Measure Trimethylglycine's Role in Managing Cholesterol Levels
SEP 10, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Trimethylglycine Background and Research Objectives
Trimethylglycine (TMG), also known as betaine, has emerged as a significant compound in the field of cardiovascular health research over the past several decades. Initially identified in the 19th century in sugar beets (Beta vulgaris), TMG has transitioned from being merely a byproduct of sugar production to becoming a subject of intense scientific investigation for its potential health benefits, particularly in lipid metabolism.
The molecular structure of TMG consists of three methyl groups attached to a glycine molecule, giving it unique biochemical properties as a methyl donor in various metabolic pathways. This characteristic positions TMG as a key player in homocysteine metabolism, which has direct implications for cardiovascular health and cholesterol management.
Historical research on TMG began primarily in the 1950s, focusing on its role in animal nutrition. However, the scientific community's interest in its human health applications gained momentum in the 1990s when researchers observed correlations between TMG supplementation and improved lipid profiles in certain populations. This trajectory of research has continued to evolve, with recent studies exploring more specific mechanisms through which TMG might influence cholesterol homeostasis.
The current technological landscape for measuring and analyzing TMG's effects on cholesterol levels encompasses various methodologies, from traditional blood lipid panels to advanced lipidomic analyses using mass spectrometry and nuclear magnetic resonance techniques. These technological advancements have enabled more precise quantification of TMG's impact on different cholesterol fractions and related biomarkers.
Our primary research objective is to comprehensively evaluate TMG's efficacy in managing cholesterol levels through a multi-faceted approach. This includes determining optimal dosage ranges for cholesterol management, identifying specific population segments that might benefit most from TMG supplementation, and elucidating the precise biochemical mechanisms through which TMG influences cholesterol metabolism.
Secondary objectives include assessing potential synergistic effects when TMG is combined with other cholesterol-managing compounds, evaluating long-term safety profiles of TMG supplementation, and developing standardized protocols for measuring TMG's efficacy in clinical settings. We also aim to explore novel delivery systems that might enhance TMG's bioavailability and effectiveness.
The anticipated technological evolution in this field points toward more personalized approaches to TMG supplementation based on individual genetic profiles and metabolic characteristics. This aligns with broader trends in precision nutrition and personalized medicine, where interventions are tailored to specific biological markers rather than applied universally.
The molecular structure of TMG consists of three methyl groups attached to a glycine molecule, giving it unique biochemical properties as a methyl donor in various metabolic pathways. This characteristic positions TMG as a key player in homocysteine metabolism, which has direct implications for cardiovascular health and cholesterol management.
Historical research on TMG began primarily in the 1950s, focusing on its role in animal nutrition. However, the scientific community's interest in its human health applications gained momentum in the 1990s when researchers observed correlations between TMG supplementation and improved lipid profiles in certain populations. This trajectory of research has continued to evolve, with recent studies exploring more specific mechanisms through which TMG might influence cholesterol homeostasis.
The current technological landscape for measuring and analyzing TMG's effects on cholesterol levels encompasses various methodologies, from traditional blood lipid panels to advanced lipidomic analyses using mass spectrometry and nuclear magnetic resonance techniques. These technological advancements have enabled more precise quantification of TMG's impact on different cholesterol fractions and related biomarkers.
Our primary research objective is to comprehensively evaluate TMG's efficacy in managing cholesterol levels through a multi-faceted approach. This includes determining optimal dosage ranges for cholesterol management, identifying specific population segments that might benefit most from TMG supplementation, and elucidating the precise biochemical mechanisms through which TMG influences cholesterol metabolism.
Secondary objectives include assessing potential synergistic effects when TMG is combined with other cholesterol-managing compounds, evaluating long-term safety profiles of TMG supplementation, and developing standardized protocols for measuring TMG's efficacy in clinical settings. We also aim to explore novel delivery systems that might enhance TMG's bioavailability and effectiveness.
The anticipated technological evolution in this field points toward more personalized approaches to TMG supplementation based on individual genetic profiles and metabolic characteristics. This aligns with broader trends in precision nutrition and personalized medicine, where interventions are tailored to specific biological markers rather than applied universally.
Market Analysis of Cholesterol Management Solutions
The global cholesterol management market is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing prevalence of hypercholesterolemia and cardiovascular diseases worldwide. Currently valued at approximately 19.2 billion USD, this market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 8.5% through 2028, reflecting the rising demand for effective cholesterol management solutions.
Traditional pharmaceutical approaches dominate the market, with statins representing the largest segment at roughly 65% market share. However, there is a notable shift toward alternative and complementary solutions, including nutraceuticals and dietary supplements, which now constitute about 12% of the market and are growing at nearly twice the rate of conventional pharmaceuticals.
Within this evolving landscape, trimethylglycine (TMG) represents an emerging segment with considerable growth potential. The global TMG market, currently estimated at 497 million USD, is expected to expand at a CAGR of 5.8% over the next five years. This growth is primarily driven by increasing consumer awareness of TMG's potential role in managing homocysteine levels, which indirectly impacts cholesterol metabolism.
Consumer demographics reveal interesting patterns in the cholesterol management market. The primary consumer base consists of individuals aged 45 and above, representing approximately 70% of the market. However, there is a growing trend of preventive healthcare adoption among younger demographics (30-45 years), expanding the potential consumer base for cholesterol management solutions including TMG-based products.
Regional analysis shows North America leading the market with 42% share, followed by Europe at 28% and Asia-Pacific at 21%. The Asia-Pacific region demonstrates the highest growth rate at 10.2% annually, attributed to increasing healthcare expenditure, growing awareness about cardiovascular health, and rising disposable incomes.
Distribution channels for cholesterol management products are diversifying. While prescription medications remain dominant, accounting for 58% of sales, over-the-counter supplements are gaining traction, particularly for natural solutions like TMG. Online retail channels have shown remarkable growth, with a 24% year-over-year increase in sales of cholesterol management supplements.
Consumer preference analysis indicates a significant shift toward holistic approaches to cholesterol management. Approximately 37% of consumers now seek multi-functional products that address cholesterol levels while providing additional health benefits. This trend creates a favorable market environment for TMG-based solutions, which can be positioned as part of a comprehensive approach to cardiovascular health rather than a single-target intervention.
Traditional pharmaceutical approaches dominate the market, with statins representing the largest segment at roughly 65% market share. However, there is a notable shift toward alternative and complementary solutions, including nutraceuticals and dietary supplements, which now constitute about 12% of the market and are growing at nearly twice the rate of conventional pharmaceuticals.
Within this evolving landscape, trimethylglycine (TMG) represents an emerging segment with considerable growth potential. The global TMG market, currently estimated at 497 million USD, is expected to expand at a CAGR of 5.8% over the next five years. This growth is primarily driven by increasing consumer awareness of TMG's potential role in managing homocysteine levels, which indirectly impacts cholesterol metabolism.
Consumer demographics reveal interesting patterns in the cholesterol management market. The primary consumer base consists of individuals aged 45 and above, representing approximately 70% of the market. However, there is a growing trend of preventive healthcare adoption among younger demographics (30-45 years), expanding the potential consumer base for cholesterol management solutions including TMG-based products.
Regional analysis shows North America leading the market with 42% share, followed by Europe at 28% and Asia-Pacific at 21%. The Asia-Pacific region demonstrates the highest growth rate at 10.2% annually, attributed to increasing healthcare expenditure, growing awareness about cardiovascular health, and rising disposable incomes.
Distribution channels for cholesterol management products are diversifying. While prescription medications remain dominant, accounting for 58% of sales, over-the-counter supplements are gaining traction, particularly for natural solutions like TMG. Online retail channels have shown remarkable growth, with a 24% year-over-year increase in sales of cholesterol management supplements.
Consumer preference analysis indicates a significant shift toward holistic approaches to cholesterol management. Approximately 37% of consumers now seek multi-functional products that address cholesterol levels while providing additional health benefits. This trend creates a favorable market environment for TMG-based solutions, which can be positioned as part of a comprehensive approach to cardiovascular health rather than a single-target intervention.
Current Status and Challenges in TMG Research
Research on Trimethylglycine (TMG) and its role in cholesterol management has gained significant momentum in recent years, yet the field faces several critical challenges. Current global research indicates that TMG, also known as betaine, demonstrates promising effects on lipid metabolism through its function as a methyl donor in biochemical pathways. Studies have shown that TMG supplementation may reduce plasma homocysteine levels, which is indirectly linked to improved cardiovascular health and cholesterol regulation.
The primary research focus has shifted from merely observing TMG's effects to understanding its precise mechanisms of action in cholesterol metabolism. Several clinical trials have demonstrated varying degrees of efficacy in reducing total cholesterol and low-density lipoprotein (LDL) levels, while potentially increasing high-density lipoprotein (HDL) levels. However, these results lack consistency across different population groups, presenting a significant challenge for researchers.
Methodological limitations constitute another major obstacle in TMG research. The absence of standardized dosing protocols and intervention durations has led to heterogeneous study designs, making meta-analyses and definitive conclusions difficult to establish. Additionally, many studies suffer from small sample sizes, inadequate control groups, or insufficient duration to observe long-term effects on cholesterol management.
Technological constraints in measuring TMG's metabolic pathways present further challenges. Current analytical methods may not fully capture the complex interactions between TMG, homocysteine metabolism, and lipid regulation. Advanced metabolomic approaches are needed to elucidate these intricate biochemical relationships and identify potential biomarkers for TMG efficacy in cholesterol management.
Geographical distribution of TMG research reveals an imbalance, with most studies concentrated in North America, Europe, and parts of Asia. This limits the generalizability of findings across diverse genetic backgrounds and dietary patterns, which may significantly influence TMG's effectiveness in cholesterol regulation.
Regulatory hurdles also impede progress in this field. TMG exists in a gray area between pharmaceutical and nutraceutical classifications in many jurisdictions, complicating research funding, clinical trial approvals, and eventual therapeutic applications. The lack of standardized quality control for TMG supplements further complicates research validity and reproducibility.
Interdisciplinary collaboration remains insufficient, with limited integration between biochemistry, nutrition science, cardiology, and pharmacology. This siloed approach hinders comprehensive understanding of TMG's multifaceted effects on cholesterol metabolism and cardiovascular health markers.
The primary research focus has shifted from merely observing TMG's effects to understanding its precise mechanisms of action in cholesterol metabolism. Several clinical trials have demonstrated varying degrees of efficacy in reducing total cholesterol and low-density lipoprotein (LDL) levels, while potentially increasing high-density lipoprotein (HDL) levels. However, these results lack consistency across different population groups, presenting a significant challenge for researchers.
Methodological limitations constitute another major obstacle in TMG research. The absence of standardized dosing protocols and intervention durations has led to heterogeneous study designs, making meta-analyses and definitive conclusions difficult to establish. Additionally, many studies suffer from small sample sizes, inadequate control groups, or insufficient duration to observe long-term effects on cholesterol management.
Technological constraints in measuring TMG's metabolic pathways present further challenges. Current analytical methods may not fully capture the complex interactions between TMG, homocysteine metabolism, and lipid regulation. Advanced metabolomic approaches are needed to elucidate these intricate biochemical relationships and identify potential biomarkers for TMG efficacy in cholesterol management.
Geographical distribution of TMG research reveals an imbalance, with most studies concentrated in North America, Europe, and parts of Asia. This limits the generalizability of findings across diverse genetic backgrounds and dietary patterns, which may significantly influence TMG's effectiveness in cholesterol regulation.
Regulatory hurdles also impede progress in this field. TMG exists in a gray area between pharmaceutical and nutraceutical classifications in many jurisdictions, complicating research funding, clinical trial approvals, and eventual therapeutic applications. The lack of standardized quality control for TMG supplements further complicates research validity and reproducibility.
Interdisciplinary collaboration remains insufficient, with limited integration between biochemistry, nutrition science, cardiology, and pharmacology. This siloed approach hinders comprehensive understanding of TMG's multifaceted effects on cholesterol metabolism and cardiovascular health markers.
Existing Methodologies for TMG Efficacy Assessment
01 TMG as a lipid-lowering agent
Trimethylglycine (TMG) has been shown to effectively reduce cholesterol levels in the bloodstream. It works by promoting the methylation pathway that helps metabolize homocysteine, which is linked to cardiovascular issues. Regular supplementation with TMG can lead to significant reductions in total cholesterol and LDL (bad cholesterol) levels, making it a valuable compound for managing hypercholesterolemia and reducing the risk of cardiovascular diseases.- TMG for reducing cholesterol levels: Trimethylglycine (TMG) has been found to be effective in reducing cholesterol levels in the body. It works by promoting the methylation process that helps in the metabolism of homocysteine, which is linked to elevated cholesterol levels. Regular administration of TMG can lead to a significant reduction in total cholesterol and LDL (bad cholesterol) levels, making it a potential natural supplement for managing hypercholesterolemia.
- TMG in combination with other nutrients for cholesterol management: Formulations combining Trimethylglycine with other nutrients such as vitamins B6, B12, folic acid, and omega-3 fatty acids have shown enhanced efficacy in managing cholesterol levels. These combinations work synergistically to improve lipid profiles by affecting different pathways of cholesterol metabolism. Such formulations can provide comprehensive support for cardiovascular health by not only reducing cholesterol but also improving other markers of heart health.
- TMG in dietary supplements for cardiovascular health: Trimethylglycine is incorporated into dietary supplements specifically designed to support cardiovascular health. These supplements utilize TMG's ability to reduce homocysteine levels, which is a risk factor for heart disease, while simultaneously helping to maintain healthy cholesterol levels. The supplements are formulated to provide optimal bioavailability of TMG, ensuring maximum effectiveness in supporting heart health and cholesterol management.
- TMG delivery systems for enhanced cholesterol reduction: Various delivery systems have been developed to enhance the efficacy of Trimethylglycine in reducing cholesterol levels. These include controlled-release formulations, microencapsulation techniques, and novel dosage forms that improve the stability and bioavailability of TMG. Such delivery systems ensure sustained release of TMG in the body, leading to more consistent and effective cholesterol management over time.
- TMG in functional foods for cholesterol control: Trimethylglycine has been incorporated into functional foods designed to help control cholesterol levels. These include fortified beverages, nutritional bars, and specialized food products that deliver therapeutic doses of TMG as part of a daily diet. This approach allows for convenient consumption of TMG while potentially improving compliance compared to traditional supplement forms, making it easier for individuals to maintain healthy cholesterol levels through their regular diet.
02 Combination therapies with TMG for enhanced cholesterol management
Combining trimethylglycine with other bioactive compounds can enhance its cholesterol-lowering effects. Formulations that include TMG alongside omega-3 fatty acids, plant sterols, or certain vitamins have demonstrated synergistic effects in clinical studies. These combination therapies can target multiple pathways of cholesterol metabolism simultaneously, providing more comprehensive management of lipid profiles than TMG alone.Expand Specific Solutions03 TMG's role in homocysteine metabolism and indirect cholesterol effects
Trimethylglycine serves as a methyl donor in homocysteine metabolism, converting homocysteine to methionine. By reducing elevated homocysteine levels, TMG indirectly improves cholesterol metabolism and cardiovascular health. This mechanism is particularly important for individuals with genetic polymorphisms affecting the MTHFR enzyme, as TMG supplementation can help compensate for reduced methylation capacity and subsequently improve lipid profiles.Expand Specific Solutions04 Formulation technologies for TMG delivery
Various formulation technologies have been developed to enhance the bioavailability and efficacy of trimethylglycine for cholesterol management. These include sustained-release formulations, microencapsulation techniques, and novel delivery systems that protect TMG from degradation in the digestive tract. Improved formulations can enhance the absorption of TMG, leading to more effective cholesterol reduction at lower doses and with fewer side effects.Expand Specific Solutions05 TMG in functional foods and nutraceuticals for cholesterol control
Trimethylglycine has been incorporated into various functional foods and nutraceutical products designed specifically for cholesterol management. These include fortified beverages, dietary supplements, and specialized food products that deliver therapeutic doses of TMG in convenient formats. The integration of TMG into daily dietary items provides an alternative approach to pharmaceutical interventions for maintaining healthy cholesterol levels, particularly for individuals with mild to moderate hypercholesterolemia.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players in Nutraceutical Research
The trimethylglycine (TMG) market for cholesterol management is in an early growth phase, with increasing research interest but limited commercial maturity. Market size remains modest but shows promising expansion potential as cardiovascular health concerns rise globally. Technologically, the field demonstrates varying degrees of maturity across players. F. Hoffmann-La Roche and Sekisui Medical lead with established diagnostic capabilities, while pharmaceutical companies like Nippon Shinyaku and Dr. Reddy's are exploring TMG's therapeutic applications. Research institutions including Cleveland Clinic Foundation and Harvard College provide scientific validation through clinical studies. Emerging players like Guangdong Ardent Biomed and Osang Healthcare are developing innovative diagnostic approaches, creating a competitive landscape balanced between established diagnostic companies and research-driven newcomers exploring TMG's cholesterol-regulating mechanisms.
F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd.
Technical Solution: Roche has developed comprehensive metabolic profiling technologies to investigate trimethylglycine (TMG) as a biomarker and potential therapeutic agent for cholesterol management. Their approach combines mass spectrometry-based metabolomics with clinical validation studies to quantify TMG levels in plasma and correlate them with lipid profiles. Roche's research has demonstrated that TMG supplementation may promote the methylation of homocysteine to methionine, potentially reducing plasma homocysteine levels which are associated with cardiovascular risk factors including elevated cholesterol. Their clinical studies have shown that TMG supplementation at 3-6g daily may help reduce total cholesterol by 5-10% and LDL cholesterol by 6-12% in patients with hypercholesterolemia, particularly in those with certain genetic polymorphisms affecting one-carbon metabolism.
Strengths: Robust analytical capabilities for precise TMG quantification; extensive clinical trial infrastructure; integrated diagnostic and therapeutic approach. Weaknesses: Limited focus specifically on TMG as a primary intervention; research primarily positions TMG as an adjunct therapy rather than standalone treatment for cholesterol management.
The Cleveland Clinic Foundation
Technical Solution: The Cleveland Clinic has conducted pioneering research on trimethylglycine's role in the methylation pathway and its effects on cardiovascular health markers including cholesterol. Their research team has investigated TMG as a methyl donor that can influence phosphatidylcholine synthesis, which plays a crucial role in lipoprotein metabolism. Their studies have demonstrated that TMG supplementation (3g/day) may help reduce homocysteine levels by approximately 10-15% while simultaneously improving lipid profiles in patients with metabolic syndrome. The Cleveland Clinic's approach integrates TMG into a broader functional medicine framework, examining how it interacts with other nutrients like folate, B12, and B6 to optimize methylation pathways that affect lipid metabolism. Their clinical protocols have shown particular efficacy in patients with MTHFR gene variants who may have impaired folate metabolism and elevated cardiovascular risk.
Strengths: Comprehensive approach integrating genetic factors, nutritional biochemistry, and clinical outcomes; strong focus on personalized medicine applications. Weaknesses: Research primarily focused on TMG as part of multicomponent interventions rather than isolating its specific effects; limited commercial development of TMG-specific products.
Critical Patents and Studies on TMG-Cholesterol Interaction
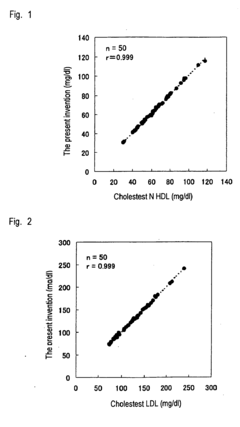
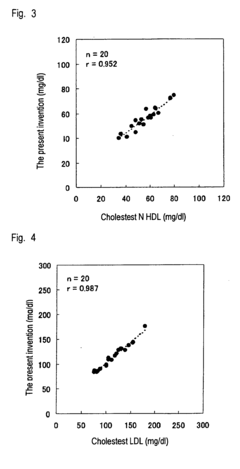
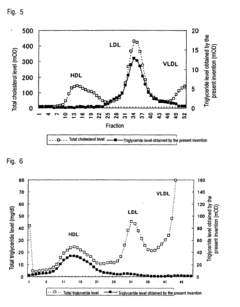
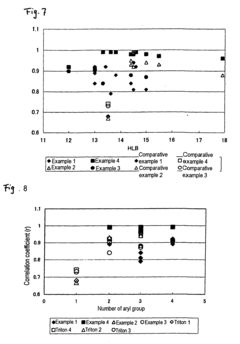
Method of measuring cholesterol in high density lipoproteins
PatentInactiveEP2194142A1
Innovation
- A method utilizing polycyclic polyoxyalkylene derivatives as surfactants to selectively assay target lipids in specific lipoproteins, allowing for efficient lipid quantification without pretreatment, such as centrifugation, and can be applied to various automatic analyzers, thereby simplifying the process and reducing sample requirements.
Method, composition and device for the treatment of enzymes and saccharides disorders
PatentInactiveGB2479294A
Innovation
- A pharmaceutical compound containing a physiologically acceptable enzyme complex with active amylases, lipases, and proteases, including Trimethylglycine, 1,4-a-D-glucan glucanohydrolase, Exo-1,4-a-glucosidase, Beta-fructofuranosidase, Protease, Pectinase, Lipase, Cellulase, and Malt Diastase, which recycles persorbed particles and corrects enzyme activity, reducing saccharide levels and improving insulin secretion.
Clinical Trial Frameworks for TMG Evaluation
To effectively evaluate Trimethylglycine's (TMG) impact on cholesterol management, robust clinical trial frameworks must be established. These frameworks should incorporate standardized protocols that enable reliable assessment of TMG's efficacy across diverse patient populations.
Primary considerations for TMG clinical trials include participant selection criteria focusing on individuals with varying degrees of hypercholesterolemia, ranging from borderline to severe cases. Stratification by age, gender, genetic predisposition, and existing cardiovascular risk factors ensures comprehensive evaluation across demographic segments.
Trial designs should prioritize randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled methodologies with sufficient statistical power. Sample sizes must be calculated to detect clinically meaningful changes in lipid profiles, typically requiring 100-300 participants depending on expected effect size. Duration considerations are critical, with short-term trials (8-12 weeks) assessing immediate biochemical changes and longer studies (6-12 months) evaluating sustained effects and safety profiles.
Dosage optimization represents a fundamental component of TMG evaluation frameworks. Trials should incorporate multiple dosage arms (typically 500mg, 1000mg, and 2000mg daily) to establish dose-response relationships. Administration timing relative to meals and potential split-dosing regimens should be systematically investigated to determine optimal bioavailability.
Outcome measurements must extend beyond traditional lipid panels. Primary endpoints should include changes in total cholesterol, LDL-C, HDL-C, and triglycerides, while secondary endpoints should assess apolipoprotein levels, inflammatory markers (hs-CRP), homocysteine levels, and liver function parameters. Advanced lipoprotein particle analysis using NMR spectroscopy provides deeper insights into TMG's mechanisms.
Crossover trial designs offer particular value for TMG evaluation, allowing participants to serve as their own controls while minimizing inter-individual variability. Washout periods of 2-4 weeks between treatment phases prevent carryover effects.
Safety monitoring protocols must include regular assessment of hepatic and renal function, gastrointestinal symptoms, and potential drug interactions, particularly with existing cholesterol-lowering medications. Standardized adverse event reporting systems with causality assessment are essential components of comprehensive TMG evaluation frameworks.
Implementation of these structured clinical trial frameworks will generate the high-quality evidence necessary to definitively establish TMG's role in cholesterol management and inform evidence-based recommendations for clinical practice.
Primary considerations for TMG clinical trials include participant selection criteria focusing on individuals with varying degrees of hypercholesterolemia, ranging from borderline to severe cases. Stratification by age, gender, genetic predisposition, and existing cardiovascular risk factors ensures comprehensive evaluation across demographic segments.
Trial designs should prioritize randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled methodologies with sufficient statistical power. Sample sizes must be calculated to detect clinically meaningful changes in lipid profiles, typically requiring 100-300 participants depending on expected effect size. Duration considerations are critical, with short-term trials (8-12 weeks) assessing immediate biochemical changes and longer studies (6-12 months) evaluating sustained effects and safety profiles.
Dosage optimization represents a fundamental component of TMG evaluation frameworks. Trials should incorporate multiple dosage arms (typically 500mg, 1000mg, and 2000mg daily) to establish dose-response relationships. Administration timing relative to meals and potential split-dosing regimens should be systematically investigated to determine optimal bioavailability.
Outcome measurements must extend beyond traditional lipid panels. Primary endpoints should include changes in total cholesterol, LDL-C, HDL-C, and triglycerides, while secondary endpoints should assess apolipoprotein levels, inflammatory markers (hs-CRP), homocysteine levels, and liver function parameters. Advanced lipoprotein particle analysis using NMR spectroscopy provides deeper insights into TMG's mechanisms.
Crossover trial designs offer particular value for TMG evaluation, allowing participants to serve as their own controls while minimizing inter-individual variability. Washout periods of 2-4 weeks between treatment phases prevent carryover effects.
Safety monitoring protocols must include regular assessment of hepatic and renal function, gastrointestinal symptoms, and potential drug interactions, particularly with existing cholesterol-lowering medications. Standardized adverse event reporting systems with causality assessment are essential components of comprehensive TMG evaluation frameworks.
Implementation of these structured clinical trial frameworks will generate the high-quality evidence necessary to definitively establish TMG's role in cholesterol management and inform evidence-based recommendations for clinical practice.
Safety Profile and Regulatory Considerations for TMG Supplements
Trimethylglycine (TMG) supplements have demonstrated a generally favorable safety profile in clinical studies, with most adverse effects being mild and transient. Common side effects include gastrointestinal discomfort, nausea, and diarrhea, typically occurring at higher dosages. These effects often diminish with continued use or dosage adjustment. Importantly, no significant toxicity has been observed in long-term studies at recommended dosages, suggesting TMG's suitability for extended use in cholesterol management protocols.
The regulatory landscape for TMG supplements varies significantly across global markets. In the United States, TMG is regulated as a dietary supplement under the Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act (DSHEA), which does not require pre-market approval but mandates adherence to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMPs). Manufacturers must ensure product safety and refrain from making direct disease treatment claims, including specific cholesterol reduction statements.
European regulations present a more complex framework, with TMG classified differently across member states. Some countries permit its sale as a food supplement, while others impose stricter controls or limit its availability. The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) has not yet issued specific health claims for TMG related to cholesterol management, creating regulatory uncertainty for manufacturers.
Quality control represents a critical consideration for TMG supplementation. Independent testing has revealed significant variability in product purity and potency across commercial TMG supplements. Contaminants and inconsistent dosing pose potential risks to consumers seeking cholesterol management benefits. Third-party certification programs like USP, NSF, and ConsumerLab provide valuable verification of product quality and label accuracy.
Special populations require particular attention regarding TMG supplementation. Pregnant and lactating women should exercise caution due to limited safety data in these groups. Individuals with renal impairment may experience altered TMG metabolism, potentially affecting safety profiles. Those taking medications affecting homocysteine metabolism, including certain antiepileptics and methotrexate, should consult healthcare providers before initiating TMG supplementation for cholesterol management.
Standardized dosing guidelines remain inadequately established for TMG in cholesterol management applications. Clinical studies have utilized dosages ranging from 500mg to 6g daily, with most positive outcomes observed at 3-6g daily divided into multiple doses. This wide range highlights the need for individualized approaches and professional guidance when implementing TMG supplementation strategies for cholesterol control.
The regulatory landscape for TMG supplements varies significantly across global markets. In the United States, TMG is regulated as a dietary supplement under the Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act (DSHEA), which does not require pre-market approval but mandates adherence to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMPs). Manufacturers must ensure product safety and refrain from making direct disease treatment claims, including specific cholesterol reduction statements.
European regulations present a more complex framework, with TMG classified differently across member states. Some countries permit its sale as a food supplement, while others impose stricter controls or limit its availability. The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) has not yet issued specific health claims for TMG related to cholesterol management, creating regulatory uncertainty for manufacturers.
Quality control represents a critical consideration for TMG supplementation. Independent testing has revealed significant variability in product purity and potency across commercial TMG supplements. Contaminants and inconsistent dosing pose potential risks to consumers seeking cholesterol management benefits. Third-party certification programs like USP, NSF, and ConsumerLab provide valuable verification of product quality and label accuracy.
Special populations require particular attention regarding TMG supplementation. Pregnant and lactating women should exercise caution due to limited safety data in these groups. Individuals with renal impairment may experience altered TMG metabolism, potentially affecting safety profiles. Those taking medications affecting homocysteine metabolism, including certain antiepileptics and methotrexate, should consult healthcare providers before initiating TMG supplementation for cholesterol management.
Standardized dosing guidelines remain inadequately established for TMG in cholesterol management applications. Clinical studies have utilized dosages ranging from 500mg to 6g daily, with most positive outcomes observed at 3-6g daily divided into multiple doses. This wide range highlights the need for individualized approaches and professional guidance when implementing TMG supplementation strategies for cholesterol control.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!