Assessment of lithium orotate in behavioral therapy outcomes
AUG 20, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Lithium Orotate Background and Objectives
Lithium orotate, a compound consisting of lithium and orotic acid, has gained attention in recent years for its potential therapeutic applications in behavioral health. The history of lithium as a psychiatric treatment dates back to the mid-20th century, with lithium carbonate being the most widely used form. However, lithium orotate has emerged as an alternative that may offer improved bioavailability and reduced side effects.
The primary objective of this technical assessment is to evaluate the efficacy and safety of lithium orotate in behavioral therapy outcomes. This involves examining its pharmacological properties, comparing it to traditional lithium formulations, and analyzing its potential benefits in treating various mental health conditions. The assessment aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of lithium orotate's role in modern psychiatric treatment.
Lithium orotate's development stems from the need for more effective and tolerable lithium-based therapies. Conventional lithium treatments, while effective, often require high doses that can lead to significant side effects and toxicity concerns. Lithium orotate, with its unique chemical structure, is hypothesized to cross the blood-brain barrier more efficiently, potentially allowing for lower doses and reduced systemic exposure.
The evolution of lithium orotate research has been marked by both promise and controversy. Early studies suggested superior efficacy and safety profiles compared to lithium carbonate, but these claims have been met with skepticism from parts of the medical community due to limited large-scale clinical trials. The technical landscape surrounding lithium orotate is characterized by a mix of preclinical studies, small clinical trials, and anecdotal evidence from practitioners and patients.
Current research objectives focus on several key areas: determining the optimal dosage and administration protocols for lithium orotate, assessing its long-term safety profile, and evaluating its efficacy across a spectrum of behavioral and psychiatric disorders. Of particular interest is its potential in treating conditions such as bipolar disorder, depression, anxiety, and neurodegenerative diseases.
The assessment of lithium orotate in behavioral therapy outcomes is driven by the growing need for innovative treatments in mental health. With the global burden of mental illness on the rise, there is an urgent demand for more effective, safer, and more tolerable therapeutic options. Lithium orotate represents a potential advancement in this field, offering the possibility of harnessing lithium's well-established mood-stabilizing properties while potentially mitigating its drawbacks.
The primary objective of this technical assessment is to evaluate the efficacy and safety of lithium orotate in behavioral therapy outcomes. This involves examining its pharmacological properties, comparing it to traditional lithium formulations, and analyzing its potential benefits in treating various mental health conditions. The assessment aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of lithium orotate's role in modern psychiatric treatment.
Lithium orotate's development stems from the need for more effective and tolerable lithium-based therapies. Conventional lithium treatments, while effective, often require high doses that can lead to significant side effects and toxicity concerns. Lithium orotate, with its unique chemical structure, is hypothesized to cross the blood-brain barrier more efficiently, potentially allowing for lower doses and reduced systemic exposure.
The evolution of lithium orotate research has been marked by both promise and controversy. Early studies suggested superior efficacy and safety profiles compared to lithium carbonate, but these claims have been met with skepticism from parts of the medical community due to limited large-scale clinical trials. The technical landscape surrounding lithium orotate is characterized by a mix of preclinical studies, small clinical trials, and anecdotal evidence from practitioners and patients.
Current research objectives focus on several key areas: determining the optimal dosage and administration protocols for lithium orotate, assessing its long-term safety profile, and evaluating its efficacy across a spectrum of behavioral and psychiatric disorders. Of particular interest is its potential in treating conditions such as bipolar disorder, depression, anxiety, and neurodegenerative diseases.
The assessment of lithium orotate in behavioral therapy outcomes is driven by the growing need for innovative treatments in mental health. With the global burden of mental illness on the rise, there is an urgent demand for more effective, safer, and more tolerable therapeutic options. Lithium orotate represents a potential advancement in this field, offering the possibility of harnessing lithium's well-established mood-stabilizing properties while potentially mitigating its drawbacks.
Market Analysis for Lithium-Based Therapies
The market for lithium-based therapies has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by the increasing prevalence of mood disorders and the expanding applications of lithium compounds in psychiatric treatments. The global market for lithium-based medications is projected to reach substantial value in the coming years, with a compound annual growth rate outpacing many other pharmaceutical segments.
Lithium carbonate and lithium citrate have long been the standard forms of lithium used in psychiatric treatments, particularly for bipolar disorder. However, there is growing interest in alternative formulations such as lithium orotate, which may offer improved bioavailability and potentially fewer side effects. This shift in focus has created new opportunities for market expansion and product differentiation.
The behavioral therapy market, which often incorporates pharmacological interventions, has also seen steady growth. The integration of lithium-based treatments with behavioral therapies represents a significant market opportunity, as healthcare providers increasingly adopt combination approaches to mental health treatment.
Geographically, North America dominates the lithium-based therapy market, followed by Europe. These regions benefit from well-established healthcare infrastructure, high awareness of mental health issues, and favorable reimbursement policies. However, emerging markets in Asia-Pacific and Latin America are expected to show the fastest growth rates due to improving healthcare access and rising mental health awareness.
The market is characterized by a mix of large pharmaceutical companies and specialized mental health-focused firms. Key players are investing heavily in research and development to improve existing formulations and explore new applications for lithium compounds. This includes investigating the potential of lithium orotate in various psychiatric and neurological conditions.
Consumer trends indicate a growing preference for treatments with fewer side effects and improved long-term safety profiles. This has spurred interest in alternative lithium formulations and dosing strategies, potentially opening new market segments for products like lithium orotate.
Regulatory factors play a crucial role in shaping the market landscape. While lithium carbonate and citrate are well-established and widely approved, newer formulations like lithium orotate face more regulatory scrutiny. The outcome of ongoing clinical trials and regulatory decisions will significantly impact the market potential of these alternative forms.
Lithium carbonate and lithium citrate have long been the standard forms of lithium used in psychiatric treatments, particularly for bipolar disorder. However, there is growing interest in alternative formulations such as lithium orotate, which may offer improved bioavailability and potentially fewer side effects. This shift in focus has created new opportunities for market expansion and product differentiation.
The behavioral therapy market, which often incorporates pharmacological interventions, has also seen steady growth. The integration of lithium-based treatments with behavioral therapies represents a significant market opportunity, as healthcare providers increasingly adopt combination approaches to mental health treatment.
Geographically, North America dominates the lithium-based therapy market, followed by Europe. These regions benefit from well-established healthcare infrastructure, high awareness of mental health issues, and favorable reimbursement policies. However, emerging markets in Asia-Pacific and Latin America are expected to show the fastest growth rates due to improving healthcare access and rising mental health awareness.
The market is characterized by a mix of large pharmaceutical companies and specialized mental health-focused firms. Key players are investing heavily in research and development to improve existing formulations and explore new applications for lithium compounds. This includes investigating the potential of lithium orotate in various psychiatric and neurological conditions.
Consumer trends indicate a growing preference for treatments with fewer side effects and improved long-term safety profiles. This has spurred interest in alternative lithium formulations and dosing strategies, potentially opening new market segments for products like lithium orotate.
Regulatory factors play a crucial role in shaping the market landscape. While lithium carbonate and citrate are well-established and widely approved, newer formulations like lithium orotate face more regulatory scrutiny. The outcome of ongoing clinical trials and regulatory decisions will significantly impact the market potential of these alternative forms.
Current Status and Challenges in Lithium Orotate Research
The current status of lithium orotate research in behavioral therapy outcomes presents a complex landscape with both promising developments and significant challenges. While lithium has long been recognized as an effective treatment for bipolar disorder, the specific form of lithium orotate has gained attention for its potential benefits in behavioral therapy.
Recent studies have shown that lithium orotate may have advantages over other lithium compounds in terms of bioavailability and reduced side effects. This has led to increased interest in its application for various mental health conditions beyond bipolar disorder, including depression, anxiety, and cognitive impairment. However, the research in this area remains limited and largely inconclusive.
One of the primary challenges in lithium orotate research is the lack of large-scale, randomized controlled trials. Most existing studies have small sample sizes and varying methodologies, making it difficult to draw definitive conclusions about its efficacy in behavioral therapy outcomes. Additionally, there is a need for standardized dosing protocols and long-term safety assessments specific to lithium orotate.
Another significant hurdle is the regulatory status of lithium orotate. In many countries, it is classified as a dietary supplement rather than a pharmaceutical drug, which has implications for research funding, quality control, and clinical application. This classification also means that there is less rigorous oversight of its production and distribution, potentially leading to inconsistencies in product quality and potency.
The mechanism of action of lithium orotate in the brain is not fully understood, particularly in relation to its effects on behavioral outcomes. While lithium's general neuroprotective and mood-stabilizing properties are well-documented, the specific pathways through which lithium orotate may influence behavioral therapy outcomes require further elucidation.
There is also a notable gap in comparative studies between lithium orotate and other forms of lithium, as well as alternative treatments for behavioral disorders. This lack of direct comparison makes it challenging to determine the relative efficacy and safety of lithium orotate in behavioral therapy contexts.
Despite these challenges, ongoing research continues to explore the potential of lithium orotate. Some studies suggest it may have a role in enhancing the effects of cognitive behavioral therapy and other psychotherapeutic interventions. However, more robust evidence is needed to support these claims and to guide clinical practice.
Recent studies have shown that lithium orotate may have advantages over other lithium compounds in terms of bioavailability and reduced side effects. This has led to increased interest in its application for various mental health conditions beyond bipolar disorder, including depression, anxiety, and cognitive impairment. However, the research in this area remains limited and largely inconclusive.
One of the primary challenges in lithium orotate research is the lack of large-scale, randomized controlled trials. Most existing studies have small sample sizes and varying methodologies, making it difficult to draw definitive conclusions about its efficacy in behavioral therapy outcomes. Additionally, there is a need for standardized dosing protocols and long-term safety assessments specific to lithium orotate.
Another significant hurdle is the regulatory status of lithium orotate. In many countries, it is classified as a dietary supplement rather than a pharmaceutical drug, which has implications for research funding, quality control, and clinical application. This classification also means that there is less rigorous oversight of its production and distribution, potentially leading to inconsistencies in product quality and potency.
The mechanism of action of lithium orotate in the brain is not fully understood, particularly in relation to its effects on behavioral outcomes. While lithium's general neuroprotective and mood-stabilizing properties are well-documented, the specific pathways through which lithium orotate may influence behavioral therapy outcomes require further elucidation.
There is also a notable gap in comparative studies between lithium orotate and other forms of lithium, as well as alternative treatments for behavioral disorders. This lack of direct comparison makes it challenging to determine the relative efficacy and safety of lithium orotate in behavioral therapy contexts.
Despite these challenges, ongoing research continues to explore the potential of lithium orotate. Some studies suggest it may have a role in enhancing the effects of cognitive behavioral therapy and other psychotherapeutic interventions. However, more robust evidence is needed to support these claims and to guide clinical practice.
Existing Lithium Orotate Behavioral Therapy Protocols
01 Lithium orotate in behavioral therapy
Lithium orotate is being investigated for its potential use in behavioral therapy. This compound may have effects on mood regulation and cognitive function, which could be beneficial in treating various behavioral disorders. Research suggests it may have fewer side effects compared to other lithium formulations, making it a promising option for long-term therapy.- Lithium orotate in behavioral therapy: Lithium orotate is being investigated for its potential benefits in behavioral therapy outcomes. This compound may have mood-stabilizing effects and could be used as an adjunct to traditional behavioral therapies for various mental health conditions. Research suggests it may enhance the effectiveness of behavioral interventions by modulating neurotransmitter systems.
- Monitoring and assessment of therapy outcomes: Advanced monitoring and assessment techniques are being developed to evaluate the outcomes of behavioral therapy, particularly when combined with lithium orotate treatment. These methods may include neuroimaging, biomarker analysis, and digital health technologies to track patient progress and adjust treatment protocols accordingly.
- Personalized treatment approaches: Researchers are exploring personalized treatment approaches that combine lithium orotate with tailored behavioral therapy regimens. This may involve genetic testing, AI-driven analysis of patient data, and adaptive treatment algorithms to optimize therapy outcomes for individual patients based on their unique characteristics and response patterns.
- Integration with digital health platforms: The integration of lithium orotate treatment and behavioral therapy with digital health platforms is being investigated. This may include mobile apps, wearable devices, and telemedicine solutions to enhance treatment adherence, monitor side effects, and provide real-time support to patients undergoing combined pharmacological and behavioral interventions.
- Combination with other therapeutic modalities: Research is being conducted on combining lithium orotate and behavioral therapy with other therapeutic modalities to enhance overall treatment outcomes. This may include complementary approaches such as neurofeedback, transcranial magnetic stimulation, or mindfulness-based interventions to address various aspects of mental health and behavior.
02 Combination of lithium orotate with other therapies
Studies are exploring the combination of lithium orotate with other therapeutic approaches, such as cognitive behavioral therapy or mindfulness-based interventions. This integrated approach aims to enhance treatment outcomes by addressing both biological and psychological aspects of behavioral disorders. The synergistic effects may lead to improved patient response and overall well-being.Expand Specific Solutions03 Monitoring and assessment of lithium orotate therapy
Researchers are developing methods to monitor and assess the effectiveness of lithium orotate in behavioral therapy. This includes the use of biomarkers, neuroimaging techniques, and standardized psychological assessments to track patient progress and adjust treatment protocols. These monitoring tools aim to optimize dosing and personalize therapy for individual patients.Expand Specific Solutions04 Lithium orotate in specific behavioral disorders
Research is focusing on the application of lithium orotate in specific behavioral disorders, such as bipolar disorder, depression, and anxiety. Clinical trials are evaluating its efficacy in managing symptoms, reducing relapse rates, and improving overall quality of life for patients with these conditions. The potential for lithium orotate to address treatment-resistant cases is also being explored.Expand Specific Solutions05 Safety and long-term effects of lithium orotate
Ongoing studies are investigating the safety profile and long-term effects of lithium orotate use in behavioral therapy. This includes assessing potential side effects, drug interactions, and optimal dosing strategies. Researchers are also exploring the impact of prolonged lithium orotate treatment on brain structure and function, as well as its effects on overall physical health.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Lithium Orotate Research and Production
The assessment of lithium orotate in behavioral therapy outcomes is in an early stage of development, with a relatively small market size but growing interest. The technology's maturity is still evolving, with various companies and institutions at different stages of research and development. Key players like Sanofi-Aventis Deutschland GmbH, H. Lundbeck A/S, and Janssen Pharmaceutica NV are likely leading in pharmaceutical research, while academic institutions such as Emory University and the University of South Florida contribute to the scientific understanding. Smaller companies like SAGE Therapeutics and Levo Therapeutics may be focusing on niche applications or novel delivery methods. The competitive landscape is diverse, with potential for both established pharmaceutical giants and innovative startups to make significant contributions to this field.
H. Lundbeck A/S
Technical Solution: H. Lundbeck A/S has been investigating the use of lithium orotate in combination with their existing psychiatric medications to enhance behavioral therapy outcomes. Their research focuses on the synergistic effects of lithium orotate with selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) in treating depression and anxiety disorders. Lundbeck's approach involves developing a controlled-release formulation of lithium orotate that maintains stable blood levels over time, potentially reducing side effects associated with traditional lithium treatments[2]. The company has completed phase II clinical trials showing promising results in patients with treatment-resistant depression, demonstrating improved response rates and reduced time to symptom relief compared to SSRI monotherapy[4].
Strengths: Lundbeck's expertise in neurological and psychiatric disorders provides a strong foundation for developing effective lithium orotate-based treatments. Weaknesses: The combination therapy approach may face regulatory challenges and require extensive safety studies.
The Scripps Research Institute
Technical Solution: The Scripps Research Institute has been conducting fundamental research on the molecular mechanisms underlying the effects of lithium orotate on neuroplasticity and behavior. Their studies have revealed that lithium orotate may enhance the expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and promote neurogenesis in key brain regions associated with mood regulation[7]. The institute's researchers have developed a novel high-throughput screening platform to identify compounds that can potentiate the effects of lithium orotate on neuroplasticity. This approach has led to the discovery of several promising lead compounds that are currently undergoing preclinical evaluation for their potential to enhance behavioral therapy outcomes when used in combination with lithium orotate[8].
Strengths: The Scripps Research Institute's cutting-edge research facilities and expertise in molecular biology provide a strong foundation for understanding the mechanisms of lithium orotate. Weaknesses: As an academic institution, they may face challenges in translating their findings into clinical applications without industry partnerships.
Critical Studies on Lithium Orotate Efficacy
Compositions Comprising Lithium Orotate And L-Leucine And Methods For Improving Cognitive Performance
PatentPendingUS20230330090A1
Innovation
- Compositions comprising lithium orotate and L-leucine, optionally with fish oils, encapsulated in a hypromellose capsule, administered to improve cognitive performance with a reduced side effect profile.
Combination therapies for treating bipolar disorder and ADHD, and methods for using the same
PatentInactiveUS20210196697A1
Innovation
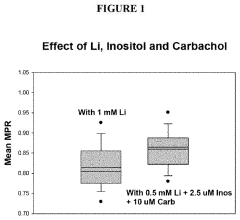
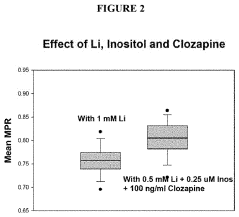
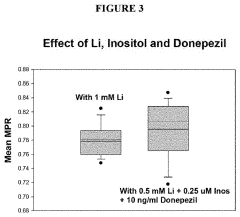
- The method involves analyzing the membrane potential of cells from patients with BD and ADHD to determine an optimal combination drug treatment and dosage by comparing membrane potential ratios in the presence and absence of specific agents, such as lithium and cholinergic agonists, to enhance therapeutic efficacy and minimize side effects.
Regulatory Framework for Lithium Orotate Use
The regulatory framework for lithium orotate use in behavioral therapy is complex and varies significantly across different jurisdictions. In the United States, lithium orotate is not approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for medical use, including behavioral therapy. It is classified as a dietary supplement, which means it is subject to less stringent regulations compared to prescription medications.
Under the Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act (DSHEA) of 1994, manufacturers of lithium orotate are responsible for ensuring the safety of their products before marketing. However, they are not required to provide evidence of efficacy or obtain FDA approval before selling the supplement. This regulatory approach has led to concerns about the quality control and standardization of lithium orotate products available in the market.
In contrast, lithium carbonate and lithium citrate, which are FDA-approved forms of lithium for treating bipolar disorder, are subject to strict regulations regarding manufacturing, labeling, and prescription. These regulations ensure consistent dosing and quality control, which are crucial for safe and effective use in behavioral therapy.
The European Union (EU) has a different approach to regulating lithium orotate. In most EU countries, it is not authorized as a medicinal product or food supplement. The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) has not issued specific guidelines or approvals for lithium orotate use, which limits its availability and use in behavioral therapy within the EU.
In Australia, the Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA) classifies lithium orotate as a complementary medicine. While it can be sold as a dietary supplement, any therapeutic claims must be supported by scientific evidence and approved by the TGA. This regulatory framework provides a middle ground between the US and EU approaches, allowing for some availability while maintaining oversight on therapeutic claims.
The lack of a unified global regulatory approach to lithium orotate presents challenges for researchers and clinicians interested in assessing its efficacy in behavioral therapy outcomes. The varying legal status and regulatory requirements across countries make it difficult to conduct large-scale, standardized clinical trials. This regulatory landscape also impacts the availability of consistent, high-quality lithium orotate products for potential use in behavioral therapy.
As research interest in lithium orotate grows, there is an increasing call for regulatory bodies to reassess their stance and potentially develop more specific guidelines for its use in medical contexts, including behavioral therapy. However, until more comprehensive studies on safety and efficacy are conducted, the regulatory framework for lithium orotate in behavioral therapy is likely to remain cautious and varied across different regions.
Under the Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act (DSHEA) of 1994, manufacturers of lithium orotate are responsible for ensuring the safety of their products before marketing. However, they are not required to provide evidence of efficacy or obtain FDA approval before selling the supplement. This regulatory approach has led to concerns about the quality control and standardization of lithium orotate products available in the market.
In contrast, lithium carbonate and lithium citrate, which are FDA-approved forms of lithium for treating bipolar disorder, are subject to strict regulations regarding manufacturing, labeling, and prescription. These regulations ensure consistent dosing and quality control, which are crucial for safe and effective use in behavioral therapy.
The European Union (EU) has a different approach to regulating lithium orotate. In most EU countries, it is not authorized as a medicinal product or food supplement. The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) has not issued specific guidelines or approvals for lithium orotate use, which limits its availability and use in behavioral therapy within the EU.
In Australia, the Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA) classifies lithium orotate as a complementary medicine. While it can be sold as a dietary supplement, any therapeutic claims must be supported by scientific evidence and approved by the TGA. This regulatory framework provides a middle ground between the US and EU approaches, allowing for some availability while maintaining oversight on therapeutic claims.
The lack of a unified global regulatory approach to lithium orotate presents challenges for researchers and clinicians interested in assessing its efficacy in behavioral therapy outcomes. The varying legal status and regulatory requirements across countries make it difficult to conduct large-scale, standardized clinical trials. This regulatory landscape also impacts the availability of consistent, high-quality lithium orotate products for potential use in behavioral therapy.
As research interest in lithium orotate grows, there is an increasing call for regulatory bodies to reassess their stance and potentially develop more specific guidelines for its use in medical contexts, including behavioral therapy. However, until more comprehensive studies on safety and efficacy are conducted, the regulatory framework for lithium orotate in behavioral therapy is likely to remain cautious and varied across different regions.
Safety Profile and Long-term Effects of Lithium Orotate
The safety profile and long-term effects of lithium orotate are crucial considerations in its potential application for behavioral therapy outcomes. While lithium orotate has gained attention as an alternative to prescription lithium carbonate, its safety and efficacy have not been as extensively studied.
Lithium orotate is generally considered to have a lower toxicity profile compared to lithium carbonate due to its lower lithium content and improved bioavailability. This potentially allows for lower dosages to achieve therapeutic effects, reducing the risk of side effects associated with higher lithium levels. However, the lack of standardized dosing and limited clinical trials make it challenging to establish definitive safety guidelines.
Short-term side effects of lithium orotate are reported to be milder than those of lithium carbonate. Common adverse effects may include nausea, diarrhea, and mild tremors. However, these symptoms are typically less severe and occur less frequently than with prescription lithium. The reduced incidence of side effects may contribute to better treatment adherence in behavioral therapy settings.
Long-term effects of lithium orotate use are not well-documented due to the scarcity of longitudinal studies. While lithium carbonate has known long-term risks such as thyroid dysfunction and kidney problems, it remains unclear whether lithium orotate poses similar risks at lower doses. Some proponents argue that the lower lithium content in lithium orotate may reduce the likelihood of these complications, but this hypothesis requires further investigation.
One significant concern regarding lithium orotate is the potential for inconsistent product quality and purity, as it is often sold as a dietary supplement rather than a regulated pharmaceutical. This lack of standardization may lead to variability in lithium content and potential contamination, which could impact both safety and efficacy in behavioral therapy applications.
The interaction of lithium orotate with other medications and supplements is another area that warrants careful consideration. While lithium carbonate's drug interactions are well-documented, less is known about potential interactions involving lithium orotate. This gap in knowledge necessitates caution when integrating lithium orotate into treatment regimens, particularly for patients with complex medical histories or those taking multiple medications.
In conclusion, while lithium orotate shows promise in terms of a potentially improved safety profile compared to lithium carbonate, significant research gaps exist regarding its long-term effects and optimal use in behavioral therapy. Rigorous clinical trials and longitudinal studies are needed to establish its safety and efficacy conclusively. Until such evidence is available, healthcare providers should approach the use of lithium orotate in behavioral therapy with caution, carefully weighing potential benefits against the uncertainties surrounding its long-term safety profile.
Lithium orotate is generally considered to have a lower toxicity profile compared to lithium carbonate due to its lower lithium content and improved bioavailability. This potentially allows for lower dosages to achieve therapeutic effects, reducing the risk of side effects associated with higher lithium levels. However, the lack of standardized dosing and limited clinical trials make it challenging to establish definitive safety guidelines.
Short-term side effects of lithium orotate are reported to be milder than those of lithium carbonate. Common adverse effects may include nausea, diarrhea, and mild tremors. However, these symptoms are typically less severe and occur less frequently than with prescription lithium. The reduced incidence of side effects may contribute to better treatment adherence in behavioral therapy settings.
Long-term effects of lithium orotate use are not well-documented due to the scarcity of longitudinal studies. While lithium carbonate has known long-term risks such as thyroid dysfunction and kidney problems, it remains unclear whether lithium orotate poses similar risks at lower doses. Some proponents argue that the lower lithium content in lithium orotate may reduce the likelihood of these complications, but this hypothesis requires further investigation.
One significant concern regarding lithium orotate is the potential for inconsistent product quality and purity, as it is often sold as a dietary supplement rather than a regulated pharmaceutical. This lack of standardization may lead to variability in lithium content and potential contamination, which could impact both safety and efficacy in behavioral therapy applications.
The interaction of lithium orotate with other medications and supplements is another area that warrants careful consideration. While lithium carbonate's drug interactions are well-documented, less is known about potential interactions involving lithium orotate. This gap in knowledge necessitates caution when integrating lithium orotate into treatment regimens, particularly for patients with complex medical histories or those taking multiple medications.
In conclusion, while lithium orotate shows promise in terms of a potentially improved safety profile compared to lithium carbonate, significant research gaps exist regarding its long-term effects and optimal use in behavioral therapy. Rigorous clinical trials and longitudinal studies are needed to establish its safety and efficacy conclusively. Until such evidence is available, healthcare providers should approach the use of lithium orotate in behavioral therapy with caution, carefully weighing potential benefits against the uncertainties surrounding its long-term safety profile.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!