, with payback periods typically ranging from 12-24 months.
The sustainability profile of sealing processes is further enhanced by recent innovations in chemical formulations. Vegetable-based sealants derived from renewable resources have demonstrated efficacy comparable to conventional options while reducing dependence on petrochemical derivatives. These bio-based alternatives typically decompose 60-70% faster than their synthetic counterparts when released into the environment.
Regulatory frameworks worldwide are increasingly emphasizing environmental performance in industrial processes. The European Union's Industrial Emissions Directive and similar regulations in North America and Asia have established stringent standards for wastewater quality and air emissions from anodizing facilities. Companies adopting more sustainable sealing technologies gain competitive advantages through regulatory compliance and access to environmentally conscious markets.
Life cycle assessment studies indicate that improvements in sealing process sustainability can reduce the overall environmental impact of anodized aluminum products by 15-25%, primarily through decreased energy consumption, reduced chemical usage, and minimized waste generation. This environmental performance enhancement represents a significant opportunity for manufacturers seeking to improve their sustainability credentials while maintaining product quality and durability.
Cold sealing alternatives, particularly nickel-based processes, present their own environmental challenges. Nickel compounds are classified as carcinogenic and pose risks to aquatic ecosystems when discharged in wastewater. Studies indicate that even at concentrations as low as 0.1 mg/L, nickel can adversely affect aquatic organisms, necessitating costly wastewater treatment systems.
Recent advancements in mid-temperature sealing technologies have demonstrated promising environmental benefits. These processes operate at 60-80°C, reducing energy consumption by approximately 40% compared to traditional hot water sealing while maintaining comparable durability performance. Additionally, the incorporation of biodegradable additives in these systems has shown potential for reducing the environmental persistence of chemical agents.
Water consumption represents another critical environmental consideration. Conventional sealing processes require 10-15 liters of water per square meter of anodized surface. Closed-loop water recycling systems have emerged as an effective solution, capable of reducing freshwater consumption by up to 80% while simultaneously minimizing wastewater discharge. Several manufacturers have reported significant cost savings following implementation of these systems, with payback periods typically ranging from 12-24 months.
The sustainability profile of sealing processes is further enhanced by recent innovations in chemical formulations. Vegetable-based sealants derived from renewable resources have demonstrated efficacy comparable to conventional options while reducing dependence on petrochemical derivatives. These bio-based alternatives typically decompose 60-70% faster than their synthetic counterparts when released into the environment.
Regulatory frameworks worldwide are increasingly emphasizing environmental performance in industrial processes. The European Union's Industrial Emissions Directive and similar regulations in North America and Asia have established stringent standards for wastewater quality and air emissions from anodizing facilities. Companies adopting more sustainable sealing technologies gain competitive advantages through regulatory compliance and access to environmentally conscious markets.
Life cycle assessment studies indicate that improvements in sealing process sustainability can reduce the overall environmental impact of anodized aluminum products by 15-25%, primarily through decreased energy consumption, reduced chemical usage, and minimized waste generation. This environmental performance enhancement represents a significant opportunity for manufacturers seeking to improve their sustainability credentials while maintaining product quality and durability.
Quality Control and Testing Standards for Sealed Anodized Surfaces
Quality control and testing standards play a crucial role in ensuring the effectiveness and reliability of sealed anodized aluminum surfaces. The industry has developed comprehensive testing methodologies that evaluate both the immediate quality of sealing processes and the long-term durability of treated surfaces. These standards have evolved significantly over the past decades, becoming increasingly sophisticated and precise.
The most widely recognized testing methods include the dye stain test (ISO 2143), which assesses sealing quality by measuring the absorption of specific dyes into the anodic film. A properly sealed surface will resist dye penetration, while inadequately sealed surfaces show visible staining. The acid dissolution test (ISO 3210) provides quantitative data on sealing quality by measuring weight loss after immersion in acidic solutions, with lower weight loss indicating superior sealing integrity.
For more demanding applications, salt spray testing (ASTM B117) evaluates corrosion resistance by exposing sealed surfaces to aggressive saline environments for extended periods. This test is particularly valuable for predicting performance in marine or coastal applications. Complementing these methods, accelerated weathering tests (ISO 11341) simulate years of environmental exposure through controlled UV radiation, temperature cycling, and moisture exposure.
Advanced analytical techniques have also been incorporated into quality control protocols. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) provides detailed insights into the electrochemical properties of sealed surfaces, allowing for early detection of potential sealing deficiencies. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) enables visual examination of pore structures at nanoscale resolution, confirming complete pore closure in properly sealed surfaces.
Industry standards vary by application sector, with aerospace (AMS 2471, AMS 2472) and architectural (AAMA 611) specifications being particularly stringent. These standards not only define acceptable test results but also prescribe specific testing frequencies and sampling methodologies to ensure statistical validity of quality assessments.
Recent developments in quality control include the integration of real-time monitoring systems that continuously evaluate sealing bath parameters such as pH, temperature, and chemical composition. These systems, coupled with statistical process control methodologies, enable manufacturers to detect and correct process deviations before they result in quality issues, significantly reducing rejection rates and improving overall process efficiency.
The most widely recognized testing methods include the dye stain test (ISO 2143), which assesses sealing quality by measuring the absorption of specific dyes into the anodic film. A properly sealed surface will resist dye penetration, while inadequately sealed surfaces show visible staining. The acid dissolution test (ISO 3210) provides quantitative data on sealing quality by measuring weight loss after immersion in acidic solutions, with lower weight loss indicating superior sealing integrity.
For more demanding applications, salt spray testing (ASTM B117) evaluates corrosion resistance by exposing sealed surfaces to aggressive saline environments for extended periods. This test is particularly valuable for predicting performance in marine or coastal applications. Complementing these methods, accelerated weathering tests (ISO 11341) simulate years of environmental exposure through controlled UV radiation, temperature cycling, and moisture exposure.
Advanced analytical techniques have also been incorporated into quality control protocols. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) provides detailed insights into the electrochemical properties of sealed surfaces, allowing for early detection of potential sealing deficiencies. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) enables visual examination of pore structures at nanoscale resolution, confirming complete pore closure in properly sealed surfaces.
Industry standards vary by application sector, with aerospace (AMS 2471, AMS 2472) and architectural (AAMA 611) specifications being particularly stringent. These standards not only define acceptable test results but also prescribe specific testing frequencies and sampling methodologies to ensure statistical validity of quality assessments.
Recent developments in quality control include the integration of real-time monitoring systems that continuously evaluate sealing bath parameters such as pH, temperature, and chemical composition. These systems, coupled with statistical process control methodologies, enable manufacturers to detect and correct process deviations before they result in quality issues, significantly reducing rejection rates and improving overall process efficiency.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!