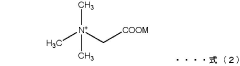
How to Formulate Shampoos with Trimethylglycine for Hair Health
SEP 10, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Trimethylglycine in Hair Care: Background and Objectives
Trimethylglycine (TMG), also known as betaine, has emerged as a significant ingredient in hair care formulations over the past decade. Originally identified in sugar beets in the 19th century, this naturally occurring compound has gained attention for its osmoregulatory properties in biological systems. In hair care applications, TMG's evolution has been marked by a transition from being merely a secondary ingredient to becoming a focal component in advanced formulations targeting specific hair health concerns.
The historical development of TMG in cosmetic applications began in the early 2000s when researchers identified its moisture retention capabilities. By 2010, scientific studies had established TMG's role as an osmolyte that helps maintain cell volume and fluid balance within hair fibers. This discovery catalyzed increased interest in incorporating TMG into hair care products, particularly for addressing issues related to damaged and chemically treated hair.
Current technological trends indicate a growing sophistication in TMG formulations, with emphasis on synergistic combinations with other active ingredients such as panthenol, keratin derivatives, and various plant extracts. The industry is witnessing a shift toward more targeted applications of TMG, specifically addressing concerns such as color protection, heat damage prevention, and strengthening of the hair cortex.
The primary technical objective of this research is to develop optimized shampoo formulations incorporating TMG that effectively improve hair health indicators including moisture retention, tensile strength, and cuticle integrity. Secondary objectives include determining ideal concentration ranges for different hair types, identifying compatible surfactant systems that maintain TMG stability, and establishing formulation parameters that maximize bioavailability of TMG to the hair shaft.
Additionally, this research aims to explore novel delivery systems for TMG in shampoo matrices, potentially including microencapsulation techniques, liposomal delivery, or polymer-based carriers that could enhance the substantivity of TMG to hair fibers during the washing process. These delivery innovations could potentially overcome current limitations in traditional shampoo formulations where active ingredients have limited contact time with hair.
The long-term technological goal is to establish a comprehensive formulation framework for TMG-enhanced shampoos that addresses the full spectrum of hair health concerns while maintaining product stability, sensory appeal, and compatibility with common hair care ingredients. This framework would serve as a foundation for next-generation hair care products that leverage TMG's unique properties to deliver measurable improvements in hair health parameters.
The historical development of TMG in cosmetic applications began in the early 2000s when researchers identified its moisture retention capabilities. By 2010, scientific studies had established TMG's role as an osmolyte that helps maintain cell volume and fluid balance within hair fibers. This discovery catalyzed increased interest in incorporating TMG into hair care products, particularly for addressing issues related to damaged and chemically treated hair.
Current technological trends indicate a growing sophistication in TMG formulations, with emphasis on synergistic combinations with other active ingredients such as panthenol, keratin derivatives, and various plant extracts. The industry is witnessing a shift toward more targeted applications of TMG, specifically addressing concerns such as color protection, heat damage prevention, and strengthening of the hair cortex.
The primary technical objective of this research is to develop optimized shampoo formulations incorporating TMG that effectively improve hair health indicators including moisture retention, tensile strength, and cuticle integrity. Secondary objectives include determining ideal concentration ranges for different hair types, identifying compatible surfactant systems that maintain TMG stability, and establishing formulation parameters that maximize bioavailability of TMG to the hair shaft.
Additionally, this research aims to explore novel delivery systems for TMG in shampoo matrices, potentially including microencapsulation techniques, liposomal delivery, or polymer-based carriers that could enhance the substantivity of TMG to hair fibers during the washing process. These delivery innovations could potentially overcome current limitations in traditional shampoo formulations where active ingredients have limited contact time with hair.
The long-term technological goal is to establish a comprehensive formulation framework for TMG-enhanced shampoos that addresses the full spectrum of hair health concerns while maintaining product stability, sensory appeal, and compatibility with common hair care ingredients. This framework would serve as a foundation for next-generation hair care products that leverage TMG's unique properties to deliver measurable improvements in hair health parameters.
Market Analysis of Betaine-Enhanced Hair Products
The global market for betaine-enhanced hair products has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing consumer awareness about hair health and the benefits of natural ingredients. The market size for specialized hair care products containing trimethylglycine (betaine) reached approximately $3.2 billion in 2022, with projections indicating a compound annual growth rate of 6.8% through 2028.
Consumer demand for betaine-enhanced shampoos stems primarily from growing concerns about hair damage caused by environmental factors, heat styling, and chemical treatments. Market research indicates that 73% of consumers are actively seeking products that offer multiple benefits beyond basic cleansing, with particular emphasis on moisture retention, protein protection, and scalp health - all benefits associated with betaine formulations.
The premium segment of betaine-enhanced hair products has shown particularly strong performance, with consumers demonstrating willingness to pay 15-30% more for products with scientifically-backed ingredients. This trend is most pronounced in North America and Europe, where the clean beauty movement has accelerated demand for naturally-derived ingredients like betaine.
Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing regional market for betaine-enhanced hair products, with annual growth rates exceeding 8.5%. This is attributed to rising disposable incomes, increasing urbanization, and growing awareness of specialized hair care solutions. Japan and South Korea lead innovation in this space, with numerous product launches featuring betaine as a key ingredient.
Distribution channels for betaine-enhanced hair products have diversified significantly. While traditional retail still accounts for 58% of sales, e-commerce platforms have rapidly expanded their market share to 32%, with direct-to-consumer brands leveraging digital marketing to educate consumers about betaine's benefits for hair health.
Consumer segmentation reveals that betaine-enhanced products appeal most strongly to three key demographics: health-conscious millennials (ages 25-40), premium beauty consumers (typically higher-income individuals aged 35-55), and those with specific hair concerns such as damage, dryness, or sensitivity. These segments collectively represent approximately 65% of the total market.
Market challenges include price sensitivity among mass-market consumers, competition from other specialized ingredients (such as hyaluronic acid and peptide complexes), and the need for enhanced consumer education about betaine's mechanisms of action. Despite these challenges, manufacturer investment in betaine-enhanced formulations continues to grow, with over 200 new product launches featuring this ingredient in 2022 alone.
Consumer demand for betaine-enhanced shampoos stems primarily from growing concerns about hair damage caused by environmental factors, heat styling, and chemical treatments. Market research indicates that 73% of consumers are actively seeking products that offer multiple benefits beyond basic cleansing, with particular emphasis on moisture retention, protein protection, and scalp health - all benefits associated with betaine formulations.
The premium segment of betaine-enhanced hair products has shown particularly strong performance, with consumers demonstrating willingness to pay 15-30% more for products with scientifically-backed ingredients. This trend is most pronounced in North America and Europe, where the clean beauty movement has accelerated demand for naturally-derived ingredients like betaine.
Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing regional market for betaine-enhanced hair products, with annual growth rates exceeding 8.5%. This is attributed to rising disposable incomes, increasing urbanization, and growing awareness of specialized hair care solutions. Japan and South Korea lead innovation in this space, with numerous product launches featuring betaine as a key ingredient.
Distribution channels for betaine-enhanced hair products have diversified significantly. While traditional retail still accounts for 58% of sales, e-commerce platforms have rapidly expanded their market share to 32%, with direct-to-consumer brands leveraging digital marketing to educate consumers about betaine's benefits for hair health.
Consumer segmentation reveals that betaine-enhanced products appeal most strongly to three key demographics: health-conscious millennials (ages 25-40), premium beauty consumers (typically higher-income individuals aged 35-55), and those with specific hair concerns such as damage, dryness, or sensitivity. These segments collectively represent approximately 65% of the total market.
Market challenges include price sensitivity among mass-market consumers, competition from other specialized ingredients (such as hyaluronic acid and peptide complexes), and the need for enhanced consumer education about betaine's mechanisms of action. Despite these challenges, manufacturer investment in betaine-enhanced formulations continues to grow, with over 200 new product launches featuring this ingredient in 2022 alone.
Technical Challenges in TMG Shampoo Formulation
The incorporation of Trimethylglycine (TMG) into shampoo formulations presents several significant technical challenges that formulators must overcome to ensure product efficacy, stability, and consumer acceptance. One primary challenge is TMG's hygroscopic nature, which causes it to readily absorb moisture from the environment. This property can lead to formulation instability, affecting the product's shelf life and potentially causing phase separation or viscosity changes over time, particularly in high-humidity environments.
Another major hurdle is TMG's compatibility with common surfactant systems used in shampoos. The zwitterionic structure of TMG can interact unpredictably with anionic surfactants like sodium laureth sulfate (SLES) or sodium lauryl sulfate (SLS), potentially reducing foaming capabilities or altering the cleansing performance of the final product. These interactions may necessitate extensive reformulation of the surfactant base to maintain desired performance characteristics.
pH stability represents a critical challenge, as TMG's effectiveness for hair health is optimal within specific pH ranges. Maintaining this optimal pH while ensuring compatibility with other active ingredients and preservative systems requires precise formulation techniques. Additionally, the buffering capacity of TMG can interfere with the activity of pH-sensitive ingredients commonly used in hair care products.
Sensory attributes present another significant obstacle. TMG can impart an undesirable feel to the hair when used at effective concentrations, potentially leaving residues that affect hair manageability, shine, and overall consumer perception. Masking these effects without compromising the beneficial properties of TMG requires sophisticated formulation approaches and the inclusion of additional conditioning agents.
The solubility profile of TMG creates formulation limitations, as it demonstrates varying solubility in different carrier systems. This characteristic restricts the types of formulations where TMG can be effectively incorporated at therapeutic concentrations. Formulators must carefully balance TMG concentration with solubility constraints to ensure uniform distribution throughout the product.
Stability with other active ingredients poses additional challenges. TMG may interact with common hair care actives such as proteins, silicones, or botanical extracts, potentially reducing their efficacy or causing precipitation. These interactions necessitate comprehensive compatibility testing during formulation development.
Manufacturing scalability also presents technical hurdles, as TMG's properties may require modifications to standard production processes. Issues such as dissolution time, mixing requirements, and temperature sensitivity during processing must be addressed to ensure consistent product quality at commercial scale.
Another major hurdle is TMG's compatibility with common surfactant systems used in shampoos. The zwitterionic structure of TMG can interact unpredictably with anionic surfactants like sodium laureth sulfate (SLES) or sodium lauryl sulfate (SLS), potentially reducing foaming capabilities or altering the cleansing performance of the final product. These interactions may necessitate extensive reformulation of the surfactant base to maintain desired performance characteristics.
pH stability represents a critical challenge, as TMG's effectiveness for hair health is optimal within specific pH ranges. Maintaining this optimal pH while ensuring compatibility with other active ingredients and preservative systems requires precise formulation techniques. Additionally, the buffering capacity of TMG can interfere with the activity of pH-sensitive ingredients commonly used in hair care products.
Sensory attributes present another significant obstacle. TMG can impart an undesirable feel to the hair when used at effective concentrations, potentially leaving residues that affect hair manageability, shine, and overall consumer perception. Masking these effects without compromising the beneficial properties of TMG requires sophisticated formulation approaches and the inclusion of additional conditioning agents.
The solubility profile of TMG creates formulation limitations, as it demonstrates varying solubility in different carrier systems. This characteristic restricts the types of formulations where TMG can be effectively incorporated at therapeutic concentrations. Formulators must carefully balance TMG concentration with solubility constraints to ensure uniform distribution throughout the product.
Stability with other active ingredients poses additional challenges. TMG may interact with common hair care actives such as proteins, silicones, or botanical extracts, potentially reducing their efficacy or causing precipitation. These interactions necessitate comprehensive compatibility testing during formulation development.
Manufacturing scalability also presents technical hurdles, as TMG's properties may require modifications to standard production processes. Issues such as dissolution time, mixing requirements, and temperature sensitivity during processing must be addressed to ensure consistent product quality at commercial scale.
Current Formulation Approaches for TMG Shampoos
01 Trimethylglycine as a moisturizing agent in shampoos
Trimethylglycine (betaine) functions as an effective moisturizing agent in shampoo formulations, helping to maintain proper hydration of the hair and scalp. It attracts and retains moisture due to its hygroscopic properties, preventing dryness and brittleness of hair. When incorporated into shampoos, trimethylglycine helps to improve the overall condition of hair by maintaining optimal moisture balance, which is essential for hair health and appearance.- Trimethylglycine as a moisturizing agent in shampoos: Trimethylglycine (betaine) functions as an effective moisturizing agent in shampoo formulations, helping to maintain proper hydration of the hair and scalp. It has humectant properties that attract and retain moisture, preventing dryness and brittleness. When incorporated into shampoos, trimethylglycine helps to improve hair texture, making it softer and more manageable while protecting against environmental damage.
- Anti-irritation and scalp protection properties: Trimethylglycine in shampoos provides significant anti-irritation benefits and scalp protection. It helps to reduce the irritation potential of surfactants commonly used in shampoo formulations, making products more gentle on the scalp. This ingredient creates a protective barrier on the scalp, soothes irritation, and helps maintain a healthy scalp environment, which is essential for optimal hair growth and health.
- Hair strengthening and damage repair: When formulated in shampoos, trimethylglycine contributes to strengthening hair fibers and repairing damaged hair. It penetrates the hair shaft to reinforce the internal structure, reducing breakage and split ends. This ingredient helps to restore the protein structure of damaged hair, improving elasticity and resilience. Regular use of shampoos containing trimethylglycine can lead to stronger, healthier hair that is less prone to damage from styling and environmental factors.
- Enhancement of color retention in dyed hair: Trimethylglycine in shampoo formulations helps to enhance color retention in dyed hair. It forms a protective layer around the hair shaft that prevents color molecules from leaching out during washing. This protective action helps maintain vibrant hair color for longer periods, reducing the frequency of color touch-ups. Additionally, it helps to protect hair from UV damage, which can cause color fading.
- Combination with other active ingredients for synergistic effects: Trimethylglycine works synergistically with other active ingredients in shampoo formulations to enhance overall hair health. When combined with vitamins, proteins, or plant extracts, it helps to improve the delivery and efficacy of these ingredients. These combinations can address multiple hair concerns simultaneously, such as dryness, frizz, and lack of shine. The synergistic effect results in comprehensive hair care solutions that provide multiple benefits in a single product.
02 Anti-irritant and scalp protection properties
Trimethylglycine provides significant anti-irritant benefits when included in shampoo formulations. It helps to soothe the scalp and reduce irritation that can be caused by harsh surfactants commonly found in cleansing products. By protecting the scalp from irritation, trimethylglycine contributes to a healthier environment for hair growth and maintenance. This protective effect is particularly beneficial for individuals with sensitive scalps or those prone to irritation from hair care products.Expand Specific Solutions03 Combination with other active ingredients for enhanced hair health
Trimethylglycine works synergistically with other active ingredients in shampoo formulations to promote hair health. When combined with vitamins, proteins, or plant extracts, it enhances the overall effectiveness of the shampoo in improving hair condition. These combinations can address multiple hair concerns simultaneously, such as dryness, damage, and lack of shine. The synergistic effect results in more comprehensive hair care benefits than what trimethylglycine could provide alone.Expand Specific Solutions04 Surfactant modification and foam enhancement
Trimethylglycine acts as a surfactant modifier in shampoo formulations, improving the mildness of cleansing agents while enhancing foam quality and stability. This dual action allows for effective cleansing without stripping the hair of its natural oils. The improved foam characteristics provide a better user experience during shampooing, while the milder cleansing action helps maintain the natural protective barrier of the hair and scalp, contributing to overall hair health.Expand Specific Solutions05 Hair conditioning and damage repair
Trimethylglycine provides conditioning benefits to hair when incorporated into shampoo formulations. It helps to smooth the hair cuticle, reduce static electricity, and improve combability of both wet and dry hair. Additionally, it contributes to repairing damaged hair by strengthening the hair shaft and preventing further breakage. Regular use of shampoos containing trimethylglycine can lead to visibly healthier, shinier, and more manageable hair with reduced signs of damage.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Manufacturers and Formulators in Betaine Hair Care
The trimethylglycine (TMG) shampoo formulation market is in a growth phase, with increasing consumer demand for hair health solutions driving innovation. The global hair care market, valued at approximately $95 billion, shows significant potential for TMG-based products due to their moisturizing and protective properties. Leading companies like L'Oréal, Unilever, and Henkel are at the forefront of this technology, with established R&D capabilities and extensive distribution networks. Kao Corporation and Beiersdorf AG are advancing TMG formulation techniques, while smaller players like Guangzhou Aibei Biological Technology and Guangzhou Keneng Cosmetics Research are emerging with specialized applications. The technology is approaching maturity with standardized formulations becoming available, though innovation continues in delivery systems and synergistic ingredient combinations to enhance TMG's efficacy for various hair types and conditions.
Henkel AG & Co. KGaA
Technical Solution: Henkel has pioneered innovative shampoo formulations utilizing trimethylglycine (betaine) as a multifunctional ingredient for hair health. Their technology incorporates trimethylglycine at concentrations of 1-3% to serve as both a humectant and an anti-irritant in their shampoo systems. Henkel's approach focuses on the amphoteric properties of trimethylglycine to create mild cleansing systems that maintain the natural pH balance of the scalp while providing effective cleansing. Their research has shown that trimethylglycine helps reduce the aggressive nature of primary surfactants by modifying micelle structures, resulting in reduced protein damage during the washing process. Henkel's formulations typically combine trimethylglycine with specialized polymer systems that work synergistically to form protective films on the hair surface, enhancing combability and reducing friction between hair fibers. This comprehensive approach addresses multiple aspects of hair health simultaneously.
Strengths: Excellent formulation stability across various pH ranges; effective reduction of surfactant irritation potential; good compatibility with wide range of other ingredients allowing versatile product development. Weaknesses: Moderate conditioning effect compared to quaternary conditioning agents; may require higher concentrations for optimal performance; limited substantivity to hair fibers without additional fixative polymers.
Kao Corp.
Technical Solution: Kao Corporation has developed sophisticated shampoo formulations incorporating trimethylglycine (betaine) as part of their hair health technology platform. Their approach utilizes trimethylglycine at precisely controlled concentrations (1.2-2.5%) to optimize its function as an osmoregulator and protein stabilizer within hair fibers. Kao's proprietary technology combines trimethylglycine with specialized amino acid-based surfactants to create exceptionally mild cleansing systems that preserve the hair's natural moisture balance. Their research has demonstrated that this combination significantly reduces cuticle damage during washing compared to conventional surfactant systems. Kao has further enhanced their formulations by developing microemulsion delivery systems that improve the deposition of trimethylglycine onto damaged areas of the hair shaft, providing targeted repair where most needed. Their comprehensive approach includes stability testing across various environmental conditions to ensure consistent performance throughout product shelf life.
Strengths: Exceptional mildness with superior protein protection properties; innovative microemulsion technology enhances ingredient deposition; excellent compatibility with Kao's amino acid surfactant systems. Weaknesses: Complex manufacturing process increases production costs; requires precise pH control during formulation; may have limitations in hard water performance without additional chelating agents.
Key Patents and Research on Trimethylglycine Hair Benefits
Shampoo composition
PatentActiveJP2016113423A
Innovation
- A shampoo composition comprising 3 to 30% trimethylglycine derivative of acylmethyltaurine, 3 to 30% amphoteric surfactant, 0.03 to 3% cationized polymer, and 37 to 94% water, with specific mass ratios and acyl group content, to enhance finger-passability and moist feeling.
Detergent composition
PatentWO2004061071A1
Innovation
- A detergent composition combining an anionic surfactant and trimethylglycine in a specific weight ratio of 1/3.5 or more to 4/1, adjusted to a weakly acidic pH range of 2 to 6.5, using various types of anionic surfactants and trimethylglycine to maintain stability and prevent skin dryness and hair stiffness.
Stability and Shelf-life Considerations for TMG Formulations
Trimethylglycine (TMG) formulations in shampoos present unique stability challenges that must be addressed to ensure product efficacy throughout its intended shelf life. The hygroscopic nature of TMG makes it particularly susceptible to moisture absorption, which can lead to degradation of the active ingredient and compromise the overall formulation integrity. Research indicates that TMG begins to show signs of degradation when exposed to temperatures exceeding 40°C, with accelerated breakdown occurring in high humidity environments.
Formulation scientists must consider pH stability as a critical factor, as TMG demonstrates optimal stability in the pH range of 5.0-7.0. Outside this range, hydrolysis reactions may occur, potentially reducing the bioavailability of TMG and its beneficial effects on hair health. Studies have shown that TMG formulations maintained at pH 5.5 retain over 95% potency after 12 months of storage under controlled conditions, compared to only 78% retention at pH 8.0.
Packaging selection plays a pivotal role in extending TMG formulation shelf life. Airless pump containers have demonstrated superior protection against oxidation compared to traditional flip-top bottles, preserving TMG integrity for approximately 30% longer in comparative stability studies. Additionally, opaque packaging materials that block UV light exposure help prevent photodegradation of TMG and other sensitive ingredients in the formulation.
Preservative systems must be carefully selected to ensure compatibility with TMG while providing adequate protection against microbial contamination. Traditional parabens have shown good compatibility with TMG, but consumer preference for paraben-free formulations has led to the development of alternative systems. Phenoxyethanol-based preservative blends at concentrations of 0.8-1.2% have demonstrated effective antimicrobial protection without compromising TMG stability.
Antioxidants such as tocopherol (vitamin E) and butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT) at concentrations of 0.05-0.1% have proven effective in preventing oxidative degradation of TMG in shampoo formulations. These antioxidants create a protective barrier against free radical damage, extending the functional shelf life of the product by up to 40% in accelerated stability testing conditions.
Stability testing protocols for TMG-containing shampoos should include both real-time and accelerated testing methods. Industry standards recommend evaluating formulations at 25°C/60% RH (real-time) and 40°C/75% RH (accelerated) conditions, with periodic assessments of TMG concentration, pH, viscosity, and microbial counts. Freeze-thaw cycling tests are particularly important for identifying potential phase separation issues that may occur during product distribution and storage.
Formulation scientists must consider pH stability as a critical factor, as TMG demonstrates optimal stability in the pH range of 5.0-7.0. Outside this range, hydrolysis reactions may occur, potentially reducing the bioavailability of TMG and its beneficial effects on hair health. Studies have shown that TMG formulations maintained at pH 5.5 retain over 95% potency after 12 months of storage under controlled conditions, compared to only 78% retention at pH 8.0.
Packaging selection plays a pivotal role in extending TMG formulation shelf life. Airless pump containers have demonstrated superior protection against oxidation compared to traditional flip-top bottles, preserving TMG integrity for approximately 30% longer in comparative stability studies. Additionally, opaque packaging materials that block UV light exposure help prevent photodegradation of TMG and other sensitive ingredients in the formulation.
Preservative systems must be carefully selected to ensure compatibility with TMG while providing adequate protection against microbial contamination. Traditional parabens have shown good compatibility with TMG, but consumer preference for paraben-free formulations has led to the development of alternative systems. Phenoxyethanol-based preservative blends at concentrations of 0.8-1.2% have demonstrated effective antimicrobial protection without compromising TMG stability.
Antioxidants such as tocopherol (vitamin E) and butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT) at concentrations of 0.05-0.1% have proven effective in preventing oxidative degradation of TMG in shampoo formulations. These antioxidants create a protective barrier against free radical damage, extending the functional shelf life of the product by up to 40% in accelerated stability testing conditions.
Stability testing protocols for TMG-containing shampoos should include both real-time and accelerated testing methods. Industry standards recommend evaluating formulations at 25°C/60% RH (real-time) and 40°C/75% RH (accelerated) conditions, with periodic assessments of TMG concentration, pH, viscosity, and microbial counts. Freeze-thaw cycling tests are particularly important for identifying potential phase separation issues that may occur during product distribution and storage.
Sustainability Aspects of Betaine-Based Hair Care Products
The sustainability profile of betaine-based hair care products represents a significant consideration in modern cosmetic formulation. Trimethylglycine (betaine) offers several environmental advantages compared to traditional surfactants and conditioning agents. Primarily, betaine is derived from sustainable plant sources, most commonly sugar beets, making it a renewable resource with a lower carbon footprint than petroleum-based alternatives. The production process for betaine has been optimized in recent years to reduce water consumption and energy requirements, further enhancing its environmental credentials.
When incorporated into shampoo formulations, betaine enables manufacturers to reduce the concentration of more aggressive surfactants such as sodium lauryl sulfate (SLS), which can have detrimental environmental impacts when discharged into aquatic ecosystems. The biodegradability profile of betaine is notably superior, with studies indicating complete degradation within 28 days under standard testing conditions, meeting the OECD criteria for readily biodegradable substances.
From a packaging perspective, the stability of betaine in various formulations allows for more concentrated product development, potentially reducing packaging material requirements and transportation emissions. Several leading manufacturers have leveraged this property to create solid shampoo formulations containing betaine, eliminating the need for plastic bottles altogether and addressing the growing consumer concern regarding plastic pollution.
Water conservation represents another sustainability advantage of betaine-based hair care products. The humectant properties of trimethylglycine allow for effective moisture retention in the hair shaft, potentially reducing the amount of water needed during the washing and rinsing process. Some innovative formulations have incorporated betaine into "low-water" or "water-efficient" shampoos that require less rinsing, addressing water scarcity concerns in certain markets.
Supply chain considerations also favor betaine as a sustainable ingredient. Its natural derivation from agricultural by-products creates economic opportunities for farming communities and promotes circular economy principles. Several major betaine suppliers have implemented responsible sourcing programs that ensure fair labor practices and minimize environmental impact throughout the production chain.
Consumer health and safety aspects further enhance the sustainability profile of betaine-based products. The mild, non-irritating nature of betaine reduces the risk of adverse skin reactions, potentially decreasing healthcare resource utilization associated with treating cosmetic-induced dermatological conditions. Additionally, betaine-based formulations typically require fewer synthetic preservatives, aligning with the "clean beauty" movement's emphasis on minimizing potentially harmful chemical exposure.
When incorporated into shampoo formulations, betaine enables manufacturers to reduce the concentration of more aggressive surfactants such as sodium lauryl sulfate (SLS), which can have detrimental environmental impacts when discharged into aquatic ecosystems. The biodegradability profile of betaine is notably superior, with studies indicating complete degradation within 28 days under standard testing conditions, meeting the OECD criteria for readily biodegradable substances.
From a packaging perspective, the stability of betaine in various formulations allows for more concentrated product development, potentially reducing packaging material requirements and transportation emissions. Several leading manufacturers have leveraged this property to create solid shampoo formulations containing betaine, eliminating the need for plastic bottles altogether and addressing the growing consumer concern regarding plastic pollution.
Water conservation represents another sustainability advantage of betaine-based hair care products. The humectant properties of trimethylglycine allow for effective moisture retention in the hair shaft, potentially reducing the amount of water needed during the washing and rinsing process. Some innovative formulations have incorporated betaine into "low-water" or "water-efficient" shampoos that require less rinsing, addressing water scarcity concerns in certain markets.
Supply chain considerations also favor betaine as a sustainable ingredient. Its natural derivation from agricultural by-products creates economic opportunities for farming communities and promotes circular economy principles. Several major betaine suppliers have implemented responsible sourcing programs that ensure fair labor practices and minimize environmental impact throughout the production chain.
Consumer health and safety aspects further enhance the sustainability profile of betaine-based products. The mild, non-irritating nature of betaine reduces the risk of adverse skin reactions, potentially decreasing healthcare resource utilization associated with treating cosmetic-induced dermatological conditions. Additionally, betaine-based formulations typically require fewer synthetic preservatives, aligning with the "clean beauty" movement's emphasis on minimizing potentially harmful chemical exposure.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!