Versatile Audio Engineering Opportunities through LDAC
JUL 4, 20258 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
LDAC Technology Evolution
LDAC, developed by Sony in 2015, has undergone significant evolution since its inception. Initially designed to address the limitations of Bluetooth audio transmission, LDAC has continuously improved to meet the growing demands of high-quality wireless audio streaming.
In its early stages, LDAC focused on increasing data transfer rates over Bluetooth connections. The technology achieved a maximum transfer rate of 990 kbps, a substantial improvement over the standard SBC codec's 328 kbps. This breakthrough allowed for near CD-quality audio transmission wirelessly, a feat previously thought impossible within Bluetooth's constraints.
As the technology matured, LDAC's developers concentrated on optimizing its efficiency and compatibility. By 2017, LDAC had been integrated into the Android Open Source Project (AOSP), making it available to a wider range of devices beyond Sony's ecosystem. This move significantly expanded LDAC's reach and accelerated its adoption in the audio industry.
The next phase of LDAC's evolution saw improvements in its adaptive bitrate capabilities. The codec became more intelligent in adjusting its transmission rate based on connection quality, ensuring stable audio performance even in challenging wireless environments. This adaptability enhanced LDAC's reliability and user experience across various scenarios.
Recent developments in LDAC have focused on reducing latency and improving power efficiency. These advancements have made LDAC more suitable for real-time applications such as gaming and video streaming, where minimal audio delay is crucial. The reduced power consumption has also addressed concerns about battery life in wireless audio devices.
Looking ahead, LDAC's evolution is likely to continue in several directions. One potential area of development is further increasing the maximum bitrate to support even higher resolution audio formats. Another focus could be on improving LDAC's integration with emerging wireless technologies, such as Wi-Fi 6 and 5G, to exploit their higher bandwidth capabilities.
The technology is also expected to evolve in response to the growing trend of spatial audio and immersive sound experiences. Future iterations of LDAC may incorporate enhanced channel separation and 3D audio processing capabilities to support these advanced audio formats in wireless transmission.
As the audio industry moves towards more sustainable and eco-friendly solutions, LDAC's evolution may also include optimizations for energy efficiency and compatibility with low-power devices. This could open up new applications in IoT and wearable technology sectors.
In its early stages, LDAC focused on increasing data transfer rates over Bluetooth connections. The technology achieved a maximum transfer rate of 990 kbps, a substantial improvement over the standard SBC codec's 328 kbps. This breakthrough allowed for near CD-quality audio transmission wirelessly, a feat previously thought impossible within Bluetooth's constraints.
As the technology matured, LDAC's developers concentrated on optimizing its efficiency and compatibility. By 2017, LDAC had been integrated into the Android Open Source Project (AOSP), making it available to a wider range of devices beyond Sony's ecosystem. This move significantly expanded LDAC's reach and accelerated its adoption in the audio industry.
The next phase of LDAC's evolution saw improvements in its adaptive bitrate capabilities. The codec became more intelligent in adjusting its transmission rate based on connection quality, ensuring stable audio performance even in challenging wireless environments. This adaptability enhanced LDAC's reliability and user experience across various scenarios.
Recent developments in LDAC have focused on reducing latency and improving power efficiency. These advancements have made LDAC more suitable for real-time applications such as gaming and video streaming, where minimal audio delay is crucial. The reduced power consumption has also addressed concerns about battery life in wireless audio devices.
Looking ahead, LDAC's evolution is likely to continue in several directions. One potential area of development is further increasing the maximum bitrate to support even higher resolution audio formats. Another focus could be on improving LDAC's integration with emerging wireless technologies, such as Wi-Fi 6 and 5G, to exploit their higher bandwidth capabilities.
The technology is also expected to evolve in response to the growing trend of spatial audio and immersive sound experiences. Future iterations of LDAC may incorporate enhanced channel separation and 3D audio processing capabilities to support these advanced audio formats in wireless transmission.
As the audio industry moves towards more sustainable and eco-friendly solutions, LDAC's evolution may also include optimizations for energy efficiency and compatibility with low-power devices. This could open up new applications in IoT and wearable technology sectors.
Audio Market Demand Analysis
The audio market has experienced significant growth and transformation in recent years, driven by technological advancements and changing consumer preferences. The demand for high-quality audio solutions has surged across various sectors, including consumer electronics, automotive, gaming, and professional audio equipment.
In the consumer electronics segment, the rise of wireless audio devices, particularly true wireless stereo (TWS) earbuds and smart speakers, has been a major catalyst for market expansion. The global TWS market is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 20% in the coming years, reflecting the strong consumer appetite for convenient and high-quality audio solutions.
The automotive industry has also become a key driver of audio market demand. As vehicles evolve into connected, intelligent platforms, the importance of in-car audio systems has increased dramatically. Premium audio systems are now considered a crucial differentiator for automakers, with consumers willing to pay a premium for enhanced audio experiences during their commutes and travels.
The gaming industry's rapid growth has further fueled demand for advanced audio solutions. Immersive audio technologies, such as 3D spatial audio and surround sound, have become essential components of modern gaming experiences. This trend has led to increased demand for gaming headsets and speakers capable of delivering precise, high-fidelity audio.
Professional audio equipment has seen steady growth, driven by the expansion of the music production, live events, and broadcast industries. The shift towards digital audio workflows and the increasing popularity of podcasting and streaming have created new opportunities for audio technology providers.
The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated certain audio market trends, particularly in the work-from-home and remote collaboration segments. The sudden increase in video conferencing and remote work has boosted demand for high-quality microphones, headsets, and audio processing solutions for improved communication clarity.
LDAC technology, developed by Sony, addresses many of these market demands by offering high-resolution wireless audio transmission. Its ability to transmit audio at up to 990 kbps makes it particularly attractive for applications requiring superior audio quality, such as premium headphones, automotive audio systems, and professional audio equipment.
The growing emphasis on audio quality across various industries presents significant opportunities for LDAC technology. As consumers become more discerning about audio experiences, technologies that can deliver near-lossless wireless audio transmission are likely to see increased adoption and integration into a wide range of products and applications.
In the consumer electronics segment, the rise of wireless audio devices, particularly true wireless stereo (TWS) earbuds and smart speakers, has been a major catalyst for market expansion. The global TWS market is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 20% in the coming years, reflecting the strong consumer appetite for convenient and high-quality audio solutions.
The automotive industry has also become a key driver of audio market demand. As vehicles evolve into connected, intelligent platforms, the importance of in-car audio systems has increased dramatically. Premium audio systems are now considered a crucial differentiator for automakers, with consumers willing to pay a premium for enhanced audio experiences during their commutes and travels.
The gaming industry's rapid growth has further fueled demand for advanced audio solutions. Immersive audio technologies, such as 3D spatial audio and surround sound, have become essential components of modern gaming experiences. This trend has led to increased demand for gaming headsets and speakers capable of delivering precise, high-fidelity audio.
Professional audio equipment has seen steady growth, driven by the expansion of the music production, live events, and broadcast industries. The shift towards digital audio workflows and the increasing popularity of podcasting and streaming have created new opportunities for audio technology providers.
The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated certain audio market trends, particularly in the work-from-home and remote collaboration segments. The sudden increase in video conferencing and remote work has boosted demand for high-quality microphones, headsets, and audio processing solutions for improved communication clarity.
LDAC technology, developed by Sony, addresses many of these market demands by offering high-resolution wireless audio transmission. Its ability to transmit audio at up to 990 kbps makes it particularly attractive for applications requiring superior audio quality, such as premium headphones, automotive audio systems, and professional audio equipment.
The growing emphasis on audio quality across various industries presents significant opportunities for LDAC technology. As consumers become more discerning about audio experiences, technologies that can deliver near-lossless wireless audio transmission are likely to see increased adoption and integration into a wide range of products and applications.
LDAC Technical Challenges
LDAC, developed by Sony, represents a significant advancement in Bluetooth audio codec technology. However, it faces several technical challenges that need to be addressed for wider adoption and improved performance.
One of the primary challenges is the high computational complexity required for real-time encoding and decoding of LDAC streams. This complexity can lead to increased power consumption, particularly on mobile devices with limited processing capabilities. As a result, manufacturers must carefully balance audio quality with battery life, often leading to compromises in implementation.
Another significant challenge is maintaining consistent audio quality across various network conditions. LDAC's adaptive bitrate feature, while beneficial, can sometimes result in noticeable fluctuations in audio quality during playback. This issue is particularly pronounced in environments with high electromagnetic interference or when multiple Bluetooth devices are operating in close proximity.
Compatibility and interoperability present additional hurdles for LDAC. As a proprietary technology, its adoption is limited to devices and audio systems that have licensed the codec. This restriction can create fragmentation in the market and limit consumer choice, especially when considering the wide range of Bluetooth-enabled devices available.
Latency is another critical concern for LDAC, particularly in scenarios requiring precise audio-video synchronization, such as gaming or video playback. While LDAC offers lower latency compared to some other high-quality codecs, achieving consistently low latency across different device configurations and use cases remains challenging.
The codec's performance in multi-device scenarios also presents technical difficulties. Managing simultaneous connections to multiple audio output devices while maintaining high-quality audio streams can strain both the transmitting device's resources and the Bluetooth bandwidth.
Furthermore, LDAC's integration with existing audio processing chains and digital signal processing (DSP) algorithms can be complex. Ensuring seamless operation with various audio enhancement technologies, such as noise cancellation or spatial audio rendering, requires careful optimization and testing.
Lastly, the challenge of backward compatibility with older Bluetooth standards and devices cannot be overlooked. While LDAC offers superior audio quality, ensuring graceful degradation and acceptable performance on devices that do not fully support the codec's advanced features is crucial for widespread adoption and user satisfaction.
One of the primary challenges is the high computational complexity required for real-time encoding and decoding of LDAC streams. This complexity can lead to increased power consumption, particularly on mobile devices with limited processing capabilities. As a result, manufacturers must carefully balance audio quality with battery life, often leading to compromises in implementation.
Another significant challenge is maintaining consistent audio quality across various network conditions. LDAC's adaptive bitrate feature, while beneficial, can sometimes result in noticeable fluctuations in audio quality during playback. This issue is particularly pronounced in environments with high electromagnetic interference or when multiple Bluetooth devices are operating in close proximity.
Compatibility and interoperability present additional hurdles for LDAC. As a proprietary technology, its adoption is limited to devices and audio systems that have licensed the codec. This restriction can create fragmentation in the market and limit consumer choice, especially when considering the wide range of Bluetooth-enabled devices available.
Latency is another critical concern for LDAC, particularly in scenarios requiring precise audio-video synchronization, such as gaming or video playback. While LDAC offers lower latency compared to some other high-quality codecs, achieving consistently low latency across different device configurations and use cases remains challenging.
The codec's performance in multi-device scenarios also presents technical difficulties. Managing simultaneous connections to multiple audio output devices while maintaining high-quality audio streams can strain both the transmitting device's resources and the Bluetooth bandwidth.
Furthermore, LDAC's integration with existing audio processing chains and digital signal processing (DSP) algorithms can be complex. Ensuring seamless operation with various audio enhancement technologies, such as noise cancellation or spatial audio rendering, requires careful optimization and testing.
Lastly, the challenge of backward compatibility with older Bluetooth standards and devices cannot be overlooked. While LDAC offers superior audio quality, ensuring graceful degradation and acceptable performance on devices that do not fully support the codec's advanced features is crucial for widespread adoption and user satisfaction.
Current LDAC Implementations
01 LDAC audio codec implementation
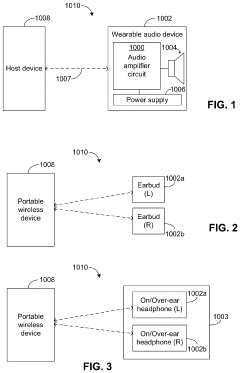
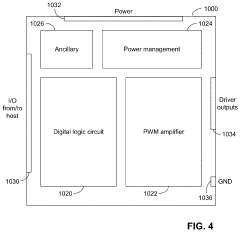
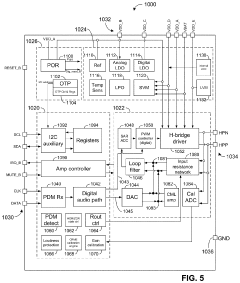
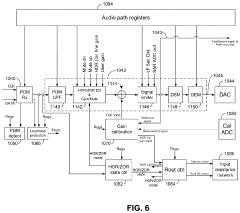
LDAC is a high-quality audio codec developed for Bluetooth audio transmission. It allows for efficient encoding and decoding of audio data, providing high-resolution audio playback over wireless connections. The codec is designed to maintain audio quality while optimizing bandwidth usage.- Audio codec technology for wireless devices: LDAC is an advanced audio codec technology developed for high-quality wireless audio transmission. It enables the transmission of high-resolution audio data over Bluetooth connections, offering improved sound quality compared to standard Bluetooth codecs. LDAC supports various bit rates and can adapt to different network conditions to maintain optimal audio performance.
- Integration with audio processing systems: LDAC can be integrated into various audio processing systems and devices. This includes implementation in smartphones, wireless headphones, speakers, and other audio equipment. The technology allows for seamless compatibility with existing Bluetooth infrastructure while providing enhanced audio quality for supported devices.
- Adaptive bit rate and transmission optimization: LDAC employs adaptive bit rate technology to optimize audio transmission based on network conditions and device capabilities. This feature allows the codec to adjust its performance dynamically, ensuring stable connections and maintaining the best possible audio quality under varying circumstances.
- Application in multi-channel audio systems: LDAC technology can be applied to multi-channel audio systems, supporting high-quality surround sound experiences in wireless setups. This enables the transmission of complex audio data for immersive audio environments, such as home theater systems or professional audio installations.
- Energy efficiency and battery life optimization: LDAC incorporates energy-efficient encoding and decoding processes, which help optimize battery life in wireless audio devices. This is particularly important for portable devices like wireless headphones and speakers, where power consumption is a critical factor in overall performance and user experience.
02 LDAC integration in audio devices
Various audio devices, including smartphones, headphones, and speakers, incorporate LDAC technology to enhance wireless audio transmission. The integration involves hardware and software components to support encoding and decoding of LDAC audio streams, ensuring compatibility and optimal performance.Expand Specific Solutions03 LDAC in automotive audio systems
LDAC technology is being implemented in automotive audio systems to improve in-car entertainment experiences. This includes integration with infotainment systems, wireless connectivity for mobile devices, and enhanced audio quality for music streaming and hands-free calling.Expand Specific Solutions04 LDAC power efficiency improvements
Efforts are being made to improve the power efficiency of LDAC codec implementation, particularly in battery-powered devices. This involves optimizing encoding and decoding processes, as well as developing more energy-efficient hardware solutions for LDAC-enabled devices.Expand Specific Solutions05 LDAC compatibility and interoperability
Research and development focus on ensuring LDAC compatibility across various devices and platforms. This includes creating standardized implementations, developing testing protocols, and improving interoperability with other audio codecs and wireless technologies.Expand Specific Solutions
Key LDAC Industry Players
The LDAC audio engineering landscape is characterized by a competitive and rapidly evolving market. As the technology matures, major players like Sony (developer of LDAC), Samsung, Apple, and Intel are investing heavily in this field. The market is in a growth phase, with increasing demand for high-quality wireless audio solutions driving innovation. Companies like Fraunhofer-Gesellschaft and Analog Devices are contributing to advancements in audio codecs and signal processing. The market size is expanding, fueled by the proliferation of wireless audio devices and streaming services. While LDAC technology is relatively mature, ongoing research by universities like Beihang and companies such as IBM and Philips continues to push the boundaries of audio compression and transmission quality.
Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Samsung has embraced LDAC technology across its Galaxy line of smartphones and wireless earbuds. The company's implementation focuses on maximizing audio quality, supporting the full 990kbps bitrate for compatible devices[2]. Samsung has also developed a proprietary scalable codec that works alongside LDAC, allowing for dynamic bitrate adjustment between 88kbps and 512kbps. This hybrid approach enables Samsung devices to maintain high-quality audio transmission even in challenging wireless environments. Furthermore, Samsung has integrated LDAC with its UHQ (Ultra High Quality) audio upscaling technology, which can enhance 16-bit audio to 24-bit quality[4].
Strengths: Wide device compatibility, advanced bitrate scaling for stable connections. Weaknesses: Proprietary features may not be fully utilized on non-Samsung devices.
Apple, Inc.
Technical Solution: Apple has integrated LDAC support into its audio ecosystem, particularly in its AirPods and HomePod product lines. The company's implementation focuses on optimizing LDAC for low-latency performance, crucial for real-time audio applications. Apple's approach involves adaptive bitrate selection, dynamically adjusting between 330kbps and 990kbps based on network conditions and device capabilities[1]. This allows for maintaining high audio quality while ensuring stable connections. Additionally, Apple has developed custom DSP algorithms to work in tandem with LDAC, enhancing spatial audio experiences and noise cancellation features[3].
Strengths: Seamless integration with Apple ecosystem, optimized for low-latency applications. Weaknesses: Limited compatibility with non-Apple devices, potentially restricting wider adoption.
LDAC Core Innovations
Network dedication system
PatentInactiveUS6856990B2
Innovation
- A system that allows users to specify and insert dedication content, including messages and media, between segments of a playlist or as voice-overs, using a network connection, enabling users to share experiences and personalize their media playback with content from others.
Digital-to-analog converter architecture for audio amplifiers
PatentPendingUS20230102120A1
Innovation
- A digital-to-analog converter (DAC) architecture with a variable bit cell array that adjusts its active population based on signal conditions, consuming quiescent current only when necessary, and dynamically switching between different modes to optimize power usage and audio quality.
LDAC Ecosystem Integration
The integration of LDAC into the audio ecosystem represents a significant advancement in wireless audio technology. As a high-resolution audio codec developed by Sony, LDAC has the potential to revolutionize the way we experience audio across various devices and platforms.
LDAC's ecosystem integration begins with its implementation in source devices, such as smartphones, tablets, and digital audio players. Many Android devices now support LDAC natively, allowing for seamless transmission of high-quality audio to compatible receivers. This integration extends to various operating systems and platforms, ensuring broad compatibility and accessibility for users.
On the receiving end, LDAC is being incorporated into a wide range of audio devices. Wireless headphones, earbuds, and speakers from multiple manufacturers are adopting LDAC technology to deliver superior audio quality. Home audio systems, including soundbars and AV receivers, are also integrating LDAC to enhance the listening experience in home entertainment setups.
The automotive industry is another sector where LDAC integration is gaining traction. Car audio systems are incorporating LDAC to provide high-fidelity wireless audio streaming for drivers and passengers. This integration aligns with the growing trend of connected and smart vehicles, offering a premium audio experience on the go.
Professional audio equipment manufacturers are also exploring LDAC integration for studio-grade wireless monitoring and recording applications. This opens up new possibilities for audio professionals to work with high-resolution audio in wireless setups without compromising on quality.
LDAC's ecosystem integration extends beyond hardware to software applications and streaming services. Music streaming platforms are increasingly supporting LDAC codec for their high-fidelity tiers, allowing subscribers to take full advantage of the codec's capabilities when using compatible devices.
The integration of LDAC into various audio ecosystems is driving innovation in related technologies. For instance, it is spurring advancements in Bluetooth audio transmission, pushing the boundaries of what's possible in terms of wireless audio quality and bandwidth efficiency.
As LDAC continues to expand its presence across different audio ecosystems, it is fostering collaboration between hardware manufacturers, software developers, and content providers. This collaborative approach is crucial for creating a cohesive and seamless user experience across the entire audio chain, from content creation to playback.
LDAC's ecosystem integration begins with its implementation in source devices, such as smartphones, tablets, and digital audio players. Many Android devices now support LDAC natively, allowing for seamless transmission of high-quality audio to compatible receivers. This integration extends to various operating systems and platforms, ensuring broad compatibility and accessibility for users.
On the receiving end, LDAC is being incorporated into a wide range of audio devices. Wireless headphones, earbuds, and speakers from multiple manufacturers are adopting LDAC technology to deliver superior audio quality. Home audio systems, including soundbars and AV receivers, are also integrating LDAC to enhance the listening experience in home entertainment setups.
The automotive industry is another sector where LDAC integration is gaining traction. Car audio systems are incorporating LDAC to provide high-fidelity wireless audio streaming for drivers and passengers. This integration aligns with the growing trend of connected and smart vehicles, offering a premium audio experience on the go.
Professional audio equipment manufacturers are also exploring LDAC integration for studio-grade wireless monitoring and recording applications. This opens up new possibilities for audio professionals to work with high-resolution audio in wireless setups without compromising on quality.
LDAC's ecosystem integration extends beyond hardware to software applications and streaming services. Music streaming platforms are increasingly supporting LDAC codec for their high-fidelity tiers, allowing subscribers to take full advantage of the codec's capabilities when using compatible devices.
The integration of LDAC into various audio ecosystems is driving innovation in related technologies. For instance, it is spurring advancements in Bluetooth audio transmission, pushing the boundaries of what's possible in terms of wireless audio quality and bandwidth efficiency.
As LDAC continues to expand its presence across different audio ecosystems, it is fostering collaboration between hardware manufacturers, software developers, and content providers. This collaborative approach is crucial for creating a cohesive and seamless user experience across the entire audio chain, from content creation to playback.
LDAC Standardization Efforts
LDAC standardization efforts have been a crucial aspect of Sony's strategy to establish LDAC as a widely adopted high-quality audio codec. The process began in 2015 when Sony introduced LDAC as a proprietary technology. Recognizing the importance of industry-wide acceptance, Sony initiated efforts to standardize LDAC through various international bodies.
In 2016, Sony submitted LDAC to the Bluetooth Special Interest Group (SIG) for consideration as a standard codec. This move was significant as it aimed to integrate LDAC into the Bluetooth audio ecosystem, potentially making it available to a broader range of devices and manufacturers. The Bluetooth SIG's evaluation process involved rigorous testing and review of the codec's performance, efficiency, and compatibility with existing Bluetooth protocols.
Concurrently, Sony engaged with the Japan Audio Society (JAS) to establish LDAC as a recognized high-resolution wireless audio transmission technology. This collaboration resulted in LDAC receiving certification from JAS, further solidifying its position as a premium audio codec.
The standardization process gained momentum in 2017 when the Android Open Source Project (AOSP) incorporated LDAC into its codebase. This integration made LDAC available to Android device manufacturers, significantly expanding its potential user base and encouraging wider adoption across the mobile industry.
In 2019, LDAC achieved a major milestone when it was officially adopted as part of the Bluetooth standard. This inclusion in the Bluetooth Core Specification meant that LDAC became one of the officially supported codecs for Bluetooth audio transmission, alongside established formats like SBC, AAC, and aptX.
Throughout the standardization process, Sony has continued to refine and improve LDAC technology. The company has worked closely with industry partners to ensure compatibility and optimal performance across various devices and platforms. This ongoing collaboration has been essential in addressing technical challenges and enhancing the codec's capabilities.
The standardization efforts have also involved extensive documentation and technical support to facilitate implementation by third-party manufacturers. Sony has provided detailed specifications, integration guidelines, and reference designs to assist hardware and software developers in incorporating LDAC into their products.
As a result of these comprehensive standardization efforts, LDAC has gained widespread recognition and adoption in the audio industry. It is now supported by numerous smartphone manufacturers, audio equipment producers, and streaming services, cementing its position as a leading high-quality audio codec in the wireless audio market.
In 2016, Sony submitted LDAC to the Bluetooth Special Interest Group (SIG) for consideration as a standard codec. This move was significant as it aimed to integrate LDAC into the Bluetooth audio ecosystem, potentially making it available to a broader range of devices and manufacturers. The Bluetooth SIG's evaluation process involved rigorous testing and review of the codec's performance, efficiency, and compatibility with existing Bluetooth protocols.
Concurrently, Sony engaged with the Japan Audio Society (JAS) to establish LDAC as a recognized high-resolution wireless audio transmission technology. This collaboration resulted in LDAC receiving certification from JAS, further solidifying its position as a premium audio codec.
The standardization process gained momentum in 2017 when the Android Open Source Project (AOSP) incorporated LDAC into its codebase. This integration made LDAC available to Android device manufacturers, significantly expanding its potential user base and encouraging wider adoption across the mobile industry.
In 2019, LDAC achieved a major milestone when it was officially adopted as part of the Bluetooth standard. This inclusion in the Bluetooth Core Specification meant that LDAC became one of the officially supported codecs for Bluetooth audio transmission, alongside established formats like SBC, AAC, and aptX.
Throughout the standardization process, Sony has continued to refine and improve LDAC technology. The company has worked closely with industry partners to ensure compatibility and optimal performance across various devices and platforms. This ongoing collaboration has been essential in addressing technical challenges and enhancing the codec's capabilities.
The standardization efforts have also involved extensive documentation and technical support to facilitate implementation by third-party manufacturers. Sony has provided detailed specifications, integration guidelines, and reference designs to assist hardware and software developers in incorporating LDAC into their products.
As a result of these comprehensive standardization efforts, LDAC has gained widespread recognition and adoption in the audio industry. It is now supported by numerous smartphone manufacturers, audio equipment producers, and streaming services, cementing its position as a leading high-quality audio codec in the wireless audio market.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!