The potential for mild hybrid tractors in agriculture
AUG 18, 202510 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Mild Hybrid Tractor Technology Evolution and Objectives
Mild hybrid technology in tractors represents a significant evolution in agricultural machinery, blending traditional combustion engines with electric power systems. This technological advancement aims to enhance fuel efficiency, reduce emissions, and improve overall performance in farming operations. The development of mild hybrid tractors can be traced back to the early 2000s when environmental concerns and rising fuel costs prompted manufacturers to explore alternative power solutions.
The primary objective of mild hybrid tractor technology is to optimize energy utilization while maintaining the robust performance required in agricultural settings. By integrating electric motors and advanced energy recovery systems, these tractors can capture and reuse energy that would otherwise be lost during braking or idling. This regenerative capability not only improves fuel economy but also contributes to reduced environmental impact, aligning with global sustainability goals.
Another key aim of this technology is to enhance the versatility of tractors in various farming applications. Mild hybrid systems can provide instant torque boost, enabling smoother operation during high-load tasks such as plowing or harvesting. This feature addresses the need for improved power management in modern agriculture, where precision and efficiency are paramount.
The evolution of mild hybrid tractor technology has been marked by incremental improvements in battery technology, power electronics, and control systems. Early iterations focused on simple start-stop functionality, while more recent developments have expanded to include electric power assist during acceleration and auxiliary power for implements. This progression reflects the industry's commitment to pushing the boundaries of what's possible in agricultural machinery.
Looking ahead, the objectives for mild hybrid tractor technology include further integration of smart farming practices. Future iterations aim to incorporate advanced sensors and AI-driven systems that can optimize power distribution based on real-time field conditions and task requirements. This convergence of hybrid technology with precision agriculture techniques promises to revolutionize farming practices, offering unprecedented levels of efficiency and sustainability.
As the agricultural sector faces increasing pressure to reduce its carbon footprint, mild hybrid tractors are positioned as a crucial stepping stone towards fully electric farm equipment. The technology serves as a bridge, allowing farmers to transition gradually to more sustainable practices without compromising on the power and reliability they depend on. This evolutionary approach ensures that the adoption of greener technologies in agriculture can proceed at a pace that aligns with the industry's readiness and infrastructure development.
The primary objective of mild hybrid tractor technology is to optimize energy utilization while maintaining the robust performance required in agricultural settings. By integrating electric motors and advanced energy recovery systems, these tractors can capture and reuse energy that would otherwise be lost during braking or idling. This regenerative capability not only improves fuel economy but also contributes to reduced environmental impact, aligning with global sustainability goals.
Another key aim of this technology is to enhance the versatility of tractors in various farming applications. Mild hybrid systems can provide instant torque boost, enabling smoother operation during high-load tasks such as plowing or harvesting. This feature addresses the need for improved power management in modern agriculture, where precision and efficiency are paramount.
The evolution of mild hybrid tractor technology has been marked by incremental improvements in battery technology, power electronics, and control systems. Early iterations focused on simple start-stop functionality, while more recent developments have expanded to include electric power assist during acceleration and auxiliary power for implements. This progression reflects the industry's commitment to pushing the boundaries of what's possible in agricultural machinery.
Looking ahead, the objectives for mild hybrid tractor technology include further integration of smart farming practices. Future iterations aim to incorporate advanced sensors and AI-driven systems that can optimize power distribution based on real-time field conditions and task requirements. This convergence of hybrid technology with precision agriculture techniques promises to revolutionize farming practices, offering unprecedented levels of efficiency and sustainability.
As the agricultural sector faces increasing pressure to reduce its carbon footprint, mild hybrid tractors are positioned as a crucial stepping stone towards fully electric farm equipment. The technology serves as a bridge, allowing farmers to transition gradually to more sustainable practices without compromising on the power and reliability they depend on. This evolutionary approach ensures that the adoption of greener technologies in agriculture can proceed at a pace that aligns with the industry's readiness and infrastructure development.
Agricultural Market Demand for Mild Hybrid Tractors
The agricultural sector is experiencing a growing demand for mild hybrid tractors, driven by several key factors. Farmers are increasingly recognizing the potential benefits of this technology in terms of improved fuel efficiency, reduced emissions, and enhanced operational performance. The market for mild hybrid tractors is expected to expand significantly in the coming years, as agricultural businesses seek to optimize their operations and reduce their environmental impact.
One of the primary drivers of demand is the potential for cost savings through improved fuel efficiency. Mild hybrid systems can reduce fuel consumption by up to 15-20% compared to conventional tractors, depending on the specific application and usage patterns. This translates to substantial savings for farmers, especially in regions where fuel costs are a significant portion of operational expenses. As fuel prices continue to fluctuate and environmental regulations become more stringent, the economic incentives for adopting mild hybrid technology are becoming increasingly compelling.
Environmental concerns are also playing a crucial role in shaping market demand. Many countries are implementing stricter emissions regulations for agricultural machinery, pushing farmers to adopt cleaner technologies. Mild hybrid tractors offer a practical solution, as they can significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions and other pollutants without requiring a complete overhaul of existing infrastructure. This makes them an attractive option for farmers looking to comply with regulations while minimizing disruption to their operations.
The versatility of mild hybrid tractors is another factor driving market demand. These machines can seamlessly switch between electric and diesel power, providing optimal performance across a range of agricultural tasks. This flexibility is particularly valuable in operations that require varying power outputs, such as plowing, harvesting, and transportation. Farmers appreciate the ability to leverage electric power for lighter tasks and switch to diesel for more demanding applications, all within a single machine.
Market research indicates that large-scale commercial farms are currently the primary adopters of mild hybrid tractors, due to their ability to make significant upfront investments and realize long-term benefits. However, there is growing interest from medium-sized farms as well, particularly in regions with strong government incentives for sustainable farming practices. The market is also seeing increased demand from specialty crop producers, who value the precise control and reduced noise levels offered by hybrid systems.
Geographically, North America and Europe are leading the adoption of mild hybrid tractors, driven by a combination of stringent environmental regulations, high labor costs, and a strong focus on precision agriculture. However, emerging markets in Asia and South America are showing rapid growth potential, as these regions seek to modernize their agricultural sectors and improve productivity.
As the technology matures and production scales up, the cost of mild hybrid tractors is expected to decrease, making them more accessible to a broader range of farmers. This trend, coupled with increasing awareness of the benefits and potential government incentives, is likely to accelerate market growth in the coming years. The agricultural sector's ongoing shift towards sustainable and efficient practices suggests that the demand for mild hybrid tractors will continue to rise, reshaping the landscape of farm machinery and agricultural operations.
One of the primary drivers of demand is the potential for cost savings through improved fuel efficiency. Mild hybrid systems can reduce fuel consumption by up to 15-20% compared to conventional tractors, depending on the specific application and usage patterns. This translates to substantial savings for farmers, especially in regions where fuel costs are a significant portion of operational expenses. As fuel prices continue to fluctuate and environmental regulations become more stringent, the economic incentives for adopting mild hybrid technology are becoming increasingly compelling.
Environmental concerns are also playing a crucial role in shaping market demand. Many countries are implementing stricter emissions regulations for agricultural machinery, pushing farmers to adopt cleaner technologies. Mild hybrid tractors offer a practical solution, as they can significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions and other pollutants without requiring a complete overhaul of existing infrastructure. This makes them an attractive option for farmers looking to comply with regulations while minimizing disruption to their operations.
The versatility of mild hybrid tractors is another factor driving market demand. These machines can seamlessly switch between electric and diesel power, providing optimal performance across a range of agricultural tasks. This flexibility is particularly valuable in operations that require varying power outputs, such as plowing, harvesting, and transportation. Farmers appreciate the ability to leverage electric power for lighter tasks and switch to diesel for more demanding applications, all within a single machine.
Market research indicates that large-scale commercial farms are currently the primary adopters of mild hybrid tractors, due to their ability to make significant upfront investments and realize long-term benefits. However, there is growing interest from medium-sized farms as well, particularly in regions with strong government incentives for sustainable farming practices. The market is also seeing increased demand from specialty crop producers, who value the precise control and reduced noise levels offered by hybrid systems.
Geographically, North America and Europe are leading the adoption of mild hybrid tractors, driven by a combination of stringent environmental regulations, high labor costs, and a strong focus on precision agriculture. However, emerging markets in Asia and South America are showing rapid growth potential, as these regions seek to modernize their agricultural sectors and improve productivity.
As the technology matures and production scales up, the cost of mild hybrid tractors is expected to decrease, making them more accessible to a broader range of farmers. This trend, coupled with increasing awareness of the benefits and potential government incentives, is likely to accelerate market growth in the coming years. The agricultural sector's ongoing shift towards sustainable and efficient practices suggests that the demand for mild hybrid tractors will continue to rise, reshaping the landscape of farm machinery and agricultural operations.
Current State and Challenges in Mild Hybrid Tractor Development
The development of mild hybrid tractors in agriculture is currently in a transitional phase, with significant progress made in recent years but still facing several challenges. Major agricultural equipment manufacturers have introduced mild hybrid tractor models, demonstrating the industry's recognition of the technology's potential. These tractors typically combine a conventional diesel engine with an electric motor and a small battery pack, allowing for improved fuel efficiency and reduced emissions.
One of the primary advantages of mild hybrid tractors is their ability to provide additional power during peak load operations, such as plowing or harvesting, without significantly increasing fuel consumption. This feature has been well-received by farmers looking to optimize their operations while reducing costs. Additionally, the regenerative braking systems in these tractors help capture and store energy that would otherwise be lost, further enhancing overall efficiency.
However, the widespread adoption of mild hybrid technology in agriculture faces several challenges. The most significant hurdle is the higher initial cost compared to conventional tractors. While the long-term savings in fuel consumption and maintenance can offset this cost, many farmers are hesitant to make the upfront investment, particularly in regions with tight agricultural budgets.
Another challenge is the complexity of integrating hybrid systems into existing tractor designs. Manufacturers must balance the addition of electric components with the need to maintain the robustness and reliability that farmers expect from their equipment. This integration often requires redesigning various subsystems, which can lead to increased development costs and potential reliability issues in early models.
The limited battery capacity of mild hybrid tractors also presents a challenge, particularly for operations requiring sustained high power output. While the hybrid system can provide short bursts of additional power, it may not be sufficient for prolonged heavy-duty tasks without relying primarily on the diesel engine. This limitation has led to ongoing research into more advanced battery technologies and energy management systems.
Maintenance and repair of mild hybrid tractors pose another challenge, as they require specialized knowledge and tools. Many rural areas lack technicians with expertise in both traditional mechanical systems and the new electrical components, potentially leading to longer downtime and higher repair costs for farmers.
Despite these challenges, the potential benefits of mild hybrid tractors continue to drive innovation in the agricultural sector. Manufacturers are investing in research and development to address current limitations, focusing on improving battery technology, optimizing power management systems, and reducing production costs. As environmental regulations become stricter and fuel prices remain volatile, the demand for more efficient and sustainable agricultural equipment is expected to grow, potentially accelerating the adoption of mild hybrid technology in tractors.
One of the primary advantages of mild hybrid tractors is their ability to provide additional power during peak load operations, such as plowing or harvesting, without significantly increasing fuel consumption. This feature has been well-received by farmers looking to optimize their operations while reducing costs. Additionally, the regenerative braking systems in these tractors help capture and store energy that would otherwise be lost, further enhancing overall efficiency.
However, the widespread adoption of mild hybrid technology in agriculture faces several challenges. The most significant hurdle is the higher initial cost compared to conventional tractors. While the long-term savings in fuel consumption and maintenance can offset this cost, many farmers are hesitant to make the upfront investment, particularly in regions with tight agricultural budgets.
Another challenge is the complexity of integrating hybrid systems into existing tractor designs. Manufacturers must balance the addition of electric components with the need to maintain the robustness and reliability that farmers expect from their equipment. This integration often requires redesigning various subsystems, which can lead to increased development costs and potential reliability issues in early models.
The limited battery capacity of mild hybrid tractors also presents a challenge, particularly for operations requiring sustained high power output. While the hybrid system can provide short bursts of additional power, it may not be sufficient for prolonged heavy-duty tasks without relying primarily on the diesel engine. This limitation has led to ongoing research into more advanced battery technologies and energy management systems.
Maintenance and repair of mild hybrid tractors pose another challenge, as they require specialized knowledge and tools. Many rural areas lack technicians with expertise in both traditional mechanical systems and the new electrical components, potentially leading to longer downtime and higher repair costs for farmers.
Despite these challenges, the potential benefits of mild hybrid tractors continue to drive innovation in the agricultural sector. Manufacturers are investing in research and development to address current limitations, focusing on improving battery technology, optimizing power management systems, and reducing production costs. As environmental regulations become stricter and fuel prices remain volatile, the demand for more efficient and sustainable agricultural equipment is expected to grow, potentially accelerating the adoption of mild hybrid technology in tractors.
Existing Mild Hybrid Solutions for Agricultural Tractors
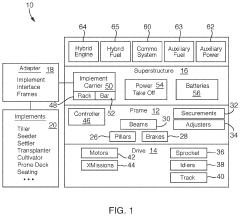
01 Hybrid powertrain systems for tractors
Mild hybrid tractors incorporate hybrid powertrain systems that combine internal combustion engines with electric motors. These systems improve fuel efficiency, reduce emissions, and provide additional power when needed for various agricultural operations.- Hybrid powertrain systems for tractors: Mild hybrid tractors incorporate electric motors alongside traditional combustion engines to improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions. These systems can provide electric assist during high-load operations, regenerative braking, and start-stop functionality, enhancing overall performance and reducing environmental impact.
- Energy management and control systems: Advanced control systems are implemented to optimize power distribution between the electric motor and combustion engine in mild hybrid tractors. These systems manage energy flow, battery charging, and power output based on operating conditions and driver input, maximizing efficiency and performance.
- Battery and electrical system integration: Mild hybrid tractors feature integrated battery systems and electrical architectures designed to support the hybrid powertrain. These systems include high-voltage batteries, power electronics, and cooling systems tailored for agricultural applications, ensuring durability and reliability in demanding environments.
- Hydraulic system electrification: Electrification of hydraulic systems in mild hybrid tractors allows for more precise control and improved efficiency. Electric pumps and actuators can replace or supplement traditional hydraulic components, reducing power losses and enabling variable flow control for implements and attachments.
- Transmission and driveline innovations: Mild hybrid tractors incorporate specialized transmissions and drivelines designed to integrate electric motors with conventional powertrains. These innovations may include electrically-assisted continuously variable transmissions (CVTs) or power-split devices that optimize power delivery and efficiency across various operating conditions.
02 Energy management and regenerative braking
Mild hybrid tractors utilize advanced energy management systems and regenerative braking technology. These features allow for the capture and storage of energy during braking or deceleration, which can then be used to assist the engine or power auxiliary systems, improving overall efficiency.Expand Specific Solutions03 Electric power take-off (PTO) systems
Some mild hybrid tractors incorporate electric power take-off systems, which use electric motors to drive implements instead of traditional mechanical PTOs. This allows for more precise control of implement speed and power, as well as reduced fuel consumption when operating PTO-driven equipment.Expand Specific Solutions04 Intelligent power distribution and control
Mild hybrid tractors feature sophisticated control systems that optimize power distribution between the internal combustion engine and electric motor(s). These systems adapt to varying load conditions and operational requirements, ensuring efficient use of available power sources and minimizing fuel consumption.Expand Specific Solutions05 Integration with precision agriculture technologies
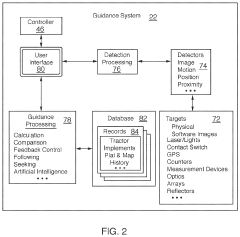
Mild hybrid tractor systems are often integrated with precision agriculture technologies, such as GPS guidance and automated steering systems. This integration allows for optimized field operations, reduced overlap, and improved overall efficiency in various agricultural tasks.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Mild Hybrid Tractor Manufacturing
The potential for mild hybrid tractors in agriculture is in an early development stage, with the market size still relatively small but growing. The technology's maturity is advancing, driven by increasing environmental concerns and fuel efficiency demands. Key players like CNH Industrial, Deere & Co., and Escorts Kubota are investing in research and development to bring innovative hybrid solutions to market. Universities such as MIT and China Agricultural University are contributing to technological advancements. The industry is seeing collaborations between established agricultural machinery manufacturers and automotive companies like Hyundai Motor Co., leveraging expertise in hybrid technologies. While adoption is gradual, the sector shows promise for future growth as farmers seek more sustainable and cost-effective solutions.
First Tractor Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: First Tractor Co., Ltd. has developed a mild hybrid tractor system that incorporates a small electric motor alongside the traditional diesel engine. Their approach focuses on integrating the electric motor into the transmission system, allowing for seamless power blending between the two power sources. The company's mild hybrid tractors utilize a 48V electrical system to power auxiliary components and implement electric-driven features such as air conditioning and power steering[5]. First Tractor has also implemented a smart energy management system that optimizes the use of electric power based on the tractor's workload and operating conditions. This system includes features like electric boost during high-load operations and engine-off coasting during low-load periods[6].
Strengths: Seamless integration of hybrid technology into existing tractor designs, potential for retrofitting older models. Weaknesses: Limited power output of the electric motor compared to some competitors, potential challenges in scaling up production.
CNH Industrial America LLC
Technical Solution: CNH Industrial has developed a mild hybrid tractor system under its New Holland brand. The company's approach combines a diesel engine with an electric motor and a compact battery pack. CNH's system focuses on using the electric motor to provide additional torque during high-load operations and to power auxiliary systems. The mild hybrid technology includes a smart power management system that optimizes the use of electric power based on the tractor's workload and operating conditions. CNH has also implemented regenerative braking to capture and store energy during deceleration[7]. The company's mild hybrid tractors feature a 48V electrical system that supports electrification of various implements and allows for reduced idling time through an advanced start-stop system[8].
Strengths: Strong global presence and distribution network, integration with existing agricultural technology ecosystems. Weaknesses: Potential challenges in balancing performance improvements with cost-effectiveness for farmers.
Core Innovations in Mild Hybrid Tractor Technology
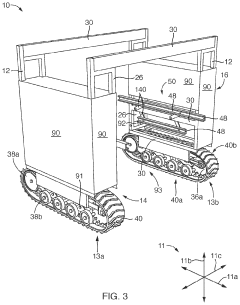
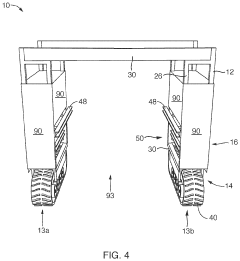
Compact, extensible, track laying, agricultural tractor
PatentActiveUS20210219481A1
Innovation
- A lightweight track-laying tractor system with adjustable width and independent track motors, allowing for reduced ground pressure and the ability to carry multiple implements, including a personnel carrier, to facilitate hand-weeding and harvesting on small plots.
Method for micro-ridge mixed-sowing cultivation of dryland crops
PatentActiveUS20220304222A1
Innovation
- The micro-ridge mixed-sowing cultivation method involves forming ecological ridges and trenches, mixing seeds, fertilizers, and soil to create a fertile seedbed, which promotes seedling growth and suppresses weeds, combined with the use of young chickens for pest control, thereby reducing pesticide input and improving fertilizer utilization.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability of Mild Hybrid Tractors
The adoption of mild hybrid tractors in agriculture represents a significant step towards reducing the environmental impact of farming operations and enhancing overall sustainability. These advanced machines combine conventional diesel engines with electric motors and battery systems, offering a range of benefits that contribute to a more eco-friendly agricultural sector.
One of the primary environmental advantages of mild hybrid tractors is their potential to reduce fuel consumption and, consequently, greenhouse gas emissions. By utilizing electric power for low-load operations and assisting the diesel engine during high-demand tasks, these tractors can achieve fuel savings of up to 25% compared to traditional models. This reduction in fuel usage directly translates to lower carbon dioxide emissions, helping to mitigate the agricultural sector's contribution to climate change.
Moreover, mild hybrid tractors contribute to improved air quality in rural areas. The reduced reliance on diesel engines, particularly during idling and low-speed operations, results in decreased emissions of particulate matter and nitrogen oxides. These pollutants are known to have adverse effects on human health and local ecosystems, making their reduction a crucial aspect of sustainable agriculture.
The integration of regenerative braking systems in mild hybrid tractors further enhances their environmental credentials. By capturing and storing energy that would otherwise be lost during braking or deceleration, these tractors can replenish their batteries without additional fuel consumption. This feature not only improves overall energy efficiency but also extends the life of brake components, reducing the need for replacement parts and associated waste.
From a sustainability perspective, mild hybrid tractors align well with the principles of precision agriculture. The electric components of these machines allow for more precise control of implements and operations, potentially reducing over-application of inputs such as fertilizers and pesticides. This precision not only minimizes environmental contamination but also contributes to resource conservation and improved crop yields.
The reduced noise pollution associated with mild hybrid tractors is another significant environmental benefit. During electric-only operation, these machines produce substantially less noise compared to conventional diesel tractors. This reduction in noise levels can have positive impacts on wildlife habitats and rural communities, contributing to a more harmonious coexistence between agricultural activities and the surrounding environment.
Looking towards the future, mild hybrid tractors serve as a stepping stone towards fully electric agricultural machinery. As battery technology continues to advance and charging infrastructure improves, the lessons learned from mild hybrid systems will pave the way for even more sustainable farming practices. This gradual transition allows farmers to adapt to new technologies while immediately reaping the environmental benefits of hybrid systems.
One of the primary environmental advantages of mild hybrid tractors is their potential to reduce fuel consumption and, consequently, greenhouse gas emissions. By utilizing electric power for low-load operations and assisting the diesel engine during high-demand tasks, these tractors can achieve fuel savings of up to 25% compared to traditional models. This reduction in fuel usage directly translates to lower carbon dioxide emissions, helping to mitigate the agricultural sector's contribution to climate change.
Moreover, mild hybrid tractors contribute to improved air quality in rural areas. The reduced reliance on diesel engines, particularly during idling and low-speed operations, results in decreased emissions of particulate matter and nitrogen oxides. These pollutants are known to have adverse effects on human health and local ecosystems, making their reduction a crucial aspect of sustainable agriculture.
The integration of regenerative braking systems in mild hybrid tractors further enhances their environmental credentials. By capturing and storing energy that would otherwise be lost during braking or deceleration, these tractors can replenish their batteries without additional fuel consumption. This feature not only improves overall energy efficiency but also extends the life of brake components, reducing the need for replacement parts and associated waste.
From a sustainability perspective, mild hybrid tractors align well with the principles of precision agriculture. The electric components of these machines allow for more precise control of implements and operations, potentially reducing over-application of inputs such as fertilizers and pesticides. This precision not only minimizes environmental contamination but also contributes to resource conservation and improved crop yields.
The reduced noise pollution associated with mild hybrid tractors is another significant environmental benefit. During electric-only operation, these machines produce substantially less noise compared to conventional diesel tractors. This reduction in noise levels can have positive impacts on wildlife habitats and rural communities, contributing to a more harmonious coexistence between agricultural activities and the surrounding environment.
Looking towards the future, mild hybrid tractors serve as a stepping stone towards fully electric agricultural machinery. As battery technology continues to advance and charging infrastructure improves, the lessons learned from mild hybrid systems will pave the way for even more sustainable farming practices. This gradual transition allows farmers to adapt to new technologies while immediately reaping the environmental benefits of hybrid systems.
Economic Feasibility and ROI for Farmers
The economic feasibility and return on investment (ROI) for farmers adopting mild hybrid tractors in agriculture is a critical consideration in the technology's potential widespread adoption. Initial investment costs for mild hybrid tractors are typically higher than conventional models, ranging from 10% to 30% more expensive. However, these upfront costs can be offset by significant operational savings over time.
Fuel efficiency improvements are a primary driver of economic benefits. Mild hybrid tractors can reduce fuel consumption by 15-25% compared to traditional diesel-only models, depending on the specific hybrid system and usage patterns. This translates to substantial savings in fuel costs, especially for large-scale farming operations or in regions with high fuel prices.
Maintenance costs also play a role in the economic equation. While hybrid systems introduce additional components that may require specialized maintenance, they can also reduce wear on traditional engine components. The net effect is often a slight reduction in overall maintenance expenses, typically in the range of 5-10% annually.
The ROI timeline for mild hybrid tractors varies based on farm size, usage intensity, and local economic factors. On average, farmers can expect to recoup their additional investment within 3-5 years through fuel savings and reduced maintenance costs. For high-usage scenarios or in areas with elevated fuel prices, this payback period can be as short as 2-3 years.
Government incentives and subsidies can significantly impact the economic feasibility of mild hybrid tractors. Many countries offer tax credits, grants, or low-interest loans for the adoption of environmentally friendly agricultural equipment. These incentives can reduce the initial cost barrier and accelerate the ROI timeline for farmers.
Productivity gains, while more challenging to quantify, also contribute to the economic case for mild hybrid tractors. The improved torque characteristics of hybrid systems can enhance performance in certain tasks, potentially leading to time savings and increased output. Additionally, the ability to use electric power for auxiliary systems can improve the versatility of the equipment, potentially reducing the need for separate specialized machinery.
Long-term economic benefits extend beyond direct cost savings. As environmental regulations become more stringent, early adopters of hybrid technology may gain a competitive advantage. Furthermore, the potential for carbon credits or participation in emerging environmental markets could provide additional revenue streams for farmers utilizing this technology.
Fuel efficiency improvements are a primary driver of economic benefits. Mild hybrid tractors can reduce fuel consumption by 15-25% compared to traditional diesel-only models, depending on the specific hybrid system and usage patterns. This translates to substantial savings in fuel costs, especially for large-scale farming operations or in regions with high fuel prices.
Maintenance costs also play a role in the economic equation. While hybrid systems introduce additional components that may require specialized maintenance, they can also reduce wear on traditional engine components. The net effect is often a slight reduction in overall maintenance expenses, typically in the range of 5-10% annually.
The ROI timeline for mild hybrid tractors varies based on farm size, usage intensity, and local economic factors. On average, farmers can expect to recoup their additional investment within 3-5 years through fuel savings and reduced maintenance costs. For high-usage scenarios or in areas with elevated fuel prices, this payback period can be as short as 2-3 years.
Government incentives and subsidies can significantly impact the economic feasibility of mild hybrid tractors. Many countries offer tax credits, grants, or low-interest loans for the adoption of environmentally friendly agricultural equipment. These incentives can reduce the initial cost barrier and accelerate the ROI timeline for farmers.
Productivity gains, while more challenging to quantify, also contribute to the economic case for mild hybrid tractors. The improved torque characteristics of hybrid systems can enhance performance in certain tasks, potentially leading to time savings and increased output. Additionally, the ability to use electric power for auxiliary systems can improve the versatility of the equipment, potentially reducing the need for separate specialized machinery.
Long-term economic benefits extend beyond direct cost savings. As environmental regulations become more stringent, early adopters of hybrid technology may gain a competitive advantage. Furthermore, the potential for carbon credits or participation in emerging environmental markets could provide additional revenue streams for farmers utilizing this technology.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!