Sodium Percarbonate: Stability Enhancement in Powdered Detergents
JUL 22, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Sodium Percarbonate Evolution and Objectives
Sodium percarbonate, a key component in powdered detergents, has undergone significant evolution since its introduction in the early 20th century. Initially developed as a stable source of hydrogen peroxide, its journey in the laundry industry has been marked by continuous improvements in stability and efficacy.
The evolution of sodium percarbonate began with its synthesis and initial applications in bleaching and cleaning products. Early formulations faced challenges related to stability, particularly in the presence of moisture and metal ions commonly found in detergent formulations. These issues led to reduced shelf life and diminished cleaning performance, prompting researchers to focus on enhancing its stability.
Throughout the mid-20th century, advancements in coating technologies emerged as a pivotal turning point. The development of various coating materials, such as silicates and borates, significantly improved the stability of sodium percarbonate in detergent matrices. These coatings acted as protective barriers, shielding the compound from premature decomposition and extending its shelf life.
The late 20th and early 21st centuries saw a shift towards more environmentally friendly and efficient formulations. This period witnessed the introduction of advanced stabilization techniques, including the use of chelating agents and pH buffers, which further enhanced the stability of sodium percarbonate in diverse detergent formulations.
Recent years have brought about a focus on nanotechnology and smart delivery systems. These innovations aim to not only stabilize sodium percarbonate but also to control its release during the washing process, optimizing its bleaching and cleaning efficacy.
The primary objective in the ongoing evolution of sodium percarbonate stability is to develop formulations that maintain the compound's efficacy under various storage conditions and throughout the product's shelf life. This includes enhancing resistance to humidity, temperature fluctuations, and the presence of catalytic impurities in detergent formulations.
Another crucial goal is to improve the compatibility of sodium percarbonate with other detergent ingredients, particularly enzymes and fragrances, which can be sensitive to oxidation. Achieving this balance is essential for creating high-performance, multi-functional detergent products that meet consumer expectations for cleaning power and freshness.
Furthermore, there is a growing emphasis on developing eco-friendly stabilization methods that align with the increasing demand for sustainable and biodegradable cleaning products. This objective drives research into natural and renewable stabilizers that can replace synthetic alternatives without compromising on performance or cost-effectiveness.
The evolution of sodium percarbonate began with its synthesis and initial applications in bleaching and cleaning products. Early formulations faced challenges related to stability, particularly in the presence of moisture and metal ions commonly found in detergent formulations. These issues led to reduced shelf life and diminished cleaning performance, prompting researchers to focus on enhancing its stability.
Throughout the mid-20th century, advancements in coating technologies emerged as a pivotal turning point. The development of various coating materials, such as silicates and borates, significantly improved the stability of sodium percarbonate in detergent matrices. These coatings acted as protective barriers, shielding the compound from premature decomposition and extending its shelf life.
The late 20th and early 21st centuries saw a shift towards more environmentally friendly and efficient formulations. This period witnessed the introduction of advanced stabilization techniques, including the use of chelating agents and pH buffers, which further enhanced the stability of sodium percarbonate in diverse detergent formulations.
Recent years have brought about a focus on nanotechnology and smart delivery systems. These innovations aim to not only stabilize sodium percarbonate but also to control its release during the washing process, optimizing its bleaching and cleaning efficacy.
The primary objective in the ongoing evolution of sodium percarbonate stability is to develop formulations that maintain the compound's efficacy under various storage conditions and throughout the product's shelf life. This includes enhancing resistance to humidity, temperature fluctuations, and the presence of catalytic impurities in detergent formulations.
Another crucial goal is to improve the compatibility of sodium percarbonate with other detergent ingredients, particularly enzymes and fragrances, which can be sensitive to oxidation. Achieving this balance is essential for creating high-performance, multi-functional detergent products that meet consumer expectations for cleaning power and freshness.
Furthermore, there is a growing emphasis on developing eco-friendly stabilization methods that align with the increasing demand for sustainable and biodegradable cleaning products. This objective drives research into natural and renewable stabilizers that can replace synthetic alternatives without compromising on performance or cost-effectiveness.
Market Analysis for Stable Detergent Formulations
The global market for stable detergent formulations has been experiencing steady growth, driven by increasing consumer demand for effective and long-lasting cleaning products. The powdered detergent segment, in particular, has shown resilience despite the rising popularity of liquid detergents. This can be attributed to the cost-effectiveness and convenience of powdered formulations, especially in developing markets.
Sodium percarbonate, a key ingredient in many powdered detergents, plays a crucial role in the market dynamics. Its ability to release oxygen and act as a bleaching agent makes it highly desirable for consumers seeking powerful stain removal properties. However, the stability issues associated with sodium percarbonate have created both challenges and opportunities within the industry.
Market research indicates that consumers are increasingly prioritizing product efficacy and shelf life when making purchasing decisions. This trend has led to a growing demand for detergent formulations that can maintain their potency over extended periods, even in challenging storage conditions. Manufacturers who can successfully address the stability concerns of sodium percarbonate stand to gain a significant competitive advantage in this evolving market landscape.
The Asia-Pacific region has emerged as a key growth area for stable detergent formulations, with rapidly expanding middle-class populations driving increased consumption. North America and Europe, while more mature markets, continue to show steady demand for high-performance, stable detergent products. This global distribution of demand underscores the importance of developing robust formulations that can withstand various environmental conditions and transportation challenges.
Environmental concerns and sustainability initiatives are also shaping market trends. Consumers are increasingly seeking eco-friendly options, which has led to a growing interest in concentrated detergent formulations. These products not only reduce packaging waste but also require enhanced stability to maintain their effectiveness in smaller quantities.
The competitive landscape of the stable detergent formulation market is characterized by a mix of multinational corporations and regional players. Major companies are investing heavily in research and development to overcome the stability challenges associated with sodium percarbonate and other active ingredients. This has led to a surge in patent filings and collaborations between detergent manufacturers and chemical suppliers.
In conclusion, the market analysis for stable detergent formulations reveals a dynamic and growing sector with significant opportunities for innovation. The ability to enhance the stability of sodium percarbonate in powdered detergents is poised to be a key differentiator in this competitive landscape, driving both consumer satisfaction and market share growth for successful manufacturers.
Sodium percarbonate, a key ingredient in many powdered detergents, plays a crucial role in the market dynamics. Its ability to release oxygen and act as a bleaching agent makes it highly desirable for consumers seeking powerful stain removal properties. However, the stability issues associated with sodium percarbonate have created both challenges and opportunities within the industry.
Market research indicates that consumers are increasingly prioritizing product efficacy and shelf life when making purchasing decisions. This trend has led to a growing demand for detergent formulations that can maintain their potency over extended periods, even in challenging storage conditions. Manufacturers who can successfully address the stability concerns of sodium percarbonate stand to gain a significant competitive advantage in this evolving market landscape.
The Asia-Pacific region has emerged as a key growth area for stable detergent formulations, with rapidly expanding middle-class populations driving increased consumption. North America and Europe, while more mature markets, continue to show steady demand for high-performance, stable detergent products. This global distribution of demand underscores the importance of developing robust formulations that can withstand various environmental conditions and transportation challenges.
Environmental concerns and sustainability initiatives are also shaping market trends. Consumers are increasingly seeking eco-friendly options, which has led to a growing interest in concentrated detergent formulations. These products not only reduce packaging waste but also require enhanced stability to maintain their effectiveness in smaller quantities.
The competitive landscape of the stable detergent formulation market is characterized by a mix of multinational corporations and regional players. Major companies are investing heavily in research and development to overcome the stability challenges associated with sodium percarbonate and other active ingredients. This has led to a surge in patent filings and collaborations between detergent manufacturers and chemical suppliers.
In conclusion, the market analysis for stable detergent formulations reveals a dynamic and growing sector with significant opportunities for innovation. The ability to enhance the stability of sodium percarbonate in powdered detergents is poised to be a key differentiator in this competitive landscape, driving both consumer satisfaction and market share growth for successful manufacturers.
Current Challenges in Sodium Percarbonate Stability
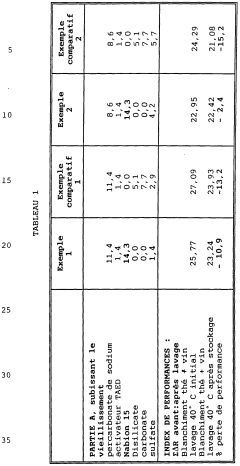
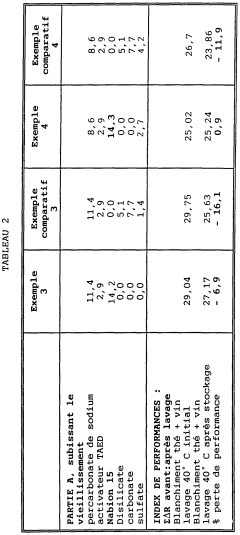
Sodium percarbonate, a key ingredient in many powdered detergents, faces several stability challenges that hinder its effectiveness and shelf life. One of the primary issues is its susceptibility to moisture-induced decomposition. When exposed to even small amounts of humidity, sodium percarbonate can break down prematurely, releasing hydrogen peroxide and sodium carbonate. This not only reduces the cleaning power of the detergent but also leads to caking and clumping of the powder, making it difficult to dispense and use.
Another significant challenge is the thermal instability of sodium percarbonate. High temperatures, which can occur during storage or transportation, accelerate the decomposition process. This thermal sensitivity limits the geographical regions where sodium percarbonate-based detergents can be effectively distributed and stored without significant loss of active oxygen content.
The presence of metal ions, particularly transition metals like iron and copper, poses a further stability issue. These ions can catalyze the decomposition of sodium percarbonate, leading to a rapid loss of its bleaching and cleaning capabilities. This is particularly problematic in hard water areas or when the detergent comes into contact with metal surfaces during use or storage.
Particle size and morphology of sodium percarbonate also play a crucial role in its stability. Finer particles, while offering better dissolution rates, are more prone to degradation due to their increased surface area. Conversely, larger particles may be more stable but can compromise the overall performance of the detergent.
The interaction between sodium percarbonate and other detergent components presents additional challenges. Some surfactants and enzymes commonly used in detergent formulations can negatively impact the stability of sodium percarbonate. Finding the right balance of ingredients that maintain cleaning efficacy without compromising stability is an ongoing challenge for detergent manufacturers.
Packaging materials and conditions also significantly affect sodium percarbonate stability. Inadequate moisture barriers or packaging that allows light penetration can accelerate decomposition. This necessitates careful consideration of packaging design and materials, which can add to production costs and environmental concerns.
Lastly, the environmental and regulatory landscape poses challenges to sodium percarbonate stability enhancement. As consumers and regulators demand more environmentally friendly products, traditional stabilizing additives may need to be replaced with greener alternatives, potentially compromising the established stability profiles of existing formulations.
Another significant challenge is the thermal instability of sodium percarbonate. High temperatures, which can occur during storage or transportation, accelerate the decomposition process. This thermal sensitivity limits the geographical regions where sodium percarbonate-based detergents can be effectively distributed and stored without significant loss of active oxygen content.
The presence of metal ions, particularly transition metals like iron and copper, poses a further stability issue. These ions can catalyze the decomposition of sodium percarbonate, leading to a rapid loss of its bleaching and cleaning capabilities. This is particularly problematic in hard water areas or when the detergent comes into contact with metal surfaces during use or storage.
Particle size and morphology of sodium percarbonate also play a crucial role in its stability. Finer particles, while offering better dissolution rates, are more prone to degradation due to their increased surface area. Conversely, larger particles may be more stable but can compromise the overall performance of the detergent.
The interaction between sodium percarbonate and other detergent components presents additional challenges. Some surfactants and enzymes commonly used in detergent formulations can negatively impact the stability of sodium percarbonate. Finding the right balance of ingredients that maintain cleaning efficacy without compromising stability is an ongoing challenge for detergent manufacturers.
Packaging materials and conditions also significantly affect sodium percarbonate stability. Inadequate moisture barriers or packaging that allows light penetration can accelerate decomposition. This necessitates careful consideration of packaging design and materials, which can add to production costs and environmental concerns.
Lastly, the environmental and regulatory landscape poses challenges to sodium percarbonate stability enhancement. As consumers and regulators demand more environmentally friendly products, traditional stabilizing additives may need to be replaced with greener alternatives, potentially compromising the established stability profiles of existing formulations.
Existing Stabilization Techniques for Sodium Percarbonate
01 Coating and encapsulation techniques
Various coating and encapsulation methods are employed to enhance the stability of sodium percarbonate. These techniques involve applying protective layers or encapsulating the particles to shield them from moisture and other destabilizing factors. This approach significantly improves the shelf life and effectiveness of sodium percarbonate in various applications.- Coating and encapsulation techniques: Various coating and encapsulation methods are used to improve the stability of sodium percarbonate. These techniques involve applying protective layers or encapsulating the particles to prevent moisture absorption and decomposition. Common materials used for coating include silicates, borates, and organic polymers. These methods help to maintain the effectiveness of sodium percarbonate in various applications.
- Stabilizing additives: The addition of specific stabilizing agents can significantly enhance the stability of sodium percarbonate. These additives include inorganic compounds such as magnesium silicate, sodium silicate, and boric acid, as well as organic compounds like carboxymethyl cellulose. These stabilizers work by reducing moisture absorption, preventing decomposition, and maintaining the active oxygen content of sodium percarbonate.
- Particle size and shape optimization: Controlling the particle size and shape of sodium percarbonate can improve its stability. Smaller particles with a more uniform shape tend to have better stability due to reduced surface area and improved packing. Techniques such as spray drying, fluidized bed granulation, and extrusion can be used to produce particles with optimal size and shape characteristics for enhanced stability.
- Moisture control and packaging: Effective moisture control during production, storage, and packaging is crucial for maintaining sodium percarbonate stability. This includes using low-humidity environments during manufacturing, incorporating desiccants in packaging, and using moisture-resistant packaging materials. Proper packaging techniques help prevent moisture absorption and maintain the product's effectiveness over time.
- Temperature and pH control: Maintaining appropriate temperature and pH conditions is essential for sodium percarbonate stability. Lower temperatures and slightly alkaline conditions generally favor stability. Controlling these parameters during production, storage, and application helps prevent premature decomposition and ensures the longevity of the product's active oxygen content.
02 Use of stabilizing additives
Incorporating specific stabilizing additives into sodium percarbonate formulations can greatly improve its stability. These additives may include inorganic salts, organic compounds, or polymers that help to prevent decomposition and maintain the active oxygen content. The choice of stabilizers depends on the intended application and storage conditions.Expand Specific Solutions03 Particle size and morphology control
Optimizing the particle size and morphology of sodium percarbonate can enhance its stability. Controlling these parameters during the manufacturing process can result in more uniform and stable particles. This approach can improve resistance to moisture and reduce the likelihood of caking or clumping during storage.Expand Specific Solutions04 Moisture control and packaging
Implementing effective moisture control measures and appropriate packaging solutions is crucial for maintaining sodium percarbonate stability. This includes using moisture-resistant packaging materials, adding desiccants, and controlling humidity during storage and transportation. Proper packaging helps to prevent premature decomposition and ensures product efficacy.Expand Specific Solutions05 Temperature management
Controlling storage and handling temperatures is essential for preserving sodium percarbonate stability. Exposure to high temperatures can accelerate decomposition, while maintaining cooler conditions can significantly extend shelf life. Implementing proper temperature management strategies throughout the supply chain is crucial for maintaining product quality.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players and Competitive Landscape
The sodium percarbonate market for powdered detergents is in a mature stage, with a steady global demand driven by the household and industrial cleaning sectors. The market size is substantial, estimated to be in the billions of dollars annually. Technologically, the focus is on enhancing stability and efficiency, with major players like Solvay SA, Evonik Operations GmbH, and Henkel AG & Co. KGaA leading innovation efforts. These companies, along with others such as Kemira Oyj and Zhejiang Jinke Daily Chemical Co. Ltd., are investing in research and development to improve product performance and sustainability. The technology's maturity is evident, but ongoing advancements in formulation and production processes continue to drive incremental improvements in stability and effectiveness.
Solvay SA
Technical Solution: Solvay has developed a proprietary technology called OXYPER® for enhancing the stability of sodium percarbonate in powdered detergents. This technology involves coating sodium percarbonate particles with a protective layer of inorganic salts and organic compounds. The coating process is optimized to create a uniform, dense layer that significantly improves the stability of sodium percarbonate in the presence of moisture and other detergent ingredients. Solvay's method also incorporates specific stabilizers and chelating agents that further enhance the longevity of the active oxygen content in the final product[1][3].
Strengths: Highly effective in improving sodium percarbonate stability, applicable to various detergent formulations. Weaknesses: May increase production costs, potential compatibility issues with some detergent ingredients.
Evonik Operations GmbH
Technical Solution: Evonik has developed an innovative approach to stabilizing sodium percarbonate in powdered detergents through their PEROXID® technology. This method involves a multi-layer coating process that encapsulates sodium percarbonate particles with a combination of silicates and organic compounds. The coating is designed to be both moisture-resistant and slowly soluble, ensuring a controlled release of the active oxygen during the washing process. Evonik's technology also incorporates specific metal ion scavengers and pH buffers within the coating layers to neutralize potential destabilizing factors in the detergent matrix[2][4].
Strengths: Provides excellent stability and controlled release of active oxygen, suitable for various detergent formulations. Weaknesses: Complex production process may lead to higher costs, potential limitations in high-temperature storage conditions.
Innovative Approaches to Enhance Percarbonate Stability
Powder detergent composition comprising stabilized percarbonate
PatentWO1995032273A1
Innovation
- Incorporating cogranules composed of alkali metal carbonate, alkali metal silicate, and water into the detergent composition to stabilize sodium or potassium percarbonate, with a specific water-to-silicate ratio, which improves storage stability without the need for intimate contact or additional treatments.
Method for the preparation of sodium percarbonate granules having enhanced stability
PatentInactiveEP1227063A3
Innovation
- A method involving the surface modification of sodium percarbonate granules using a reaction with carbon dioxide dissolved in water to form a dense sodium bicarbonate film, followed by additional coating layers, enhancing the granules' stability and chemical resistance.
Environmental Impact of Stabilized Percarbonate Detergents
The environmental impact of stabilized percarbonate detergents is a crucial consideration in the development and use of these cleaning products. Sodium percarbonate, when stabilized effectively, offers several environmental benefits compared to traditional detergent formulations.
One of the primary advantages of stabilized percarbonate detergents is their reduced environmental footprint during production and use. The manufacturing process of sodium percarbonate generates fewer harmful byproducts compared to other bleaching agents, resulting in lower emissions and waste. Additionally, the stability enhancements allow for more concentrated formulations, reducing packaging materials and transportation-related emissions.
When used in laundry applications, stabilized percarbonate detergents contribute to energy savings. These formulations are effective at lower washing temperatures, enabling consumers to reduce hot water usage and associated energy consumption. This not only decreases household energy bills but also lowers the overall carbon footprint of laundry activities on a global scale.
The biodegradability of sodium percarbonate is another significant environmental advantage. Upon activation, it breaks down into oxygen, water, and sodium carbonate, all of which are naturally occurring and environmentally benign substances. This characteristic minimizes the long-term impact on aquatic ecosystems and reduces the burden on wastewater treatment facilities.
However, the environmental impact of stabilized percarbonate detergents is not without challenges. The production of stability-enhancing additives may involve chemical processes that have their own environmental considerations. Manufacturers must carefully balance the benefits of improved stability against the potential environmental costs of producing these additives.
Furthermore, the increased efficacy of stabilized percarbonate detergents may lead to overuse by consumers, potentially resulting in excessive chemical discharge into water systems. Education and clear usage instructions are essential to mitigate this risk and ensure responsible consumption.
The disposal of packaging materials remains an environmental concern, despite the reduced volume due to more concentrated formulations. Efforts to develop eco-friendly packaging solutions and improve recycling processes are ongoing to address this issue.
In conclusion, while stabilized percarbonate detergents offer significant environmental benefits, including reduced energy consumption, lower emissions, and improved biodegradability, there are still areas for improvement. Continued research and development in this field should focus on further minimizing the environmental impact of both the product and its packaging, ensuring a more sustainable future for laundry and cleaning products.
One of the primary advantages of stabilized percarbonate detergents is their reduced environmental footprint during production and use. The manufacturing process of sodium percarbonate generates fewer harmful byproducts compared to other bleaching agents, resulting in lower emissions and waste. Additionally, the stability enhancements allow for more concentrated formulations, reducing packaging materials and transportation-related emissions.
When used in laundry applications, stabilized percarbonate detergents contribute to energy savings. These formulations are effective at lower washing temperatures, enabling consumers to reduce hot water usage and associated energy consumption. This not only decreases household energy bills but also lowers the overall carbon footprint of laundry activities on a global scale.
The biodegradability of sodium percarbonate is another significant environmental advantage. Upon activation, it breaks down into oxygen, water, and sodium carbonate, all of which are naturally occurring and environmentally benign substances. This characteristic minimizes the long-term impact on aquatic ecosystems and reduces the burden on wastewater treatment facilities.
However, the environmental impact of stabilized percarbonate detergents is not without challenges. The production of stability-enhancing additives may involve chemical processes that have their own environmental considerations. Manufacturers must carefully balance the benefits of improved stability against the potential environmental costs of producing these additives.
Furthermore, the increased efficacy of stabilized percarbonate detergents may lead to overuse by consumers, potentially resulting in excessive chemical discharge into water systems. Education and clear usage instructions are essential to mitigate this risk and ensure responsible consumption.
The disposal of packaging materials remains an environmental concern, despite the reduced volume due to more concentrated formulations. Efforts to develop eco-friendly packaging solutions and improve recycling processes are ongoing to address this issue.
In conclusion, while stabilized percarbonate detergents offer significant environmental benefits, including reduced energy consumption, lower emissions, and improved biodegradability, there are still areas for improvement. Continued research and development in this field should focus on further minimizing the environmental impact of both the product and its packaging, ensuring a more sustainable future for laundry and cleaning products.
Regulatory Framework for Detergent Additives
The regulatory framework for detergent additives plays a crucial role in ensuring the safety and efficacy of products containing sodium percarbonate. In the context of stability enhancement in powdered detergents, manufacturers must navigate a complex landscape of regulations and standards.
At the international level, organizations such as the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the Codex Alimentarius Commission provide guidelines for detergent formulations and safety standards. These guidelines often serve as a basis for national and regional regulations.
In the European Union, the Detergents Regulation (EC) No 648/2004 sets forth requirements for the biodegradability of surfactants and the labeling of detergent products. This regulation also addresses the use of oxidizing agents like sodium percarbonate, mandating specific safety assessments and documentation.
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulates detergents under the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act. While the FDA does not specifically regulate sodium percarbonate, it requires manufacturers to ensure the safety of all ingredients used in household cleaning products.
Many countries have implemented their own regulatory frameworks for detergent additives. For instance, Japan's Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare has established guidelines for household products, including specific requirements for oxidizing agents in detergents.
Environmental regulations also impact the use of sodium percarbonate in detergents. The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) under the REACH regulation requires registration and safety assessments for chemicals used in significant quantities, including sodium percarbonate.
Manufacturers must consider regulations related to packaging and storage of detergents containing sodium percarbonate. Many jurisdictions have specific requirements for child-resistant packaging and proper labeling of oxidizing agents.
As sustainability becomes increasingly important, regulations are evolving to address the environmental impact of detergents. This includes requirements for biodegradability, reduced phosphate content, and the use of more environmentally friendly ingredients.
Compliance with these diverse regulatory frameworks necessitates ongoing monitoring and adaptation by manufacturers. As research into sodium percarbonate stability continues, new findings may lead to updates in regulatory requirements, particularly concerning storage conditions and product shelf life.
At the international level, organizations such as the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the Codex Alimentarius Commission provide guidelines for detergent formulations and safety standards. These guidelines often serve as a basis for national and regional regulations.
In the European Union, the Detergents Regulation (EC) No 648/2004 sets forth requirements for the biodegradability of surfactants and the labeling of detergent products. This regulation also addresses the use of oxidizing agents like sodium percarbonate, mandating specific safety assessments and documentation.
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulates detergents under the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act. While the FDA does not specifically regulate sodium percarbonate, it requires manufacturers to ensure the safety of all ingredients used in household cleaning products.
Many countries have implemented their own regulatory frameworks for detergent additives. For instance, Japan's Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare has established guidelines for household products, including specific requirements for oxidizing agents in detergents.
Environmental regulations also impact the use of sodium percarbonate in detergents. The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) under the REACH regulation requires registration and safety assessments for chemicals used in significant quantities, including sodium percarbonate.
Manufacturers must consider regulations related to packaging and storage of detergents containing sodium percarbonate. Many jurisdictions have specific requirements for child-resistant packaging and proper labeling of oxidizing agents.
As sustainability becomes increasingly important, regulations are evolving to address the environmental impact of detergents. This includes requirements for biodegradability, reduced phosphate content, and the use of more environmentally friendly ingredients.
Compliance with these diverse regulatory frameworks necessitates ongoing monitoring and adaptation by manufacturers. As research into sodium percarbonate stability continues, new findings may lead to updates in regulatory requirements, particularly concerning storage conditions and product shelf life.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!