Phospholipid Effects on Cognitive Function Studies
JUL 16, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Phospholipid Research Background and Objectives
Phospholipids have been a subject of intense scientific interest for decades, with their potential effects on cognitive function emerging as a particularly compelling area of research. The study of phospholipids in relation to brain health and cognitive performance has its roots in the mid-20th century, when researchers first began to explore the complex composition of cell membranes and their role in neuronal function.
The evolution of phospholipid research has been marked by significant milestones, including the discovery of their crucial role in maintaining membrane fluidity and the subsequent understanding of how this impacts synaptic transmission and neuroplasticity. As our knowledge of brain biochemistry has advanced, so too has our appreciation for the multifaceted ways in which phospholipids contribute to cognitive processes.
In recent years, the focus has shifted towards understanding how specific phospholipids, such as phosphatidylserine and phosphatidylcholine, may influence cognitive abilities. This has been driven by a growing body of evidence suggesting that these compounds could play a role in supporting memory, attention, and overall cognitive performance, particularly in aging populations and those at risk of neurodegenerative disorders.
The current landscape of phospholipid research is characterized by a convergence of disciplines, including neuroscience, biochemistry, and nutrition. This interdisciplinary approach has led to more comprehensive investigations into the mechanisms by which phospholipids may exert their effects on brain function, from cellular-level interactions to observable cognitive outcomes.
The primary objectives of contemporary phospholipid research in relation to cognitive function are multifaceted. Researchers aim to elucidate the precise mechanisms through which different phospholipids influence neural activity and cognitive processes. There is a strong emphasis on identifying potential therapeutic applications, particularly in the context of age-related cognitive decline and neurodegenerative diseases.
Another key goal is to establish standardized methodologies for assessing the impact of phospholipid supplementation on cognitive function. This includes developing more sensitive and specific cognitive tests, as well as exploring advanced neuroimaging techniques to visualize changes in brain structure and function associated with phospholipid intake.
Furthermore, there is a growing interest in personalized approaches to phospholipid supplementation. Researchers are investigating how individual differences in genetics, metabolism, and lifestyle factors may influence the efficacy of phospholipid interventions on cognitive performance. This personalized medicine approach holds promise for tailoring treatments to maximize cognitive benefits while minimizing potential side effects.
As the field progresses, there is also an increasing focus on long-term studies to assess the sustained effects of phospholipid supplementation on cognitive health over extended periods. These longitudinal investigations are crucial for understanding the potential of phospholipids as preventive or therapeutic agents in maintaining cognitive function throughout the lifespan.
The evolution of phospholipid research has been marked by significant milestones, including the discovery of their crucial role in maintaining membrane fluidity and the subsequent understanding of how this impacts synaptic transmission and neuroplasticity. As our knowledge of brain biochemistry has advanced, so too has our appreciation for the multifaceted ways in which phospholipids contribute to cognitive processes.
In recent years, the focus has shifted towards understanding how specific phospholipids, such as phosphatidylserine and phosphatidylcholine, may influence cognitive abilities. This has been driven by a growing body of evidence suggesting that these compounds could play a role in supporting memory, attention, and overall cognitive performance, particularly in aging populations and those at risk of neurodegenerative disorders.
The current landscape of phospholipid research is characterized by a convergence of disciplines, including neuroscience, biochemistry, and nutrition. This interdisciplinary approach has led to more comprehensive investigations into the mechanisms by which phospholipids may exert their effects on brain function, from cellular-level interactions to observable cognitive outcomes.
The primary objectives of contemporary phospholipid research in relation to cognitive function are multifaceted. Researchers aim to elucidate the precise mechanisms through which different phospholipids influence neural activity and cognitive processes. There is a strong emphasis on identifying potential therapeutic applications, particularly in the context of age-related cognitive decline and neurodegenerative diseases.
Another key goal is to establish standardized methodologies for assessing the impact of phospholipid supplementation on cognitive function. This includes developing more sensitive and specific cognitive tests, as well as exploring advanced neuroimaging techniques to visualize changes in brain structure and function associated with phospholipid intake.
Furthermore, there is a growing interest in personalized approaches to phospholipid supplementation. Researchers are investigating how individual differences in genetics, metabolism, and lifestyle factors may influence the efficacy of phospholipid interventions on cognitive performance. This personalized medicine approach holds promise for tailoring treatments to maximize cognitive benefits while minimizing potential side effects.
As the field progresses, there is also an increasing focus on long-term studies to assess the sustained effects of phospholipid supplementation on cognitive health over extended periods. These longitudinal investigations are crucial for understanding the potential of phospholipids as preventive or therapeutic agents in maintaining cognitive function throughout the lifespan.
Cognitive Enhancement Market Analysis
The cognitive enhancement market has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing awareness of mental health, rising prevalence of cognitive disorders, and a growing aging population. This market encompasses a wide range of products and services, including pharmaceuticals, nutraceuticals, brain training programs, and medical devices aimed at improving cognitive function.
The global cognitive enhancement market size was valued at approximately $6.2 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $15.3 billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of 13.7% during the forecast period. North America currently holds the largest market share, followed by Europe and Asia-Pacific. The United States, in particular, dominates the market due to high healthcare expenditure and a large consumer base for cognitive health products.
Within this market, the segment focusing on phospholipid-based cognitive enhancement products is gaining traction. Phospholipids, particularly those containing omega-3 fatty acids like docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) and eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), have shown promising results in improving cognitive function. The market for phospholipid-based cognitive enhancers is expected to grow at a CAGR of 9.5% from 2021 to 2028.
Key factors driving the growth of the cognitive enhancement market include the increasing prevalence of neurological disorders, rising geriatric population, and growing consumer interest in preventive healthcare. Additionally, the COVID-19 pandemic has heightened awareness of mental health and cognitive well-being, further fueling market growth.
The market is characterized by intense competition, with major players including Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited, Allergan plc, Shire plc, and Novartis AG. These companies are investing heavily in research and development to create innovative cognitive enhancement products, including those based on phospholipids.
Challenges facing the market include stringent regulatory requirements, potential side effects of cognitive enhancement drugs, and the need for long-term studies to establish efficacy and safety. However, ongoing research into phospholipid effects on cognitive function presents significant opportunities for market expansion and product development.
In conclusion, the cognitive enhancement market, particularly the segment focused on phospholipid-based products, shows strong growth potential. As research continues to uncover the benefits of phospholipids in cognitive function, this market segment is likely to see increased investment and product innovation in the coming years.
The global cognitive enhancement market size was valued at approximately $6.2 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $15.3 billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of 13.7% during the forecast period. North America currently holds the largest market share, followed by Europe and Asia-Pacific. The United States, in particular, dominates the market due to high healthcare expenditure and a large consumer base for cognitive health products.
Within this market, the segment focusing on phospholipid-based cognitive enhancement products is gaining traction. Phospholipids, particularly those containing omega-3 fatty acids like docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) and eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), have shown promising results in improving cognitive function. The market for phospholipid-based cognitive enhancers is expected to grow at a CAGR of 9.5% from 2021 to 2028.
Key factors driving the growth of the cognitive enhancement market include the increasing prevalence of neurological disorders, rising geriatric population, and growing consumer interest in preventive healthcare. Additionally, the COVID-19 pandemic has heightened awareness of mental health and cognitive well-being, further fueling market growth.
The market is characterized by intense competition, with major players including Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited, Allergan plc, Shire plc, and Novartis AG. These companies are investing heavily in research and development to create innovative cognitive enhancement products, including those based on phospholipids.
Challenges facing the market include stringent regulatory requirements, potential side effects of cognitive enhancement drugs, and the need for long-term studies to establish efficacy and safety. However, ongoing research into phospholipid effects on cognitive function presents significant opportunities for market expansion and product development.
In conclusion, the cognitive enhancement market, particularly the segment focused on phospholipid-based products, shows strong growth potential. As research continues to uncover the benefits of phospholipids in cognitive function, this market segment is likely to see increased investment and product innovation in the coming years.
Current State of Phospholipid-Cognition Research
The field of phospholipid-cognition research has seen significant advancements in recent years, with a growing body of evidence supporting the potential benefits of phospholipids on cognitive function. Current research focuses on several key areas, including the role of phospholipids in neuronal membrane structure and function, their impact on neurotransmitter signaling, and their potential neuroprotective effects.
One of the primary areas of investigation is the role of phosphatidylcholine (PC) and phosphatidylserine (PS) in maintaining cognitive health. Studies have shown that these phospholipids are crucial components of neuronal membranes and play a vital role in synaptic plasticity and neurotransmission. Researchers have observed that supplementation with PS may improve memory and cognitive performance, particularly in older adults experiencing age-related cognitive decline.
Another significant focus of current research is the potential of omega-3 fatty acid-rich phospholipids, such as those found in krill oil, in supporting cognitive function. These phospholipids have been shown to have anti-inflammatory properties and may help protect against oxidative stress in the brain. Some studies suggest that they may also enhance the delivery of essential fatty acids to the brain, potentially improving cognitive performance and reducing the risk of neurodegenerative diseases.
The relationship between phospholipids and neurotransmitter function is also a key area of investigation. Researchers are exploring how phospholipids influence the synthesis, release, and reuptake of neurotransmitters such as acetylcholine, which plays a crucial role in memory and learning. Some studies have indicated that phospholipid supplementation may enhance cholinergic function, potentially leading to improvements in cognitive performance.
Recent research has also focused on the potential of phospholipids in mitigating the effects of neuroinflammation and oxidative stress, both of which are implicated in cognitive decline and neurodegenerative disorders. Some studies have shown that certain phospholipids may have antioxidant properties and can help reduce inflammation in the brain, potentially slowing cognitive decline and protecting against neurodegenerative diseases.
While the current state of phospholipid-cognition research is promising, it is important to note that many studies are still in their early stages, and more extensive clinical trials are needed to fully understand the effects of phospholipids on cognitive function. Researchers are working to elucidate the precise mechanisms by which phospholipids influence brain health and to determine optimal dosages and formulations for potential therapeutic applications.
One of the primary areas of investigation is the role of phosphatidylcholine (PC) and phosphatidylserine (PS) in maintaining cognitive health. Studies have shown that these phospholipids are crucial components of neuronal membranes and play a vital role in synaptic plasticity and neurotransmission. Researchers have observed that supplementation with PS may improve memory and cognitive performance, particularly in older adults experiencing age-related cognitive decline.
Another significant focus of current research is the potential of omega-3 fatty acid-rich phospholipids, such as those found in krill oil, in supporting cognitive function. These phospholipids have been shown to have anti-inflammatory properties and may help protect against oxidative stress in the brain. Some studies suggest that they may also enhance the delivery of essential fatty acids to the brain, potentially improving cognitive performance and reducing the risk of neurodegenerative diseases.
The relationship between phospholipids and neurotransmitter function is also a key area of investigation. Researchers are exploring how phospholipids influence the synthesis, release, and reuptake of neurotransmitters such as acetylcholine, which plays a crucial role in memory and learning. Some studies have indicated that phospholipid supplementation may enhance cholinergic function, potentially leading to improvements in cognitive performance.
Recent research has also focused on the potential of phospholipids in mitigating the effects of neuroinflammation and oxidative stress, both of which are implicated in cognitive decline and neurodegenerative disorders. Some studies have shown that certain phospholipids may have antioxidant properties and can help reduce inflammation in the brain, potentially slowing cognitive decline and protecting against neurodegenerative diseases.
While the current state of phospholipid-cognition research is promising, it is important to note that many studies are still in their early stages, and more extensive clinical trials are needed to fully understand the effects of phospholipids on cognitive function. Researchers are working to elucidate the precise mechanisms by which phospholipids influence brain health and to determine optimal dosages and formulations for potential therapeutic applications.
Phospholipid Mechanisms in Cognitive Function
01 Phospholipid compositions for cognitive enhancement
Specific phospholipid formulations are developed to improve cognitive function. These compositions may include various types of phospholipids, such as phosphatidylcholine or phosphatidylserine, which are known to support brain health and enhance cognitive performance. The formulations can be designed for oral administration or other delivery methods to maximize their effectiveness in supporting memory, focus, and overall cognitive abilities.- Phospholipid-based compositions for cognitive enhancement: Formulations containing specific phospholipids have been developed to improve cognitive function. These compositions may include various types of phospholipids, such as phosphatidylcholine or phosphatidylserine, which are believed to support brain health and enhance memory, attention, and overall cognitive performance.
- Phospholipid delivery systems for brain-targeted therapies: Novel delivery systems utilizing phospholipids have been designed to improve the transport of therapeutic agents across the blood-brain barrier. These systems aim to enhance the efficacy of treatments for cognitive disorders by increasing the bioavailability of active compounds in the brain.
- Phospholipid-based biomarkers for cognitive function assessment: Research has identified specific phospholipid profiles in biological samples that may serve as biomarkers for cognitive function and neurological disorders. These biomarkers could potentially be used for early detection, diagnosis, and monitoring of cognitive decline or improvement.
- Phospholipid supplementation for cognitive health: Dietary supplements and functional foods enriched with specific phospholipids have been developed to support cognitive health. These products are designed to provide the brain with essential nutrients that may help maintain or improve cognitive function, particularly in aging populations.
- Phospholipid-based neuroprotective strategies: Research has explored the neuroprotective properties of certain phospholipids and their potential use in preventing or mitigating cognitive decline. These strategies involve the use of phospholipids to support neuronal membrane integrity, reduce oxidative stress, and promote synaptic plasticity in the brain.
02 Phospholipid-based nanoparticles for targeted brain delivery
Nanoparticle systems incorporating phospholipids are developed for targeted delivery of cognitive-enhancing compounds to the brain. These nanoparticles can be designed to cross the blood-brain barrier more effectively, allowing for improved bioavailability of active ingredients. The use of phospholipids in the nanoparticle structure can enhance the stability and efficacy of the cognitive-enhancing formulations.Expand Specific Solutions03 Phospholipid-enriched dietary supplements for cognitive health
Dietary supplements enriched with specific phospholipids are formulated to support cognitive function. These supplements may combine phospholipids with other nutrients known to benefit brain health, such as omega-3 fatty acids or antioxidants. The goal is to provide a comprehensive nutritional approach to maintaining and improving cognitive abilities through regular dietary supplementation.Expand Specific Solutions04 Phospholipid-based biomarkers for cognitive assessment
Research into phospholipid-based biomarkers is conducted to develop new methods for assessing cognitive function and diagnosing cognitive disorders. By analyzing specific phospholipid profiles in biological samples, researchers aim to identify early indicators of cognitive decline or neurodegenerative diseases. This approach could lead to more accurate and earlier diagnosis of cognitive impairments.Expand Specific Solutions05 Phospholipid membrane modulation for cognitive enhancement
Techniques are developed to modulate neuronal membrane phospholipid composition to enhance cognitive function. This approach focuses on altering the fluidity and functionality of neuronal membranes through targeted phospholipid interventions. By optimizing membrane properties, researchers aim to improve synaptic plasticity, neurotransmitter signaling, and overall cognitive performance.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Phospholipid Research
The field of phospholipid effects on cognitive function is in a growth phase, with increasing market size and research interest. The technology is maturing, but still has significant room for development. Key players include established pharmaceutical companies like Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp. and Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbH, as well as specialized firms such as Enzymotec Ltd. and Nutritional Therapeutics, Inc. Academic institutions like Maastricht University and Juntendo University are also contributing to research. The competitive landscape is diverse, with companies focusing on different aspects of phospholipid research and applications in cognitive health, ranging from dietary supplements to potential pharmaceutical interventions.
Nutricia NV
Technical Solution: Nutricia, a subsidiary of Danone, has developed a medical nutrition product called "Souvenaid" specifically designed to support memory function in early Alzheimer's disease. The product contains a unique combination of nutrients, including phospholipids, omega-3 fatty acids, and B vitamins. Nutricia's approach focuses on providing precursors and cofactors necessary for synapse formation and function[4]. Clinical trials have shown that daily consumption of Souvenaid for 24 weeks can improve memory performance in mild Alzheimer's disease patients[5]. The company is also investigating the potential of this nutrient combination in other cognitive disorders and exploring personalized nutrition approaches based on individual phospholipid profiles[6].
Strengths: Clinically proven product, targeted approach for specific cognitive conditions. Weaknesses: Limited to medical nutrition market, may require prescription in some countries.
Société des Produits Nestlé SA
Technical Solution: Nestlé has developed a proprietary phospholipid blend called "Brain PS Gold" for cognitive function enhancement. This blend combines phosphatidylserine (PS) with DHA-rich phosphatidylcholine (PC) to support brain health and cognitive performance. The company has conducted clinical trials demonstrating improved memory and cognitive function in elderly subjects[1]. Nestlé's research focuses on the synergistic effects of these phospholipids on neuronal membrane fluidity and neurotransmitter release, potentially leading to improved synaptic plasticity and cognitive function[2]. The company is also exploring the use of liposomal delivery systems to enhance the bioavailability of these phospholipids in the brain[3].
Strengths: Strong research backing, proprietary blend, and established clinical efficacy. Weaknesses: Limited to specific phospholipid combinations, potentially higher cost due to proprietary formulation.
Breakthrough Studies on Phospholipids and Cognition
Phospholipid compound containing unsaturated fatty acid derivative having cyclopropane ring
PatentInactiveJPWO2014126191A1
Innovation
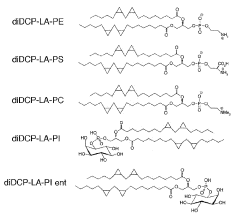
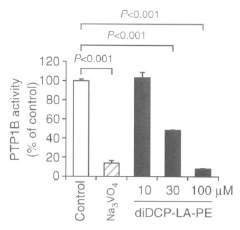
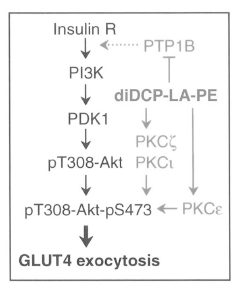
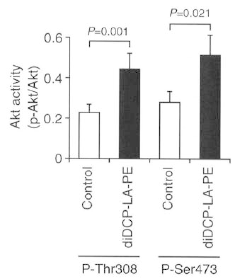
- Development of phospholipid compounds containing unsaturated fatty acid derivatives with a cyclopropane ring, specifically 8-[2-(2-pentyl-cyclopropylmethyl)-cyclopropyl]-octanoic acid, in various phospholipid forms, which exhibit pharmacological effects such as PTP1B inhibition, Akt activation, PKC activation, and GLUT4 translocation, useful for treating dementia and diabetes.
Novel therapeutic and dietetic uses of a brain phospholipid-based complex
PatentInactiveEP0719152A1
Innovation
- A preparation of cerebral phospholipids from pig brains, rich in long-chain fatty acids, is administered orally or intravenously to regenerate cell membranes and provide essential fatty acids, combined with natural antioxidants and fish oil, to slow down degradation and improve cognitive functions.
Regulatory Framework for Cognitive Enhancers
The regulatory framework for cognitive enhancers, particularly those involving phospholipids, is a complex and evolving landscape. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) plays a crucial role in overseeing the development and marketing of such products. Cognitive enhancers, depending on their specific formulation and intended use, may be classified as dietary supplements, foods, or drugs, each category subject to different regulatory requirements.
For phospholipid-based cognitive enhancers marketed as dietary supplements, the Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act (DSHEA) of 1994 provides the primary regulatory framework. Under DSHEA, manufacturers are responsible for ensuring the safety of their products before marketing. However, they are not required to obtain FDA approval before introducing a dietary supplement to the market. This relatively lenient approach has led to a proliferation of phospholipid-based products claiming cognitive benefits.
In contrast, if a phospholipid-based product is intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent a disease, it would be classified as a drug and subject to the rigorous FDA approval process. This process involves extensive clinical trials to demonstrate safety and efficacy before the product can be marketed. The regulatory pathway for drugs is significantly more stringent and time-consuming compared to dietary supplements.
The European Union (EU) has a different regulatory approach. The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) evaluates health claims for food and dietary supplements, including those related to cognitive function. The EFSA has set high standards for scientific evidence required to support health claims, leading to relatively few approved claims for cognitive enhancement products.
In Japan, the Foods for Specified Health Uses (FOSHU) system allows for functional claims on certain foods and supplements, including those targeting cognitive function. This system requires pre-market approval and scientific evidence to support the claimed health benefits.
Globally, there is a growing trend towards stricter regulation of cognitive enhancers. Regulatory bodies are increasingly scrutinizing the scientific evidence behind cognitive enhancement claims and demanding higher standards of proof. This trend is partly driven by concerns over the potential misuse of cognitive enhancers and their long-term effects on brain health.
The regulatory landscape also reflects the challenges in defining and measuring cognitive enhancement. Unlike traditional pharmaceutical endpoints, cognitive function improvements can be subtle and multifaceted, making it difficult to establish clear regulatory guidelines. As research in phospholipids and cognitive function advances, regulatory frameworks are likely to evolve to better address the unique characteristics of these products.
For phospholipid-based cognitive enhancers marketed as dietary supplements, the Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act (DSHEA) of 1994 provides the primary regulatory framework. Under DSHEA, manufacturers are responsible for ensuring the safety of their products before marketing. However, they are not required to obtain FDA approval before introducing a dietary supplement to the market. This relatively lenient approach has led to a proliferation of phospholipid-based products claiming cognitive benefits.
In contrast, if a phospholipid-based product is intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent a disease, it would be classified as a drug and subject to the rigorous FDA approval process. This process involves extensive clinical trials to demonstrate safety and efficacy before the product can be marketed. The regulatory pathway for drugs is significantly more stringent and time-consuming compared to dietary supplements.
The European Union (EU) has a different regulatory approach. The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) evaluates health claims for food and dietary supplements, including those related to cognitive function. The EFSA has set high standards for scientific evidence required to support health claims, leading to relatively few approved claims for cognitive enhancement products.
In Japan, the Foods for Specified Health Uses (FOSHU) system allows for functional claims on certain foods and supplements, including those targeting cognitive function. This system requires pre-market approval and scientific evidence to support the claimed health benefits.
Globally, there is a growing trend towards stricter regulation of cognitive enhancers. Regulatory bodies are increasingly scrutinizing the scientific evidence behind cognitive enhancement claims and demanding higher standards of proof. This trend is partly driven by concerns over the potential misuse of cognitive enhancers and their long-term effects on brain health.
The regulatory landscape also reflects the challenges in defining and measuring cognitive enhancement. Unlike traditional pharmaceutical endpoints, cognitive function improvements can be subtle and multifaceted, making it difficult to establish clear regulatory guidelines. As research in phospholipids and cognitive function advances, regulatory frameworks are likely to evolve to better address the unique characteristics of these products.
Ethical Considerations in Cognitive Enhancement
The ethical considerations surrounding cognitive enhancement through phospholipid supplementation are complex and multifaceted. As research on phospholipids' effects on cognitive function progresses, it is crucial to address the ethical implications of their potential use for cognitive enhancement.
One primary concern is the issue of fairness and equality. If phospholipid supplementation proves effective in enhancing cognitive abilities, it may create or exacerbate existing social inequalities. Those with access to such supplements could gain significant advantages in academic, professional, and personal spheres, potentially widening the gap between socioeconomic classes. This raises questions about distributive justice and equal opportunities in society.
Another ethical consideration is the potential for coercion or pressure to use cognitive enhancers. In competitive environments such as academia or high-performance workplaces, individuals might feel compelled to use phospholipid supplements to keep up with enhanced peers or meet increasing performance expectations. This could lead to a form of "cognitive arms race" where enhancement becomes a necessity rather than a choice.
The long-term effects of phospholipid supplementation on cognitive function are not yet fully understood. There are concerns about potential side effects or unintended consequences that may only become apparent after prolonged use. This uncertainty raises ethical questions about the responsible development and implementation of such cognitive enhancement technologies.
Privacy and autonomy are also significant ethical concerns. The use of cognitive enhancers may require monitoring and data collection to assess their effectiveness and safety. This could potentially infringe on individual privacy rights and raise questions about data ownership and use.
There are also philosophical and existential questions to consider. The use of cognitive enhancers challenges our understanding of human nature and what it means to be "normal" or "enhanced." It raises debates about authenticity, personal identity, and the value we place on natural versus artificially enhanced cognitive abilities.
The potential for misuse or abuse of cognitive enhancers is another ethical concern. There may be risks associated with off-label use, self-experimentation, or the development of black markets for these substances. Regulatory frameworks and ethical guidelines will need to be developed to address these issues.
Lastly, there are concerns about the allocation of research resources. As more attention is given to cognitive enhancement, there is a risk that research efforts may be diverted from addressing cognitive decline and disorders, potentially neglecting those who are most in need of cognitive interventions.
One primary concern is the issue of fairness and equality. If phospholipid supplementation proves effective in enhancing cognitive abilities, it may create or exacerbate existing social inequalities. Those with access to such supplements could gain significant advantages in academic, professional, and personal spheres, potentially widening the gap between socioeconomic classes. This raises questions about distributive justice and equal opportunities in society.
Another ethical consideration is the potential for coercion or pressure to use cognitive enhancers. In competitive environments such as academia or high-performance workplaces, individuals might feel compelled to use phospholipid supplements to keep up with enhanced peers or meet increasing performance expectations. This could lead to a form of "cognitive arms race" where enhancement becomes a necessity rather than a choice.
The long-term effects of phospholipid supplementation on cognitive function are not yet fully understood. There are concerns about potential side effects or unintended consequences that may only become apparent after prolonged use. This uncertainty raises ethical questions about the responsible development and implementation of such cognitive enhancement technologies.
Privacy and autonomy are also significant ethical concerns. The use of cognitive enhancers may require monitoring and data collection to assess their effectiveness and safety. This could potentially infringe on individual privacy rights and raise questions about data ownership and use.
There are also philosophical and existential questions to consider. The use of cognitive enhancers challenges our understanding of human nature and what it means to be "normal" or "enhanced." It raises debates about authenticity, personal identity, and the value we place on natural versus artificially enhanced cognitive abilities.
The potential for misuse or abuse of cognitive enhancers is another ethical concern. There may be risks associated with off-label use, self-experimentation, or the development of black markets for these substances. Regulatory frameworks and ethical guidelines will need to be developed to address these issues.
Lastly, there are concerns about the allocation of research resources. As more attention is given to cognitive enhancement, there is a risk that research efforts may be diverted from addressing cognitive decline and disorders, potentially neglecting those who are most in need of cognitive interventions.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!