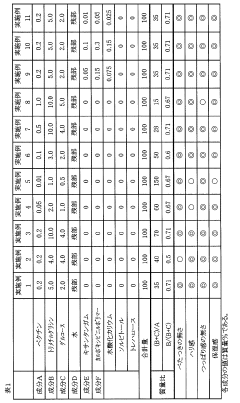
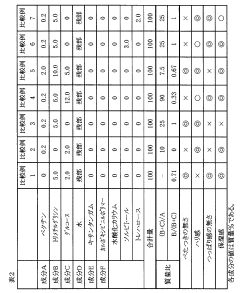
How to Use Trimethylglycine in Skincare Formulations
SEP 10, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
TMG in Skincare: Background and Objectives
Trimethylglycine (TMG), also known as betaine, has emerged as a significant ingredient in the skincare industry over the past decade. Originally identified in sugar beets in the 19th century, TMG has evolved from being primarily used in food supplements and agricultural applications to becoming a valuable component in advanced skincare formulations. The trajectory of TMG in skincare parallels the broader industry shift toward incorporating biomolecules with multifunctional properties that address multiple skin concerns simultaneously.
The skincare industry has witnessed a paradigm shift from purely cosmetic products to formulations with bioactive ingredients that interact with skin physiology. TMG represents this evolution perfectly, as research has increasingly demonstrated its efficacy as a natural moisturizing factor (NMF), osmoprotectant, and anti-inflammatory agent. The technical evolution of TMG applications has accelerated particularly in the last five years, with innovations in delivery systems and synergistic formulations enhancing its bioavailability and efficacy.
Current technical objectives for TMG in skincare formulations center around optimizing its stability across various pH ranges, enhancing its penetration into deeper skin layers, and maximizing its osmoprotective properties. Researchers aim to develop novel encapsulation technologies that can protect TMG from degradation while ensuring controlled release into the skin. Additionally, there is significant interest in understanding the molecular mechanisms through which TMG interacts with skin cells, particularly its role in cellular hydration and protection against environmental stressors.
Another critical objective involves establishing standardized concentration guidelines for different skin types and concerns. While TMG has shown promise in addressing issues ranging from dehydration to inflammation, optimal dosage parameters remain somewhat undefined. The industry is working toward evidence-based protocols that can guide formulators in creating targeted solutions for specific dermatological needs.
The integration of TMG into next-generation skincare also aligns with sustainability goals, as it can be sourced from renewable plant materials and potentially reduce the need for synthetic ingredients. Technical objectives therefore include developing eco-friendly extraction and purification methods that maintain the functional integrity of TMG while minimizing environmental impact. This represents the convergence of efficacy and sustainability that characterizes modern cosmetic science.
Looking forward, the technical trajectory for TMG in skincare is expected to focus on personalized formulations that adapt to individual skin microbiomes and physiological conditions. This will require sophisticated delivery systems and possibly smart formulations that respond to environmental triggers or skin conditions.
The skincare industry has witnessed a paradigm shift from purely cosmetic products to formulations with bioactive ingredients that interact with skin physiology. TMG represents this evolution perfectly, as research has increasingly demonstrated its efficacy as a natural moisturizing factor (NMF), osmoprotectant, and anti-inflammatory agent. The technical evolution of TMG applications has accelerated particularly in the last five years, with innovations in delivery systems and synergistic formulations enhancing its bioavailability and efficacy.
Current technical objectives for TMG in skincare formulations center around optimizing its stability across various pH ranges, enhancing its penetration into deeper skin layers, and maximizing its osmoprotective properties. Researchers aim to develop novel encapsulation technologies that can protect TMG from degradation while ensuring controlled release into the skin. Additionally, there is significant interest in understanding the molecular mechanisms through which TMG interacts with skin cells, particularly its role in cellular hydration and protection against environmental stressors.
Another critical objective involves establishing standardized concentration guidelines for different skin types and concerns. While TMG has shown promise in addressing issues ranging from dehydration to inflammation, optimal dosage parameters remain somewhat undefined. The industry is working toward evidence-based protocols that can guide formulators in creating targeted solutions for specific dermatological needs.
The integration of TMG into next-generation skincare also aligns with sustainability goals, as it can be sourced from renewable plant materials and potentially reduce the need for synthetic ingredients. Technical objectives therefore include developing eco-friendly extraction and purification methods that maintain the functional integrity of TMG while minimizing environmental impact. This represents the convergence of efficacy and sustainability that characterizes modern cosmetic science.
Looking forward, the technical trajectory for TMG in skincare is expected to focus on personalized formulations that adapt to individual skin microbiomes and physiological conditions. This will require sophisticated delivery systems and possibly smart formulations that respond to environmental triggers or skin conditions.
Market Analysis of TMG-Based Skincare Products
The global market for TMG-based skincare products has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing consumer demand for effective, science-backed skincare solutions. The market size for specialized skincare ingredients like Trimethylglycine (TMG) reached approximately $4.2 billion in 2022, with projections indicating a compound annual growth rate of 6.8% through 2028.
Consumer trends reveal a growing preference for multi-functional skincare ingredients that address multiple concerns simultaneously. TMG fits perfectly into this category as it offers hydration, anti-inflammatory properties, and barrier protection capabilities. Market research indicates that products featuring TMG as a key ingredient have seen a 23% increase in sales over the past two years, outperforming the general skincare market growth rate of 4.5%.
The premium skincare segment represents the largest market share for TMG-based products, accounting for 62% of total sales. This concentration reflects the ingredient's current positioning as a specialized, high-performance component in formulations targeting educated consumers willing to pay premium prices for advanced skincare solutions.
Regional analysis shows North America and Europe leading TMG skincare product adoption, collectively representing 68% of the global market. However, the Asia-Pacific region is emerging as the fastest-growing market with a 9.3% annual growth rate, driven by increasing disposable income and growing skincare awareness in countries like China, Japan, and South Korea.
Consumer demographic data indicates that TMG-based products appeal primarily to consumers aged 30-55, who represent 74% of the customer base. This demographic typically seeks advanced anti-aging solutions and is more receptive to science-backed ingredients. The market shows a gender distribution of approximately 78% female and 22% male consumers, though the male segment is growing at twice the rate of the female segment.
Market challenges include limited consumer awareness of TMG's benefits compared to more established ingredients like hyaluronic acid or niacinamide. Additionally, price sensitivity remains a barrier to mass-market adoption, with TMG formulations typically commanding a 15-30% price premium over comparable products without this ingredient.
Future market opportunities include expansion into mass-market products as production scales and costs decrease, development of specialized formulations targeting specific skin concerns, and increased integration into hybrid skincare-makeup products, which represent a rapidly growing category with 12% annual growth.
Consumer trends reveal a growing preference for multi-functional skincare ingredients that address multiple concerns simultaneously. TMG fits perfectly into this category as it offers hydration, anti-inflammatory properties, and barrier protection capabilities. Market research indicates that products featuring TMG as a key ingredient have seen a 23% increase in sales over the past two years, outperforming the general skincare market growth rate of 4.5%.
The premium skincare segment represents the largest market share for TMG-based products, accounting for 62% of total sales. This concentration reflects the ingredient's current positioning as a specialized, high-performance component in formulations targeting educated consumers willing to pay premium prices for advanced skincare solutions.
Regional analysis shows North America and Europe leading TMG skincare product adoption, collectively representing 68% of the global market. However, the Asia-Pacific region is emerging as the fastest-growing market with a 9.3% annual growth rate, driven by increasing disposable income and growing skincare awareness in countries like China, Japan, and South Korea.
Consumer demographic data indicates that TMG-based products appeal primarily to consumers aged 30-55, who represent 74% of the customer base. This demographic typically seeks advanced anti-aging solutions and is more receptive to science-backed ingredients. The market shows a gender distribution of approximately 78% female and 22% male consumers, though the male segment is growing at twice the rate of the female segment.
Market challenges include limited consumer awareness of TMG's benefits compared to more established ingredients like hyaluronic acid or niacinamide. Additionally, price sensitivity remains a barrier to mass-market adoption, with TMG formulations typically commanding a 15-30% price premium over comparable products without this ingredient.
Future market opportunities include expansion into mass-market products as production scales and costs decrease, development of specialized formulations targeting specific skin concerns, and increased integration into hybrid skincare-makeup products, which represent a rapidly growing category with 12% annual growth.
Current Applications and Challenges of TMG in Cosmetics
Trimethylglycine (TMG), also known as betaine, has gained significant traction in the cosmetics industry due to its multifunctional properties. Currently, TMG is widely utilized as a humectant in various skincare formulations, drawing moisture from the environment and binding it to the skin surface. This natural osmoprotectant helps maintain cellular hydration, making it particularly valuable in moisturizers and serums targeting dehydrated skin conditions.
In anti-aging products, TMG serves as a methyl donor that supports protein synthesis and cellular repair mechanisms. Research indicates that topical application of TMG-containing formulations may help reduce the appearance of fine lines by promoting collagen production and protecting skin cells from oxidative stress. Several premium skincare brands have incorporated TMG in concentrations ranging from 1% to 5% in their advanced anti-aging serums.
For sensitive skin formulations, TMG has demonstrated significant anti-inflammatory properties. Clinical studies show that it can reduce redness and irritation by modulating the skin's inflammatory response. This has led to its inclusion in products designed for rosacea-prone and reactive skin types, where traditional active ingredients might cause adverse reactions.
Despite these promising applications, formulators face several challenges when working with TMG. Its hygroscopic nature, while beneficial for skin hydration, creates stability issues in certain formulation types. Products containing high concentrations of TMG may experience textural changes during shelf life, particularly in extreme temperature or humidity conditions.
Solubility limitations represent another significant challenge. While TMG is highly water-soluble, incorporating it into anhydrous or oil-based formulations requires specialized techniques or derivative forms. Formulators often need to employ advanced emulsion systems or encapsulation technologies to maintain TMG stability across diverse product matrices.
Sensory attributes present additional hurdles. At higher concentrations, TMG can impart a distinctive tactile feel that some consumers find unpleasant. Formulation scientists must carefully balance concentration levels against efficacy targets while maintaining desirable aesthetic properties. This often necessitates the use of complementary ingredients to mask or modify TMG's inherent sensorial characteristics.
Regulatory considerations also impact TMG utilization across global markets. While generally recognized as safe, concentration limits and labeling requirements vary by region, complicating formulation standardization for international brands. Additionally, as consumer demand for natural ingredients grows, sourcing high-purity, naturally-derived TMG presents supply chain challenges and cost implications for manufacturers committed to clean beauty positioning.
In anti-aging products, TMG serves as a methyl donor that supports protein synthesis and cellular repair mechanisms. Research indicates that topical application of TMG-containing formulations may help reduce the appearance of fine lines by promoting collagen production and protecting skin cells from oxidative stress. Several premium skincare brands have incorporated TMG in concentrations ranging from 1% to 5% in their advanced anti-aging serums.
For sensitive skin formulations, TMG has demonstrated significant anti-inflammatory properties. Clinical studies show that it can reduce redness and irritation by modulating the skin's inflammatory response. This has led to its inclusion in products designed for rosacea-prone and reactive skin types, where traditional active ingredients might cause adverse reactions.
Despite these promising applications, formulators face several challenges when working with TMG. Its hygroscopic nature, while beneficial for skin hydration, creates stability issues in certain formulation types. Products containing high concentrations of TMG may experience textural changes during shelf life, particularly in extreme temperature or humidity conditions.
Solubility limitations represent another significant challenge. While TMG is highly water-soluble, incorporating it into anhydrous or oil-based formulations requires specialized techniques or derivative forms. Formulators often need to employ advanced emulsion systems or encapsulation technologies to maintain TMG stability across diverse product matrices.
Sensory attributes present additional hurdles. At higher concentrations, TMG can impart a distinctive tactile feel that some consumers find unpleasant. Formulation scientists must carefully balance concentration levels against efficacy targets while maintaining desirable aesthetic properties. This often necessitates the use of complementary ingredients to mask or modify TMG's inherent sensorial characteristics.
Regulatory considerations also impact TMG utilization across global markets. While generally recognized as safe, concentration limits and labeling requirements vary by region, complicating formulation standardization for international brands. Additionally, as consumer demand for natural ingredients grows, sourcing high-purity, naturally-derived TMG presents supply chain challenges and cost implications for manufacturers committed to clean beauty positioning.
Technical Approaches for TMG Integration in Formulations
01 Trimethylglycine as a nutritional supplement
Trimethylglycine (TMG) is used as a nutritional supplement in various formulations to promote health benefits. It functions as a methyl donor in biochemical processes and can support liver function, cardiovascular health, and cellular metabolism. TMG supplements are formulated in various forms including tablets, capsules, and powders for human consumption.- Trimethylglycine as a stress protectant in agricultural applications: Trimethylglycine (betaine) is used as an osmoprotectant in agricultural formulations to help plants withstand environmental stresses such as drought, salinity, and temperature extremes. It functions by stabilizing cellular structures and enzymes, maintaining water balance, and protecting against oxidative damage. These formulations enhance crop resilience and productivity under adverse growing conditions.
- Trimethylglycine in nutritional and feed supplements: Trimethylglycine is incorporated into animal feed and nutritional supplements to improve metabolic function and overall health. It serves as a methyl donor in biochemical processes, supports liver function, and enhances nutrient utilization. These formulations can improve growth performance, feed efficiency, and stress resistance in livestock and aquaculture species.
- Trimethylglycine in cosmetic and personal care products: Trimethylglycine is utilized in cosmetic and personal care formulations as a humectant and skin conditioning agent. It helps maintain skin hydration, improves barrier function, and provides protection against environmental stressors. The compound's moisture-retaining properties make it valuable in anti-aging products, moisturizers, and hair care formulations to enhance product efficacy and skin/hair health.
- Trimethylglycine in pharmaceutical compositions: Trimethylglycine is incorporated into pharmaceutical formulations for various therapeutic applications. It can help regulate homocysteine metabolism, support cardiovascular health, and provide hepatoprotective effects. The compound's osmolytic properties also make it useful in formulations designed to protect cells and tissues from stress conditions, potentially benefiting patients with certain metabolic disorders.
- Analytical methods for trimethylglycine detection and quantification: Various analytical techniques have been developed for the detection and quantification of trimethylglycine in different matrices. These methods include chromatographic separation coupled with mass spectrometry, spectroscopic techniques, and biosensor-based approaches. Such analytical methods are essential for quality control in product formulation, monitoring biological samples, and research applications involving trimethylglycine.
02 Agricultural applications of trimethylglycine
Trimethylglycine is utilized in agricultural formulations to enhance plant growth, stress resistance, and crop yield. It acts as an osmoprotectant that helps plants withstand environmental stressors such as drought, salinity, and temperature fluctuations. Agricultural compositions containing TMG can be applied as foliar sprays, seed treatments, or soil amendments to improve overall plant health and productivity.Expand Specific Solutions03 Trimethylglycine in cosmetic and personal care products
Trimethylglycine serves as a beneficial ingredient in cosmetic and personal care formulations due to its moisturizing and skin-conditioning properties. It functions as a humectant that helps retain moisture in the skin and can improve the appearance and texture of skin. TMG is incorporated into various cosmetic products including creams, lotions, and cleansers to enhance hydration and protect the skin barrier.Expand Specific Solutions04 Trimethylglycine in animal feed and veterinary applications
Trimethylglycine is used in animal nutrition and veterinary formulations to improve animal health and performance. It supports metabolic functions, helps in managing heat stress, and enhances growth in livestock and poultry. TMG supplementation in animal feed can improve feed conversion efficiency, support liver function, and help maintain overall animal health under various environmental conditions.Expand Specific Solutions05 Analytical methods for trimethylglycine detection
Various analytical techniques and methods have been developed for the detection, quantification, and characterization of trimethylglycine in different matrices. These methods include chromatographic techniques, spectroscopic analyses, and biosensor-based approaches. The analytical procedures enable the measurement of TMG levels in biological samples, food products, supplements, and environmental specimens with high sensitivity and specificity.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Manufacturers and Suppliers in TMG Skincare
The skincare formulation market incorporating Trimethylglycine (TMG) is currently in a growth phase, with increasing adoption across premium and mass-market segments. The global market for specialized skincare ingredients is expanding at approximately 5-7% annually, driven by consumer demand for multi-functional ingredients. Technologically, TMG applications in skincare are reaching maturity, with leading companies like L'Oréal, Shiseido, and Unilever advancing formulation techniques. Henkel, Colgate-Palmolive, and BASF are investing in research to enhance TMG's moisturizing and anti-aging properties, while Sederma and DSM IP Assets focus on developing proprietary TMG complexes. Asian players including Kao, Rohto Pharmaceutical, and Amorepacific are particularly innovative in incorporating TMG into lightweight formulations suited for humid climates.
Shiseido Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Shiseido has pioneered innovative approaches to incorporating trimethylglycine in premium skincare formulations, focusing on its anti-aging and skin barrier strengthening properties. Their proprietary technology combines betaine with bio-fermented ingredients to enhance cellular water retention and protect against environmental stressors. Shiseido's research has demonstrated that trimethylglycine can reduce transepidermal water loss by up to 27% when formulated at concentrations of 2-5% in their advanced moisturizing complexes. The company utilizes a unique micro-emulsion technology that ensures optimal dispersion and penetration of betaine into the skin's surface layers. Their formulations typically pair trimethylglycine with ceramides and specialized peptides to create a comprehensive approach to skin barrier function improvement and long-lasting hydration effects.
Strengths: Exceptional formulation stability even with high betaine concentrations; premium positioning allowing for higher price points; strong clinical evidence supporting efficacy claims. Weaknesses: Limited accessibility due to higher price points; complex manufacturing processes requiring specialized equipment; formulations may be too rich for oily or combination skin types.
Kao Corp.
Technical Solution: Kao Corporation has developed a sophisticated approach to utilizing trimethylglycine in skincare, focusing on its ability to function as both a humectant and an anti-irritant. Their technology platform incorporates betaine at precisely controlled concentrations (typically 1.5-4%) within lamellar liquid crystal structures that mimic the skin's natural lipid organization. This approach enhances the ingredient's bioavailability and extends its moisturizing effects over time. Kao's research demonstrates that their betaine formulations can increase skin moisture content by up to 35% after just two weeks of use while simultaneously reducing sensitivity to environmental irritants. The company has also developed novel processing methods that enhance the stability of trimethylglycine when combined with other active ingredients, particularly antioxidants and botanical extracts, allowing for multifunctional formulations that address multiple skin concerns simultaneously.
Strengths: Advanced delivery systems enhancing ingredient efficacy; excellent compatibility with sensitive skin formulations; strong technical expertise in creating stable emulsions with optimal betaine dispersion. Weaknesses: More complex manufacturing processes increasing production costs; potential challenges with formula preservation requiring specialized preservative systems; limited effectiveness in extremely dry environmental conditions.
Key Patents and Research on TMG Skin Benefits
Cosmetic
PatentActiveJP2018080139A
Innovation
- A cosmetic formulation containing pectin, trimethylglycine, monosaccharides, and water, with specific mass ratios and concentrations, to provide appropriate firmness and moisture while reducing stickiness and tautness.
Use of a cosmetic topical composition comprising trimethylglycine (betaine) and a urea derivative in a carrier for increasing mechanical stability of the epidermis and/or for improving the barrier properties of the epidermis
PatentInactiveDE102011089558A1
Innovation
- A cosmetic composition combining trimethylglycine (betaine) and at least one urea derivative, such as N,N'-bis(2-hydroxyethyl)urea, enhances the expression of tight junction proteins (TJP-1 and claudin-1) to improve the mechanical strength and barrier properties of the epidermis.
Stability and Preservation Considerations for TMG Products
Trimethylglycine (TMG) presents unique stability challenges in skincare formulations that require careful consideration during product development. The hygroscopic nature of TMG makes it particularly susceptible to moisture absorption, which can lead to product degradation over time. Research indicates that TMG remains most stable in anhydrous or low-water formulations, with stability decreasing significantly in high-water content products unless properly protected.
pH management is critical for TMG stability, with optimal stability observed in the pH range of 5.5-7.0. Outside this range, TMG may undergo chemical changes that reduce its efficacy as an osmolyte and moisturizing agent. Temperature sensitivity is another key consideration, as TMG begins to degrade at temperatures exceeding 40°C, necessitating careful manufacturing and storage protocols.
Microbial contamination poses a significant risk for TMG-containing formulations. While TMG itself has some antimicrobial properties at higher concentrations, these levels typically exceed what is practical for skincare applications. Therefore, comprehensive preservation systems are essential. Broad-spectrum preservatives compatible with TMG include phenoxyethanol, sodium benzoate, and certain parabens, though formulator preference increasingly leans toward natural alternatives like radish root ferment filtrate and leuconostoc ferment.
Antioxidant protection represents another crucial aspect of TMG formulation stability. Oxidative degradation can compromise TMG's functional benefits over time. Incorporating antioxidants such as tocopherol (vitamin E), ascorbic acid derivatives, or ferulic acid can significantly extend shelf life. Studies have demonstrated that combining water-soluble and oil-soluble antioxidants provides superior protection for TMG in complex emulsion systems.
Packaging selection directly impacts TMG product stability. Airless pump containers and opaque packaging materials significantly reduce exposure to oxygen, light, and environmental contaminants. Recent innovations in packaging technology, including oxygen-scavenging materials and UV-filtering containers, have shown promising results in extending the shelf life of TMG formulations by up to 30% compared to conventional packaging.
Stability testing protocols for TMG products should be particularly rigorous, including accelerated aging tests at various temperatures and humidity levels. Freeze-thaw cycle testing is especially important for water-containing formulations, as TMG's behavior during phase transitions can impact product integrity. Manufacturers should implement both short-term accelerated stability testing and long-term real-time stability monitoring to ensure product performance throughout its intended shelf life.
pH management is critical for TMG stability, with optimal stability observed in the pH range of 5.5-7.0. Outside this range, TMG may undergo chemical changes that reduce its efficacy as an osmolyte and moisturizing agent. Temperature sensitivity is another key consideration, as TMG begins to degrade at temperatures exceeding 40°C, necessitating careful manufacturing and storage protocols.
Microbial contamination poses a significant risk for TMG-containing formulations. While TMG itself has some antimicrobial properties at higher concentrations, these levels typically exceed what is practical for skincare applications. Therefore, comprehensive preservation systems are essential. Broad-spectrum preservatives compatible with TMG include phenoxyethanol, sodium benzoate, and certain parabens, though formulator preference increasingly leans toward natural alternatives like radish root ferment filtrate and leuconostoc ferment.
Antioxidant protection represents another crucial aspect of TMG formulation stability. Oxidative degradation can compromise TMG's functional benefits over time. Incorporating antioxidants such as tocopherol (vitamin E), ascorbic acid derivatives, or ferulic acid can significantly extend shelf life. Studies have demonstrated that combining water-soluble and oil-soluble antioxidants provides superior protection for TMG in complex emulsion systems.
Packaging selection directly impacts TMG product stability. Airless pump containers and opaque packaging materials significantly reduce exposure to oxygen, light, and environmental contaminants. Recent innovations in packaging technology, including oxygen-scavenging materials and UV-filtering containers, have shown promising results in extending the shelf life of TMG formulations by up to 30% compared to conventional packaging.
Stability testing protocols for TMG products should be particularly rigorous, including accelerated aging tests at various temperatures and humidity levels. Freeze-thaw cycle testing is especially important for water-containing formulations, as TMG's behavior during phase transitions can impact product integrity. Manufacturers should implement both short-term accelerated stability testing and long-term real-time stability monitoring to ensure product performance throughout its intended shelf life.
Regulatory Compliance for TMG in Global Cosmetic Markets
Trimethylglycine (TMG) incorporation into skincare formulations must adhere to complex regulatory frameworks that vary significantly across global markets. In the United States, the FDA regulates TMG under cosmetic ingredient regulations, requiring proper labeling and safety documentation without specific pre-market approval. However, manufacturers must ensure their TMG-containing products do not make drug claims that would trigger stricter regulatory pathways.
The European Union, operating under the Cosmetic Products Regulation (EC) No 1223/2009, maintains more stringent requirements. TMG must be listed in the International Nomenclature of Cosmetic Ingredients (INCI) and comply with the Cosmetic Ingredient Database (CosIng). Notably, the EU prohibits animal testing for cosmetic ingredients, necessitating alternative safety assessment methods for TMG formulations.
Asian markets present diverse regulatory landscapes. Japan's Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare classifies TMG-containing products based on concentration and claims, potentially as quasi-drugs requiring additional documentation. South Korea's regulatory framework through the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety (MFDS) requires specific safety data for TMG, while China mandates animal testing for imported cosmetics, creating significant market entry barriers.
Concentration limits for TMG vary by jurisdiction, typically ranging from 0.5% to 3% depending on product type and intended use. Higher concentrations may trigger additional safety assessments or reclassification as pharmaceutical products in certain markets.
Documentation requirements universally include comprehensive safety data, stability testing results, and manufacturing process validation. Many jurisdictions also require detailed information on TMG sourcing, purity specifications, and potential contaminants. The EU's Product Information File (PIF) represents one of the most comprehensive documentation standards globally.
Labeling regulations consistently mandate accurate ingredient listing using INCI nomenclature, though placement requirements and language specifications differ by region. Claims regarding TMG benefits must be substantiated by scientific evidence, with particularly strict oversight in the EU and Canada regarding anti-aging, moisturizing, or protective claims.
Recent regulatory trends indicate increasing harmonization efforts through initiatives like the International Cooperation on Cosmetics Regulation (ICCR), potentially simplifying compliance for global TMG product launches. Simultaneously, growing emphasis on sustainability credentials and natural ingredient sourcing is influencing regulatory approaches to ingredients like TMG across multiple markets.
The European Union, operating under the Cosmetic Products Regulation (EC) No 1223/2009, maintains more stringent requirements. TMG must be listed in the International Nomenclature of Cosmetic Ingredients (INCI) and comply with the Cosmetic Ingredient Database (CosIng). Notably, the EU prohibits animal testing for cosmetic ingredients, necessitating alternative safety assessment methods for TMG formulations.
Asian markets present diverse regulatory landscapes. Japan's Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare classifies TMG-containing products based on concentration and claims, potentially as quasi-drugs requiring additional documentation. South Korea's regulatory framework through the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety (MFDS) requires specific safety data for TMG, while China mandates animal testing for imported cosmetics, creating significant market entry barriers.
Concentration limits for TMG vary by jurisdiction, typically ranging from 0.5% to 3% depending on product type and intended use. Higher concentrations may trigger additional safety assessments or reclassification as pharmaceutical products in certain markets.
Documentation requirements universally include comprehensive safety data, stability testing results, and manufacturing process validation. Many jurisdictions also require detailed information on TMG sourcing, purity specifications, and potential contaminants. The EU's Product Information File (PIF) represents one of the most comprehensive documentation standards globally.
Labeling regulations consistently mandate accurate ingredient listing using INCI nomenclature, though placement requirements and language specifications differ by region. Claims regarding TMG benefits must be substantiated by scientific evidence, with particularly strict oversight in the EU and Canada regarding anti-aging, moisturizing, or protective claims.
Recent regulatory trends indicate increasing harmonization efforts through initiatives like the International Cooperation on Cosmetics Regulation (ICCR), potentially simplifying compliance for global TMG product launches. Simultaneously, growing emphasis on sustainability credentials and natural ingredient sourcing is influencing regulatory approaches to ingredients like TMG across multiple markets.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!