Comparative study of mild hybrid and plug-in hybrid market dynamics
AUG 18, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Hybrid Tech Evolution
The evolution of hybrid technology has been a significant journey in the automotive industry, marked by continuous innovation and market adaptation. Initially, mild hybrid systems emerged as a cost-effective solution to improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions. These systems typically use a small electric motor to assist the internal combustion engine, primarily during acceleration and deceleration phases.
As technology progressed, plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs) entered the market, offering a more substantial electric-only driving range and greater fuel savings. This evolution represented a significant leap forward in hybrid technology, bridging the gap between conventional hybrids and fully electric vehicles.
The market dynamics between mild hybrids and PHEVs have been shaped by various factors, including consumer preferences, government regulations, and technological advancements. Mild hybrids gained traction due to their lower cost and ease of integration into existing vehicle platforms. They offered a compromise between improved efficiency and minimal changes to driving habits, making them attractive to consumers hesitant about full electrification.
PHEVs, on the other hand, have appealed to consumers seeking more substantial electric driving capabilities without the range anxiety associated with fully electric vehicles. Their ability to operate in pure electric mode for short trips while retaining the flexibility of a gasoline engine for longer journeys has positioned them as a versatile option in the market.
The evolution of battery technology has played a crucial role in the development of both mild hybrids and PHEVs. Advancements in energy density, charging speeds, and cost reduction have enabled manufacturers to offer more capable and affordable hybrid vehicles. This has led to a gradual shift in market preference towards PHEVs, as they offer a more comprehensive electrification experience.
Government policies and environmental regulations have also significantly influenced the trajectory of hybrid technology. Stricter emissions standards and incentives for low-emission vehicles have accelerated the adoption of both mild hybrids and PHEVs. However, the impact has been more pronounced for PHEVs due to their greater potential for emissions reduction and alignment with long-term electrification goals.
As the automotive industry continues to evolve, the distinction between mild hybrids and PHEVs is becoming increasingly blurred. Some manufacturers are developing more advanced mild hybrid systems that offer enhanced electric capabilities, while others are focusing on improving the efficiency and affordability of PHEV technology. This convergence is likely to shape the future market dynamics of hybrid vehicles, potentially leading to a more diverse range of electrification options for consumers.
As technology progressed, plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs) entered the market, offering a more substantial electric-only driving range and greater fuel savings. This evolution represented a significant leap forward in hybrid technology, bridging the gap between conventional hybrids and fully electric vehicles.
The market dynamics between mild hybrids and PHEVs have been shaped by various factors, including consumer preferences, government regulations, and technological advancements. Mild hybrids gained traction due to their lower cost and ease of integration into existing vehicle platforms. They offered a compromise between improved efficiency and minimal changes to driving habits, making them attractive to consumers hesitant about full electrification.
PHEVs, on the other hand, have appealed to consumers seeking more substantial electric driving capabilities without the range anxiety associated with fully electric vehicles. Their ability to operate in pure electric mode for short trips while retaining the flexibility of a gasoline engine for longer journeys has positioned them as a versatile option in the market.
The evolution of battery technology has played a crucial role in the development of both mild hybrids and PHEVs. Advancements in energy density, charging speeds, and cost reduction have enabled manufacturers to offer more capable and affordable hybrid vehicles. This has led to a gradual shift in market preference towards PHEVs, as they offer a more comprehensive electrification experience.
Government policies and environmental regulations have also significantly influenced the trajectory of hybrid technology. Stricter emissions standards and incentives for low-emission vehicles have accelerated the adoption of both mild hybrids and PHEVs. However, the impact has been more pronounced for PHEVs due to their greater potential for emissions reduction and alignment with long-term electrification goals.
As the automotive industry continues to evolve, the distinction between mild hybrids and PHEVs is becoming increasingly blurred. Some manufacturers are developing more advanced mild hybrid systems that offer enhanced electric capabilities, while others are focusing on improving the efficiency and affordability of PHEV technology. This convergence is likely to shape the future market dynamics of hybrid vehicles, potentially leading to a more diverse range of electrification options for consumers.
Market Demand Analysis
The market demand for mild hybrid and plug-in hybrid vehicles has been steadily increasing in recent years, driven by growing environmental concerns, stricter emissions regulations, and advancements in battery technology. Mild hybrid systems, which offer modest fuel economy improvements and reduced emissions at a lower cost, have gained significant traction in the mass-market segment. These systems are particularly popular in regions with less developed charging infrastructure, as they do not require external charging.
Plug-in hybrid vehicles, on the other hand, have seen a surge in demand among consumers seeking greater electric-only driving range and the flexibility of both electric and gasoline powertrains. This technology appeals to urban dwellers and those with access to charging facilities, as it allows for significant reductions in fuel consumption and emissions during daily commutes while retaining the ability to undertake longer journeys without range anxiety.
The market dynamics between mild hybrids and plug-in hybrids vary significantly across different regions. In Europe, stringent CO2 emissions targets have led to a rapid adoption of both technologies, with plug-in hybrids gaining market share due to government incentives and an expanding charging network. In contrast, the North American market has shown a preference for mild hybrid systems in larger vehicles, such as SUVs and trucks, where the technology offers improved fuel economy without compromising performance or utility.
Asian markets, particularly China and Japan, have embraced both mild and plug-in hybrid technologies. China's "New Energy Vehicle" policies have stimulated demand for plug-in hybrids, while Japan's mature hybrid market has seen a gradual shift towards more advanced mild hybrid systems in compact and mid-size vehicles.
The global market size for hybrid vehicles is projected to grow significantly in the coming years. Mild hybrid systems are expected to see widespread adoption across various vehicle segments due to their cost-effectiveness and ease of integration into existing vehicle platforms. Plug-in hybrids are anticipated to experience robust growth in premium and luxury vehicle segments, where higher costs can be more easily absorbed.
Consumer preferences are evolving, with an increasing emphasis on total cost of ownership, environmental impact, and vehicle performance. This shift is driving automakers to offer a diverse range of hybrid options across their product lines. The market is also seeing a trend towards more powerful and efficient hybrid powertrains, blurring the lines between mild and plug-in hybrid technologies.
As battery technology continues to improve and production scales up, the cost differential between mild and plug-in hybrid systems is expected to narrow. This convergence may lead to a more competitive landscape, with consumers having a wider range of choices at various price points. The future market dynamics will likely be shaped by factors such as government policies, advancements in charging infrastructure, and the pace of battery technology development.
Plug-in hybrid vehicles, on the other hand, have seen a surge in demand among consumers seeking greater electric-only driving range and the flexibility of both electric and gasoline powertrains. This technology appeals to urban dwellers and those with access to charging facilities, as it allows for significant reductions in fuel consumption and emissions during daily commutes while retaining the ability to undertake longer journeys without range anxiety.
The market dynamics between mild hybrids and plug-in hybrids vary significantly across different regions. In Europe, stringent CO2 emissions targets have led to a rapid adoption of both technologies, with plug-in hybrids gaining market share due to government incentives and an expanding charging network. In contrast, the North American market has shown a preference for mild hybrid systems in larger vehicles, such as SUVs and trucks, where the technology offers improved fuel economy without compromising performance or utility.
Asian markets, particularly China and Japan, have embraced both mild and plug-in hybrid technologies. China's "New Energy Vehicle" policies have stimulated demand for plug-in hybrids, while Japan's mature hybrid market has seen a gradual shift towards more advanced mild hybrid systems in compact and mid-size vehicles.
The global market size for hybrid vehicles is projected to grow significantly in the coming years. Mild hybrid systems are expected to see widespread adoption across various vehicle segments due to their cost-effectiveness and ease of integration into existing vehicle platforms. Plug-in hybrids are anticipated to experience robust growth in premium and luxury vehicle segments, where higher costs can be more easily absorbed.
Consumer preferences are evolving, with an increasing emphasis on total cost of ownership, environmental impact, and vehicle performance. This shift is driving automakers to offer a diverse range of hybrid options across their product lines. The market is also seeing a trend towards more powerful and efficient hybrid powertrains, blurring the lines between mild and plug-in hybrid technologies.
As battery technology continues to improve and production scales up, the cost differential between mild and plug-in hybrid systems is expected to narrow. This convergence may lead to a more competitive landscape, with consumers having a wider range of choices at various price points. The future market dynamics will likely be shaped by factors such as government policies, advancements in charging infrastructure, and the pace of battery technology development.
Tech Challenges
The comparative study of mild hybrid and plug-in hybrid market dynamics reveals several significant technological challenges that both systems face in their development and adoption. One of the primary challenges for mild hybrid systems is the limited electric-only range, which restricts their ability to operate solely on electric power. This limitation stems from the smaller battery capacity and less powerful electric motors typically used in mild hybrid configurations.
For plug-in hybrid vehicles, a major technological hurdle is the integration of larger battery packs without significantly compromising vehicle weight and interior space. The increased battery size necessary for extended electric-only range often leads to design compromises and higher production costs. Additionally, the complexity of managing two distinct power sources – the internal combustion engine and the electric motor – presents ongoing challenges in terms of system optimization and control strategies.
Both mild and plug-in hybrid systems face challenges related to battery technology. The need for more energy-dense, longer-lasting, and faster-charging batteries is crucial for improving overall system performance and consumer acceptance. Current lithium-ion battery technology, while continuously improving, still falls short of ideal specifications in terms of energy density, charging speed, and lifecycle durability.
Another shared challenge is the development of more efficient power electronics and electric motors. As these components play a critical role in energy conversion and propulsion, advancements in their design and manufacturing are essential for enhancing overall system efficiency and reducing costs. The miniaturization and thermal management of these components remain ongoing areas of research and development.
The integration of regenerative braking systems presents challenges for both mild and plug-in hybrids, particularly in terms of optimizing energy recovery without compromising brake feel and performance. Engineers must balance the desire for maximum energy recuperation with the need for smooth and predictable braking characteristics that meet driver expectations and safety standards.
For plug-in hybrids specifically, the development of efficient and reliable charging infrastructure remains a significant challenge. The need for widespread, fast-charging stations is critical for the broader adoption of these vehicles, especially for consumers who rely on public charging options. The standardization of charging protocols and the implementation of smart grid technologies to manage increased electricity demand are additional hurdles that need to be addressed.
Lastly, both mild and plug-in hybrid systems face challenges related to cost reduction. The additional components required for hybridization, particularly in plug-in systems, contribute to higher vehicle prices compared to conventional internal combustion engine vehicles. Achieving cost parity through economies of scale, improved manufacturing processes, and technological advancements remains a key focus for automakers and suppliers in the hybrid vehicle market.
For plug-in hybrid vehicles, a major technological hurdle is the integration of larger battery packs without significantly compromising vehicle weight and interior space. The increased battery size necessary for extended electric-only range often leads to design compromises and higher production costs. Additionally, the complexity of managing two distinct power sources – the internal combustion engine and the electric motor – presents ongoing challenges in terms of system optimization and control strategies.
Both mild and plug-in hybrid systems face challenges related to battery technology. The need for more energy-dense, longer-lasting, and faster-charging batteries is crucial for improving overall system performance and consumer acceptance. Current lithium-ion battery technology, while continuously improving, still falls short of ideal specifications in terms of energy density, charging speed, and lifecycle durability.
Another shared challenge is the development of more efficient power electronics and electric motors. As these components play a critical role in energy conversion and propulsion, advancements in their design and manufacturing are essential for enhancing overall system efficiency and reducing costs. The miniaturization and thermal management of these components remain ongoing areas of research and development.
The integration of regenerative braking systems presents challenges for both mild and plug-in hybrids, particularly in terms of optimizing energy recovery without compromising brake feel and performance. Engineers must balance the desire for maximum energy recuperation with the need for smooth and predictable braking characteristics that meet driver expectations and safety standards.
For plug-in hybrids specifically, the development of efficient and reliable charging infrastructure remains a significant challenge. The need for widespread, fast-charging stations is critical for the broader adoption of these vehicles, especially for consumers who rely on public charging options. The standardization of charging protocols and the implementation of smart grid technologies to manage increased electricity demand are additional hurdles that need to be addressed.
Lastly, both mild and plug-in hybrid systems face challenges related to cost reduction. The additional components required for hybridization, particularly in plug-in systems, contribute to higher vehicle prices compared to conventional internal combustion engine vehicles. Achieving cost parity through economies of scale, improved manufacturing processes, and technological advancements remains a key focus for automakers and suppliers in the hybrid vehicle market.
Current Hybrid Solutions
01 Market growth and consumer adoption
The mild hybrid and plug-in hybrid vehicle market is experiencing significant growth due to increasing consumer awareness of environmental issues and government incentives. Factors such as improved fuel efficiency, reduced emissions, and lower operating costs are driving adoption. Manufacturers are expanding their hybrid vehicle lineups to meet growing demand across various vehicle segments.- Market growth and consumer adoption: The mild hybrid and plug-in hybrid vehicle market is experiencing significant growth due to increasing consumer awareness of environmental issues and government incentives. Factors such as improved fuel efficiency, reduced emissions, and lower operating costs are driving consumer adoption. Manufacturers are expanding their hybrid vehicle offerings to meet growing demand across various vehicle segments.
- Technological advancements in hybrid powertrains: Ongoing technological improvements in hybrid powertrains are enhancing vehicle performance and efficiency. These advancements include better battery technology, more efficient electric motors, and improved power management systems. Innovations in regenerative braking and energy recovery systems are also contributing to increased range and overall system efficiency in hybrid vehicles.
- Integration of hybrid systems with autonomous driving technologies: The convergence of hybrid powertrain technology with autonomous driving systems is creating new opportunities in the automotive industry. This integration is leading to the development of more efficient and intelligent vehicles that can optimize energy usage based on driving conditions and route planning. The combination of these technologies is expected to further drive market growth and innovation.
- Regulatory environment and government policies: Government regulations and policies play a crucial role in shaping the mild hybrid and plug-in hybrid vehicle market. Stricter emissions standards, tax incentives, and subsidies for hybrid vehicles are influencing both manufacturer strategies and consumer purchasing decisions. The evolving regulatory landscape is driving investment in hybrid technologies and accelerating the transition towards electrified transportation.
- Charging infrastructure development: The expansion of charging infrastructure is a critical factor in the growth of the plug-in hybrid vehicle market. Investments in public and private charging stations, as well as the development of fast-charging technologies, are addressing range anxiety concerns and improving the practicality of plug-in hybrid vehicles for consumers. The availability of charging options is becoming increasingly important in driving market adoption.
02 Technological advancements in hybrid powertrains
Ongoing technological improvements in hybrid powertrains are enhancing performance, efficiency, and reliability. Innovations include advanced battery technologies, more efficient electric motors, and sophisticated power management systems. These advancements are contributing to increased range, faster charging times, and improved overall vehicle performance.Expand Specific Solutions03 Integration of hybrid systems with autonomous driving technologies
The convergence of hybrid powertrain technologies with autonomous driving systems is creating new opportunities in the market. This integration is leading to the development of more efficient and intelligent vehicles, capable of optimizing energy usage and enhancing overall driving experience. The combination of these technologies is expected to play a crucial role in shaping the future of transportation.Expand Specific Solutions04 Charging infrastructure development
The expansion of charging infrastructure is critical for the growth of the plug-in hybrid vehicle market. Investments in public and private charging stations, along with the development of fast-charging technologies, are addressing range anxiety concerns and improving the practicality of plug-in hybrid vehicles for everyday use. This infrastructure development is key to accelerating market adoption.Expand Specific Solutions05 Regulatory landscape and environmental policies
Government regulations and environmental policies play a significant role in shaping the mild hybrid and plug-in hybrid vehicle market. Stricter emissions standards, tax incentives, and subsidies are driving manufacturers to invest in hybrid technologies. These policies are influencing consumer behavior and accelerating the transition towards more sustainable transportation options.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The comparative study of mild hybrid and plug-in hybrid market dynamics reveals a complex competitive landscape. The industry is in a transitional phase, with both technologies gaining traction as automakers seek to meet stringent emissions regulations. The global market size for hybrid vehicles is expanding rapidly, driven by increasing environmental awareness and government incentives. Technologically, mild hybrids are more mature and widely adopted, offering a cost-effective solution for manufacturers like Hyundai, Kia, and GM. However, plug-in hybrids, championed by companies such as BYD and Geely, are advancing quickly, offering greater electric-only range and fuel efficiency. The competition is intensifying as traditional automakers and new entrants like Huawei and Chery Automobile vie for market share in this evolving sector.
Hyundai Motor Co., Ltd.
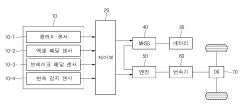
Technical Solution: Hyundai has developed a comprehensive strategy for both mild hybrid and plug-in hybrid vehicles. Their mild hybrid system, often referred to as 48V technology, is integrated into various models to improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions. The system includes a 48V lithium-ion battery, a mild hybrid starter-generator (MHSG), and a low voltage DC/DC converter[1]. For plug-in hybrids, Hyundai utilizes a parallel hybrid system with a high-capacity battery that allows for extended electric-only driving range. Their PHEV models, such as the Ioniq and Santa Fe, typically offer 30-50 km of electric range[2]. Hyundai's hybrid technology focuses on seamless integration of electric and combustion powertrains, with advanced power management systems to optimize efficiency across various driving conditions.
Strengths: Wide range of hybrid offerings, from mild to plug-in, catering to different consumer needs. Advanced integration of electric and combustion systems. Weaknesses: Electric-only range in PHEVs still limited compared to some competitors. Mild hybrid system benefits may be less noticeable to consumers compared to full hybrids.
GM Global Technology Operations LLC
Technical Solution: General Motors has invested heavily in both mild hybrid and plug-in hybrid technologies. Their mild hybrid system, eAssist, uses a 24V lithium-ion battery and a motor-generator unit to provide electric assist and regenerative braking[3]. This system is designed to improve fuel economy without significantly increasing vehicle cost. For plug-in hybrids, GM's Voltec powertrain, used in the Chevrolet Volt and other models, combines a high-capacity lithium-ion battery with a range-extending gasoline engine. The latest generation offers up to 85 km of electric-only range[4]. GM's approach focuses on flexibility, allowing for all-electric operation for daily commutes while providing extended range capabilities for longer trips.
Strengths: Pioneering Voltec PHEV technology with significant electric-only range. Cost-effective mild hybrid solution. Weaknesses: Limited deployment of mild hybrid technology across model range. PHEV offerings less diverse than some competitors.
Core Hybrid Innovations
Mild hybrid vehicle and method of mild hybrid vehicle
PatentPendingKR1020220008436A
Innovation
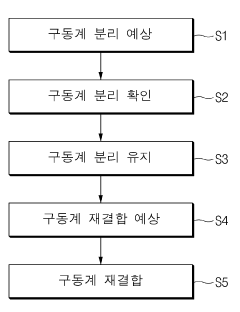
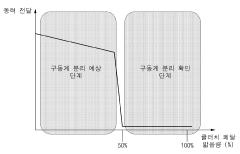
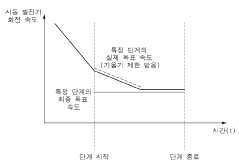
- A mild hybrid vehicle system with a sensor unit and control unit that detects driver intentions and controls the Mild Hybrid Starter & Generator (MHSG) to manage engine rpm and shaft synchronization, including steps for drive system separation, maintenance, and reconnection to optimize fuel efficiency and reduce vibrations.
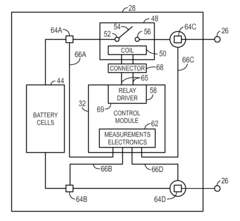
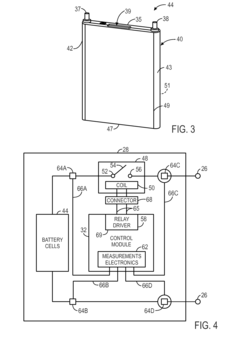
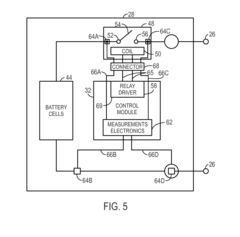
Integrated connector having sense and switching conductors for a relay used in a battery module
PatentActiveUS20160093456A1
Innovation
- Relays with internal connections on both sides of their switches are used in conjunction with a connector that integrates switch control lines with sensing conductors, allowing these lines to be routed together, reducing the number of separate connections and eliminating external sensing conductor connections.
Regulatory Landscape
The regulatory landscape for mild hybrid and plug-in hybrid vehicles has been evolving rapidly in recent years, significantly influencing market dynamics. Governments worldwide have implemented various policies and regulations to promote the adoption of these technologies, aiming to reduce carbon emissions and improve fuel efficiency in the transportation sector.
In the European Union, stringent CO2 emission standards have been a key driver for the adoption of hybrid technologies. The EU has set a target of 95g CO2/km for new passenger cars by 2021, with further reductions planned for 2025 and 2030. These regulations have incentivized automakers to invest heavily in hybrid technologies, particularly mild hybrids, as a cost-effective way to meet these targets.
China, the world's largest automotive market, has also implemented policies favoring hybrid vehicles. The country's dual-credit policy, which came into effect in 2018, rewards manufacturers for producing new energy vehicles, including plug-in hybrids. This has led to a surge in plug-in hybrid offerings in the Chinese market.
In the United States, the regulatory landscape is more complex due to the interplay between federal and state-level policies. While federal fuel economy standards have been a driving force for hybrid adoption, individual states like California have implemented their own, more stringent regulations. The California Air Resources Board (CARB) has set ambitious targets for zero-emission vehicle sales, which has indirectly boosted the market for plug-in hybrids as a transitional technology.
Tax incentives and subsidies have played a crucial role in shaping the market dynamics for hybrid vehicles. Many countries offer tax credits or rebates for the purchase of plug-in hybrid vehicles, making them more attractive to consumers. However, these incentives are often less generous for mild hybrids, which has influenced consumer preferences and market segmentation.
The regulatory landscape has also impacted the technological development of hybrid systems. For instance, the shift towards more stringent real-world driving emissions tests in Europe has led to the development of more sophisticated mild hybrid systems that can operate in electric-only mode for short distances.
Looking ahead, the regulatory landscape is expected to continue evolving, with a general trend towards stricter emissions standards and increased support for electrification. This is likely to further shape the market dynamics of mild hybrid and plug-in hybrid vehicles, potentially accelerating the transition towards fully electric vehicles in the long term.
In the European Union, stringent CO2 emission standards have been a key driver for the adoption of hybrid technologies. The EU has set a target of 95g CO2/km for new passenger cars by 2021, with further reductions planned for 2025 and 2030. These regulations have incentivized automakers to invest heavily in hybrid technologies, particularly mild hybrids, as a cost-effective way to meet these targets.
China, the world's largest automotive market, has also implemented policies favoring hybrid vehicles. The country's dual-credit policy, which came into effect in 2018, rewards manufacturers for producing new energy vehicles, including plug-in hybrids. This has led to a surge in plug-in hybrid offerings in the Chinese market.
In the United States, the regulatory landscape is more complex due to the interplay between federal and state-level policies. While federal fuel economy standards have been a driving force for hybrid adoption, individual states like California have implemented their own, more stringent regulations. The California Air Resources Board (CARB) has set ambitious targets for zero-emission vehicle sales, which has indirectly boosted the market for plug-in hybrids as a transitional technology.
Tax incentives and subsidies have played a crucial role in shaping the market dynamics for hybrid vehicles. Many countries offer tax credits or rebates for the purchase of plug-in hybrid vehicles, making them more attractive to consumers. However, these incentives are often less generous for mild hybrids, which has influenced consumer preferences and market segmentation.
The regulatory landscape has also impacted the technological development of hybrid systems. For instance, the shift towards more stringent real-world driving emissions tests in Europe has led to the development of more sophisticated mild hybrid systems that can operate in electric-only mode for short distances.
Looking ahead, the regulatory landscape is expected to continue evolving, with a general trend towards stricter emissions standards and increased support for electrification. This is likely to further shape the market dynamics of mild hybrid and plug-in hybrid vehicles, potentially accelerating the transition towards fully electric vehicles in the long term.
Environmental Impact
The environmental impact of mild hybrid and plug-in hybrid vehicles is a crucial factor in their market dynamics. Both technologies aim to reduce emissions and improve fuel efficiency, but their approaches and outcomes differ significantly.
Mild hybrid systems, which use a small electric motor to assist the internal combustion engine, offer modest improvements in fuel economy and emissions reduction. These systems typically achieve a 10-15% reduction in CO2 emissions compared to conventional vehicles. The primary environmental benefit comes from improved efficiency in urban driving conditions, where frequent starts and stops allow for energy recuperation through regenerative braking.
Plug-in hybrid vehicles, on the other hand, have a more substantial environmental impact. With larger battery packs and the ability to run on electric power alone for short distances, plug-in hybrids can significantly reduce tailpipe emissions. When operating in electric mode, these vehicles produce zero direct emissions, potentially reducing local air pollution in urban areas. Studies have shown that plug-in hybrids can reduce CO2 emissions by 30-60% compared to conventional vehicles, depending on driving patterns and electricity sources.
However, the full environmental impact of plug-in hybrids depends heavily on the source of electricity used for charging. In regions with clean energy grids, the overall emissions reduction can be substantial. Conversely, in areas reliant on coal-fired power plants, the net environmental benefit may be less pronounced.
The production of batteries for both mild and plug-in hybrids also carries environmental considerations. The mining and processing of materials like lithium and cobalt have ecological implications, including habitat disruption and water usage. Plug-in hybrids, with their larger battery packs, have a more significant production-related environmental footprint than mild hybrids.
End-of-life considerations also play a role in the environmental impact assessment. The recycling and disposal of hybrid vehicle batteries present both challenges and opportunities. Advancements in battery recycling technologies are crucial for minimizing the long-term environmental impact of hybrid vehicles.
In terms of market dynamics, the perceived environmental benefits of hybrid vehicles significantly influence consumer choices and regulatory policies. Governments worldwide are implementing stricter emissions standards and offering incentives for low-emission vehicles, which has accelerated the adoption of both mild and plug-in hybrid technologies. The varying degrees of environmental impact between these two hybrid types are reflected in different levels of government support and consumer acceptance across markets.
Mild hybrid systems, which use a small electric motor to assist the internal combustion engine, offer modest improvements in fuel economy and emissions reduction. These systems typically achieve a 10-15% reduction in CO2 emissions compared to conventional vehicles. The primary environmental benefit comes from improved efficiency in urban driving conditions, where frequent starts and stops allow for energy recuperation through regenerative braking.
Plug-in hybrid vehicles, on the other hand, have a more substantial environmental impact. With larger battery packs and the ability to run on electric power alone for short distances, plug-in hybrids can significantly reduce tailpipe emissions. When operating in electric mode, these vehicles produce zero direct emissions, potentially reducing local air pollution in urban areas. Studies have shown that plug-in hybrids can reduce CO2 emissions by 30-60% compared to conventional vehicles, depending on driving patterns and electricity sources.
However, the full environmental impact of plug-in hybrids depends heavily on the source of electricity used for charging. In regions with clean energy grids, the overall emissions reduction can be substantial. Conversely, in areas reliant on coal-fired power plants, the net environmental benefit may be less pronounced.
The production of batteries for both mild and plug-in hybrids also carries environmental considerations. The mining and processing of materials like lithium and cobalt have ecological implications, including habitat disruption and water usage. Plug-in hybrids, with their larger battery packs, have a more significant production-related environmental footprint than mild hybrids.
End-of-life considerations also play a role in the environmental impact assessment. The recycling and disposal of hybrid vehicle batteries present both challenges and opportunities. Advancements in battery recycling technologies are crucial for minimizing the long-term environmental impact of hybrid vehicles.
In terms of market dynamics, the perceived environmental benefits of hybrid vehicles significantly influence consumer choices and regulatory policies. Governments worldwide are implementing stricter emissions standards and offering incentives for low-emission vehicles, which has accelerated the adoption of both mild and plug-in hybrid technologies. The varying degrees of environmental impact between these two hybrid types are reflected in different levels of government support and consumer acceptance across markets.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!