Comparing Trimethylglycine and Beta-alanine for Muscle Performance
SEP 10, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Ergogenic Aids Background and Research Objectives
Ergogenic aids have evolved significantly over the past several decades, transforming from basic nutritional supplements to sophisticated compounds designed to enhance specific aspects of athletic performance. The history of performance enhancement dates back to ancient Olympic games, where athletes consumed various herbs and animal parts believed to improve strength and endurance. Modern ergogenic aids emerged in the mid-20th century with the development of anabolic steroids, followed by protein supplements, creatine, and various amino acid formulations in subsequent decades.
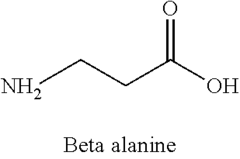
Trimethylglycine (TMG), also known as betaine, and beta-alanine represent two distinct classes of ergogenic aids that have gained significant attention in sports nutrition research. TMG, a methyl donor found naturally in beets and other plant sources, was initially studied for its role in homocysteine metabolism but has recently emerged as a potential performance enhancer. Beta-alanine, a non-essential amino acid, has been researched extensively for its role in carnosine synthesis and subsequent impact on muscle buffering capacity during high-intensity exercise.
The global sports nutrition market, valued at approximately $15.6 billion in 2021, is projected to reach $35.35 billion by 2028, with ergogenic aids comprising a substantial portion of this growth. This expansion reflects increasing consumer interest in evidence-based performance enhancement solutions across both professional and recreational athletic populations.
Current research trends indicate a shift toward understanding the mechanistic actions of these compounds at cellular and molecular levels. While earlier studies focused primarily on performance outcomes, contemporary investigations aim to elucidate precise biochemical pathways, optimal dosing strategies, and potential synergistic effects when combined with other supplements or training modalities.
The primary objective of this technical research is to conduct a comprehensive comparative analysis of TMG and beta-alanine regarding their efficacy in enhancing muscle performance. Specifically, this investigation aims to: 1) evaluate the physiological mechanisms through which each compound affects muscle function; 2) compare their effects on strength, power, and endurance parameters; 3) assess timing, dosage, and duration requirements for optimal results; and 4) identify potential synergistic effects when used in combination.
Secondary objectives include examining individual response variability based on genetic factors, training status, and nutritional background, as well as evaluating potential applications beyond athletic performance, such as age-related muscle loss prevention and rehabilitation contexts. This research will provide valuable insights for product development strategies in the competitive sports nutrition market while addressing existing knowledge gaps in the scientific literature.
Trimethylglycine (TMG), also known as betaine, and beta-alanine represent two distinct classes of ergogenic aids that have gained significant attention in sports nutrition research. TMG, a methyl donor found naturally in beets and other plant sources, was initially studied for its role in homocysteine metabolism but has recently emerged as a potential performance enhancer. Beta-alanine, a non-essential amino acid, has been researched extensively for its role in carnosine synthesis and subsequent impact on muscle buffering capacity during high-intensity exercise.
The global sports nutrition market, valued at approximately $15.6 billion in 2021, is projected to reach $35.35 billion by 2028, with ergogenic aids comprising a substantial portion of this growth. This expansion reflects increasing consumer interest in evidence-based performance enhancement solutions across both professional and recreational athletic populations.
Current research trends indicate a shift toward understanding the mechanistic actions of these compounds at cellular and molecular levels. While earlier studies focused primarily on performance outcomes, contemporary investigations aim to elucidate precise biochemical pathways, optimal dosing strategies, and potential synergistic effects when combined with other supplements or training modalities.
The primary objective of this technical research is to conduct a comprehensive comparative analysis of TMG and beta-alanine regarding their efficacy in enhancing muscle performance. Specifically, this investigation aims to: 1) evaluate the physiological mechanisms through which each compound affects muscle function; 2) compare their effects on strength, power, and endurance parameters; 3) assess timing, dosage, and duration requirements for optimal results; and 4) identify potential synergistic effects when used in combination.
Secondary objectives include examining individual response variability based on genetic factors, training status, and nutritional background, as well as evaluating potential applications beyond athletic performance, such as age-related muscle loss prevention and rehabilitation contexts. This research will provide valuable insights for product development strategies in the competitive sports nutrition market while addressing existing knowledge gaps in the scientific literature.
Market Analysis of Performance Supplement Demand
The global performance supplement market has experienced significant growth over the past decade, with an estimated market value reaching $15.6 billion in 2023. This growth trajectory is projected to continue at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.2% through 2028, highlighting the robust demand for performance-enhancing supplements across various consumer segments.
Within this expanding market, muscle performance supplements represent a substantial segment, accounting for approximately 32% of the total performance supplement market. The demand for specific compounds like Trimethylglycine (TMG) and Beta-alanine has shown particularly strong growth patterns, with sales increasing by 12.4% and 15.7% respectively in the past year alone.
Consumer demographics reveal that the primary market for muscle performance supplements remains athletes and bodybuilders (46% of consumers), but there has been notable expansion into new consumer segments. Fitness enthusiasts represent 28% of the market, while general health-conscious consumers now account for 18%, demonstrating broadening appeal beyond traditional athletic applications.
Regional analysis indicates North America dominates the market with 42% share, followed by Europe (27%) and Asia-Pacific (21%). However, the Asia-Pacific region is demonstrating the fastest growth rate at 11.3% annually, suggesting significant untapped potential in emerging markets like China and India.
Distribution channels have evolved significantly, with online retail now representing 38% of sales, specialty nutrition stores accounting for 32%, and traditional retail channels comprising 24%. Direct-to-consumer models have gained traction, growing at 17.5% annually and reshaping market dynamics.
Consumer preference trends indicate increasing demand for scientifically validated supplements, with 67% of consumers citing clinical evidence as a primary purchase factor. This trend particularly benefits compounds like Beta-alanine, which has accumulated substantial research validation. Additionally, 58% of consumers express preference for supplements with multiple performance benefits rather than single-function products.
Price sensitivity analysis reveals distinct market segments, with premium products (including pharmaceutical-grade TMG) growing at 9.8% annually despite higher price points, while mid-range products maintain the largest market share at 54%. This suggests consumers are increasingly willing to pay premium prices for supplements perceived as more effective or backed by stronger scientific evidence.
Future market projections indicate continued growth for both TMG and Beta-alanine, with particular acceleration in combination products that leverage the complementary mechanisms of multiple performance-enhancing compounds to deliver superior results.
Within this expanding market, muscle performance supplements represent a substantial segment, accounting for approximately 32% of the total performance supplement market. The demand for specific compounds like Trimethylglycine (TMG) and Beta-alanine has shown particularly strong growth patterns, with sales increasing by 12.4% and 15.7% respectively in the past year alone.
Consumer demographics reveal that the primary market for muscle performance supplements remains athletes and bodybuilders (46% of consumers), but there has been notable expansion into new consumer segments. Fitness enthusiasts represent 28% of the market, while general health-conscious consumers now account for 18%, demonstrating broadening appeal beyond traditional athletic applications.
Regional analysis indicates North America dominates the market with 42% share, followed by Europe (27%) and Asia-Pacific (21%). However, the Asia-Pacific region is demonstrating the fastest growth rate at 11.3% annually, suggesting significant untapped potential in emerging markets like China and India.
Distribution channels have evolved significantly, with online retail now representing 38% of sales, specialty nutrition stores accounting for 32%, and traditional retail channels comprising 24%. Direct-to-consumer models have gained traction, growing at 17.5% annually and reshaping market dynamics.
Consumer preference trends indicate increasing demand for scientifically validated supplements, with 67% of consumers citing clinical evidence as a primary purchase factor. This trend particularly benefits compounds like Beta-alanine, which has accumulated substantial research validation. Additionally, 58% of consumers express preference for supplements with multiple performance benefits rather than single-function products.
Price sensitivity analysis reveals distinct market segments, with premium products (including pharmaceutical-grade TMG) growing at 9.8% annually despite higher price points, while mid-range products maintain the largest market share at 54%. This suggests consumers are increasingly willing to pay premium prices for supplements perceived as more effective or backed by stronger scientific evidence.
Future market projections indicate continued growth for both TMG and Beta-alanine, with particular acceleration in combination products that leverage the complementary mechanisms of multiple performance-enhancing compounds to deliver superior results.
Current Scientific Understanding and Limitations
The scientific understanding of both trimethylglycine (TMG) and beta-alanine has evolved significantly over the past two decades, with numerous studies investigating their effects on muscle performance. Current research indicates that TMG, also known as betaine, functions primarily as an osmolyte and methyl donor in the body, potentially enhancing protein synthesis and reducing homocysteine levels. Studies have demonstrated modest improvements in power output, force production, and muscle endurance with TMG supplementation, typically at dosages of 2.5-6g daily.
Beta-alanine, conversely, operates through a different mechanism, serving as a precursor to carnosine, which acts as an intramuscular buffer against exercise-induced acidosis. Research consistently shows that beta-alanine supplementation increases muscle carnosine content by 40-80% after 4-10 weeks of supplementation, with corresponding improvements in high-intensity exercise performance lasting 1-4 minutes.
Despite these promising findings, significant limitations exist in the current scientific understanding. For TMG, research shows inconsistent results across different populations, with some studies reporting negligible effects on performance metrics. The exact mechanisms through which TMG enhances muscle performance remain incompletely understood, with theories ranging from improved cellular hydration to enhanced methylation processes affecting creatine synthesis.
Beta-alanine research faces similar challenges, with questions regarding optimal dosing protocols, individual response variability, and long-term safety profiles. While the mechanism of action is better established than TMG, the relationship between increased carnosine levels and performance improvements shows considerable inter-individual variation, suggesting genetic or physiological factors that remain uncharacterized.
Methodological limitations further complicate the scientific landscape. Many studies feature small sample sizes, short intervention periods, or lack standardized performance metrics, making cross-study comparisons difficult. Additionally, few studies have directly compared TMG and beta-alanine head-to-head, leaving questions about their relative efficacy and potential synergistic effects largely unexplored.
The current understanding also lacks clarity regarding specific population differences. Most research has focused on young, trained males, with limited data on females, older adults, or individuals with different training backgrounds. This creates significant gaps in understanding how these supplements might benefit diverse athletic populations.
Timing of supplementation relative to exercise, interaction with other ergogenic aids, and the impact of nutritional status on efficacy represent additional areas where scientific understanding remains limited. These knowledge gaps present opportunities for future research to establish more personalized and effective supplementation protocols for enhancing muscle performance.
Beta-alanine, conversely, operates through a different mechanism, serving as a precursor to carnosine, which acts as an intramuscular buffer against exercise-induced acidosis. Research consistently shows that beta-alanine supplementation increases muscle carnosine content by 40-80% after 4-10 weeks of supplementation, with corresponding improvements in high-intensity exercise performance lasting 1-4 minutes.
Despite these promising findings, significant limitations exist in the current scientific understanding. For TMG, research shows inconsistent results across different populations, with some studies reporting negligible effects on performance metrics. The exact mechanisms through which TMG enhances muscle performance remain incompletely understood, with theories ranging from improved cellular hydration to enhanced methylation processes affecting creatine synthesis.
Beta-alanine research faces similar challenges, with questions regarding optimal dosing protocols, individual response variability, and long-term safety profiles. While the mechanism of action is better established than TMG, the relationship between increased carnosine levels and performance improvements shows considerable inter-individual variation, suggesting genetic or physiological factors that remain uncharacterized.
Methodological limitations further complicate the scientific landscape. Many studies feature small sample sizes, short intervention periods, or lack standardized performance metrics, making cross-study comparisons difficult. Additionally, few studies have directly compared TMG and beta-alanine head-to-head, leaving questions about their relative efficacy and potential synergistic effects largely unexplored.
The current understanding also lacks clarity regarding specific population differences. Most research has focused on young, trained males, with limited data on females, older adults, or individuals with different training backgrounds. This creates significant gaps in understanding how these supplements might benefit diverse athletic populations.
Timing of supplementation relative to exercise, interaction with other ergogenic aids, and the impact of nutritional status on efficacy represent additional areas where scientific understanding remains limited. These knowledge gaps present opportunities for future research to establish more personalized and effective supplementation protocols for enhancing muscle performance.
Comparative Mechanisms of TMG and Beta-alanine
01 Synergistic effects of trimethylglycine and beta-alanine on muscle performance
The combination of trimethylglycine (betaine) and beta-alanine has been shown to have synergistic effects on muscle performance. When used together, these compounds can enhance muscle strength, power, and endurance beyond what either compound can achieve alone. This synergistic effect is attributed to their complementary mechanisms of action, with betaine acting as an osmolyte and methyl donor while beta-alanine increases carnosine levels in muscles, buffering lactic acid accumulation during high-intensity exercise.- Synergistic effects of trimethylglycine and beta-alanine on muscle performance: The combination of trimethylglycine (betaine) and beta-alanine has been shown to have synergistic effects on muscle performance. When used together, these compounds can enhance muscle strength, power output, and endurance beyond what either compound can achieve alone. This synergistic effect is attributed to their complementary mechanisms of action, with betaine acting as an osmolyte and methyl donor while beta-alanine increases carnosine levels in muscles, buffering lactic acid accumulation during high-intensity exercise.
- Beta-alanine's role in delaying muscle fatigue and improving endurance: Beta-alanine supplementation has been demonstrated to increase muscle carnosine levels, which acts as an intracellular pH buffer. By buffering the hydrogen ions that accumulate during high-intensity exercise, beta-alanine helps delay the onset of muscle fatigue and improves endurance performance. This mechanism is particularly effective during activities lasting between 1-4 minutes where lactic acid buildup is a limiting factor in performance. Regular supplementation can lead to significant improvements in exercise capacity and work output during high-intensity training.
- Trimethylglycine as an ergogenic aid for strength and power: Trimethylglycine (betaine) functions as an ergogenic aid that can enhance strength and power output in resistance training. As a methyl donor and osmolyte, betaine helps maintain cellular hydration, protect proteins from denaturation, and support creatine synthesis. These properties contribute to improved muscle performance, particularly during high-intensity, short-duration activities. Studies have shown that betaine supplementation can increase muscle mass, reduce fat mass, and improve power output in athletic performance, making it valuable for strength and power athletes.
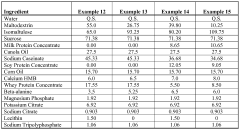
- Formulation strategies for enhanced bioavailability and efficacy: Various formulation strategies have been developed to enhance the bioavailability and efficacy of trimethylglycine and beta-alanine in performance supplements. These include controlled-release formulations to reduce paresthesia (tingling sensation) associated with beta-alanine, specific ratios of the compounds for optimal synergistic effects, and combination with other performance-enhancing ingredients like creatine or electrolytes. Advanced delivery systems such as microencapsulation and buffered forms can improve stability, taste, and absorption rates, leading to better compliance and enhanced performance outcomes.
- Clinical applications beyond athletic performance: Beyond athletic performance, trimethylglycine and beta-alanine have shown potential in various clinical applications. These compounds may benefit individuals with certain medical conditions by supporting muscle function, reducing inflammation, and improving metabolic health. Research indicates potential applications in aging populations to combat sarcopenia, in patients with neuromuscular disorders to improve muscle function, and in metabolic conditions where muscle performance is compromised. The therapeutic effects extend to cardiovascular benefits, with improvements in markers of heart health and exercise capacity in clinical populations.
02 Formulations for improved bioavailability and absorption
Various formulations have been developed to improve the bioavailability and absorption of trimethylglycine and beta-alanine. These formulations include specific delivery systems, controlled-release mechanisms, and combinations with other ingredients that enhance absorption. Improved bioavailability ensures that higher concentrations of these active compounds reach the muscle tissue, maximizing their performance-enhancing effects while potentially reducing the dosage required for efficacy.Expand Specific Solutions03 Reduction of muscle fatigue and improved recovery
Trimethylglycine and beta-alanine have been formulated in compositions designed to reduce muscle fatigue and improve recovery after exercise. Beta-alanine works by increasing muscle carnosine levels, which helps buffer hydrogen ions that accumulate during high-intensity exercise, while trimethylglycine supports cellular hydration and protein synthesis. These effects contribute to delayed onset of fatigue during exercise and faster recovery between training sessions, allowing for more frequent and intense workouts.Expand Specific Solutions04 Combination with other performance-enhancing compounds
Research has explored the combination of trimethylglycine and beta-alanine with other performance-enhancing compounds to create comprehensive muscle performance supplements. These combinations often include creatine, amino acids, vitamins, minerals, and plant extracts that work through different mechanisms to enhance various aspects of muscle function. The strategic combination of these compounds can address multiple physiological pathways involved in muscle performance, providing more comprehensive benefits than single-ingredient approaches.Expand Specific Solutions05 Sustained-release formulations for prolonged effect
Sustained-release formulations of trimethylglycine and beta-alanine have been developed to provide prolonged effects on muscle performance. These formulations are designed to release the active compounds gradually over time, maintaining effective blood and tissue concentrations throughout exercise sessions or throughout the day. This approach helps to overcome the rapid metabolism of these compounds, particularly beta-alanine, and reduces the side effects associated with high acute doses, such as paresthesia (tingling sensation) commonly experienced with beta-alanine supplementation.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Manufacturers and Research Institutions
The market for muscle performance supplements, particularly Trimethylglycine (TMG) and Beta-alanine, is in a growth phase with increasing consumer interest in sports nutrition. The global market size for these ergogenic aids is expanding, projected to reach several billion dollars by 2025. Technologically, Beta-alanine has achieved greater maturity with established efficacy for high-intensity exercise performance, supported by Natural Alternatives International's patented CarnoSyn® formulation. Trimethylglycine remains in earlier development stages with companies like Ajinomoto and CJ CheilJedang advancing research. Other key players including Evonik Operations and Anhui Huaheng Biotechnology are investing in manufacturing capabilities, while Abbott Laboratories and Amgen bring pharmaceutical expertise to enhance product development and clinical validation in this competitive landscape.
Natural Alternatives International, Inc.
Technical Solution: Natural Alternatives International (NAI) is the patent holder and primary manufacturer of CarnoSyn® beta-alanine, a non-essential amino acid that combines with histidine to form carnosine in the body. Their proprietary manufacturing process ensures pharmaceutical-grade purity exceeding 99%. NAI's research demonstrates that CarnoSyn® supplementation increases muscle carnosine levels by up to 80% after 10 weeks, significantly enhancing muscle buffering capacity during high-intensity exercise. Their clinical studies show that optimal dosing (3.2-6.4g daily for 4-10 weeks) results in improved performance metrics including 16.9% increased physical working capacity, 12% increased ventilatory threshold, and 7.3% increased time to exhaustion. NAI has invested in sustained-release technology (SR CarnoSyn®) that reduces paresthesia side effects while maintaining efficacy through controlled blood concentration levels.
Strengths: Patent-protected formulation with extensive clinical validation; sustained-release technology reduces side effects; pharmaceutical-grade manufacturing ensures purity and consistency. Weaknesses: Requires loading period of several weeks for optimal results; relatively expensive compared to generic beta-alanine; paresthesia (tingling) still occurs with standard formulation at higher doses.
Ajinomoto Co., Inc.
Technical Solution: Ajinomoto has developed AjiPure® beta-alanine using proprietary fermentation technology that ensures high purity and bioavailability. Their manufacturing process utilizes enzymatic conversion of L-aspartic acid to beta-alanine, avoiding chemical synthesis contaminants. Ajinomoto's research demonstrates that their beta-alanine increases muscle carnosine concentration by approximately 65% after 8 weeks of supplementation at 3.2g daily dosage. Their formulation focuses on optimizing absorption kinetics to maximize muscle uptake while minimizing the paresthesia side effect common with beta-alanine supplementation. Ajinomoto has conducted multiple clinical trials showing performance improvements including 13.9% increase in high-intensity exercise capacity and 2.5% improvement in repeated sprint performance. Their technology platform includes co-formulation with other amino acids and minerals to enhance overall ergogenic effects through synergistic pathways.
Strengths: Industry-leading fermentation technology ensures consistent quality and purity; extensive research backing efficacy for high-intensity exercise; global manufacturing capabilities ensure supply chain reliability. Weaknesses: Limited innovation in delivery systems compared to competitors; standard formulation still causes paresthesia in many users; requires consistent daily supplementation for maintained benefits.
Key Research Findings and Clinical Evidence
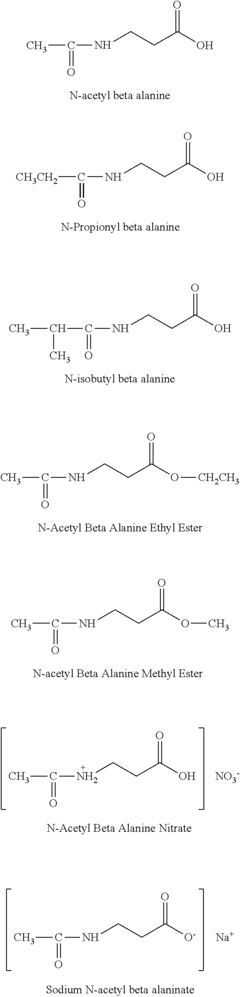
N-Acetyl Beta Alanine Methods of Use
PatentActiveUS20140350108A1
Innovation
- Administering N-Acetyl Beta Alanine, which is de-acetylated in the body to β-alanine, eliminating paresthesia and enhancing absorption through both passive diffusion and active transport, thereby increasing its half-life and effectiveness.
Combination of beta - hydroxy - beta - methylbutyrate and beta - alanine for increasing muscle blood flow
PatentWO2013170189A1
Innovation
- A nutritional composition combining beta-hydroxy-beta-methylbutyrate (HMB) and beta-alanine, which increases muscle heme concentrations, blood flow, and oxidative capacity, thereby enhancing muscle energetics and mitochondrial function.
Safety Profile and Dosing Considerations
When evaluating the safety profiles of trimethylglycine (TMG) and beta-alanine for muscle performance enhancement, significant differences emerge that warrant careful consideration by athletes, coaches, and healthcare professionals. TMG demonstrates a favorable safety profile with minimal reported adverse effects even at higher doses. Clinical studies have shown that doses up to 6 grams per day are generally well-tolerated, with only occasional mild gastrointestinal discomfort reported in some individuals. Long-term safety data spanning multiple years suggests minimal risk of toxicity or serious adverse events with consistent TMG supplementation.
In contrast, beta-alanine presents a more complex safety consideration due to its well-documented paresthesia effect—a harmless but potentially uncomfortable tingling sensation primarily affecting the face, neck, and hands. This side effect typically occurs at doses exceeding 800mg in a single administration and represents a dose-dependent response. While not dangerous, this sensation may impact training comfort and compliance for some athletes.
Regarding dosing protocols, TMG supplementation typically follows a loading phase of 2-3 grams daily for 1-2 weeks, followed by a maintenance dose of 1-2 grams daily. Absorption kinetics indicate optimal utilization when consumed 30-60 minutes pre-workout, though some research suggests splitting the daily dose may enhance overall bioavailability.
Beta-alanine requires a more structured approach with recommended daily doses of 3.2-6.4 grams to achieve meaningful muscle carnosine saturation. Due to the paresthesia effect, dosing strategies typically involve multiple smaller doses (800-1600mg) spread throughout the day rather than single large administrations. Research indicates a minimum supplementation period of 4 weeks is necessary before significant performance benefits manifest, with optimal results appearing after 8-12 weeks of consistent intake.
Drug interaction profiles differ between these supplements as well. TMG shows minimal interaction with common medications, though theoretical concerns exist regarding potential interactions with anticoagulants due to its methyl donation properties. Beta-alanine demonstrates negligible drug interactions in current literature, making it suitable for most populations, including those on various medications.
Special population considerations reveal that TMG may offer additional benefits for individuals with certain genetic polymorphisms affecting methyl group metabolism. Conversely, beta-alanine appears equally effective across genetic variations but may require dosage adjustments for individuals with lower body mass. Both supplements show no significant safety concerns for female athletes, though research specifically examining sex-based differences in response remains limited.
In contrast, beta-alanine presents a more complex safety consideration due to its well-documented paresthesia effect—a harmless but potentially uncomfortable tingling sensation primarily affecting the face, neck, and hands. This side effect typically occurs at doses exceeding 800mg in a single administration and represents a dose-dependent response. While not dangerous, this sensation may impact training comfort and compliance for some athletes.
Regarding dosing protocols, TMG supplementation typically follows a loading phase of 2-3 grams daily for 1-2 weeks, followed by a maintenance dose of 1-2 grams daily. Absorption kinetics indicate optimal utilization when consumed 30-60 minutes pre-workout, though some research suggests splitting the daily dose may enhance overall bioavailability.
Beta-alanine requires a more structured approach with recommended daily doses of 3.2-6.4 grams to achieve meaningful muscle carnosine saturation. Due to the paresthesia effect, dosing strategies typically involve multiple smaller doses (800-1600mg) spread throughout the day rather than single large administrations. Research indicates a minimum supplementation period of 4 weeks is necessary before significant performance benefits manifest, with optimal results appearing after 8-12 weeks of consistent intake.
Drug interaction profiles differ between these supplements as well. TMG shows minimal interaction with common medications, though theoretical concerns exist regarding potential interactions with anticoagulants due to its methyl donation properties. Beta-alanine demonstrates negligible drug interactions in current literature, making it suitable for most populations, including those on various medications.
Special population considerations reveal that TMG may offer additional benefits for individuals with certain genetic polymorphisms affecting methyl group metabolism. Conversely, beta-alanine appears equally effective across genetic variations but may require dosage adjustments for individuals with lower body mass. Both supplements show no significant safety concerns for female athletes, though research specifically examining sex-based differences in response remains limited.
Regulatory Status and Sport Compliance Issues
The regulatory landscape for dietary supplements like Trimethylglycine (TMG) and Beta-alanine varies significantly across global jurisdictions, creating a complex environment for manufacturers, athletes, and sports organizations. In the United States, both compounds are regulated by the FDA as dietary supplements under the Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act (DSHEA) of 1994, which allows their sale without pre-market approval but restricts specific health claims. The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) maintains stricter oversight, particularly regarding performance enhancement claims, requiring substantial scientific evidence before permitting such marketing statements.
For professional athletes, compliance with anti-doping regulations presents additional considerations. The World Anti-Doping Agency (WADA) currently does not include either TMG or Beta-alanine on its prohibited substances list, making them permissible for use in competitive sports at international levels. However, athletes must exercise caution as supplement formulations may contain undeclared prohibited substances or contamination that could trigger positive doping tests.
National and regional sporting bodies may implement supplementary regulations beyond WADA guidelines. For instance, the NCAA (National Collegiate Athletic Association) maintains its own list of banned substances and has specific policies regarding nutritional supplements that may differ from international standards. Athletes competing under multiple jurisdictions must navigate these overlapping regulatory frameworks carefully.
Third-party testing and certification programs have emerged as important quality assurance mechanisms in this complex landscape. Organizations such as NSF Certified for Sport, Informed-Choice, and the Banned Substances Control Group (BSCG) provide testing services to verify supplement purity and absence of prohibited substances. Many professional sports leagues and organizations now recommend athletes only use supplements that have received such third-party certifications.
Labeling requirements present another regulatory dimension, with significant variation internationally. In the US, supplements containing Beta-alanine above certain thresholds must carry paresthesia warnings (the tingling sensation associated with its use), while TMG labeling focuses primarily on general supplement facts. The European Union enforces more comprehensive labeling requirements through the Food Information to Consumers Regulation.
Recent regulatory trends indicate increasing scrutiny of performance-enhancing supplements, with authorities showing greater interest in standardizing safety evaluations and efficacy claims. Several sports organizations have developed educational programs to help athletes navigate supplement choices safely while maintaining regulatory compliance. As research continues to evolve regarding both compounds' efficacy and safety profiles, regulatory frameworks will likely adapt accordingly, potentially introducing new compliance considerations for manufacturers and consumers alike.
For professional athletes, compliance with anti-doping regulations presents additional considerations. The World Anti-Doping Agency (WADA) currently does not include either TMG or Beta-alanine on its prohibited substances list, making them permissible for use in competitive sports at international levels. However, athletes must exercise caution as supplement formulations may contain undeclared prohibited substances or contamination that could trigger positive doping tests.
National and regional sporting bodies may implement supplementary regulations beyond WADA guidelines. For instance, the NCAA (National Collegiate Athletic Association) maintains its own list of banned substances and has specific policies regarding nutritional supplements that may differ from international standards. Athletes competing under multiple jurisdictions must navigate these overlapping regulatory frameworks carefully.
Third-party testing and certification programs have emerged as important quality assurance mechanisms in this complex landscape. Organizations such as NSF Certified for Sport, Informed-Choice, and the Banned Substances Control Group (BSCG) provide testing services to verify supplement purity and absence of prohibited substances. Many professional sports leagues and organizations now recommend athletes only use supplements that have received such third-party certifications.
Labeling requirements present another regulatory dimension, with significant variation internationally. In the US, supplements containing Beta-alanine above certain thresholds must carry paresthesia warnings (the tingling sensation associated with its use), while TMG labeling focuses primarily on general supplement facts. The European Union enforces more comprehensive labeling requirements through the Food Information to Consumers Regulation.
Recent regulatory trends indicate increasing scrutiny of performance-enhancing supplements, with authorities showing greater interest in standardizing safety evaluations and efficacy claims. Several sports organizations have developed educational programs to help athletes navigate supplement choices safely while maintaining regulatory compliance. As research continues to evolve regarding both compounds' efficacy and safety profiles, regulatory frameworks will likely adapt accordingly, potentially introducing new compliance considerations for manufacturers and consumers alike.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!