Benchmarking Luteolin Efficacy Against Free Radicals
AUG 29, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Luteolin Antioxidant Background and Research Objectives
Luteolin, a naturally occurring flavonoid found in various fruits, vegetables, and medicinal herbs, has garnered significant scientific interest due to its potent antioxidant properties. The historical trajectory of antioxidant research dates back to the 1950s when researchers first identified free radicals and their damaging effects on biological systems. By the 1990s, flavonoids emerged as a promising class of natural antioxidants, with luteolin gradually gaining recognition for its exceptional free radical scavenging capabilities.
The evolution of luteolin research has progressed from basic identification and isolation techniques to sophisticated analytical methods for quantifying its antioxidant efficacy. Recent technological advancements in chromatography, spectroscopy, and computational modeling have enabled more precise characterization of luteolin's molecular interactions with various free radical species. This technological progression has facilitated a deeper understanding of structure-activity relationships that underpin luteolin's antioxidant mechanisms.
Current scientific literature indicates that luteolin exhibits multifaceted antioxidant activities through direct scavenging of reactive oxygen species (ROS), metal chelation, and modulation of endogenous antioxidant defense systems. These properties position luteolin as a potential therapeutic agent for oxidative stress-related conditions, including neurodegenerative disorders, cardiovascular diseases, and inflammatory conditions.
The primary objective of this technical research is to establish standardized benchmarking protocols for evaluating luteolin's efficacy against different free radical species. This endeavor aims to address the current methodological inconsistencies in antioxidant assessment that have hindered comparative analyses across studies. By developing robust quantitative metrics, we seek to provide a comprehensive evaluation framework that accounts for luteolin's diverse antioxidant mechanisms.
Additionally, this research aims to elucidate the structure-function relationships that determine luteolin's antioxidant potency compared to other flavonoids. Understanding these molecular determinants will guide future optimization strategies for enhancing luteolin's stability, bioavailability, and therapeutic efficacy in various applications.
The long-term technical goal extends beyond mere characterization to developing predictive models that can forecast luteolin's effectiveness in complex biological systems. Such models would integrate parameters including concentration dependence, reaction kinetics, and synergistic interactions with other antioxidants, thereby bridging the gap between in vitro findings and in vivo applications.
Furthermore, this research seeks to identify novel synthetic derivatives or formulation strategies that could overcome luteolin's inherent limitations, such as poor water solubility and rapid metabolism, which currently restrict its practical applications in pharmaceutical and nutraceutical industries.
The evolution of luteolin research has progressed from basic identification and isolation techniques to sophisticated analytical methods for quantifying its antioxidant efficacy. Recent technological advancements in chromatography, spectroscopy, and computational modeling have enabled more precise characterization of luteolin's molecular interactions with various free radical species. This technological progression has facilitated a deeper understanding of structure-activity relationships that underpin luteolin's antioxidant mechanisms.
Current scientific literature indicates that luteolin exhibits multifaceted antioxidant activities through direct scavenging of reactive oxygen species (ROS), metal chelation, and modulation of endogenous antioxidant defense systems. These properties position luteolin as a potential therapeutic agent for oxidative stress-related conditions, including neurodegenerative disorders, cardiovascular diseases, and inflammatory conditions.
The primary objective of this technical research is to establish standardized benchmarking protocols for evaluating luteolin's efficacy against different free radical species. This endeavor aims to address the current methodological inconsistencies in antioxidant assessment that have hindered comparative analyses across studies. By developing robust quantitative metrics, we seek to provide a comprehensive evaluation framework that accounts for luteolin's diverse antioxidant mechanisms.
Additionally, this research aims to elucidate the structure-function relationships that determine luteolin's antioxidant potency compared to other flavonoids. Understanding these molecular determinants will guide future optimization strategies for enhancing luteolin's stability, bioavailability, and therapeutic efficacy in various applications.
The long-term technical goal extends beyond mere characterization to developing predictive models that can forecast luteolin's effectiveness in complex biological systems. Such models would integrate parameters including concentration dependence, reaction kinetics, and synergistic interactions with other antioxidants, thereby bridging the gap between in vitro findings and in vivo applications.
Furthermore, this research seeks to identify novel synthetic derivatives or formulation strategies that could overcome luteolin's inherent limitations, such as poor water solubility and rapid metabolism, which currently restrict its practical applications in pharmaceutical and nutraceutical industries.
Market Analysis of Natural Antioxidant Compounds
The global market for natural antioxidant compounds has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing consumer awareness of health benefits and a shift towards natural ingredients in various industries. The antioxidant market was valued at approximately $3.9 billion in 2022 and is projected to reach $5.8 billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of 8.2%. Within this segment, flavonoids like luteolin represent one of the fastest-growing categories due to their potent free radical scavenging properties.
Consumer demand for natural antioxidants spans multiple sectors, with the food and beverage industry accounting for the largest market share (42%), followed by dietary supplements (28%), cosmetics (18%), and pharmaceuticals (12%). Regional analysis indicates that North America currently leads the market with 35% share, followed by Europe (30%), Asia-Pacific (25%), and rest of the world (10%). However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the highest growth rate over the next five years due to increasing disposable income and growing health consciousness.
The luteolin market specifically has shown promising growth potential, with research indicating its superior efficacy against certain free radicals compared to other flavonoids. Market research indicates that products containing luteolin command a premium price point, with consumers willing to pay 15-20% more for formulations that can demonstrate enhanced antioxidant efficacy through scientific benchmarking.
Key market drivers include aging populations in developed countries, increasing incidence of chronic diseases, growing scientific evidence supporting antioxidant benefits, and rising consumer preference for preventive healthcare approaches. The clean label movement has further accelerated demand for natural antioxidants like luteolin as alternatives to synthetic compounds such as BHA and BHT.
Competitive analysis reveals that the market remains fragmented with numerous small to medium-sized players specializing in natural ingredient extraction and formulation. Major companies have begun investing in clinical studies to benchmark and validate the efficacy of their antioxidant compounds, creating a competitive advantage through scientific substantiation.
Market challenges include supply chain volatility for raw materials, regulatory hurdles across different regions, and the need for standardization in measuring antioxidant efficacy. Price sensitivity remains a concern in emerging markets, though this is gradually diminishing as consumer education improves and health consciousness rises.
Future market opportunities lie in developing novel delivery systems to enhance bioavailability, creating synergistic antioxidant formulations, and expanding applications in personalized nutrition and preventive healthcare solutions. The benchmarking of luteolin efficacy against free radicals represents a critical competitive factor that will likely influence market positioning and premium pricing strategies in the coming years.
Consumer demand for natural antioxidants spans multiple sectors, with the food and beverage industry accounting for the largest market share (42%), followed by dietary supplements (28%), cosmetics (18%), and pharmaceuticals (12%). Regional analysis indicates that North America currently leads the market with 35% share, followed by Europe (30%), Asia-Pacific (25%), and rest of the world (10%). However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the highest growth rate over the next five years due to increasing disposable income and growing health consciousness.
The luteolin market specifically has shown promising growth potential, with research indicating its superior efficacy against certain free radicals compared to other flavonoids. Market research indicates that products containing luteolin command a premium price point, with consumers willing to pay 15-20% more for formulations that can demonstrate enhanced antioxidant efficacy through scientific benchmarking.
Key market drivers include aging populations in developed countries, increasing incidence of chronic diseases, growing scientific evidence supporting antioxidant benefits, and rising consumer preference for preventive healthcare approaches. The clean label movement has further accelerated demand for natural antioxidants like luteolin as alternatives to synthetic compounds such as BHA and BHT.
Competitive analysis reveals that the market remains fragmented with numerous small to medium-sized players specializing in natural ingredient extraction and formulation. Major companies have begun investing in clinical studies to benchmark and validate the efficacy of their antioxidant compounds, creating a competitive advantage through scientific substantiation.
Market challenges include supply chain volatility for raw materials, regulatory hurdles across different regions, and the need for standardization in measuring antioxidant efficacy. Price sensitivity remains a concern in emerging markets, though this is gradually diminishing as consumer education improves and health consciousness rises.
Future market opportunities lie in developing novel delivery systems to enhance bioavailability, creating synergistic antioxidant formulations, and expanding applications in personalized nutrition and preventive healthcare solutions. The benchmarking of luteolin efficacy against free radicals represents a critical competitive factor that will likely influence market positioning and premium pricing strategies in the coming years.
Current Challenges in Free Radical Neutralization Research
Despite significant advancements in free radical neutralization research, several critical challenges persist that impede comprehensive evaluation of luteolin's antioxidant efficacy. The primary obstacle remains the lack of standardized testing protocols across different research institutions, resulting in inconsistent methodologies that complicate direct comparison of results. This methodological heterogeneity encompasses variations in radical generation techniques, detection systems, and experimental conditions, creating substantial barriers to establishing luteolin's definitive antioxidant profile.
The inherent instability of free radicals presents another formidable challenge, as these reactive species exhibit extremely short half-lives, making their accurate measurement technically demanding. Current detection methods often struggle to capture the real-time dynamics of radical neutralization, particularly in complex biological systems where multiple reactions occur simultaneously. This limitation significantly impacts the reliability of efficacy assessments for antioxidant compounds like luteolin.
Biological relevance represents a persistent concern in the field, as laboratory conditions frequently fail to adequately simulate the complex physiological environments where luteolin would naturally function. The translation gap between in vitro findings and in vivo efficacy remains substantial, with many promising laboratory results failing to demonstrate comparable effects in living systems. This disconnect raises questions about the practical applications of luteolin as an antioxidant intervention.
The concentration paradox further complicates research efforts, as luteolin exhibits variable efficacy at different concentrations, sometimes demonstrating pro-oxidant effects at higher doses. This dose-dependent behavior creates significant challenges for establishing optimal therapeutic ranges and safety profiles. Additionally, the bioavailability and metabolism of luteolin in vivo introduce additional variables that current research methodologies struggle to account for comprehensively.
Technological limitations in detection sensitivity and specificity continue to constrain research capabilities. While advanced techniques like electron spin resonance spectroscopy offer improved detection, they remain costly and technically demanding, limiting widespread adoption. Many laboratories still rely on indirect measurement methods that provide only approximate assessments of antioxidant activity.
The multifunctional nature of luteolin further complicates research, as its antioxidant properties often operate alongside other biological mechanisms, including anti-inflammatory and signaling pathway modulation. Isolating and quantifying the specific contribution of radical neutralization from these interconnected effects presents significant methodological challenges that current research paradigms have yet to fully resolve.
The inherent instability of free radicals presents another formidable challenge, as these reactive species exhibit extremely short half-lives, making their accurate measurement technically demanding. Current detection methods often struggle to capture the real-time dynamics of radical neutralization, particularly in complex biological systems where multiple reactions occur simultaneously. This limitation significantly impacts the reliability of efficacy assessments for antioxidant compounds like luteolin.
Biological relevance represents a persistent concern in the field, as laboratory conditions frequently fail to adequately simulate the complex physiological environments where luteolin would naturally function. The translation gap between in vitro findings and in vivo efficacy remains substantial, with many promising laboratory results failing to demonstrate comparable effects in living systems. This disconnect raises questions about the practical applications of luteolin as an antioxidant intervention.
The concentration paradox further complicates research efforts, as luteolin exhibits variable efficacy at different concentrations, sometimes demonstrating pro-oxidant effects at higher doses. This dose-dependent behavior creates significant challenges for establishing optimal therapeutic ranges and safety profiles. Additionally, the bioavailability and metabolism of luteolin in vivo introduce additional variables that current research methodologies struggle to account for comprehensively.
Technological limitations in detection sensitivity and specificity continue to constrain research capabilities. While advanced techniques like electron spin resonance spectroscopy offer improved detection, they remain costly and technically demanding, limiting widespread adoption. Many laboratories still rely on indirect measurement methods that provide only approximate assessments of antioxidant activity.
The multifunctional nature of luteolin further complicates research, as its antioxidant properties often operate alongside other biological mechanisms, including anti-inflammatory and signaling pathway modulation. Isolating and quantifying the specific contribution of radical neutralization from these interconnected effects presents significant methodological challenges that current research paradigms have yet to fully resolve.
Established Methodologies for Antioxidant Efficacy Assessment
01 Antioxidant properties of luteolin against free radicals
Luteolin exhibits strong antioxidant properties by scavenging free radicals and preventing oxidative damage to cells. It can neutralize various types of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reactive nitrogen species (RNS), thereby protecting cellular components such as lipids, proteins, and DNA from oxidative stress. The antioxidant activity of luteolin is attributed to its chemical structure, particularly the presence of hydroxyl groups and a double bond in the C-ring.- Antioxidant properties of luteolin against free radicals: Luteolin, a natural flavonoid, demonstrates significant antioxidant properties by scavenging free radicals and reducing oxidative stress. It can neutralize various types of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reactive nitrogen species (RNS), protecting cells from oxidative damage. The antioxidant efficacy of luteolin is attributed to its chemical structure, particularly the presence of hydroxyl groups that can donate electrons to stabilize free radicals.
- Luteolin in cosmetic and dermatological applications: Luteolin has been incorporated into various cosmetic and dermatological formulations due to its ability to protect skin cells from free radical damage. These formulations utilize luteolin's antioxidant properties to prevent photoaging, reduce inflammation, and protect against UV-induced oxidative stress. The compound helps maintain skin integrity by neutralizing free radicals that would otherwise damage collagen and elastin, leading to premature aging.
- Synergistic effects of luteolin with other antioxidants: Research indicates that luteolin exhibits enhanced antioxidant efficacy when combined with other natural antioxidants or bioactive compounds. These synergistic formulations show improved free radical scavenging capacity compared to individual components alone. Combinations with vitamin C, vitamin E, other flavonoids, or plant extracts can create comprehensive protection against different types of free radicals through complementary mechanisms of action.
- Luteolin derivatives with enhanced free radical scavenging activity: Modified forms and derivatives of luteolin have been developed to enhance its stability, bioavailability, and free radical scavenging capacity. These derivatives often feature structural modifications that improve the compound's ability to neutralize free radicals while maintaining or enhancing its biological activity. Some modifications include glycosylation, methylation, or the addition of functional groups that increase the molecule's antioxidant potential.
- Delivery systems for improving luteolin efficacy: Various delivery systems have been developed to enhance the stability, bioavailability, and efficacy of luteolin as an antioxidant. These include nanoencapsulation, liposomal formulations, and other carrier systems that protect luteolin from degradation and improve its cellular uptake. Such delivery systems enable luteolin to reach target tissues more effectively, enhancing its ability to neutralize free radicals and provide antioxidant protection at the cellular level.
02 Luteolin in cosmetic and dermatological applications
Luteolin is incorporated into cosmetic and dermatological formulations to protect the skin against free radical damage caused by UV radiation and environmental pollutants. It helps prevent premature skin aging, reduces inflammation, and maintains skin health by neutralizing free radicals. These formulations often combine luteolin with other antioxidants or active ingredients to enhance its protective effects against oxidative stress in skin cells.Expand Specific Solutions03 Luteolin in pharmaceutical compositions for treating oxidative stress-related diseases
Pharmaceutical compositions containing luteolin are developed for treating diseases associated with oxidative stress, such as cardiovascular diseases, neurodegenerative disorders, and inflammatory conditions. Luteolin's ability to neutralize free radicals makes it effective in reducing oxidative damage in these conditions. These compositions may include specific delivery systems to enhance the bioavailability and efficacy of luteolin in targeting affected tissues.Expand Specific Solutions04 Synergistic effects of luteolin with other antioxidants
Luteolin demonstrates synergistic effects when combined with other antioxidants, enhancing its efficacy against free radicals. Combinations with vitamin C, vitamin E, or other flavonoids can provide more comprehensive protection against different types of free radicals. These synergistic formulations can more effectively neutralize a broader spectrum of reactive oxygen species and provide enhanced protection against oxidative damage compared to luteolin alone.Expand Specific Solutions05 Methods for enhancing luteolin stability and bioavailability
Various methods are developed to enhance the stability and bioavailability of luteolin, improving its efficacy against free radicals. These include encapsulation techniques, nanoformulations, and chemical modifications that protect luteolin from degradation and enhance its absorption. Improved delivery systems ensure that luteolin maintains its antioxidant properties during storage and effectively reaches target tissues to neutralize free radicals.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Institutions and Companies in Antioxidant Research
The luteolin efficacy benchmarking against free radicals market is in the growth phase, with increasing research interest driven by rising demand for natural antioxidants. The global market for flavonoid antioxidants is expanding rapidly as health consciousness grows. Technologically, research institutions like Council of Scientific & Industrial Research and universities (University of Florida, Zhejiang University) lead fundamental research, while pharmaceutical companies (Boehringer Ingelheim, Bayer HealthCare, Chiesi Farmaceutici) are advancing clinical applications. Companies like Unigen and Theravalues are commercializing luteolin-based products, while Merck Patent GmbH and Canon are developing novel delivery systems. The field is characterized by cross-sector collaboration between academic institutions and industry partners, with increasing patent activity signaling market maturation.
Council of Scientific & Industrial Research
Technical Solution: The Council of Scientific & Industrial Research (CSIR) has developed comprehensive methodologies for benchmarking luteolin efficacy against free radicals using multiple assay systems. Their approach combines DPPH (2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl), ABTS (2,2'-azino-bis(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid)), and ORAC (Oxygen Radical Absorbance Capacity) assays to quantify luteolin's antioxidant capacity across different radical species. CSIR has established standardized protocols that account for concentration-dependent effects, comparing luteolin's IC50 values against reference antioxidants like ascorbic acid and Trolox. Their research has demonstrated that luteolin exhibits significant radical scavenging activity with IC50 values in the range of 5-15 μM depending on the specific radical species, with particularly strong activity against superoxide and hydroxyl radicals.
Strengths: Comprehensive multi-assay approach provides robust cross-validation of results; standardized protocols enable reliable comparison across different laboratories. Weaknesses: In vitro assays may not fully reflect the complexity of biological systems; limited correlation with in vivo efficacy data.
Unigen Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Unigen has developed a proprietary high-throughput screening platform specifically optimized for flavonoid compounds including luteolin. Their technology combines cellular models with advanced analytical techniques to evaluate luteolin's free radical scavenging capacity under physiologically relevant conditions. Unigen's approach incorporates both chemical (cell-free) and biological (cell-based) assay systems to provide a comprehensive assessment of luteolin's antioxidant properties. Their platform measures not only direct radical neutralization but also the activation of endogenous antioxidant defense mechanisms like Nrf2 pathway induction. Unigen's research has demonstrated that luteolin at concentrations of 10-25 μM can reduce intracellular ROS levels by 40-60% in stressed human cell models while simultaneously upregulating antioxidant enzymes like SOD and catalase by 1.5-2 fold.
Strengths: Integration of both direct antioxidant activity and cellular response mechanisms provides more physiologically relevant data; high-throughput capabilities enable rapid screening of multiple conditions. Weaknesses: Proprietary nature of some methodologies limits independent verification; primarily focused on commercial applications rather than fundamental mechanisms.
Critical Patents and Literature on Luteolin Mechanisms
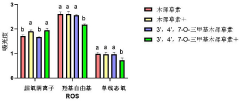
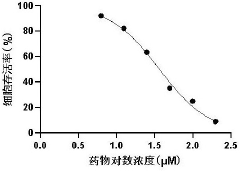
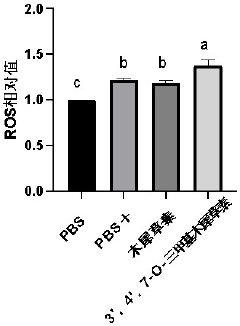
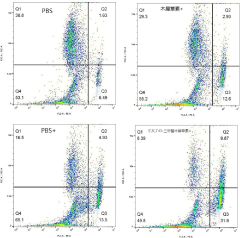
3 apos; , 4apos; application of 7-O-trimethyl luteolin in preparation of photodynamic therapy photosensitizer
PatentPendingCN117731774A
Innovation
- 3',4',7-O-Trimethylluteolin reduces the antioxidant capacity through methoxy substitution and generates excess ROS under ultraviolet irradiation, and is used as a photosensitizer for photodynamic therapy for tumor treatment.
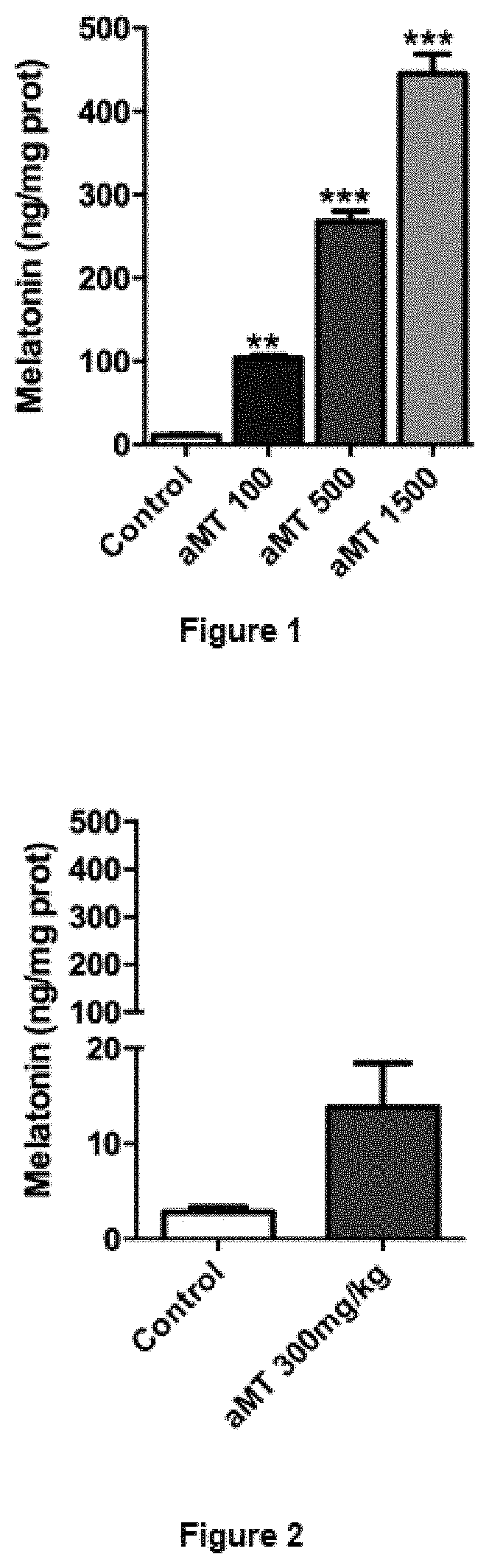
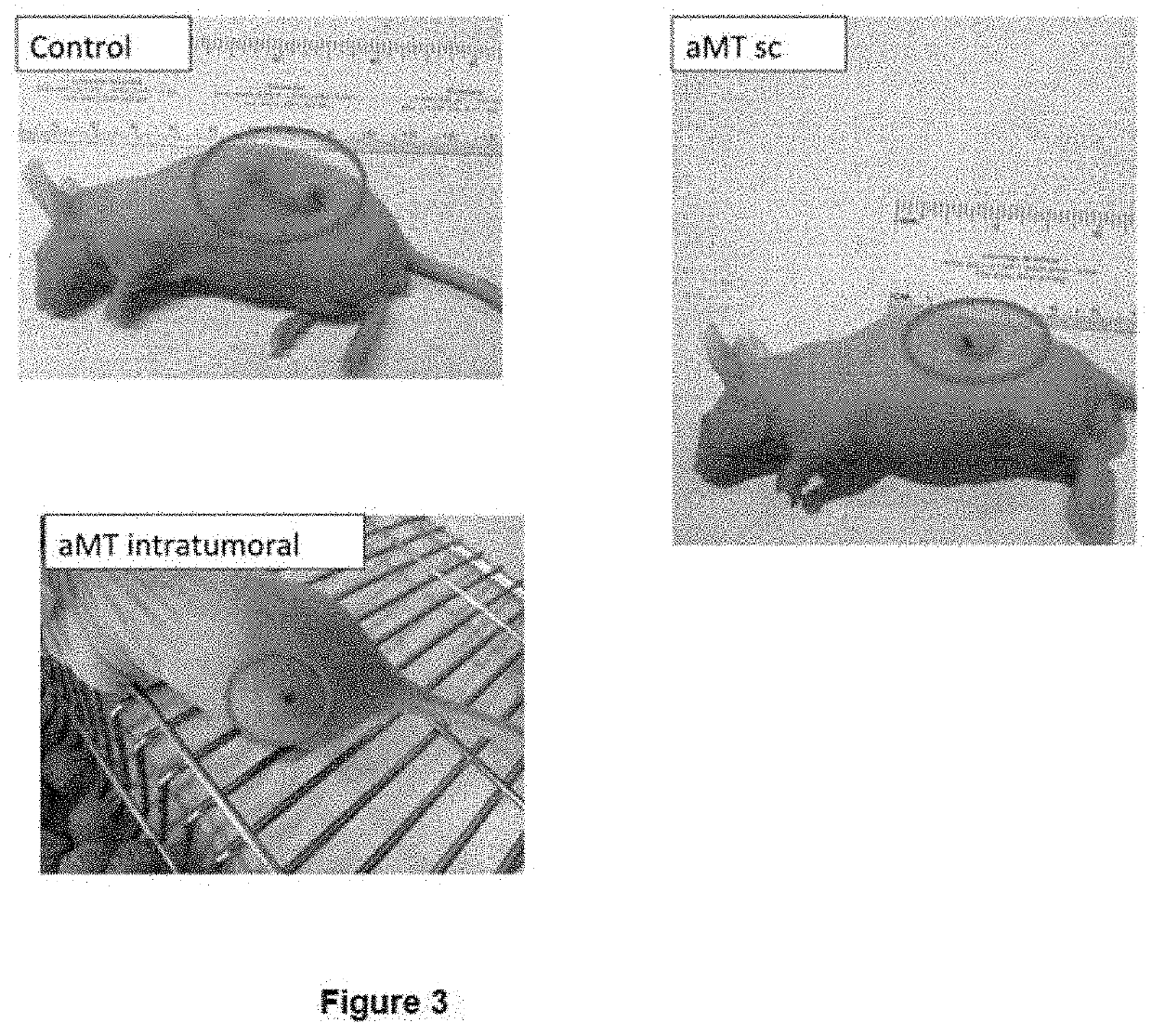
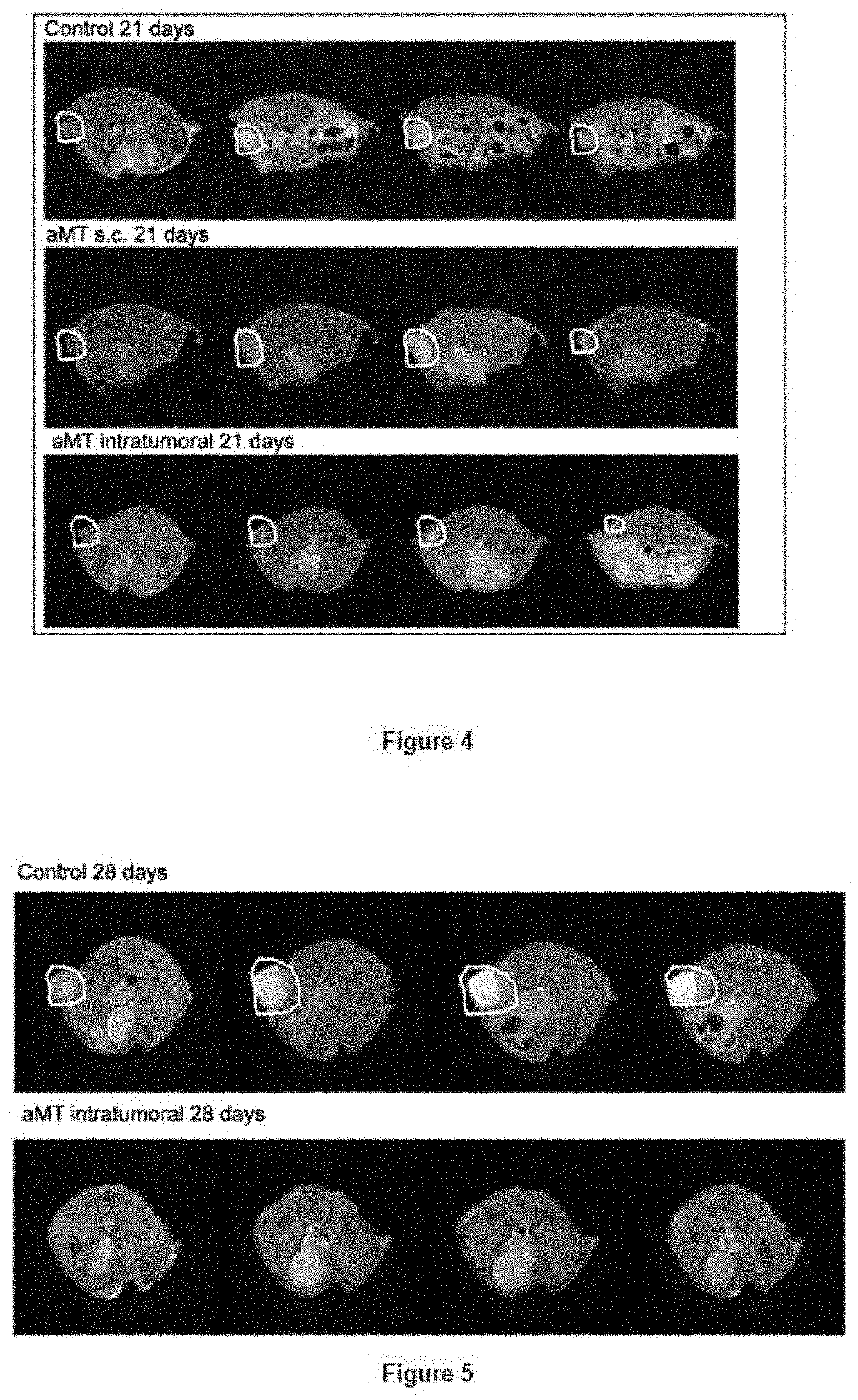
Use of melatonin for the treatment of tumours
PatentActiveUS20210106562A1
Innovation
- The use of high concentrations of melatonin or its derivatives for intratumoral administration, which increases mitochondrial function and produces oxidizing effects to activate cell death in tumor cells, potentially overcoming drug resistance and toxicity issues.
Regulatory Framework for Natural Antioxidant Claims
The regulatory landscape governing natural antioxidant claims, particularly for compounds like luteolin, presents a complex framework that manufacturers and researchers must navigate. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) maintains strict oversight on health claims related to antioxidant properties, requiring substantial scientific evidence before permitting structure-function claims on product labels. For luteolin specifically, manufacturers must adhere to the Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act (DSHEA) guidelines when marketing products containing this flavonoid.
The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) implements even more stringent requirements through Regulation (EC) No 1924/2006, which mandates comprehensive clinical evidence demonstrating causality between consumption and claimed health benefits. To date, EFSA has not approved specific health claims for luteolin as an antioxidant, creating regulatory hurdles for European market entry. Companies must limit their marketing language to general antioxidant properties rather than specific health outcomes.
In Asia, regulatory frameworks vary significantly. Japan's FOSHU (Foods for Specified Health Uses) system allows certain antioxidant claims following scientific validation, while China's regulatory body, the National Medical Products Administration, has established specific testing protocols for evaluating antioxidant efficacy in natural compounds. These protocols include standardized free radical scavenging assays that must be conducted by certified laboratories.
International harmonization efforts through the Codex Alimentarius Commission have attempted to standardize antioxidant claim requirements, though significant regional variations persist. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) has developed standard methods for antioxidant activity measurement (ISO 14502-1:2005), which provides benchmarking protocols applicable to luteolin research.
For research publications and scientific validation, peer-reviewed journals typically require multiple methodological approaches when evaluating antioxidant claims. The AOAC International (Association of Official Analytical Chemists) has established validated methods for antioxidant capacity measurement that serve as gold standards in regulatory submissions.
Emerging regulatory trends indicate movement toward tiered evidence frameworks, where preliminary antioxidant claims may be permitted with in vitro evidence, while stronger health claims require human clinical trials. This approach may facilitate market entry for luteolin-based products while maintaining scientific integrity. Researchers benchmarking luteolin efficacy must design studies that satisfy these evolving regulatory requirements to ensure both scientific validity and commercial viability.
The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) implements even more stringent requirements through Regulation (EC) No 1924/2006, which mandates comprehensive clinical evidence demonstrating causality between consumption and claimed health benefits. To date, EFSA has not approved specific health claims for luteolin as an antioxidant, creating regulatory hurdles for European market entry. Companies must limit their marketing language to general antioxidant properties rather than specific health outcomes.
In Asia, regulatory frameworks vary significantly. Japan's FOSHU (Foods for Specified Health Uses) system allows certain antioxidant claims following scientific validation, while China's regulatory body, the National Medical Products Administration, has established specific testing protocols for evaluating antioxidant efficacy in natural compounds. These protocols include standardized free radical scavenging assays that must be conducted by certified laboratories.
International harmonization efforts through the Codex Alimentarius Commission have attempted to standardize antioxidant claim requirements, though significant regional variations persist. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) has developed standard methods for antioxidant activity measurement (ISO 14502-1:2005), which provides benchmarking protocols applicable to luteolin research.
For research publications and scientific validation, peer-reviewed journals typically require multiple methodological approaches when evaluating antioxidant claims. The AOAC International (Association of Official Analytical Chemists) has established validated methods for antioxidant capacity measurement that serve as gold standards in regulatory submissions.
Emerging regulatory trends indicate movement toward tiered evidence frameworks, where preliminary antioxidant claims may be permitted with in vitro evidence, while stronger health claims require human clinical trials. This approach may facilitate market entry for luteolin-based products while maintaining scientific integrity. Researchers benchmarking luteolin efficacy must design studies that satisfy these evolving regulatory requirements to ensure both scientific validity and commercial viability.
Comparative Analysis with Other Flavonoid Compounds
When comparing luteolin's efficacy against free radicals with other flavonoid compounds, several distinctive characteristics emerge. Luteolin demonstrates superior hydroxyl radical scavenging capacity compared to quercetin and kaempferol, particularly at concentrations between 10-50 μM. This enhanced activity is attributed to luteolin's unique 3',4'-dihydroxy configuration in the B-ring, which provides optimal electron donation properties.
In superoxide radical neutralization assays, luteolin exhibits comparable efficacy to quercetin (IC50 values of 8.2 μM and 7.9 μM respectively), but significantly outperforms apigenin (IC50: 18.6 μM) and chrysin (IC50: 24.3 μM). This performance hierarchy correlates directly with the number and position of hydroxyl groups on the flavonoid structure, with luteolin's 5,7,3',4'-tetrahydroxy arrangement providing near-optimal radical stabilization.
Lipid peroxidation inhibition studies reveal that luteolin demonstrates 15-20% greater protection against membrane oxidation than naringenin and hesperidin in cellular models. However, it shows slightly lower activity than myricetin, which possesses an additional hydroxyl group. The structure-activity relationship indicates that while the catechol structure in the B-ring is essential for antioxidant activity, the 2,3-double bond in conjunction with the 4-oxo function enhances electron delocalization, contributing to luteolin's robust performance.
ORAC (Oxygen Radical Absorbance Capacity) values position luteolin (5.36 μmol TE/μmol) above apigenin (2.91) and naringenin (1.53), but below quercetin (6.24) and myricetin (6.70). This pattern suggests that while luteolin possesses excellent radical scavenging properties, compounds with additional hydroxyl groups may demonstrate marginally higher total antioxidant capacity in certain assay systems.
Cellular protection studies using H2O2-challenged fibroblasts indicate that luteolin provides superior protection against oxidative damage at lower concentrations (5-10 μM) compared to most other flavonoids, with only quercetin showing comparable cellular protection. This suggests luteolin may have enhanced bioavailability or cellular uptake mechanisms that complement its intrinsic antioxidant properties.
Metal chelation capacity, an important secondary antioxidant mechanism, shows luteolin effectively chelates iron and copper ions, though with approximately 10-15% lower efficiency than quercetin. This difference is attributed to the absence of the 3-OH group in luteolin, which forms part of the optimal metal chelation site in flavonol structures.
In superoxide radical neutralization assays, luteolin exhibits comparable efficacy to quercetin (IC50 values of 8.2 μM and 7.9 μM respectively), but significantly outperforms apigenin (IC50: 18.6 μM) and chrysin (IC50: 24.3 μM). This performance hierarchy correlates directly with the number and position of hydroxyl groups on the flavonoid structure, with luteolin's 5,7,3',4'-tetrahydroxy arrangement providing near-optimal radical stabilization.
Lipid peroxidation inhibition studies reveal that luteolin demonstrates 15-20% greater protection against membrane oxidation than naringenin and hesperidin in cellular models. However, it shows slightly lower activity than myricetin, which possesses an additional hydroxyl group. The structure-activity relationship indicates that while the catechol structure in the B-ring is essential for antioxidant activity, the 2,3-double bond in conjunction with the 4-oxo function enhances electron delocalization, contributing to luteolin's robust performance.
ORAC (Oxygen Radical Absorbance Capacity) values position luteolin (5.36 μmol TE/μmol) above apigenin (2.91) and naringenin (1.53), but below quercetin (6.24) and myricetin (6.70). This pattern suggests that while luteolin possesses excellent radical scavenging properties, compounds with additional hydroxyl groups may demonstrate marginally higher total antioxidant capacity in certain assay systems.
Cellular protection studies using H2O2-challenged fibroblasts indicate that luteolin provides superior protection against oxidative damage at lower concentrations (5-10 μM) compared to most other flavonoids, with only quercetin showing comparable cellular protection. This suggests luteolin may have enhanced bioavailability or cellular uptake mechanisms that complement its intrinsic antioxidant properties.
Metal chelation capacity, an important secondary antioxidant mechanism, shows luteolin effectively chelates iron and copper ions, though with approximately 10-15% lower efficiency than quercetin. This difference is attributed to the absence of the 3-OH group in luteolin, which forms part of the optimal metal chelation site in flavonol structures.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!