Benchmarking Moisture Absorption with Lithium Chloride
AUG 28, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Lithium Chloride Moisture Absorption Technology Background
Lithium chloride (LiCl) has emerged as a significant compound in moisture absorption technology, with its history dating back to early 20th century applications in air conditioning and dehumidification systems. The hygroscopic properties of LiCl make it exceptionally effective at absorbing moisture from the atmosphere, even at low relative humidity levels, which distinguishes it from other desiccants and moisture-absorbing materials.
The evolution of LiCl moisture absorption technology has been marked by continuous improvements in formulation, application methods, and integration with various systems. Initially used in basic dehumidification processes, LiCl has progressively found applications in more sophisticated systems including HVAC equipment, pharmaceutical storage, electronics manufacturing, and preservation of sensitive materials.
Recent technological advancements have focused on enhancing the efficiency and sustainability of LiCl-based moisture absorption systems. Researchers have developed composite materials incorporating LiCl with various substrates to improve absorption capacity, regeneration efficiency, and mechanical stability. These developments have addressed historical limitations such as deliquescence (turning into liquid when saturated) and corrosivity.
The fundamental principle behind LiCl's moisture absorption capability lies in its strong ionic interactions with water molecules. With a deliquescence relative humidity (DRH) of approximately 11% at standard conditions, LiCl can effectively remove moisture from air even in relatively dry environments. This property has positioned it as a benchmark material against which other desiccants are often compared.
Current research trends in LiCl moisture absorption technology include the development of nanoporous materials impregnated with LiCl, exploration of LiCl-based liquid desiccant systems for energy-efficient air conditioning, and integration with renewable energy sources for regeneration processes. These innovations aim to reduce energy consumption while maintaining or improving moisture absorption performance.
The technical objectives in this field now extend beyond simple moisture removal to include precise humidity control, energy efficiency, environmental sustainability, and cost-effectiveness. Researchers are particularly focused on developing LiCl-based systems that can be regenerated at lower temperatures, thereby reducing the energy requirements for the desorption phase of the absorption-desorption cycle.
Global interest in LiCl moisture absorption technology has intensified with growing concerns about indoor air quality, energy conservation, and climate change adaptation. The technology is increasingly viewed as a critical component in creating energy-efficient buildings and maintaining optimal conditions for sensitive processes and materials in various industries.
The evolution of LiCl moisture absorption technology has been marked by continuous improvements in formulation, application methods, and integration with various systems. Initially used in basic dehumidification processes, LiCl has progressively found applications in more sophisticated systems including HVAC equipment, pharmaceutical storage, electronics manufacturing, and preservation of sensitive materials.
Recent technological advancements have focused on enhancing the efficiency and sustainability of LiCl-based moisture absorption systems. Researchers have developed composite materials incorporating LiCl with various substrates to improve absorption capacity, regeneration efficiency, and mechanical stability. These developments have addressed historical limitations such as deliquescence (turning into liquid when saturated) and corrosivity.
The fundamental principle behind LiCl's moisture absorption capability lies in its strong ionic interactions with water molecules. With a deliquescence relative humidity (DRH) of approximately 11% at standard conditions, LiCl can effectively remove moisture from air even in relatively dry environments. This property has positioned it as a benchmark material against which other desiccants are often compared.
Current research trends in LiCl moisture absorption technology include the development of nanoporous materials impregnated with LiCl, exploration of LiCl-based liquid desiccant systems for energy-efficient air conditioning, and integration with renewable energy sources for regeneration processes. These innovations aim to reduce energy consumption while maintaining or improving moisture absorption performance.
The technical objectives in this field now extend beyond simple moisture removal to include precise humidity control, energy efficiency, environmental sustainability, and cost-effectiveness. Researchers are particularly focused on developing LiCl-based systems that can be regenerated at lower temperatures, thereby reducing the energy requirements for the desorption phase of the absorption-desorption cycle.
Global interest in LiCl moisture absorption technology has intensified with growing concerns about indoor air quality, energy conservation, and climate change adaptation. The technology is increasingly viewed as a critical component in creating energy-efficient buildings and maintaining optimal conditions for sensitive processes and materials in various industries.
Market Analysis for Moisture Control Solutions
The global moisture control solutions market is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing awareness of the importance of humidity management across various industries. Currently valued at approximately 3.2 billion USD, this market is projected to reach 4.7 billion USD by 2027, representing a compound annual growth rate of 7.8%. This growth trajectory is particularly evident in sectors such as pharmaceuticals, food processing, electronics manufacturing, and building materials, where precise moisture control is critical for product quality and operational efficiency.
Lithium chloride-based moisture absorption technologies hold a substantial market share within this landscape, accounting for roughly 18% of the total moisture control solutions market. The unique hygroscopic properties of lithium chloride make it exceptionally effective for applications requiring precise humidity control in challenging environments. This has positioned lithium chloride as a premium solution in high-value industries where performance reliability outweighs cost considerations.
Regionally, North America and Europe currently dominate the moisture control market, collectively representing 58% of global demand. However, the Asia-Pacific region is emerging as the fastest-growing market, with an anticipated growth rate of 9.3% over the next five years. This regional shift is primarily driven by rapid industrialization in countries like China and India, coupled with increasing adoption of advanced manufacturing practices that require sophisticated environmental control systems.
Consumer trends indicate a growing preference for integrated moisture control solutions that offer real-time monitoring capabilities and automated adjustment features. This shift is creating new market opportunities for smart moisture control systems that incorporate lithium chloride technology with IoT connectivity, allowing for remote monitoring and predictive maintenance.
The competitive landscape features both established industrial giants and specialized technology providers. Major players include Honeywell International, Munters Group, and Bry-Air, who collectively control approximately 35% of the global market. These companies are increasingly focusing on developing benchmark standards for moisture absorption efficiency, with lithium chloride-based solutions often serving as the performance reference point against which alternative technologies are measured.
Price sensitivity varies significantly across market segments, with industrial applications demonstrating greater willingness to invest in premium solutions like lithium chloride systems when performance requirements are stringent. The average return on investment period for advanced moisture control systems ranges from 18 to 36 months, depending on the application environment and energy efficiency gains achieved.
Lithium chloride-based moisture absorption technologies hold a substantial market share within this landscape, accounting for roughly 18% of the total moisture control solutions market. The unique hygroscopic properties of lithium chloride make it exceptionally effective for applications requiring precise humidity control in challenging environments. This has positioned lithium chloride as a premium solution in high-value industries where performance reliability outweighs cost considerations.
Regionally, North America and Europe currently dominate the moisture control market, collectively representing 58% of global demand. However, the Asia-Pacific region is emerging as the fastest-growing market, with an anticipated growth rate of 9.3% over the next five years. This regional shift is primarily driven by rapid industrialization in countries like China and India, coupled with increasing adoption of advanced manufacturing practices that require sophisticated environmental control systems.
Consumer trends indicate a growing preference for integrated moisture control solutions that offer real-time monitoring capabilities and automated adjustment features. This shift is creating new market opportunities for smart moisture control systems that incorporate lithium chloride technology with IoT connectivity, allowing for remote monitoring and predictive maintenance.
The competitive landscape features both established industrial giants and specialized technology providers. Major players include Honeywell International, Munters Group, and Bry-Air, who collectively control approximately 35% of the global market. These companies are increasingly focusing on developing benchmark standards for moisture absorption efficiency, with lithium chloride-based solutions often serving as the performance reference point against which alternative technologies are measured.
Price sensitivity varies significantly across market segments, with industrial applications demonstrating greater willingness to invest in premium solutions like lithium chloride systems when performance requirements are stringent. The average return on investment period for advanced moisture control systems ranges from 18 to 36 months, depending on the application environment and energy efficiency gains achieved.
Current Challenges in Hygroscopic Material Benchmarking
Despite significant advancements in hygroscopic material testing, the field of moisture absorption benchmarking faces several persistent challenges that impede standardization and reliable comparison across different materials and testing environments. The use of lithium chloride as a reference material, while beneficial, introduces its own set of complexities that researchers and industry professionals must navigate.
One primary challenge is the lack of universally accepted testing protocols. Different laboratories employ varying methodologies for sample preparation, conditioning, and measurement, leading to inconsistent results even when testing identical materials. This variability makes cross-study comparisons difficult and hampers the development of comprehensive material databases.
Environmental control presents another significant hurdle. Moisture absorption properties are highly sensitive to temperature fluctuations, air movement, and ambient humidity levels. Even minor variations in these parameters can produce substantially different results, necessitating extremely precise environmental chambers that many facilities lack or cannot maintain consistently.
The time-dependent nature of moisture absorption processes further complicates benchmarking efforts. Hygroscopic materials often exhibit different absorption rates and equilibrium points depending on exposure duration. Short-term tests may fail to capture long-term behavioral patterns, while extended testing periods are resource-intensive and may be impractical for routine quality control applications.
Sample geometry and size effects introduce additional variables. Surface area-to-volume ratios significantly impact moisture absorption kinetics, yet standardizing sample dimensions across diverse material types remains problematic. This geometric dependency makes it difficult to establish truly comparable benchmarks across material categories.
When specifically considering lithium chloride as a benchmarking standard, its extreme hygroscopicity presents both advantages and challenges. While its pronounced moisture absorption properties make it sensitive enough to detect subtle environmental variations, this same sensitivity requires exceptional handling protocols to prevent contamination or premature moisture exposure that could compromise test validity.
Instrument calibration and measurement technique standardization represent ongoing challenges. Different moisture determination methods—from gravimetric analysis to specialized moisture meters and spectroscopic techniques—produce varying results that are not always directly comparable, creating confusion when establishing reference values.
Data interpretation and reporting conventions lack consistency across the field. Without standardized metrics for expressing moisture absorption characteristics, comparing results from different sources becomes an exercise in translation rather than direct analysis, limiting the practical utility of published benchmarking data.
One primary challenge is the lack of universally accepted testing protocols. Different laboratories employ varying methodologies for sample preparation, conditioning, and measurement, leading to inconsistent results even when testing identical materials. This variability makes cross-study comparisons difficult and hampers the development of comprehensive material databases.
Environmental control presents another significant hurdle. Moisture absorption properties are highly sensitive to temperature fluctuations, air movement, and ambient humidity levels. Even minor variations in these parameters can produce substantially different results, necessitating extremely precise environmental chambers that many facilities lack or cannot maintain consistently.
The time-dependent nature of moisture absorption processes further complicates benchmarking efforts. Hygroscopic materials often exhibit different absorption rates and equilibrium points depending on exposure duration. Short-term tests may fail to capture long-term behavioral patterns, while extended testing periods are resource-intensive and may be impractical for routine quality control applications.
Sample geometry and size effects introduce additional variables. Surface area-to-volume ratios significantly impact moisture absorption kinetics, yet standardizing sample dimensions across diverse material types remains problematic. This geometric dependency makes it difficult to establish truly comparable benchmarks across material categories.
When specifically considering lithium chloride as a benchmarking standard, its extreme hygroscopicity presents both advantages and challenges. While its pronounced moisture absorption properties make it sensitive enough to detect subtle environmental variations, this same sensitivity requires exceptional handling protocols to prevent contamination or premature moisture exposure that could compromise test validity.
Instrument calibration and measurement technique standardization represent ongoing challenges. Different moisture determination methods—from gravimetric analysis to specialized moisture meters and spectroscopic techniques—produce varying results that are not always directly comparable, creating confusion when establishing reference values.
Data interpretation and reporting conventions lack consistency across the field. Without standardized metrics for expressing moisture absorption characteristics, comparing results from different sources becomes an exercise in translation rather than direct analysis, limiting the practical utility of published benchmarking data.
Standard Benchmarking Methodologies for LiCl Absorption
01 Lithium chloride as a moisture absorbing agent
Lithium chloride is widely used as an effective moisture absorbing agent due to its hygroscopic properties. It can absorb moisture from the surrounding environment, making it suitable for applications requiring humidity control. The compound has a high affinity for water molecules and can maintain low humidity levels in enclosed spaces, which is beneficial for moisture-sensitive products and environments.- Lithium chloride as a desiccant in moisture absorption systems: Lithium chloride is widely used as an effective desiccant in various moisture absorption systems due to its high hygroscopic properties. It can absorb moisture from the surrounding environment, making it suitable for applications requiring humidity control. These systems often incorporate lithium chloride into specialized structures or devices designed to maximize surface area for moisture absorption and improve efficiency in controlling relative humidity in enclosed spaces.
- Moisture absorption devices incorporating lithium chloride: Various devices have been developed that utilize lithium chloride's moisture absorption capabilities. These include dehumidifiers, air conditioning systems, and specialized moisture control units. The designs often feature containers, cartridges, or modules that hold lithium chloride in a manner that optimizes its interaction with humid air while preventing leakage or contamination. Some devices incorporate mechanisms for regeneration of the lithium chloride after it becomes saturated with moisture.
- Lithium chloride compositions for enhanced moisture absorption: Research has focused on developing specialized compositions containing lithium chloride to enhance its moisture absorption capabilities. These compositions may include additional compounds, carriers, or structural elements that improve the efficiency, capacity, or rate of moisture absorption. Some formulations combine lithium chloride with other hygroscopic materials or incorporate it into matrices that increase surface area and stability while maintaining or enhancing its moisture absorption properties.
- Industrial applications of lithium chloride for moisture control: Lithium chloride is employed in various industrial applications for moisture control, including gas drying systems, industrial dehumidification processes, and moisture removal in manufacturing environments. These applications often require specialized equipment and processes to effectively utilize lithium chloride's hygroscopic properties at scale. Industrial systems may incorporate regeneration cycles, continuous operation capabilities, and integration with other industrial processes to maintain optimal humidity levels.
- Novel technologies improving lithium chloride moisture absorption efficiency: Recent technological advancements have focused on improving the efficiency and effectiveness of lithium chloride as a moisture absorbent. These innovations include new material combinations, structural designs, and process improvements that enhance absorption capacity, reduce regeneration energy requirements, or extend the operational lifetime of lithium chloride-based systems. Some technologies incorporate smart controls, specialized coatings, or novel physical arrangements to optimize moisture absorption performance under various environmental conditions.
02 Desiccant systems incorporating lithium chloride
Desiccant systems that incorporate lithium chloride are designed for efficient moisture removal in various applications. These systems utilize the hygroscopic properties of lithium chloride to absorb moisture from air or other gases. The desiccant systems can be configured in different forms such as packets, cartridges, or integrated into larger dehumidification equipment to provide controlled humidity environments.Expand Specific Solutions03 Lithium chloride in energy storage and battery applications
Lithium chloride is utilized in energy storage and battery applications where moisture control is critical. The compound helps maintain dry conditions within battery cells and energy storage systems, preventing moisture-related degradation and extending operational life. Its moisture absorption capabilities contribute to the stability and efficiency of lithium-based batteries and other energy storage technologies.Expand Specific Solutions04 Regeneration methods for lithium chloride desiccants
Various methods have been developed for regenerating lithium chloride after it has absorbed moisture. These regeneration techniques involve heating or other processes to remove the absorbed water, allowing the lithium chloride to be reused for further moisture absorption cycles. Efficient regeneration methods enhance the cost-effectiveness and sustainability of lithium chloride-based moisture control systems.Expand Specific Solutions05 Composite materials with lithium chloride for enhanced moisture absorption
Composite materials that incorporate lithium chloride have been developed to enhance moisture absorption performance. These composites combine lithium chloride with carrier materials such as silica gel, polymers, or other substrates to improve handling, increase surface area for moisture absorption, and control the rate of moisture uptake. The resulting materials offer improved efficiency and versatility for various dehumidification applications.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Companies in Hygroscopic Materials Industry
The lithium chloride moisture absorption benchmarking market is in a growth phase, with increasing applications in humidity control systems, energy storage, and pharmaceutical industries. The market is projected to expand significantly due to rising demand for precise moisture management solutions. Technologically, the field shows varying maturity levels across applications. Leading players include Qinghai Salt Lake Industry and Ganfeng Lithium Group from China, who dominate raw material supply, while companies like LG Chem, BYD, and DENSO focus on advanced applications in batteries and automotive systems. Japanese firms Nippon Shokubai and Sumitomo Metal Mining contribute specialized technical expertise, creating a competitive landscape balanced between raw material suppliers and technology innovators.
Qinghai Salt Lake Industry Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Qinghai Salt Lake Industry has implemented a proprietary lithium chloride moisture absorption benchmarking system tailored for industrial-scale lithium extraction operations. Their technical solution centers on a standardized comparison framework that utilizes precisely calibrated lithium chloride solutions (15-35% concentration) as reference standards for moisture absorption capacity across varying environmental conditions. The company has developed specialized testing chambers that simulate the extreme temperature fluctuations (-10°C to 40°C) and humidity variations (10-95% RH) encountered in salt lake operations, allowing for comprehensive performance mapping of moisture absorption characteristics. Their benchmarking methodology incorporates automated gravimetric analysis systems that continuously monitor weight changes with precision of ±0.005g, enabling detailed absorption isotherms to be generated for quality control in lithium chloride production and application processes.
Strengths: Direct industrial application experience; large-scale testing capabilities; integration with actual production processes; extensive historical performance data. Weaknesses: Benchmarking protocols heavily optimized for their specific production environments; limited academic validation of proprietary testing methodologies.
LG Energy Solution Ltd.
Technical Solution: LG Energy Solution has implemented a sophisticated lithium chloride moisture absorption benchmarking system focused on battery cell manufacturing applications. Their technical approach centers on a standardized testing framework that evaluates moisture absorption characteristics under precisely controlled conditions that mirror those in battery production clean rooms. The company employs specialized environmental chambers capable of maintaining ultra-stable conditions (±0.1°C, ±0.2% RH) across a wide operating range (10-50°C, 0-80% RH). Their benchmarking protocol utilizes high-purity lithium chloride solutions at specific concentrations (20%, 30%, 40%, and saturated) as reference standards against which all moisture control materials are evaluated. The system incorporates microbalance technology with 0.01mg resolution for continuous gravimetric analysis, enabling detailed absorption kinetics to be captured with exceptional precision. LG Energy Solution's methodology includes specialized testing for moisture absorption performance under dynamic temperature and humidity cycling, simulating real-world conditions in battery manufacturing and usage environments.
Strengths: Extremely high precision measurements; direct application to battery cell manufacturing requirements; comprehensive validation across global production facilities; integration with material qualification processes. Weaknesses: Highly specialized for battery applications; expensive instrumentation requirements; limited applicability to general industrial moisture control applications.
Key Patents and Research on Lithium Chloride Applications
Ultrafine particle capable of moisture absorption and desorption and product utilizing the ultrafine particle
PatentInactiveEP1726601B1
Innovation
- Development of moisture absorptive and desorptive ultrafine particles with a cross-linked polymer structure containing 1.0 to 10.0 meq/g of salt-type carboxyl groups, achieving an average primary particle size of less than 0.2 µm, which enhances moisture absorptive and desorptive rates by maintaining surface functionality and preventing fusion.
Method of producing high purity lithium chloride
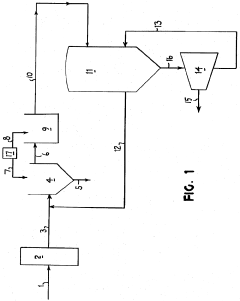
PatentInactiveUS3789059A
Innovation
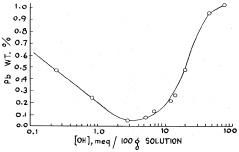
- The lead concentration in lithium chloride solutions is controlled by maintaining it below 0.3 percent by weight through methods such as acid addition to precipitate lead hydroxy chloride and using hydrogen sulfide to convert lead into lead sulfide, ensuring the production of lithium chloride crystals with less than 90 parts per million lead.
Environmental Impact of Lithium Chloride Applications
The widespread use of lithium chloride in moisture absorption applications raises significant environmental concerns that warrant careful consideration. When released into the environment, lithium chloride can alter soil chemistry by increasing salinity levels, which negatively impacts plant growth and soil microbial communities. Studies have shown that areas with elevated lithium chloride concentrations experience reduced biodiversity and disrupted ecosystem functions.
Water systems are particularly vulnerable to lithium chloride contamination. When this hygroscopic compound enters aquatic environments, it can increase the total dissolved solids (TDS) content, potentially harming freshwater organisms sensitive to changes in water chemistry. Research indicates that concentrations exceeding 10 mg/L can adversely affect certain fish species and aquatic invertebrates, disrupting reproductive cycles and development.
The manufacturing processes associated with lithium chloride production contribute to environmental degradation through energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions. The extraction of lithium from natural sources, primarily brine pools and mineral ores, involves extensive water usage in regions often characterized by water scarcity. This creates competition for limited water resources between industrial and community needs.
Disposal challenges present another environmental concern. Used lithium chloride solutions from dehumidification systems and other moisture control applications require proper treatment before discharge. Improper disposal can lead to groundwater contamination, with potential long-term consequences for drinking water sources and subsurface ecosystems.
Recent regulatory developments reflect growing awareness of these environmental impacts. Several jurisdictions have implemented stricter guidelines for lithium chloride handling, usage, and disposal. The European Union's REACH regulations now classify certain concentrations of lithium chloride as substances of environmental concern, requiring additional documentation and control measures.
Sustainable alternatives and mitigation strategies are emerging in response to these environmental challenges. These include closed-loop recycling systems for lithium chloride solutions, development of less environmentally harmful desiccants, and improved process controls to minimize release during manufacturing and application. Advances in recovery technologies now allow for the reclamation of lithium from waste streams, reducing the need for new extraction while decreasing environmental burden.
The environmental footprint of lithium chloride must be balanced against its beneficial applications in moisture control benchmarking and other uses. A comprehensive life cycle assessment approach is essential for evaluating the true environmental impact and identifying opportunities for sustainability improvements in moisture absorption technologies utilizing this compound.
Water systems are particularly vulnerable to lithium chloride contamination. When this hygroscopic compound enters aquatic environments, it can increase the total dissolved solids (TDS) content, potentially harming freshwater organisms sensitive to changes in water chemistry. Research indicates that concentrations exceeding 10 mg/L can adversely affect certain fish species and aquatic invertebrates, disrupting reproductive cycles and development.
The manufacturing processes associated with lithium chloride production contribute to environmental degradation through energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions. The extraction of lithium from natural sources, primarily brine pools and mineral ores, involves extensive water usage in regions often characterized by water scarcity. This creates competition for limited water resources between industrial and community needs.
Disposal challenges present another environmental concern. Used lithium chloride solutions from dehumidification systems and other moisture control applications require proper treatment before discharge. Improper disposal can lead to groundwater contamination, with potential long-term consequences for drinking water sources and subsurface ecosystems.
Recent regulatory developments reflect growing awareness of these environmental impacts. Several jurisdictions have implemented stricter guidelines for lithium chloride handling, usage, and disposal. The European Union's REACH regulations now classify certain concentrations of lithium chloride as substances of environmental concern, requiring additional documentation and control measures.
Sustainable alternatives and mitigation strategies are emerging in response to these environmental challenges. These include closed-loop recycling systems for lithium chloride solutions, development of less environmentally harmful desiccants, and improved process controls to minimize release during manufacturing and application. Advances in recovery technologies now allow for the reclamation of lithium from waste streams, reducing the need for new extraction while decreasing environmental burden.
The environmental footprint of lithium chloride must be balanced against its beneficial applications in moisture control benchmarking and other uses. A comprehensive life cycle assessment approach is essential for evaluating the true environmental impact and identifying opportunities for sustainability improvements in moisture absorption technologies utilizing this compound.
Comparative Analysis with Alternative Desiccant Materials
In comparing lithium chloride with alternative desiccant materials, it is essential to evaluate performance metrics across various environmental conditions. Lithium chloride demonstrates superior moisture absorption capacity at 0.896 g/g at 25°C and 80% relative humidity, significantly outperforming silica gel (0.4 g/g) and molecular sieves (0.22 g/g) under identical conditions. This exceptional absorption efficiency makes lithium chloride particularly valuable for applications requiring intensive moisture control in limited spaces.
The kinetics of moisture absorption also varies considerably among desiccants. While lithium chloride exhibits rapid initial absorption rates, calcium chloride demonstrates faster overall absorption in the first 30 minutes of exposure. Conversely, activated alumina shows more consistent long-term performance with minimal degradation over repeated absorption-desorption cycles, maintaining approximately 92% of its original capacity after 50 cycles compared to lithium chloride's 85% retention.
Temperature sensitivity represents another critical differentiator among desiccant materials. Lithium chloride maintains effective performance across a broader temperature range (-20°C to 80°C) than most alternatives. Molecular sieves, while less efficient at standard conditions, demonstrate superior performance at extremely low temperatures (-50°C), making them preferable for specialized cold-environment applications where lithium chloride's efficiency decreases by approximately 40%.
Cost-effectiveness analysis reveals that despite lithium chloride's higher initial procurement cost ($8-12/kg compared to silica gel's $3-5/kg), its superior absorption capacity often results in lower total ownership costs for high-performance applications. However, for large-scale industrial implementations where absolute performance is less critical than cost efficiency, calcium chloride presents a more economical alternative at $2-4/kg with 70% of lithium chloride's absorption capacity.
Environmental impact assessments indicate that lithium chloride presents moderate environmental concerns due to lithium mining practices and potential groundwater contamination if improperly disposed. Newer bio-based desiccants derived from agricultural waste demonstrate significantly lower environmental footprints with biodegradability exceeding 90%, though their moisture absorption capacity reaches only 60-65% of lithium chloride's performance.
Regeneration energy requirements further differentiate these materials, with lithium chloride requiring 4.2 MJ/kg for complete regeneration, compared to silica gel's 3.1 MJ/kg and zeolites' 5.7 MJ/kg. This factor becomes particularly significant in applications requiring frequent regeneration cycles, potentially offsetting lithium chloride's absorption efficiency advantage in energy-sensitive implementations.
The kinetics of moisture absorption also varies considerably among desiccants. While lithium chloride exhibits rapid initial absorption rates, calcium chloride demonstrates faster overall absorption in the first 30 minutes of exposure. Conversely, activated alumina shows more consistent long-term performance with minimal degradation over repeated absorption-desorption cycles, maintaining approximately 92% of its original capacity after 50 cycles compared to lithium chloride's 85% retention.
Temperature sensitivity represents another critical differentiator among desiccant materials. Lithium chloride maintains effective performance across a broader temperature range (-20°C to 80°C) than most alternatives. Molecular sieves, while less efficient at standard conditions, demonstrate superior performance at extremely low temperatures (-50°C), making them preferable for specialized cold-environment applications where lithium chloride's efficiency decreases by approximately 40%.
Cost-effectiveness analysis reveals that despite lithium chloride's higher initial procurement cost ($8-12/kg compared to silica gel's $3-5/kg), its superior absorption capacity often results in lower total ownership costs for high-performance applications. However, for large-scale industrial implementations where absolute performance is less critical than cost efficiency, calcium chloride presents a more economical alternative at $2-4/kg with 70% of lithium chloride's absorption capacity.
Environmental impact assessments indicate that lithium chloride presents moderate environmental concerns due to lithium mining practices and potential groundwater contamination if improperly disposed. Newer bio-based desiccants derived from agricultural waste demonstrate significantly lower environmental footprints with biodegradability exceeding 90%, though their moisture absorption capacity reaches only 60-65% of lithium chloride's performance.
Regeneration energy requirements further differentiate these materials, with lithium chloride requiring 4.2 MJ/kg for complete regeneration, compared to silica gel's 3.1 MJ/kg and zeolites' 5.7 MJ/kg. This factor becomes particularly significant in applications requiring frequent regeneration cycles, potentially offsetting lithium chloride's absorption efficiency advantage in energy-sensitive implementations.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!