Strategizing Audio Solutions Implementing LDAC Techniques?
JUL 4, 20258 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
LDAC Audio Evolution
LDAC, developed by Sony in 2015, represents a significant milestone in the evolution of high-quality audio transmission over Bluetooth. This codec emerged as a response to the growing demand for wireless audio solutions that could deliver near-lossless audio quality, addressing the limitations of previous Bluetooth audio codecs such as SBC and AAC.
The evolution of LDAC can be traced through several key stages. Initially, LDAC was introduced as a proprietary technology exclusive to Sony devices, offering a maximum bitrate of 990 kbps. This was a substantial improvement over existing codecs, which typically operated at much lower bitrates, resulting in noticeable audio quality degradation.
In 2017, a crucial development occurred when Sony made LDAC open-source, integrating it into the Android Open Source Project (AOSP) with Android 8.0 Oreo. This move significantly expanded LDAC's reach, making it available to a wide range of Android devices and third-party manufacturers. The open-source nature of LDAC fostered innovation and adoption across the audio industry.
Subsequent iterations of LDAC focused on improving efficiency and compatibility. The codec's adaptive bitrate feature was refined, allowing it to dynamically adjust between 330 kbps, 660 kbps, and 990 kbps based on connection stability and device capabilities. This adaptability ensured optimal performance across various usage scenarios and environments.
Recent developments in LDAC have centered on enhancing its energy efficiency and reducing latency, critical factors for mobile devices and real-time audio applications. Efforts have been made to optimize the codec's performance on low-power devices, extending battery life without compromising audio quality.
The latest advancements in LDAC technology have explored integration with other audio enhancement technologies, such as 360 Reality Audio and DSEE Extreme (Digital Sound Enhancement Engine). These integrations aim to provide a more immersive and high-fidelity audio experience, pushing the boundaries of wireless audio reproduction.
Looking forward, the evolution of LDAC is likely to continue in several directions. Increased bitrates beyond the current 990 kbps maximum are being explored to further close the gap with wired audio quality. Additionally, research is ongoing to improve LDAC's performance in challenging wireless environments and to reduce its computational demands, making it more accessible to a broader range of devices.
The evolution of LDAC can be traced through several key stages. Initially, LDAC was introduced as a proprietary technology exclusive to Sony devices, offering a maximum bitrate of 990 kbps. This was a substantial improvement over existing codecs, which typically operated at much lower bitrates, resulting in noticeable audio quality degradation.
In 2017, a crucial development occurred when Sony made LDAC open-source, integrating it into the Android Open Source Project (AOSP) with Android 8.0 Oreo. This move significantly expanded LDAC's reach, making it available to a wide range of Android devices and third-party manufacturers. The open-source nature of LDAC fostered innovation and adoption across the audio industry.
Subsequent iterations of LDAC focused on improving efficiency and compatibility. The codec's adaptive bitrate feature was refined, allowing it to dynamically adjust between 330 kbps, 660 kbps, and 990 kbps based on connection stability and device capabilities. This adaptability ensured optimal performance across various usage scenarios and environments.
Recent developments in LDAC have centered on enhancing its energy efficiency and reducing latency, critical factors for mobile devices and real-time audio applications. Efforts have been made to optimize the codec's performance on low-power devices, extending battery life without compromising audio quality.
The latest advancements in LDAC technology have explored integration with other audio enhancement technologies, such as 360 Reality Audio and DSEE Extreme (Digital Sound Enhancement Engine). These integrations aim to provide a more immersive and high-fidelity audio experience, pushing the boundaries of wireless audio reproduction.
Looking forward, the evolution of LDAC is likely to continue in several directions. Increased bitrates beyond the current 990 kbps maximum are being explored to further close the gap with wired audio quality. Additionally, research is ongoing to improve LDAC's performance in challenging wireless environments and to reduce its computational demands, making it more accessible to a broader range of devices.
Market Demand Analysis
The market demand for audio solutions implementing LDAC techniques has been steadily growing in recent years, driven by the increasing consumer appetite for high-quality wireless audio experiences. As more users adopt wireless headphones, earbuds, and speakers, there is a growing awareness and desire for audio codecs that can deliver near-lossless sound quality over Bluetooth connections.
LDAC, developed by Sony, has positioned itself as a premium audio codec capable of transmitting high-resolution audio wirelessly. This technology has gained significant traction in the high-end audio market, where consumers are willing to pay a premium for superior sound quality. The demand for LDAC-enabled devices is particularly strong among audiophiles and music enthusiasts who seek to preserve the fidelity of their audio sources.
The market for LDAC-compatible devices extends beyond just headphones and earbuds. There is a growing interest in implementing LDAC in various audio products, including wireless speakers, car audio systems, and home theater setups. This expansion of use cases is contributing to the overall market growth for LDAC-enabled solutions.
In the smartphone market, there is an increasing trend of manufacturers incorporating LDAC support into their devices. This is partly driven by consumer demand for high-quality audio playback and the desire to future-proof devices against evolving audio standards. As more smartphones support LDAC, it creates a ripple effect, stimulating demand for compatible audio accessories.
The professional audio sector also shows potential for LDAC adoption. Recording studios, live sound engineers, and broadcast professionals are exploring wireless solutions that can maintain audio quality comparable to wired connections. LDAC's ability to transmit high-resolution audio wirelessly makes it an attractive option for these applications.
Market analysis indicates that the Asia-Pacific region, particularly Japan and South Korea, leads in the adoption of LDAC technology. However, there is growing interest and market potential in North America and Europe as awareness of high-resolution audio increases among consumers in these regions.
The COVID-19 pandemic has inadvertently boosted the demand for high-quality audio solutions as more people work and entertain themselves at home. This has led to increased investment in personal audio equipment, with a segment of consumers opting for premium solutions that incorporate technologies like LDAC.
Looking ahead, the market for LDAC-enabled audio solutions is expected to continue its growth trajectory. Factors such as the proliferation of 5G networks, advancements in Bluetooth technology, and the increasing availability of high-resolution audio content are likely to fuel this growth. However, the market will also face competition from other high-quality audio codecs and technologies, necessitating ongoing innovation and marketing efforts to maintain and expand LDAC's market share.
LDAC, developed by Sony, has positioned itself as a premium audio codec capable of transmitting high-resolution audio wirelessly. This technology has gained significant traction in the high-end audio market, where consumers are willing to pay a premium for superior sound quality. The demand for LDAC-enabled devices is particularly strong among audiophiles and music enthusiasts who seek to preserve the fidelity of their audio sources.
The market for LDAC-compatible devices extends beyond just headphones and earbuds. There is a growing interest in implementing LDAC in various audio products, including wireless speakers, car audio systems, and home theater setups. This expansion of use cases is contributing to the overall market growth for LDAC-enabled solutions.
In the smartphone market, there is an increasing trend of manufacturers incorporating LDAC support into their devices. This is partly driven by consumer demand for high-quality audio playback and the desire to future-proof devices against evolving audio standards. As more smartphones support LDAC, it creates a ripple effect, stimulating demand for compatible audio accessories.
The professional audio sector also shows potential for LDAC adoption. Recording studios, live sound engineers, and broadcast professionals are exploring wireless solutions that can maintain audio quality comparable to wired connections. LDAC's ability to transmit high-resolution audio wirelessly makes it an attractive option for these applications.
Market analysis indicates that the Asia-Pacific region, particularly Japan and South Korea, leads in the adoption of LDAC technology. However, there is growing interest and market potential in North America and Europe as awareness of high-resolution audio increases among consumers in these regions.
The COVID-19 pandemic has inadvertently boosted the demand for high-quality audio solutions as more people work and entertain themselves at home. This has led to increased investment in personal audio equipment, with a segment of consumers opting for premium solutions that incorporate technologies like LDAC.
Looking ahead, the market for LDAC-enabled audio solutions is expected to continue its growth trajectory. Factors such as the proliferation of 5G networks, advancements in Bluetooth technology, and the increasing availability of high-resolution audio content are likely to fuel this growth. However, the market will also face competition from other high-quality audio codecs and technologies, necessitating ongoing innovation and marketing efforts to maintain and expand LDAC's market share.
LDAC Challenges
LDAC, developed by Sony, represents a significant advancement in wireless audio transmission. However, its implementation faces several challenges that need to be addressed for widespread adoption and optimal performance.
One of the primary challenges is the high bandwidth requirement of LDAC. The codec operates at bit rates up to 990 kbps, which is significantly higher than conventional Bluetooth audio codecs. This high bandwidth demand can strain the capabilities of existing Bluetooth hardware, particularly in environments with signal interference or when multiple devices are connected.
Power consumption is another critical issue. The complex encoding and decoding processes of LDAC require more computational power, leading to increased battery drain on both transmitting and receiving devices. This can be particularly problematic for portable devices like smartphones and wireless earbuds, where battery life is a crucial factor for user satisfaction.
Compatibility presents a significant hurdle for LDAC adoption. As a proprietary technology, it is not universally supported across all devices and platforms. This limitation can create fragmentation in the market, where users may experience inconsistent audio quality depending on their device ecosystem.
The complexity of LDAC's implementation also poses challenges for manufacturers. Integrating LDAC into devices requires specialized knowledge and potentially additional hardware components, which can increase production costs and time-to-market for new products.
Latency is another area of concern, especially for applications requiring real-time audio synchronization, such as gaming or video playback. While LDAC offers improved latency compared to some other high-quality codecs, achieving consistently low latency across various devices and use cases remains challenging.
Signal stability and range limitations are also notable challenges. LDAC's high bit rate can make it more susceptible to connection drops or quality degradation in challenging wireless environments, potentially compromising the user experience in real-world scenarios.
Lastly, the trade-off between audio quality and connection stability presents an ongoing challenge. While LDAC offers multiple bit rate modes to adapt to different conditions, optimizing this balance in diverse and dynamic environments requires sophisticated algorithms and continuous refinement.
Addressing these challenges is crucial for the wider adoption and success of LDAC technology in the competitive landscape of wireless audio solutions. Overcoming these hurdles will require collaborative efforts from hardware manufacturers, software developers, and audio engineers to push the boundaries of wireless audio transmission while maintaining reliability and user-friendly implementation.
One of the primary challenges is the high bandwidth requirement of LDAC. The codec operates at bit rates up to 990 kbps, which is significantly higher than conventional Bluetooth audio codecs. This high bandwidth demand can strain the capabilities of existing Bluetooth hardware, particularly in environments with signal interference or when multiple devices are connected.
Power consumption is another critical issue. The complex encoding and decoding processes of LDAC require more computational power, leading to increased battery drain on both transmitting and receiving devices. This can be particularly problematic for portable devices like smartphones and wireless earbuds, where battery life is a crucial factor for user satisfaction.
Compatibility presents a significant hurdle for LDAC adoption. As a proprietary technology, it is not universally supported across all devices and platforms. This limitation can create fragmentation in the market, where users may experience inconsistent audio quality depending on their device ecosystem.
The complexity of LDAC's implementation also poses challenges for manufacturers. Integrating LDAC into devices requires specialized knowledge and potentially additional hardware components, which can increase production costs and time-to-market for new products.
Latency is another area of concern, especially for applications requiring real-time audio synchronization, such as gaming or video playback. While LDAC offers improved latency compared to some other high-quality codecs, achieving consistently low latency across various devices and use cases remains challenging.
Signal stability and range limitations are also notable challenges. LDAC's high bit rate can make it more susceptible to connection drops or quality degradation in challenging wireless environments, potentially compromising the user experience in real-world scenarios.
Lastly, the trade-off between audio quality and connection stability presents an ongoing challenge. While LDAC offers multiple bit rate modes to adapt to different conditions, optimizing this balance in diverse and dynamic environments requires sophisticated algorithms and continuous refinement.
Addressing these challenges is crucial for the wider adoption and success of LDAC technology in the competitive landscape of wireless audio solutions. Overcoming these hurdles will require collaborative efforts from hardware manufacturers, software developers, and audio engineers to push the boundaries of wireless audio transmission while maintaining reliability and user-friendly implementation.
Current LDAC Solutions
01 LDAC codec implementation for high-quality audio transmission
LDAC is a high-resolution audio codec developed for Bluetooth audio transmission. It enables the transfer of high-quality audio data over Bluetooth connections, offering improved sound quality compared to standard codecs. LDAC supports various bit rates and can adapt to different network conditions to maintain optimal audio performance.- LDAC codec implementation for high-quality audio transmission: LDAC is a high-resolution audio codec developed for Bluetooth audio transmission. It enables the transfer of high-quality audio data over Bluetooth connections, offering improved sound quality compared to standard codecs. LDAC supports various bit rates and sampling frequencies, allowing for flexible adaptation to different audio sources and network conditions.
- Audio quality enhancement through signal processing: Various signal processing techniques are employed to enhance audio quality in LDAC-enabled devices. These may include noise reduction, dynamic range compression, and equalization. Advanced algorithms are used to optimize the audio signal before encoding, ensuring the best possible sound quality within the constraints of the Bluetooth transmission.
- Adaptive bit rate and sampling frequency selection: LDAC incorporates adaptive bit rate and sampling frequency selection mechanisms to maintain optimal audio quality under varying network conditions. The system can dynamically adjust these parameters based on the available bandwidth and connection stability, ensuring a consistent listening experience.
- Integration with audio playback devices and systems: LDAC technology is integrated into various audio playback devices and systems, including smartphones, headphones, and home audio equipment. This integration involves hardware and software optimizations to ensure seamless operation and maximum audio quality across different platforms and device types.
- Compatibility and interoperability with other audio technologies: LDAC is designed to be compatible and interoperable with other audio technologies and standards. This includes seamless switching between different codecs, support for various audio formats, and integration with existing audio processing pipelines. Such compatibility ensures a wide range of devices can benefit from LDAC's high-quality audio capabilities.
02 Audio quality enhancement through signal processing
Various signal processing techniques are employed to enhance audio quality in LDAC systems. These may include noise reduction, dynamic range compression, and frequency response correction. Advanced algorithms are used to optimize the audio signal before encoding and after decoding, resulting in improved overall sound quality.Expand Specific Solutions03 Adaptive bit rate and sampling frequency adjustment
LDAC systems can dynamically adjust bit rates and sampling frequencies based on network conditions and device capabilities. This adaptive approach ensures optimal audio quality while maintaining stable connections. The system can switch between different quality modes to balance audio fidelity and connection stability.Expand Specific Solutions04 Integration with audio playback devices and systems
LDAC technology is integrated into various audio playback devices and systems, including smartphones, headphones, and home audio equipment. This integration allows for seamless high-quality audio streaming across different devices and platforms, enhancing the overall user experience in audio consumption.Expand Specific Solutions05 Compatibility and interoperability with other audio codecs
LDAC is designed to be compatible and interoperable with other audio codecs and transmission protocols. This ensures that devices supporting LDAC can still function with non-LDAC equipment, providing flexibility and backward compatibility in various audio streaming scenarios.Expand Specific Solutions
LDAC Industry Players
The competitive landscape for strategizing audio solutions implementing LDAC techniques is characterized by a mature market with significant growth potential. The technology has reached a high level of sophistication, with major players like Sony Group Corp., the original developer of LDAC, leading the way. Other key competitors include Harman International Industries, Bose Corp., and Huawei Technologies, each leveraging LDAC to enhance their audio product offerings. The market is driven by increasing demand for high-quality wireless audio experiences, with companies focusing on innovation in areas such as codec efficiency, latency reduction, and integration with various devices. As the technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see further advancements and wider adoption across the consumer electronics and automotive sectors.
Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Huawei has been actively working on implementing and improving LDAC in their devices, particularly in their smartphones and audio accessories. Their strategy involves not only adopting LDAC but also developing complementary technologies to enhance the overall audio experience. Huawei has implemented LDAC in their EMUI operating system, allowing their devices to transmit high-quality audio to compatible receivers[10]. Additionally, Huawei has been developing their own audio technologies, such as Histen sound effects and AI noise cancellation, which can work in conjunction with LDAC to further improve audio quality. Huawei's approach also includes optimizing power consumption when using high-bitrate codecs like LDAC, ensuring longer battery life without compromising on audio quality[11].
Strengths: Wide implementation across device ecosystem, complementary audio enhancement technologies, focus on power efficiency. Weaknesses: Geopolitical challenges may limit global market reach, dependence on Android for some LDAC implementations.
Bose Corp.
Technical Solution: Bose has been implementing advanced audio solutions that, while not directly using LDAC, compete in the same space of high-quality wireless audio. Their strategy involves proprietary technologies like ActiveSense and Volume-optimized Active EQ[6]. Bose has focused on developing their own codec solutions and noise-cancelling technologies to deliver high-quality audio experiences. They've also been working on spatial audio technologies to create immersive soundscapes. While not directly implementing LDAC, Bose's approach to high-quality wireless audio often involves similar goals of minimizing latency and maximizing audio fidelity within the constraints of wireless transmission[7].
Strengths: Strong brand recognition, proprietary audio enhancement technologies, focus on user experience. Weaknesses: Not utilizing LDAC specifically, which may limit compatibility with some high-res audio sources.
LDAC Core Innovations
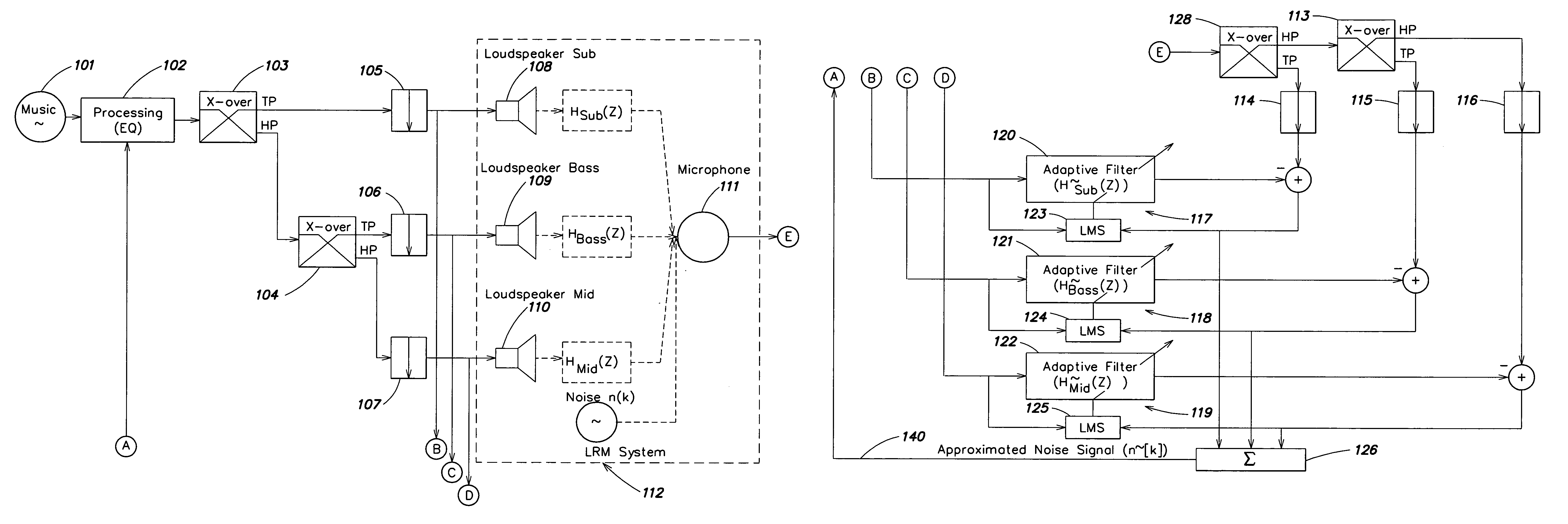
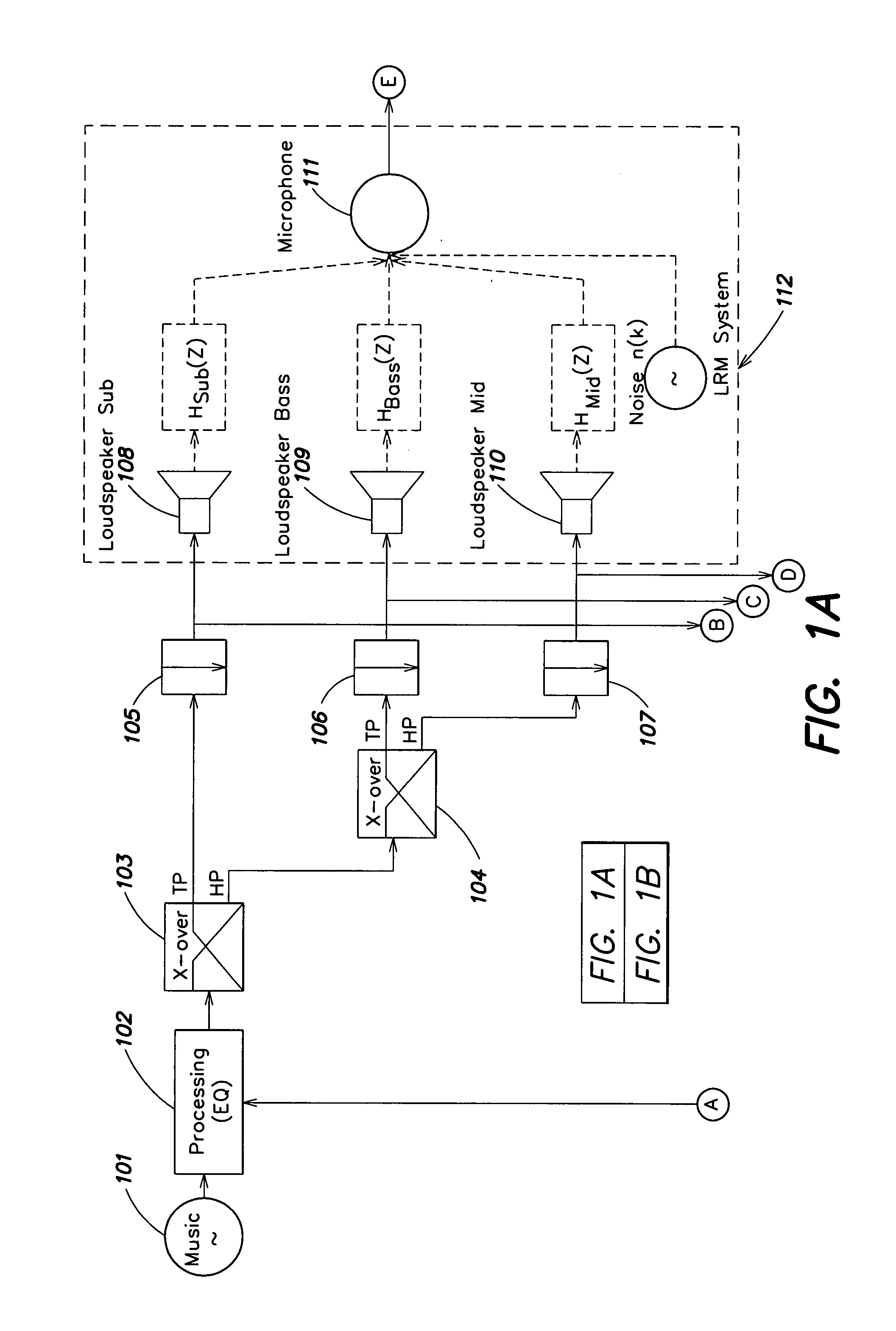
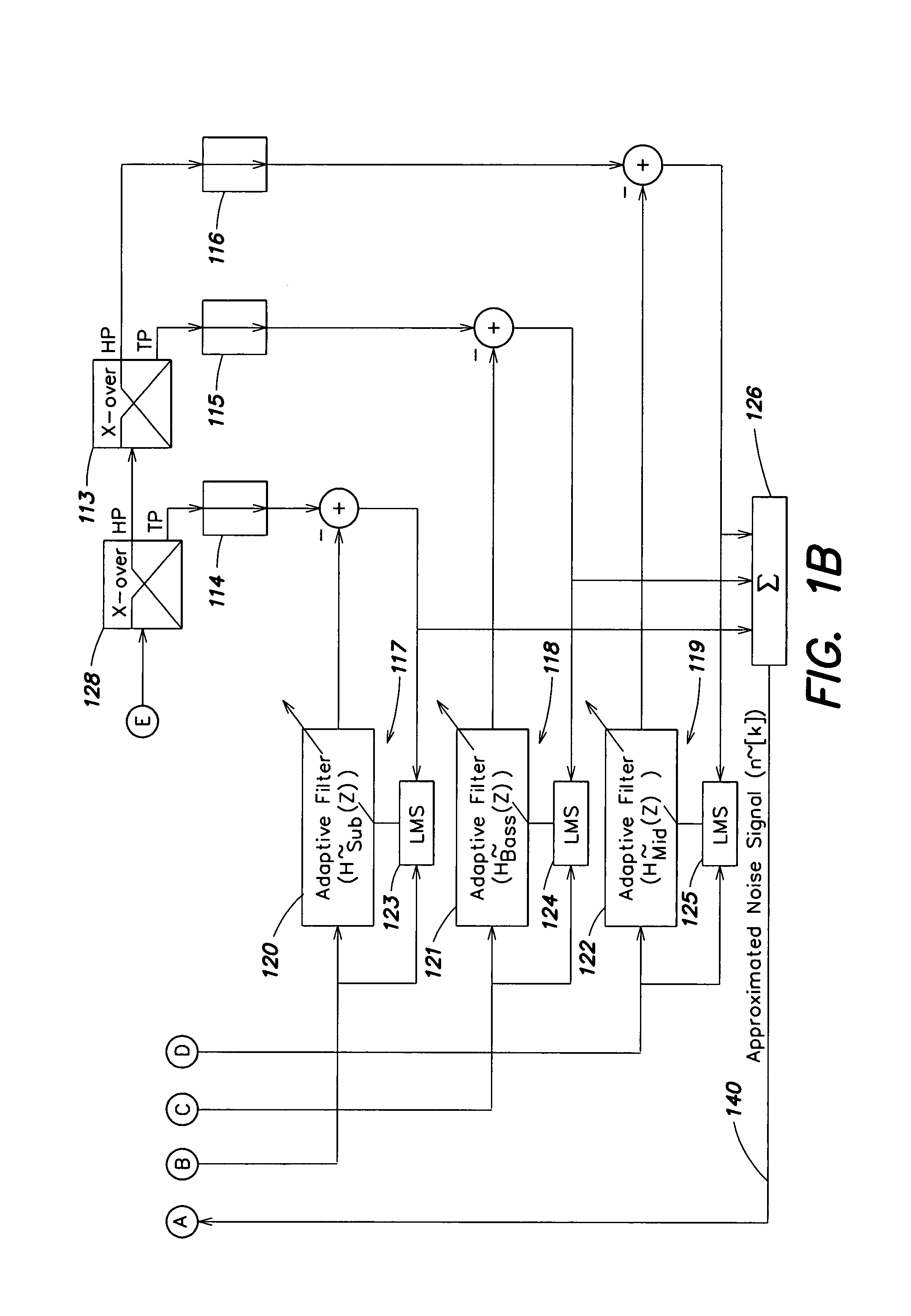
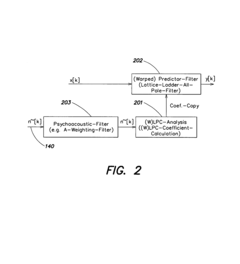
Audio enhancement system
PatentInactiveUS7302062B2
Innovation
- A dynamic equalizer control system that uses linear predictive coding (LPC) to analyze ambient noise and adjust sound output, considering the spectral distribution of noise and psychoacoustic aspects, to enhance the audio listening experience by boosting music levels and controlling gain and equalization accordingly.
Method and System for implementing Stereo Dimensional Array signal processing in a Compact Single Enclosure Active Loudspeaker Product
PatentActiveUS20180192185A1
Innovation
- Implementing digital signal processing methods, including time delay and specific driver configurations, in a compact single enclosure loudspeaker system to simulate the optimal placement of sub and main speakers, allowing for a smaller form factor while maintaining a wide and stable acoustic image.
LDAC Standardization
LDAC standardization has been a crucial process in establishing this high-resolution audio codec as a widely accepted industry standard. The standardization efforts have been primarily driven by Sony Corporation, the original developer of LDAC technology. The process began with Sony's initial introduction of LDAC in 2015, followed by its submission to the Bluetooth Special Interest Group (SIG) for consideration as a standard codec.
The Bluetooth SIG, recognizing the potential of LDAC to enhance audio quality in wireless transmission, initiated a thorough evaluation process. This involved rigorous testing of the codec's performance, compatibility with existing Bluetooth protocols, and its ability to meet the growing demand for high-quality audio streaming. The standardization process also included extensive collaboration between Sony and other industry stakeholders to ensure interoperability and widespread adoption.
In 2017, LDAC achieved a significant milestone when it was officially adopted by the Android Open Source Project (AOSP). This integration into the Android ecosystem marked a turning point in LDAC's journey towards becoming a standard, as it made the codec readily available to a vast array of Android devices and manufacturers. The inclusion in AOSP also facilitated easier implementation for device makers, further accelerating LDAC's adoption across the industry.
The standardization process also involved the development of comprehensive documentation and specifications. These technical guidelines outlined the implementation requirements, encoding and decoding processes, and performance metrics for LDAC. This documentation was crucial in ensuring consistent implementation across different devices and platforms, maintaining the codec's high-quality audio performance regardless of the hardware.
As part of the standardization efforts, Sony actively engaged with audio equipment manufacturers, encouraging them to incorporate LDAC support in their products. This collaborative approach helped create a robust ecosystem of LDAC-compatible devices, ranging from smartphones and tablets to headphones, speakers, and car audio systems. The growing number of compatible devices further solidified LDAC's position as a standard in the high-resolution audio market.
The standardization of LDAC has also involved ongoing refinement and optimization of the codec. Sony has continued to improve LDAC's performance, addressing feedback from manufacturers and users to enhance its efficiency and compatibility. These iterative improvements have been crucial in maintaining LDAC's relevance and competitiveness in the rapidly evolving audio technology landscape.
The Bluetooth SIG, recognizing the potential of LDAC to enhance audio quality in wireless transmission, initiated a thorough evaluation process. This involved rigorous testing of the codec's performance, compatibility with existing Bluetooth protocols, and its ability to meet the growing demand for high-quality audio streaming. The standardization process also included extensive collaboration between Sony and other industry stakeholders to ensure interoperability and widespread adoption.
In 2017, LDAC achieved a significant milestone when it was officially adopted by the Android Open Source Project (AOSP). This integration into the Android ecosystem marked a turning point in LDAC's journey towards becoming a standard, as it made the codec readily available to a vast array of Android devices and manufacturers. The inclusion in AOSP also facilitated easier implementation for device makers, further accelerating LDAC's adoption across the industry.
The standardization process also involved the development of comprehensive documentation and specifications. These technical guidelines outlined the implementation requirements, encoding and decoding processes, and performance metrics for LDAC. This documentation was crucial in ensuring consistent implementation across different devices and platforms, maintaining the codec's high-quality audio performance regardless of the hardware.
As part of the standardization efforts, Sony actively engaged with audio equipment manufacturers, encouraging them to incorporate LDAC support in their products. This collaborative approach helped create a robust ecosystem of LDAC-compatible devices, ranging from smartphones and tablets to headphones, speakers, and car audio systems. The growing number of compatible devices further solidified LDAC's position as a standard in the high-resolution audio market.
The standardization of LDAC has also involved ongoing refinement and optimization of the codec. Sony has continued to improve LDAC's performance, addressing feedback from manufacturers and users to enhance its efficiency and compatibility. These iterative improvements have been crucial in maintaining LDAC's relevance and competitiveness in the rapidly evolving audio technology landscape.
LDAC Energy Efficiency
LDAC, developed by Sony, stands as a pinnacle of energy-efficient audio coding technology. This codec achieves remarkable audio quality while maintaining low power consumption, a critical factor in portable audio devices. LDAC's energy efficiency stems from its adaptive bit rate system, which dynamically adjusts the transmission rate based on wireless conditions and device capabilities.
The codec employs sophisticated algorithms to compress audio data without significant loss of quality. By utilizing advanced psychoacoustic modeling, LDAC can efficiently encode audio signals, reducing the amount of data that needs to be transmitted. This reduction in data transmission directly correlates to lower power consumption in both the transmitting and receiving devices.
LDAC's energy efficiency is further enhanced by its ability to operate at multiple bit rates. The codec can switch between 330 kbps, 660 kbps, and 990 kbps, allowing devices to balance audio quality with power consumption based on their current needs and battery status. This flexibility ensures optimal performance across various scenarios, from high-fidelity playback to extended battery life.
The implementation of LDAC in Bluetooth audio devices has shown significant improvements in energy efficiency compared to traditional codecs. Studies have demonstrated that LDAC can achieve up to 30% better battery life in certain scenarios, particularly when streaming high-quality audio content. This efficiency gain is crucial for the longevity of wireless audio devices, especially in an era where consumers demand both high-quality sound and extended usage times.
Moreover, LDAC's energy efficiency extends beyond the codec itself. The technology's integration with modern Bluetooth chipsets has led to optimizations at the hardware level. Manufacturers have developed specialized chips that can process LDAC streams with minimal power draw, further enhancing the overall energy efficiency of audio systems implementing this codec.
The energy-efficient nature of LDAC has implications beyond personal audio devices. As the Internet of Things (IoT) continues to expand, the need for low-power, high-quality audio transmission becomes increasingly important. LDAC's capabilities make it a suitable candidate for integration into smart home devices, wearables, and other IoT applications where audio quality and battery life are critical factors.
The codec employs sophisticated algorithms to compress audio data without significant loss of quality. By utilizing advanced psychoacoustic modeling, LDAC can efficiently encode audio signals, reducing the amount of data that needs to be transmitted. This reduction in data transmission directly correlates to lower power consumption in both the transmitting and receiving devices.
LDAC's energy efficiency is further enhanced by its ability to operate at multiple bit rates. The codec can switch between 330 kbps, 660 kbps, and 990 kbps, allowing devices to balance audio quality with power consumption based on their current needs and battery status. This flexibility ensures optimal performance across various scenarios, from high-fidelity playback to extended battery life.
The implementation of LDAC in Bluetooth audio devices has shown significant improvements in energy efficiency compared to traditional codecs. Studies have demonstrated that LDAC can achieve up to 30% better battery life in certain scenarios, particularly when streaming high-quality audio content. This efficiency gain is crucial for the longevity of wireless audio devices, especially in an era where consumers demand both high-quality sound and extended usage times.
Moreover, LDAC's energy efficiency extends beyond the codec itself. The technology's integration with modern Bluetooth chipsets has led to optimizations at the hardware level. Manufacturers have developed specialized chips that can process LDAC streams with minimal power draw, further enhancing the overall energy efficiency of audio systems implementing this codec.
The energy-efficient nature of LDAC has implications beyond personal audio devices. As the Internet of Things (IoT) continues to expand, the need for low-power, high-quality audio transmission becomes increasingly important. LDAC's capabilities make it a suitable candidate for integration into smart home devices, wearables, and other IoT applications where audio quality and battery life are critical factors.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!