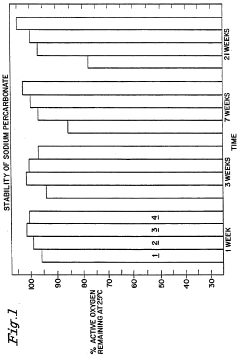
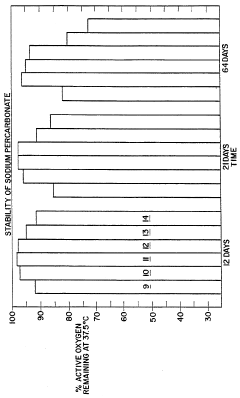
Sodium Percarbonate's Stabilizing Effect on Liquid Disinfectant Formulations
JUL 22, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Sodium Percarbonate Stabilization Background
Sodium percarbonate, a compound formed by the combination of sodium carbonate and hydrogen peroxide, has gained significant attention in the field of liquid disinfectant formulations due to its unique stabilizing properties. This adduct, also known as sodium carbonate peroxide, has been utilized in various cleaning and disinfecting applications for decades, but its role in stabilizing liquid disinfectant formulations represents a relatively recent development in the industry.
The journey of sodium percarbonate as a stabilizing agent began in the late 20th century when researchers and manufacturers started exploring more effective and environmentally friendly alternatives to traditional disinfectant formulations. The increasing demand for stable, long-lasting, and efficient disinfectant products drove the investigation into compounds that could enhance the shelf life and efficacy of liquid formulations without compromising their safety or environmental impact.
Sodium percarbonate's ability to release hydrogen peroxide in a controlled manner when dissolved in water made it an attractive candidate for stabilizing liquid disinfectants. This controlled release mechanism allows for a sustained disinfecting action, addressing one of the primary challenges in liquid formulations: maintaining long-term stability and effectiveness.
The evolution of sodium percarbonate's use in this context has been marked by several key developments. Initially, it was primarily used in powder form for laundry detergents and other cleaning products. However, as research progressed, scientists discovered its potential in liquid systems, particularly in enhancing the stability of active ingredients in disinfectant formulations.
One of the critical breakthroughs in this field was the development of encapsulation techniques for sodium percarbonate. These methods allowed for better control over the release of hydrogen peroxide, further improving its stabilizing effects in liquid environments. This innovation opened up new possibilities for incorporating sodium percarbonate into a wider range of liquid disinfectant products.
The growing emphasis on sustainable and eco-friendly cleaning solutions has further propelled the interest in sodium percarbonate. Its decomposition into harmless byproducts (water, oxygen, and sodium carbonate) aligns well with the increasing consumer demand for environmentally responsible products. This aspect has been a significant driver in the continued research and development efforts focused on optimizing sodium percarbonate's stabilizing effects in liquid disinfectant formulations.
As the technology continues to evolve, researchers are exploring new ways to enhance the synergy between sodium percarbonate and other components in liquid disinfectants. This ongoing work aims to develop more efficient, stable, and versatile formulations that can meet the diverse needs of various industries, from healthcare to household cleaning.
The journey of sodium percarbonate as a stabilizing agent began in the late 20th century when researchers and manufacturers started exploring more effective and environmentally friendly alternatives to traditional disinfectant formulations. The increasing demand for stable, long-lasting, and efficient disinfectant products drove the investigation into compounds that could enhance the shelf life and efficacy of liquid formulations without compromising their safety or environmental impact.
Sodium percarbonate's ability to release hydrogen peroxide in a controlled manner when dissolved in water made it an attractive candidate for stabilizing liquid disinfectants. This controlled release mechanism allows for a sustained disinfecting action, addressing one of the primary challenges in liquid formulations: maintaining long-term stability and effectiveness.
The evolution of sodium percarbonate's use in this context has been marked by several key developments. Initially, it was primarily used in powder form for laundry detergents and other cleaning products. However, as research progressed, scientists discovered its potential in liquid systems, particularly in enhancing the stability of active ingredients in disinfectant formulations.
One of the critical breakthroughs in this field was the development of encapsulation techniques for sodium percarbonate. These methods allowed for better control over the release of hydrogen peroxide, further improving its stabilizing effects in liquid environments. This innovation opened up new possibilities for incorporating sodium percarbonate into a wider range of liquid disinfectant products.
The growing emphasis on sustainable and eco-friendly cleaning solutions has further propelled the interest in sodium percarbonate. Its decomposition into harmless byproducts (water, oxygen, and sodium carbonate) aligns well with the increasing consumer demand for environmentally responsible products. This aspect has been a significant driver in the continued research and development efforts focused on optimizing sodium percarbonate's stabilizing effects in liquid disinfectant formulations.
As the technology continues to evolve, researchers are exploring new ways to enhance the synergy between sodium percarbonate and other components in liquid disinfectants. This ongoing work aims to develop more efficient, stable, and versatile formulations that can meet the diverse needs of various industries, from healthcare to household cleaning.
Market Analysis for Stable Liquid Disinfectants
The market for stable liquid disinfectants has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing awareness of hygiene and sanitation across various sectors. The global liquid disinfectant market was valued at approximately $3.5 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $5.8 billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of 7.5% during the forecast period.
The healthcare sector remains the largest consumer of stable liquid disinfectants, accounting for nearly 40% of the market share. Hospitals, clinics, and other healthcare facilities require reliable and long-lasting disinfectant solutions to maintain sterile environments and prevent healthcare-associated infections. The COVID-19 pandemic has further accelerated demand in this sector, with heightened focus on surface disinfection and infection control protocols.
The food and beverage industry is another significant market for stable liquid disinfectants, representing approximately 25% of the market share. Stringent food safety regulations and increasing consumer awareness of foodborne illnesses have driven the adoption of effective disinfection solutions in food processing facilities, restaurants, and commercial kitchens.
The household cleaning segment has also witnessed substantial growth, particularly in the wake of the global pandemic. Consumers are increasingly seeking powerful yet safe disinfectant products for home use, contributing to a market share of around 20%. This trend is expected to continue as hygiene habits formed during the pandemic become long-term behaviors.
Geographically, North America and Europe dominate the stable liquid disinfectant market, collectively accounting for over 60% of the global market share. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to exhibit the highest growth rate in the coming years, driven by rapid urbanization, increasing healthcare expenditure, and growing awareness of hygiene practices in emerging economies like China and India.
Key market drivers include the rising prevalence of infectious diseases, stringent regulations regarding sanitation and hygiene in various industries, and technological advancements in disinfectant formulations. The development of eco-friendly and biodegradable disinfectants is emerging as a significant trend, addressing growing environmental concerns and regulatory pressures.
Challenges in the market include the potential for antimicrobial resistance development, concerns over the safety of chemical disinfectants, and the need for products with broader spectrum efficacy against various pathogens. These factors are driving research and development efforts towards more innovative and sustainable disinfectant solutions.
The healthcare sector remains the largest consumer of stable liquid disinfectants, accounting for nearly 40% of the market share. Hospitals, clinics, and other healthcare facilities require reliable and long-lasting disinfectant solutions to maintain sterile environments and prevent healthcare-associated infections. The COVID-19 pandemic has further accelerated demand in this sector, with heightened focus on surface disinfection and infection control protocols.
The food and beverage industry is another significant market for stable liquid disinfectants, representing approximately 25% of the market share. Stringent food safety regulations and increasing consumer awareness of foodborne illnesses have driven the adoption of effective disinfection solutions in food processing facilities, restaurants, and commercial kitchens.
The household cleaning segment has also witnessed substantial growth, particularly in the wake of the global pandemic. Consumers are increasingly seeking powerful yet safe disinfectant products for home use, contributing to a market share of around 20%. This trend is expected to continue as hygiene habits formed during the pandemic become long-term behaviors.
Geographically, North America and Europe dominate the stable liquid disinfectant market, collectively accounting for over 60% of the global market share. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to exhibit the highest growth rate in the coming years, driven by rapid urbanization, increasing healthcare expenditure, and growing awareness of hygiene practices in emerging economies like China and India.
Key market drivers include the rising prevalence of infectious diseases, stringent regulations regarding sanitation and hygiene in various industries, and technological advancements in disinfectant formulations. The development of eco-friendly and biodegradable disinfectants is emerging as a significant trend, addressing growing environmental concerns and regulatory pressures.
Challenges in the market include the potential for antimicrobial resistance development, concerns over the safety of chemical disinfectants, and the need for products with broader spectrum efficacy against various pathogens. These factors are driving research and development efforts towards more innovative and sustainable disinfectant solutions.
Technical Challenges in Disinfectant Stabilization
The stabilization of liquid disinfectant formulations presents several technical challenges that researchers and manufacturers must overcome to ensure product efficacy and longevity. One of the primary issues is the inherent instability of active ingredients in aqueous solutions. Many disinfectant compounds, such as chlorine-based agents or hydrogen peroxide, tend to degrade over time when dissolved in water, leading to a reduction in antimicrobial potency.
Another significant challenge is the interaction between different components in the formulation. Stabilizers, surfactants, and other additives may react with the active ingredients, potentially neutralizing their disinfectant properties or creating unwanted by-products. This complexity requires careful selection and balancing of ingredients to maintain stability without compromising effectiveness.
pH control is crucial in disinfectant stabilization, as many active ingredients are sensitive to pH fluctuations. Maintaining an optimal pH range throughout the product's shelf life is challenging, especially when considering the diverse environmental conditions the product may encounter during storage and use.
Temperature sensitivity poses another hurdle in disinfectant stabilization. Many liquid formulations can degrade rapidly at elevated temperatures, while extremely low temperatures may cause separation or crystallization of components. Developing formulations that remain stable across a wide temperature range is essential for practical use and storage.
Packaging materials can also impact disinfectant stability. Certain plastics or metals may react with the active ingredients or allow permeation of gases, leading to degradation. Selecting appropriate packaging that maintains product integrity without introducing contaminants or catalyzing breakdown reactions is a critical consideration.
Microbial contamination of the product itself is a paradoxical challenge in disinfectant stabilization. While the formulation is designed to kill microorganisms, it must also resist colonization by resistant strains that could compromise its effectiveness or safety.
The demand for environmentally friendly and less toxic disinfectants introduces additional stabilization challenges. Green alternatives often have shorter shelf lives or are more susceptible to degradation, requiring innovative approaches to maintain their stability without resorting to harsh chemical stabilizers.
Achieving long-term stability while ensuring rapid activation upon use is another technical hurdle. Some disinfectants require a certain contact time to be effective, but must also remain stable during storage. Balancing these opposing requirements necessitates sophisticated formulation strategies.
In the context of sodium percarbonate's use in liquid disinfectant formulations, specific challenges arise due to its nature as a solid compound that releases hydrogen peroxide in aqueous solutions. Controlling the rate of decomposition and ensuring uniform distribution of the active oxygen species throughout the liquid medium are key areas of focus for researchers and formulators.
Another significant challenge is the interaction between different components in the formulation. Stabilizers, surfactants, and other additives may react with the active ingredients, potentially neutralizing their disinfectant properties or creating unwanted by-products. This complexity requires careful selection and balancing of ingredients to maintain stability without compromising effectiveness.
pH control is crucial in disinfectant stabilization, as many active ingredients are sensitive to pH fluctuations. Maintaining an optimal pH range throughout the product's shelf life is challenging, especially when considering the diverse environmental conditions the product may encounter during storage and use.
Temperature sensitivity poses another hurdle in disinfectant stabilization. Many liquid formulations can degrade rapidly at elevated temperatures, while extremely low temperatures may cause separation or crystallization of components. Developing formulations that remain stable across a wide temperature range is essential for practical use and storage.
Packaging materials can also impact disinfectant stability. Certain plastics or metals may react with the active ingredients or allow permeation of gases, leading to degradation. Selecting appropriate packaging that maintains product integrity without introducing contaminants or catalyzing breakdown reactions is a critical consideration.
Microbial contamination of the product itself is a paradoxical challenge in disinfectant stabilization. While the formulation is designed to kill microorganisms, it must also resist colonization by resistant strains that could compromise its effectiveness or safety.
The demand for environmentally friendly and less toxic disinfectants introduces additional stabilization challenges. Green alternatives often have shorter shelf lives or are more susceptible to degradation, requiring innovative approaches to maintain their stability without resorting to harsh chemical stabilizers.
Achieving long-term stability while ensuring rapid activation upon use is another technical hurdle. Some disinfectants require a certain contact time to be effective, but must also remain stable during storage. Balancing these opposing requirements necessitates sophisticated formulation strategies.
In the context of sodium percarbonate's use in liquid disinfectant formulations, specific challenges arise due to its nature as a solid compound that releases hydrogen peroxide in aqueous solutions. Controlling the rate of decomposition and ensuring uniform distribution of the active oxygen species throughout the liquid medium are key areas of focus for researchers and formulators.
Current Sodium Percarbonate Stabilization Techniques
01 Coating or encapsulation of sodium percarbonate
Stabilizing sodium percarbonate by coating or encapsulating it with various materials such as silicates, borates, or polymers. This protective layer helps prevent moisture absorption and premature decomposition, thereby enhancing the stability and shelf life of the compound.- Coating or encapsulation techniques: Stabilizing sodium percarbonate by coating or encapsulating it with various materials. This can include inorganic compounds, polymers, or other protective layers that prevent moisture from reaching the sodium percarbonate particles, thus enhancing their stability and shelf life.
- Addition of stabilizing agents: Incorporating specific stabilizing agents into the sodium percarbonate composition. These agents can include metal salts, silicates, or organic compounds that help to prevent decomposition and maintain the active oxygen content of sodium percarbonate during storage and use.
- Control of particle size and morphology: Optimizing the particle size distribution and morphology of sodium percarbonate crystals to improve stability. This can involve specific crystallization techniques or post-processing methods to achieve desired particle characteristics that enhance resistance to decomposition.
- Moisture control and packaging: Implementing strategies to control moisture exposure during production, storage, and packaging of sodium percarbonate. This may include using moisture-resistant packaging materials, adding desiccants, or controlling environmental conditions to minimize humidity exposure.
- Synergistic stabilization methods: Combining multiple stabilization techniques to achieve a synergistic effect on sodium percarbonate stability. This can involve using a combination of coating methods, stabilizing agents, and moisture control strategies to maximize the overall stability and shelf life of the product.
02 Addition of stabilizing agents
Incorporating specific stabilizing agents into sodium percarbonate formulations to improve its stability. These agents may include metal salts, organic compounds, or inorganic additives that help maintain the integrity of sodium percarbonate during storage and use.Expand Specific Solutions03 Control of particle size and morphology
Optimizing the particle size and shape of sodium percarbonate to enhance its stability. This may involve specific manufacturing processes or post-production treatments to achieve desired particle characteristics that contribute to improved stability.Expand Specific Solutions04 Moisture control and packaging
Implementing moisture control measures and specialized packaging techniques to protect sodium percarbonate from humidity and environmental factors. This may include the use of desiccants, moisture-resistant packaging materials, or specific storage conditions to maintain stability.Expand Specific Solutions05 Synergistic stabilization methods
Combining multiple stabilization techniques to achieve a synergistic effect on sodium percarbonate stability. This may involve using a combination of coating, additives, and process modifications to create a more robust and stable product.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Disinfectant Formulation Industry
The market for sodium percarbonate's stabilizing effect on liquid disinfectant formulations is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demand for effective and environmentally friendly cleaning solutions. The global market size is expanding, with key players like Solvay SA, Kemira Oyj, and Evonik Operations GmbH leading innovation. These companies are investing in R&D to enhance the technology's efficacy and stability. The technology's maturity is advancing, with companies like Zhejiang Jinke Daily Chemical Co. Ltd. and Henkel AG & Co. KGaA developing proprietary formulations. However, there's still room for improvement in long-term stability and compatibility with various disinfectant ingredients, indicating ongoing research opportunities in this competitive landscape.
Solvay SA
Technical Solution: Solvay SA has developed a stabilized sodium percarbonate formulation for liquid disinfectants. Their approach involves encapsulating sodium percarbonate particles with a protective layer, which prevents premature decomposition in aqueous environments. This technology utilizes a combination of inorganic and organic coating materials to create a barrier that is both water-resistant and permeable to active oxygen release[1]. The stabilized particles are designed to maintain their efficacy over extended periods, even in the presence of moisture and other destabilizing factors commonly found in liquid formulations[3].
Strengths: Enhanced stability in liquid formulations, prolonged shelf life, controlled release of active oxygen. Weaknesses: Potentially higher production costs, may require specialized manufacturing processes.
Kemira Oyj
Technical Solution: Kemira Oyj has innovated a stabilization technique for sodium percarbonate in liquid disinfectants using a proprietary blend of chelating agents and pH buffers. Their method involves creating a protective ionic environment around the percarbonate molecules, which inhibits their decomposition in aqueous solutions. This approach allows for a higher concentration of active ingredients in the final product while maintaining stability[2]. Kemira's formulation also incorporates surfactants that enhance the dispersion of sodium percarbonate particles, ensuring uniform distribution and efficacy throughout the liquid medium[4].
Strengths: High concentration of active ingredients, improved stability in various pH conditions. Weaknesses: May be sensitive to extreme temperature fluctuations, potential interactions with other formulation components.
Innovative Approaches in Percarbonate Stabilization
Stable sodium percarbonate formulation
PatentInactiveUS5374368A
Innovation
- A formulation comprising 55-90% polyalkylene glycol, 5-20% sodium percarbonate, 0.5-3% colloidal silica, 1-5% alkali metal pyrophosphate, and 0.2-1% water, with optional stabilizers like sodium silicate, magnesium silicate, or magnesium sulfate, enhances stability and maintains active oxygen release under ambient conditions.
Stabilised disinfectant composition, method for producing a stabilised disinfectant composition, disinfectant product, use of a composition and use of a product
PatentWO2015003233A1
Innovation
- A stabilized disinfectant composition comprising 1-6% hydrogen peroxide and 1-5% lactic acid, with added stabilizers, antifoams, and surfactants, particularly cationic quaternary ammonium compounds, which synergistically enhance biocidal action against a broad spectrum of microorganisms.
Environmental Impact of Stabilized Disinfectants
The stabilization of liquid disinfectant formulations using sodium percarbonate has significant environmental implications. This innovative approach not only enhances the efficacy and shelf life of disinfectants but also contributes to a more sustainable cleaning industry. By improving the stability of liquid disinfectants, sodium percarbonate reduces the need for frequent product replacements, thereby minimizing waste generation and resource consumption.
One of the primary environmental benefits of stabilized disinfectants is the reduction in packaging waste. As these formulations maintain their potency for extended periods, fewer containers are required over time, leading to a decrease in plastic and other packaging materials entering the waste stream. This reduction in packaging waste aligns with global efforts to combat plastic pollution and promote circular economy principles.
Furthermore, the enhanced stability of these disinfectants results in lower transportation requirements. With products lasting longer, the frequency of shipments from manufacturers to retailers and end-users decreases, contributing to reduced carbon emissions associated with transportation. This aspect is particularly significant in the context of global efforts to mitigate climate change and reduce the carbon footprint of consumer goods.
The use of sodium percarbonate as a stabilizing agent also offers environmental advantages over traditional stabilizers. Being a derivative of hydrogen peroxide, sodium percarbonate breaks down into harmless byproducts – water and oxygen – when released into the environment. This characteristic makes it a more eco-friendly alternative to conventional stabilizers that may persist in ecosystems or contribute to water pollution.
Additionally, the improved stability of disinfectants leads to more efficient use of active ingredients. By preventing premature degradation, these formulations ensure that the full potential of the disinfectant is realized, reducing the overall quantity of chemicals needed for effective sanitation. This efficiency not only conserves resources but also minimizes the release of potentially harmful substances into the environment.
The environmental impact extends to water treatment processes as well. Stabilized disinfectants are less likely to lose their efficacy during storage, resulting in more consistent and reliable disinfection performance. This reliability can lead to optimized water treatment protocols, potentially reducing the overall chemical load in treated water systems and minimizing the environmental impact of water treatment facilities.
In conclusion, the stabilization of liquid disinfectants using sodium percarbonate represents a significant step towards more environmentally friendly cleaning solutions. By addressing issues of product longevity, waste reduction, and chemical efficiency, this technology contributes to the broader goals of environmental sustainability in the cleaning and sanitation industry.
One of the primary environmental benefits of stabilized disinfectants is the reduction in packaging waste. As these formulations maintain their potency for extended periods, fewer containers are required over time, leading to a decrease in plastic and other packaging materials entering the waste stream. This reduction in packaging waste aligns with global efforts to combat plastic pollution and promote circular economy principles.
Furthermore, the enhanced stability of these disinfectants results in lower transportation requirements. With products lasting longer, the frequency of shipments from manufacturers to retailers and end-users decreases, contributing to reduced carbon emissions associated with transportation. This aspect is particularly significant in the context of global efforts to mitigate climate change and reduce the carbon footprint of consumer goods.
The use of sodium percarbonate as a stabilizing agent also offers environmental advantages over traditional stabilizers. Being a derivative of hydrogen peroxide, sodium percarbonate breaks down into harmless byproducts – water and oxygen – when released into the environment. This characteristic makes it a more eco-friendly alternative to conventional stabilizers that may persist in ecosystems or contribute to water pollution.
Additionally, the improved stability of disinfectants leads to more efficient use of active ingredients. By preventing premature degradation, these formulations ensure that the full potential of the disinfectant is realized, reducing the overall quantity of chemicals needed for effective sanitation. This efficiency not only conserves resources but also minimizes the release of potentially harmful substances into the environment.
The environmental impact extends to water treatment processes as well. Stabilized disinfectants are less likely to lose their efficacy during storage, resulting in more consistent and reliable disinfection performance. This reliability can lead to optimized water treatment protocols, potentially reducing the overall chemical load in treated water systems and minimizing the environmental impact of water treatment facilities.
In conclusion, the stabilization of liquid disinfectants using sodium percarbonate represents a significant step towards more environmentally friendly cleaning solutions. By addressing issues of product longevity, waste reduction, and chemical efficiency, this technology contributes to the broader goals of environmental sustainability in the cleaning and sanitation industry.
Regulatory Framework for Disinfectant Formulations
The regulatory framework for disinfectant formulations plays a crucial role in ensuring the safety and efficacy of products containing sodium percarbonate as a stabilizing agent. In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) is the primary regulatory body overseeing disinfectants under the Federal Insecticide, Fungicide, and Rodenticide Act (FIFRA). The EPA requires manufacturers to register their products and provide extensive data on their composition, efficacy, and safety.
For liquid disinfectant formulations containing sodium percarbonate, manufacturers must demonstrate compliance with specific guidelines related to active ingredient stability, shelf life, and performance under various environmental conditions. The EPA's Antimicrobial Division reviews these submissions, focusing on the product's ability to maintain its disinfectant properties over time.
In the European Union, the Biocidal Products Regulation (BPR) governs the authorization of disinfectants. The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) oversees the implementation of this regulation, which requires a thorough assessment of the product's active substances and their potential risks to human health and the environment. Sodium percarbonate, when used as a stabilizer in liquid disinfectants, must be evaluated for its impact on the overall formulation's safety and efficacy.
The regulatory landscape also includes international standards set by organizations such as the World Health Organization (WHO) and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). These standards provide guidelines for testing methods and performance criteria that manufacturers must adhere to when developing and marketing disinfectant products.
In Japan, the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare regulates disinfectants under the Pharmaceutical Affairs Law. Products containing sodium percarbonate as a stabilizer must undergo rigorous testing to ensure they meet the country's strict safety and efficacy standards. Similarly, in Canada, Health Canada's Pest Management Regulatory Agency (PMRA) oversees the registration of disinfectants, including those with sodium percarbonate, under the Pest Control Products Act.
Globally, there is a trend towards harmonization of regulatory requirements for disinfectants. Initiatives such as the Global Harmonization Task Force aim to streamline approval processes and reduce redundant testing across different jurisdictions. This harmonization effort is particularly relevant for innovative formulations utilizing sodium percarbonate, as it may facilitate faster market entry in multiple regions.
Manufacturers must also consider specific regulations related to labeling, packaging, and transportation of disinfectant products containing sodium percarbonate. These regulations often vary by country and may include requirements for hazard symbols, safety data sheets, and proper storage instructions.
For liquid disinfectant formulations containing sodium percarbonate, manufacturers must demonstrate compliance with specific guidelines related to active ingredient stability, shelf life, and performance under various environmental conditions. The EPA's Antimicrobial Division reviews these submissions, focusing on the product's ability to maintain its disinfectant properties over time.
In the European Union, the Biocidal Products Regulation (BPR) governs the authorization of disinfectants. The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) oversees the implementation of this regulation, which requires a thorough assessment of the product's active substances and their potential risks to human health and the environment. Sodium percarbonate, when used as a stabilizer in liquid disinfectants, must be evaluated for its impact on the overall formulation's safety and efficacy.
The regulatory landscape also includes international standards set by organizations such as the World Health Organization (WHO) and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). These standards provide guidelines for testing methods and performance criteria that manufacturers must adhere to when developing and marketing disinfectant products.
In Japan, the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare regulates disinfectants under the Pharmaceutical Affairs Law. Products containing sodium percarbonate as a stabilizer must undergo rigorous testing to ensure they meet the country's strict safety and efficacy standards. Similarly, in Canada, Health Canada's Pest Management Regulatory Agency (PMRA) oversees the registration of disinfectants, including those with sodium percarbonate, under the Pest Control Products Act.
Globally, there is a trend towards harmonization of regulatory requirements for disinfectants. Initiatives such as the Global Harmonization Task Force aim to streamline approval processes and reduce redundant testing across different jurisdictions. This harmonization effort is particularly relevant for innovative formulations utilizing sodium percarbonate, as it may facilitate faster market entry in multiple regions.
Manufacturers must also consider specific regulations related to labeling, packaging, and transportation of disinfectant products containing sodium percarbonate. These regulations often vary by country and may include requirements for hazard symbols, safety data sheets, and proper storage instructions.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!