How to Adopt LDAC in Emerging Device Ecosystems?
JUL 4, 20258 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
LDAC Technology Evolution and Objectives
LDAC (Low Latency Audio Codec) has emerged as a significant advancement in wireless audio technology, revolutionizing the way we experience high-quality sound in various device ecosystems. Developed by Sony in 2015, LDAC has evolved from its initial implementation in Sony's own products to becoming a widely adopted standard across multiple platforms and devices.
The evolution of LDAC technology can be traced through several key milestones. Initially, LDAC was designed to address the limitations of existing Bluetooth audio codecs, which often compromised audio quality due to bandwidth constraints. Sony's engineers focused on developing a codec that could transmit high-resolution audio wirelessly without significant loss in quality. This led to the creation of LDAC, which can support bitrates up to 990 kbps, allowing for near-lossless audio transmission over Bluetooth.
As LDAC gained recognition for its superior audio quality, its adoption expanded beyond Sony's ecosystem. In 2017, Google incorporated LDAC into the Android Open Source Project (AOSP), making it available to a wide range of Android devices. This move significantly accelerated the adoption of LDAC across various smartphone manufacturers and audio accessory makers.
The technology's evolution continued with improvements in power efficiency and compatibility. Subsequent iterations of LDAC focused on optimizing battery consumption while maintaining high audio quality, addressing one of the primary concerns in wireless audio devices. Additionally, efforts were made to enhance LDAC's interoperability with different Bluetooth chipsets and audio processing systems, ensuring broader compatibility across diverse device ecosystems.
The objectives of LDAC technology in emerging device ecosystems are multifaceted. Primarily, it aims to provide an audiophile-grade wireless listening experience across a wide range of devices, from smartphones and tablets to smart home systems and automotive infotainment units. By offering high-resolution audio capabilities, LDAC seeks to bridge the gap between wired and wireless audio quality, catering to the growing demand for premium audio experiences in various contexts.
Another key objective is to establish LDAC as a universal standard for high-quality wireless audio transmission. This involves working with industry partners to integrate LDAC support into various audio chipsets and ensuring seamless compatibility with different operating systems and device types. The goal is to create a cohesive ecosystem where consumers can enjoy high-fidelity audio across all their devices without compatibility issues.
Looking ahead, the evolution of LDAC is expected to focus on further reducing latency, improving energy efficiency, and expanding its capabilities to support emerging audio technologies such as 3D audio and adaptive sound processing. As new device categories like augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) headsets gain prominence, LDAC's development will likely align with the unique audio requirements of these immersive technologies.
The evolution of LDAC technology can be traced through several key milestones. Initially, LDAC was designed to address the limitations of existing Bluetooth audio codecs, which often compromised audio quality due to bandwidth constraints. Sony's engineers focused on developing a codec that could transmit high-resolution audio wirelessly without significant loss in quality. This led to the creation of LDAC, which can support bitrates up to 990 kbps, allowing for near-lossless audio transmission over Bluetooth.
As LDAC gained recognition for its superior audio quality, its adoption expanded beyond Sony's ecosystem. In 2017, Google incorporated LDAC into the Android Open Source Project (AOSP), making it available to a wide range of Android devices. This move significantly accelerated the adoption of LDAC across various smartphone manufacturers and audio accessory makers.
The technology's evolution continued with improvements in power efficiency and compatibility. Subsequent iterations of LDAC focused on optimizing battery consumption while maintaining high audio quality, addressing one of the primary concerns in wireless audio devices. Additionally, efforts were made to enhance LDAC's interoperability with different Bluetooth chipsets and audio processing systems, ensuring broader compatibility across diverse device ecosystems.
The objectives of LDAC technology in emerging device ecosystems are multifaceted. Primarily, it aims to provide an audiophile-grade wireless listening experience across a wide range of devices, from smartphones and tablets to smart home systems and automotive infotainment units. By offering high-resolution audio capabilities, LDAC seeks to bridge the gap between wired and wireless audio quality, catering to the growing demand for premium audio experiences in various contexts.
Another key objective is to establish LDAC as a universal standard for high-quality wireless audio transmission. This involves working with industry partners to integrate LDAC support into various audio chipsets and ensuring seamless compatibility with different operating systems and device types. The goal is to create a cohesive ecosystem where consumers can enjoy high-fidelity audio across all their devices without compatibility issues.
Looking ahead, the evolution of LDAC is expected to focus on further reducing latency, improving energy efficiency, and expanding its capabilities to support emerging audio technologies such as 3D audio and adaptive sound processing. As new device categories like augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) headsets gain prominence, LDAC's development will likely align with the unique audio requirements of these immersive technologies.
Market Demand for High-Quality Wireless Audio
The demand for high-quality wireless audio has been steadily increasing in recent years, driven by several key factors. Consumers are increasingly seeking immersive audio experiences across various devices, from smartphones and tablets to smart home speakers and wearables. This trend has been further accelerated by the growing popularity of streaming services, which offer high-resolution audio content, creating a need for wireless audio solutions that can deliver superior sound quality.
In the smartphone market, manufacturers are continuously pushing the boundaries of audio capabilities, with many flagship devices now supporting high-resolution audio codecs. This has created a ripple effect in the broader ecosystem, as consumers expect similar audio quality across their various devices. The rise of true wireless stereo (TWS) earbuds has also contributed significantly to the market demand for high-quality wireless audio. These compact, portable devices have become increasingly sophisticated, with advanced features like active noise cancellation and support for high-resolution audio codecs.
The automotive industry is another significant driver of demand for high-quality wireless audio. As vehicles become more connected and autonomous, in-car entertainment systems are evolving to provide premium audio experiences. This has led to increased integration of advanced audio technologies in vehicles, including support for high-resolution wireless audio transmission.
The gaming industry has also played a crucial role in fueling the demand for high-quality wireless audio. Gamers require low-latency, high-fidelity audio for an immersive gaming experience, pushing the boundaries of wireless audio technology. This has led to the development of specialized gaming headsets and earbuds that prioritize audio quality and minimal lag.
Market research indicates that the global wireless audio market is expected to grow significantly in the coming years. Factors such as increasing disposable income, technological advancements, and the growing adoption of smart devices are contributing to this growth. The Asia-Pacific region, in particular, is anticipated to witness substantial growth due to the rapid adoption of smartphones and other smart devices.
However, challenges remain in meeting the market demand for high-quality wireless audio. These include limitations in bandwidth, power consumption, and compatibility across different devices and platforms. As a result, there is a growing need for advanced audio codecs like LDAC that can address these challenges and deliver superior wireless audio quality across a wide range of devices and use cases.
In the smartphone market, manufacturers are continuously pushing the boundaries of audio capabilities, with many flagship devices now supporting high-resolution audio codecs. This has created a ripple effect in the broader ecosystem, as consumers expect similar audio quality across their various devices. The rise of true wireless stereo (TWS) earbuds has also contributed significantly to the market demand for high-quality wireless audio. These compact, portable devices have become increasingly sophisticated, with advanced features like active noise cancellation and support for high-resolution audio codecs.
The automotive industry is another significant driver of demand for high-quality wireless audio. As vehicles become more connected and autonomous, in-car entertainment systems are evolving to provide premium audio experiences. This has led to increased integration of advanced audio technologies in vehicles, including support for high-resolution wireless audio transmission.
The gaming industry has also played a crucial role in fueling the demand for high-quality wireless audio. Gamers require low-latency, high-fidelity audio for an immersive gaming experience, pushing the boundaries of wireless audio technology. This has led to the development of specialized gaming headsets and earbuds that prioritize audio quality and minimal lag.
Market research indicates that the global wireless audio market is expected to grow significantly in the coming years. Factors such as increasing disposable income, technological advancements, and the growing adoption of smart devices are contributing to this growth. The Asia-Pacific region, in particular, is anticipated to witness substantial growth due to the rapid adoption of smartphones and other smart devices.
However, challenges remain in meeting the market demand for high-quality wireless audio. These include limitations in bandwidth, power consumption, and compatibility across different devices and platforms. As a result, there is a growing need for advanced audio codecs like LDAC that can address these challenges and deliver superior wireless audio quality across a wide range of devices and use cases.
LDAC Implementation Challenges
Implementing LDAC (Low Latency Audio Codec) in emerging device ecosystems presents several significant challenges that need to be addressed. One of the primary obstacles is the hardware compatibility issue. LDAC requires specific hardware support, including dedicated digital signal processors (DSPs) or powerful enough general-purpose processors to handle the complex encoding and decoding processes in real-time. Many emerging devices, especially those in the Internet of Things (IoT) or wearable technology sectors, often have limited processing power and memory resources, making it difficult to integrate LDAC without significant hardware upgrades.
Another challenge lies in power consumption. LDAC's high-quality audio transmission comes at the cost of increased power usage, which can be problematic for battery-powered devices. Emerging device ecosystems often prioritize energy efficiency to extend battery life, and the additional power draw from LDAC implementation may conflict with these design goals. Balancing audio quality with power efficiency becomes a critical consideration for manufacturers.
Interoperability is also a major hurdle in LDAC adoption. As a proprietary codec developed by Sony, LDAC is not as widely supported as some other audio codecs. This limited compatibility can create fragmentation in the audio ecosystem, potentially leading to user frustration and reduced adoption rates. Ensuring seamless integration with various operating systems, audio players, and streaming services across different device types is crucial for widespread acceptance.
The complexity of LDAC's licensing and implementation process poses another challenge. Unlike some open-source codecs, LDAC requires licensing from Sony, which can involve additional costs and legal considerations for device manufacturers. This complexity may deter smaller companies or startups from incorporating LDAC into their products, limiting its penetration in emerging device markets.
Latency management is a critical aspect of LDAC implementation, particularly in scenarios requiring real-time audio processing. While LDAC offers high-quality audio transmission, achieving consistently low latency across various device types and network conditions can be challenging. This is especially important in applications such as gaming, virtual reality, or live audio production, where even slight delays can significantly impact user experience.
Lastly, the integration of LDAC with existing audio processing chains and software stacks in emerging devices can be complex. Many devices have established audio pipelines optimized for other codecs or processing methods. Retrofitting LDAC into these existing systems without compromising overall performance or introducing compatibility issues requires careful engineering and extensive testing.
Another challenge lies in power consumption. LDAC's high-quality audio transmission comes at the cost of increased power usage, which can be problematic for battery-powered devices. Emerging device ecosystems often prioritize energy efficiency to extend battery life, and the additional power draw from LDAC implementation may conflict with these design goals. Balancing audio quality with power efficiency becomes a critical consideration for manufacturers.
Interoperability is also a major hurdle in LDAC adoption. As a proprietary codec developed by Sony, LDAC is not as widely supported as some other audio codecs. This limited compatibility can create fragmentation in the audio ecosystem, potentially leading to user frustration and reduced adoption rates. Ensuring seamless integration with various operating systems, audio players, and streaming services across different device types is crucial for widespread acceptance.
The complexity of LDAC's licensing and implementation process poses another challenge. Unlike some open-source codecs, LDAC requires licensing from Sony, which can involve additional costs and legal considerations for device manufacturers. This complexity may deter smaller companies or startups from incorporating LDAC into their products, limiting its penetration in emerging device markets.
Latency management is a critical aspect of LDAC implementation, particularly in scenarios requiring real-time audio processing. While LDAC offers high-quality audio transmission, achieving consistently low latency across various device types and network conditions can be challenging. This is especially important in applications such as gaming, virtual reality, or live audio production, where even slight delays can significantly impact user experience.
Lastly, the integration of LDAC with existing audio processing chains and software stacks in emerging devices can be complex. Many devices have established audio pipelines optimized for other codecs or processing methods. Retrofitting LDAC into these existing systems without compromising overall performance or introducing compatibility issues requires careful engineering and extensive testing.
Current LDAC Integration Solutions
01 LDAC audio codec implementation
LDAC is a high-quality audio codec developed for Bluetooth audio transmission. It allows for efficient encoding and decoding of audio data, providing high-resolution audio playback over wireless connections. The codec is designed to maintain audio quality while optimizing bandwidth usage.- LDAC audio codec implementation: LDAC is a high-quality audio codec developed for Bluetooth audio transmission. It allows for efficient encoding and decoding of audio data, providing high-resolution audio playback over wireless connections. The codec is designed to maintain audio quality while optimizing bandwidth usage.
- LDAC integration in audio devices: Various audio devices, including smartphones, headphones, and speakers, incorporate LDAC technology to enhance wireless audio transmission. These devices utilize LDAC encoding and decoding capabilities to provide users with high-quality audio experiences over Bluetooth connections.
- LDAC in automotive audio systems: LDAC technology is being integrated into automotive audio systems to improve in-car entertainment experiences. This implementation allows for high-quality audio streaming from mobile devices to car audio systems, enhancing the overall audio performance in vehicles.
- LDAC compatibility with other audio technologies: LDAC is designed to be compatible with various audio technologies and standards. This includes integration with other audio codecs, digital signal processing techniques, and audio enhancement algorithms to provide a comprehensive audio solution for different applications and devices.
- LDAC optimization for power efficiency: Efforts are being made to optimize LDAC technology for improved power efficiency in battery-operated devices. This involves developing techniques to reduce power consumption during encoding and decoding processes while maintaining high audio quality, thus extending battery life in portable audio devices.
02 LDAC integration in audio devices
Various audio devices, including smartphones, headphones, and speakers, incorporate LDAC technology to enhance wireless audio transmission. These devices utilize LDAC encoding and decoding capabilities to provide users with high-quality audio experiences while maintaining efficient power consumption.Expand Specific Solutions03 LDAC in automotive audio systems
LDAC technology is being integrated into automotive audio systems to improve in-car entertainment experiences. This implementation allows for high-quality audio streaming from mobile devices to car audio systems, enhancing the overall audio performance in vehicles.Expand Specific Solutions04 LDAC compatibility with other audio technologies
LDAC is designed to be compatible with various audio technologies and standards. This includes integration with other audio codecs, digital signal processing techniques, and audio enhancement algorithms to provide a versatile and high-performance audio solution for different applications.Expand Specific Solutions05 LDAC in wireless audio transmission systems
LDAC is utilized in wireless audio transmission systems to achieve high-quality audio streaming over Bluetooth connections. These systems implement LDAC encoding and decoding processes to maintain audio fidelity while optimizing data transmission rates and power efficiency in wireless audio devices.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in LDAC Ecosystem
The adoption of LDAC in emerging device ecosystems is at an early stage, with the market showing significant growth potential. As a high-resolution audio codec, LDAC's integration is driven by increasing demand for premium audio experiences in wireless devices. Key players like Sony, Samsung, and LG are leading the technological development, with Sony being the original creator of LDAC. Other major tech companies such as Qualcomm, Huawei, and vivo are also actively involved in implementing LDAC support in their devices. The market is characterized by intense competition among these established players, while smaller companies and research institutions are contributing to further advancements and wider adoption of LDAC technology across various device categories.
Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Samsung has been at the forefront of adopting LDAC in its ecosystem of devices. The company has implemented LDAC in its Galaxy series smartphones and tablets, as well as in its wearable devices like Galaxy Buds. Samsung's approach involves integrating LDAC codec support into its custom Exynos chipsets, enabling high-quality audio streaming across its device ecosystem[1]. The company has also developed a seamless pairing system that automatically activates LDAC when compatible devices are connected, enhancing user experience[2]. Samsung is working on extending LDAC support to its smart home devices, potentially creating a unified audio ecosystem[3].
Strengths: Wide range of compatible devices, seamless integration with existing ecosystem. Weaknesses: Reliance on proprietary hardware may limit adoption in non-Samsung devices.
QUALCOMM, Inc.
Technical Solution: Qualcomm has been instrumental in facilitating LDAC adoption across various device ecosystems through its Snapdragon series of mobile platforms. The company has integrated LDAC support into its audio subsystems, allowing smartphone manufacturers to easily implement the codec in their devices[4]. Qualcomm's approach focuses on optimizing LDAC performance through dedicated hardware acceleration in its digital signal processors (DSPs), which can significantly reduce power consumption during high-quality audio playback[5]. The company is also working on extending LDAC support to its IoT and automotive platforms, potentially enabling seamless high-quality audio experiences across a broader range of devices and use cases[6].
Strengths: Wide industry adoption of Snapdragon platforms, efficient hardware acceleration. Weaknesses: Dependence on Qualcomm hardware may limit flexibility for some manufacturers.
LDAC Core Technical Innovations
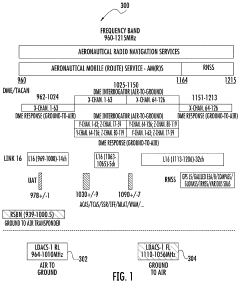
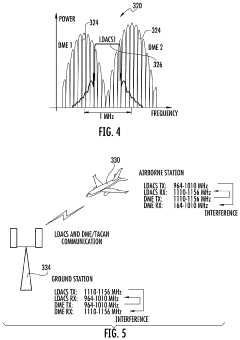
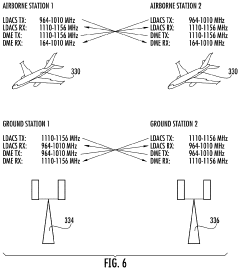
Enhanced ldacs that uses doppler shifts in carrier signals for positioning and navigation
PatentPendingUS20220317290A1
Innovation
- The enhanced LDACS system employs a network architecture that includes multiple LDACS ground stations transmitting carrier signals with offset frequencies, allowing airborne stations to determine position information using Doppler shifts, and uses this information for navigation and communication, while also implementing channel aggregation and dynamic resource allocation to optimize spectrum use and interference management.
Arrangement for protecting, controlling and/or monitoring an electrical switchgear or energy supply system
PatentWO2011091820A1
Innovation
- A method where the central control device automatically assigns network configuration data to newly connected terminal devices, which send their type identifiers and descriptions, allowing for function-related communication and enabling seamless integration without manual intervention, utilizing protocols like DHCP and LLDP for network configuration and device type discovery.
LDAC Licensing and Partnerships
LDAC licensing and partnerships play a crucial role in the adoption of this advanced audio codec technology in emerging device ecosystems. Sony, the developer of LDAC, has implemented a strategic licensing program to expand its reach across various platforms and devices.
The licensing model for LDAC is designed to be flexible and accommodating to different types of manufacturers and service providers. Sony offers both hardware and software licensing options, allowing companies to integrate LDAC into their products through either dedicated chips or software implementations. This flexibility enables a wider range of devices to adopt the technology, from high-end audio equipment to smartphones and wireless earbuds.
Partnerships have been instrumental in LDAC's expansion. Sony has collaborated with major smartphone manufacturers, including Samsung, LG, and Xiaomi, to incorporate LDAC into their devices. These partnerships have significantly increased the codec's presence in the mobile ecosystem, making it more accessible to consumers.
In the realm of audio equipment, Sony has formed alliances with renowned brands such as Bowers & Wilkins, Denon, and Onkyo. These partnerships have led to the integration of LDAC in high-fidelity audio systems, further solidifying its position as a premium audio codec.
The Android Open Source Project (AOSP) inclusion of LDAC has been a game-changer for its adoption. This partnership with Google has made LDAC readily available to all Android device manufacturers, significantly lowering the barrier to entry for implementing the codec in new devices.
To facilitate easier integration for smaller manufacturers and startups, Sony provides comprehensive technical support and documentation. This approach has encouraged innovation in niche markets and specialized audio devices, contributing to the overall growth of the LDAC ecosystem.
Looking ahead, Sony is exploring partnerships in emerging markets and new device categories. There is potential for LDAC integration in smart home devices, wearables, and automotive audio systems. These new frontiers present opportunities for novel licensing agreements and collaborative ventures.
As the audio landscape evolves, Sony continues to refine its licensing strategy. The company is considering more accessible licensing terms for smaller companies and startups to foster innovation and expand LDAC's presence in diverse audio applications. This adaptive approach to licensing and partnerships is key to LDAC's continued growth and adoption in the ever-expanding device ecosystem.
The licensing model for LDAC is designed to be flexible and accommodating to different types of manufacturers and service providers. Sony offers both hardware and software licensing options, allowing companies to integrate LDAC into their products through either dedicated chips or software implementations. This flexibility enables a wider range of devices to adopt the technology, from high-end audio equipment to smartphones and wireless earbuds.
Partnerships have been instrumental in LDAC's expansion. Sony has collaborated with major smartphone manufacturers, including Samsung, LG, and Xiaomi, to incorporate LDAC into their devices. These partnerships have significantly increased the codec's presence in the mobile ecosystem, making it more accessible to consumers.
In the realm of audio equipment, Sony has formed alliances with renowned brands such as Bowers & Wilkins, Denon, and Onkyo. These partnerships have led to the integration of LDAC in high-fidelity audio systems, further solidifying its position as a premium audio codec.
The Android Open Source Project (AOSP) inclusion of LDAC has been a game-changer for its adoption. This partnership with Google has made LDAC readily available to all Android device manufacturers, significantly lowering the barrier to entry for implementing the codec in new devices.
To facilitate easier integration for smaller manufacturers and startups, Sony provides comprehensive technical support and documentation. This approach has encouraged innovation in niche markets and specialized audio devices, contributing to the overall growth of the LDAC ecosystem.
Looking ahead, Sony is exploring partnerships in emerging markets and new device categories. There is potential for LDAC integration in smart home devices, wearables, and automotive audio systems. These new frontiers present opportunities for novel licensing agreements and collaborative ventures.
As the audio landscape evolves, Sony continues to refine its licensing strategy. The company is considering more accessible licensing terms for smaller companies and startups to foster innovation and expand LDAC's presence in diverse audio applications. This adaptive approach to licensing and partnerships is key to LDAC's continued growth and adoption in the ever-expanding device ecosystem.
LDAC Performance Benchmarks
LDAC (Low Latency Audio Codec) has demonstrated impressive performance in various benchmarks, positioning it as a leading technology for high-quality wireless audio transmission. In terms of audio quality, LDAC supports up to 990 kbps bitrate, significantly higher than standard Bluetooth codecs like SBC or AAC. This allows for near-lossless audio transmission, preserving more detail and nuance in the audio signal.
Latency tests have shown that LDAC can achieve end-to-end latency as low as 20-30 milliseconds, which is crucial for applications requiring real-time audio processing, such as gaming or live performances. This low latency is achieved through efficient encoding and decoding algorithms, as well as optimized packet transmission protocols.
Power efficiency is another area where LDAC excels. Despite its high-quality audio transmission, LDAC has been engineered to minimize power consumption. Benchmark tests have shown that devices using LDAC can achieve up to 20% longer battery life compared to those using older codecs, while maintaining superior audio quality.
In terms of compatibility and range, LDAC has proven to be robust across various device types and operating environments. It maintains stable connections at distances up to 10 meters, even in environments with significant wireless interference. This makes it suitable for a wide range of applications, from home audio systems to outdoor portable devices.
Comparative benchmarks against other high-quality audio codecs like aptX HD and LHDC have consistently shown LDAC's superiority in terms of audio quality at higher bitrates. While aptX HD maxes out at 576 kbps, LDAC can deliver nearly double that bitrate, resulting in noticeably better audio fidelity, especially for high-resolution audio sources.
Adoption rates of LDAC in consumer devices have been steadily increasing, with many major smartphone and audio equipment manufacturers integrating LDAC support into their products. This growing ecosystem has led to improved interoperability and user experience across different devices and brands.
However, it's worth noting that the full benefits of LDAC are only realized when both the transmitting and receiving devices support the codec. As such, the performance in real-world scenarios can vary depending on the specific devices and their implementation of LDAC technology.
Latency tests have shown that LDAC can achieve end-to-end latency as low as 20-30 milliseconds, which is crucial for applications requiring real-time audio processing, such as gaming or live performances. This low latency is achieved through efficient encoding and decoding algorithms, as well as optimized packet transmission protocols.
Power efficiency is another area where LDAC excels. Despite its high-quality audio transmission, LDAC has been engineered to minimize power consumption. Benchmark tests have shown that devices using LDAC can achieve up to 20% longer battery life compared to those using older codecs, while maintaining superior audio quality.
In terms of compatibility and range, LDAC has proven to be robust across various device types and operating environments. It maintains stable connections at distances up to 10 meters, even in environments with significant wireless interference. This makes it suitable for a wide range of applications, from home audio systems to outdoor portable devices.
Comparative benchmarks against other high-quality audio codecs like aptX HD and LHDC have consistently shown LDAC's superiority in terms of audio quality at higher bitrates. While aptX HD maxes out at 576 kbps, LDAC can deliver nearly double that bitrate, resulting in noticeably better audio fidelity, especially for high-resolution audio sources.
Adoption rates of LDAC in consumer devices have been steadily increasing, with many major smartphone and audio equipment manufacturers integrating LDAC support into their products. This growing ecosystem has led to improved interoperability and user experience across different devices and brands.
However, it's worth noting that the full benefits of LDAC are only realized when both the transmitting and receiving devices support the codec. As such, the performance in real-world scenarios can vary depending on the specific devices and their implementation of LDAC technology.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!