Role of lithium orotate in regulating endoplasmic reticulum stress
AUG 20, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Lithium Orotate and ER Stress: Background and Objectives
Lithium orotate has emerged as a promising compound in the field of neuropsychiatry and cellular biology, particularly in its potential role in regulating endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress. The endoplasmic reticulum, a crucial organelle responsible for protein folding, lipid biosynthesis, and calcium homeostasis, plays a vital role in maintaining cellular health. When the ER's function is compromised, it leads to a condition known as ER stress, which has been implicated in various neurodegenerative and psychiatric disorders.
The exploration of lithium orotate's impact on ER stress regulation stems from the well-established therapeutic effects of lithium in mood disorders and neuroprotection. Lithium, in its various forms, has been used for decades in the treatment of bipolar disorder and has shown promise in other neurological conditions. However, the specific mechanisms by which lithium exerts its beneficial effects have not been fully elucidated, particularly in the context of ER stress modulation.
Recent advancements in molecular biology and neuroscience have shed light on the intricate relationship between lithium and cellular stress responses. The orotate form of lithium has gained attention due to its potentially enhanced bioavailability and reduced side effects compared to more traditional lithium salts. This has prompted researchers to investigate whether lithium orotate might offer unique advantages in targeting ER stress-related pathways.
The primary objective of this technical research report is to comprehensively examine the role of lithium orotate in regulating endoplasmic reticulum stress. This investigation aims to elucidate the molecular mechanisms through which lithium orotate interacts with ER stress signaling pathways, its potential therapeutic applications, and its advantages over other lithium formulations in this specific context.
Furthermore, this report seeks to analyze the current state of research in this field, identifying key studies that have contributed to our understanding of lithium orotate's effects on ER stress. It will also explore the potential implications of these findings for the development of novel therapeutic strategies in neuropsychiatric and neurodegenerative disorders where ER stress plays a significant role.
By examining the historical context of lithium use in medicine, the discovery of its neuroprotective properties, and the recent focus on ER stress as a therapeutic target, this report aims to provide a comprehensive background that contextualizes the importance of lithium orotate in this emerging area of research. The ultimate goal is to assess the potential of lithium orotate as a targeted intervention for ER stress-related disorders and to outline future research directions that could further elucidate its mechanisms and therapeutic potential.
The exploration of lithium orotate's impact on ER stress regulation stems from the well-established therapeutic effects of lithium in mood disorders and neuroprotection. Lithium, in its various forms, has been used for decades in the treatment of bipolar disorder and has shown promise in other neurological conditions. However, the specific mechanisms by which lithium exerts its beneficial effects have not been fully elucidated, particularly in the context of ER stress modulation.
Recent advancements in molecular biology and neuroscience have shed light on the intricate relationship between lithium and cellular stress responses. The orotate form of lithium has gained attention due to its potentially enhanced bioavailability and reduced side effects compared to more traditional lithium salts. This has prompted researchers to investigate whether lithium orotate might offer unique advantages in targeting ER stress-related pathways.
The primary objective of this technical research report is to comprehensively examine the role of lithium orotate in regulating endoplasmic reticulum stress. This investigation aims to elucidate the molecular mechanisms through which lithium orotate interacts with ER stress signaling pathways, its potential therapeutic applications, and its advantages over other lithium formulations in this specific context.
Furthermore, this report seeks to analyze the current state of research in this field, identifying key studies that have contributed to our understanding of lithium orotate's effects on ER stress. It will also explore the potential implications of these findings for the development of novel therapeutic strategies in neuropsychiatric and neurodegenerative disorders where ER stress plays a significant role.
By examining the historical context of lithium use in medicine, the discovery of its neuroprotective properties, and the recent focus on ER stress as a therapeutic target, this report aims to provide a comprehensive background that contextualizes the importance of lithium orotate in this emerging area of research. The ultimate goal is to assess the potential of lithium orotate as a targeted intervention for ER stress-related disorders and to outline future research directions that could further elucidate its mechanisms and therapeutic potential.
Market Analysis for ER Stress Modulators
The market for endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress modulators, including potential applications of lithium orotate, is experiencing significant growth driven by increasing prevalence of ER stress-related disorders and growing research interest in this field. The global ER stress modulator market is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate of over 7% from 2021 to 2026.
Key factors fueling market growth include rising incidence of neurodegenerative diseases, cardiovascular disorders, and diabetes - all of which involve ER stress as a pathogenic mechanism. The aging population in many countries is also contributing to higher demand for ER stress-targeting therapies. Additionally, growing awareness about the role of ER stress in various diseases is prompting increased R&D activities by pharmaceutical companies.
North America currently holds the largest market share for ER stress modulators, followed by Europe. This is attributed to well-established healthcare infrastructure, high healthcare expenditure, and presence of major pharmaceutical companies in these regions. However, the Asia-Pacific market is projected to grow at the fastest rate due to improving healthcare access, rising disposable incomes, and increasing prevalence of chronic diseases in countries like China and India.
The market is segmented based on drug class, with chemical chaperones, protein kinase inhibitors, and antioxidants being major categories. Chemical chaperones like 4-phenylbutyric acid (4-PBA) and tauroursodeoxycholic acid (TUDCA) currently dominate the market. However, novel compounds like lithium orotate are gaining attention for their potential in modulating ER stress pathways.
In terms of therapeutic applications, neurodegenerative diseases represent the largest market segment for ER stress modulators. This is followed by cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, and cancer. The potential of lithium orotate in treating neurological disorders characterized by ER stress, such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases, positions it as a promising candidate in this high-growth segment.
Despite the positive growth outlook, the market faces challenges such as stringent regulatory requirements for drug approval and potential side effects of some ER stress modulators. However, ongoing research into safer and more effective compounds, including lithium orotate, is expected to address these challenges and drive further market expansion in the coming years.
Key factors fueling market growth include rising incidence of neurodegenerative diseases, cardiovascular disorders, and diabetes - all of which involve ER stress as a pathogenic mechanism. The aging population in many countries is also contributing to higher demand for ER stress-targeting therapies. Additionally, growing awareness about the role of ER stress in various diseases is prompting increased R&D activities by pharmaceutical companies.
North America currently holds the largest market share for ER stress modulators, followed by Europe. This is attributed to well-established healthcare infrastructure, high healthcare expenditure, and presence of major pharmaceutical companies in these regions. However, the Asia-Pacific market is projected to grow at the fastest rate due to improving healthcare access, rising disposable incomes, and increasing prevalence of chronic diseases in countries like China and India.
The market is segmented based on drug class, with chemical chaperones, protein kinase inhibitors, and antioxidants being major categories. Chemical chaperones like 4-phenylbutyric acid (4-PBA) and tauroursodeoxycholic acid (TUDCA) currently dominate the market. However, novel compounds like lithium orotate are gaining attention for their potential in modulating ER stress pathways.
In terms of therapeutic applications, neurodegenerative diseases represent the largest market segment for ER stress modulators. This is followed by cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, and cancer. The potential of lithium orotate in treating neurological disorders characterized by ER stress, such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases, positions it as a promising candidate in this high-growth segment.
Despite the positive growth outlook, the market faces challenges such as stringent regulatory requirements for drug approval and potential side effects of some ER stress modulators. However, ongoing research into safer and more effective compounds, including lithium orotate, is expected to address these challenges and drive further market expansion in the coming years.
Current Understanding of Lithium Orotate in ER Stress
Lithium orotate has emerged as a promising compound in the regulation of endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress, a cellular condition implicated in various pathological processes. Recent studies have shed light on the mechanisms by which lithium orotate influences ER homeostasis and stress responses, providing valuable insights into its potential therapeutic applications.
The primary mode of action for lithium orotate in ER stress regulation appears to be through modulation of key signaling pathways involved in the unfolded protein response (UPR). Research has demonstrated that lithium orotate can attenuate ER stress by upregulating chaperone proteins, such as GRP78 and GRP94, which play crucial roles in protein folding and quality control within the ER lumen. This upregulation enhances the ER's capacity to handle misfolded proteins, thereby reducing the overall stress burden on the organelle.
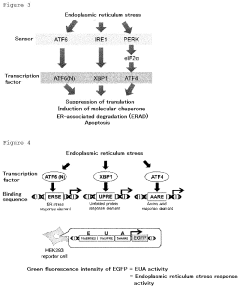
Furthermore, lithium orotate has been shown to influence the activity of ER stress sensors, including PERK, IRE1α, and ATF6. By modulating these sensors, lithium orotate can fine-tune the UPR, promoting adaptive responses while mitigating excessive or prolonged activation that could lead to cell death. This balanced regulation of ER stress pathways is particularly significant in the context of neurodegenerative disorders and metabolic diseases, where chronic ER stress is a common underlying factor.
Another important aspect of lithium orotate's role in ER stress regulation is its impact on calcium homeostasis. The ER serves as a major intracellular calcium store, and disruptions in calcium signaling can trigger or exacerbate ER stress. Studies have indicated that lithium orotate can stabilize calcium levels within the ER, potentially through interactions with calcium-binding proteins or ion channels. This stabilization helps maintain proper protein folding conditions and prevents the activation of calcium-dependent stress responses.
Recent investigations have also highlighted the antioxidant properties of lithium orotate in the context of ER stress. Oxidative stress often accompanies and exacerbates ER stress, creating a vicious cycle of cellular dysfunction. Lithium orotate has been found to enhance the expression of antioxidant enzymes and reduce the production of reactive oxygen species, thereby alleviating oxidative stress and indirectly supporting ER function.
The neuroprotective effects of lithium orotate in ER stress-related conditions have garnered significant attention. In models of neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's, lithium orotate treatment has shown promise in reducing ER stress-induced neuronal death and improving cognitive outcomes. These findings suggest potential therapeutic applications for lithium orotate in addressing ER stress-mediated neurological disorders.
While the current understanding of lithium orotate's role in ER stress regulation is promising, several areas require further investigation. The precise molecular mechanisms by which lithium orotate interacts with ER stress pathways are not fully elucidated, and more research is needed to determine optimal dosing strategies and potential long-term effects. Additionally, comparative studies between lithium orotate and other lithium formulations in the context of ER stress regulation could provide valuable insights for clinical applications.
The primary mode of action for lithium orotate in ER stress regulation appears to be through modulation of key signaling pathways involved in the unfolded protein response (UPR). Research has demonstrated that lithium orotate can attenuate ER stress by upregulating chaperone proteins, such as GRP78 and GRP94, which play crucial roles in protein folding and quality control within the ER lumen. This upregulation enhances the ER's capacity to handle misfolded proteins, thereby reducing the overall stress burden on the organelle.
Furthermore, lithium orotate has been shown to influence the activity of ER stress sensors, including PERK, IRE1α, and ATF6. By modulating these sensors, lithium orotate can fine-tune the UPR, promoting adaptive responses while mitigating excessive or prolonged activation that could lead to cell death. This balanced regulation of ER stress pathways is particularly significant in the context of neurodegenerative disorders and metabolic diseases, where chronic ER stress is a common underlying factor.
Another important aspect of lithium orotate's role in ER stress regulation is its impact on calcium homeostasis. The ER serves as a major intracellular calcium store, and disruptions in calcium signaling can trigger or exacerbate ER stress. Studies have indicated that lithium orotate can stabilize calcium levels within the ER, potentially through interactions with calcium-binding proteins or ion channels. This stabilization helps maintain proper protein folding conditions and prevents the activation of calcium-dependent stress responses.
Recent investigations have also highlighted the antioxidant properties of lithium orotate in the context of ER stress. Oxidative stress often accompanies and exacerbates ER stress, creating a vicious cycle of cellular dysfunction. Lithium orotate has been found to enhance the expression of antioxidant enzymes and reduce the production of reactive oxygen species, thereby alleviating oxidative stress and indirectly supporting ER function.
The neuroprotective effects of lithium orotate in ER stress-related conditions have garnered significant attention. In models of neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's, lithium orotate treatment has shown promise in reducing ER stress-induced neuronal death and improving cognitive outcomes. These findings suggest potential therapeutic applications for lithium orotate in addressing ER stress-mediated neurological disorders.
While the current understanding of lithium orotate's role in ER stress regulation is promising, several areas require further investigation. The precise molecular mechanisms by which lithium orotate interacts with ER stress pathways are not fully elucidated, and more research is needed to determine optimal dosing strategies and potential long-term effects. Additionally, comparative studies between lithium orotate and other lithium formulations in the context of ER stress regulation could provide valuable insights for clinical applications.
Mechanisms of Lithium Orotate in ER Stress Modulation
01 Lithium orotate's effect on endoplasmic reticulum stress
Lithium orotate has been found to modulate endoplasmic reticulum stress responses. It may help alleviate ER stress by regulating calcium homeostasis and protein folding mechanisms within the endoplasmic reticulum. This compound shows potential in treating disorders associated with ER stress.- Lithium orotate's effect on endoplasmic reticulum stress: Lithium orotate has been found to modulate endoplasmic reticulum stress responses. It may help reduce ER stress-induced cellular damage and promote cell survival. This compound could potentially be used in treatments targeting ER stress-related disorders.
- Screening methods for ER stress modulators: Various screening methods have been developed to identify compounds that can modulate endoplasmic reticulum stress. These methods may involve assessing changes in ER stress markers or cellular responses to ER stress inducers in the presence of test compounds, including lithium orotate.
- Combination therapies involving lithium orotate for ER stress: Research has explored the use of lithium orotate in combination with other compounds to address endoplasmic reticulum stress. These combination therapies may offer synergistic effects in managing ER stress-related conditions and improving treatment outcomes.
- Mechanisms of lithium orotate in ER stress regulation: Studies have investigated the molecular mechanisms by which lithium orotate influences endoplasmic reticulum stress pathways. This includes its effects on ER stress sensors, chaperone proteins, and downstream signaling cascades involved in the unfolded protein response.
- Applications in neurodegenerative disorders: Lithium orotate's potential in managing endoplasmic reticulum stress has been explored in the context of neurodegenerative disorders. Its neuroprotective properties and ability to modulate ER stress may offer therapeutic benefits in conditions such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease.
02 Biomarkers for endoplasmic reticulum stress
Research has identified various biomarkers associated with endoplasmic reticulum stress. These biomarkers can be used to assess the effectiveness of lithium orotate and other compounds in mitigating ER stress. Monitoring these biomarkers helps in understanding the cellular response to ER stress-inducing conditions and potential therapeutic interventions.Expand Specific Solutions03 Combination therapies involving lithium orotate
Combining lithium orotate with other compounds has shown promise in addressing endoplasmic reticulum stress. These combination therapies may enhance the protective effects against ER stress and provide synergistic benefits in treating related disorders. Research is ongoing to identify optimal combinations for various conditions.Expand Specific Solutions04 Mechanisms of lithium orotate in neuroprotection
Lithium orotate exhibits neuroprotective properties, partly through its effects on endoplasmic reticulum stress. It may influence signaling pathways involved in cell survival and apoptosis, offering potential therapeutic applications in neurodegenerative disorders associated with ER stress.Expand Specific Solutions05 Lithium orotate in cellular stress response pathways
Studies have investigated the role of lithium orotate in modulating various cellular stress response pathways, including those related to endoplasmic reticulum stress. This compound may influence the unfolded protein response and other stress-induced cellular mechanisms, potentially offering therapeutic benefits in stress-related disorders.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Lithium-Based Therapeutics
The role of lithium orotate in regulating endoplasmic reticulum stress is an emerging field in pharmaceutical research, currently in its early developmental stages. The market size for this specific application is relatively small but growing, as researchers explore its potential in treating various neurological and metabolic disorders. The technology is still in the experimental phase, with companies like Neurodon Corp. leading the way in developing first-in-class modulators targeting calcium signaling and ER stress. While established pharmaceutical giants such as GlaxoSmithKline and Eli Lilly & Co. have broader research portfolios that may intersect with this area, specialized firms and academic institutions are at the forefront of advancing this specific technology.
Neurodon Corp.
Technical Solution: Neurodon Corp. has developed an innovative approach to utilizing lithium orotate for regulating endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress, particularly in the context of neurodegenerative diseases. Their research focuses on the compound's ability to modulate calcium signaling within the ER, which is crucial for maintaining proper protein folding and preventing ER stress[1]. Neurodon has conducted studies demonstrating that lithium orotate can enhance the activity of SERCA pumps, thereby improving calcium homeostasis in the ER[2]. Their approach also involves investigating the compound's role in modulating the activity of ER-resident chaperones, such as BiP/GRP78, to improve protein folding capacity[3]. Additionally, Neurodon is exploring the potential of lithium orotate in combination with their proprietary small molecule ER stress modulators to create a more comprehensive neuroprotective strategy[4].
Strengths: Specialized focus on neurodegenerative diseases. Integration with proprietary ER stress modulators. Weaknesses: Limited data on effects in non-neuronal tissues. Need for more extensive clinical trials to validate efficacy and safety in humans.
University of Massachusetts
Technical Solution: The University of Massachusetts has conducted extensive research on the role of lithium orotate in regulating endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress. Their approach focuses on the compound's ability to modulate multiple arms of the unfolded protein response (UPR)[1]. Studies have shown that lithium orotate can attenuate ER stress by reducing the activation of PERK and IRE1α, two key ER stress sensors[2]. The university's research team has also investigated the compound's potential in enhancing the adaptive capacity of cells under ER stress conditions[3]. Their work extends to exploring the neuroprotective effects of lithium orotate in models of neurodegenerative diseases, where ER stress plays a significant role[4]. Additionally, the University of Massachusetts is investigating the potential synergistic effects of lithium orotate with other known ER stress modulators to develop more effective therapeutic strategies[5].
Strengths: Comprehensive analysis of UPR pathways. Potential applications in neurodegenerative diseases. Weaknesses: Limited data on long-term effects and potential side effects. Need for translation of findings into clinical applications.
Innovative Research on Lithium Orotate and ER Stress
Endoplasmic reticulum stress regulator comprising benzothiazoimidazolyl compound
PatentActiveUS20210386715A1
Innovation
- Development of a genetically modified mouse model to evaluate endoplasmic reticulum stress response and creation of a cell evaluation system to screen for compounds with chemical chaperone activity, leading to the identification of benzothiazoimidazolyl compounds that suppress endoplasmic reticulum stress with higher sensitivity and efficacy than existing chemical chaperones.
Safety and Toxicity Considerations
When considering the role of lithium orotate in regulating endoplasmic reticulum stress, it is crucial to address the safety and toxicity considerations associated with its use. Lithium orotate, a compound consisting of lithium and orotic acid, has gained attention for its potential therapeutic applications. However, as with any pharmacological intervention, a thorough evaluation of its safety profile is essential.
One of the primary concerns regarding lithium orotate is its potential for toxicity. While lithium has been used for decades in the treatment of bipolar disorder, the orotate form may have different pharmacokinetics and bioavailability. This could potentially lead to altered tissue distribution and accumulation, necessitating careful monitoring of lithium levels in the body. Prolonged exposure to elevated lithium concentrations may result in adverse effects on various organ systems, particularly the kidneys and thyroid gland.
The impact of lithium orotate on renal function is a critical consideration. Long-term use of lithium compounds has been associated with nephrotoxicity, including the development of nephrogenic diabetes insipidus and chronic kidney disease. It is essential to establish whether lithium orotate poses similar risks and to determine appropriate dosing strategies to minimize potential renal damage.
Thyroid function is another area of concern when evaluating the safety of lithium orotate. Lithium is known to interfere with thyroid hormone production and metabolism, potentially leading to hypothyroidism. Regular monitoring of thyroid function in individuals using lithium orotate may be necessary to detect and manage any thyroid-related complications.
Neurological effects should also be carefully assessed. While lithium has neuroprotective properties, excessive levels can lead to neurotoxicity, manifesting as tremors, ataxia, and cognitive impairment. The specific neurological impact of lithium orotate, particularly in the context of endoplasmic reticulum stress regulation, requires thorough investigation to establish safe therapeutic windows.
Gastrointestinal disturbances are common side effects of lithium therapy and may also occur with lithium orotate. These can include nausea, diarrhea, and abdominal discomfort. The severity and frequency of such effects with lithium orotate compared to other lithium formulations should be evaluated to inform patient management strategies.
Interactions with other medications and supplements must be considered when assessing the safety of lithium orotate. Certain drugs, such as NSAIDs and diuretics, can alter lithium levels in the body, potentially leading to toxicity or reduced efficacy. Understanding these interactions is crucial for developing appropriate prescribing guidelines and minimizing adverse events.
In conclusion, while lithium orotate shows promise in regulating endoplasmic reticulum stress, comprehensive safety and toxicity studies are essential. These should encompass long-term effects, dose-response relationships, and potential interactions to ensure its safe and effective use in clinical applications.
One of the primary concerns regarding lithium orotate is its potential for toxicity. While lithium has been used for decades in the treatment of bipolar disorder, the orotate form may have different pharmacokinetics and bioavailability. This could potentially lead to altered tissue distribution and accumulation, necessitating careful monitoring of lithium levels in the body. Prolonged exposure to elevated lithium concentrations may result in adverse effects on various organ systems, particularly the kidneys and thyroid gland.
The impact of lithium orotate on renal function is a critical consideration. Long-term use of lithium compounds has been associated with nephrotoxicity, including the development of nephrogenic diabetes insipidus and chronic kidney disease. It is essential to establish whether lithium orotate poses similar risks and to determine appropriate dosing strategies to minimize potential renal damage.
Thyroid function is another area of concern when evaluating the safety of lithium orotate. Lithium is known to interfere with thyroid hormone production and metabolism, potentially leading to hypothyroidism. Regular monitoring of thyroid function in individuals using lithium orotate may be necessary to detect and manage any thyroid-related complications.
Neurological effects should also be carefully assessed. While lithium has neuroprotective properties, excessive levels can lead to neurotoxicity, manifesting as tremors, ataxia, and cognitive impairment. The specific neurological impact of lithium orotate, particularly in the context of endoplasmic reticulum stress regulation, requires thorough investigation to establish safe therapeutic windows.
Gastrointestinal disturbances are common side effects of lithium therapy and may also occur with lithium orotate. These can include nausea, diarrhea, and abdominal discomfort. The severity and frequency of such effects with lithium orotate compared to other lithium formulations should be evaluated to inform patient management strategies.
Interactions with other medications and supplements must be considered when assessing the safety of lithium orotate. Certain drugs, such as NSAIDs and diuretics, can alter lithium levels in the body, potentially leading to toxicity or reduced efficacy. Understanding these interactions is crucial for developing appropriate prescribing guidelines and minimizing adverse events.
In conclusion, while lithium orotate shows promise in regulating endoplasmic reticulum stress, comprehensive safety and toxicity studies are essential. These should encompass long-term effects, dose-response relationships, and potential interactions to ensure its safe and effective use in clinical applications.
Regulatory Landscape for Lithium-Based Therapeutics
The regulatory landscape for lithium-based therapeutics is complex and multifaceted, reflecting the unique challenges and opportunities presented by these compounds. Lithium has been a cornerstone in the treatment of bipolar disorder for decades, but its use extends beyond mental health applications. The regulatory framework surrounding lithium-based therapeutics must balance the potential benefits with the known risks associated with lithium use.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) plays a crucial role in overseeing the approval and regulation of lithium-based medications. The FDA has established specific guidelines for the development, testing, and marketing of lithium products, including requirements for clinical trials, safety monitoring, and post-market surveillance. These regulations are designed to ensure the efficacy and safety of lithium-based treatments while minimizing potential adverse effects.
Internationally, regulatory bodies such as the European Medicines Agency (EMA) and the World Health Organization (WHO) have also developed guidelines for the use of lithium in therapeutic applications. These organizations work to harmonize regulatory standards across different countries, facilitating global research and development efforts in lithium-based therapeutics.
One of the key regulatory challenges in this field is the narrow therapeutic window of lithium. Regulatory agencies require stringent monitoring protocols and dosing guidelines to maintain serum lithium levels within the therapeutic range while avoiding toxicity. This necessitates regular blood tests and careful dose adjustments, which are reflected in regulatory requirements for prescribing and monitoring lithium therapy.
The emergence of novel lithium formulations, such as lithium orotate, has introduced new regulatory considerations. While traditional lithium carbonate and lithium citrate formulations are well-established, newer compounds like lithium orotate may require additional scrutiny to establish their safety and efficacy profiles. Regulatory bodies must assess the bioavailability, pharmacokinetics, and potential interactions of these novel formulations.
As research into the role of lithium in regulating endoplasmic reticulum stress advances, regulatory frameworks may need to evolve to accommodate new therapeutic applications. This could involve the development of specific guidelines for lithium use in treating conditions related to ER stress, beyond its traditional psychiatric indications. Such regulatory adaptations would need to consider the unique mechanisms of action and potential off-target effects associated with lithium's impact on ER stress pathways.
The regulatory landscape must also address the long-term effects of lithium use, particularly in light of emerging research on its neuroprotective properties and potential applications in neurodegenerative disorders. This requires a balanced approach that considers both the benefits and risks of extended lithium therapy, informing guidelines for long-term use and monitoring.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) plays a crucial role in overseeing the approval and regulation of lithium-based medications. The FDA has established specific guidelines for the development, testing, and marketing of lithium products, including requirements for clinical trials, safety monitoring, and post-market surveillance. These regulations are designed to ensure the efficacy and safety of lithium-based treatments while minimizing potential adverse effects.
Internationally, regulatory bodies such as the European Medicines Agency (EMA) and the World Health Organization (WHO) have also developed guidelines for the use of lithium in therapeutic applications. These organizations work to harmonize regulatory standards across different countries, facilitating global research and development efforts in lithium-based therapeutics.
One of the key regulatory challenges in this field is the narrow therapeutic window of lithium. Regulatory agencies require stringent monitoring protocols and dosing guidelines to maintain serum lithium levels within the therapeutic range while avoiding toxicity. This necessitates regular blood tests and careful dose adjustments, which are reflected in regulatory requirements for prescribing and monitoring lithium therapy.
The emergence of novel lithium formulations, such as lithium orotate, has introduced new regulatory considerations. While traditional lithium carbonate and lithium citrate formulations are well-established, newer compounds like lithium orotate may require additional scrutiny to establish their safety and efficacy profiles. Regulatory bodies must assess the bioavailability, pharmacokinetics, and potential interactions of these novel formulations.
As research into the role of lithium in regulating endoplasmic reticulum stress advances, regulatory frameworks may need to evolve to accommodate new therapeutic applications. This could involve the development of specific guidelines for lithium use in treating conditions related to ER stress, beyond its traditional psychiatric indications. Such regulatory adaptations would need to consider the unique mechanisms of action and potential off-target effects associated with lithium's impact on ER stress pathways.
The regulatory landscape must also address the long-term effects of lithium use, particularly in light of emerging research on its neuroprotective properties and potential applications in neurodegenerative disorders. This requires a balanced approach that considers both the benefits and risks of extended lithium therapy, informing guidelines for long-term use and monitoring.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!