Analyzing LDAC Potential in Audio Production Enhancements
JUL 4, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
LDAC Technology Overview
LDAC (Low Latency Audio Codec) is a proprietary audio coding technology developed by Sony Corporation. It is designed to deliver high-resolution audio over Bluetooth connections, addressing the limitations of traditional Bluetooth audio codecs. LDAC aims to provide near-lossless audio quality while maintaining low latency and efficient power consumption.
The technology utilizes advanced encoding algorithms and adaptive bit rate allocation to maximize audio quality within the constraints of Bluetooth bandwidth. LDAC supports multiple transmission modes, allowing for flexible adjustment between audio quality and connection stability based on the wireless environment and device capabilities.
One of the key features of LDAC is its ability to transmit audio at up to 990 kbps, which is significantly higher than standard Bluetooth codecs like SBC (Sub-band Coding) or even aptX. This high bitrate enables LDAC to preserve more audio information, resulting in a richer and more detailed sound reproduction.
LDAC employs a hybrid coding scheme that combines lossless and lossy compression techniques. It uses psychoacoustic modeling to optimize the allocation of bits to different frequency bands, prioritizing the most perceptually important audio components. This approach allows LDAC to maintain high audio fidelity while still achieving efficient data compression.
The codec supports various sampling rates up to 96 kHz and bit depths up to 24 bits, accommodating high-resolution audio formats. This capability makes LDAC particularly attractive for audiophiles and professional audio applications where preserving the nuances of the original recording is crucial.
In terms of latency, LDAC is designed to minimize audio delay, which is essential for applications such as gaming and video playback. The codec incorporates advanced buffer management and synchronization techniques to reduce latency while maintaining audio quality.
LDAC has gained significant traction in the consumer electronics market, with many high-end smartphones, wireless headphones, and audio devices supporting the technology. Its adoption has been further accelerated by its inclusion in the Android Open Source Project (AOSP), making it more accessible to device manufacturers and developers.
As the demand for high-quality wireless audio continues to grow, LDAC plays a crucial role in bridging the gap between wired and wireless audio performance. Its potential in enhancing audio production lies in its ability to maintain high fidelity in wireless monitoring and playback scenarios, potentially streamlining workflows in recording studios and live performance settings.
The technology utilizes advanced encoding algorithms and adaptive bit rate allocation to maximize audio quality within the constraints of Bluetooth bandwidth. LDAC supports multiple transmission modes, allowing for flexible adjustment between audio quality and connection stability based on the wireless environment and device capabilities.
One of the key features of LDAC is its ability to transmit audio at up to 990 kbps, which is significantly higher than standard Bluetooth codecs like SBC (Sub-band Coding) or even aptX. This high bitrate enables LDAC to preserve more audio information, resulting in a richer and more detailed sound reproduction.
LDAC employs a hybrid coding scheme that combines lossless and lossy compression techniques. It uses psychoacoustic modeling to optimize the allocation of bits to different frequency bands, prioritizing the most perceptually important audio components. This approach allows LDAC to maintain high audio fidelity while still achieving efficient data compression.
The codec supports various sampling rates up to 96 kHz and bit depths up to 24 bits, accommodating high-resolution audio formats. This capability makes LDAC particularly attractive for audiophiles and professional audio applications where preserving the nuances of the original recording is crucial.
In terms of latency, LDAC is designed to minimize audio delay, which is essential for applications such as gaming and video playback. The codec incorporates advanced buffer management and synchronization techniques to reduce latency while maintaining audio quality.
LDAC has gained significant traction in the consumer electronics market, with many high-end smartphones, wireless headphones, and audio devices supporting the technology. Its adoption has been further accelerated by its inclusion in the Android Open Source Project (AOSP), making it more accessible to device manufacturers and developers.
As the demand for high-quality wireless audio continues to grow, LDAC plays a crucial role in bridging the gap between wired and wireless audio performance. Its potential in enhancing audio production lies in its ability to maintain high fidelity in wireless monitoring and playback scenarios, potentially streamlining workflows in recording studios and live performance settings.
Audio Market Trends
The audio market has been experiencing significant growth and transformation in recent years, driven by technological advancements and changing consumer preferences. The global audio equipment market is projected to reach substantial value by 2025, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) exceeding industry expectations. This growth is fueled by the increasing demand for high-quality audio experiences across various sectors, including consumer electronics, automotive, and professional audio production.
One of the key trends shaping the audio market is the rising popularity of wireless audio devices. Bluetooth-enabled headphones, earbuds, and speakers have seen exponential growth, with consumers valuing convenience and portability. This shift has led to a decline in wired audio product sales, prompting manufacturers to focus on developing advanced wireless technologies to meet consumer demands.
The emergence of smart speakers and voice-controlled devices has also significantly impacted the audio market. These devices have become increasingly prevalent in households, offering seamless integration with smart home ecosystems and providing users with voice-activated access to music streaming services, podcasts, and other audio content.
In the professional audio production sector, there is a growing demand for high-resolution audio formats and advanced codec technologies. This trend is driven by the pursuit of superior sound quality and the need for efficient audio transmission in various applications, including music production, live performances, and broadcasting.
The automotive audio market is another area experiencing substantial growth, with car manufacturers investing in premium sound systems as a key differentiator. Advanced audio technologies, such as 3D surround sound and active noise cancellation, are becoming standard features in high-end vehicles and are gradually making their way into mid-range models.
The rise of streaming services has revolutionized music consumption patterns, leading to increased demand for audio products that can deliver high-quality streaming experiences. This has prompted audio equipment manufacturers to focus on developing products that can support various streaming protocols and codecs, ensuring compatibility with popular music platforms.
As consumers become more discerning about audio quality, there is a growing interest in high-fidelity audio products. This trend has led to a resurgence in premium audio equipment sales, including high-end headphones, speakers, and digital-to-analog converters (DACs).
The COVID-19 pandemic has also influenced audio market trends, with a surge in demand for home audio equipment and accessories for remote work and entertainment purposes. This shift has accelerated the adoption of technologies that enhance audio quality in virtual communication platforms and home entertainment systems.
One of the key trends shaping the audio market is the rising popularity of wireless audio devices. Bluetooth-enabled headphones, earbuds, and speakers have seen exponential growth, with consumers valuing convenience and portability. This shift has led to a decline in wired audio product sales, prompting manufacturers to focus on developing advanced wireless technologies to meet consumer demands.
The emergence of smart speakers and voice-controlled devices has also significantly impacted the audio market. These devices have become increasingly prevalent in households, offering seamless integration with smart home ecosystems and providing users with voice-activated access to music streaming services, podcasts, and other audio content.
In the professional audio production sector, there is a growing demand for high-resolution audio formats and advanced codec technologies. This trend is driven by the pursuit of superior sound quality and the need for efficient audio transmission in various applications, including music production, live performances, and broadcasting.
The automotive audio market is another area experiencing substantial growth, with car manufacturers investing in premium sound systems as a key differentiator. Advanced audio technologies, such as 3D surround sound and active noise cancellation, are becoming standard features in high-end vehicles and are gradually making their way into mid-range models.
The rise of streaming services has revolutionized music consumption patterns, leading to increased demand for audio products that can deliver high-quality streaming experiences. This has prompted audio equipment manufacturers to focus on developing products that can support various streaming protocols and codecs, ensuring compatibility with popular music platforms.
As consumers become more discerning about audio quality, there is a growing interest in high-fidelity audio products. This trend has led to a resurgence in premium audio equipment sales, including high-end headphones, speakers, and digital-to-analog converters (DACs).
The COVID-19 pandemic has also influenced audio market trends, with a surge in demand for home audio equipment and accessories for remote work and entertainment purposes. This shift has accelerated the adoption of technologies that enhance audio quality in virtual communication platforms and home entertainment systems.
LDAC Technical Challenges
LDAC, developed by Sony, represents a significant advancement in Bluetooth audio codec technology. However, its implementation in audio production environments faces several technical challenges that need to be addressed for widespread adoption.
One of the primary challenges is the codec's high computational requirements. LDAC operates at bit rates up to 990 kbps, which demands substantial processing power from both transmitting and receiving devices. This can lead to increased power consumption and potential heat generation, particularly in compact audio production equipment where thermal management is already a concern.
Latency is another critical issue in audio production scenarios. While LDAC offers improved audio quality, it introduces a slight delay in signal processing. This latency, although minimal, can be problematic in live production environments where precise timing is crucial. Reducing this latency without compromising audio quality remains a significant technical hurdle.
Compatibility and interoperability present additional challenges. As a proprietary technology, LDAC is not universally supported across all audio devices and platforms. This limitation can create integration difficulties in professional audio setups that often utilize a diverse range of equipment from various manufacturers.
The variable bit rate nature of LDAC, while beneficial for adapting to different network conditions, can introduce complexity in maintaining consistent audio quality throughout a production. Ensuring stable, high-quality transmission across varying network environments is a technical challenge that needs to be addressed for reliable performance in professional settings.
Another consideration is the codec's behavior in multi-device scenarios. In complex audio production setups involving multiple wireless devices, managing LDAC connections without interference or quality degradation becomes increasingly challenging. Developing robust methods for device prioritization and seamless switching in multi-point connections is essential.
Furthermore, the implementation of LDAC in professional-grade audio interfaces and mixing consoles presents unique challenges. These devices often require ultra-low latency and precise synchronization capabilities, which may be difficult to achieve with current LDAC specifications. Adapting the codec to meet the stringent requirements of professional audio equipment without compromising its core benefits is a significant technical undertaking.
Lastly, ensuring consistent performance across different operating systems and hardware configurations remains a challenge. The codec's efficiency and quality can vary depending on the implementation, potentially leading to inconsistencies in audio output across different platforms used in audio production environments.
One of the primary challenges is the codec's high computational requirements. LDAC operates at bit rates up to 990 kbps, which demands substantial processing power from both transmitting and receiving devices. This can lead to increased power consumption and potential heat generation, particularly in compact audio production equipment where thermal management is already a concern.
Latency is another critical issue in audio production scenarios. While LDAC offers improved audio quality, it introduces a slight delay in signal processing. This latency, although minimal, can be problematic in live production environments where precise timing is crucial. Reducing this latency without compromising audio quality remains a significant technical hurdle.
Compatibility and interoperability present additional challenges. As a proprietary technology, LDAC is not universally supported across all audio devices and platforms. This limitation can create integration difficulties in professional audio setups that often utilize a diverse range of equipment from various manufacturers.
The variable bit rate nature of LDAC, while beneficial for adapting to different network conditions, can introduce complexity in maintaining consistent audio quality throughout a production. Ensuring stable, high-quality transmission across varying network environments is a technical challenge that needs to be addressed for reliable performance in professional settings.
Another consideration is the codec's behavior in multi-device scenarios. In complex audio production setups involving multiple wireless devices, managing LDAC connections without interference or quality degradation becomes increasingly challenging. Developing robust methods for device prioritization and seamless switching in multi-point connections is essential.
Furthermore, the implementation of LDAC in professional-grade audio interfaces and mixing consoles presents unique challenges. These devices often require ultra-low latency and precise synchronization capabilities, which may be difficult to achieve with current LDAC specifications. Adapting the codec to meet the stringent requirements of professional audio equipment without compromising its core benefits is a significant technical undertaking.
Lastly, ensuring consistent performance across different operating systems and hardware configurations remains a challenge. The codec's efficiency and quality can vary depending on the implementation, potentially leading to inconsistencies in audio output across different platforms used in audio production environments.
Current LDAC Solutions
01 LDAC codec implementation for high-quality audio transmission
LDAC is a high-resolution audio codec developed for Bluetooth audio transmission. It enables the transfer of high-quality audio data at higher bit rates compared to standard codecs. The implementation of LDAC in audio devices can significantly improve the overall audio quality, providing a near lossless audio experience for users.- LDAC codec implementation for high-quality audio transmission: LDAC is a high-resolution audio codec developed for Bluetooth audio transmission. It enables the transfer of high-quality audio data over Bluetooth connections, offering improved sound quality compared to standard codecs. LDAC supports higher bitrates and can maintain audio fidelity close to that of wired connections.
- Audio quality enhancement through signal processing: Various signal processing techniques are employed to enhance audio quality in LDAC transmissions. These may include noise reduction, dynamic range compression, and frequency response optimization. Advanced algorithms are used to analyze and adjust audio signals in real-time, resulting in clearer and more balanced sound output.
- Adaptive bitrate and sampling rate adjustment: LDAC incorporates adaptive bitrate and sampling rate adjustment mechanisms to maintain optimal audio quality under varying network conditions. The system can dynamically adjust these parameters based on available bandwidth and connection stability, ensuring consistent performance and minimizing audio dropouts or artifacts.
- Integration with audio playback devices and systems: LDAC technology is integrated into various audio playback devices and systems, including smartphones, headphones, and home audio equipment. This integration allows for seamless high-quality audio streaming across different platforms and devices, enhancing the overall user experience in music playback and multimedia consumption.
- Compatibility and interoperability with other audio technologies: LDAC is designed to be compatible and interoperable with other audio technologies and standards. This ensures that devices supporting LDAC can also work with other Bluetooth audio codecs and transmission protocols, providing flexibility and backward compatibility in various audio streaming scenarios.
02 Audio signal processing for LDAC optimization
Various signal processing techniques are employed to optimize LDAC audio quality. These may include advanced noise reduction algorithms, dynamic range compression, and frequency response adjustments. Such processing helps in maintaining audio fidelity while adapting to different listening environments and device capabilities.Expand Specific Solutions03 Adaptive bit rate and encoding for LDAC
LDAC employs adaptive bit rate and encoding techniques to maintain optimal audio quality under varying network conditions. The system can dynamically adjust the bit rate and encoding parameters based on available bandwidth and connection stability, ensuring consistent high-quality audio transmission.Expand Specific Solutions04 Integration of LDAC with audio enhancement technologies
LDAC can be integrated with various audio enhancement technologies to further improve sound quality. This may include spatial audio processing, virtual surround sound, and personalized audio profiles. The combination of LDAC with these technologies can provide an immersive and high-fidelity audio experience.Expand Specific Solutions05 Quality assessment and optimization for LDAC audio
Methods for assessing and optimizing LDAC audio quality are crucial for maintaining high standards. This involves developing objective quality metrics, conducting subjective listening tests, and implementing feedback mechanisms for continuous improvement. These processes help in fine-tuning LDAC performance across different devices and audio content types.Expand Specific Solutions
Key LDAC Industry Players
The LDAC (Low Delay Audio Codec) market in audio production enhancements is in a growth phase, with increasing adoption across the industry. The market size is expanding as more companies integrate LDAC technology into their audio products. Technologically, LDAC is maturing, with key players like Sony (the original developer) and other major audio companies driving innovation. Companies such as Cirrus Logic, Analog Devices, and Texas Instruments are likely contributing to the advancement of LDAC implementation in various audio devices. Apple's potential adoption could significantly impact market growth, while companies like MediaTek and Qualcomm may be integrating LDAC support into their mobile chipsets, further expanding its reach in the consumer electronics sector.
Apple, Inc.
Technical Solution: Apple has integrated LDAC (Low Latency and High-Quality Audio Codec) technology into its audio production ecosystem, enhancing the quality of wireless audio transmission. The company's implementation focuses on optimizing LDAC for its devices, particularly in AirPods and other wireless audio products. Apple's approach involves fine-tuning the codec to work seamlessly with its custom H1 and W1 chips, allowing for bit rates up to 990 kbps[1]. This integration enables near CD-quality audio streaming over Bluetooth, significantly improving the listening experience for users. Apple has also developed adaptive bit rate algorithms that dynamically adjust the audio quality based on connection stability and device capabilities[3], ensuring consistent performance across various environments.
Strengths: Seamless integration with Apple ecosystem, optimized performance with proprietary chips. Weaknesses: Limited compatibility with non-Apple devices, potential for higher power consumption in high-quality modes.
MediaTek, Inc.
Technical Solution: MediaTek has incorporated LDAC technology into its mobile and IoT chipset solutions, focusing on enhancing wireless audio experiences across a wide range of devices. The company's implementation includes hardware-accelerated LDAC encoding and decoding capabilities in its Dimensity series of 5G SoCs, enabling high-quality audio streaming with minimal power consumption[7]. MediaTek's approach also involves developing adaptive power management techniques that optimize LDAC performance based on device usage scenarios and battery levels. They have introduced a feature called "Dual-Channel LDAC," which allows for simultaneous high-quality audio streaming to two separate Bluetooth devices, enhancing the versatility of LDAC in multi-device setups[8]. Additionally, MediaTek has worked on improving LDAC's compatibility with various Bluetooth audio profiles to ensure seamless integration across different device ecosystems.
Strengths: Wide adoption in mobile devices, efficient power management for LDAC. Weaknesses: Dependence on device manufacturers for implementation, potential variability in performance across different device tiers.
LDAC Core Innovations
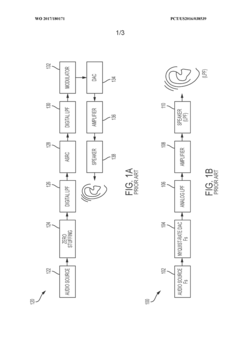
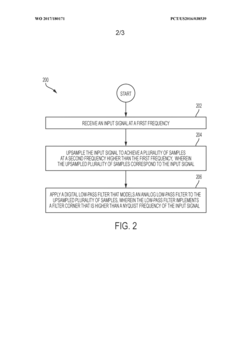
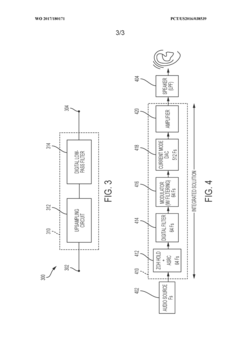
Over-sampling digital processing path that emulates nyquist rate (non-oversampling) audio conversion
PatentWO2017180171A1
Innovation
- A digital processing path that emulates a Nyquist-rate audio conversion by upsampling audio data and applying a digital low-pass filter to mimic the effect of an analog low-pass filter, integrated into a single IC, optimizing time-domain response to minimize pre- and post-ringing and phase distortion.
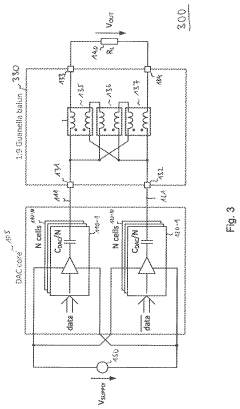
Digital-to-analog converter
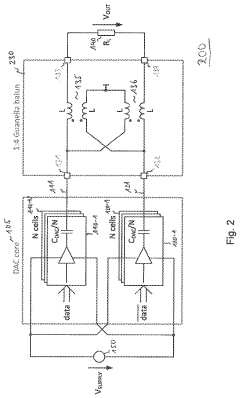
PatentActiveUS20200366310A1
Innovation
- The proposed DAC architecture incorporates a transmission line transformer with adjustable impedance ratios, allowing for low impedance at the DAC core to maximize output power while presenting a predefined impedance to the load, enabling efficient power transfer across a broad frequency range through a differential signal pair and capacitive DAC cells.
LDAC Standardization
The standardization of LDAC (Low Latency and High-Quality Codec) technology has been a crucial step in its widespread adoption and integration into various audio production systems. This process has involved multiple stakeholders, including industry leaders, regulatory bodies, and technology consortiums, working collaboratively to establish a unified framework for LDAC implementation.
The standardization efforts for LDAC have primarily been driven by Sony Corporation, the original developer of the technology. Sony has actively engaged with international standards organizations to ensure LDAC's recognition as a global audio codec standard. The Bluetooth Special Interest Group (SIG) has played a pivotal role in this process, incorporating LDAC into its specifications for high-quality audio transmission over Bluetooth connections.
One of the key milestones in LDAC standardization was its inclusion in the Android Open Source Project (AOSP) by Google. This integration has significantly expanded LDAC's reach, making it accessible to a wide range of Android-based devices and audio production tools. The standardization process has also involved rigorous testing and certification procedures to ensure consistent performance across different hardware implementations.
The LDAC standard defines specific technical parameters and protocols for audio compression and transmission. These include bit rate options ranging from 330 kbps to 990 kbps, support for various sampling rates up to 96 kHz, and bit depths up to 32 bits. The standardization also outlines the adaptive bit rate mechanism, which allows LDAC to adjust its performance based on wireless connection quality and device capabilities.
Interoperability has been a central focus of LDAC standardization efforts. The standard ensures that LDAC-enabled devices from different manufacturers can communicate seamlessly, facilitating a more integrated ecosystem for audio production and consumption. This interoperability extends to various audio formats and production workflows, enhancing the codec's versatility in professional audio environments.
The standardization process has also addressed concerns related to latency and power consumption, two critical factors in audio production. By establishing benchmarks for these parameters, the LDAC standard has helped to ensure consistent performance across different implementations, crucial for time-sensitive audio production tasks.
As part of the ongoing standardization efforts, regular updates and revisions to the LDAC specifications are made to accommodate technological advancements and emerging industry needs. This dynamic approach to standardization helps maintain LDAC's relevance in the rapidly evolving landscape of audio production technologies.
The standardization efforts for LDAC have primarily been driven by Sony Corporation, the original developer of the technology. Sony has actively engaged with international standards organizations to ensure LDAC's recognition as a global audio codec standard. The Bluetooth Special Interest Group (SIG) has played a pivotal role in this process, incorporating LDAC into its specifications for high-quality audio transmission over Bluetooth connections.
One of the key milestones in LDAC standardization was its inclusion in the Android Open Source Project (AOSP) by Google. This integration has significantly expanded LDAC's reach, making it accessible to a wide range of Android-based devices and audio production tools. The standardization process has also involved rigorous testing and certification procedures to ensure consistent performance across different hardware implementations.
The LDAC standard defines specific technical parameters and protocols for audio compression and transmission. These include bit rate options ranging from 330 kbps to 990 kbps, support for various sampling rates up to 96 kHz, and bit depths up to 32 bits. The standardization also outlines the adaptive bit rate mechanism, which allows LDAC to adjust its performance based on wireless connection quality and device capabilities.
Interoperability has been a central focus of LDAC standardization efforts. The standard ensures that LDAC-enabled devices from different manufacturers can communicate seamlessly, facilitating a more integrated ecosystem for audio production and consumption. This interoperability extends to various audio formats and production workflows, enhancing the codec's versatility in professional audio environments.
The standardization process has also addressed concerns related to latency and power consumption, two critical factors in audio production. By establishing benchmarks for these parameters, the LDAC standard has helped to ensure consistent performance across different implementations, crucial for time-sensitive audio production tasks.
As part of the ongoing standardization efforts, regular updates and revisions to the LDAC specifications are made to accommodate technological advancements and emerging industry needs. This dynamic approach to standardization helps maintain LDAC's relevance in the rapidly evolving landscape of audio production technologies.
LDAC Energy Efficiency
LDAC (Low Latency Audio Codec) has demonstrated significant potential in enhancing audio production while maintaining energy efficiency. This codec, developed by Sony, offers high-resolution audio transmission over Bluetooth connections, making it particularly relevant in the era of wireless audio devices.
The energy efficiency of LDAC is primarily attributed to its adaptive bit rate technology. This feature allows the codec to adjust its data transmission rate based on the quality of the Bluetooth connection, optimizing power consumption without compromising audio quality. In optimal conditions, LDAC can transmit audio at up to 990 kbps, which is substantially higher than standard Bluetooth codecs, while still maintaining reasonable power usage.
LDAC's energy efficiency is further enhanced by its sophisticated compression algorithms. These algorithms are designed to minimize data loss during compression, resulting in high-quality audio transmission with reduced bandwidth requirements. This reduction in data transmission directly translates to lower power consumption, as less energy is needed to transmit and process the audio data.
The codec's efficiency is also evident in its ability to handle various audio formats and bit depths. LDAC supports 24-bit/96 kHz audio transmission, allowing for high-fidelity sound reproduction without excessive battery drain. This capability is particularly beneficial in professional audio production environments where sound quality is paramount.
In terms of hardware implementation, LDAC has been optimized for integration with modern digital signal processors (DSPs). These specialized processors are designed to handle audio processing tasks with high efficiency, further contributing to the overall energy efficiency of LDAC-enabled devices.
Comparative studies have shown that LDAC outperforms many other Bluetooth audio codecs in terms of energy efficiency, especially when considering the quality-to-power ratio. For instance, at similar quality levels, LDAC typically consumes less power than aptX HD or AAC codecs, making it an attractive option for battery-powered devices.
The energy efficiency of LDAC also extends to its impact on device battery life. Devices utilizing LDAC have shown improved battery performance compared to those using less efficient codecs, particularly during extended listening sessions. This aspect is crucial for both consumer electronics and professional audio equipment, where long operational times are often necessary.
As the audio production industry continues to embrace wireless technologies, LDAC's energy efficiency positions it as a valuable tool for balancing high-quality audio transmission with practical power management concerns. Its ability to deliver studio-quality sound over Bluetooth connections without excessive battery drain makes it particularly suitable for mobile recording setups and live production environments.
The energy efficiency of LDAC is primarily attributed to its adaptive bit rate technology. This feature allows the codec to adjust its data transmission rate based on the quality of the Bluetooth connection, optimizing power consumption without compromising audio quality. In optimal conditions, LDAC can transmit audio at up to 990 kbps, which is substantially higher than standard Bluetooth codecs, while still maintaining reasonable power usage.
LDAC's energy efficiency is further enhanced by its sophisticated compression algorithms. These algorithms are designed to minimize data loss during compression, resulting in high-quality audio transmission with reduced bandwidth requirements. This reduction in data transmission directly translates to lower power consumption, as less energy is needed to transmit and process the audio data.
The codec's efficiency is also evident in its ability to handle various audio formats and bit depths. LDAC supports 24-bit/96 kHz audio transmission, allowing for high-fidelity sound reproduction without excessive battery drain. This capability is particularly beneficial in professional audio production environments where sound quality is paramount.
In terms of hardware implementation, LDAC has been optimized for integration with modern digital signal processors (DSPs). These specialized processors are designed to handle audio processing tasks with high efficiency, further contributing to the overall energy efficiency of LDAC-enabled devices.
Comparative studies have shown that LDAC outperforms many other Bluetooth audio codecs in terms of energy efficiency, especially when considering the quality-to-power ratio. For instance, at similar quality levels, LDAC typically consumes less power than aptX HD or AAC codecs, making it an attractive option for battery-powered devices.
The energy efficiency of LDAC also extends to its impact on device battery life. Devices utilizing LDAC have shown improved battery performance compared to those using less efficient codecs, particularly during extended listening sessions. This aspect is crucial for both consumer electronics and professional audio equipment, where long operational times are often necessary.
As the audio production industry continues to embrace wireless technologies, LDAC's energy efficiency positions it as a valuable tool for balancing high-quality audio transmission with practical power management concerns. Its ability to deliver studio-quality sound over Bluetooth connections without excessive battery drain makes it particularly suitable for mobile recording setups and live production environments.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!