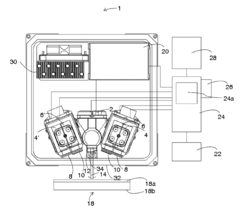
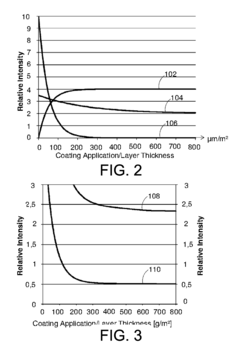
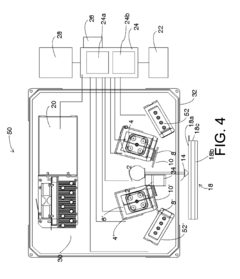
Standards and regulations for zinc coating thickness measurement
OCT 11, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Zinc Coating Thickness Measurement Background and Objectives
Zinc coating, also known as galvanization, has been a cornerstone of corrosion protection for steel and iron materials since its industrial application began in the 19th century. The process involves applying a protective zinc layer to metal surfaces, significantly extending their lifespan by providing sacrificial protection against environmental degradation. Over the decades, the technology has evolved from hot-dip galvanizing to include electrogalvanizing, mechanical plating, and zinc-rich paints, each offering specific advantages for different applications.
The measurement of zinc coating thickness has become increasingly critical as industries demand more precise control over material specifications, quality assurance, and cost optimization. Historically, destructive testing methods were predominant, but technological advancements have shifted the focus toward non-destructive techniques that preserve the integrity of the coated materials while providing accurate measurements.
Current technological trends in zinc coating thickness measurement are moving toward automated, real-time monitoring systems that integrate with production lines, allowing for immediate adjustments and quality control. Digital transformation in manufacturing has accelerated the development of smart sensors and IoT-enabled devices that can continuously monitor coating thickness during production processes, generating valuable data for process optimization and predictive maintenance.
The primary objective of zinc coating thickness measurement standards and regulations is to establish universally accepted methodologies that ensure consistency, reliability, and comparability of measurements across different industries and geographical regions. These standards aim to define acceptable thickness ranges for various applications, specify appropriate measurement techniques, and establish calibration procedures to maintain measurement accuracy.
Additionally, regulatory frameworks seek to balance technical requirements with environmental and safety considerations, as zinc coatings must meet increasingly stringent sustainability criteria while maintaining their protective properties. The evolution of these standards reflects the growing emphasis on lifecycle assessment and circular economy principles in manufacturing processes.
The convergence of material science, sensor technology, and data analytics presents opportunities for revolutionary approaches to zinc coating thickness measurement. Future developments are likely to focus on miniaturization of measurement devices, enhanced precision at nanometer scales, and integration with artificial intelligence for automated quality control systems that can adapt to varying production conditions and material characteristics.
The measurement of zinc coating thickness has become increasingly critical as industries demand more precise control over material specifications, quality assurance, and cost optimization. Historically, destructive testing methods were predominant, but technological advancements have shifted the focus toward non-destructive techniques that preserve the integrity of the coated materials while providing accurate measurements.
Current technological trends in zinc coating thickness measurement are moving toward automated, real-time monitoring systems that integrate with production lines, allowing for immediate adjustments and quality control. Digital transformation in manufacturing has accelerated the development of smart sensors and IoT-enabled devices that can continuously monitor coating thickness during production processes, generating valuable data for process optimization and predictive maintenance.
The primary objective of zinc coating thickness measurement standards and regulations is to establish universally accepted methodologies that ensure consistency, reliability, and comparability of measurements across different industries and geographical regions. These standards aim to define acceptable thickness ranges for various applications, specify appropriate measurement techniques, and establish calibration procedures to maintain measurement accuracy.
Additionally, regulatory frameworks seek to balance technical requirements with environmental and safety considerations, as zinc coatings must meet increasingly stringent sustainability criteria while maintaining their protective properties. The evolution of these standards reflects the growing emphasis on lifecycle assessment and circular economy principles in manufacturing processes.
The convergence of material science, sensor technology, and data analytics presents opportunities for revolutionary approaches to zinc coating thickness measurement. Future developments are likely to focus on miniaturization of measurement devices, enhanced precision at nanometer scales, and integration with artificial intelligence for automated quality control systems that can adapt to varying production conditions and material characteristics.
Market Demand Analysis for Zinc Coating Thickness Standards
The global market for zinc coating thickness measurement standards and regulations has witnessed significant growth in recent years, driven primarily by the expanding applications of galvanized steel across multiple industries. The corrosion protection market, valued at approximately $21.3 billion in 2022, is projected to reach $30.4 billion by 2028, with zinc coatings representing a substantial segment of this market. This growth underscores the increasing demand for standardized measurement techniques to ensure quality and compliance.
In the automotive sector, which consumes nearly 20% of global galvanized steel production, manufacturers require precise zinc coating thickness measurements to meet stringent quality standards while optimizing material usage. The construction industry, accounting for over 50% of galvanized steel consumption, similarly demands reliable measurement standards to ensure structural integrity and longevity of buildings and infrastructure.
Regional analysis reveals varying levels of market maturity. North America and Europe have established comprehensive regulatory frameworks for zinc coating thickness measurements, with standards like ASTM B633 and ISO 1461 widely adopted. The Asia-Pacific region, particularly China and India, shows the fastest growth rate at 7.2% annually, driven by rapid industrialization and infrastructure development, creating substantial demand for standardized measurement protocols.
Consumer electronics and renewable energy sectors are emerging as significant drivers for specialized zinc coating measurement standards. The miniaturization trend in electronics necessitates ultra-thin zinc coatings with precise thickness control, while solar panel mounting structures and wind turbine components require corrosion-resistant coatings with verified durability.
Market research indicates that 78% of industrial manufacturers cite regulatory compliance as a primary concern when implementing zinc coating processes, highlighting the critical importance of standardized measurement techniques. Additionally, 63% of surveyed companies reported challenges in maintaining consistent coating thickness across production batches, emphasizing the need for improved measurement standards and technologies.
The economic impact of inadequate coating thickness measurement is substantial, with industry reports estimating that improper zinc coating thickness contributes to approximately $2.5 billion in premature product failures annually worldwide. This economic burden has intensified market demand for more precise, reliable, and universally accepted measurement standards.
Environmental regulations are also shaping market demands, with 42% of manufacturers seeking measurement standards that can help optimize zinc usage while maintaining protective properties, thereby reducing environmental impact and material costs simultaneously.
In the automotive sector, which consumes nearly 20% of global galvanized steel production, manufacturers require precise zinc coating thickness measurements to meet stringent quality standards while optimizing material usage. The construction industry, accounting for over 50% of galvanized steel consumption, similarly demands reliable measurement standards to ensure structural integrity and longevity of buildings and infrastructure.
Regional analysis reveals varying levels of market maturity. North America and Europe have established comprehensive regulatory frameworks for zinc coating thickness measurements, with standards like ASTM B633 and ISO 1461 widely adopted. The Asia-Pacific region, particularly China and India, shows the fastest growth rate at 7.2% annually, driven by rapid industrialization and infrastructure development, creating substantial demand for standardized measurement protocols.
Consumer electronics and renewable energy sectors are emerging as significant drivers for specialized zinc coating measurement standards. The miniaturization trend in electronics necessitates ultra-thin zinc coatings with precise thickness control, while solar panel mounting structures and wind turbine components require corrosion-resistant coatings with verified durability.
Market research indicates that 78% of industrial manufacturers cite regulatory compliance as a primary concern when implementing zinc coating processes, highlighting the critical importance of standardized measurement techniques. Additionally, 63% of surveyed companies reported challenges in maintaining consistent coating thickness across production batches, emphasizing the need for improved measurement standards and technologies.
The economic impact of inadequate coating thickness measurement is substantial, with industry reports estimating that improper zinc coating thickness contributes to approximately $2.5 billion in premature product failures annually worldwide. This economic burden has intensified market demand for more precise, reliable, and universally accepted measurement standards.
Environmental regulations are also shaping market demands, with 42% of manufacturers seeking measurement standards that can help optimize zinc usage while maintaining protective properties, thereby reducing environmental impact and material costs simultaneously.
Current Standards and Technical Challenges in Measurement
The measurement of zinc coating thickness is governed by a comprehensive framework of international and regional standards that ensure consistency, reliability, and comparability of results across different industries and applications. The most widely recognized standards include ISO 1461, ASTM A123, ASTM B633, and EN ISO 2178, which provide detailed specifications for hot-dip galvanized coatings on various substrates. These standards not only define acceptable thickness ranges but also prescribe specific measurement methodologies and sampling procedures.
Despite the existence of established standards, the industry faces several technical challenges in zinc coating thickness measurement. Non-uniform coating distribution remains a significant issue, particularly on complex geometries where zinc tends to accumulate unevenly during the galvanizing process. This non-uniformity necessitates multiple measurement points to obtain a representative average thickness, increasing inspection time and cost.
Surface roughness presents another major challenge, as it can significantly affect measurement accuracy, especially when using magnetic or electromagnetic methods. Rough surfaces create air gaps between the measuring instrument and the coating, leading to erroneous readings that may not reflect the actual protective capacity of the coating.
The presence of alloy layers at the zinc-steel interface complicates thickness measurements further. These layers, composed of zinc-iron intermetallics, have different magnetic properties than pure zinc, potentially confounding magnetic measurement techniques which are among the most commonly used non-destructive testing methods in the industry.
Calibration and traceability issues also persist across the sector. Measurement devices require regular calibration against certified reference materials, but the availability and quality of such standards vary globally. This inconsistency can lead to measurement discrepancies between different facilities or regions, undermining the harmonization efforts of international standards.
Emerging technologies and materials present new challenges as well. Advanced zinc alloy coatings containing elements like aluminum, magnesium, or nickel exhibit different physical properties than traditional zinc coatings, necessitating adjustments to existing measurement techniques or the development of new methodologies altogether.
Environmental factors such as temperature and humidity can influence measurement accuracy, particularly for electronic instruments. Current standards often do not adequately address these variables, leaving a gap in measurement protocols that can affect result consistency in different operating environments.
Despite the existence of established standards, the industry faces several technical challenges in zinc coating thickness measurement. Non-uniform coating distribution remains a significant issue, particularly on complex geometries where zinc tends to accumulate unevenly during the galvanizing process. This non-uniformity necessitates multiple measurement points to obtain a representative average thickness, increasing inspection time and cost.
Surface roughness presents another major challenge, as it can significantly affect measurement accuracy, especially when using magnetic or electromagnetic methods. Rough surfaces create air gaps between the measuring instrument and the coating, leading to erroneous readings that may not reflect the actual protective capacity of the coating.
The presence of alloy layers at the zinc-steel interface complicates thickness measurements further. These layers, composed of zinc-iron intermetallics, have different magnetic properties than pure zinc, potentially confounding magnetic measurement techniques which are among the most commonly used non-destructive testing methods in the industry.
Calibration and traceability issues also persist across the sector. Measurement devices require regular calibration against certified reference materials, but the availability and quality of such standards vary globally. This inconsistency can lead to measurement discrepancies between different facilities or regions, undermining the harmonization efforts of international standards.
Emerging technologies and materials present new challenges as well. Advanced zinc alloy coatings containing elements like aluminum, magnesium, or nickel exhibit different physical properties than traditional zinc coatings, necessitating adjustments to existing measurement techniques or the development of new methodologies altogether.
Environmental factors such as temperature and humidity can influence measurement accuracy, particularly for electronic instruments. Current standards often do not adequately address these variables, leaving a gap in measurement protocols that can affect result consistency in different operating environments.
Existing Measurement Methods and Compliance Solutions
01 Electromagnetic methods for zinc coating thickness measurement
Electromagnetic methods are widely used for measuring zinc coating thickness on various substrates. These methods utilize principles such as eddy current, magnetic induction, or electromagnetic waves to determine coating thickness without damaging the sample. The techniques can provide accurate measurements by analyzing the interaction between electromagnetic fields and the zinc coating layer, with the measurement results often being influenced by the electrical conductivity and magnetic permeability of both the coating and substrate materials.- Electromagnetic methods for zinc coating thickness measurement: Electromagnetic methods are widely used for measuring zinc coating thickness on various substrates. These methods utilize principles such as eddy current, magnetic induction, or electromagnetic field interactions to determine coating thickness non-destructively. The techniques can provide accurate measurements without damaging the coating or substrate and are suitable for both online and offline inspection processes. These methods can compensate for substrate variations and provide real-time thickness data.
- Optical and spectroscopic measurement techniques: Optical methods including laser, infrared, and spectroscopic techniques are employed for zinc coating thickness measurement. These approaches analyze the reflection, absorption, or transmission of light through the coating to determine its thickness. Advanced optical systems may incorporate image processing algorithms to enhance measurement accuracy. These non-contact methods are particularly valuable for measuring thickness on complex geometries or when electromagnetic methods are not suitable due to substrate properties.
- X-ray fluorescence and radiation-based measurement systems: X-ray fluorescence (XRF) and other radiation-based techniques provide highly accurate zinc coating thickness measurements. These methods analyze the characteristic radiation emitted or reflected from the coating when exposed to X-rays or other radiation sources. The intensity of the fluorescence is proportional to the coating thickness. These systems can measure multiple coating layers simultaneously and are effective for both galvanized and galvannealed coatings, though they require safety precautions due to radiation exposure.
- Online continuous monitoring systems for production lines: Specialized systems designed for continuous, real-time monitoring of zinc coating thickness in production environments enable quality control during manufacturing. These systems typically integrate with production lines and provide immediate feedback for process control. They often combine multiple measurement technologies and include automated calibration features to maintain accuracy during extended operation. Advanced systems may incorporate artificial intelligence for adaptive measurement and predictive maintenance capabilities.
- Calibration methods and reference standards for thickness measurement: Proper calibration techniques and reference standards are essential for accurate zinc coating thickness measurement. These methods include the use of certified reference materials with known coating thicknesses, calibration procedures to account for substrate variations, and statistical approaches to validate measurement accuracy. Calibration protocols may involve multi-point calibration curves and periodic verification against physical standards. These techniques ensure measurement reliability across different instruments and measurement conditions.
02 Optical and radiation-based measurement techniques
Optical and radiation-based techniques offer non-contact methods for measuring zinc coating thickness. These include X-ray fluorescence (XRF), which analyzes characteristic radiation emitted by zinc atoms when excited by X-rays, and optical methods such as reflectometry and interferometry that measure thickness based on light interaction with the coating. These techniques provide high precision measurements and can be used for both offline quality control and online process monitoring in galvanizing production lines.Expand Specific Solutions03 Automated and continuous monitoring systems
Advanced systems for continuous and automated monitoring of zinc coating thickness have been developed for industrial applications. These systems integrate measurement sensors with automated handling mechanisms and data processing capabilities to provide real-time thickness measurements during production. They often include features such as multi-point measurement, statistical analysis, and integration with production control systems to enable immediate process adjustments when thickness variations are detected.Expand Specific Solutions04 Calibration and reference standards for thickness measurement
Accurate calibration and reference standards are essential for reliable zinc coating thickness measurements. Various methods have been developed to create and maintain calibration standards with known coating thicknesses. These standards are used to calibrate measurement instruments and verify their accuracy. Calibration procedures may involve comparison with certified reference materials, statistical validation methods, and compensation for factors that could affect measurement accuracy such as substrate composition, surface roughness, and environmental conditions.Expand Specific Solutions05 Portable and handheld thickness measurement devices
Portable and handheld devices for measuring zinc coating thickness provide flexibility for on-site inspections and quality control. These compact instruments typically employ electromagnetic or optical measurement principles and are designed for ease of use in field conditions. Modern portable devices often feature digital displays, data storage capabilities, statistical analysis functions, and wireless connectivity for data transfer. They allow for quick spot-checking of coating thickness at multiple locations without the need for sample preparation or destruction.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Organizations and Regulatory Bodies in Zinc Coating Industry
The zinc coating thickness measurement standards and regulations landscape is evolving within a maturing industry that generates approximately $40 billion annually in the galvanized steel market. The competitive field features established steel manufacturers like Nippon Steel, Baoshan Iron & Steel, and thyssenkrupp Steel Europe leading technological development, alongside specialized coating companies such as Bekaert, Hempel, and Fontaine Engineering. These players are advancing measurement technologies from traditional destructive testing toward non-contact optical and electromagnetic methods with improved precision and automation capabilities. The regulatory framework is increasingly harmonized globally through ISO standards, with regional variations in ASTM (North America), EN (Europe), and GB (China) specifications driving innovation in measurement equipment and methodologies to meet stricter quality control requirements.
NIPPON STEEL CORP.
Technical Solution: NIPPON STEEL has developed advanced zinc coating thickness measurement systems that integrate multiple technologies for comprehensive quality control. Their approach combines X-ray fluorescence (XRF) spectroscopy with electromagnetic methods for real-time monitoring during galvanizing processes. The company has implemented in-line measurement systems that comply with ISO 1461 and ASTM A123/A123M standards, allowing continuous monitoring without interrupting production. Their technology can detect coating thickness variations as small as ±2 μm across wide steel strips, ensuring uniform corrosion protection. NIPPON STEEL's systems incorporate automatic calibration features that reference standard samples at programmed intervals, maintaining measurement accuracy over extended production runs. The company has also developed specialized algorithms that compensate for substrate composition variations, which traditionally interfere with accurate zinc thickness readings.
Strengths: High precision measurements with excellent repeatability; integrated quality management systems that provide comprehensive data analytics; compliance with multiple international standards. Weaknesses: Higher implementation costs compared to simpler systems; requires specialized technical expertise for maintenance and calibration; some technologies may be proprietary and not compatible with third-party systems.
Bekaert SA
Technical Solution: Bekaert has pioneered non-destructive testing technologies for zinc coating thickness measurement that align with EN 10346 and ASTM A653 standards. Their approach utilizes a combination of eddy current technology and magnetic induction methods specifically calibrated for various zinc coating types including galvanized, galvannealed, and Galfan coatings. Bekaert's measurement systems feature dual-sensor arrays that simultaneously measure both sides of coated materials, enabling thickness differential analysis critical for specialized applications. Their technology incorporates temperature compensation algorithms that adjust readings based on substrate temperature variations during production, improving accuracy in hot-dip galvanizing environments. Bekaert has also developed portable measurement devices that comply with ISO 2178 standards for field testing, featuring wireless data transmission capabilities for integration with quality management systems. Their systems are designed to detect coating thickness from 5 to 500 μm with a precision of ±1.5% across varying substrate compositions.
Strengths: Versatile measurement capabilities across multiple zinc coating types; excellent portability options for field testing; strong integration with production control systems. Weaknesses: Some systems require more frequent calibration in harsh industrial environments; higher sensitivity to substrate composition variations; limited measurement range for ultra-thin coatings below 3 μm.
Critical Standards and Technical Specifications Analysis
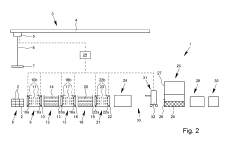
System and method for measuring the thickness of a zinc layer on steel and for measuring the iron concentration in a zinc layer
PatentInactiveUS20120328075A1
Innovation
- A system and method utilizing x-ray radiation and dispersive ionization chambers to measure zinc layer thickness and iron content, combining fluorescence and Compton scattering techniques to determine zinc layer thickness over a broader range and accurately assess iron content, with specific angle and energy ranges optimized for different zinc layer thicknesses.
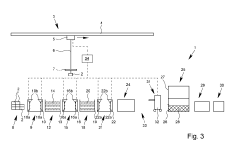
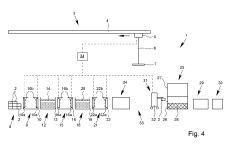
Hot-dip galvanization system and hot-dip galvanization method
PatentActiveUS20190100830A1
Innovation
- A system and method for hot-dip galvanizing using a zinc/aluminum melt, where components are treated in a separated and singled-out state, with automated flux application and precise control of the galvanizing process, including spray application of flux and surface treatment agents, to ensure uniform coating and reduced zinc ash accumulation.
International Compliance Requirements and Harmonization
The global nature of zinc coating applications necessitates a comprehensive understanding of international standards and regulatory frameworks. Currently, several major international organizations establish and maintain standards for zinc coating thickness measurement, including the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), ASTM International, and various regional bodies such as the European Committee for Standardization (CEN).
ISO 1461 and ISO 2063 represent cornerstone standards for hot-dip galvanized coatings and thermal sprayed zinc coatings respectively, providing globally recognized specifications for thickness requirements and measurement methodologies. These standards are widely adopted across multiple jurisdictions, serving as the foundation for national regulations in many countries.
Regional variations in compliance requirements present significant challenges for manufacturers operating in global markets. The European Union enforces the Construction Products Regulation (CPR) which mandates CE marking for zinc-coated products used in construction, requiring specific thickness verification protocols. North American markets follow ASTM A123/A123M standards, which differ in certain measurement parameters and acceptance criteria from their ISO counterparts.
Harmonization efforts have gained momentum in recent years, with international working groups focusing on aligning measurement methodologies and acceptance criteria. The International Committee for Non-Destructive Testing (ICNDT) has established collaborative initiatives to develop unified approaches to coating thickness measurement, particularly for non-destructive testing methods like magnetic and eddy current techniques.
Mutual recognition agreements (MRAs) between major economies have facilitated cross-border acceptance of test results and certifications. These agreements reduce redundant testing requirements and streamline compliance processes for manufacturers. Notable examples include the EU-US MRA for conformity assessment and similar arrangements between Australia, Japan, and Canada.
Emerging markets present unique regulatory challenges, with countries like China, India, and Brazil developing their own national standards that incorporate elements from both ISO and ASTM frameworks while adding market-specific requirements. This regulatory diversity necessitates sophisticated compliance strategies for global manufacturers.
Digital compliance management systems are increasingly being adopted to navigate this complex regulatory landscape. These platforms integrate real-time updates on regulatory changes, automated compliance checking, and documentation management to ensure continuous adherence to evolving international requirements for zinc coating thickness measurement and reporting.
ISO 1461 and ISO 2063 represent cornerstone standards for hot-dip galvanized coatings and thermal sprayed zinc coatings respectively, providing globally recognized specifications for thickness requirements and measurement methodologies. These standards are widely adopted across multiple jurisdictions, serving as the foundation for national regulations in many countries.
Regional variations in compliance requirements present significant challenges for manufacturers operating in global markets. The European Union enforces the Construction Products Regulation (CPR) which mandates CE marking for zinc-coated products used in construction, requiring specific thickness verification protocols. North American markets follow ASTM A123/A123M standards, which differ in certain measurement parameters and acceptance criteria from their ISO counterparts.
Harmonization efforts have gained momentum in recent years, with international working groups focusing on aligning measurement methodologies and acceptance criteria. The International Committee for Non-Destructive Testing (ICNDT) has established collaborative initiatives to develop unified approaches to coating thickness measurement, particularly for non-destructive testing methods like magnetic and eddy current techniques.
Mutual recognition agreements (MRAs) between major economies have facilitated cross-border acceptance of test results and certifications. These agreements reduce redundant testing requirements and streamline compliance processes for manufacturers. Notable examples include the EU-US MRA for conformity assessment and similar arrangements between Australia, Japan, and Canada.
Emerging markets present unique regulatory challenges, with countries like China, India, and Brazil developing their own national standards that incorporate elements from both ISO and ASTM frameworks while adding market-specific requirements. This regulatory diversity necessitates sophisticated compliance strategies for global manufacturers.
Digital compliance management systems are increasingly being adopted to navigate this complex regulatory landscape. These platforms integrate real-time updates on regulatory changes, automated compliance checking, and documentation management to ensure continuous adherence to evolving international requirements for zinc coating thickness measurement and reporting.
Environmental and Sustainability Considerations in Zinc Coating
The environmental impact of zinc coating processes has gained significant attention as industries strive for more sustainable manufacturing practices. Traditional zinc coating methods often involve energy-intensive processes and potentially hazardous chemicals, raising concerns about their environmental footprint. Recent regulations have increasingly focused on reducing the environmental impact of these processes while maintaining coating quality and thickness standards.
Zinc coating thickness measurement standards now incorporate environmental considerations, with many regulatory bodies requiring documentation of environmental compliance alongside thickness verification. The EU's RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) and REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization and Restriction of Chemicals) regulations have established strict parameters for zinc coatings, including thickness requirements that balance corrosion protection with minimal material usage.
Life cycle assessment (LCA) has become an integral part of zinc coating thickness standards, evaluating environmental impacts from raw material extraction through disposal. This holistic approach ensures that thickness measurements consider not just functional requirements but also resource efficiency. ISO 14040 series standards provide frameworks for these assessments, complementing traditional thickness measurement standards like ISO 1461 and ASTM A123.
Water conservation represents another critical aspect of sustainable zinc coating practices. Modern thickness measurement protocols often include evaluations of process efficiency to minimize water usage during galvanizing operations. Closed-loop systems that recycle process water have become industry benchmarks, with thickness measurement standards increasingly recognizing facilities that implement such systems.
Energy efficiency metrics are now frequently integrated with thickness measurement standards. The correlation between coating thickness and energy consumption during application has led to optimized thickness specifications that balance protection requirements with energy conservation. The International Energy Agency (IEA) has developed guidelines that many national standards bodies have incorporated into their zinc coating thickness regulations.
Waste reduction strategies have evolved alongside thickness measurement technologies. Non-destructive testing methods that minimize material waste during quality control are now preferred in sustainability-focused standards. Additionally, thickness measurement standards increasingly promote the use of recycled zinc in coating processes, with specifications for verifying the performance of coatings containing recycled content.
Carbon footprint considerations have become embedded in zinc coating thickness regulations, with some jurisdictions implementing carbon taxation that affects coating thickness decisions. Manufacturers must now document the carbon emissions associated with different coating thickness options, driving innovation in low-emission application technologies and measurement systems that can verify compliance with both environmental and protection requirements.
Zinc coating thickness measurement standards now incorporate environmental considerations, with many regulatory bodies requiring documentation of environmental compliance alongside thickness verification. The EU's RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) and REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization and Restriction of Chemicals) regulations have established strict parameters for zinc coatings, including thickness requirements that balance corrosion protection with minimal material usage.
Life cycle assessment (LCA) has become an integral part of zinc coating thickness standards, evaluating environmental impacts from raw material extraction through disposal. This holistic approach ensures that thickness measurements consider not just functional requirements but also resource efficiency. ISO 14040 series standards provide frameworks for these assessments, complementing traditional thickness measurement standards like ISO 1461 and ASTM A123.
Water conservation represents another critical aspect of sustainable zinc coating practices. Modern thickness measurement protocols often include evaluations of process efficiency to minimize water usage during galvanizing operations. Closed-loop systems that recycle process water have become industry benchmarks, with thickness measurement standards increasingly recognizing facilities that implement such systems.
Energy efficiency metrics are now frequently integrated with thickness measurement standards. The correlation between coating thickness and energy consumption during application has led to optimized thickness specifications that balance protection requirements with energy conservation. The International Energy Agency (IEA) has developed guidelines that many national standards bodies have incorporated into their zinc coating thickness regulations.
Waste reduction strategies have evolved alongside thickness measurement technologies. Non-destructive testing methods that minimize material waste during quality control are now preferred in sustainability-focused standards. Additionally, thickness measurement standards increasingly promote the use of recycled zinc in coating processes, with specifications for verifying the performance of coatings containing recycled content.
Carbon footprint considerations have become embedded in zinc coating thickness regulations, with some jurisdictions implementing carbon taxation that affects coating thickness decisions. Manufacturers must now document the carbon emissions associated with different coating thickness options, driving innovation in low-emission application technologies and measurement systems that can verify compliance with both environmental and protection requirements.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!