Sodium Percarbonate in Food Processing: Safety Measures and Benefits
JUL 22, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Sodium Percarbonate Overview and Objectives
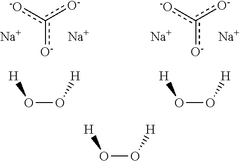
Sodium percarbonate, a white crystalline compound with the chemical formula 2Na2CO3·3H2O2, has emerged as a versatile and eco-friendly oxidizing agent in various industries, including food processing. This adduct of sodium carbonate and hydrogen peroxide has gained significant attention due to its unique properties and potential applications in ensuring food safety and quality.
The evolution of sodium percarbonate in the food processing industry can be traced back to the early 20th century when it was first synthesized. However, its widespread adoption in food-related applications has only gained momentum in recent decades. This surge in interest is primarily attributed to the growing demand for safer and more environmentally friendly alternatives to traditional chemical treatments in food processing.
As a powerful oxidizing agent, sodium percarbonate releases hydrogen peroxide when dissolved in water, making it an effective bleaching and disinfecting agent. In the context of food processing, this property has proven invaluable for sanitizing equipment, surfaces, and even certain food products. The compound's ability to decompose into harmless byproducts - water and oxygen - after use has further enhanced its appeal in an industry increasingly focused on sustainability and minimal environmental impact.
The primary objectives of utilizing sodium percarbonate in food processing are multifaceted. Firstly, it aims to enhance food safety by effectively eliminating harmful microorganisms and pathogens that may contaminate food products or processing equipment. Secondly, it seeks to improve the overall quality and shelf life of food products by preventing spoilage and maintaining freshness. Additionally, the use of sodium percarbonate aligns with the industry's growing emphasis on adopting more sustainable and environmentally friendly practices.
As the food processing industry continues to evolve, driven by consumer demands for safer, higher-quality products and stricter regulatory standards, the role of sodium percarbonate is expected to expand. Research and development efforts are ongoing to explore new applications and optimize existing processes involving this compound. These efforts aim to harness its full potential while addressing any potential limitations or safety concerns associated with its use in food-related contexts.
The technological trajectory of sodium percarbonate in food processing is closely intertwined with broader trends in the industry, such as the push for cleaner labels, reduced chemical usage, and improved sustainability. As such, understanding the current state and future potential of sodium percarbonate is crucial for stakeholders in the food processing sector, from manufacturers and researchers to regulatory bodies and consumers.
The evolution of sodium percarbonate in the food processing industry can be traced back to the early 20th century when it was first synthesized. However, its widespread adoption in food-related applications has only gained momentum in recent decades. This surge in interest is primarily attributed to the growing demand for safer and more environmentally friendly alternatives to traditional chemical treatments in food processing.
As a powerful oxidizing agent, sodium percarbonate releases hydrogen peroxide when dissolved in water, making it an effective bleaching and disinfecting agent. In the context of food processing, this property has proven invaluable for sanitizing equipment, surfaces, and even certain food products. The compound's ability to decompose into harmless byproducts - water and oxygen - after use has further enhanced its appeal in an industry increasingly focused on sustainability and minimal environmental impact.
The primary objectives of utilizing sodium percarbonate in food processing are multifaceted. Firstly, it aims to enhance food safety by effectively eliminating harmful microorganisms and pathogens that may contaminate food products or processing equipment. Secondly, it seeks to improve the overall quality and shelf life of food products by preventing spoilage and maintaining freshness. Additionally, the use of sodium percarbonate aligns with the industry's growing emphasis on adopting more sustainable and environmentally friendly practices.
As the food processing industry continues to evolve, driven by consumer demands for safer, higher-quality products and stricter regulatory standards, the role of sodium percarbonate is expected to expand. Research and development efforts are ongoing to explore new applications and optimize existing processes involving this compound. These efforts aim to harness its full potential while addressing any potential limitations or safety concerns associated with its use in food-related contexts.
The technological trajectory of sodium percarbonate in food processing is closely intertwined with broader trends in the industry, such as the push for cleaner labels, reduced chemical usage, and improved sustainability. As such, understanding the current state and future potential of sodium percarbonate is crucial for stakeholders in the food processing sector, from manufacturers and researchers to regulatory bodies and consumers.
Food Industry Demand Analysis
The food industry has shown a growing interest in sodium percarbonate as a versatile and effective food processing aid. This compound, also known as sodium carbonate peroxyhydrate, offers a unique combination of cleaning, bleaching, and antimicrobial properties that align well with the evolving needs of food manufacturers and processors.
Market analysis indicates a rising demand for sodium percarbonate in food processing applications, driven by several key factors. Firstly, there is an increasing consumer preference for clean-label products with minimal chemical additives. Sodium percarbonate, being a naturally derived compound that breaks down into harmless substances, fits well with this trend. It provides an alternative to traditional chlorine-based sanitizers and bleaching agents, which have faced scrutiny due to potential health and environmental concerns.
The global push for more sustainable and environmentally friendly food processing methods has also contributed to the growing interest in sodium percarbonate. As a biodegradable compound, it aligns with the industry's efforts to reduce its ecological footprint. This aspect has become particularly important as food companies face increasing pressure from consumers and regulatory bodies to adopt greener practices throughout their supply chains.
Furthermore, the food industry's focus on food safety and quality control has intensified the need for effective antimicrobial agents. Sodium percarbonate's ability to generate hydrogen peroxide, a potent antimicrobial agent, makes it an attractive option for sanitizing food contact surfaces and equipment. This property is particularly valuable in light of stringent food safety regulations and the need to prevent foodborne illnesses.
The dairy sector has emerged as a significant market for sodium percarbonate, particularly in cheese production and milk processing. Its effectiveness in removing milk residues and preventing biofilm formation on processing equipment has led to increased adoption. Similarly, the fruit and vegetable processing industry has shown growing interest in sodium percarbonate for its ability to extend shelf life and maintain product quality without leaving harmful residues.
Market projections suggest a steady growth in the demand for sodium percarbonate in food processing over the coming years. This growth is expected to be particularly strong in regions with stringent food safety regulations and a high consumer awareness of food quality and safety issues. North America and Europe are currently the leading markets, but rapid growth is anticipated in Asia-Pacific as food safety standards in the region continue to evolve.
However, the adoption of sodium percarbonate in food processing is not without challenges. Concerns about proper handling and storage, as well as the need for precise dosing to ensure efficacy without compromising food quality, have led to a demand for comprehensive training and safety protocols. This has created opportunities for companies offering specialized consulting and training services in the safe and effective use of sodium percarbonate in food processing environments.
Market analysis indicates a rising demand for sodium percarbonate in food processing applications, driven by several key factors. Firstly, there is an increasing consumer preference for clean-label products with minimal chemical additives. Sodium percarbonate, being a naturally derived compound that breaks down into harmless substances, fits well with this trend. It provides an alternative to traditional chlorine-based sanitizers and bleaching agents, which have faced scrutiny due to potential health and environmental concerns.
The global push for more sustainable and environmentally friendly food processing methods has also contributed to the growing interest in sodium percarbonate. As a biodegradable compound, it aligns with the industry's efforts to reduce its ecological footprint. This aspect has become particularly important as food companies face increasing pressure from consumers and regulatory bodies to adopt greener practices throughout their supply chains.
Furthermore, the food industry's focus on food safety and quality control has intensified the need for effective antimicrobial agents. Sodium percarbonate's ability to generate hydrogen peroxide, a potent antimicrobial agent, makes it an attractive option for sanitizing food contact surfaces and equipment. This property is particularly valuable in light of stringent food safety regulations and the need to prevent foodborne illnesses.
The dairy sector has emerged as a significant market for sodium percarbonate, particularly in cheese production and milk processing. Its effectiveness in removing milk residues and preventing biofilm formation on processing equipment has led to increased adoption. Similarly, the fruit and vegetable processing industry has shown growing interest in sodium percarbonate for its ability to extend shelf life and maintain product quality without leaving harmful residues.
Market projections suggest a steady growth in the demand for sodium percarbonate in food processing over the coming years. This growth is expected to be particularly strong in regions with stringent food safety regulations and a high consumer awareness of food quality and safety issues. North America and Europe are currently the leading markets, but rapid growth is anticipated in Asia-Pacific as food safety standards in the region continue to evolve.
However, the adoption of sodium percarbonate in food processing is not without challenges. Concerns about proper handling and storage, as well as the need for precise dosing to ensure efficacy without compromising food quality, have led to a demand for comprehensive training and safety protocols. This has created opportunities for companies offering specialized consulting and training services in the safe and effective use of sodium percarbonate in food processing environments.
Current Applications and Challenges
Sodium percarbonate, a compound of sodium carbonate and hydrogen peroxide, has gained significant traction in food processing applications due to its versatile properties as a bleaching agent, sanitizer, and oxidizing compound. Currently, it is widely used in the dairy industry for cleaning and sanitizing equipment, as well as in the production of baked goods as a dough conditioner and leavening agent.
In the meat and poultry processing sector, sodium percarbonate is employed as an antimicrobial agent, helping to reduce bacterial contamination and extend shelf life. Its effectiveness in removing biofilms from food contact surfaces has made it a popular choice for cleaning and sanitizing in various food processing facilities.
The beverage industry has also adopted sodium percarbonate for bottle washing and equipment cleaning, particularly in the production of carbonated drinks and beer. Its ability to break down organic matter and remove stubborn stains without leaving harmful residues has contributed to its widespread use.
Despite its numerous applications, the use of sodium percarbonate in food processing faces several challenges. One primary concern is the potential for residual hydrogen peroxide to remain on food surfaces, which could lead to off-flavors or undesirable chemical reactions in the final product. This necessitates careful monitoring and rinsing procedures to ensure complete removal of the compound after treatment.
Another challenge lies in maintaining the stability of sodium percarbonate during storage and use. The compound can decompose when exposed to moisture or high temperatures, reducing its effectiveness and potentially leading to inconsistent results in food processing applications. This requires proper storage conditions and handling protocols to be implemented throughout the supply chain.
The regulatory landscape surrounding sodium percarbonate usage in food processing varies across different regions, presenting a challenge for global food manufacturers. While it is generally recognized as safe (GRAS) by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, other countries may have different regulations or restrictions on its use, necessitating careful compliance management for international food producers.
Environmental concerns also pose a challenge, as the increased use of sodium percarbonate in food processing can lead to higher levels of sodium and peroxide in wastewater streams. This requires food processors to implement effective wastewater treatment systems to mitigate potential environmental impacts and comply with local discharge regulations.
As the food industry continues to seek more sustainable and efficient processing methods, research is ongoing to optimize the use of sodium percarbonate and address these challenges. This includes developing improved formulations for enhanced stability, exploring novel application techniques to minimize residual peroxide, and investigating synergistic combinations with other food-safe compounds to enhance its antimicrobial and cleaning properties.
In the meat and poultry processing sector, sodium percarbonate is employed as an antimicrobial agent, helping to reduce bacterial contamination and extend shelf life. Its effectiveness in removing biofilms from food contact surfaces has made it a popular choice for cleaning and sanitizing in various food processing facilities.
The beverage industry has also adopted sodium percarbonate for bottle washing and equipment cleaning, particularly in the production of carbonated drinks and beer. Its ability to break down organic matter and remove stubborn stains without leaving harmful residues has contributed to its widespread use.
Despite its numerous applications, the use of sodium percarbonate in food processing faces several challenges. One primary concern is the potential for residual hydrogen peroxide to remain on food surfaces, which could lead to off-flavors or undesirable chemical reactions in the final product. This necessitates careful monitoring and rinsing procedures to ensure complete removal of the compound after treatment.
Another challenge lies in maintaining the stability of sodium percarbonate during storage and use. The compound can decompose when exposed to moisture or high temperatures, reducing its effectiveness and potentially leading to inconsistent results in food processing applications. This requires proper storage conditions and handling protocols to be implemented throughout the supply chain.
The regulatory landscape surrounding sodium percarbonate usage in food processing varies across different regions, presenting a challenge for global food manufacturers. While it is generally recognized as safe (GRAS) by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, other countries may have different regulations or restrictions on its use, necessitating careful compliance management for international food producers.
Environmental concerns also pose a challenge, as the increased use of sodium percarbonate in food processing can lead to higher levels of sodium and peroxide in wastewater streams. This requires food processors to implement effective wastewater treatment systems to mitigate potential environmental impacts and comply with local discharge regulations.
As the food industry continues to seek more sustainable and efficient processing methods, research is ongoing to optimize the use of sodium percarbonate and address these challenges. This includes developing improved formulations for enhanced stability, exploring novel application techniques to minimize residual peroxide, and investigating synergistic combinations with other food-safe compounds to enhance its antimicrobial and cleaning properties.
Existing Safety Protocols for Sodium Percarbonate Use
01 Safety considerations in handling and storage
Sodium percarbonate requires careful handling and storage due to its oxidizing properties. Proper safety measures should be implemented to prevent accidents and ensure worker safety. This includes using appropriate personal protective equipment, storing in a cool, dry place away from combustible materials, and avoiding contact with acids or moisture.- Safety considerations in handling and storage: Sodium percarbonate requires careful handling and storage due to its oxidizing properties. Proper safety measures should be implemented to prevent accidents and ensure worker safety. This includes using appropriate personal protective equipment, storing in a cool, dry place away from combustible materials, and avoiding contact with acids or moisture.
- Environmental impact and biodegradability: Sodium percarbonate is considered environmentally friendly as it decomposes into oxygen, water, and sodium carbonate. Its biodegradability makes it a preferred choice in various applications. However, proper disposal methods should be followed to minimize any potential environmental impact.
- Stability and decomposition products: The stability of sodium percarbonate is an important safety consideration. Under certain conditions, it may decompose to release oxygen, which can accelerate the combustion of other materials. Understanding the factors affecting its stability and the nature of its decomposition products is crucial for safe handling and use.
- Use in consumer products and safety regulations: Sodium percarbonate is widely used in consumer products such as laundry detergents and cleaning agents. Safety regulations govern its use in these applications to ensure consumer safety. Proper labeling, packaging, and concentration limits are important aspects of its safe use in household products.
- Industrial safety measures and risk assessment: In industrial settings, comprehensive safety measures and risk assessments are necessary when working with sodium percarbonate. This includes implementing proper ventilation systems, emergency response procedures, and regular safety training for personnel. Conducting thorough risk assessments helps identify potential hazards and establish appropriate control measures.
02 Stability and decomposition
The stability of sodium percarbonate is an important safety consideration. Factors affecting its stability include temperature, humidity, and presence of impurities. Understanding the decomposition process and potential byproducts is crucial for safe handling and use. Stabilizers may be added to improve shelf life and reduce the risk of uncontrolled decomposition.Expand Specific Solutions03 Environmental and health impacts
Assessing the environmental and health impacts of sodium percarbonate is essential for its safe use. This includes evaluating its biodegradability, potential effects on aquatic life, and any risks associated with human exposure. Proper disposal methods should be employed to minimize environmental impact.Expand Specific Solutions04 Safety in consumer products
When used in consumer products such as laundry detergents or cleaning agents, the safety of sodium percarbonate must be carefully considered. This includes ensuring proper packaging, clear usage instructions, and appropriate warning labels. The concentration and formulation should be optimized to maintain efficacy while minimizing potential risks to users.Expand Specific Solutions05 Industrial safety measures
In industrial settings, comprehensive safety measures are required for the production, handling, and transportation of sodium percarbonate. This includes implementing proper ventilation systems, emergency response procedures, and regular safety training for personnel. Risk assessments should be conducted to identify and mitigate potential hazards associated with large-scale use of the compound.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Food Safety Solutions
The sodium percarbonate market in food processing is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demand for eco-friendly cleaning and sanitizing agents. The global market size is expanding, with projections indicating steady growth due to rising food safety concerns and stringent regulations. Technologically, sodium percarbonate is well-established, but innovations continue in formulation and application methods. Key players like Solvay SA, Evonik Operations GmbH, and Kemira Oyj are investing in R&D to enhance product efficiency and safety. Emerging companies such as Zhejiang Jinke Daily Chemical Co. Ltd. and Carus Corp. are also contributing to market competitiveness, focusing on specialized applications and regional markets. The industry is characterized by a mix of established multinational corporations and innovative smaller firms, fostering a dynamic competitive landscape.
Solvay SA
Technical Solution: Solvay SA has developed advanced sodium percarbonate production techniques, focusing on improving stability and efficacy for food processing applications. Their patented coating technology enhances the shelf life and performance of sodium percarbonate in various food processing environments[1]. The company has also implemented a controlled release mechanism, allowing for sustained antimicrobial activity throughout the food processing chain[2]. Solvay's sodium percarbonate formulations are designed to be effective at lower temperatures, reducing energy consumption in food processing operations while maintaining high sanitization standards[3].
Strengths: Advanced coating technology, controlled release mechanism, and energy-efficient formulations. Weaknesses: Potentially higher cost compared to traditional sanitizers, may require specialized handling and storage.
Cargill, Inc.
Technical Solution: Cargill has developed a proprietary sodium percarbonate-based sanitization system specifically tailored for the food processing industry. Their technology incorporates a multi-stage application process that maximizes the effectiveness of sodium percarbonate while minimizing residual chemicals in food products[4]. Cargill's system includes real-time monitoring of sanitizer levels and automated dosing mechanisms to ensure consistent and safe application throughout the food processing line[5]. Additionally, they have developed biodegradable stabilizers that enhance the stability of sodium percarbonate solutions in various food processing environments, extending its effective lifespan[6].
Strengths: Tailored for food industry, automated dosing and monitoring, enhanced stability with biodegradable additives. Weaknesses: May require significant initial investment in equipment and training.
Innovative Applications in Food Processing
Percarbonate compositions and uses thereof
PatentPendingUS20250041335A1
Innovation
- The administration of sodium percarbonate in oral doses of 2-10 grams, preferably in capsule form, has been found to increase endurance, strength, reduce lactic acid burn, and improve recovery from exercise without causing detrimental gastrointestinal effects.
Sodium percarbonate particles, process for their production, their use and detergent compositions containing them.
PatentInactiveEP1612186A1
Innovation
- Development of sodium percarbonate particles with a coating layer containing small sodium percarbonate particles and inorganic coating agents, such as sodium silicate or borate, to enhance stability, along with specific manufacturing processes that include drying and coating steps to maintain core particle size and moisture content.
Regulatory Framework for Food Additives
The regulatory framework for food additives plays a crucial role in ensuring the safety and efficacy of substances used in food processing, including sodium percarbonate. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) is the primary regulatory body responsible for overseeing food additives. The FDA's regulatory approach is based on the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (FD&C Act) and its subsequent amendments.
Under this framework, sodium percarbonate falls into the category of indirect food additives, as it is not intended to be directly added to food but may come into contact with food during processing. The FDA maintains a list of approved indirect food additives in the Code of Federal Regulations (CFR), Title 21, Part 178. Manufacturers must ensure that the use of sodium percarbonate complies with these regulations.
In the European Union, the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) is responsible for evaluating the safety of food additives. The use of food additives is regulated under Regulation (EC) No 1333/2008, which establishes a Union list of approved food additives. While sodium percarbonate is not directly listed as a food additive, its components (sodium carbonate and hydrogen peroxide) are subject to specific regulations.
The Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA) provides international standards for food additives. Although JECFA has not specifically evaluated sodium percarbonate, it has assessed the safety of its components. These assessments contribute to the global harmonization of food additive regulations.
Food processors using sodium percarbonate must adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMPs) as outlined in various regulatory frameworks. These practices ensure that the use of the substance does not result in adulteration of food products or pose safety risks to consumers. Additionally, manufacturers are required to maintain detailed records of the use of food additives and implement appropriate quality control measures.
Labeling requirements also form a significant part of the regulatory framework. In many jurisdictions, the presence of food additives, including those used in processing, must be declared on product labels. This transparency allows consumers to make informed choices about the products they purchase and consume.
As scientific knowledge advances and new data becomes available, regulatory bodies continuously review and update their guidelines. This dynamic process ensures that the regulatory framework remains current and effective in protecting public health while allowing for innovation in food processing technologies.
Under this framework, sodium percarbonate falls into the category of indirect food additives, as it is not intended to be directly added to food but may come into contact with food during processing. The FDA maintains a list of approved indirect food additives in the Code of Federal Regulations (CFR), Title 21, Part 178. Manufacturers must ensure that the use of sodium percarbonate complies with these regulations.
In the European Union, the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) is responsible for evaluating the safety of food additives. The use of food additives is regulated under Regulation (EC) No 1333/2008, which establishes a Union list of approved food additives. While sodium percarbonate is not directly listed as a food additive, its components (sodium carbonate and hydrogen peroxide) are subject to specific regulations.
The Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA) provides international standards for food additives. Although JECFA has not specifically evaluated sodium percarbonate, it has assessed the safety of its components. These assessments contribute to the global harmonization of food additive regulations.
Food processors using sodium percarbonate must adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMPs) as outlined in various regulatory frameworks. These practices ensure that the use of the substance does not result in adulteration of food products or pose safety risks to consumers. Additionally, manufacturers are required to maintain detailed records of the use of food additives and implement appropriate quality control measures.
Labeling requirements also form a significant part of the regulatory framework. In many jurisdictions, the presence of food additives, including those used in processing, must be declared on product labels. This transparency allows consumers to make informed choices about the products they purchase and consume.
As scientific knowledge advances and new data becomes available, regulatory bodies continuously review and update their guidelines. This dynamic process ensures that the regulatory framework remains current and effective in protecting public health while allowing for innovation in food processing technologies.
Environmental Impact Assessment
The use of sodium percarbonate in food processing has significant environmental implications that warrant careful consideration. This compound, when dissolved in water, releases hydrogen peroxide and sodium carbonate, both of which can impact the environment in various ways.
One of the primary environmental concerns associated with sodium percarbonate is its potential to alter aquatic ecosystems. When released into water bodies, the hydrogen peroxide component can affect the oxygen levels, potentially harming aquatic life. However, it's important to note that hydrogen peroxide quickly breaks down into water and oxygen, minimizing long-term effects.
The sodium carbonate component of sodium percarbonate can lead to increased alkalinity in water systems. This change in pH levels may disrupt the delicate balance of aquatic environments, affecting the growth and survival of certain species. However, the impact is generally localized and temporary, as natural buffering systems in water bodies tend to neutralize these effects over time.
On a positive note, sodium percarbonate is considered an environmentally friendly alternative to many harsher cleaning agents used in food processing. Its decomposition products are non-toxic and do not persist in the environment, reducing the overall ecological footprint of food processing operations.
The use of sodium percarbonate can also contribute to water conservation efforts in food processing. Its effectiveness as a cleaning and sanitizing agent often allows for reduced water usage in cleaning processes, thereby conserving this valuable resource and minimizing wastewater generation.
In terms of air quality, sodium percarbonate has minimal impact. Unlike some chemical cleaning agents, it does not release volatile organic compounds (VOCs) or other harmful gases during use, contributing to better air quality in food processing facilities and surrounding areas.
The production of sodium percarbonate does have some environmental considerations. The manufacturing process requires energy and resources, contributing to carbon emissions. However, advancements in production technologies have led to more efficient and environmentally friendly manufacturing methods, reducing the overall environmental impact.
Proper handling and disposal of sodium percarbonate and its solutions are crucial to minimize environmental risks. When used correctly and in appropriate concentrations, the environmental impact is generally low. However, accidental spills or improper disposal can lead to localized environmental issues, emphasizing the need for proper training and handling protocols in food processing facilities.
In conclusion, while sodium percarbonate use in food processing does have some environmental implications, its overall impact is relatively low compared to many alternative cleaning agents. The benefits of improved food safety and reduced water consumption often outweigh the potential environmental risks, especially when proper handling and disposal practices are implemented.
One of the primary environmental concerns associated with sodium percarbonate is its potential to alter aquatic ecosystems. When released into water bodies, the hydrogen peroxide component can affect the oxygen levels, potentially harming aquatic life. However, it's important to note that hydrogen peroxide quickly breaks down into water and oxygen, minimizing long-term effects.
The sodium carbonate component of sodium percarbonate can lead to increased alkalinity in water systems. This change in pH levels may disrupt the delicate balance of aquatic environments, affecting the growth and survival of certain species. However, the impact is generally localized and temporary, as natural buffering systems in water bodies tend to neutralize these effects over time.
On a positive note, sodium percarbonate is considered an environmentally friendly alternative to many harsher cleaning agents used in food processing. Its decomposition products are non-toxic and do not persist in the environment, reducing the overall ecological footprint of food processing operations.
The use of sodium percarbonate can also contribute to water conservation efforts in food processing. Its effectiveness as a cleaning and sanitizing agent often allows for reduced water usage in cleaning processes, thereby conserving this valuable resource and minimizing wastewater generation.
In terms of air quality, sodium percarbonate has minimal impact. Unlike some chemical cleaning agents, it does not release volatile organic compounds (VOCs) or other harmful gases during use, contributing to better air quality in food processing facilities and surrounding areas.
The production of sodium percarbonate does have some environmental considerations. The manufacturing process requires energy and resources, contributing to carbon emissions. However, advancements in production technologies have led to more efficient and environmentally friendly manufacturing methods, reducing the overall environmental impact.
Proper handling and disposal of sodium percarbonate and its solutions are crucial to minimize environmental risks. When used correctly and in appropriate concentrations, the environmental impact is generally low. However, accidental spills or improper disposal can lead to localized environmental issues, emphasizing the need for proper training and handling protocols in food processing facilities.
In conclusion, while sodium percarbonate use in food processing does have some environmental implications, its overall impact is relatively low compared to many alternative cleaning agents. The benefits of improved food safety and reduced water consumption often outweigh the potential environmental risks, especially when proper handling and disposal practices are implemented.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!