Comparison of disposable vs. reusable laryngoscopes.
JUL 14, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Laryngoscope Evolution
The evolution of laryngoscopes has been a significant journey in the field of medical technology, particularly in anesthesiology and emergency medicine. The first laryngoscope, invented by Manuel Garcia in 1854, was a simple mirror device used to view the larynx. However, it wasn't until the early 20th century that laryngoscopes became practical tools for intubation.
In 1913, Dr. Chevalier Jackson introduced the first direct laryngoscope, which revolutionized airway management. This design featured a handle with a light source and a blade to displace the tongue and provide a direct view of the larynx. The Jackson laryngoscope set the foundation for modern laryngoscope designs.
The 1940s saw the development of the Macintosh laryngoscope by Sir Robert Macintosh. This curved blade design quickly became the standard for adult intubation due to its ability to provide an improved view of the larynx. Around the same time, Dr. Robert Miller introduced the straight blade laryngoscope, which remains popular for pediatric intubations.
The advent of fiber optic technology in the 1960s marked another significant milestone in laryngoscope evolution. Fiber optic laryngoscopes offered improved illumination and visualization, leading to better intubation success rates. This technology paved the way for video laryngoscopes in the late 1990s and early 2000s.
Video laryngoscopes, incorporating miniature cameras and LCD screens, represented a paradigm shift in airway management. These devices provided a clear, magnified view of the larynx without requiring direct line-of-sight, significantly improving the ease and success of difficult intubations.
In recent years, the debate between disposable and reusable laryngoscopes has gained prominence. Disposable laryngoscopes, introduced in the early 2000s, offer advantages in infection control and maintenance costs. However, reusable laryngoscopes continue to be widely used due to their durability and cost-effectiveness over time.
The latest developments in laryngoscope technology include smart laryngoscopes with integrated vital sign monitors, augmented reality displays, and artificial intelligence-assisted intubation guidance. These advancements aim to further improve intubation success rates and patient safety.
As we look to the future, the evolution of laryngoscopes is likely to continue with a focus on enhancing visualization, reducing complications, and improving ease of use for healthcare providers. The ongoing comparison between disposable and reusable options will likely drive innovation in both categories, ultimately benefiting patient care in critical situations.
In 1913, Dr. Chevalier Jackson introduced the first direct laryngoscope, which revolutionized airway management. This design featured a handle with a light source and a blade to displace the tongue and provide a direct view of the larynx. The Jackson laryngoscope set the foundation for modern laryngoscope designs.
The 1940s saw the development of the Macintosh laryngoscope by Sir Robert Macintosh. This curved blade design quickly became the standard for adult intubation due to its ability to provide an improved view of the larynx. Around the same time, Dr. Robert Miller introduced the straight blade laryngoscope, which remains popular for pediatric intubations.
The advent of fiber optic technology in the 1960s marked another significant milestone in laryngoscope evolution. Fiber optic laryngoscopes offered improved illumination and visualization, leading to better intubation success rates. This technology paved the way for video laryngoscopes in the late 1990s and early 2000s.
Video laryngoscopes, incorporating miniature cameras and LCD screens, represented a paradigm shift in airway management. These devices provided a clear, magnified view of the larynx without requiring direct line-of-sight, significantly improving the ease and success of difficult intubations.
In recent years, the debate between disposable and reusable laryngoscopes has gained prominence. Disposable laryngoscopes, introduced in the early 2000s, offer advantages in infection control and maintenance costs. However, reusable laryngoscopes continue to be widely used due to their durability and cost-effectiveness over time.
The latest developments in laryngoscope technology include smart laryngoscopes with integrated vital sign monitors, augmented reality displays, and artificial intelligence-assisted intubation guidance. These advancements aim to further improve intubation success rates and patient safety.
As we look to the future, the evolution of laryngoscopes is likely to continue with a focus on enhancing visualization, reducing complications, and improving ease of use for healthcare providers. The ongoing comparison between disposable and reusable options will likely drive innovation in both categories, ultimately benefiting patient care in critical situations.
Market Demand Analysis
The market demand for laryngoscopes has been steadily increasing due to the rising prevalence of respiratory diseases, growth in surgical procedures, and the aging population. Both disposable and reusable laryngoscopes play crucial roles in this expanding market, each catering to different needs and preferences within the healthcare sector.
Disposable laryngoscopes have gained significant traction in recent years, driven by concerns over cross-contamination and hospital-acquired infections. Healthcare facilities are increasingly adopting single-use devices to mitigate infection risks and reduce the costs associated with sterilization processes. The COVID-19 pandemic has further accelerated this trend, as healthcare providers prioritize infection control measures.
Reusable laryngoscopes, on the other hand, continue to maintain a strong presence in the market due to their durability, cost-effectiveness over time, and environmental considerations. Many healthcare institutions, particularly in developing countries or resource-constrained settings, prefer reusable devices for their long-term economic benefits.
The global laryngoscope market is experiencing robust growth, with projections indicating continued expansion in the coming years. Factors such as technological advancements, increasing healthcare expenditure, and the growing number of surgical procedures contribute to this positive outlook.
Geographically, North America and Europe lead the market due to advanced healthcare infrastructure and stringent infection control regulations. However, emerging economies in Asia-Pacific and Latin America are expected to witness rapid growth in demand for both disposable and reusable laryngoscopes, driven by improving healthcare access and rising medical tourism.
The market is characterized by a shift towards video laryngoscopes, which offer improved visualization and ease of use compared to traditional direct laryngoscopes. This trend is observed in both disposable and reusable segments, with manufacturers investing in innovative designs and enhanced imaging technologies.
Healthcare providers are increasingly focusing on total cost of ownership when making purchasing decisions. While disposable laryngoscopes offer advantages in terms of infection control and reduced reprocessing costs, reusable devices may prove more economical in high-volume settings. This cost-benefit analysis varies depending on factors such as facility size, patient volume, and local regulations.
Environmental concerns are also shaping market demand, with growing awareness of the ecological impact of medical waste. This has led to increased interest in sustainable healthcare practices, potentially influencing the choice between disposable and reusable laryngoscopes in some markets.
Disposable laryngoscopes have gained significant traction in recent years, driven by concerns over cross-contamination and hospital-acquired infections. Healthcare facilities are increasingly adopting single-use devices to mitigate infection risks and reduce the costs associated with sterilization processes. The COVID-19 pandemic has further accelerated this trend, as healthcare providers prioritize infection control measures.
Reusable laryngoscopes, on the other hand, continue to maintain a strong presence in the market due to their durability, cost-effectiveness over time, and environmental considerations. Many healthcare institutions, particularly in developing countries or resource-constrained settings, prefer reusable devices for their long-term economic benefits.
The global laryngoscope market is experiencing robust growth, with projections indicating continued expansion in the coming years. Factors such as technological advancements, increasing healthcare expenditure, and the growing number of surgical procedures contribute to this positive outlook.
Geographically, North America and Europe lead the market due to advanced healthcare infrastructure and stringent infection control regulations. However, emerging economies in Asia-Pacific and Latin America are expected to witness rapid growth in demand for both disposable and reusable laryngoscopes, driven by improving healthcare access and rising medical tourism.
The market is characterized by a shift towards video laryngoscopes, which offer improved visualization and ease of use compared to traditional direct laryngoscopes. This trend is observed in both disposable and reusable segments, with manufacturers investing in innovative designs and enhanced imaging technologies.
Healthcare providers are increasingly focusing on total cost of ownership when making purchasing decisions. While disposable laryngoscopes offer advantages in terms of infection control and reduced reprocessing costs, reusable devices may prove more economical in high-volume settings. This cost-benefit analysis varies depending on factors such as facility size, patient volume, and local regulations.
Environmental concerns are also shaping market demand, with growing awareness of the ecological impact of medical waste. This has led to increased interest in sustainable healthcare practices, potentially influencing the choice between disposable and reusable laryngoscopes in some markets.
Technical Challenges
The comparison of disposable and reusable laryngoscopes presents several technical challenges that impact their adoption and effectiveness in clinical settings. One of the primary challenges is achieving consistent performance across both types of devices. Reusable laryngoscopes have traditionally been the gold standard, offering reliable functionality and familiarity to healthcare professionals. However, ensuring that disposable alternatives can match this level of performance consistently is a significant hurdle.
Material selection poses another challenge, particularly for disposable laryngoscopes. These devices must be manufactured from materials that are cost-effective yet durable enough to withstand the rigors of intubation procedures. Balancing these requirements while maintaining optical clarity and light transmission efficiency is a complex engineering task. For reusable laryngoscopes, the challenge lies in selecting materials that can withstand repeated sterilization processes without degradation of performance or structural integrity.
Sterilization and infection control present distinct challenges for both types of laryngoscopes. Reusable devices require thorough cleaning and sterilization between uses, which can be time-consuming and resource-intensive. There is also the risk of inadequate sterilization leading to cross-contamination. Disposable laryngoscopes eliminate this risk but introduce new challenges in terms of waste management and environmental impact.
The optical system design is a critical area of focus for both types of laryngoscopes. Achieving optimal visualization of the larynx while maintaining a compact form factor is technically demanding. For disposable devices, the challenge is to create a high-quality optical system that is also cost-effective to produce in large quantities. Reusable laryngoscopes face the challenge of maintaining optical performance over time, despite repeated use and sterilization cycles.
Power source and illumination present another set of technical hurdles. Disposable laryngoscopes often utilize integrated, non-rechargeable power sources, which must provide sufficient illumination for the duration of the procedure while keeping costs low. Reusable devices typically use rechargeable batteries or external power sources, which introduce challenges related to battery life, charging efficiency, and connection reliability.
Ergonomics and user interface design are crucial for both types of laryngoscopes. The devices must be comfortable to hold and manipulate, even in high-stress situations. For disposable laryngoscopes, achieving this level of ergonomic design while keeping production costs low is particularly challenging. Reusable devices must maintain their ergonomic qualities over time, despite repeated use and potential wear.
Finally, the integration of advanced features such as video capabilities introduces additional technical complexities. Incorporating high-resolution cameras and display systems into laryngoscopes while maintaining their core functionality and ease of use is a significant engineering challenge. This is particularly true for disposable devices, where the cost implications of such features must be carefully balanced against their clinical benefits.
Material selection poses another challenge, particularly for disposable laryngoscopes. These devices must be manufactured from materials that are cost-effective yet durable enough to withstand the rigors of intubation procedures. Balancing these requirements while maintaining optical clarity and light transmission efficiency is a complex engineering task. For reusable laryngoscopes, the challenge lies in selecting materials that can withstand repeated sterilization processes without degradation of performance or structural integrity.
Sterilization and infection control present distinct challenges for both types of laryngoscopes. Reusable devices require thorough cleaning and sterilization between uses, which can be time-consuming and resource-intensive. There is also the risk of inadequate sterilization leading to cross-contamination. Disposable laryngoscopes eliminate this risk but introduce new challenges in terms of waste management and environmental impact.
The optical system design is a critical area of focus for both types of laryngoscopes. Achieving optimal visualization of the larynx while maintaining a compact form factor is technically demanding. For disposable devices, the challenge is to create a high-quality optical system that is also cost-effective to produce in large quantities. Reusable laryngoscopes face the challenge of maintaining optical performance over time, despite repeated use and sterilization cycles.
Power source and illumination present another set of technical hurdles. Disposable laryngoscopes often utilize integrated, non-rechargeable power sources, which must provide sufficient illumination for the duration of the procedure while keeping costs low. Reusable devices typically use rechargeable batteries or external power sources, which introduce challenges related to battery life, charging efficiency, and connection reliability.
Ergonomics and user interface design are crucial for both types of laryngoscopes. The devices must be comfortable to hold and manipulate, even in high-stress situations. For disposable laryngoscopes, achieving this level of ergonomic design while keeping production costs low is particularly challenging. Reusable devices must maintain their ergonomic qualities over time, despite repeated use and potential wear.
Finally, the integration of advanced features such as video capabilities introduces additional technical complexities. Incorporating high-resolution cameras and display systems into laryngoscopes while maintaining their core functionality and ease of use is a significant engineering challenge. This is particularly true for disposable devices, where the cost implications of such features must be carefully balanced against their clinical benefits.
Current Solutions
01 Design improvements for enhanced visibility
Laryngoscopes have been developed with improved designs to enhance visibility during intubation procedures. These designs may include adjustable blades, enhanced lighting systems, or specialized optical components to provide a clearer view of the larynx and surrounding structures.- Illumination systems for laryngoscopes: Laryngoscopes often incorporate advanced illumination systems to improve visibility during intubation procedures. These systems may include LED lights, fiber optic cables, or other innovative lighting technologies to provide clear and focused illumination of the larynx and surrounding structures.
- Blade design and materials: The design and materials used in laryngoscope blades are crucial for effective intubation. Innovations in this area focus on creating blades with optimal curvature, flexibility, and durability. Advanced materials may be used to reduce weight, increase strength, or improve sterilization capabilities.
- Video laryngoscopes: Video laryngoscopes incorporate small cameras and screens to provide a clear view of the airway during intubation. These devices can improve the success rate of intubation procedures, especially in difficult cases, by offering a magnified and adjustable view of the larynx.
- Disposable and single-use laryngoscopes: To address concerns about cross-contamination and sterilization, disposable or single-use laryngoscopes have been developed. These devices are designed to be cost-effective while maintaining the necessary functionality for successful intubation procedures.
- Ergonomic handle designs: Innovations in laryngoscope handle designs focus on improving ergonomics and user comfort. These designs may include adjustable grips, lightweight materials, and improved balance to reduce hand fatigue during prolonged use and enhance overall maneuverability.
02 Integration of video technology
Modern laryngoscopes often incorporate video technology, allowing for real-time visualization of the intubation process on external screens. This advancement aids in teaching, documentation, and improving the success rate of intubation procedures.Expand Specific Solutions03 Disposable and single-use laryngoscopes
To address concerns about cross-contamination and improve hygiene, disposable or single-use laryngoscopes have been developed. These devices are designed to be cost-effective while maintaining the necessary functionality for intubation procedures.Expand Specific Solutions04 Ergonomic handle designs
Laryngoscopes with ergonomic handle designs have been created to improve user comfort and control during intubation procedures. These designs may include features such as textured grips, adjustable angles, or lightweight materials to reduce user fatigue.Expand Specific Solutions05 Specialized laryngoscopes for difficult intubations
Specialized laryngoscopes have been developed to address challenging intubation scenarios, such as those involving patients with anatomical abnormalities or limited neck mobility. These devices may incorporate features like flexible blades, alternative insertion techniques, or advanced imaging capabilities.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The market for laryngoscopes is evolving as healthcare providers increasingly consider the trade-offs between disposable and reusable options. The industry is in a transitional phase, with growing demand for single-use devices driven by infection control concerns and cost-effectiveness in certain settings. Market size is expanding, fueled by rising surgical procedures and emergency interventions globally. Technologically, both disposable and reusable laryngoscopes are advancing, with companies like Verathon, Intersurgical, and Olympus leading innovation in video laryngoscopy and ergonomic designs. While reusable devices still dominate in many hospitals, disposable options from firms such as Teleflex Medical and Prodol Meditec are gaining traction, especially in ambulatory and emergency care settings.
Zhejiang Youyi Medical Equipment Co Ltd
Technical Solution: Zhejiang Youyi Medical Equipment Co Ltd has developed a range of disposable laryngoscopes that aim to address infection control concerns while maintaining cost-effectiveness. Their disposable laryngoscopes feature lightweight, ergonomic designs with high-quality, single-use blades. The company has focused on improving the manufacturing process to reduce costs and environmental impact, using recyclable materials where possible[9]. Zhejiang Youyi has also introduced LED lighting technology in their disposable laryngoscopes, providing enhanced illumination comparable to traditional reusable devices. To address concerns about waste generation, the company has implemented a take-back program for proper disposal and recycling of used laryngoscopes[10]. This approach aims to balance the benefits of disposable devices with environmental responsibility.
Strengths: Reduced risk of cross-contamination, no need for sterilization, and consistent performance. Weaknesses: Potential for increased waste generation and higher long-term costs compared to reusable options.
Verathon, Inc.
Technical Solution: Verathon, Inc. has developed the GlideScope video laryngoscope, a reusable device that utilizes advanced video technology for improved laryngeal visualization. The GlideScope features a high-resolution camera and anti-fog lens, providing a clear view of the airway on an external monitor. This system allows for easier intubation in both routine and difficult airway scenarios[1]. The device's ergonomic design and range of blade sizes cater to various patient anatomies. Verathon has also implemented single-use sterile blades to address infection control concerns while maintaining the reusable nature of the main device[2]. This hybrid approach combines the benefits of both disposable and reusable technologies.
Strengths: Superior visualization, versatility for different patient types, and reduced risk of cross-contamination. Weaknesses: Higher initial cost compared to traditional laryngoscopes and potential for technical malfunctions.
Innovative Designs
Video laryngoscopes
PatentWO2016184851A1
Innovation
- A compact, inexpensive laryngoscope design featuring a display screen housing and grip portion that provides a balanced grip, with a unitary housing component integrating the body, blade, and display screen housing, using high-strength materials and a microcontroller for initialization, eliminating the need for expensive processors and connectors.
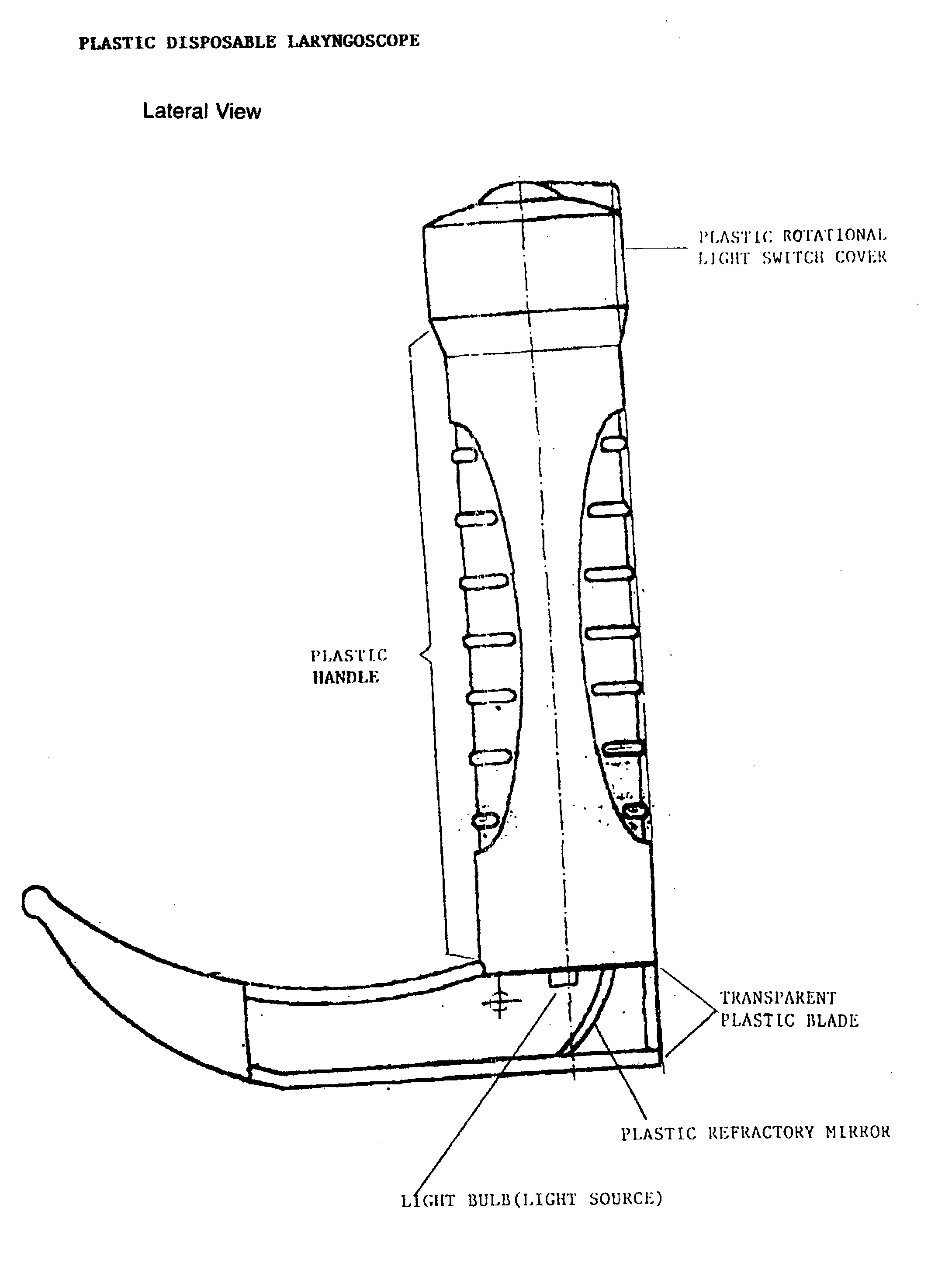
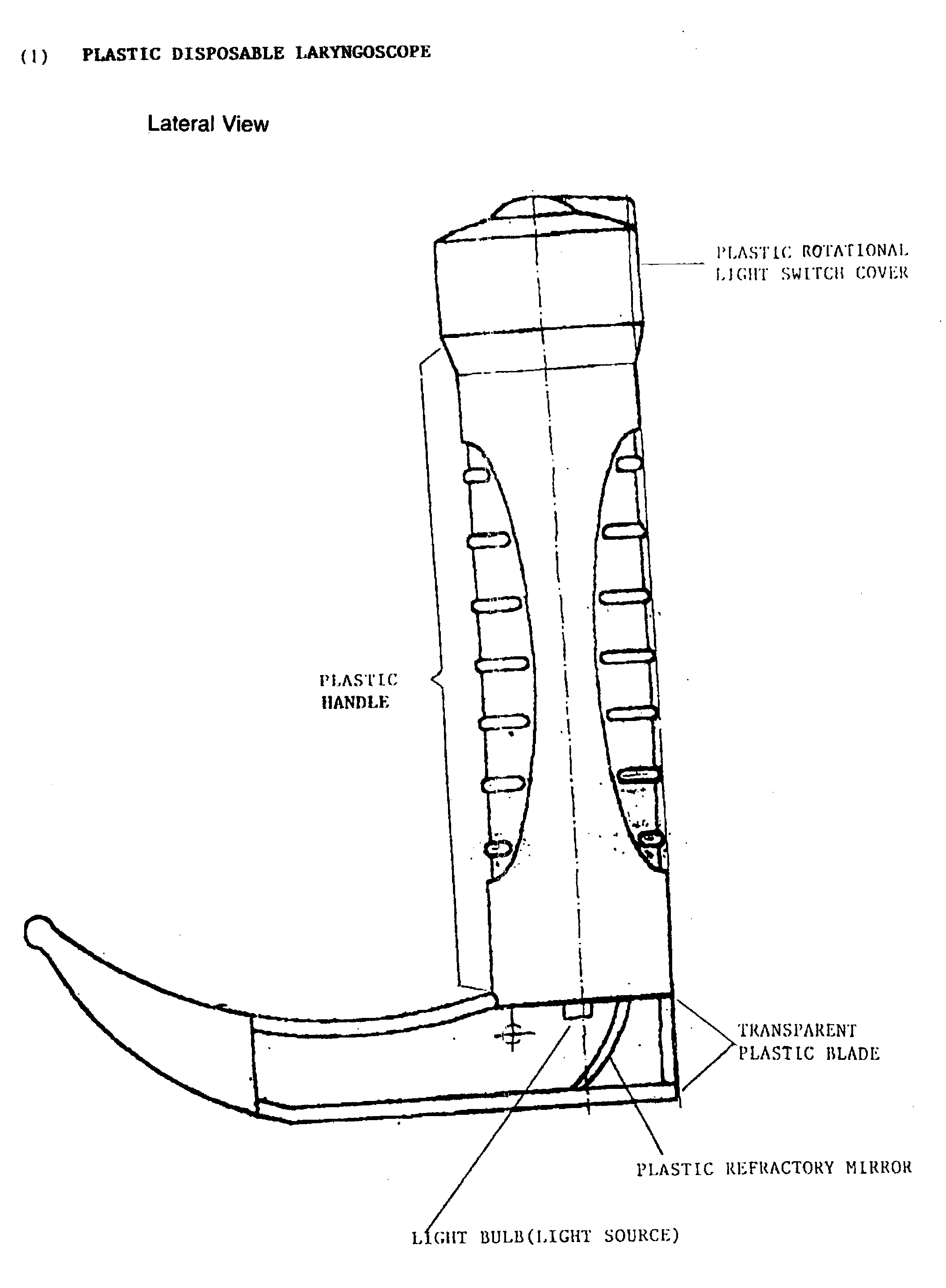
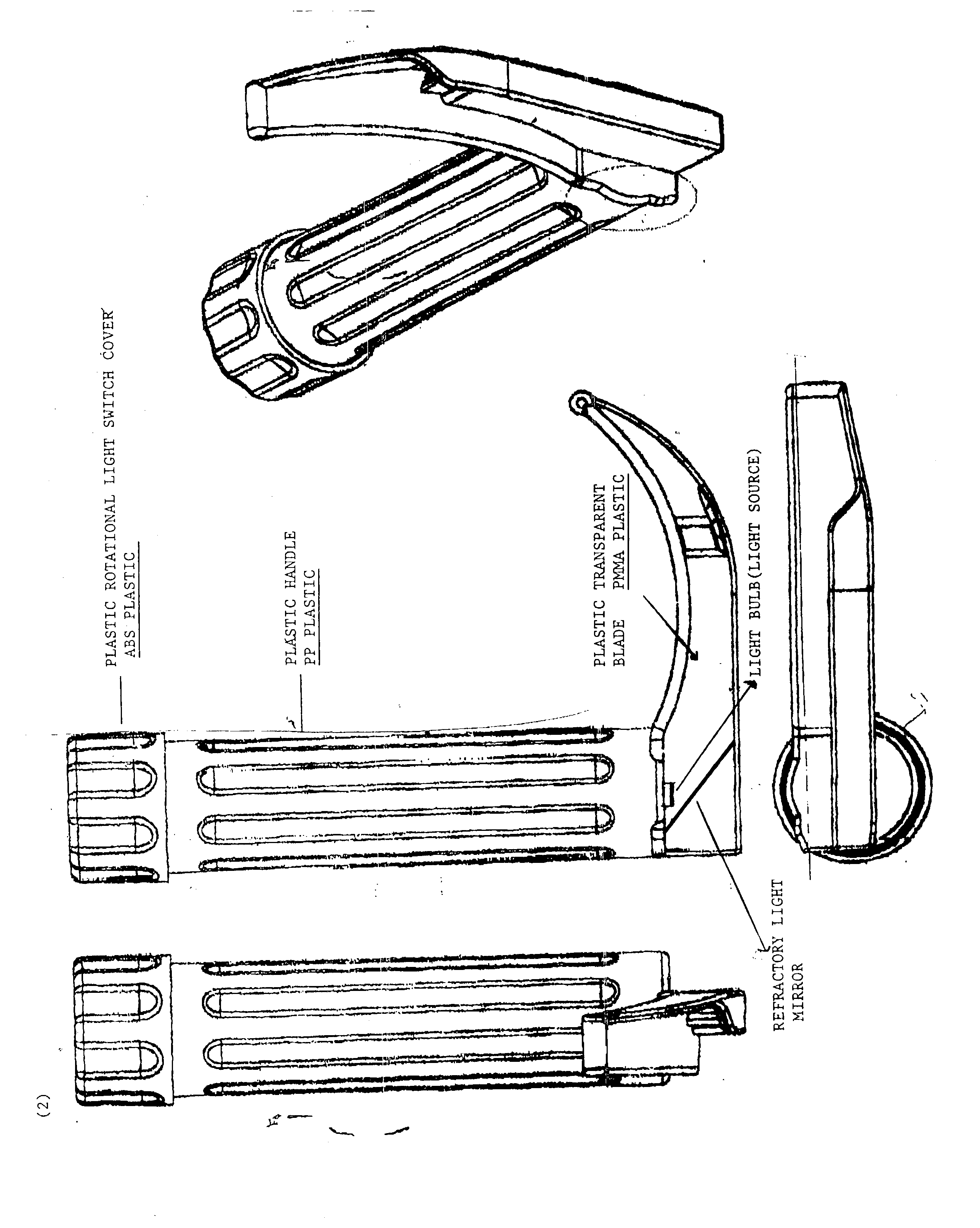
Disposable plastic laryngoscope with built in refractroy light source for the examination of the larynx
PatentInactiveUS20040210115A1
Innovation
- A disposable plastic laryngoscope with a built-in magnified light source, powered by 'C' batteries, featuring a plastic rotational light switch, handle with internal/external power sources, and a transparent plastic blade with refracted light for enhanced visibility of the larynx.
Regulatory Compliance
Regulatory compliance is a critical aspect in the comparison of disposable and reusable laryngoscopes. Both types of devices must adhere to stringent guidelines set by regulatory bodies such as the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in the United States and the European Medicines Agency (EMA) in Europe.
For disposable laryngoscopes, manufacturers must demonstrate compliance with safety and performance standards, including biocompatibility testing to ensure the materials used are safe for patient contact. These devices are typically classified as Class I or Class II medical devices, depending on their specific features and intended use. The regulatory pathway for disposable laryngoscopes often involves a 510(k) premarket notification in the US, which requires manufacturers to demonstrate substantial equivalence to a legally marketed predicate device.
Reusable laryngoscopes face additional regulatory scrutiny due to their repeated use nature. Manufacturers must provide comprehensive instructions for cleaning, disinfection, and sterilization processes. These devices are usually classified as Class II medical devices and require more extensive documentation, including validation of reprocessing methods. The FDA's guidance on reprocessing medical devices emphasizes the importance of clear, validated instructions to ensure patient safety across multiple uses.
Both disposable and reusable laryngoscopes must comply with international standards such as ISO 13485 for quality management systems in medical devices. Additionally, they must meet specific performance standards like ISO 7376 for anaesthetic and respiratory equipment - laryngoscopes for tracheal intubation.
In the European Union, both types of laryngoscopes must conform to the Medical Device Regulation (MDR), which replaced the previous Medical Device Directive (MDD) in 2021. This regulation imposes stricter requirements on clinical evaluation, post-market surveillance, and traceability of medical devices.
Regulatory bodies are increasingly focusing on the environmental impact of medical devices. While disposable laryngoscopes may face scrutiny regarding waste generation, reusable devices must demonstrate effective decontamination processes and durability over multiple uses. This environmental consideration is becoming an important factor in regulatory assessments and healthcare facility procurement decisions.
Manufacturers of both disposable and reusable laryngoscopes must maintain ongoing compliance through post-market surveillance, reporting adverse events, and implementing corrective actions when necessary. The regulatory landscape continues to evolve, with increasing emphasis on real-world evidence and the integration of digital technologies in medical devices, which may impact future compliance requirements for laryngoscopes.
For disposable laryngoscopes, manufacturers must demonstrate compliance with safety and performance standards, including biocompatibility testing to ensure the materials used are safe for patient contact. These devices are typically classified as Class I or Class II medical devices, depending on their specific features and intended use. The regulatory pathway for disposable laryngoscopes often involves a 510(k) premarket notification in the US, which requires manufacturers to demonstrate substantial equivalence to a legally marketed predicate device.
Reusable laryngoscopes face additional regulatory scrutiny due to their repeated use nature. Manufacturers must provide comprehensive instructions for cleaning, disinfection, and sterilization processes. These devices are usually classified as Class II medical devices and require more extensive documentation, including validation of reprocessing methods. The FDA's guidance on reprocessing medical devices emphasizes the importance of clear, validated instructions to ensure patient safety across multiple uses.
Both disposable and reusable laryngoscopes must comply with international standards such as ISO 13485 for quality management systems in medical devices. Additionally, they must meet specific performance standards like ISO 7376 for anaesthetic and respiratory equipment - laryngoscopes for tracheal intubation.
In the European Union, both types of laryngoscopes must conform to the Medical Device Regulation (MDR), which replaced the previous Medical Device Directive (MDD) in 2021. This regulation imposes stricter requirements on clinical evaluation, post-market surveillance, and traceability of medical devices.
Regulatory bodies are increasingly focusing on the environmental impact of medical devices. While disposable laryngoscopes may face scrutiny regarding waste generation, reusable devices must demonstrate effective decontamination processes and durability over multiple uses. This environmental consideration is becoming an important factor in regulatory assessments and healthcare facility procurement decisions.
Manufacturers of both disposable and reusable laryngoscopes must maintain ongoing compliance through post-market surveillance, reporting adverse events, and implementing corrective actions when necessary. The regulatory landscape continues to evolve, with increasing emphasis on real-world evidence and the integration of digital technologies in medical devices, which may impact future compliance requirements for laryngoscopes.
Cost-Benefit Analysis
The cost-benefit analysis of disposable versus reusable laryngoscopes is a critical consideration for healthcare facilities. Initial costs favor disposable laryngoscopes, as they require no upfront investment in expensive equipment. However, the long-term financial implications are more complex.
Reusable laryngoscopes have higher initial costs due to the purchase of durable equipment and sterilization systems. These costs can be significant, especially for smaller healthcare facilities. However, over time, the per-use cost of reusable laryngoscopes decreases, potentially offering long-term savings.
Disposable laryngoscopes, while cheaper initially, incur ongoing costs with each use. These costs can accumulate rapidly in high-volume settings. Additionally, the environmental impact and disposal costs of single-use devices must be factored into the overall expense.
Maintenance and repair costs are exclusive to reusable laryngoscopes. These devices require regular servicing, battery replacements, and occasional repairs, which add to their total cost of ownership. Conversely, disposable laryngoscopes eliminate these ongoing maintenance expenses.
Time costs associated with cleaning and sterilization are significant for reusable laryngoscopes. This process requires dedicated staff time and resources, which can impact overall operational efficiency. Disposable laryngoscopes offer time savings in this regard, as they require no reprocessing.
Quality and performance considerations also factor into the cost-benefit analysis. Reusable laryngoscopes often provide superior image quality and durability, potentially leading to improved clinical outcomes and reduced procedure times. This can indirectly contribute to cost savings through increased efficiency and reduced complications.
Risk management is another crucial aspect. Disposable laryngoscopes minimize the risk of cross-contamination, potentially reducing healthcare-associated infections and their associated costs. Reusable devices, if not properly sterilized, can pose infection risks, leading to potential legal and financial liabilities.
Storage and inventory management costs differ between the two options. Disposable laryngoscopes require more storage space and frequent restocking, which can increase inventory management costs. Reusable devices, while requiring less storage, necessitate dedicated space and systems for cleaning and sterilization.
In conclusion, the cost-benefit analysis of disposable versus reusable laryngoscopes is multifaceted, involving considerations beyond simple per-unit costs. Healthcare facilities must carefully evaluate their specific usage patterns, patient volumes, and long-term financial strategies to determine the most cost-effective solution for their needs.
Reusable laryngoscopes have higher initial costs due to the purchase of durable equipment and sterilization systems. These costs can be significant, especially for smaller healthcare facilities. However, over time, the per-use cost of reusable laryngoscopes decreases, potentially offering long-term savings.
Disposable laryngoscopes, while cheaper initially, incur ongoing costs with each use. These costs can accumulate rapidly in high-volume settings. Additionally, the environmental impact and disposal costs of single-use devices must be factored into the overall expense.
Maintenance and repair costs are exclusive to reusable laryngoscopes. These devices require regular servicing, battery replacements, and occasional repairs, which add to their total cost of ownership. Conversely, disposable laryngoscopes eliminate these ongoing maintenance expenses.
Time costs associated with cleaning and sterilization are significant for reusable laryngoscopes. This process requires dedicated staff time and resources, which can impact overall operational efficiency. Disposable laryngoscopes offer time savings in this regard, as they require no reprocessing.
Quality and performance considerations also factor into the cost-benefit analysis. Reusable laryngoscopes often provide superior image quality and durability, potentially leading to improved clinical outcomes and reduced procedure times. This can indirectly contribute to cost savings through increased efficiency and reduced complications.
Risk management is another crucial aspect. Disposable laryngoscopes minimize the risk of cross-contamination, potentially reducing healthcare-associated infections and their associated costs. Reusable devices, if not properly sterilized, can pose infection risks, leading to potential legal and financial liabilities.
Storage and inventory management costs differ between the two options. Disposable laryngoscopes require more storage space and frequent restocking, which can increase inventory management costs. Reusable devices, while requiring less storage, necessitate dedicated space and systems for cleaning and sterilization.
In conclusion, the cost-benefit analysis of disposable versus reusable laryngoscopes is multifaceted, involving considerations beyond simple per-unit costs. Healthcare facilities must carefully evaluate their specific usage patterns, patient volumes, and long-term financial strategies to determine the most cost-effective solution for their needs.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!