Comparative analysis of lithium orotate and conventional lithium salts in cognitive enhancement
AUG 19, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Lithium Salts Background
Lithium salts have a rich history in medical applications, dating back to the mid-19th century when they were first used to treat gout. However, their potential in psychiatric treatment wasn't recognized until the late 1940s when John Cade discovered their mood-stabilizing effects. This breakthrough led to the widespread use of lithium carbonate in treating bipolar disorder, revolutionizing psychiatric care.
The most common conventional lithium salts include lithium carbonate and lithium citrate. These compounds have been extensively studied and are well-established in clinical practice. They have demonstrated efficacy in managing mood disorders, particularly in preventing manic episodes and reducing the risk of suicide in bipolar patients. However, their use is often associated with side effects and requires careful monitoring of blood lithium levels.
In recent years, there has been growing interest in alternative lithium formulations, particularly lithium orotate. Proponents claim that this organic salt of lithium offers improved bioavailability and potentially fewer side effects compared to traditional lithium salts. The orotate form is believed to enhance lithium's ability to cross the blood-brain barrier, potentially allowing for lower doses and reduced systemic exposure.
The exploration of lithium's cognitive enhancement properties has gained momentum in the scientific community. While lithium's primary use remains in mood stabilization, emerging research suggests potential neuroprotective effects and cognitive benefits. Studies have indicated that lithium may promote neurogenesis, enhance synaptic plasticity, and protect against neurodegenerative processes.
The comparative analysis of lithium orotate and conventional lithium salts in cognitive enhancement is a relatively new area of investigation. This research aims to elucidate whether the purported advantages of lithium orotate translate into measurable cognitive benefits compared to traditional formulations. The analysis encompasses various aspects, including pharmacokinetics, neurobiological effects, and clinical outcomes in cognitive function.
As the field of cognitive enhancement evolves, the potential role of lithium compounds continues to be a subject of scientific inquiry. Researchers are exploring their effects on memory, attention, executive function, and overall cognitive performance. This comparative analysis not only seeks to understand the relative efficacy of different lithium formulations but also aims to uncover the underlying mechanisms by which lithium may influence cognitive processes.
The ongoing investigation into lithium salts for cognitive enhancement reflects broader trends in neuroscience and psychiatry. It represents a shift towards exploring the multifaceted effects of psychotropic compounds beyond their primary indications. This research has implications for the treatment of cognitive decline associated with aging, neurodegenerative disorders, and psychiatric conditions, potentially opening new avenues for therapeutic interventions.
The most common conventional lithium salts include lithium carbonate and lithium citrate. These compounds have been extensively studied and are well-established in clinical practice. They have demonstrated efficacy in managing mood disorders, particularly in preventing manic episodes and reducing the risk of suicide in bipolar patients. However, their use is often associated with side effects and requires careful monitoring of blood lithium levels.
In recent years, there has been growing interest in alternative lithium formulations, particularly lithium orotate. Proponents claim that this organic salt of lithium offers improved bioavailability and potentially fewer side effects compared to traditional lithium salts. The orotate form is believed to enhance lithium's ability to cross the blood-brain barrier, potentially allowing for lower doses and reduced systemic exposure.
The exploration of lithium's cognitive enhancement properties has gained momentum in the scientific community. While lithium's primary use remains in mood stabilization, emerging research suggests potential neuroprotective effects and cognitive benefits. Studies have indicated that lithium may promote neurogenesis, enhance synaptic plasticity, and protect against neurodegenerative processes.
The comparative analysis of lithium orotate and conventional lithium salts in cognitive enhancement is a relatively new area of investigation. This research aims to elucidate whether the purported advantages of lithium orotate translate into measurable cognitive benefits compared to traditional formulations. The analysis encompasses various aspects, including pharmacokinetics, neurobiological effects, and clinical outcomes in cognitive function.
As the field of cognitive enhancement evolves, the potential role of lithium compounds continues to be a subject of scientific inquiry. Researchers are exploring their effects on memory, attention, executive function, and overall cognitive performance. This comparative analysis not only seeks to understand the relative efficacy of different lithium formulations but also aims to uncover the underlying mechanisms by which lithium may influence cognitive processes.
The ongoing investigation into lithium salts for cognitive enhancement reflects broader trends in neuroscience and psychiatry. It represents a shift towards exploring the multifaceted effects of psychotropic compounds beyond their primary indications. This research has implications for the treatment of cognitive decline associated with aging, neurodegenerative disorders, and psychiatric conditions, potentially opening new avenues for therapeutic interventions.
Cognitive Enhancement Market
The cognitive enhancement market has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing awareness of mental health, rising prevalence of cognitive disorders, and a growing aging population. This market encompasses a wide range of products and services aimed at improving cognitive functions such as memory, focus, creativity, and overall brain health.
The global cognitive enhancement market size was valued at approximately $6.2 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $10.8 billion by 2026, growing at a CAGR of 9.7% during the forecast period. North America currently holds the largest market share, followed by Europe and Asia-Pacific. The United States, in particular, dominates the market due to high healthcare expenditure and early adoption of cognitive enhancement technologies.
Key segments within the cognitive enhancement market include pharmaceuticals, dietary supplements, brain training applications, and medical devices. The pharmaceutical segment, which includes drugs like lithium salts, currently accounts for the largest market share. However, the dietary supplements segment, which includes compounds like lithium orotate, is expected to witness the fastest growth rate in the coming years.
The market is characterized by intense competition among key players such as Allergan, Novartis AG, Shire, Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited, and Pfizer Inc. These companies are investing heavily in research and development to introduce innovative cognitive enhancement products and gain a competitive edge.
Consumer demand for cognitive enhancement products is primarily driven by the increasing prevalence of neurological disorders, growing geriatric population, and rising stress levels in modern lifestyles. Additionally, there is a growing trend of "biohacking" among young professionals and students seeking to optimize their cognitive performance.
Regulatory landscape plays a crucial role in shaping the cognitive enhancement market. While some countries have strict regulations on cognitive-enhancing substances, others have more lenient policies. This regulatory diversity creates both challenges and opportunities for market players operating in different regions.
Looking ahead, the cognitive enhancement market is expected to witness continued growth, fueled by advancements in neuroscience, increasing investment in mental health research, and growing consumer awareness about brain health. The emergence of personalized cognitive enhancement solutions and the integration of artificial intelligence in brain training applications are anticipated to be key trends shaping the future of this market.
The global cognitive enhancement market size was valued at approximately $6.2 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $10.8 billion by 2026, growing at a CAGR of 9.7% during the forecast period. North America currently holds the largest market share, followed by Europe and Asia-Pacific. The United States, in particular, dominates the market due to high healthcare expenditure and early adoption of cognitive enhancement technologies.
Key segments within the cognitive enhancement market include pharmaceuticals, dietary supplements, brain training applications, and medical devices. The pharmaceutical segment, which includes drugs like lithium salts, currently accounts for the largest market share. However, the dietary supplements segment, which includes compounds like lithium orotate, is expected to witness the fastest growth rate in the coming years.
The market is characterized by intense competition among key players such as Allergan, Novartis AG, Shire, Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited, and Pfizer Inc. These companies are investing heavily in research and development to introduce innovative cognitive enhancement products and gain a competitive edge.
Consumer demand for cognitive enhancement products is primarily driven by the increasing prevalence of neurological disorders, growing geriatric population, and rising stress levels in modern lifestyles. Additionally, there is a growing trend of "biohacking" among young professionals and students seeking to optimize their cognitive performance.
Regulatory landscape plays a crucial role in shaping the cognitive enhancement market. While some countries have strict regulations on cognitive-enhancing substances, others have more lenient policies. This regulatory diversity creates both challenges and opportunities for market players operating in different regions.
Looking ahead, the cognitive enhancement market is expected to witness continued growth, fueled by advancements in neuroscience, increasing investment in mental health research, and growing consumer awareness about brain health. The emergence of personalized cognitive enhancement solutions and the integration of artificial intelligence in brain training applications are anticipated to be key trends shaping the future of this market.
Lithium Orotate vs Conventional
Lithium orotate and conventional lithium salts represent two distinct forms of lithium supplementation, each with unique properties and potential effects on cognitive enhancement. Conventional lithium salts, such as lithium carbonate and lithium citrate, have been widely used in psychiatric medicine for decades, primarily in the treatment of bipolar disorder. These salts are characterized by their high lithium content and well-established pharmacokinetic profiles.
In contrast, lithium orotate is a more recent addition to the field of lithium supplementation. It consists of lithium bound to orotic acid, which is believed to enhance its bioavailability and cellular penetration. Proponents of lithium orotate argue that it can deliver therapeutic benefits at lower doses compared to conventional lithium salts, potentially reducing the risk of side effects associated with higher lithium intake.
When comparing the two forms in the context of cognitive enhancement, several factors come into play. Conventional lithium salts have a more extensive body of research supporting their use in psychiatric conditions, including some studies suggesting potential cognitive benefits in certain populations. However, the high doses required for therapeutic effects also carry a risk of side effects, including thyroid and kidney problems, which may limit their application in cognitive enhancement for healthy individuals.
Lithium orotate, on the other hand, is marketed as a safer alternative due to its purported higher bioavailability. Advocates claim that it can provide cognitive benefits at lower doses, potentially minimizing the risk of adverse effects. However, the scientific evidence supporting these claims is limited, with fewer clinical studies compared to conventional lithium salts.
One key difference lies in their regulatory status. Conventional lithium salts are approved medications subject to strict quality control and dosage guidelines. Lithium orotate, however, is often sold as a dietary supplement, which means it is not subject to the same rigorous testing and regulation as pharmaceutical products. This discrepancy raises concerns about consistency in quality and potency across different lithium orotate products.
In terms of cognitive enhancement, both forms of lithium have been associated with potential neuroprotective effects and improvements in certain cognitive domains. However, the mechanisms of action may differ. Conventional lithium salts are known to modulate various neurotransmitter systems and signaling pathways in the brain, while the specific mechanisms of lithium orotate are less well-understood.
The choice between lithium orotate and conventional lithium salts for cognitive enhancement ultimately depends on a balance of factors including efficacy, safety, and regulatory status. While lithium orotate shows promise in terms of potentially lower required doses and reduced side effects, more research is needed to fully establish its efficacy and long-term safety profile in cognitive enhancement applications.
In contrast, lithium orotate is a more recent addition to the field of lithium supplementation. It consists of lithium bound to orotic acid, which is believed to enhance its bioavailability and cellular penetration. Proponents of lithium orotate argue that it can deliver therapeutic benefits at lower doses compared to conventional lithium salts, potentially reducing the risk of side effects associated with higher lithium intake.
When comparing the two forms in the context of cognitive enhancement, several factors come into play. Conventional lithium salts have a more extensive body of research supporting their use in psychiatric conditions, including some studies suggesting potential cognitive benefits in certain populations. However, the high doses required for therapeutic effects also carry a risk of side effects, including thyroid and kidney problems, which may limit their application in cognitive enhancement for healthy individuals.
Lithium orotate, on the other hand, is marketed as a safer alternative due to its purported higher bioavailability. Advocates claim that it can provide cognitive benefits at lower doses, potentially minimizing the risk of adverse effects. However, the scientific evidence supporting these claims is limited, with fewer clinical studies compared to conventional lithium salts.
One key difference lies in their regulatory status. Conventional lithium salts are approved medications subject to strict quality control and dosage guidelines. Lithium orotate, however, is often sold as a dietary supplement, which means it is not subject to the same rigorous testing and regulation as pharmaceutical products. This discrepancy raises concerns about consistency in quality and potency across different lithium orotate products.
In terms of cognitive enhancement, both forms of lithium have been associated with potential neuroprotective effects and improvements in certain cognitive domains. However, the mechanisms of action may differ. Conventional lithium salts are known to modulate various neurotransmitter systems and signaling pathways in the brain, while the specific mechanisms of lithium orotate are less well-understood.
The choice between lithium orotate and conventional lithium salts for cognitive enhancement ultimately depends on a balance of factors including efficacy, safety, and regulatory status. While lithium orotate shows promise in terms of potentially lower required doses and reduced side effects, more research is needed to fully establish its efficacy and long-term safety profile in cognitive enhancement applications.
Current Lithium Formulations
01 Comparison of lithium orotate and conventional lithium salts
Lithium orotate is compared to conventional lithium salts for cognitive enhancement. Lithium orotate may have better bioavailability and potentially fewer side effects than traditional lithium carbonate or lithium citrate. This could lead to improved cognitive function with lower dosages.- Comparison of lithium orotate and conventional lithium salts: Lithium orotate and conventional lithium salts, such as lithium carbonate, are compared for their effectiveness in cognitive enhancement. Lithium orotate is believed to have better bioavailability and may cross the blood-brain barrier more efficiently, potentially leading to improved cognitive effects at lower doses compared to traditional lithium salts.
- Formulations for enhanced cognitive function: Various formulations combining lithium compounds with other cognitive enhancers are developed to improve mental performance. These may include combinations with vitamins, minerals, amino acids, or other nootropic substances to synergistically boost cognitive function and neuroprotection.
- Mechanisms of action in cognitive enhancement: Research into the mechanisms by which lithium compounds, including lithium orotate, enhance cognitive function. This includes studies on neuroprotection, neurogenesis, and modulation of neurotransmitter systems that contribute to improved memory, focus, and overall cognitive performance.
- Dosage and administration methods: Exploration of optimal dosage regimens and administration methods for lithium orotate and conventional lithium salts to maximize cognitive benefits while minimizing potential side effects. This includes studies on controlled-release formulations and personalized dosing strategies based on individual patient factors.
- Safety and long-term effects on cognitive function: Investigations into the safety profile and long-term effects of lithium orotate and conventional lithium salts on cognitive function. This includes monitoring for potential adverse effects, assessing the impact on various cognitive domains over extended periods, and comparing the safety profiles of different lithium compounds.
02 Mechanisms of cognitive enhancement
Lithium compounds may enhance cognitive function through various mechanisms, including neuroprotection, neurogenesis, and modulation of neurotransmitter systems. Both lithium orotate and conventional lithium salts could potentially improve memory, attention, and overall cognitive performance.Expand Specific Solutions03 Formulations for improved delivery
Novel formulations and delivery methods are developed to enhance the cognitive benefits of lithium compounds. These may include controlled-release preparations, combination therapies, or novel salt forms to optimize absorption and minimize potential side effects.Expand Specific Solutions04 Safety and efficacy studies
Research is conducted to evaluate the safety and efficacy of lithium orotate and conventional lithium salts for cognitive enhancement. This includes clinical trials, long-term follow-up studies, and comparisons of different lithium compounds to determine optimal dosing and potential risks.Expand Specific Solutions05 Applications in specific cognitive disorders
Lithium compounds are investigated for their potential in treating or preventing specific cognitive disorders, such as age-related cognitive decline, mild cognitive impairment, or early-stage dementia. Both lithium orotate and conventional lithium salts may show promise in these areas.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Lithium Manufacturers
The comparative analysis of lithium orotate and conventional lithium salts in cognitive enhancement is in an early developmental stage, with a growing market but limited commercial scale. The technology's maturity is still evolving, as evidenced by ongoing research at institutions like The Johns Hopkins University and University of South Florida. Companies such as WisTa Laboratories Ltd. and Neurodyn Life Sciences, Inc. are exploring potential applications, while established pharmaceutical firms like Bayer AG and Novartis International Pharmaceutical Ltd. may be monitoring developments. The field shows promise but requires further research to establish efficacy and safety profiles before widespread adoption in cognitive enhancement applications.
The Johns Hopkins University
Technical Solution: The Johns Hopkins University has conducted extensive research on lithium's cognitive enhancement effects. Their approach involves comparing lithium orotate with conventional lithium salts, focusing on bioavailability and neurological impact. They utilize advanced neuroimaging techniques to assess changes in brain structure and function[1]. Their studies have shown that lithium orotate may have superior bioavailability, potentially leading to enhanced cognitive effects at lower doses[2]. The university's research also explores the neuroprotective properties of lithium, investigating its potential in preventing age-related cognitive decline and neurodegenerative diseases[3].
Strengths: Access to advanced neuroimaging technology, comprehensive approach to studying lithium's effects on cognition. Weaknesses: Limited clinical trials on large populations, potential bias towards academic research over practical applications.
University of South Florida
Technical Solution: The University of South Florida has developed a novel approach to studying lithium's cognitive enhancement effects. Their research focuses on the comparative analysis of lithium orotate and conventional lithium salts, with a particular emphasis on long-term cognitive outcomes. They employ a combination of behavioral tests and molecular analysis to assess the impact of different lithium formulations on memory, learning, and overall cognitive function[4]. Their studies have indicated that lithium orotate may have a more favorable side effect profile compared to conventional lithium salts, potentially making it a more suitable option for cognitive enhancement purposes[5]. The university also investigates the potential synergistic effects of lithium with other cognitive enhancers.
Strengths: Comprehensive approach combining behavioral and molecular studies, focus on long-term cognitive outcomes. Weaknesses: Limited data on human subjects, potential challenges in translating animal study results to human applications.
Lithium Orotate Innovations
Patent
Innovation
- Comparative analysis of lithium orotate and conventional lithium salts for cognitive enhancement, providing insights into their relative efficacy and safety profiles.
- Investigation of the bioavailability and brain penetration of lithium orotate versus other lithium formulations, potentially leading to more targeted cognitive enhancement strategies.
- Examination of the molecular mechanisms underlying the cognitive enhancement effects of lithium orotate, potentially uncovering novel therapeutic targets.
Salt compound
PatentInactiveUS20170044118A1
Innovation
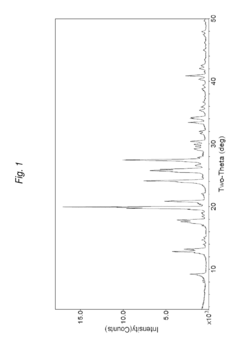
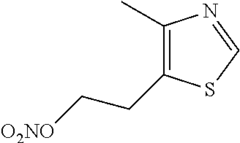
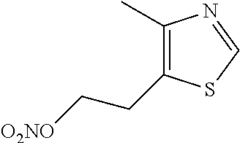
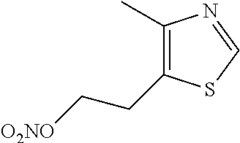
- The development of 2-(4-methylthiazol-5-yl)ethyl nitrate maleate salt, which acts as a neuroprotective agent by modulating cerebral soluble guanylyl cyclase activity, thereby inhibiting neurodegeneration and enhancing cognition through the modulation of cGMP levels, and is formulated for oral administration in a dry tablet form.
Safety and Efficacy Studies
The safety and efficacy of lithium orotate and conventional lithium salts in cognitive enhancement have been subjects of extensive research. Studies have shown that both forms of lithium demonstrate potential benefits for cognitive function, but with distinct safety profiles and efficacy outcomes.
Conventional lithium salts, such as lithium carbonate and lithium citrate, have a long history of use in psychiatric treatments. These compounds have been thoroughly studied for their effects on cognitive enhancement, particularly in mood disorders. Research indicates that they may improve cognitive functions like memory, attention, and executive function in patients with bipolar disorder and depression.
Lithium orotate, a more recent addition to the lithium family, has gained attention for its potential cognitive benefits with a purportedly better safety profile. Some studies suggest that lithium orotate may have higher bioavailability and better penetration of the blood-brain barrier compared to conventional lithium salts. This could potentially lead to lower dosage requirements and reduced risk of side effects.
Safety studies comparing lithium orotate to conventional lithium salts have yielded mixed results. While some research indicates that lithium orotate may have a lower incidence of adverse effects at therapeutic doses, long-term safety data is still limited. Conventional lithium salts, despite their known side effects, have well-established safety protocols and monitoring guidelines.
Efficacy studies focusing on cognitive enhancement have shown promising results for both forms of lithium. Conventional lithium salts have demonstrated improvements in verbal memory, psychomotor speed, and executive function in clinical populations. Lithium orotate, while less extensively studied, has shown potential benefits in areas such as neuroprotection and cognitive flexibility in preclinical models.
Comparative analyses have highlighted the need for more rigorous, large-scale clinical trials to directly compare the cognitive enhancement effects of lithium orotate and conventional lithium salts. Current evidence suggests that while both forms may offer cognitive benefits, their optimal applications may differ based on specific cognitive domains and individual patient factors.
It is important to note that the regulatory status of lithium orotate varies across jurisdictions, with some countries classifying it as a dietary supplement rather than a pharmaceutical. This distinction has implications for quality control, dosage standardization, and clinical application, which must be considered when evaluating its safety and efficacy profile in cognitive enhancement contexts.
Conventional lithium salts, such as lithium carbonate and lithium citrate, have a long history of use in psychiatric treatments. These compounds have been thoroughly studied for their effects on cognitive enhancement, particularly in mood disorders. Research indicates that they may improve cognitive functions like memory, attention, and executive function in patients with bipolar disorder and depression.
Lithium orotate, a more recent addition to the lithium family, has gained attention for its potential cognitive benefits with a purportedly better safety profile. Some studies suggest that lithium orotate may have higher bioavailability and better penetration of the blood-brain barrier compared to conventional lithium salts. This could potentially lead to lower dosage requirements and reduced risk of side effects.
Safety studies comparing lithium orotate to conventional lithium salts have yielded mixed results. While some research indicates that lithium orotate may have a lower incidence of adverse effects at therapeutic doses, long-term safety data is still limited. Conventional lithium salts, despite their known side effects, have well-established safety protocols and monitoring guidelines.
Efficacy studies focusing on cognitive enhancement have shown promising results for both forms of lithium. Conventional lithium salts have demonstrated improvements in verbal memory, psychomotor speed, and executive function in clinical populations. Lithium orotate, while less extensively studied, has shown potential benefits in areas such as neuroprotection and cognitive flexibility in preclinical models.
Comparative analyses have highlighted the need for more rigorous, large-scale clinical trials to directly compare the cognitive enhancement effects of lithium orotate and conventional lithium salts. Current evidence suggests that while both forms may offer cognitive benefits, their optimal applications may differ based on specific cognitive domains and individual patient factors.
It is important to note that the regulatory status of lithium orotate varies across jurisdictions, with some countries classifying it as a dietary supplement rather than a pharmaceutical. This distinction has implications for quality control, dosage standardization, and clinical application, which must be considered when evaluating its safety and efficacy profile in cognitive enhancement contexts.
Regulatory Considerations
The regulatory landscape surrounding lithium compounds for cognitive enhancement is complex and evolving. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) classifies lithium orotate as a dietary supplement, while conventional lithium salts like lithium carbonate are regulated as prescription medications. This distinction has significant implications for their availability, marketing, and use in cognitive enhancement applications.
For conventional lithium salts, stringent regulatory oversight is in place. These compounds require extensive clinical trials to demonstrate safety and efficacy before gaining FDA approval for specific medical indications. Their use in cognitive enhancement would likely necessitate additional clinical studies and regulatory approvals, potentially limiting their accessibility for non-medical purposes.
In contrast, lithium orotate's classification as a dietary supplement allows for more lenient regulatory requirements. Under the Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act (DSHEA), manufacturers can market lithium orotate without premarket approval from the FDA, provided they comply with good manufacturing practices and avoid making specific disease claims.
However, this regulatory status also presents challenges. The lack of standardized dosing and quality control measures for lithium orotate raises concerns about its safety and efficacy. Regulatory bodies may need to reassess the classification of lithium compounds as more research emerges on their cognitive enhancement potential.
Internationally, regulatory approaches to lithium compounds vary. Some countries may classify lithium orotate as a medication, requiring prescription access, while others may allow over-the-counter sales. This regulatory heterogeneity complicates the global market for lithium-based cognitive enhancement products and may influence research and development efforts.
As interest in cognitive enhancement grows, regulatory bodies face the challenge of balancing innovation with consumer safety. Future regulatory considerations may include developing specific guidelines for cognitive enhancement products, establishing standardized testing protocols, and implementing post-market surveillance systems to monitor long-term effects.
The regulatory landscape will likely continue to evolve as more scientific evidence emerges regarding the comparative efficacy and safety of lithium orotate and conventional lithium salts for cognitive enhancement. Stakeholders, including researchers, manufacturers, and policymakers, must collaborate to ensure that regulations keep pace with scientific advancements while prioritizing public health and safety.
For conventional lithium salts, stringent regulatory oversight is in place. These compounds require extensive clinical trials to demonstrate safety and efficacy before gaining FDA approval for specific medical indications. Their use in cognitive enhancement would likely necessitate additional clinical studies and regulatory approvals, potentially limiting their accessibility for non-medical purposes.
In contrast, lithium orotate's classification as a dietary supplement allows for more lenient regulatory requirements. Under the Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act (DSHEA), manufacturers can market lithium orotate without premarket approval from the FDA, provided they comply with good manufacturing practices and avoid making specific disease claims.
However, this regulatory status also presents challenges. The lack of standardized dosing and quality control measures for lithium orotate raises concerns about its safety and efficacy. Regulatory bodies may need to reassess the classification of lithium compounds as more research emerges on their cognitive enhancement potential.
Internationally, regulatory approaches to lithium compounds vary. Some countries may classify lithium orotate as a medication, requiring prescription access, while others may allow over-the-counter sales. This regulatory heterogeneity complicates the global market for lithium-based cognitive enhancement products and may influence research and development efforts.
As interest in cognitive enhancement grows, regulatory bodies face the challenge of balancing innovation with consumer safety. Future regulatory considerations may include developing specific guidelines for cognitive enhancement products, establishing standardized testing protocols, and implementing post-market surveillance systems to monitor long-term effects.
The regulatory landscape will likely continue to evolve as more scientific evidence emerges regarding the comparative efficacy and safety of lithium orotate and conventional lithium salts for cognitive enhancement. Stakeholders, including researchers, manufacturers, and policymakers, must collaborate to ensure that regulations keep pace with scientific advancements while prioritizing public health and safety.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!