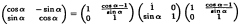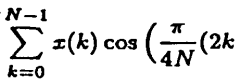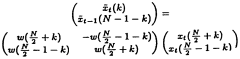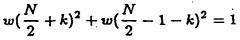Transforming Audio Fidelity Through LDAC Practice
JUL 4, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
LDAC Technology Evolution
LDAC, developed by Sony in 2015, represents a significant milestone in the evolution of high-quality audio transmission technology. This codec has undergone several iterations, each enhancing its capabilities and expanding its applications in the audio industry.
The initial release of LDAC introduced a groundbreaking approach to Bluetooth audio transmission, offering up to 990 kbps bitrate - a substantial improvement over previous codecs. This innovation allowed for near-lossless audio quality over wireless connections, a feat previously thought unattainable due to bandwidth limitations.
In subsequent years, LDAC saw incremental improvements in efficiency and compatibility. The 2017 update brought enhanced stability and reduced power consumption, addressing early concerns about battery life in LDAC-enabled devices. This version also introduced adaptive bitrate selection, allowing the codec to dynamically adjust its performance based on connection quality and device capabilities.
The integration of LDAC into the Android Open Source Project in 2018 marked a pivotal moment in its evolution. This move significantly broadened LDAC's reach, making it available to a vast array of Android devices and encouraging wider adoption among manufacturers.
2019 saw LDAC's expansion into new product categories, including wireless speakers and car audio systems. This diversification demonstrated the codec's versatility and its potential to enhance audio quality across various consumer electronics segments.
In 2020, LDAC underwent further refinement with the introduction of improved error correction algorithms. These enhancements resulted in more stable connections and better audio quality in challenging wireless environments, such as areas with high electromagnetic interference.
The most recent developments in LDAC technology have focused on reducing latency while maintaining high audio quality. This advancement is particularly crucial for gaming and video applications, where synchronization between audio and visual elements is critical.
Looking ahead, the evolution of LDAC is likely to continue in several directions. One potential area of development is the integration with emerging wireless technologies like Wi-Fi 6 and 5G, which could further enhance transmission speeds and stability. Additionally, there's ongoing research into expanding LDAC's capabilities to support higher resolution audio formats and multi-channel surround sound, pushing the boundaries of wireless audio fidelity even further.
The initial release of LDAC introduced a groundbreaking approach to Bluetooth audio transmission, offering up to 990 kbps bitrate - a substantial improvement over previous codecs. This innovation allowed for near-lossless audio quality over wireless connections, a feat previously thought unattainable due to bandwidth limitations.
In subsequent years, LDAC saw incremental improvements in efficiency and compatibility. The 2017 update brought enhanced stability and reduced power consumption, addressing early concerns about battery life in LDAC-enabled devices. This version also introduced adaptive bitrate selection, allowing the codec to dynamically adjust its performance based on connection quality and device capabilities.
The integration of LDAC into the Android Open Source Project in 2018 marked a pivotal moment in its evolution. This move significantly broadened LDAC's reach, making it available to a vast array of Android devices and encouraging wider adoption among manufacturers.
2019 saw LDAC's expansion into new product categories, including wireless speakers and car audio systems. This diversification demonstrated the codec's versatility and its potential to enhance audio quality across various consumer electronics segments.
In 2020, LDAC underwent further refinement with the introduction of improved error correction algorithms. These enhancements resulted in more stable connections and better audio quality in challenging wireless environments, such as areas with high electromagnetic interference.
The most recent developments in LDAC technology have focused on reducing latency while maintaining high audio quality. This advancement is particularly crucial for gaming and video applications, where synchronization between audio and visual elements is critical.
Looking ahead, the evolution of LDAC is likely to continue in several directions. One potential area of development is the integration with emerging wireless technologies like Wi-Fi 6 and 5G, which could further enhance transmission speeds and stability. Additionally, there's ongoing research into expanding LDAC's capabilities to support higher resolution audio formats and multi-channel surround sound, pushing the boundaries of wireless audio fidelity even further.
Audio Market Demand Analysis
The audio market has experienced significant growth and transformation in recent years, driven by technological advancements and changing consumer preferences. The demand for high-quality audio experiences has surged across various sectors, including consumer electronics, automotive, and professional audio equipment.
In the consumer electronics segment, the rise of wireless audio devices, particularly true wireless stereo (TWS) earbuds and smart speakers, has been a major catalyst for market expansion. The global TWS market is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 20% in the coming years, reflecting the strong consumer appetite for convenient, high-fidelity audio solutions.
The automotive industry has also become a key driver of audio market demand. As vehicles evolve into connected, entertainment-centric spaces, car manufacturers are increasingly prioritizing premium audio systems as a differentiating factor. This trend has led to partnerships between automakers and renowned audio brands, further fueling the demand for advanced audio technologies.
The professional audio equipment market, encompassing studio recording gear, live sound systems, and broadcast equipment, continues to show steady growth. This sector's demand is propelled by the proliferation of content creation, from podcasts to streaming platforms, and the ongoing need for high-quality audio in entertainment and media production.
The advent of technologies like LDAC (Low Latency and High-Quality Audio Codec) has significantly impacted market demand. Consumers are increasingly seeking audio solutions that offer near-lossless quality, particularly in wireless devices. This shift has created a new premium segment within the audio market, where advanced codecs like LDAC are becoming key selling points for manufacturers.
The growing popularity of immersive audio experiences, such as 3D audio and spatial sound, is another factor shaping market demand. This trend is evident in the gaming industry, where realistic audio environments are crucial for player engagement, as well as in home entertainment systems that aim to replicate cinema-like experiences.
Furthermore, the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning in audio devices is opening new avenues for market growth. Smart audio products that offer personalized sound profiles, noise cancellation, and voice assistant capabilities are gaining traction among consumers, driving innovation and competition in the industry.
The COVID-19 pandemic has also influenced audio market demand, accelerating the adoption of high-quality audio solutions for remote work, online education, and home entertainment. This shift has led to increased sales of headphones, microphones, and other audio peripherals, with a particular emphasis on products that offer clear communication and noise isolation features.
As the audio market continues to evolve, the demand for technologies that can deliver superior sound quality, such as LDAC, is expected to grow. Manufacturers and developers focusing on audio fidelity improvements are likely to find significant opportunities in this expanding and increasingly sophisticated market landscape.
In the consumer electronics segment, the rise of wireless audio devices, particularly true wireless stereo (TWS) earbuds and smart speakers, has been a major catalyst for market expansion. The global TWS market is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 20% in the coming years, reflecting the strong consumer appetite for convenient, high-fidelity audio solutions.
The automotive industry has also become a key driver of audio market demand. As vehicles evolve into connected, entertainment-centric spaces, car manufacturers are increasingly prioritizing premium audio systems as a differentiating factor. This trend has led to partnerships between automakers and renowned audio brands, further fueling the demand for advanced audio technologies.
The professional audio equipment market, encompassing studio recording gear, live sound systems, and broadcast equipment, continues to show steady growth. This sector's demand is propelled by the proliferation of content creation, from podcasts to streaming platforms, and the ongoing need for high-quality audio in entertainment and media production.
The advent of technologies like LDAC (Low Latency and High-Quality Audio Codec) has significantly impacted market demand. Consumers are increasingly seeking audio solutions that offer near-lossless quality, particularly in wireless devices. This shift has created a new premium segment within the audio market, where advanced codecs like LDAC are becoming key selling points for manufacturers.
The growing popularity of immersive audio experiences, such as 3D audio and spatial sound, is another factor shaping market demand. This trend is evident in the gaming industry, where realistic audio environments are crucial for player engagement, as well as in home entertainment systems that aim to replicate cinema-like experiences.
Furthermore, the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning in audio devices is opening new avenues for market growth. Smart audio products that offer personalized sound profiles, noise cancellation, and voice assistant capabilities are gaining traction among consumers, driving innovation and competition in the industry.
The COVID-19 pandemic has also influenced audio market demand, accelerating the adoption of high-quality audio solutions for remote work, online education, and home entertainment. This shift has led to increased sales of headphones, microphones, and other audio peripherals, with a particular emphasis on products that offer clear communication and noise isolation features.
As the audio market continues to evolve, the demand for technologies that can deliver superior sound quality, such as LDAC, is expected to grow. Manufacturers and developers focusing on audio fidelity improvements are likely to find significant opportunities in this expanding and increasingly sophisticated market landscape.
LDAC Technical Challenges
LDAC, developed by Sony, represents a significant advancement in wireless audio transmission technology. However, it faces several technical challenges that need to be addressed to fully realize its potential in transforming audio fidelity.
One of the primary challenges is the high bandwidth requirement for LDAC transmission. The codec operates at bit rates up to 990 kbps, which is substantially higher than conventional Bluetooth audio codecs. This increased bandwidth demand can strain the capabilities of existing Bluetooth hardware, particularly in environments with high electromagnetic interference or when multiple devices are competing for bandwidth.
Another significant challenge lies in the power consumption of LDAC-enabled devices. The complex encoding and decoding processes required for high-fidelity audio transmission can lead to increased battery drain, especially in portable devices like smartphones and wireless headphones. Balancing audio quality with power efficiency remains a crucial area for improvement.
The implementation of LDAC also faces compatibility issues across different devices and platforms. While Sony has made efforts to open-source the technology, widespread adoption and seamless integration across various manufacturers' products remain challenging. This fragmentation in the market can lead to inconsistent user experiences and limit the overall impact of the technology.
Latency is another critical concern for LDAC, particularly in applications requiring real-time audio processing, such as gaming or live performances. Although LDAC offers improved latency compared to some other high-quality codecs, further reductions are necessary to meet the demands of time-sensitive applications.
The complexity of the LDAC algorithm presents challenges in terms of hardware requirements and implementation costs. Devices need sufficient processing power to handle the codec's demands, which can increase manufacturing costs and potentially limit adoption in lower-end products.
Maintaining consistent audio quality across varying network conditions is also a significant challenge. LDAC's adaptive bit rate feature aims to address this, but ensuring a seamless transition between different quality levels without noticeable artifacts or interruptions requires sophisticated algorithms and robust error correction mechanisms.
Lastly, the challenge of educating consumers about the benefits of LDAC and high-resolution audio in general remains. Many users may not perceive the difference in audio quality, especially when using lower-quality audio sources or non-optimized playback equipment. Overcoming this perception barrier is crucial for driving wider adoption and justifying the investment in LDAC technology.
One of the primary challenges is the high bandwidth requirement for LDAC transmission. The codec operates at bit rates up to 990 kbps, which is substantially higher than conventional Bluetooth audio codecs. This increased bandwidth demand can strain the capabilities of existing Bluetooth hardware, particularly in environments with high electromagnetic interference or when multiple devices are competing for bandwidth.
Another significant challenge lies in the power consumption of LDAC-enabled devices. The complex encoding and decoding processes required for high-fidelity audio transmission can lead to increased battery drain, especially in portable devices like smartphones and wireless headphones. Balancing audio quality with power efficiency remains a crucial area for improvement.
The implementation of LDAC also faces compatibility issues across different devices and platforms. While Sony has made efforts to open-source the technology, widespread adoption and seamless integration across various manufacturers' products remain challenging. This fragmentation in the market can lead to inconsistent user experiences and limit the overall impact of the technology.
Latency is another critical concern for LDAC, particularly in applications requiring real-time audio processing, such as gaming or live performances. Although LDAC offers improved latency compared to some other high-quality codecs, further reductions are necessary to meet the demands of time-sensitive applications.
The complexity of the LDAC algorithm presents challenges in terms of hardware requirements and implementation costs. Devices need sufficient processing power to handle the codec's demands, which can increase manufacturing costs and potentially limit adoption in lower-end products.
Maintaining consistent audio quality across varying network conditions is also a significant challenge. LDAC's adaptive bit rate feature aims to address this, but ensuring a seamless transition between different quality levels without noticeable artifacts or interruptions requires sophisticated algorithms and robust error correction mechanisms.
Lastly, the challenge of educating consumers about the benefits of LDAC and high-resolution audio in general remains. Many users may not perceive the difference in audio quality, especially when using lower-quality audio sources or non-optimized playback equipment. Overcoming this perception barrier is crucial for driving wider adoption and justifying the investment in LDAC technology.
Current LDAC Solutions
01 LDAC codec implementation for high-quality audio transmission
LDAC is a high-resolution audio codec developed for Bluetooth audio transmission. It enables the transmission of high-quality audio data over Bluetooth connections, offering improved audio fidelity compared to standard codecs. The implementation of LDAC in audio devices allows for better preservation of audio details and a wider frequency range.- LDAC codec implementation for high-quality audio transmission: LDAC is a high-resolution audio codec developed for Bluetooth audio transmission. It enables the transmission of high-quality audio data by efficiently encoding and compressing audio signals. This technology allows for improved audio fidelity in wireless audio devices, providing a near-lossless listening experience.
- Audio signal processing for enhanced fidelity: Various signal processing techniques are employed to improve audio fidelity in LDAC systems. These may include noise reduction, dynamic range compression, and frequency response optimization. Such processing helps to maintain audio quality during transmission and playback, ensuring a more accurate reproduction of the original sound.
- Adaptive bit rate and sampling frequency adjustment: LDAC systems can dynamically adjust bit rates and sampling frequencies based on network conditions and device capabilities. This adaptive approach ensures optimal audio quality while maintaining stable connections, allowing for consistent high-fidelity playback across various scenarios.
- Integration with wireless audio transmission protocols: LDAC technology is designed to work seamlessly with various wireless audio transmission protocols, particularly Bluetooth. This integration allows for high-fidelity audio streaming on compatible devices while maintaining energy efficiency and connection stability.
- Hardware optimization for LDAC audio processing: Specialized hardware designs and optimizations are implemented to support LDAC audio processing. These may include dedicated audio processors, improved DACs (Digital-to-Analog Converters), and optimized circuitry for handling high-resolution audio streams, contributing to enhanced audio fidelity in LDAC-enabled devices.
02 Audio signal processing for enhanced fidelity
Various signal processing techniques are employed to improve audio fidelity in LDAC-enabled devices. These may include noise reduction, dynamic range compression, and frequency response correction. Advanced digital signal processing algorithms are used to optimize the audio output and maintain high fidelity even in challenging transmission conditions.Expand Specific Solutions03 Bluetooth audio transmission optimization
Optimizing Bluetooth audio transmission is crucial for maintaining high fidelity with LDAC. This involves improving the stability of the Bluetooth connection, reducing latency, and managing bandwidth efficiently. Techniques such as adaptive bit rate allocation and error correction are implemented to ensure consistent audio quality.Expand Specific Solutions04 Integration of LDAC with audio playback devices
The integration of LDAC technology into various audio playback devices, such as smartphones, headphones, and speakers, is essential for widespread adoption. This involves hardware and software modifications to support the LDAC codec, ensuring compatibility and optimal performance across different devices and platforms.Expand Specific Solutions05 Audio quality assessment and calibration
To maintain high audio fidelity, LDAC-enabled systems incorporate methods for assessing and calibrating audio quality. This includes real-time analysis of audio signals, automatic adjustments based on environmental factors, and user-customizable settings to optimize the listening experience according to individual preferences.Expand Specific Solutions
Key LDAC Industry Players
The audio fidelity landscape through LDAC technology is in a dynamic growth phase, with a rapidly expanding market and evolving technological maturity. Major players like Samsung, Apple, and Qualcomm are driving innovation, while companies such as Cirrus Logic and Analog Devices contribute specialized expertise. The market is characterized by intense competition among established tech giants and niche audio specialists, with a focus on enhancing wireless audio quality. As LDAC technology matures, we're seeing increased adoption across various consumer electronics, particularly in high-end audio devices and smartphones, indicating a growing consumer demand for superior audio experiences.
Apple, Inc.
Technical Solution: Apple has developed its own implementation of LDAC-like technology for high-fidelity audio transmission. Their approach focuses on optimizing audio codec performance for their ecosystem of devices. Apple's solution likely incorporates advanced digital signal processing techniques and leverages the tight integration between their hardware and software. The company has invested in custom audio chips, such as the H1 and W1, which could play a role in enhancing audio fidelity[1]. Apple's implementation may also include adaptive bit rate adjustment to maintain optimal audio quality across varying wireless conditions[2].
Strengths: Seamless integration within Apple ecosystem, potential for lower latency due to custom hardware. Weaknesses: Limited compatibility with non-Apple devices, potentially proprietary nature limiting widespread adoption.
QUALCOMM, Inc.
Technical Solution: Qualcomm has developed aptX Adaptive, a competitor to LDAC, which aims to deliver high-quality audio over Bluetooth. The technology dynamically adjusts bit rate, audio resolution, and connection robustness based on RF environment and content type. aptX Adaptive supports 24-bit audio at sample rates up to 48 kHz, with bitrates ranging from 279 kbps to 420 kbps[3]. Qualcomm's solution incorporates advanced audio processing algorithms and leverages their expertise in wireless communication to optimize performance. The company has also introduced aptX Lossless, which can deliver CD-quality 16-bit 44.1kHz lossless audio over Bluetooth[4].
Strengths: Wide industry adoption, scalable performance across various devices and conditions. Weaknesses: May require specific hardware support, potential licensing costs for manufacturers.
LDAC Core Innovations
Error-feedback SAR-ADC
PatentActiveUS11955983B2
Innovation
- The design incorporates an input sampling buffer with an amplifier and a gain-control capacitor that doubles as both a feedback capacitor for amplification and a residue voltage receiver, eliminating the need for separate capacitors and amplifiers, thereby reducing area and power consumption.
Method and device for processing time-discrete audio sampled values
PatentWO2002103684A1
Innovation
- The method involves performing Time Domain Aliasing Cancellation (TDAC) explicitly in the time domain before transformation, using a rotation matrix represented by lifting matrices to process discrete-time samples from different quarters of a window, ensuring integer windowing and transformation with Givens rotations and rounding, resulting in an integer modified discrete cosine transformation (INT MDCT) that avoids floating-point values and allows direct entropy coding.
LDAC Standardization Efforts
LDAC standardization efforts have been a crucial aspect of the technology's development and widespread adoption. The Bluetooth Special Interest Group (SIG) has played a pivotal role in this process, recognizing LDAC as a high-quality audio codec for Bluetooth audio streaming.
The standardization journey began when Sony, the developer of LDAC, submitted the technology to the Bluetooth SIG for consideration. This move was aimed at establishing LDAC as an industry-wide standard, rather than a proprietary technology limited to Sony devices. The Bluetooth SIG's rigorous evaluation process ensured that LDAC met the necessary criteria for inclusion in the Bluetooth audio ecosystem.
In 2019, LDAC was officially adopted as part of the Bluetooth Audio LE standard, marking a significant milestone in its standardization. This inclusion allowed for broader implementation across various devices and platforms, extending beyond Sony's ecosystem. The standardization process involved detailed technical specifications, ensuring interoperability and consistent performance across different hardware implementations.
One of the key aspects of LDAC standardization was the definition of its bitrate modes. The standard specifies three primary bitrate settings: 330 kbps, 660 kbps, and 990 kbps. These standardized bitrates ensure consistent audio quality and compatibility across different devices and use cases. Additionally, the standardization efforts addressed the adaptive nature of LDAC, allowing it to dynamically adjust its bitrate based on connection quality and device capabilities.
The standardization process also focused on LDAC's integration with existing Bluetooth audio profiles, particularly the Advanced Audio Distribution Profile (A2DP). This integration ensures seamless compatibility with a wide range of Bluetooth audio devices, from headphones to speakers and car audio systems.
Furthermore, the standardization efforts have led to the development of certification programs for LDAC-enabled devices. These programs ensure that products implementing LDAC meet the required specifications and performance standards, maintaining the codec's reputation for high-quality audio transmission.
As part of the ongoing standardization process, efforts are being made to enhance LDAC's energy efficiency and optimize its performance on low-power devices. This focus aligns with the broader trend towards energy-efficient wireless audio solutions, particularly important for battery-powered devices like true wireless earbuds.
The standardization journey began when Sony, the developer of LDAC, submitted the technology to the Bluetooth SIG for consideration. This move was aimed at establishing LDAC as an industry-wide standard, rather than a proprietary technology limited to Sony devices. The Bluetooth SIG's rigorous evaluation process ensured that LDAC met the necessary criteria for inclusion in the Bluetooth audio ecosystem.
In 2019, LDAC was officially adopted as part of the Bluetooth Audio LE standard, marking a significant milestone in its standardization. This inclusion allowed for broader implementation across various devices and platforms, extending beyond Sony's ecosystem. The standardization process involved detailed technical specifications, ensuring interoperability and consistent performance across different hardware implementations.
One of the key aspects of LDAC standardization was the definition of its bitrate modes. The standard specifies three primary bitrate settings: 330 kbps, 660 kbps, and 990 kbps. These standardized bitrates ensure consistent audio quality and compatibility across different devices and use cases. Additionally, the standardization efforts addressed the adaptive nature of LDAC, allowing it to dynamically adjust its bitrate based on connection quality and device capabilities.
The standardization process also focused on LDAC's integration with existing Bluetooth audio profiles, particularly the Advanced Audio Distribution Profile (A2DP). This integration ensures seamless compatibility with a wide range of Bluetooth audio devices, from headphones to speakers and car audio systems.
Furthermore, the standardization efforts have led to the development of certification programs for LDAC-enabled devices. These programs ensure that products implementing LDAC meet the required specifications and performance standards, maintaining the codec's reputation for high-quality audio transmission.
As part of the ongoing standardization process, efforts are being made to enhance LDAC's energy efficiency and optimize its performance on low-power devices. This focus aligns with the broader trend towards energy-efficient wireless audio solutions, particularly important for battery-powered devices like true wireless earbuds.
LDAC Energy Efficiency
LDAC, developed by Sony, stands as a pinnacle of energy-efficient audio codec technology. This high-resolution audio codec achieves remarkable audio quality while maintaining low power consumption, a critical factor in portable audio devices. The energy efficiency of LDAC is primarily attributed to its adaptive bit rate mechanism and optimized encoding algorithms.
LDAC employs a sophisticated bit allocation strategy that dynamically adjusts the bit rate based on the audio content and available bandwidth. This adaptive approach ensures that only the necessary amount of data is transmitted, reducing power consumption without compromising audio quality. The codec supports multiple bit rates, ranging from 330 kbps to 990 kbps, allowing for flexible adaptation to various network conditions and device capabilities.
The encoding process of LDAC is highly optimized for energy efficiency. It utilizes advanced psychoacoustic models to identify and prioritize the most perceptually relevant audio components. By focusing computational resources on these critical elements, LDAC achieves high-quality audio reproduction while minimizing unnecessary processing and data transmission.
Furthermore, LDAC incorporates efficient error correction and concealment techniques. These mechanisms help maintain audio quality even in challenging wireless environments, reducing the need for retransmissions and thus conserving energy. The codec's robust performance in less-than-ideal conditions contributes to its overall energy efficiency by minimizing the power required for maintaining a stable audio stream.
The hardware implementation of LDAC also plays a crucial role in its energy efficiency. Sony has optimized the codec for implementation in low-power DSP (Digital Signal Processor) chips, enabling efficient real-time encoding and decoding on portable devices. This hardware optimization ensures that LDAC can deliver high-quality audio without significantly impacting battery life.
Comparative studies have shown that LDAC outperforms many other Bluetooth audio codecs in terms of energy efficiency. When compared to codecs like SBC (Subband Coding) or AAC (Advanced Audio Coding), LDAC typically achieves better audio quality at similar or lower power consumption levels. This efficiency is particularly notable at higher bit rates, where LDAC's advanced compression techniques shine.
The energy efficiency of LDAC has significant implications for the broader audio industry. It enables the development of high-fidelity wireless audio products with extended battery life, addressing a long-standing challenge in portable audio technology. As energy efficiency becomes increasingly important in consumer electronics, LDAC's approach serves as a model for future audio codec development, balancing performance with power consumption.
LDAC employs a sophisticated bit allocation strategy that dynamically adjusts the bit rate based on the audio content and available bandwidth. This adaptive approach ensures that only the necessary amount of data is transmitted, reducing power consumption without compromising audio quality. The codec supports multiple bit rates, ranging from 330 kbps to 990 kbps, allowing for flexible adaptation to various network conditions and device capabilities.
The encoding process of LDAC is highly optimized for energy efficiency. It utilizes advanced psychoacoustic models to identify and prioritize the most perceptually relevant audio components. By focusing computational resources on these critical elements, LDAC achieves high-quality audio reproduction while minimizing unnecessary processing and data transmission.
Furthermore, LDAC incorporates efficient error correction and concealment techniques. These mechanisms help maintain audio quality even in challenging wireless environments, reducing the need for retransmissions and thus conserving energy. The codec's robust performance in less-than-ideal conditions contributes to its overall energy efficiency by minimizing the power required for maintaining a stable audio stream.
The hardware implementation of LDAC also plays a crucial role in its energy efficiency. Sony has optimized the codec for implementation in low-power DSP (Digital Signal Processor) chips, enabling efficient real-time encoding and decoding on portable devices. This hardware optimization ensures that LDAC can deliver high-quality audio without significantly impacting battery life.
Comparative studies have shown that LDAC outperforms many other Bluetooth audio codecs in terms of energy efficiency. When compared to codecs like SBC (Subband Coding) or AAC (Advanced Audio Coding), LDAC typically achieves better audio quality at similar or lower power consumption levels. This efficiency is particularly notable at higher bit rates, where LDAC's advanced compression techniques shine.
The energy efficiency of LDAC has significant implications for the broader audio industry. It enables the development of high-fidelity wireless audio products with extended battery life, addressing a long-standing challenge in portable audio technology. As energy efficiency becomes increasingly important in consumer electronics, LDAC's approach serves as a model for future audio codec development, balancing performance with power consumption.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!