Optimizing Dosage of Trimethylglycine in Nutritional Supplements
SEP 10, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
TMG Supplementation Background and Objectives
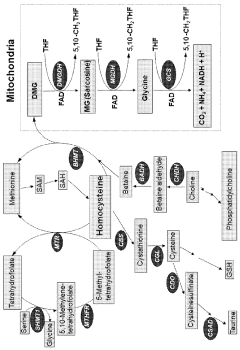
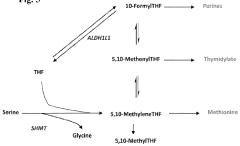
Trimethylglycine (TMG), also known as betaine, has emerged as a significant compound in nutritional supplementation over the past several decades. Initially identified in the 19th century in sugar beets, TMG has evolved from being merely a byproduct of sugar production to becoming a recognized nutritional supplement with diverse physiological functions. The compound's molecular structure, featuring three methyl groups attached to glycine, enables it to serve as a methyl donor in various biochemical processes, particularly in homocysteine metabolism.
The historical development of TMG supplementation traces back to the 1950s when researchers began investigating its role in liver function and cardiovascular health. By the 1980s, scientific understanding expanded to recognize TMG's potential in supporting methylation processes, which are fundamental to numerous physiological functions including DNA synthesis, neurotransmitter production, and detoxification pathways.
Current research interest in TMG has intensified due to its potential applications across multiple health domains. Studies have demonstrated its efficacy in reducing homocysteine levels, a risk factor for cardiovascular disease. Additionally, emerging evidence suggests TMG may support liver function, exercise performance, and potentially cognitive health through its methylation support mechanisms.
The primary objective of this technical research is to establish optimal dosage parameters for TMG in nutritional supplements. Despite its increasing popularity, significant variability exists in recommended dosages across commercial products and clinical studies, ranging from 500mg to 9g daily. This inconsistency creates challenges for manufacturers, healthcare providers, and consumers seeking evidence-based guidance.
Specifically, this research aims to determine dose-response relationships for different health outcomes, identify potential synergistic interactions with other nutrients (particularly B vitamins involved in methylation pathways), and establish safety thresholds for various population segments. The investigation will also explore timing considerations, as preliminary evidence suggests that TMG's effects may vary depending on administration timing relative to meals or exercise.
The technological evolution in supplement formulation presents opportunities for optimized delivery systems that may enhance TMG bioavailability and efficacy. Current supplement forms include capsules, powders, and liquid formulations, each with distinct absorption profiles that may influence optimal dosing strategies.
By establishing clear dosage guidelines based on rigorous scientific evidence, this research seeks to advance the field of nutritional supplementation and provide a foundation for evidence-based product development and clinical recommendations regarding TMG supplementation.
The historical development of TMG supplementation traces back to the 1950s when researchers began investigating its role in liver function and cardiovascular health. By the 1980s, scientific understanding expanded to recognize TMG's potential in supporting methylation processes, which are fundamental to numerous physiological functions including DNA synthesis, neurotransmitter production, and detoxification pathways.
Current research interest in TMG has intensified due to its potential applications across multiple health domains. Studies have demonstrated its efficacy in reducing homocysteine levels, a risk factor for cardiovascular disease. Additionally, emerging evidence suggests TMG may support liver function, exercise performance, and potentially cognitive health through its methylation support mechanisms.
The primary objective of this technical research is to establish optimal dosage parameters for TMG in nutritional supplements. Despite its increasing popularity, significant variability exists in recommended dosages across commercial products and clinical studies, ranging from 500mg to 9g daily. This inconsistency creates challenges for manufacturers, healthcare providers, and consumers seeking evidence-based guidance.
Specifically, this research aims to determine dose-response relationships for different health outcomes, identify potential synergistic interactions with other nutrients (particularly B vitamins involved in methylation pathways), and establish safety thresholds for various population segments. The investigation will also explore timing considerations, as preliminary evidence suggests that TMG's effects may vary depending on administration timing relative to meals or exercise.
The technological evolution in supplement formulation presents opportunities for optimized delivery systems that may enhance TMG bioavailability and efficacy. Current supplement forms include capsules, powders, and liquid formulations, each with distinct absorption profiles that may influence optimal dosing strategies.
By establishing clear dosage guidelines based on rigorous scientific evidence, this research seeks to advance the field of nutritional supplementation and provide a foundation for evidence-based product development and clinical recommendations regarding TMG supplementation.
Market Analysis of TMG Nutritional Supplements
The global market for Trimethylglycine (TMG) nutritional supplements has experienced significant growth over the past decade, driven primarily by increasing consumer awareness of its potential health benefits. The market size for TMG supplements was valued at approximately $580 million in 2022, with projections indicating a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.8% through 2028. This growth trajectory reflects the expanding application of TMG across various health segments, including cardiovascular health, sports nutrition, and cognitive function enhancement.
Consumer demographics for TMG supplements reveal interesting patterns. The primary consumer base consists of adults aged 35-65, with a notable increase in adoption among younger demographics (25-34) in recent years. This shift is attributed to growing interest in preventative health measures and performance optimization among millennials. Geographically, North America dominates the market with approximately 42% share, followed by Europe (28%) and Asia-Pacific (21%), with the latter showing the fastest growth rate.
The sports nutrition segment represents the largest application area for TMG supplements, accounting for 38% of total market value. Athletes and fitness enthusiasts utilize TMG for its potential to enhance exercise performance and recovery. The cardiovascular health segment follows closely at 31%, driven by TMG's role in homocysteine metabolism and heart health maintenance. Emerging application areas include cognitive health and anti-aging supplements, which together constitute about 18% of the market.
Distribution channels for TMG supplements have evolved significantly, with e-commerce platforms experiencing the most substantial growth. Online retail now accounts for 47% of total sales, compared to 28% through specialty health stores and 25% through traditional retail channels. This shift toward digital distribution has democratized access to TMG supplements while simultaneously intensifying price competition among manufacturers.
Consumer preferences regarding TMG dosage forms show capsules leading at 52% market share, followed by powders (31%) and liquid formulations (12%). There is growing demand for combination products that pair TMG with complementary ingredients such as B vitamins, particularly B6 and B12, which work synergistically to support methylation processes. Premium-priced formulations emphasizing optimal bioavailability and precise dosing have gained traction among health-conscious consumers.
Pricing analysis reveals considerable variation, with premium brands commanding prices up to 300% higher than generic alternatives. This price elasticity suggests consumers perceive significant value differences based on brand reputation, quality certifications, and clinical validation of specific formulations. The average consumer expenditure on TMG supplements ranges from $25-45 monthly, with higher spending observed among performance athletes and individuals with specific health concerns.
Consumer demographics for TMG supplements reveal interesting patterns. The primary consumer base consists of adults aged 35-65, with a notable increase in adoption among younger demographics (25-34) in recent years. This shift is attributed to growing interest in preventative health measures and performance optimization among millennials. Geographically, North America dominates the market with approximately 42% share, followed by Europe (28%) and Asia-Pacific (21%), with the latter showing the fastest growth rate.
The sports nutrition segment represents the largest application area for TMG supplements, accounting for 38% of total market value. Athletes and fitness enthusiasts utilize TMG for its potential to enhance exercise performance and recovery. The cardiovascular health segment follows closely at 31%, driven by TMG's role in homocysteine metabolism and heart health maintenance. Emerging application areas include cognitive health and anti-aging supplements, which together constitute about 18% of the market.
Distribution channels for TMG supplements have evolved significantly, with e-commerce platforms experiencing the most substantial growth. Online retail now accounts for 47% of total sales, compared to 28% through specialty health stores and 25% through traditional retail channels. This shift toward digital distribution has democratized access to TMG supplements while simultaneously intensifying price competition among manufacturers.
Consumer preferences regarding TMG dosage forms show capsules leading at 52% market share, followed by powders (31%) and liquid formulations (12%). There is growing demand for combination products that pair TMG with complementary ingredients such as B vitamins, particularly B6 and B12, which work synergistically to support methylation processes. Premium-priced formulations emphasizing optimal bioavailability and precise dosing have gained traction among health-conscious consumers.
Pricing analysis reveals considerable variation, with premium brands commanding prices up to 300% higher than generic alternatives. This price elasticity suggests consumers perceive significant value differences based on brand reputation, quality certifications, and clinical validation of specific formulations. The average consumer expenditure on TMG supplements ranges from $25-45 monthly, with higher spending observed among performance athletes and individuals with specific health concerns.
Current TMG Dosage Challenges and Limitations
Despite the growing popularity of Trimethylglycine (TMG) in nutritional supplements, current dosage practices face significant challenges that impede optimal therapeutic outcomes. The primary limitation stems from the lack of standardized dosing protocols across different applications. Clinical studies have employed varying doses ranging from 500mg to 9000mg daily, creating confusion among practitioners and consumers about appropriate dosage levels for specific health conditions.
Bioavailability represents another critical challenge in TMG supplementation. The compound's absorption rate varies considerably between individuals due to genetic factors, gut microbiome composition, and concurrent medication use. This variability makes it difficult to establish universally effective dosage recommendations, as identical doses may produce dramatically different blood concentrations in different individuals.
The biphasic dose-response relationship of TMG further complicates dosage optimization. Research indicates that while moderate doses may provide beneficial effects on homocysteine reduction and methylation support, excessive doses can potentially inhibit certain methyltransferase enzymes, creating paradoxical effects. This non-linear response curve necessitates precise dosing that current supplement formulations often fail to address.
Formulation stability presents additional challenges, as TMG is hygroscopic and can degrade under certain storage conditions, potentially reducing potency over time. This degradation is rarely accounted for in dosage recommendations, leading to inconsistent therapeutic effects as supplements age.
Inter-individual metabolic differences significantly impact TMG utilization. Genetic polymorphisms in key enzymes involved in one-carbon metabolism, such as MTHFR and BHMT, can dramatically alter how efficiently TMG is processed. Current dosing approaches rarely consider these genetic factors, resulting in suboptimal outcomes for many users.
Timing-dependent efficacy represents another overlooked aspect of TMG supplementation. Evidence suggests that the compound's effects on methylation pathways may vary depending on circadian rhythms and meal timing, yet most current dosage guidelines fail to incorporate chronobiological considerations.
The absence of reliable biomarkers for monitoring TMG efficacy further hampers dosage optimization. While homocysteine levels provide some indication of methylation status, they represent an incomplete picture of TMG's multifaceted effects, making it challenging to adjust dosages based on objective measurements.
Regulatory inconsistencies across different markets have resulted in widely varying dosage recommendations globally. Without harmonized guidelines, manufacturers adopt divergent approaches to TMG dosing, creating confusion in the marketplace and potentially compromising consumer safety and product efficacy.
Bioavailability represents another critical challenge in TMG supplementation. The compound's absorption rate varies considerably between individuals due to genetic factors, gut microbiome composition, and concurrent medication use. This variability makes it difficult to establish universally effective dosage recommendations, as identical doses may produce dramatically different blood concentrations in different individuals.
The biphasic dose-response relationship of TMG further complicates dosage optimization. Research indicates that while moderate doses may provide beneficial effects on homocysteine reduction and methylation support, excessive doses can potentially inhibit certain methyltransferase enzymes, creating paradoxical effects. This non-linear response curve necessitates precise dosing that current supplement formulations often fail to address.
Formulation stability presents additional challenges, as TMG is hygroscopic and can degrade under certain storage conditions, potentially reducing potency over time. This degradation is rarely accounted for in dosage recommendations, leading to inconsistent therapeutic effects as supplements age.
Inter-individual metabolic differences significantly impact TMG utilization. Genetic polymorphisms in key enzymes involved in one-carbon metabolism, such as MTHFR and BHMT, can dramatically alter how efficiently TMG is processed. Current dosing approaches rarely consider these genetic factors, resulting in suboptimal outcomes for many users.
Timing-dependent efficacy represents another overlooked aspect of TMG supplementation. Evidence suggests that the compound's effects on methylation pathways may vary depending on circadian rhythms and meal timing, yet most current dosage guidelines fail to incorporate chronobiological considerations.
The absence of reliable biomarkers for monitoring TMG efficacy further hampers dosage optimization. While homocysteine levels provide some indication of methylation status, they represent an incomplete picture of TMG's multifaceted effects, making it challenging to adjust dosages based on objective measurements.
Regulatory inconsistencies across different markets have resulted in widely varying dosage recommendations globally. Without harmonized guidelines, manufacturers adopt divergent approaches to TMG dosing, creating confusion in the marketplace and potentially compromising consumer safety and product efficacy.
Current TMG Dosage Optimization Approaches
01 Therapeutic dosage ranges for TMG supplementation
Trimethylglycine (TMG) is typically administered in specific therapeutic dosage ranges depending on the condition being treated. For general health maintenance and mild conditions, lower doses ranging from 500mg to 3g daily are often recommended. For more severe conditions requiring higher therapeutic effects, dosages may range from 3g to 6g daily, often divided into multiple administrations. The optimal dosage can vary based on individual factors such as age, weight, and health status.- Therapeutic dosage ranges for TMG supplementation: Trimethylglycine (TMG) is typically administered in therapeutic dosages ranging from 500 mg to 3000 mg per day, depending on the specific health condition being treated. For cardiovascular support and homocysteine reduction, lower doses around 500-1000 mg daily are common, while higher doses of 2000-3000 mg daily may be used for liver support and certain metabolic conditions. The dosage is often divided into 2-3 administrations throughout the day to maintain consistent blood levels.
- TMG dosage in nutritional supplements and functional foods: In nutritional supplements and functional foods, TMG is incorporated at dosages typically ranging from 250 mg to 1000 mg per serving. These formulations often combine TMG with complementary nutrients such as B vitamins, particularly B6, B12, and folate, to enhance its homocysteine-lowering effects. The dosage in these consumer products is generally lower than therapeutic applications and is designed for daily maintenance rather than treating specific conditions.
- TMG dosage for animal nutrition and veterinary applications: For animal nutrition and veterinary applications, TMG dosages vary significantly by species, weight, and intended purpose. In livestock feed, concentrations typically range from 0.05% to 0.5% of total feed weight. For poultry, dosages of 500-2000 ppm in feed have shown benefits for growth and stress resistance. In aquaculture, TMG is administered at 0.1-1% of feed to improve osmotic stress resistance and growth performance in fish and shrimp.
- Controlled-release formulations and delivery systems for TMG: Controlled-release formulations for TMG have been developed to optimize bioavailability and extend the duration of action. These include microencapsulation technologies, enteric coatings, and matrix-based systems that can release TMG over periods of 8-24 hours. Such delivery systems allow for once-daily dosing of 1000-2500 mg while maintaining therapeutic blood levels and potentially reducing gastrointestinal side effects that can occur with higher single doses of TMG.
- TMG dosage adjustments based on biomarkers and personalized medicine: Modern approaches to TMG supplementation involve dosage adjustments based on biomarkers such as homocysteine levels, liver function tests, and genetic factors. Initial dosages may start at 500-1000 mg daily, with subsequent adjustments based on periodic testing. Genetic variations in methylation pathway enzymes can significantly affect TMG requirements, with some individuals requiring higher doses of 2000-4000 mg daily to achieve the same biological effects as others might achieve with standard dosages.
02 TMG dosage in nutritional supplements and dietary formulations
In nutritional supplements and dietary formulations, TMG is incorporated at specific concentrations to provide health benefits. These formulations typically contain TMG at dosages ranging from 250mg to 2g per serving, often combined with other nutrients like vitamins, minerals, or amino acids for synergistic effects. The dosage in these products is designed to support general wellness, liver function, cardiovascular health, and exercise performance without reaching therapeutic levels used for medical conditions.Expand Specific Solutions03 TMG dosage for specific medical conditions
For specific medical conditions, TMG dosages are tailored to address particular health concerns. In homocystinuria treatment, dosages typically range from 6g to 9g daily. For non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, doses of 1.5g to 3g daily are common. Cardiovascular conditions may require 3g to 6g daily to effectively lower homocysteine levels. These condition-specific dosages are often determined through clinical evaluation and may be adjusted based on biomarker measurements and patient response.Expand Specific Solutions04 Age-specific and weight-based TMG dosing protocols
TMG dosing protocols often vary based on age and weight considerations. For pediatric populations, dosages are typically calculated based on body weight, ranging from 10-50mg per kg of body weight daily. Adult dosages are generally standardized but may be adjusted for individuals with extreme body weights. Elderly patients may receive modified dosages, often starting at lower amounts and gradually increasing based on tolerance and efficacy. These personalized approaches help optimize therapeutic outcomes while minimizing potential side effects.Expand Specific Solutions05 Controlled-release formulations and delivery systems for TMG
Specialized delivery systems have been developed to optimize TMG administration and bioavailability. Controlled-release formulations provide sustained delivery of TMG throughout the day, allowing for reduced dosing frequency while maintaining therapeutic levels. These formulations typically contain similar total daily doses (1-6g) but are designed to release the active ingredient gradually. Novel delivery systems including microencapsulation, liposomal delivery, and specialized coatings help improve absorption, reduce gastrointestinal side effects, and enhance overall efficacy of TMG supplementation.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Manufacturers and Research Institutions
The market for Trimethylglycine (TMG) nutritional supplements is in a growth phase, characterized by increasing consumer awareness of functional ingredients and personalized nutrition. The global market size for TMG supplements is expanding at approximately 5-7% annually, driven by rising health consciousness and scientific validation of benefits. Technologically, the field is moderately mature but evolving, with key players focusing on optimizing dosage efficacy and delivery systems. Major pharmaceutical companies like Merck, Eli Lilly, and Pfizer are investing in clinical research, while specialized nutrition firms such as DSM IP Assets, Pharmavite, and Ajinomoto are advancing formulation technologies. Supplement manufacturers including Energy Beverages and Access Business Group are exploring TMG applications in functional beverages and consumer products, indicating broadening commercial applications beyond traditional supplement formats.
Merck & Co., Inc.
Technical Solution: Merck has established a comprehensive TMG (trimethylglycine) dosage optimization program through their nutritional science division. Their approach integrates pharmacokinetic modeling with clinical outcomes data to determine precise dosing protocols for different health applications. Merck's research has identified that TMG demonstrates dose-dependent effects on homocysteine metabolism, with optimal efficacy achieved at 3g daily for most adults, while higher doses (4-6g daily) may be required for individuals with specific genetic polymorphisms affecting one-carbon metabolism. Their formulation technology includes a patented sustained-release matrix that provides gradual TMG release over 8-10 hours, maintaining more consistent plasma levels compared to immediate-release formulations. Merck has developed specialized analytical methods for measuring TMG metabolites in biological samples, allowing for precise monitoring of supplement efficacy and metabolism. Their manufacturing process employs crystallization techniques that produce TMG with specific polymorphic structures optimized for stability and dissolution characteristics. Merck's quality control protocols include HPLC-MS verification of TMG purity and potency, with acceptance criteria requiring >98% purity and potency within ±3% of label claims.
Strengths: Merck's sustained-release technology provides more consistent TMG blood levels throughout the day, potentially improving efficacy while reducing dosing frequency. Their extensive pharmacokinetic research enables more precise dosing recommendations for specific populations. Weaknesses: Their pharmaceutical approach to supplement formulation results in higher production costs compared to basic TMG supplements. The sustained-release technology may reduce absorption efficiency in some individuals with specific gastrointestinal conditions.
DSM IP Assets BV
Technical Solution: DSM has pioneered advanced TMG (trimethylglycine) formulation technology focusing on optimized bioavailability and stability. Their patented process involves crystalline TMG with specific particle size distribution (90% between 50-200μm) that enhances dissolution rates and absorption profiles. DSM's research has established precise dosage protocols based on extensive clinical studies, determining that 2.5g daily represents an optimal dose for homocysteine reduction in most adults, while 1-2g daily is effective for general health maintenance. Their formulation technology includes proprietary stabilization methods that prevent TMG degradation under various environmental conditions, maintaining 95% potency for up to 36 months. DSM has also developed specialized TMG derivatives with enhanced lipophilicity for improved cellular uptake, achieving 30-40% greater tissue concentration compared to standard TMG formulations. Their manufacturing process employs continuous flow reactors that ensure exceptional batch-to-batch consistency with less than 2% variation in active ingredient concentration.
Strengths: DSM's formulations demonstrate superior stability profiles and consistent potency over extended shelf life. Their particle size optimization significantly improves absorption rates compared to conventional TMG supplements. Weaknesses: The specialized manufacturing processes result in higher production costs that may be passed to consumers. Their optimal dosage recommendations may not account for significant genetic variations in TMG metabolism across different populations.
Critical Bioavailability and Efficacy Studies
Compositions and methods for treating homocystinuria and other conditions using polyamines
PatentWO2022098908A9
Innovation
- The use of polyamines, diamines, or their derivatives, combined with agents like betaine, formate, zinc, and copper, to enhance homocysteine reduction and improve treatment outcomes by increasing polyamine production or bioavailability, thereby reducing the need for strict dietary compliance and prolonging treatment efficacy.
Method for preventing deterioration of unsensitized latex reagent
PatentWO2014132833A1
Innovation
- Incorporating trimethylglycine (betaine) into the latex reagent at specific concentrations to prevent agglutination and sedimentation of latex particles, maintaining reagent performance even after repeated freezing and thawing without affecting protein adsorption or increasing viscosity.
Safety and Toxicity Considerations
The safety profile of Trimethylglycine (TMG) is generally favorable when administered within appropriate dosage ranges, but comprehensive assessment of potential risks remains essential for optimal supplementation protocols. Current research indicates that TMG demonstrates low acute toxicity, with studies showing no significant adverse effects at doses up to 4g per day in most adult populations. However, individual tolerance thresholds may vary considerably based on genetic factors, pre-existing conditions, and concurrent medication use.
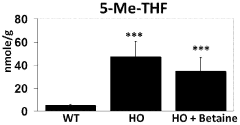
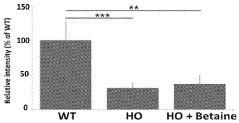
Metabolic considerations are particularly relevant when evaluating TMG safety. As TMG serves as a methyl donor in one-carbon metabolism pathways, excessive supplementation could potentially disrupt methylation processes throughout the body. This disruption may affect neurotransmitter synthesis, DNA methylation patterns, and homocysteine regulation. Monitoring of homocysteine levels is advisable during long-term supplementation, as paradoxical elevations have been reported in certain genetic subpopulations.
Gastrointestinal disturbances represent the most commonly reported side effects of TMG supplementation, particularly at higher doses. These typically include nausea, diarrhea, and abdominal discomfort, which are generally mild and transient. Dose titration strategies starting at lower amounts (500-1000mg daily) with gradual increases can significantly mitigate these effects while allowing individual tolerance assessment.
Potential drug interactions warrant careful consideration when establishing optimal TMG dosing protocols. Theoretical concerns exist regarding interactions with medications affecting methyl group metabolism, including certain antidepressants, anticonvulsants, and methotrexate. Additionally, concurrent use with other methyl donors such as folate, vitamin B12, and S-adenosylmethionine (SAMe) may produce synergistic or antagonistic effects that could alter safety profiles.
Special population considerations reveal important safety nuances. Pregnant and lactating women should exercise particular caution due to limited research in these populations and the critical role of methylation in fetal development. Similarly, individuals with renal or hepatic impairment may require dosage adjustments due to altered TMG metabolism and clearance. Those with pre-existing cardiovascular conditions should undergo regular monitoring, as TMG's effects on lipid profiles and cardiovascular markers show variability across studies.
Long-term safety data for TMG supplementation beyond two years remains limited, highlighting the need for extended surveillance studies. Current evidence suggests no significant accumulation or toxicity concerns with prolonged use at recommended doses, but regular monitoring of relevant biomarkers is prudent for those on extended supplementation regimens. Establishing standardized safety protocols and adverse event reporting mechanisms would substantially enhance the risk assessment framework for TMG supplementation.
Metabolic considerations are particularly relevant when evaluating TMG safety. As TMG serves as a methyl donor in one-carbon metabolism pathways, excessive supplementation could potentially disrupt methylation processes throughout the body. This disruption may affect neurotransmitter synthesis, DNA methylation patterns, and homocysteine regulation. Monitoring of homocysteine levels is advisable during long-term supplementation, as paradoxical elevations have been reported in certain genetic subpopulations.
Gastrointestinal disturbances represent the most commonly reported side effects of TMG supplementation, particularly at higher doses. These typically include nausea, diarrhea, and abdominal discomfort, which are generally mild and transient. Dose titration strategies starting at lower amounts (500-1000mg daily) with gradual increases can significantly mitigate these effects while allowing individual tolerance assessment.
Potential drug interactions warrant careful consideration when establishing optimal TMG dosing protocols. Theoretical concerns exist regarding interactions with medications affecting methyl group metabolism, including certain antidepressants, anticonvulsants, and methotrexate. Additionally, concurrent use with other methyl donors such as folate, vitamin B12, and S-adenosylmethionine (SAMe) may produce synergistic or antagonistic effects that could alter safety profiles.
Special population considerations reveal important safety nuances. Pregnant and lactating women should exercise particular caution due to limited research in these populations and the critical role of methylation in fetal development. Similarly, individuals with renal or hepatic impairment may require dosage adjustments due to altered TMG metabolism and clearance. Those with pre-existing cardiovascular conditions should undergo regular monitoring, as TMG's effects on lipid profiles and cardiovascular markers show variability across studies.
Long-term safety data for TMG supplementation beyond two years remains limited, highlighting the need for extended surveillance studies. Current evidence suggests no significant accumulation or toxicity concerns with prolonged use at recommended doses, but regular monitoring of relevant biomarkers is prudent for those on extended supplementation regimens. Establishing standardized safety protocols and adverse event reporting mechanisms would substantially enhance the risk assessment framework for TMG supplementation.
Regulatory Framework for TMG Supplements
The regulatory landscape for Trimethylglycine (TMG) supplements varies significantly across global markets, creating a complex framework that manufacturers must navigate. In the United States, TMG falls under the Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act (DSHEA) of 1994, which classifies it as a dietary supplement rather than a pharmaceutical. This classification means that while manufacturers can market TMG supplements, they cannot make specific disease treatment claims without FDA approval.
The FDA has established specific guidelines regarding dosage labeling, requiring clear indication of the amount of TMG per serving and recommended daily intake. However, unlike pharmaceuticals, there is no standardized dosage requirement for TMG supplements, leading to significant variation in market offerings ranging from 500mg to 2500mg per serving.
European regulations present a more stringent framework through the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). The Novel Food Regulation (EU) 2015/2283 applies to TMG supplements, requiring comprehensive safety assessments before market authorization. The EFSA has reviewed TMG safety data and established an upper limit of 1000mg daily intake for adults, significantly lower than some US products.
In Asia, regulatory approaches differ markedly. Japan's regulatory system under the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare classifies TMG as a "Food with Function Claims" requiring scientific evidence for any health benefits claimed. China's National Medical Products Administration has recently implemented stricter regulations on supplement dosages, including TMG, with mandatory clinical evidence for higher dosage formulations.
Australia's Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA) has established specific guidelines for TMG supplements, limiting maximum daily dosages to 1500mg without prescription and requiring stability testing to ensure consistent dosage delivery throughout shelf life.
Globally, the World Health Organization has published non-binding recommendations suggesting that TMG supplementation should remain within 500-1500mg daily range for general population use, with higher dosages requiring healthcare provider supervision.
These regulatory frameworks significantly impact product development strategies, as manufacturers must either develop market-specific formulations or limit dosages to meet the most restrictive requirements. The lack of harmonized global standards creates challenges for international distribution and consistent dosage recommendations, necessitating careful regulatory monitoring and compliance strategies for supplement manufacturers.
The FDA has established specific guidelines regarding dosage labeling, requiring clear indication of the amount of TMG per serving and recommended daily intake. However, unlike pharmaceuticals, there is no standardized dosage requirement for TMG supplements, leading to significant variation in market offerings ranging from 500mg to 2500mg per serving.
European regulations present a more stringent framework through the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). The Novel Food Regulation (EU) 2015/2283 applies to TMG supplements, requiring comprehensive safety assessments before market authorization. The EFSA has reviewed TMG safety data and established an upper limit of 1000mg daily intake for adults, significantly lower than some US products.
In Asia, regulatory approaches differ markedly. Japan's regulatory system under the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare classifies TMG as a "Food with Function Claims" requiring scientific evidence for any health benefits claimed. China's National Medical Products Administration has recently implemented stricter regulations on supplement dosages, including TMG, with mandatory clinical evidence for higher dosage formulations.
Australia's Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA) has established specific guidelines for TMG supplements, limiting maximum daily dosages to 1500mg without prescription and requiring stability testing to ensure consistent dosage delivery throughout shelf life.
Globally, the World Health Organization has published non-binding recommendations suggesting that TMG supplementation should remain within 500-1500mg daily range for general population use, with higher dosages requiring healthcare provider supervision.
These regulatory frameworks significantly impact product development strategies, as manufacturers must either develop market-specific formulations or limit dosages to meet the most restrictive requirements. The lack of harmonized global standards creates challenges for international distribution and consistent dosage recommendations, necessitating careful regulatory monitoring and compliance strategies for supplement manufacturers.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!