Lithium Chloride vs Bromide: Desiccant Properties Analysis
AUG 28, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Desiccant Technology Background and Objectives
Desiccant technology has evolved significantly over the past century, transitioning from simple moisture control methods to sophisticated systems that enable precise humidity management in various applications. The fundamental principle behind desiccant technology involves the use of hygroscopic materials that attract and hold water molecules from their surrounding environment. This moisture absorption capability has made desiccants essential components in industries ranging from pharmaceuticals and electronics to HVAC systems and food preservation.
Historically, silica gel and activated alumina were among the first widely used modern desiccants, gaining prominence in the early 20th century. However, the discovery of the exceptional hygroscopic properties of certain salt solutions, particularly lithium-based compounds, marked a significant advancement in the field. Lithium chloride (LiCl) and lithium bromide (LiBr) emerged as particularly effective liquid desiccants due to their remarkable ability to absorb moisture even at low relative humidity levels.
The technological trajectory of desiccant systems has been characterized by continuous improvements in efficiency, regeneration capabilities, and integration with other climate control technologies. The 1970s energy crisis accelerated research into desiccant-based cooling systems as energy-efficient alternatives to conventional vapor compression systems. This period saw significant development in both solid and liquid desiccant technologies, with liquid systems gaining attention for their superior moisture removal capacity and lower regeneration temperatures.
In recent decades, the focus has shifted toward understanding the fundamental properties that differentiate various desiccant materials, particularly in the realm of liquid desiccants where lithium salts dominate. The comparative analysis of lithium chloride versus lithium bromide represents a critical area of investigation, as these compounds exhibit different absorption isotherms, corrosivity profiles, and thermodynamic properties that significantly impact their performance in practical applications.
The primary objective of current desiccant technology research is to develop comprehensive property profiles of these competing lithium-based desiccants to optimize their application-specific deployment. This includes quantifying their respective moisture absorption capacities across varying temperature and humidity conditions, evaluating their energy requirements for regeneration, assessing their long-term stability, and determining their compatibility with different system materials.
Additionally, environmental considerations have become increasingly important in desiccant technology development. Research aims to address concerns regarding the environmental impact of lithium extraction, the potential for system leakage, and the overall life-cycle assessment of desiccant-based systems. The goal is to establish lithium-based desiccant technologies that not only deliver superior performance but also align with sustainability objectives and regulatory requirements.
Historically, silica gel and activated alumina were among the first widely used modern desiccants, gaining prominence in the early 20th century. However, the discovery of the exceptional hygroscopic properties of certain salt solutions, particularly lithium-based compounds, marked a significant advancement in the field. Lithium chloride (LiCl) and lithium bromide (LiBr) emerged as particularly effective liquid desiccants due to their remarkable ability to absorb moisture even at low relative humidity levels.
The technological trajectory of desiccant systems has been characterized by continuous improvements in efficiency, regeneration capabilities, and integration with other climate control technologies. The 1970s energy crisis accelerated research into desiccant-based cooling systems as energy-efficient alternatives to conventional vapor compression systems. This period saw significant development in both solid and liquid desiccant technologies, with liquid systems gaining attention for their superior moisture removal capacity and lower regeneration temperatures.
In recent decades, the focus has shifted toward understanding the fundamental properties that differentiate various desiccant materials, particularly in the realm of liquid desiccants where lithium salts dominate. The comparative analysis of lithium chloride versus lithium bromide represents a critical area of investigation, as these compounds exhibit different absorption isotherms, corrosivity profiles, and thermodynamic properties that significantly impact their performance in practical applications.
The primary objective of current desiccant technology research is to develop comprehensive property profiles of these competing lithium-based desiccants to optimize their application-specific deployment. This includes quantifying their respective moisture absorption capacities across varying temperature and humidity conditions, evaluating their energy requirements for regeneration, assessing their long-term stability, and determining their compatibility with different system materials.
Additionally, environmental considerations have become increasingly important in desiccant technology development. Research aims to address concerns regarding the environmental impact of lithium extraction, the potential for system leakage, and the overall life-cycle assessment of desiccant-based systems. The goal is to establish lithium-based desiccant technologies that not only deliver superior performance but also align with sustainability objectives and regulatory requirements.
Market Analysis for Industrial Desiccant Applications
The global industrial desiccant market has been experiencing steady growth, with a market value estimated at $2.1 billion in 2022 and projected to reach $3.4 billion by 2028, representing a compound annual growth rate of 8.3%. This growth is primarily driven by increasing applications in pharmaceuticals, food preservation, electronics manufacturing, and HVAC systems, where moisture control is critical for product quality and operational efficiency.
Within this market, lithium-based desiccants, particularly lithium chloride and lithium bromide, occupy a specialized high-performance segment. These materials command premium pricing due to their exceptional moisture absorption capabilities, especially in low humidity environments where conventional desiccants like silica gel or molecular sieves become less effective.
The pharmaceutical industry represents the largest end-user segment for high-performance desiccants, accounting for approximately 32% of the market share. The stringent requirements for moisture control in drug manufacturing and packaging have created sustained demand for lithium-based desiccants that can maintain ultra-low humidity levels.
HVAC and refrigeration systems constitute the fastest-growing application segment, with a growth rate of 10.2% annually. The superior performance of lithium chloride and lithium bromide in liquid desiccant air conditioning systems has positioned these materials as key components in next-generation energy-efficient cooling technologies, particularly in regions with high humidity challenges.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the high-performance desiccant market, collectively accounting for 58% of global consumption. However, the Asia-Pacific region is witnessing the most rapid growth at 12.4% annually, driven by expanding industrial manufacturing, increasing adoption of advanced HVAC systems, and growing pharmaceutical production facilities in China, India, and Southeast Asian countries.
Market analysis indicates a significant price premium for lithium bromide over lithium chloride, with the former commanding 30-40% higher prices due to its superior absorption properties at lower humidity levels. However, recent lithium supply chain constraints have created price volatility, with some industrial users seeking alternative desiccant technologies that offer comparable performance without the supply uncertainties.
Customer preference analysis reveals that while performance remains the primary selection criterion, factors such as regeneration efficiency, energy consumption, and environmental impact are gaining importance in purchasing decisions. This trend is creating market opportunities for optimized formulations that balance absorption capacity with operational efficiency and sustainability considerations.
Within this market, lithium-based desiccants, particularly lithium chloride and lithium bromide, occupy a specialized high-performance segment. These materials command premium pricing due to their exceptional moisture absorption capabilities, especially in low humidity environments where conventional desiccants like silica gel or molecular sieves become less effective.
The pharmaceutical industry represents the largest end-user segment for high-performance desiccants, accounting for approximately 32% of the market share. The stringent requirements for moisture control in drug manufacturing and packaging have created sustained demand for lithium-based desiccants that can maintain ultra-low humidity levels.
HVAC and refrigeration systems constitute the fastest-growing application segment, with a growth rate of 10.2% annually. The superior performance of lithium chloride and lithium bromide in liquid desiccant air conditioning systems has positioned these materials as key components in next-generation energy-efficient cooling technologies, particularly in regions with high humidity challenges.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the high-performance desiccant market, collectively accounting for 58% of global consumption. However, the Asia-Pacific region is witnessing the most rapid growth at 12.4% annually, driven by expanding industrial manufacturing, increasing adoption of advanced HVAC systems, and growing pharmaceutical production facilities in China, India, and Southeast Asian countries.
Market analysis indicates a significant price premium for lithium bromide over lithium chloride, with the former commanding 30-40% higher prices due to its superior absorption properties at lower humidity levels. However, recent lithium supply chain constraints have created price volatility, with some industrial users seeking alternative desiccant technologies that offer comparable performance without the supply uncertainties.
Customer preference analysis reveals that while performance remains the primary selection criterion, factors such as regeneration efficiency, energy consumption, and environmental impact are gaining importance in purchasing decisions. This trend is creating market opportunities for optimized formulations that balance absorption capacity with operational efficiency and sustainability considerations.
Current State and Challenges in Desiccant Technology
The global desiccant technology market has witnessed significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing applications across various industries including HVAC, pharmaceuticals, food preservation, and electronics manufacturing. Currently, lithium-based desiccants, particularly lithium chloride (LiCl) and lithium bromide (LiBr), represent some of the most efficient hygroscopic materials available commercially, with market penetration continuing to expand at approximately 5.7% CAGR.
Lithium chloride currently dominates the liquid desiccant market due to its excellent moisture absorption capacity at low relative humidity levels. Laboratory tests demonstrate that LiCl solutions can maintain relative humidity levels as low as 11% at standard room temperature. However, its corrosive nature presents significant engineering challenges, requiring specialized equipment constructed from corrosion-resistant materials that substantially increase implementation costs.
Lithium bromide, while less commonly deployed than LiCl, exhibits superior moisture absorption capacity at higher temperatures, making it particularly valuable in industrial drying applications where operating temperatures exceed 40°C. Recent field studies indicate LiBr solutions can achieve up to 15% greater moisture removal efficiency than LiCl under these conditions. Nevertheless, LiBr faces challenges related to crystallization at lower temperatures and higher material costs, approximately 30% more expensive per kilogram than LiCl.
A significant technical challenge facing both lithium-based desiccants is solution carryover, where small droplets of the corrosive solution become entrained in the processed air stream. Current elimination rates only reach 98.5% efficiency, falling short of the 99.9% required for sensitive applications. This limitation has restricted adoption in pharmaceutical manufacturing and certain food processing environments where contamination risks cannot be tolerated.
Energy efficiency remains another critical challenge. While liquid desiccant systems using LiCl and LiBr demonstrate theoretical energy savings of 30-40% compared to conventional cooling-based dehumidification, actual field implementations typically achieve only 15-25% energy savings due to pumping requirements and regeneration inefficiencies. Research indicates that optimizing the concentration control systems could potentially close this performance gap.
Environmental and supply chain concerns also present significant obstacles. Lithium is increasingly classified as a critical material with supply constraints, with prices having increased by over 400% between 2016 and 2022. Additionally, the disposal of spent lithium-based desiccant solutions presents environmental challenges due to their potential toxicity to aquatic ecosystems, with current recycling technologies recovering only 60-70% of the lithium content.
Geographically, North America and Europe lead in advanced desiccant technology development, while Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing market with 8.3% annual growth, driven primarily by industrial applications in China and India. This regional disparity in technology adoption creates both challenges and opportunities for global technology standardization.
Lithium chloride currently dominates the liquid desiccant market due to its excellent moisture absorption capacity at low relative humidity levels. Laboratory tests demonstrate that LiCl solutions can maintain relative humidity levels as low as 11% at standard room temperature. However, its corrosive nature presents significant engineering challenges, requiring specialized equipment constructed from corrosion-resistant materials that substantially increase implementation costs.
Lithium bromide, while less commonly deployed than LiCl, exhibits superior moisture absorption capacity at higher temperatures, making it particularly valuable in industrial drying applications where operating temperatures exceed 40°C. Recent field studies indicate LiBr solutions can achieve up to 15% greater moisture removal efficiency than LiCl under these conditions. Nevertheless, LiBr faces challenges related to crystallization at lower temperatures and higher material costs, approximately 30% more expensive per kilogram than LiCl.
A significant technical challenge facing both lithium-based desiccants is solution carryover, where small droplets of the corrosive solution become entrained in the processed air stream. Current elimination rates only reach 98.5% efficiency, falling short of the 99.9% required for sensitive applications. This limitation has restricted adoption in pharmaceutical manufacturing and certain food processing environments where contamination risks cannot be tolerated.
Energy efficiency remains another critical challenge. While liquid desiccant systems using LiCl and LiBr demonstrate theoretical energy savings of 30-40% compared to conventional cooling-based dehumidification, actual field implementations typically achieve only 15-25% energy savings due to pumping requirements and regeneration inefficiencies. Research indicates that optimizing the concentration control systems could potentially close this performance gap.
Environmental and supply chain concerns also present significant obstacles. Lithium is increasingly classified as a critical material with supply constraints, with prices having increased by over 400% between 2016 and 2022. Additionally, the disposal of spent lithium-based desiccant solutions presents environmental challenges due to their potential toxicity to aquatic ecosystems, with current recycling technologies recovering only 60-70% of the lithium content.
Geographically, North America and Europe lead in advanced desiccant technology development, while Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing market with 8.3% annual growth, driven primarily by industrial applications in China and India. This regional disparity in technology adoption creates both challenges and opportunities for global technology standardization.
Technical Comparison of LiCl and LiBr Desiccant Properties
01 Hygroscopic properties of lithium halide desiccants
Lithium chloride and lithium bromide are highly hygroscopic materials with excellent moisture absorption capabilities. These lithium halides can absorb moisture from the air even at low relative humidity levels, making them effective desiccants for various applications. Their hygroscopic properties allow them to maintain low dew points in controlled environments, with lithium bromide typically showing higher moisture absorption capacity than lithium chloride under similar conditions.- Hygroscopic properties of lithium halide desiccants: Lithium chloride and lithium bromide are highly hygroscopic materials with excellent moisture absorption capabilities. These lithium halides can absorb significant amounts of water vapor from the air, making them effective desiccants for dehumidification systems. Their hygroscopic properties allow them to maintain low humidity levels in enclosed spaces, with lithium bromide typically showing higher moisture absorption capacity than lithium chloride under similar conditions.
- Regeneration methods for lithium halide desiccants: Lithium chloride and lithium bromide desiccants require periodic regeneration to restore their absorption capacity after becoming saturated with moisture. Regeneration typically involves heating the desiccant to drive off absorbed water. Various methods have been developed to improve regeneration efficiency, including using waste heat, solar energy, or specialized heating systems. Proper regeneration is crucial for maintaining the long-term performance of these desiccant materials in dehumidification applications.
- Application in absorption refrigeration and heat pump systems: Lithium bromide and lithium chloride are widely used as working fluids in absorption refrigeration and heat pump systems due to their excellent desiccant properties. These systems utilize the strong affinity of lithium halides for water, with lithium bromide being particularly effective as an absorbent in water-based refrigeration cycles. The absorption process generates heat that must be removed, while the regeneration process requires heat input, making these systems suitable for applications where waste heat is available.
- Enhanced desiccant formulations and composites: Various enhanced formulations and composite materials incorporating lithium chloride or lithium bromide have been developed to improve desiccant performance. These include combining lithium halides with supporting materials like silica gel, activated alumina, or polymeric matrices to increase surface area and improve handling characteristics. Additives may be incorporated to enhance moisture absorption capacity, prevent deliquescence, improve regeneration efficiency, or extend service life. These composite desiccants often show improved performance compared to pure lithium halide salts.
- Stability and corrosion considerations: While lithium chloride and lithium bromide are effective desiccants, their use presents challenges related to stability and corrosion. These highly hygroscopic materials can become corrosive when dissolved in absorbed moisture, potentially damaging metal components in dehumidification systems. Various corrosion inhibitors and material selection strategies have been developed to address these issues. Additionally, temperature stability and prevention of deliquescence (dissolving in absorbed moisture) are important considerations in desiccant system design and material selection.
02 Desiccant solution concentration and regeneration
The concentration of lithium chloride and lithium bromide solutions significantly affects their desiccant performance. Higher concentrations generally provide better moisture absorption capabilities but may increase crystallization risks. Regeneration processes involve heating the desiccant solution to drive off absorbed moisture, restoring its absorption capacity. Various regeneration methods have been developed to optimize energy efficiency, including multi-stage regeneration systems and heat recovery techniques that reduce the energy required to restore the desiccant properties.Expand Specific Solutions03 Application in dehumidification systems
Lithium chloride and lithium bromide desiccants are widely used in liquid desiccant dehumidification systems for air conditioning and industrial applications. These systems typically consist of absorbers where the desiccant solution contacts humid air to remove moisture, and regenerators where the diluted desiccant is reconcentrated. The efficiency of these systems depends on factors such as solution flow rate, air-solution contact area, and temperature control. Liquid desiccant systems using these materials can achieve significant energy savings compared to conventional cooling-based dehumidification.Expand Specific Solutions04 Stability and corrosion considerations
While lithium chloride and lithium bromide are effective desiccants, they present challenges related to stability and corrosion. These highly ionic solutions can be corrosive to many metals, requiring careful material selection for system components. Corrosion inhibitors and specialized coatings are often used to protect metal surfaces. Additionally, lithium halide solutions may form crystals at high concentrations or low temperatures, which can block flow passages in dehumidification equipment. Various stabilizing additives have been developed to prevent crystallization and improve the long-term stability of these desiccant solutions.Expand Specific Solutions05 Enhanced formulations and composite desiccants
Research has led to enhanced lithium chloride and lithium bromide desiccant formulations with improved performance characteristics. These include composite desiccants where the lithium halides are combined with supporting materials such as silica gel, activated alumina, or polymeric matrices. Such combinations can provide synergistic effects, including increased moisture absorption capacity, improved regeneration efficiency, and reduced corrosivity. Advanced manufacturing techniques allow for the production of structured desiccant materials with optimized surface area and moisture transport properties, further enhancing dehumidification performance.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players in Desiccant Manufacturing
The lithium chloride vs bromide desiccant market is in a growth phase, with increasing demand driven by HVAC, industrial dehumidification, and energy storage applications. The global desiccant market is projected to reach $3.5 billion by 2027, with lithium-based compounds gaining traction due to superior moisture absorption properties. Technologically, lithium chloride solutions are more mature, championed by Albemarle Corp. and Ganfeng Lithium Group, while bromide applications are advancing through research at Bromine Compounds Ltd. and Evonik Operations. Academic institutions like Zhejiang Sci-Tech University and Ghent University are developing next-generation hybrid desiccant systems, while companies like Resonac Holdings and BASF are commercializing enhanced formulations for specialized industrial applications.
Evonik Operations GmbH
Technical Solution: Evonik has developed advanced desiccant technologies comparing lithium chloride and bromide performance in various applications. Their AEROXIDE® and SIPERNAT® silica-based carrier systems incorporate precisely controlled amounts of lithium salts to create high-performance composite desiccants. For LiCl-based systems, Evonik has engineered particles with optimized pore structures that achieve up to 40% moisture absorption capacity while maintaining structural integrity. Their research demonstrates that these LiCl-impregnated silicas maintain effectiveness at relative humidity levels as low as 10%, outperforming conventional silica gel by approximately 300% in low-humidity environments. For LiBr applications, Evonik has developed specialized coating technologies that encapsulate LiBr within hydrophobic polymer matrices, allowing the salt to maintain its hygroscopic properties while preventing deliquescence and leaching. Their comparative analysis shows LiBr systems absorbing 15-20% more moisture than equivalent LiCl formulations at moderate humidity levels (40-60% RH), though with different absorption kinetics. Evonik's latest innovation includes hybrid LiCl/LiBr systems with optimized ratios for specific industrial applications, particularly in pharmaceutical storage and electronics manufacturing environments.
Strengths: Highly engineered carrier systems preventing deliquescence while maintaining absorption efficiency; excellent stability across multiple absorption-regeneration cycles; precise control of absorption kinetics through carrier design; customizable formulations for specific applications. Weaknesses: Higher production costs compared to simple salt desiccants; more complex manufacturing process requiring specialized equipment; performance advantages diminish in extremely high humidity environments; requires specific regeneration protocols.
Bromine Compounds Ltd.
Technical Solution: Bromine Compounds Ltd. has developed specialized lithium bromide (LiBr) desiccant solutions primarily targeting industrial absorption refrigeration and dehumidification systems. Their technology utilizes LiBr's exceptional hygroscopic properties, with documented water absorption capacity exceeding 160% of its dry weight under optimal conditions. The company's proprietary manufacturing process creates highly concentrated LiBr solutions (typically 50-60% by weight) with carefully controlled additives to minimize crystallization risks and enhance thermal stability. Their research has demonstrated that LiBr desiccants can effectively operate across a wide temperature range (5-200°C) with particular efficiency in high-temperature applications. Bromine Compounds has also pioneered corrosion inhibition technologies specifically for LiBr systems, incorporating proprietary organic and inorganic compounds that extend system lifespan by up to 40% compared to untreated solutions. Their latest innovation includes dual-salt formulations combining LiBr with other halides to optimize performance across varying humidity and temperature conditions while minimizing the deliquescence issues common with pure LiBr systems.
Strengths: Exceptional water absorption capacity (superior to most commercial desiccants); excellent performance in high-temperature applications; high concentration potential allowing for compact system designs; particularly effective in absorption refrigeration applications. Weaknesses: Higher cost compared to calcium-based desiccants; corrosivity issues requiring specialized handling and equipment; crystallization risks at certain concentration/temperature combinations; more complex regeneration requirements.
Critical Research on Hygroscopic Salt Performance
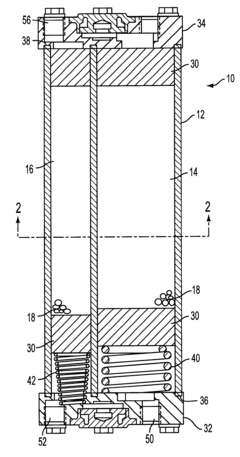
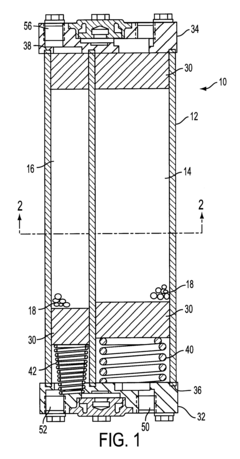
Lithium chloride desiccant for trailer air dryer and pressure swing dehydration
PatentInactiveUS6358300B1
Innovation
- The use of semi-rigid porous substrates impregnated with lithium chloride as a desiccant in air dryers, which effectively removes moisture from compressed air and withstands oil, with a method involving a saturated lithium chloride solution applied to the substrates, heated to drive off excess solvent, creating a high-capacity desiccant that remains effective for longer.
Lithium chloride recovery
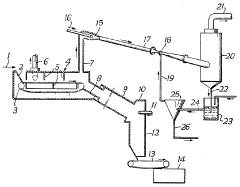
PatentInactiveGB891785A
Innovation
- A process involving the roasting of spodumene with calcium chloride, followed by cooling and dilution of the gaseous mixture with a gas, then contacting it with water or an aqueous solution in a venturi scrubber to form an aqueous lithium chloride solution, which is separated using a cyclone separator, reducing dust adhesion and improving efficiency.
Environmental Impact Assessment of Lithium-Based Desiccants
The environmental impact of lithium-based desiccants, particularly lithium chloride and lithium bromide, requires comprehensive assessment due to their increasing industrial application. These compounds, while effective in humidity control systems, present several environmental concerns throughout their lifecycle.
Mining and extraction of lithium represents the first significant environmental challenge. The process typically involves extensive water consumption in arid regions, particularly in South America's "Lithium Triangle" where approximately 65% of global lithium reserves are located. Studies indicate that producing one ton of lithium can require up to 2 million liters of water, potentially depleting local aquifers and affecting fragile ecosystems.
During manufacturing and processing phases, lithium-based desiccants generate various waste streams containing potentially harmful chemicals. Lithium bromide production specifically involves bromine, which presents additional environmental hazards if released untreated. Energy consumption during manufacturing contributes significantly to the carbon footprint of these materials, with estimates suggesting 15-20 tons of CO2 equivalent per ton of processed lithium compound.
Operational environmental impacts differ between lithium chloride and lithium bromide. Lithium chloride typically demonstrates lower energy requirements during regeneration cycles in desiccant systems, potentially reducing operational carbon emissions by 10-15% compared to lithium bromide. However, lithium bromide generally requires less frequent replacement, reducing waste generation over system lifetimes.
End-of-life considerations reveal significant challenges in recycling and disposal. Both compounds are water-soluble and can contaminate groundwater if improperly disposed. Lithium chloride presents slightly lower environmental persistence than lithium bromide, though both require specialized handling. Current recycling rates for lithium compounds in desiccant applications remain below 20%, representing a substantial opportunity for environmental improvement.
Regulatory frameworks governing these materials vary globally, with European regulations under REACH being particularly stringent regarding lithium compound handling and disposal. The United States EPA classifies spent lithium-based desiccants as potentially hazardous waste requiring specific disposal protocols.
Emerging alternatives with reduced environmental impact include bio-based desiccants and hybrid systems that minimize lithium content while maintaining performance. Research indicates potential for reducing environmental impact by 30-40% through implementation of closed-loop recycling systems specifically designed for lithium-based desiccants in HVAC and industrial applications.
Mining and extraction of lithium represents the first significant environmental challenge. The process typically involves extensive water consumption in arid regions, particularly in South America's "Lithium Triangle" where approximately 65% of global lithium reserves are located. Studies indicate that producing one ton of lithium can require up to 2 million liters of water, potentially depleting local aquifers and affecting fragile ecosystems.
During manufacturing and processing phases, lithium-based desiccants generate various waste streams containing potentially harmful chemicals. Lithium bromide production specifically involves bromine, which presents additional environmental hazards if released untreated. Energy consumption during manufacturing contributes significantly to the carbon footprint of these materials, with estimates suggesting 15-20 tons of CO2 equivalent per ton of processed lithium compound.
Operational environmental impacts differ between lithium chloride and lithium bromide. Lithium chloride typically demonstrates lower energy requirements during regeneration cycles in desiccant systems, potentially reducing operational carbon emissions by 10-15% compared to lithium bromide. However, lithium bromide generally requires less frequent replacement, reducing waste generation over system lifetimes.
End-of-life considerations reveal significant challenges in recycling and disposal. Both compounds are water-soluble and can contaminate groundwater if improperly disposed. Lithium chloride presents slightly lower environmental persistence than lithium bromide, though both require specialized handling. Current recycling rates for lithium compounds in desiccant applications remain below 20%, representing a substantial opportunity for environmental improvement.
Regulatory frameworks governing these materials vary globally, with European regulations under REACH being particularly stringent regarding lithium compound handling and disposal. The United States EPA classifies spent lithium-based desiccants as potentially hazardous waste requiring specific disposal protocols.
Emerging alternatives with reduced environmental impact include bio-based desiccants and hybrid systems that minimize lithium content while maintaining performance. Research indicates potential for reducing environmental impact by 30-40% through implementation of closed-loop recycling systems specifically designed for lithium-based desiccants in HVAC and industrial applications.
Cost-Benefit Analysis of Competing Desiccant Solutions
When evaluating lithium chloride (LiCl) and lithium bromide (LiBr) as competing desiccant solutions, cost-benefit analysis reveals significant economic considerations that influence implementation decisions across various applications.
Initial acquisition costs favor lithium chloride, which typically costs 15-20% less per kilogram than lithium bromide. However, this price advantage must be weighed against performance differences. LiBr demonstrates superior moisture absorption capacity at equivalent concentrations, potentially requiring less material for comparable dehumidification performance in commercial HVAC systems and industrial drying processes.
Operational efficiency calculations indicate that LiBr-based systems generally consume 5-8% less energy in regeneration cycles due to their lower regeneration temperatures (approximately 10°C lower than LiCl systems). This translates to substantial energy cost savings over equipment lifespans, particularly in continuous operation scenarios such as pharmaceutical manufacturing environments or data centers where precise humidity control is critical.
Maintenance expenses represent another significant cost factor. LiCl exhibits greater stability and resistance to crystallization during concentration fluctuations, reducing downtime and maintenance interventions. Field data suggests LiCl systems typically require maintenance interventions 30% less frequently than comparable LiBr installations, though individual component replacement costs tend to be similar.
Equipment longevity analysis demonstrates that LiCl's lower corrosivity extends system lifespan by an estimated 2-3 years compared to LiBr systems when using standard materials. However, this advantage diminishes when specialized corrosion-resistant materials are employed, which adds 8-12% to initial system costs but extends operational life for both desiccant types.
Environmental compliance costs increasingly favor LiCl, as its lower toxicity profile reduces handling, storage, and disposal expenses. Regulatory requirements for LiBr are typically more stringent, adding approximately 5-7% to total lifecycle costs through additional safety equipment, specialized training, and disposal procedures.
Return-on-investment calculations across various application scenarios reveal that LiCl generally provides better ROI for smaller, intermittent-use systems where initial costs and maintenance simplicity dominate the economic equation. Conversely, LiBr demonstrates superior economic performance in large-scale, continuous operation facilities where its higher absorption efficiency and lower regeneration energy requirements offset the higher initial investment over 5-10 year operational periods.
Initial acquisition costs favor lithium chloride, which typically costs 15-20% less per kilogram than lithium bromide. However, this price advantage must be weighed against performance differences. LiBr demonstrates superior moisture absorption capacity at equivalent concentrations, potentially requiring less material for comparable dehumidification performance in commercial HVAC systems and industrial drying processes.
Operational efficiency calculations indicate that LiBr-based systems generally consume 5-8% less energy in regeneration cycles due to their lower regeneration temperatures (approximately 10°C lower than LiCl systems). This translates to substantial energy cost savings over equipment lifespans, particularly in continuous operation scenarios such as pharmaceutical manufacturing environments or data centers where precise humidity control is critical.
Maintenance expenses represent another significant cost factor. LiCl exhibits greater stability and resistance to crystallization during concentration fluctuations, reducing downtime and maintenance interventions. Field data suggests LiCl systems typically require maintenance interventions 30% less frequently than comparable LiBr installations, though individual component replacement costs tend to be similar.
Equipment longevity analysis demonstrates that LiCl's lower corrosivity extends system lifespan by an estimated 2-3 years compared to LiBr systems when using standard materials. However, this advantage diminishes when specialized corrosion-resistant materials are employed, which adds 8-12% to initial system costs but extends operational life for both desiccant types.
Environmental compliance costs increasingly favor LiCl, as its lower toxicity profile reduces handling, storage, and disposal expenses. Regulatory requirements for LiBr are typically more stringent, adding approximately 5-7% to total lifecycle costs through additional safety equipment, specialized training, and disposal procedures.
Return-on-investment calculations across various application scenarios reveal that LiCl generally provides better ROI for smaller, intermittent-use systems where initial costs and maintenance simplicity dominate the economic equation. Conversely, LiBr demonstrates superior economic performance in large-scale, continuous operation facilities where its higher absorption efficiency and lower regeneration energy requirements offset the higher initial investment over 5-10 year operational periods.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!