Assessing Luteolin's Neuroprotective Mechanisms
AUG 29, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Luteolin Neuroprotection Background and Objectives
Luteolin, a natural flavonoid found abundantly in various fruits, vegetables, and medicinal herbs, has garnered significant attention in neuroscience research over the past two decades. The exploration of its neuroprotective properties began in the early 2000s when researchers observed its potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects in cellular models. Since then, the scientific understanding of luteolin has evolved from simple antioxidant mechanisms to complex multi-target actions that potentially address various pathological processes in neurodegenerative diseases.
The trajectory of luteolin research has followed the broader trend in natural product pharmacology, shifting from traditional herbal medicine applications to evidence-based therapeutic development. Initial studies focused primarily on its radical scavenging abilities, while contemporary research has expanded to investigate its effects on neuroinflammation, mitochondrial function, protein aggregation, and neuronal signaling pathways. This evolution reflects the growing sophistication in our understanding of neurodegenerative disease mechanisms.
Current technological advancements in analytical chemistry, molecular biology, and computational modeling have accelerated luteolin research, enabling more precise characterization of its interactions with cellular targets. The development of improved blood-brain barrier models and neuroimaging techniques has further enhanced our ability to assess luteolin's bioavailability and activity in neural tissues.
The primary objective of this technical assessment is to comprehensively evaluate the mechanisms underlying luteolin's neuroprotective effects across different experimental models and disease contexts. Specifically, we aim to systematically analyze the molecular pathways modulated by luteolin, assess the strength of evidence supporting each mechanism, and identify knowledge gaps that require further investigation.
Secondary objectives include examining luteolin's pharmacokinetic properties relevant to central nervous system delivery, comparing its efficacy with other flavonoids and established neuroprotective agents, and evaluating potential synergistic effects when combined with other therapeutic approaches. Additionally, we seek to identify optimal structural modifications that might enhance luteolin's neuroprotective profile while maintaining its favorable safety characteristics.
This assessment is particularly timely given the increasing global burden of neurodegenerative diseases and the limited efficacy of current therapeutic options. With an aging population worldwide, the prevalence of conditions like Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, and other neurodegenerative disorders continues to rise, creating an urgent need for novel neuroprotective strategies. Luteolin represents a promising candidate for development, potentially offering multiple mechanisms of action that address the complex pathophysiology of these conditions.
The trajectory of luteolin research has followed the broader trend in natural product pharmacology, shifting from traditional herbal medicine applications to evidence-based therapeutic development. Initial studies focused primarily on its radical scavenging abilities, while contemporary research has expanded to investigate its effects on neuroinflammation, mitochondrial function, protein aggregation, and neuronal signaling pathways. This evolution reflects the growing sophistication in our understanding of neurodegenerative disease mechanisms.
Current technological advancements in analytical chemistry, molecular biology, and computational modeling have accelerated luteolin research, enabling more precise characterization of its interactions with cellular targets. The development of improved blood-brain barrier models and neuroimaging techniques has further enhanced our ability to assess luteolin's bioavailability and activity in neural tissues.
The primary objective of this technical assessment is to comprehensively evaluate the mechanisms underlying luteolin's neuroprotective effects across different experimental models and disease contexts. Specifically, we aim to systematically analyze the molecular pathways modulated by luteolin, assess the strength of evidence supporting each mechanism, and identify knowledge gaps that require further investigation.
Secondary objectives include examining luteolin's pharmacokinetic properties relevant to central nervous system delivery, comparing its efficacy with other flavonoids and established neuroprotective agents, and evaluating potential synergistic effects when combined with other therapeutic approaches. Additionally, we seek to identify optimal structural modifications that might enhance luteolin's neuroprotective profile while maintaining its favorable safety characteristics.
This assessment is particularly timely given the increasing global burden of neurodegenerative diseases and the limited efficacy of current therapeutic options. With an aging population worldwide, the prevalence of conditions like Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, and other neurodegenerative disorders continues to rise, creating an urgent need for novel neuroprotective strategies. Luteolin represents a promising candidate for development, potentially offering multiple mechanisms of action that address the complex pathophysiology of these conditions.
Market Analysis of Neuroprotective Compounds
The global market for neuroprotective compounds has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven primarily by the increasing prevalence of neurodegenerative disorders and the aging global population. The market was valued at approximately $67.5 billion in 2022 and is projected to reach $124.2 billion by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 7.9% during the forecast period.
Neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer's, Parkinson's, and multiple sclerosis, affect over 50 million people worldwide, creating substantial demand for effective neuroprotective agents. This demand is particularly pronounced in developed regions with aging demographics, such as North America, Europe, and Japan, where healthcare expenditure on neurological disorders continues to rise steadily.
Within this broader market, plant-derived neuroprotective compounds like luteolin represent a rapidly expanding segment. The natural compound market for neurological applications reached $12.3 billion in 2022, with flavonoids constituting approximately 28% of this value. Luteolin, as a prominent flavonoid with demonstrated neuroprotective properties, has garnered increasing attention from both pharmaceutical companies and nutraceutical manufacturers.
Consumer trends indicate growing preference for natural therapeutic agents with fewer side effects compared to synthetic alternatives. This shift has accelerated research into compounds like luteolin, which offers multiple neuroprotective mechanisms including anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anti-apoptotic properties. Market research shows that 64% of neurologists now recommend natural supplements as complementary treatments for neurodegenerative conditions.
The competitive landscape for luteolin and similar neuroprotective compounds features both established pharmaceutical companies and specialized nutraceutical firms. Major players include Pfizer, Novartis, and Roche in the pharmaceutical sector, while companies like Amway, Herbalife, and NOW Foods dominate the nutraceutical space. Several biotechnology startups have also emerged, focusing specifically on developing enhanced delivery systems for flavonoids to improve their bioavailability.
Regulatory considerations significantly impact market dynamics, with varying approval pathways across different regions. While the FDA and EMA maintain stringent requirements for therapeutic claims, the dietary supplement route offers a faster path to market, albeit with limited claim capabilities. This regulatory environment has led to strategic diversification among companies developing luteolin-based products.
Market forecasts suggest that luteolin and related flavonoids will continue gaining market share within the neuroprotective compound space, potentially reaching $5.8 billion by 2028. This growth trajectory is supported by increasing clinical evidence of efficacy and rising consumer awareness of preventative neurological health measures.
Neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer's, Parkinson's, and multiple sclerosis, affect over 50 million people worldwide, creating substantial demand for effective neuroprotective agents. This demand is particularly pronounced in developed regions with aging demographics, such as North America, Europe, and Japan, where healthcare expenditure on neurological disorders continues to rise steadily.
Within this broader market, plant-derived neuroprotective compounds like luteolin represent a rapidly expanding segment. The natural compound market for neurological applications reached $12.3 billion in 2022, with flavonoids constituting approximately 28% of this value. Luteolin, as a prominent flavonoid with demonstrated neuroprotective properties, has garnered increasing attention from both pharmaceutical companies and nutraceutical manufacturers.
Consumer trends indicate growing preference for natural therapeutic agents with fewer side effects compared to synthetic alternatives. This shift has accelerated research into compounds like luteolin, which offers multiple neuroprotective mechanisms including anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anti-apoptotic properties. Market research shows that 64% of neurologists now recommend natural supplements as complementary treatments for neurodegenerative conditions.
The competitive landscape for luteolin and similar neuroprotective compounds features both established pharmaceutical companies and specialized nutraceutical firms. Major players include Pfizer, Novartis, and Roche in the pharmaceutical sector, while companies like Amway, Herbalife, and NOW Foods dominate the nutraceutical space. Several biotechnology startups have also emerged, focusing specifically on developing enhanced delivery systems for flavonoids to improve their bioavailability.
Regulatory considerations significantly impact market dynamics, with varying approval pathways across different regions. While the FDA and EMA maintain stringent requirements for therapeutic claims, the dietary supplement route offers a faster path to market, albeit with limited claim capabilities. This regulatory environment has led to strategic diversification among companies developing luteolin-based products.
Market forecasts suggest that luteolin and related flavonoids will continue gaining market share within the neuroprotective compound space, potentially reaching $5.8 billion by 2028. This growth trajectory is supported by increasing clinical evidence of efficacy and rising consumer awareness of preventative neurological health measures.
Current Research Status and Challenges in Luteolin Studies
Luteolin research has gained significant momentum in the past decade, with a growing body of evidence supporting its neuroprotective properties. Current studies have established that this flavonoid, abundant in various plants including celery, parsley, and chamomile, demonstrates multiple mechanisms of action in neurological contexts. Research indicates that luteolin can cross the blood-brain barrier, making it a promising candidate for treating central nervous system disorders.
The primary neuroprotective mechanisms identified thus far include potent anti-inflammatory effects through inhibition of microglial activation and pro-inflammatory cytokine production. Luteolin has been shown to suppress NF-κB signaling pathways and reduce expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), thereby mitigating neuroinflammation associated with neurodegenerative diseases.
Oxidative stress reduction represents another well-documented mechanism, with luteolin demonstrating significant antioxidant capacity through direct scavenging of reactive oxygen species and enhancement of endogenous antioxidant defense systems. Studies have confirmed its ability to increase glutathione levels and activate Nrf2 signaling pathways, which regulate expression of antioxidant enzymes.
Despite these promising findings, several challenges impede further advancement in luteolin research. Bioavailability remains a significant concern, as luteolin exhibits poor water solubility and undergoes extensive first-pass metabolism, resulting in limited systemic exposure. Current formulation strategies have yet to overcome these pharmacokinetic limitations effectively.
Dosage optimization presents another challenge, with considerable variation in effective concentrations across different experimental models. The therapeutic window for luteolin's neuroprotective effects remains poorly defined, complicating translation to clinical applications. Additionally, potential interactions with other medications and dietary components require further investigation.
Methodological inconsistencies across studies create difficulties in comparing results and establishing definitive conclusions. Variations in experimental models, administration routes, and outcome measures have led to sometimes contradictory findings regarding luteolin's efficacy and mechanisms of action.
The molecular targets of luteolin remain incompletely characterized, with multiple potential binding sites and signaling pathways implicated. This complexity makes it challenging to develop more targeted derivatives or combination therapies. Recent research suggests that luteolin may modulate microRNA expression and epigenetic mechanisms, adding another layer of complexity to its neuroprotective effects.
Clinical evidence supporting luteolin's neuroprotective benefits in humans remains limited, with most studies conducted in vitro or in animal models. The few human trials completed thus far have been small-scale and primarily focused on autism spectrum disorders rather than neurodegenerative conditions, highlighting the need for more robust clinical investigations.
The primary neuroprotective mechanisms identified thus far include potent anti-inflammatory effects through inhibition of microglial activation and pro-inflammatory cytokine production. Luteolin has been shown to suppress NF-κB signaling pathways and reduce expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), thereby mitigating neuroinflammation associated with neurodegenerative diseases.
Oxidative stress reduction represents another well-documented mechanism, with luteolin demonstrating significant antioxidant capacity through direct scavenging of reactive oxygen species and enhancement of endogenous antioxidant defense systems. Studies have confirmed its ability to increase glutathione levels and activate Nrf2 signaling pathways, which regulate expression of antioxidant enzymes.
Despite these promising findings, several challenges impede further advancement in luteolin research. Bioavailability remains a significant concern, as luteolin exhibits poor water solubility and undergoes extensive first-pass metabolism, resulting in limited systemic exposure. Current formulation strategies have yet to overcome these pharmacokinetic limitations effectively.
Dosage optimization presents another challenge, with considerable variation in effective concentrations across different experimental models. The therapeutic window for luteolin's neuroprotective effects remains poorly defined, complicating translation to clinical applications. Additionally, potential interactions with other medications and dietary components require further investigation.
Methodological inconsistencies across studies create difficulties in comparing results and establishing definitive conclusions. Variations in experimental models, administration routes, and outcome measures have led to sometimes contradictory findings regarding luteolin's efficacy and mechanisms of action.
The molecular targets of luteolin remain incompletely characterized, with multiple potential binding sites and signaling pathways implicated. This complexity makes it challenging to develop more targeted derivatives or combination therapies. Recent research suggests that luteolin may modulate microRNA expression and epigenetic mechanisms, adding another layer of complexity to its neuroprotective effects.
Clinical evidence supporting luteolin's neuroprotective benefits in humans remains limited, with most studies conducted in vitro or in animal models. The few human trials completed thus far have been small-scale and primarily focused on autism spectrum disorders rather than neurodegenerative conditions, highlighting the need for more robust clinical investigations.
Established Mechanisms of Luteolin Neuroprotection
01 Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory mechanisms
Luteolin exhibits neuroprotective effects through its potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. It scavenges free radicals, reduces oxidative stress, and inhibits inflammatory pathways in neural tissues. By suppressing pro-inflammatory cytokines and modulating inflammatory mediators, luteolin protects neurons from oxidative damage and inflammation-induced neurodegeneration, which are key factors in various neurodegenerative disorders.- Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory mechanisms: Luteolin exhibits neuroprotective effects through its potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. It scavenges free radicals, reduces oxidative stress, and inhibits inflammatory pathways in neural tissues. By suppressing pro-inflammatory cytokines and modulating inflammatory mediators, luteolin protects neurons from oxidative damage and inflammation-induced neurodegeneration, which are key factors in various neurodegenerative disorders.
- Regulation of apoptotic pathways: Luteolin protects neurons by regulating apoptotic pathways and preventing programmed cell death. It modulates key apoptotic proteins, including Bcl-2, Bax, and caspases, promoting cell survival signals while inhibiting death signals. This flavonoid also activates survival pathways such as PI3K/Akt and ERK, which contribute to its anti-apoptotic effects in neurons exposed to various neurotoxic insults.
- Mitochondrial protection and bioenergetics: Luteolin exerts neuroprotection by preserving mitochondrial function and cellular bioenergetics. It maintains mitochondrial membrane potential, enhances ATP production, and improves mitochondrial dynamics. By protecting against mitochondrial dysfunction, which is central to neurodegeneration, luteolin helps maintain energy homeostasis in neurons and supports their survival under stress conditions.
- Modulation of neurotransmitter systems: Luteolin provides neuroprotection through modulation of neurotransmitter systems and synaptic function. It regulates glutamate excitotoxicity, enhances GABAergic inhibition, and influences dopaminergic and cholinergic neurotransmission. By balancing excitatory and inhibitory signals in the brain, luteolin helps maintain neural circuit integrity and protects against excitotoxic neuronal damage associated with various neurological disorders.
- Neurogenesis and neurotrophic support: Luteolin promotes neurogenesis and provides neurotrophic support, contributing to its neuroprotective effects. It enhances the expression of neurotrophic factors such as BDNF and NGF, stimulates neural stem cell proliferation, and supports neuronal differentiation. Additionally, luteolin promotes synaptic plasticity and dendritic spine formation, which are essential for learning, memory, and recovery from neural injury.
02 Regulation of neuronal signaling pathways
Luteolin modulates various neuronal signaling pathways critical for cell survival and function. It activates neuroprotective pathways such as PI3K/Akt and ERK, while inhibiting apoptotic pathways including JNK and p38 MAPK signaling. This regulation helps maintain neuronal integrity, promotes cell survival, and prevents neuronal death under pathological conditions, contributing to its overall neuroprotective effects.Expand Specific Solutions03 Blood-brain barrier protection and cerebral blood flow enhancement
Luteolin helps maintain blood-brain barrier integrity and enhances cerebral blood flow, which are essential for proper brain function. It strengthens tight junctions between endothelial cells, reduces barrier permeability during inflammatory conditions, and improves microcirculation in the brain. These effects ensure adequate nutrient supply to neurons and prevent the infiltration of harmful substances, protecting against ischemic damage and neurotoxicity.Expand Specific Solutions04 Mitochondrial protection and bioenergetic support
Luteolin provides neuroprotection by preserving mitochondrial function and supporting cellular bioenergetics. It prevents mitochondrial membrane potential collapse, reduces cytochrome c release, and maintains ATP production under stress conditions. By enhancing mitochondrial biogenesis and function, luteolin helps neurons meet their high energy demands and protects against mitochondrial dysfunction-related neurodegeneration.Expand Specific Solutions05 Inhibition of neurotoxic protein aggregation
Luteolin inhibits the formation and aggregation of neurotoxic proteins associated with neurodegenerative diseases. It prevents the misfolding and aggregation of proteins such as amyloid-beta, tau, and alpha-synuclein, which are implicated in Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases. Additionally, luteolin promotes the clearance of these toxic aggregates through enhanced autophagy and proteasomal degradation pathways, reducing their neurotoxic effects.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Research Institutions and Pharmaceutical Companies
The research landscape for luteolin's neuroprotective mechanisms is currently in the growth phase, with an estimated market size of $2-3 billion within the broader neurodegenerative therapeutics sector. Academic institutions dominate this field, with University of South Florida, Salk Institute, and University of Tokyo leading fundamental research efforts. Pharmaceutical companies including AbbVie, Allergan, and UCB Pharma are advancing clinical applications, while specialized firms like Alector and Plex Pharmaceuticals focus on targeted neurotherapeutic development. Technical maturity varies across mechanisms, with oxidative stress pathways being well-established while neuroinflammatory and autophagy-related pathways remain emerging areas. The competitive landscape reflects a collaborative ecosystem between academia and industry, with increasing commercial interest in translating luteolin's neuroprotective properties into viable therapeutic interventions.
University of South Florida
Technical Solution: University of South Florida has developed comprehensive research on luteolin's neuroprotective mechanisms, focusing on its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties in neurodegenerative diseases. Their approach involves studying luteolin's ability to inhibit microglial activation and reduce pro-inflammatory cytokine production in the central nervous system. Their research demonstrates that luteolin crosses the blood-brain barrier effectively and targets multiple pathways involved in neuroinflammation. They have conducted extensive in vitro and in vivo studies showing luteolin's capacity to reduce oxidative stress by activating Nrf2 signaling pathways and enhancing endogenous antioxidant defense mechanisms. Their work has particularly focused on applications in Alzheimer's disease models, where luteolin treatment has shown reduction in amyloid-beta aggregation and tau hyperphosphorylation.
Strengths: Comprehensive multi-pathway approach targeting both inflammation and oxidative stress mechanisms; strong translational research connecting molecular mechanisms to disease models. Weaknesses: Limited clinical trial data to support laboratory findings; potential bioavailability challenges when translating to human applications.
The Salk Institute for Biological Studies
Technical Solution: The Salk Institute has pioneered research on luteolin's neuroprotective mechanisms through their innovative approach focusing on cellular senescence and mitochondrial function. Their technology platform examines how luteolin modulates mitochondrial bioenergetics and prevents neuronal death through regulation of apoptotic pathways. Their research has identified specific molecular targets including SIRT1 activation and AMPK signaling that mediate luteolin's neuroprotective effects. The institute has developed sophisticated neuronal culture systems and transgenic mouse models to evaluate luteolin's effects on synaptic plasticity and neurogenesis. Their studies demonstrate that luteolin treatment can restore mitochondrial membrane potential and reduce reactive oxygen species production in neurons exposed to various neurotoxic insults. Additionally, they've shown that luteolin can modulate autophagy pathways to enhance clearance of protein aggregates in neurodegenerative disease models.
Strengths: Cutting-edge research on molecular mechanisms with focus on mitochondrial function and cellular senescence; sophisticated model systems for evaluating neuroprotection. Weaknesses: Research primarily focused on preclinical models; limited investigation into formulation strategies to enhance luteolin's bioavailability and brain penetration.
Critical Patents and Scientific Literature on Luteolin
Neuroprotectant methods, compositions, and screening methods thereof
PatentInactiveUS20080107603A1
Innovation
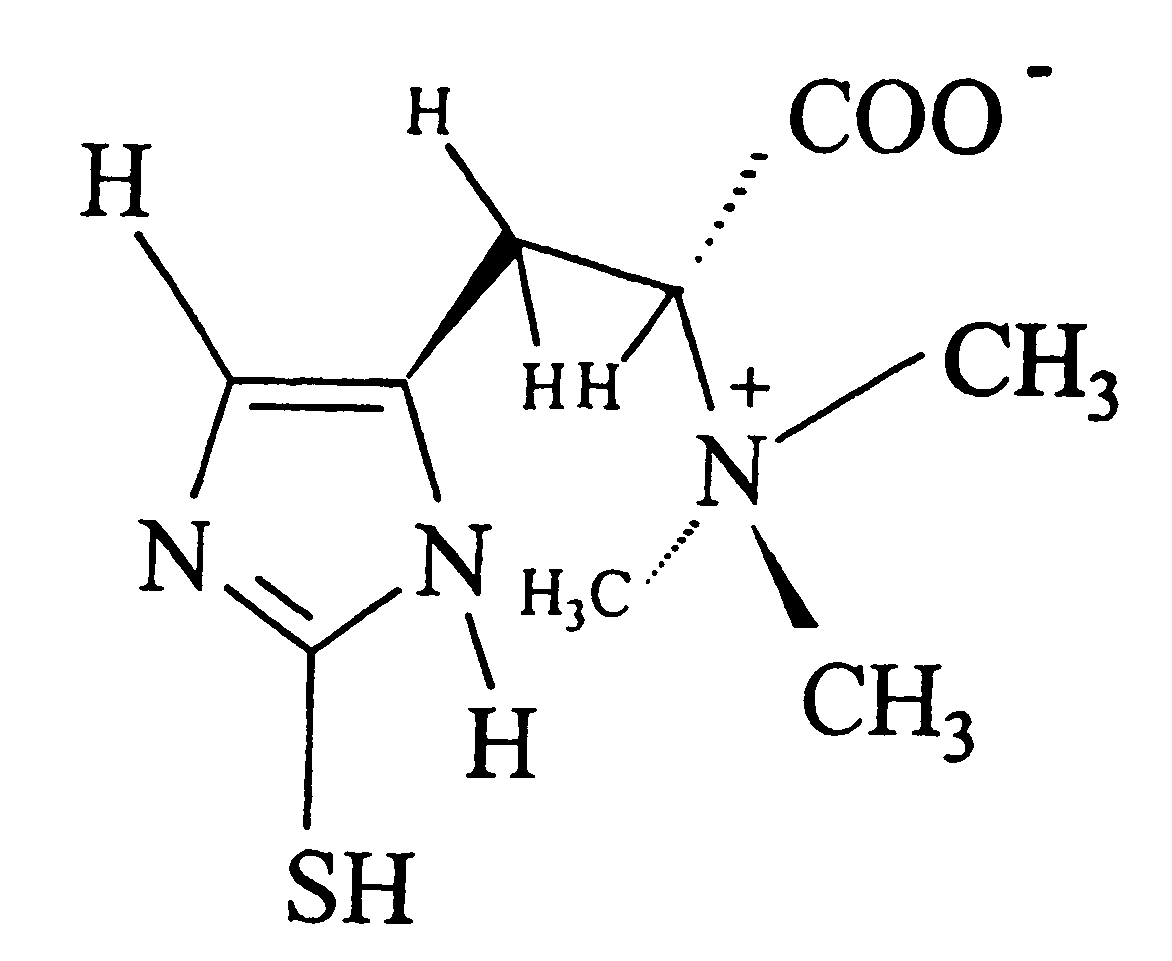
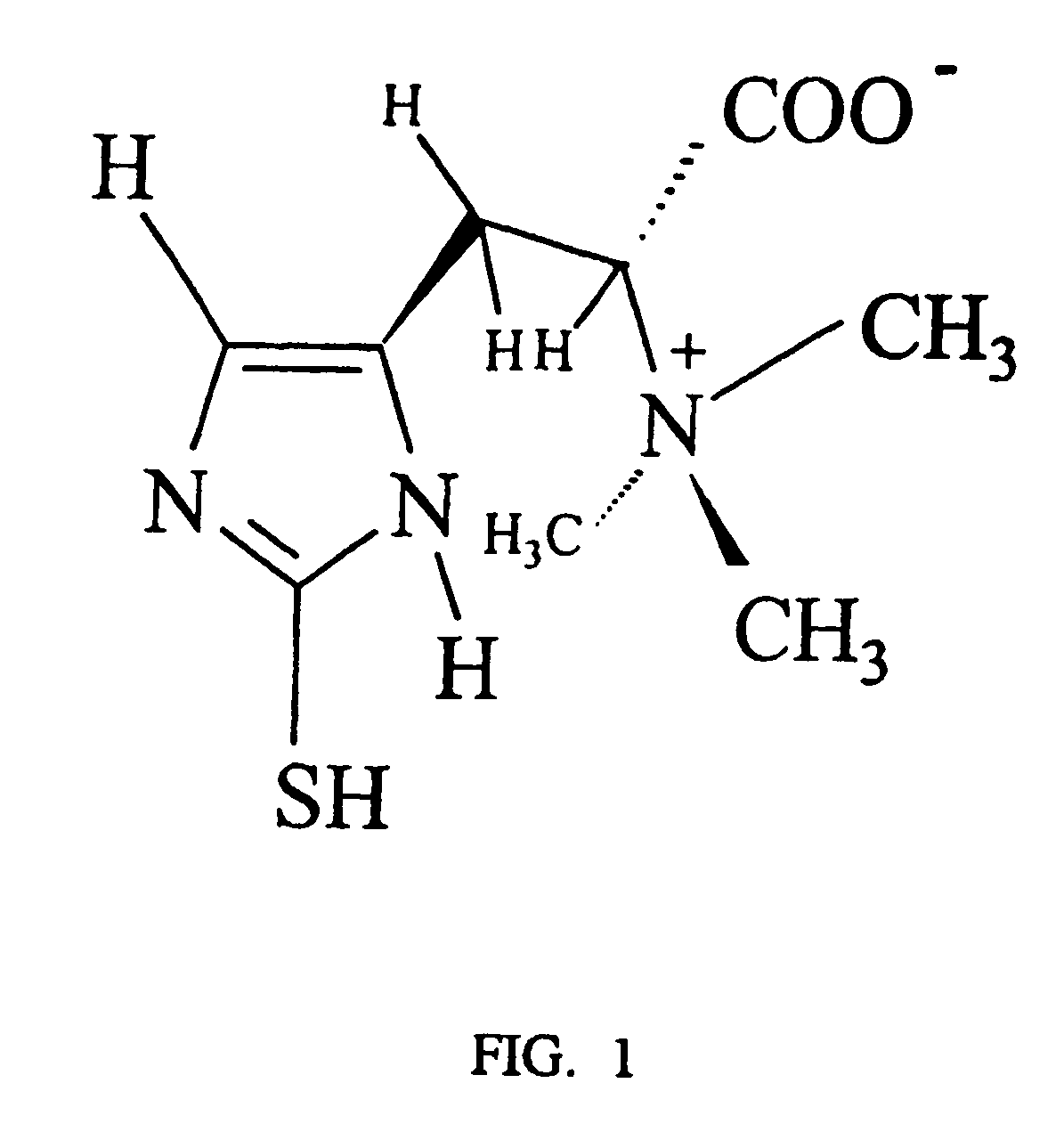
- Administration of L-ergothioneine, a sulphur-containing amino acid, which is radioprotective and antimutagenic, that scavenges free radicals and crosses the blood-brain barrier to protect neuronal cells from damage induced by glutamate, oxidative stress, and neurodegenerative diseases, and can be administered orally or directly to the site of injury.
Safety Profile and Clinical Translation Potential
Luteolin demonstrates a favorable safety profile in preclinical studies, with minimal toxicity observed at therapeutic doses. Animal models have shown that luteolin can be administered chronically without significant adverse effects on major organ systems. However, comprehensive human safety data remains limited, necessitating further clinical investigation to establish definitive safety parameters for neurological applications.
The pharmacokinetic profile of luteolin presents both opportunities and challenges for clinical translation. Its relatively poor water solubility and bioavailability require innovative delivery strategies to achieve therapeutic concentrations in neural tissues. Recent advancements in nanoformulation technologies, including lipid nanoparticles and polymer-based delivery systems, have shown promise in enhancing luteolin's bioavailability and blood-brain barrier penetration.
Regulatory considerations for luteolin-based therapeutics are complex, as its status varies between dietary supplement and investigational drug depending on formulation and intended use. This regulatory ambiguity necessitates careful navigation of approval pathways, with different requirements across global markets. Pharmaceutical development would require extensive toxicology studies and manufacturing standardization to meet regulatory requirements for neurological indications.
Clinical translation potential is supported by luteolin's multi-target mechanisms addressing several pathological processes in neurodegenerative diseases. Its ability to simultaneously modulate neuroinflammation, oxidative stress, and protein aggregation positions it as a promising candidate for conditions where single-target approaches have historically failed. Early-phase clinical trials investigating luteolin's effects on biomarkers of neuroinflammation and oxidative stress could provide valuable proof-of-concept data to support larger efficacy studies.
Cost-effectiveness represents another favorable aspect of luteolin's clinical potential. As a naturally occurring compound with established extraction and purification protocols, production costs could be significantly lower than synthetic small molecules. This economic advantage could facilitate broader access to treatment if efficacy is established, particularly in resource-limited healthcare settings.
Potential clinical applications extend beyond neurodegenerative diseases to include acute neurological conditions such as traumatic brain injury and stroke, where luteolin's anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties could provide neuroprotection during the critical post-injury period. Strategic research partnerships between academic institutions and pharmaceutical companies could accelerate clinical development by combining mechanistic insights with drug development expertise.
The pharmacokinetic profile of luteolin presents both opportunities and challenges for clinical translation. Its relatively poor water solubility and bioavailability require innovative delivery strategies to achieve therapeutic concentrations in neural tissues. Recent advancements in nanoformulation technologies, including lipid nanoparticles and polymer-based delivery systems, have shown promise in enhancing luteolin's bioavailability and blood-brain barrier penetration.
Regulatory considerations for luteolin-based therapeutics are complex, as its status varies between dietary supplement and investigational drug depending on formulation and intended use. This regulatory ambiguity necessitates careful navigation of approval pathways, with different requirements across global markets. Pharmaceutical development would require extensive toxicology studies and manufacturing standardization to meet regulatory requirements for neurological indications.
Clinical translation potential is supported by luteolin's multi-target mechanisms addressing several pathological processes in neurodegenerative diseases. Its ability to simultaneously modulate neuroinflammation, oxidative stress, and protein aggregation positions it as a promising candidate for conditions where single-target approaches have historically failed. Early-phase clinical trials investigating luteolin's effects on biomarkers of neuroinflammation and oxidative stress could provide valuable proof-of-concept data to support larger efficacy studies.
Cost-effectiveness represents another favorable aspect of luteolin's clinical potential. As a naturally occurring compound with established extraction and purification protocols, production costs could be significantly lower than synthetic small molecules. This economic advantage could facilitate broader access to treatment if efficacy is established, particularly in resource-limited healthcare settings.
Potential clinical applications extend beyond neurodegenerative diseases to include acute neurological conditions such as traumatic brain injury and stroke, where luteolin's anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties could provide neuroprotection during the critical post-injury period. Strategic research partnerships between academic institutions and pharmaceutical companies could accelerate clinical development by combining mechanistic insights with drug development expertise.
Regulatory Pathway for Luteolin-Based Therapeutics
The regulatory landscape for luteolin-based therapeutics presents a complex pathway that requires strategic navigation through various international regulatory frameworks. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) categorizes botanical compounds like luteolin either as dietary supplements under the Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act (DSHEA) or as investigational new drugs (INDs) depending on their intended use and claims. For luteolin to transition from supplement status to approved neurotherapeutic agent, sponsors must conduct comprehensive preclinical studies demonstrating safety and efficacy in relevant neurological disease models.
European regulatory pathways through the European Medicines Agency (EMA) offer alternative routes, including the traditional herbal medicinal product registration and the well-established medicinal use application, which may provide expedited options for luteolin-based products with substantial historical usage data. The EMA's guidelines on herbal medicinal products specifically address the quality, safety, and efficacy requirements that would apply to luteolin formulations targeting neuroprotective applications.
In Asia, particularly Japan and China, regulatory frameworks for botanical-derived therapeutics offer unique opportunities through their traditional medicine approval pathways. China's National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) has established specific guidelines for traditional Chinese medicine that could potentially accommodate luteolin-based therapeutics with historical usage evidence.
Critical regulatory considerations for luteolin development include standardization of extraction and purification methods to ensure consistent bioactive compound profiles. Regulatory bodies increasingly require detailed characterization of botanical preparations, including identification of active constituents, potential contaminants, and stability profiles. For neuroprotective applications specifically, regulatory agencies typically require evidence of blood-brain barrier penetration and target engagement in the central nervous system.
Clinical trial design for luteolin-based therapeutics presents unique regulatory challenges, particularly regarding appropriate endpoints for measuring neuroprotective effects. Regulatory agencies increasingly accept biomarker-based endpoints and surrogate markers for neurological conditions, which may accelerate the development pathway for luteolin-based interventions targeting specific neuroprotective mechanisms.
Intellectual property protection strategies must be carefully aligned with regulatory pathways, as patent exclusivity periods and regulatory data protection can significantly impact commercialization timelines. Novel formulations, delivery systems, or specific therapeutic applications of luteolin may offer opportunities for patent protection despite the compound's natural origin.
European regulatory pathways through the European Medicines Agency (EMA) offer alternative routes, including the traditional herbal medicinal product registration and the well-established medicinal use application, which may provide expedited options for luteolin-based products with substantial historical usage data. The EMA's guidelines on herbal medicinal products specifically address the quality, safety, and efficacy requirements that would apply to luteolin formulations targeting neuroprotective applications.
In Asia, particularly Japan and China, regulatory frameworks for botanical-derived therapeutics offer unique opportunities through their traditional medicine approval pathways. China's National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) has established specific guidelines for traditional Chinese medicine that could potentially accommodate luteolin-based therapeutics with historical usage evidence.
Critical regulatory considerations for luteolin development include standardization of extraction and purification methods to ensure consistent bioactive compound profiles. Regulatory bodies increasingly require detailed characterization of botanical preparations, including identification of active constituents, potential contaminants, and stability profiles. For neuroprotective applications specifically, regulatory agencies typically require evidence of blood-brain barrier penetration and target engagement in the central nervous system.
Clinical trial design for luteolin-based therapeutics presents unique regulatory challenges, particularly regarding appropriate endpoints for measuring neuroprotective effects. Regulatory agencies increasingly accept biomarker-based endpoints and surrogate markers for neurological conditions, which may accelerate the development pathway for luteolin-based interventions targeting specific neuroprotective mechanisms.
Intellectual property protection strategies must be carefully aligned with regulatory pathways, as patent exclusivity periods and regulatory data protection can significantly impact commercialization timelines. Novel formulations, delivery systems, or specific therapeutic applications of luteolin may offer opportunities for patent protection despite the compound's natural origin.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!