How to Achieve Audio Pristine with LDAC Advantages?
JUL 4, 20258 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
LDAC Technology Evolution and Objectives
LDAC, developed by Sony in 2015, represents a significant leap in wireless audio technology. This codec aims to deliver high-resolution audio over Bluetooth connections, addressing the limitations of previous wireless audio transmission methods. The evolution of LDAC technology is closely tied to the growing demand for superior audio quality in wireless devices, particularly as high-resolution audio content becomes more prevalent.
The primary objective of LDAC is to achieve near-lossless audio transmission over Bluetooth, offering a substantial improvement over standard codecs like SBC or AAC. LDAC supports bit rates up to 990 kbps, allowing for the transmission of audio data at up to 32-bit/96 kHz resolution. This capability far exceeds the typical 16-bit/44.1 kHz CD-quality audio, positioning LDAC as a frontrunner in high-fidelity wireless audio solutions.
Throughout its development, LDAC has undergone several iterations to enhance its performance and compatibility. Initial versions focused on establishing the core technology, while subsequent updates have aimed at improving efficiency, reducing latency, and expanding device support. The codec's adaptive bit rate feature, which allows it to adjust transmission quality based on connection stability, has been a key factor in its widespread adoption.
One of the most significant milestones in LDAC's evolution was its inclusion in the Android Open Source Project (AOSP) in 2017. This integration made LDAC accessible to a broader range of devices and manufacturers, accelerating its adoption across the audio industry. The move also aligned with the growing trend of smartphone manufacturers removing headphone jacks, further emphasizing the need for high-quality wireless audio solutions.
As LDAC technology continues to evolve, its objectives have expanded beyond mere audio quality. Current development efforts focus on reducing power consumption, improving connection stability in challenging environments, and minimizing latency for applications such as gaming and virtual reality. These advancements aim to address the remaining challenges in wireless audio transmission and further close the gap between wired and wireless audio experiences.
The future trajectory of LDAC technology is likely to involve integration with emerging audio technologies, such as 3D audio formats and adaptive sound processing. There is also a push towards achieving even higher bit rates and supporting more advanced audio formats, potentially enabling wireless transmission of ultra-high-resolution audio content. As the audio industry continues to evolve, LDAC's development objectives are expected to align with broader trends in immersive audio experiences and smart audio devices.
The primary objective of LDAC is to achieve near-lossless audio transmission over Bluetooth, offering a substantial improvement over standard codecs like SBC or AAC. LDAC supports bit rates up to 990 kbps, allowing for the transmission of audio data at up to 32-bit/96 kHz resolution. This capability far exceeds the typical 16-bit/44.1 kHz CD-quality audio, positioning LDAC as a frontrunner in high-fidelity wireless audio solutions.
Throughout its development, LDAC has undergone several iterations to enhance its performance and compatibility. Initial versions focused on establishing the core technology, while subsequent updates have aimed at improving efficiency, reducing latency, and expanding device support. The codec's adaptive bit rate feature, which allows it to adjust transmission quality based on connection stability, has been a key factor in its widespread adoption.
One of the most significant milestones in LDAC's evolution was its inclusion in the Android Open Source Project (AOSP) in 2017. This integration made LDAC accessible to a broader range of devices and manufacturers, accelerating its adoption across the audio industry. The move also aligned with the growing trend of smartphone manufacturers removing headphone jacks, further emphasizing the need for high-quality wireless audio solutions.
As LDAC technology continues to evolve, its objectives have expanded beyond mere audio quality. Current development efforts focus on reducing power consumption, improving connection stability in challenging environments, and minimizing latency for applications such as gaming and virtual reality. These advancements aim to address the remaining challenges in wireless audio transmission and further close the gap between wired and wireless audio experiences.
The future trajectory of LDAC technology is likely to involve integration with emerging audio technologies, such as 3D audio formats and adaptive sound processing. There is also a push towards achieving even higher bit rates and supporting more advanced audio formats, potentially enabling wireless transmission of ultra-high-resolution audio content. As the audio industry continues to evolve, LDAC's development objectives are expected to align with broader trends in immersive audio experiences and smart audio devices.
High-Resolution Audio Market Analysis
The high-resolution audio market has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing consumer demand for superior sound quality and advancements in audio technology. This market segment encompasses a range of products and services, including high-resolution audio players, streaming services, and compatible headphones and speakers.
The global high-resolution audio market size was valued at approximately $9.5 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $18.2 billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of 9.8% during the forecast period. This growth is attributed to several factors, including the rising popularity of lossless audio formats, the proliferation of high-quality audio streaming services, and the increasing adoption of premium audio devices.
Consumer preferences are shifting towards higher quality audio experiences, with a growing segment of audiophiles and music enthusiasts willing to invest in premium audio equipment and services. This trend is particularly evident among younger demographics, who are more likely to prioritize audio quality in their music consumption habits.
The market is segmented by product type, including hardware (such as DACs, amplifiers, and speakers) and software (streaming services and audio codecs). Hardware components currently dominate the market, accounting for approximately 65% of the total market share. However, the software segment is expected to grow at a faster rate due to the increasing popularity of high-resolution streaming services.
Geographically, North America and Europe are the leading markets for high-resolution audio, collectively accounting for over 60% of the global market share. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the highest growth rate in the coming years, driven by increasing disposable incomes and a growing tech-savvy population in countries like China, Japan, and South Korea.
Key players in the high-resolution audio market include Sony Corporation, Apple Inc., Sonos Inc., and Bose Corporation. These companies are continuously innovating to improve audio quality and develop new technologies to enhance the listening experience. The introduction of advanced audio codecs, such as LDAC, has further propelled market growth by enabling high-quality wireless audio transmission.
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a mixed impact on the high-resolution audio market. While initial supply chain disruptions caused some setbacks, the increased time spent at home has led to greater investment in home audio systems and a surge in streaming service subscriptions, ultimately benefiting the market.
The global high-resolution audio market size was valued at approximately $9.5 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $18.2 billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of 9.8% during the forecast period. This growth is attributed to several factors, including the rising popularity of lossless audio formats, the proliferation of high-quality audio streaming services, and the increasing adoption of premium audio devices.
Consumer preferences are shifting towards higher quality audio experiences, with a growing segment of audiophiles and music enthusiasts willing to invest in premium audio equipment and services. This trend is particularly evident among younger demographics, who are more likely to prioritize audio quality in their music consumption habits.
The market is segmented by product type, including hardware (such as DACs, amplifiers, and speakers) and software (streaming services and audio codecs). Hardware components currently dominate the market, accounting for approximately 65% of the total market share. However, the software segment is expected to grow at a faster rate due to the increasing popularity of high-resolution streaming services.
Geographically, North America and Europe are the leading markets for high-resolution audio, collectively accounting for over 60% of the global market share. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the highest growth rate in the coming years, driven by increasing disposable incomes and a growing tech-savvy population in countries like China, Japan, and South Korea.
Key players in the high-resolution audio market include Sony Corporation, Apple Inc., Sonos Inc., and Bose Corporation. These companies are continuously innovating to improve audio quality and develop new technologies to enhance the listening experience. The introduction of advanced audio codecs, such as LDAC, has further propelled market growth by enabling high-quality wireless audio transmission.
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a mixed impact on the high-resolution audio market. While initial supply chain disruptions caused some setbacks, the increased time spent at home has led to greater investment in home audio systems and a surge in streaming service subscriptions, ultimately benefiting the market.
LDAC Current Status and Technical Challenges
LDAC, developed by Sony, represents a significant advancement in Bluetooth audio codec technology. Currently, LDAC is widely recognized as one of the highest quality wireless audio transmission protocols available. It supports up to 990 kbps bitrate, allowing for near CD-quality audio streaming over Bluetooth connections.
Despite its advantages, LDAC faces several technical challenges in achieving pristine audio quality. One primary issue is the inherent limitations of Bluetooth technology, including bandwidth constraints and potential interference. While LDAC can theoretically transmit at 990 kbps, real-world performance often falls short due to these limitations, resulting in occasional audio dropouts or quality degradation.
Another challenge lies in device compatibility and implementation. Although LDAC has been adopted by various manufacturers, not all devices support its highest quality modes. This inconsistency can lead to suboptimal audio experiences for users, as the codec may default to lower bitrates on certain devices.
Power consumption remains a concern, particularly for mobile devices. Operating at high bitrates requires more processing power and energy, which can significantly impact battery life. Balancing audio quality with power efficiency continues to be a key area of focus for LDAC development.
Latency is another critical issue, especially for applications requiring precise audio-video synchronization. While LDAC offers improved latency compared to some other codecs, it still falls short of wired solutions, presenting challenges for gaming and video playback scenarios.
The complexity of LDAC's encoding and decoding processes also poses challenges. Implementing the codec efficiently across a wide range of devices with varying hardware capabilities requires ongoing optimization efforts. This complexity can lead to increased manufacturing costs and potential compatibility issues.
Environmental factors, such as physical obstacles and electromagnetic interference, can significantly impact LDAC's performance. Maintaining consistent high-quality audio transmission in diverse real-world settings remains a persistent challenge for the technology.
Looking ahead, the evolution of LDAC faces the challenge of keeping pace with advancing audio standards and increasing consumer expectations. As high-resolution audio becomes more prevalent, there is pressure to further improve bitrates and audio fidelity while addressing existing limitations.
Despite its advantages, LDAC faces several technical challenges in achieving pristine audio quality. One primary issue is the inherent limitations of Bluetooth technology, including bandwidth constraints and potential interference. While LDAC can theoretically transmit at 990 kbps, real-world performance often falls short due to these limitations, resulting in occasional audio dropouts or quality degradation.
Another challenge lies in device compatibility and implementation. Although LDAC has been adopted by various manufacturers, not all devices support its highest quality modes. This inconsistency can lead to suboptimal audio experiences for users, as the codec may default to lower bitrates on certain devices.
Power consumption remains a concern, particularly for mobile devices. Operating at high bitrates requires more processing power and energy, which can significantly impact battery life. Balancing audio quality with power efficiency continues to be a key area of focus for LDAC development.
Latency is another critical issue, especially for applications requiring precise audio-video synchronization. While LDAC offers improved latency compared to some other codecs, it still falls short of wired solutions, presenting challenges for gaming and video playback scenarios.
The complexity of LDAC's encoding and decoding processes also poses challenges. Implementing the codec efficiently across a wide range of devices with varying hardware capabilities requires ongoing optimization efforts. This complexity can lead to increased manufacturing costs and potential compatibility issues.
Environmental factors, such as physical obstacles and electromagnetic interference, can significantly impact LDAC's performance. Maintaining consistent high-quality audio transmission in diverse real-world settings remains a persistent challenge for the technology.
Looking ahead, the evolution of LDAC faces the challenge of keeping pace with advancing audio standards and increasing consumer expectations. As high-resolution audio becomes more prevalent, there is pressure to further improve bitrates and audio fidelity while addressing existing limitations.
LDAC Implementation Strategies
01 LDAC codec implementation for high-quality audio transmission
LDAC is a high-resolution audio codec developed for Bluetooth audio transmission. It enables the transfer of high-quality audio data over Bluetooth connections, offering improved sound quality compared to standard codecs. LDAC supports various bit rates and can adapt to different network conditions to maintain optimal audio performance.- LDAC codec implementation for high-quality audio transmission: LDAC is a high-resolution audio codec developed for Bluetooth audio transmission. It enables the transfer of high-quality audio data at higher bit rates compared to standard codecs. The implementation of LDAC in audio devices can significantly improve the overall audio quality, providing a near lossless audio experience for users.
- Audio signal processing for LDAC optimization: Various signal processing techniques are employed to optimize LDAC audio quality. These may include advanced noise reduction algorithms, dynamic range compression, and frequency response adjustments. Such processing helps in maintaining audio fidelity while adapting to different listening environments and device capabilities.
- LDAC integration with audio streaming services: The integration of LDAC codec with audio streaming services enhances the streaming quality for compatible devices. This involves optimizing the audio data transmission, managing bandwidth efficiently, and ensuring seamless playback of high-resolution audio content over Bluetooth connections.
- Hardware implementation for LDAC support: Specific hardware designs and implementations are crucial for supporting LDAC in audio devices. This includes dedicated audio processors, optimized Bluetooth chipsets, and enhanced DACs (Digital-to-Analog Converters) that can handle the high bitrate audio data transmitted through LDAC.
- LDAC quality assessment and optimization techniques: Various methods and systems are developed for assessing and optimizing LDAC audio quality. These include real-time analysis of audio streams, adaptive bit rate adjustments, and user preference-based optimizations to ensure the best possible audio experience across different devices and listening conditions.
02 Audio signal processing for LDAC enhancement
Various signal processing techniques are employed to enhance LDAC audio quality. These may include noise reduction, dynamic range compression, and equalization. Advanced algorithms are used to optimize the audio signal before encoding, ensuring the best possible sound reproduction at the receiving end.Expand Specific Solutions03 LDAC integration with audio systems and devices
LDAC technology is integrated into various audio systems and devices, including smartphones, headphones, and speakers. This integration involves hardware and software optimizations to ensure compatibility and maximize audio quality. Manufacturers implement LDAC support in their products to offer users high-fidelity wireless audio experiences.Expand Specific Solutions04 LDAC bitrate and sampling rate optimization
LDAC supports multiple bitrates and sampling rates, allowing for flexibility in audio transmission. Optimization techniques are used to select the most appropriate bitrate and sampling rate based on the audio content, available bandwidth, and device capabilities. This adaptive approach helps maintain high audio quality while managing power consumption and connection stability.Expand Specific Solutions05 Quality assessment and improvement of LDAC audio
Methods for assessing and improving LDAC audio quality are developed, including objective and subjective evaluation techniques. These may involve analyzing frequency response, distortion levels, and psychoacoustic factors. Continuous research and development efforts aim to enhance LDAC performance and address any limitations in audio reproduction.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in LDAC and Hi-Res Audio
The audio technology landscape for achieving pristine sound with LDAC advantages is in a mature yet evolving stage. The market size is substantial, driven by growing demand for high-quality wireless audio experiences. Technologically, LDAC is well-established, with key players like Sony, Qualcomm, and Samsung leading innovation. Companies such as Fraunhofer-Gesellschaft, Analog Devices, and Texas Instruments contribute significant advancements in audio processing and chip design. The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of established electronics giants and specialized audio technology firms, with ongoing research and development focused on enhancing wireless audio quality and efficiency.
QUALCOMM, Inc.
Technical Solution: Qualcomm has developed advanced audio codecs and technologies to achieve pristine audio quality, including support for LDAC. Their Snapdragon Sound technology incorporates LDAC support, enabling high-resolution audio streaming up to 24-bit/96kHz[1]. Qualcomm's implementation of LDAC allows for adaptive bitrate adjustment, ensuring optimal audio quality based on connection stability. They have also integrated LDAC with their aptX Adaptive codec, providing a seamless transition between the two technologies depending on device compatibility and network conditions[2]. Qualcomm's solution includes specialized DSP cores in their mobile platforms, optimized for efficient LDAC processing, reducing power consumption while maintaining audio fidelity[3].
Strengths: Wide adoption in mobile devices, integrated system-on-chip solutions, and adaptive bitrate technology. Weaknesses: Dependence on device manufacturers for implementation, potential licensing costs for OEMs.
Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Samsung has embraced LDAC technology in their Galaxy series smartphones and audio accessories to deliver high-quality audio experiences. Their implementation focuses on optimizing LDAC performance within the Android ecosystem. Samsung's approach includes fine-tuning the audio stack to minimize latency and maximize throughput for LDAC streams[4]. They have also developed custom audio processing algorithms that work in conjunction with LDAC to enhance perceived audio quality, such as their Adapt Sound feature, which personalizes audio output based on the user's hearing profile[5]. Samsung's Galaxy Buds Pro and subsequent models support LDAC, showcasing their commitment to high-fidelity wireless audio[6].
Strengths: Tight integration with Android ecosystem, wide range of compatible devices, and custom audio enhancements. Weaknesses: Limited to Samsung's own ecosystem for full feature set, potential battery life impact on mobile devices.
LDAC Core Patents and Innovations
Multi-channel audio reproducing device
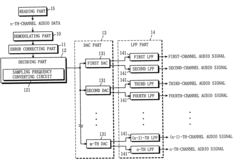
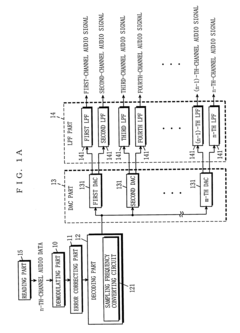
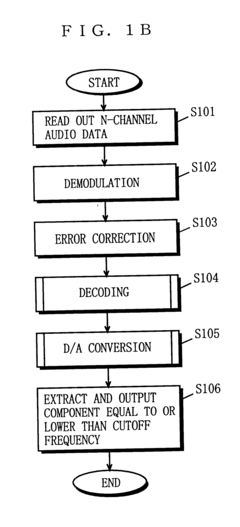
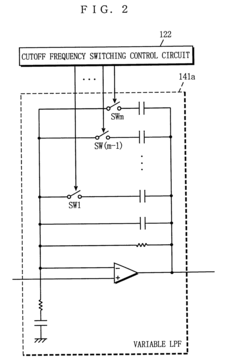
PatentInactiveUS6714825B1
Innovation
- A multi-channel audio reproducing device that includes a reading, decoding, and DAC part with a sampling frequency conversion capability, allowing for conversion of audio data from digital to analog using fewer DACs than channels, and is structurally connectable to existing audio systems using variable or fixed low-pass filters.
Method for improving doppler sound quality for colorful ultrasonic system
PatentActiveCN101427930A
Innovation
- A programmable chip is used for sound signal processing, and an N×M-1 order finite impulse response filter is constructed for upsampling operation to reduce DAC in-band distortion, improve sampling efficiency without increasing cache, and achieve uniform output of sound data. .
Bluetooth Audio Codec Comparison
Bluetooth audio codecs play a crucial role in determining the quality of wireless audio transmission. This comparison focuses on the most prominent codecs in the market, highlighting their strengths and limitations.
SBC (Sub-Band Coding) is the standard codec for Bluetooth audio, supported by all Bluetooth devices. It offers decent audio quality at lower bitrates but falls short in delivering high-fidelity sound. With a maximum bitrate of 328 kbps, SBC is suitable for casual listening but may not satisfy audiophiles.
AAC (Advanced Audio Coding) provides improved audio quality over SBC, particularly for Apple devices. It supports bitrates up to 250 kbps and offers better efficiency in compression. However, its performance can vary on non-Apple devices, potentially leading to inconsistent audio quality across different platforms.
aptX, developed by Qualcomm, aims to deliver CD-like audio quality over Bluetooth. With a bitrate of 352 kbps, it offers lower latency and better sound quality compared to SBC. aptX HD further enhances this, supporting 24-bit audio at 576 kbps, catering to high-resolution audio enthusiasts.
LDAC, Sony's proprietary codec, stands out for its high-bitrate capabilities. It can transmit audio at up to 990 kbps, allowing for near-lossless audio quality. LDAC supports three modes: 330 kbps, 660 kbps, and 990 kbps, adapting to connection stability and device capabilities.
LHDC (Low Latency High-Definition Audio Codec) is another high-bitrate codec, supporting up to 900 kbps. It aims to compete with LDAC in delivering high-resolution audio over Bluetooth, with a focus on reducing latency for a better user experience.
LC3 (Low Complexity Communication Codec) is the latest addition, designed for Bluetooth LE Audio. It promises improved audio quality at lower bitrates, potentially offering better energy efficiency and extended battery life for wireless audio devices.
When comparing these codecs, factors such as bitrate, latency, device compatibility, and power consumption must be considered. While higher bitrates generally correlate with better audio quality, the actual perceived difference can vary based on the audio source, playback device, and listener's sensitivity.
SBC (Sub-Band Coding) is the standard codec for Bluetooth audio, supported by all Bluetooth devices. It offers decent audio quality at lower bitrates but falls short in delivering high-fidelity sound. With a maximum bitrate of 328 kbps, SBC is suitable for casual listening but may not satisfy audiophiles.
AAC (Advanced Audio Coding) provides improved audio quality over SBC, particularly for Apple devices. It supports bitrates up to 250 kbps and offers better efficiency in compression. However, its performance can vary on non-Apple devices, potentially leading to inconsistent audio quality across different platforms.
aptX, developed by Qualcomm, aims to deliver CD-like audio quality over Bluetooth. With a bitrate of 352 kbps, it offers lower latency and better sound quality compared to SBC. aptX HD further enhances this, supporting 24-bit audio at 576 kbps, catering to high-resolution audio enthusiasts.
LDAC, Sony's proprietary codec, stands out for its high-bitrate capabilities. It can transmit audio at up to 990 kbps, allowing for near-lossless audio quality. LDAC supports three modes: 330 kbps, 660 kbps, and 990 kbps, adapting to connection stability and device capabilities.
LHDC (Low Latency High-Definition Audio Codec) is another high-bitrate codec, supporting up to 900 kbps. It aims to compete with LDAC in delivering high-resolution audio over Bluetooth, with a focus on reducing latency for a better user experience.
LC3 (Low Complexity Communication Codec) is the latest addition, designed for Bluetooth LE Audio. It promises improved audio quality at lower bitrates, potentially offering better energy efficiency and extended battery life for wireless audio devices.
When comparing these codecs, factors such as bitrate, latency, device compatibility, and power consumption must be considered. While higher bitrates generally correlate with better audio quality, the actual perceived difference can vary based on the audio source, playback device, and listener's sensitivity.
LDAC Integration in Audio Ecosystems
The integration of LDAC technology into audio ecosystems represents a significant advancement in high-quality wireless audio transmission. LDAC, developed by Sony, is a codec that allows for the transmission of high-resolution audio over Bluetooth connections. This integration has far-reaching implications for the entire audio industry, affecting both hardware manufacturers and content providers.
In the hardware domain, LDAC integration necessitates the development of compatible devices across the audio chain. This includes source devices such as smartphones, digital audio players, and computers, as well as receiving devices like wireless headphones, speakers, and home audio systems. Manufacturers must ensure that their products not only support LDAC but also optimize their hardware to fully leverage its capabilities, such as implementing efficient power management to balance high-quality audio with battery life.
For content providers, LDAC integration opens up new possibilities in delivering high-fidelity audio to consumers. Streaming services can offer higher bitrate options that take advantage of LDAC's increased bandwidth, providing a more immersive listening experience. This shift may drive the creation and distribution of more high-resolution audio content, potentially influencing recording and mastering practices in the music industry.
The adoption of LDAC also impacts the broader Bluetooth ecosystem. As LDAC becomes more prevalent, it may influence the development of future Bluetooth standards and other competing audio codecs. This could lead to a race for higher quality and more efficient wireless audio transmission technologies, benefiting consumers with improved audio experiences across various devices and platforms.
Furthermore, LDAC integration affects the user experience and interface design of audio products. Manufacturers need to consider how to communicate the benefits of LDAC to consumers and provide intuitive ways to enable and control LDAC settings. This may involve redesigning app interfaces, on-device controls, and product packaging to highlight LDAC as a key feature.
In the professional audio sector, LDAC integration could potentially bridge the gap between wireless convenience and the high-fidelity requirements of studio environments. This might lead to new applications in live sound reinforcement, broadcast, and recording scenarios where cable-free setups with minimal quality compromise are desirable.
In the hardware domain, LDAC integration necessitates the development of compatible devices across the audio chain. This includes source devices such as smartphones, digital audio players, and computers, as well as receiving devices like wireless headphones, speakers, and home audio systems. Manufacturers must ensure that their products not only support LDAC but also optimize their hardware to fully leverage its capabilities, such as implementing efficient power management to balance high-quality audio with battery life.
For content providers, LDAC integration opens up new possibilities in delivering high-fidelity audio to consumers. Streaming services can offer higher bitrate options that take advantage of LDAC's increased bandwidth, providing a more immersive listening experience. This shift may drive the creation and distribution of more high-resolution audio content, potentially influencing recording and mastering practices in the music industry.
The adoption of LDAC also impacts the broader Bluetooth ecosystem. As LDAC becomes more prevalent, it may influence the development of future Bluetooth standards and other competing audio codecs. This could lead to a race for higher quality and more efficient wireless audio transmission technologies, benefiting consumers with improved audio experiences across various devices and platforms.
Furthermore, LDAC integration affects the user experience and interface design of audio products. Manufacturers need to consider how to communicate the benefits of LDAC to consumers and provide intuitive ways to enable and control LDAC settings. This may involve redesigning app interfaces, on-device controls, and product packaging to highlight LDAC as a key feature.
In the professional audio sector, LDAC integration could potentially bridge the gap between wireless convenience and the high-fidelity requirements of studio environments. This might lead to new applications in live sound reinforcement, broadcast, and recording scenarios where cable-free setups with minimal quality compromise are desirable.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!