How to Empower Consumer Applications with LDAC?
JUL 4, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
LDAC Technology Overview and Objectives
LDAC (Low Latency Audio Codec) is a cutting-edge audio coding technology developed by Sony Corporation, designed to deliver high-quality wireless audio transmission. This technology has emerged as a response to the growing demand for superior audio experiences in consumer applications, particularly in the era of wireless audio devices.
The evolution of LDAC technology can be traced back to the increasing popularity of Bluetooth audio devices and the limitations of existing codecs. Traditional Bluetooth audio codecs often compromised sound quality due to bandwidth constraints, leading to a noticeable degradation in audio fidelity. LDAC was introduced to address these limitations and provide a solution that could transmit high-resolution audio wirelessly without significant loss in quality.
LDAC's primary objective is to enable the transmission of High-Resolution Audio content wirelessly, maintaining audio quality comparable to wired connections. It aims to achieve this by utilizing a more efficient encoding process and leveraging the full potential of Bluetooth bandwidth. The technology is designed to support various bit rates, allowing for adaptability based on the connection quality and device capabilities.
One of the key features of LDAC is its ability to transmit audio at up to 990 kbps, which is significantly higher than standard Bluetooth codecs. This increased data rate allows for the preservation of more audio information, resulting in a richer and more detailed sound reproduction. LDAC also employs advanced error correction and packet loss concealment techniques to maintain audio quality even in challenging wireless environments.
The development of LDAC technology aligns with the broader trend of improving wireless audio experiences in consumer electronics. As consumers increasingly adopt wireless headphones, speakers, and other audio devices, the demand for high-quality audio transmission has grown substantially. LDAC aims to bridge the gap between the convenience of wireless technology and the audio quality expectations of discerning listeners.
In the context of empowering consumer applications, LDAC technology offers several potential benefits. It enables device manufacturers to create products that can deliver superior audio quality without the need for wired connections. This opens up new possibilities for product design and user experience, as devices can be made more portable and versatile while still maintaining high audio standards.
Looking ahead, the continued development of LDAC technology is expected to focus on further improving efficiency, reducing latency, and expanding compatibility across a wider range of devices and platforms. As the technology matures, it has the potential to become a standard feature in high-end audio products and may eventually trickle down to more mainstream consumer devices, revolutionizing the wireless audio landscape.
The evolution of LDAC technology can be traced back to the increasing popularity of Bluetooth audio devices and the limitations of existing codecs. Traditional Bluetooth audio codecs often compromised sound quality due to bandwidth constraints, leading to a noticeable degradation in audio fidelity. LDAC was introduced to address these limitations and provide a solution that could transmit high-resolution audio wirelessly without significant loss in quality.
LDAC's primary objective is to enable the transmission of High-Resolution Audio content wirelessly, maintaining audio quality comparable to wired connections. It aims to achieve this by utilizing a more efficient encoding process and leveraging the full potential of Bluetooth bandwidth. The technology is designed to support various bit rates, allowing for adaptability based on the connection quality and device capabilities.
One of the key features of LDAC is its ability to transmit audio at up to 990 kbps, which is significantly higher than standard Bluetooth codecs. This increased data rate allows for the preservation of more audio information, resulting in a richer and more detailed sound reproduction. LDAC also employs advanced error correction and packet loss concealment techniques to maintain audio quality even in challenging wireless environments.
The development of LDAC technology aligns with the broader trend of improving wireless audio experiences in consumer electronics. As consumers increasingly adopt wireless headphones, speakers, and other audio devices, the demand for high-quality audio transmission has grown substantially. LDAC aims to bridge the gap between the convenience of wireless technology and the audio quality expectations of discerning listeners.
In the context of empowering consumer applications, LDAC technology offers several potential benefits. It enables device manufacturers to create products that can deliver superior audio quality without the need for wired connections. This opens up new possibilities for product design and user experience, as devices can be made more portable and versatile while still maintaining high audio standards.
Looking ahead, the continued development of LDAC technology is expected to focus on further improving efficiency, reducing latency, and expanding compatibility across a wider range of devices and platforms. As the technology matures, it has the potential to become a standard feature in high-end audio products and may eventually trickle down to more mainstream consumer devices, revolutionizing the wireless audio landscape.
Market Demand for High-Quality Audio Streaming
The demand for high-quality audio streaming has surged in recent years, driven by the increasing sophistication of consumer audio devices and the growing expectations of audiophiles and casual listeners alike. This market trend is particularly evident in the realm of wireless audio transmission, where technologies like LDAC (Low Latency Audio Codec) have gained significant traction.
Consumer appetite for premium audio experiences has been fueled by the widespread adoption of high-resolution audio formats and the proliferation of streaming services offering lossless audio options. Major players in the music streaming industry, such as Spotify, Apple Music, and Tidal, have introduced Hi-Fi tiers to cater to this demand, signaling a shift in consumer preferences towards higher audio fidelity.
The rise of wireless headphones and earbuds has further accelerated the need for advanced audio codecs like LDAC. As consumers increasingly rely on Bluetooth-enabled devices for their daily audio consumption, there is a growing awareness of the limitations of standard Bluetooth audio quality. This has created a market opportunity for technologies that can bridge the gap between wireless convenience and high-fidelity sound reproduction.
In the automotive sector, there is a notable trend towards integrating premium audio systems in vehicles, with manufacturers partnering with renowned audio brands to enhance the in-car listening experience. This trend extends to the aftermarket, where consumers are willing to invest in high-end car audio systems that support advanced audio codecs for superior sound quality.
The gaming industry has also contributed to the demand for high-quality audio streaming. With the rise of competitive gaming and immersive virtual reality experiences, gamers are increasingly seeking audio solutions that provide precise spatial awareness and rich sound detail. This has led to a growing market for gaming headsets and speakers that support advanced audio technologies.
The professional audio market, including recording studios and live performance venues, has shown interest in wireless audio solutions that can maintain studio-quality sound. This sector demands technologies that can transmit audio with minimal loss and latency, making LDAC and similar codecs attractive options for professional applications.
As smart home ecosystems continue to evolve, there is an emerging demand for high-quality audio streaming across networked speakers and multi-room audio setups. Consumers are looking for seamless integration of their audio systems with voice assistants and home automation, while maintaining superior sound quality throughout their living spaces.
The market demand for high-quality audio streaming is not limited to developed markets. Emerging economies are witnessing a growing middle class with increasing disposable income and a taste for premium audio experiences. This global expansion of the market presents significant opportunities for technologies like LDAC to gain widespread adoption across diverse consumer segments.
Consumer appetite for premium audio experiences has been fueled by the widespread adoption of high-resolution audio formats and the proliferation of streaming services offering lossless audio options. Major players in the music streaming industry, such as Spotify, Apple Music, and Tidal, have introduced Hi-Fi tiers to cater to this demand, signaling a shift in consumer preferences towards higher audio fidelity.
The rise of wireless headphones and earbuds has further accelerated the need for advanced audio codecs like LDAC. As consumers increasingly rely on Bluetooth-enabled devices for their daily audio consumption, there is a growing awareness of the limitations of standard Bluetooth audio quality. This has created a market opportunity for technologies that can bridge the gap between wireless convenience and high-fidelity sound reproduction.
In the automotive sector, there is a notable trend towards integrating premium audio systems in vehicles, with manufacturers partnering with renowned audio brands to enhance the in-car listening experience. This trend extends to the aftermarket, where consumers are willing to invest in high-end car audio systems that support advanced audio codecs for superior sound quality.
The gaming industry has also contributed to the demand for high-quality audio streaming. With the rise of competitive gaming and immersive virtual reality experiences, gamers are increasingly seeking audio solutions that provide precise spatial awareness and rich sound detail. This has led to a growing market for gaming headsets and speakers that support advanced audio technologies.
The professional audio market, including recording studios and live performance venues, has shown interest in wireless audio solutions that can maintain studio-quality sound. This sector demands technologies that can transmit audio with minimal loss and latency, making LDAC and similar codecs attractive options for professional applications.
As smart home ecosystems continue to evolve, there is an emerging demand for high-quality audio streaming across networked speakers and multi-room audio setups. Consumers are looking for seamless integration of their audio systems with voice assistants and home automation, while maintaining superior sound quality throughout their living spaces.
The market demand for high-quality audio streaming is not limited to developed markets. Emerging economies are witnessing a growing middle class with increasing disposable income and a taste for premium audio experiences. This global expansion of the market presents significant opportunities for technologies like LDAC to gain widespread adoption across diverse consumer segments.
LDAC Technical Challenges and Limitations
LDAC (Low Delay Audio Codec) faces several technical challenges and limitations in its implementation and widespread adoption in consumer applications. One of the primary challenges is the high computational complexity required for encoding and decoding LDAC streams. This demands significant processing power, which can be a constraint for low-end devices or those with limited battery life.
Another limitation is the bandwidth requirement for LDAC transmission. While LDAC offers high-quality audio at various bitrates, the highest quality settings necessitate substantial bandwidth, which may not always be available in all wireless environments or supported by all Bluetooth devices.
Compatibility issues also pose a challenge for LDAC integration. Not all devices support LDAC, limiting its widespread adoption. This fragmentation in the market creates a barrier for developers and manufacturers who must consider multiple codec options to ensure broad compatibility.
Latency is another area where LDAC faces challenges, particularly in applications requiring real-time audio processing or synchronization with video. Although LDAC is designed for low-delay transmission, it may still introduce noticeable latency in certain scenarios, affecting user experience in gaming or video applications.
The proprietary nature of LDAC technology presents another limitation. As a Sony-developed codec, its implementation requires licensing, which can be a barrier for smaller manufacturers or open-source projects. This restricted access may hinder innovation and limit the codec's integration into a wider range of applications and devices.
Power consumption is a significant concern, especially for battery-powered devices. The advanced processing required for LDAC encoding and decoding can lead to increased power draw, potentially impacting the battery life of portable devices such as smartphones and wireless headphones.
Scalability across different device types and use cases presents another challenge. While LDAC performs well in certain scenarios, adapting it to diverse consumer applications with varying requirements for audio quality, latency, and power consumption can be complex.
Lastly, the evolving landscape of wireless audio technologies poses a challenge for LDAC's long-term relevance. As new codecs and transmission standards emerge, maintaining LDAC's competitive edge and ensuring its continued development to meet future audio quality and efficiency demands will be crucial for its sustained adoption in consumer applications.
Another limitation is the bandwidth requirement for LDAC transmission. While LDAC offers high-quality audio at various bitrates, the highest quality settings necessitate substantial bandwidth, which may not always be available in all wireless environments or supported by all Bluetooth devices.
Compatibility issues also pose a challenge for LDAC integration. Not all devices support LDAC, limiting its widespread adoption. This fragmentation in the market creates a barrier for developers and manufacturers who must consider multiple codec options to ensure broad compatibility.
Latency is another area where LDAC faces challenges, particularly in applications requiring real-time audio processing or synchronization with video. Although LDAC is designed for low-delay transmission, it may still introduce noticeable latency in certain scenarios, affecting user experience in gaming or video applications.
The proprietary nature of LDAC technology presents another limitation. As a Sony-developed codec, its implementation requires licensing, which can be a barrier for smaller manufacturers or open-source projects. This restricted access may hinder innovation and limit the codec's integration into a wider range of applications and devices.
Power consumption is a significant concern, especially for battery-powered devices. The advanced processing required for LDAC encoding and decoding can lead to increased power draw, potentially impacting the battery life of portable devices such as smartphones and wireless headphones.
Scalability across different device types and use cases presents another challenge. While LDAC performs well in certain scenarios, adapting it to diverse consumer applications with varying requirements for audio quality, latency, and power consumption can be complex.
Lastly, the evolving landscape of wireless audio technologies poses a challenge for LDAC's long-term relevance. As new codecs and transmission standards emerge, maintaining LDAC's competitive edge and ensuring its continued development to meet future audio quality and efficiency demands will be crucial for its sustained adoption in consumer applications.
Current LDAC Implementation Strategies
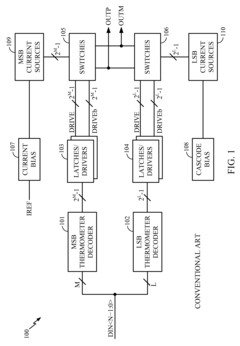
01 LDAC audio codec implementation
LDAC is a high-quality audio codec developed for Bluetooth audio transmission. It allows for higher bitrates and better audio quality compared to standard Bluetooth codecs. The implementation of LDAC in audio devices involves specific encoding and decoding processes to maintain audio fidelity while optimizing for wireless transmission.- LDAC audio codec implementation: LDAC is a high-quality audio codec developed for Bluetooth audio transmission. It enables high-resolution audio streaming over Bluetooth connections, offering improved sound quality compared to standard codecs. LDAC supports various bit rates and can adapt to different network conditions to maintain optimal audio performance.
- LDAC integration in audio devices: LDAC technology is integrated into various audio devices, including smartphones, headphones, and speakers. This integration allows for enhanced wireless audio transmission, providing users with a superior listening experience. Manufacturers implement LDAC in their products to offer high-fidelity sound reproduction in wireless audio systems.
- LDAC compatibility with other audio technologies: LDAC is designed to be compatible with various audio technologies and standards. This includes integration with other audio codecs, digital signal processing techniques, and audio enhancement features. The compatibility ensures that LDAC can be widely adopted across different audio ecosystems and devices.
- LDAC in automotive audio systems: LDAC technology is being implemented in automotive audio systems to provide high-quality wireless audio streaming in vehicles. This application enhances the in-car entertainment experience by allowing seamless connectivity between mobile devices and the vehicle's audio system while maintaining superior sound quality.
- LDAC power efficiency and optimization: Efforts are being made to optimize LDAC technology for improved power efficiency in battery-powered devices. This includes developing more energy-efficient encoding and decoding processes, as well as implementing adaptive bit rate techniques to balance audio quality and power consumption based on device capabilities and user preferences.
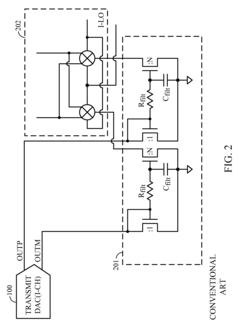
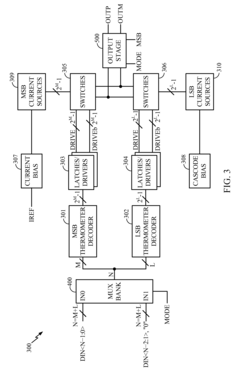
02 LDAC integration in audio systems
The integration of LDAC technology into various audio systems, including smartphones, headphones, and speakers, requires specific hardware and software configurations. This involves designing compatible chipsets, implementing LDAC algorithms, and ensuring interoperability with other Bluetooth devices.Expand Specific Solutions03 LDAC power efficiency improvements
Enhancing the power efficiency of LDAC codec implementation is crucial for battery-powered devices. This involves optimizing the encoding and decoding processes, implementing power-saving modes, and developing efficient signal processing techniques to reduce energy consumption while maintaining high audio quality.Expand Specific Solutions04 LDAC compatibility with other audio technologies
Ensuring compatibility between LDAC and other audio technologies is essential for widespread adoption. This includes developing methods for seamless switching between different codecs, integrating LDAC with various audio processing technologies, and maintaining compatibility with existing Bluetooth audio profiles.Expand Specific Solutions05 LDAC quality optimization techniques
Continuous improvement of LDAC audio quality involves developing advanced signal processing algorithms, implementing adaptive bitrate control, and optimizing the codec for various audio content types. These techniques aim to enhance the overall listening experience while maintaining efficient wireless transmission.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in LDAC Ecosystem
The LDAC technology market is in a growth phase, with increasing adoption in consumer audio applications. The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of established tech giants and specialized audio companies. Market size is expanding as demand for high-quality wireless audio grows. Technologically, LDAC is relatively mature but still evolving, with companies like Sony (the original developer), Qualcomm, and Huawei leading in implementation and improvement. Other players like Samsung, Sharp, and Analog Devices are also contributing to the ecosystem, enhancing compatibility and performance across various devices and platforms.
Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Huawei has embraced LDAC technology in its smartphones and audio devices. Their implementation focuses on optimizing the codec for their Kirin chipsets, aiming to provide a seamless high-resolution audio experience[7]. Huawei has worked on improving the power efficiency of LDAC transmission, particularly important for their wearable devices like wireless earbuds[8]. They have also developed AI-driven audio enhancements that work in conjunction with LDAC to further improve sound quality and personalization[9].
Strengths: Strong presence in the smartphone and wearable markets, advanced AI capabilities. Weaknesses: Recent geopolitical challenges may affect global market reach.
QUALCOMM, Inc.
Technical Solution: Qualcomm has developed its own aptX adaptive codec, which competes with LDAC. However, they have also incorporated LDAC support in their Snapdragon Sound technology platform[4]. Qualcomm's approach focuses on providing a comprehensive audio solution that includes both hardware and software optimizations. Their implementation of LDAC aims to reduce latency and improve power efficiency while maintaining high-quality audio transmission[5]. Qualcomm has also worked on enhancing the robustness of LDAC connections in challenging RF environments[6].
Strengths: Extensive experience in mobile chipsets, wide industry adoption. Weaknesses: May prioritize their own audio codecs over LDAC.
Core LDAC Patents and Technical Innovations
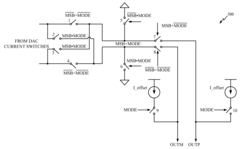
Pseudo-differential class-ab digital-to-analog converter with code dependent DC current
PatentActiveUS20080309537A1
Innovation
- A pseudo-differential class-AB digital-to-analog converter with code-dependent DC current is introduced, featuring an input stage that modifies the most significant bits and least significant bits, and an output stage that steers the average output current to a low value at the mid-point of coded values, allowing for reduced DC current without compromising signal power.
Multiplying digital-to-analog converter (MDAC) with nonlinear calibration
PatentActiveUS20210203339A1
Innovation
- Incorporating a nonlinear calibration circuit with a calibration resistor and a calibration current source that applies a calibration current based on the multi-bit code and self-heating correction parameters to adjust the MDAC output, correcting for self-heating errors and improving accuracy.
LDAC Integration Best Practices
Integrating LDAC (Low Latency Audio Codec) into consumer applications requires careful consideration of several best practices to ensure optimal performance and user experience. First and foremost, developers should focus on implementing proper buffer management techniques. This involves fine-tuning the audio buffer size to strike a balance between low latency and smooth playback. Smaller buffers reduce latency but may lead to audio dropouts, while larger buffers increase stability at the cost of higher latency. It's crucial to experiment with different buffer sizes to find the sweet spot for each specific application.
Another key aspect of LDAC integration is optimizing the codec's bitrate settings. LDAC supports multiple bitrate modes, including 330 kbps, 660 kbps, and 990 kbps. Developers should implement adaptive bitrate switching based on the connection quality and device capabilities. This ensures that the audio quality remains consistent across various scenarios while maximizing battery life and maintaining a stable connection.
Error handling and recovery mechanisms are essential for robust LDAC implementation. Applications should be designed to gracefully handle connection drops, packet loss, and other potential issues. This includes implementing fallback mechanisms to switch to lower bitrates or alternative codecs when necessary, as well as providing clear feedback to users about the current audio quality and connection status.
To fully leverage LDAC's capabilities, developers should pay attention to audio source quality. Using high-resolution audio files or streams that match or exceed LDAC's maximum bitrate of 990 kbps ensures that users can experience the full potential of the codec. Additionally, implementing proper audio preprocessing techniques, such as resampling and format conversion, can help optimize the audio signal for LDAC encoding.
Power management is another critical consideration when integrating LDAC. The codec's high-quality audio transmission can be power-intensive, so developers should implement intelligent power-saving features. This may include dynamically adjusting the codec's settings based on the device's battery level or user preferences, and providing options for users to balance audio quality with battery life.
Lastly, ensuring compatibility across different devices and platforms is crucial for widespread adoption of LDAC-enabled applications. Developers should thoroughly test their implementations on various Android devices and versions, as well as different Bluetooth audio receivers. This includes verifying proper negotiation of LDAC support during device pairing and handling scenarios where LDAC is not available or supported.
Another key aspect of LDAC integration is optimizing the codec's bitrate settings. LDAC supports multiple bitrate modes, including 330 kbps, 660 kbps, and 990 kbps. Developers should implement adaptive bitrate switching based on the connection quality and device capabilities. This ensures that the audio quality remains consistent across various scenarios while maximizing battery life and maintaining a stable connection.
Error handling and recovery mechanisms are essential for robust LDAC implementation. Applications should be designed to gracefully handle connection drops, packet loss, and other potential issues. This includes implementing fallback mechanisms to switch to lower bitrates or alternative codecs when necessary, as well as providing clear feedback to users about the current audio quality and connection status.
To fully leverage LDAC's capabilities, developers should pay attention to audio source quality. Using high-resolution audio files or streams that match or exceed LDAC's maximum bitrate of 990 kbps ensures that users can experience the full potential of the codec. Additionally, implementing proper audio preprocessing techniques, such as resampling and format conversion, can help optimize the audio signal for LDAC encoding.
Power management is another critical consideration when integrating LDAC. The codec's high-quality audio transmission can be power-intensive, so developers should implement intelligent power-saving features. This may include dynamically adjusting the codec's settings based on the device's battery level or user preferences, and providing options for users to balance audio quality with battery life.
Lastly, ensuring compatibility across different devices and platforms is crucial for widespread adoption of LDAC-enabled applications. Developers should thoroughly test their implementations on various Android devices and versions, as well as different Bluetooth audio receivers. This includes verifying proper negotiation of LDAC support during device pairing and handling scenarios where LDAC is not available or supported.
LDAC Certification and Compliance
LDAC certification and compliance are crucial aspects for consumer applications seeking to leverage the high-quality audio codec. The certification process ensures that products meet the stringent requirements set by Sony, the developer of LDAC technology. To obtain LDAC certification, manufacturers must undergo a rigorous evaluation process that includes both hardware and software testing.
The certification process begins with an application to Sony, where manufacturers provide detailed information about their product and its intended use of LDAC technology. Sony then conducts a thorough review of the application and may request additional documentation or clarifications. Once the initial review is complete, manufacturers are required to submit their products for testing at Sony-approved laboratories.
During the testing phase, products are evaluated for their ability to accurately encode and decode LDAC audio streams. This includes assessing the product's performance across various bit rates and ensuring compatibility with different audio formats. The testing process also examines the product's ability to maintain consistent audio quality under various network conditions and device configurations.
Compliance with LDAC specifications is a key component of the certification process. Manufacturers must demonstrate that their products adhere to the LDAC codec's technical requirements, including support for the full range of LDAC bit rates (330 kbps, 660 kbps, and 990 kbps) and the ability to dynamically adjust bit rates based on network conditions. Additionally, products must implement the LDAC codec correctly to ensure optimal audio quality and energy efficiency.
Once a product successfully passes all tests and meets compliance standards, Sony grants LDAC certification. This certification allows manufacturers to use the LDAC logo on their products and marketing materials, signifying to consumers that the device is capable of delivering high-resolution audio using LDAC technology.
For consumer applications, obtaining LDAC certification is essential for several reasons. Firstly, it provides assurance to users that the product can deliver the high-quality audio experience promised by LDAC technology. Secondly, certification enables seamless interoperability with other LDAC-certified devices, ensuring a consistent user experience across different brands and product categories.
Maintaining compliance with LDAC standards is an ongoing process. As the technology evolves, Sony may update the certification requirements or introduce new features. Manufacturers must stay informed about these changes and may need to recertify their products to maintain compliance and continue using the LDAC branding.
The certification process begins with an application to Sony, where manufacturers provide detailed information about their product and its intended use of LDAC technology. Sony then conducts a thorough review of the application and may request additional documentation or clarifications. Once the initial review is complete, manufacturers are required to submit their products for testing at Sony-approved laboratories.
During the testing phase, products are evaluated for their ability to accurately encode and decode LDAC audio streams. This includes assessing the product's performance across various bit rates and ensuring compatibility with different audio formats. The testing process also examines the product's ability to maintain consistent audio quality under various network conditions and device configurations.
Compliance with LDAC specifications is a key component of the certification process. Manufacturers must demonstrate that their products adhere to the LDAC codec's technical requirements, including support for the full range of LDAC bit rates (330 kbps, 660 kbps, and 990 kbps) and the ability to dynamically adjust bit rates based on network conditions. Additionally, products must implement the LDAC codec correctly to ensure optimal audio quality and energy efficiency.
Once a product successfully passes all tests and meets compliance standards, Sony grants LDAC certification. This certification allows manufacturers to use the LDAC logo on their products and marketing materials, signifying to consumers that the device is capable of delivering high-resolution audio using LDAC technology.
For consumer applications, obtaining LDAC certification is essential for several reasons. Firstly, it provides assurance to users that the product can deliver the high-quality audio experience promised by LDAC technology. Secondly, certification enables seamless interoperability with other LDAC-certified devices, ensuring a consistent user experience across different brands and product categories.
Maintaining compliance with LDAC standards is an ongoing process. As the technology evolves, Sony may update the certification requirements or introduce new features. Manufacturers must stay informed about these changes and may need to recertify their products to maintain compliance and continue using the LDAC branding.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!