The impact of tele-surgery on laryngoscope fittings.
JUL 14, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Telesurgery Laryngoscopy Background and Objectives
Telesurgery, a revolutionary advancement in medical technology, has significantly impacted various surgical procedures, including laryngoscope fittings. This innovative approach combines robotics, telecommunications, and surgical expertise to enable remote surgical interventions. The development of telesurgery for laryngoscopy stems from the need to address geographical barriers and improve access to specialized care in underserved areas.
The evolution of telesurgery in laryngoscopy can be traced back to the early 2000s when robotic surgical systems were first introduced. Initially, these systems were primarily used for minimally invasive procedures in other medical fields. However, as technology advanced, researchers and medical professionals recognized the potential for applying telesurgery techniques to laryngoscope fittings.
The primary objective of implementing telesurgery in laryngoscope fittings is to enhance the precision and effectiveness of the procedure while overcoming geographical limitations. By allowing skilled surgeons to operate remotely, telesurgery aims to provide high-quality care to patients in remote or underserved areas who may not have access to specialized laryngology expertise.
Another crucial goal is to improve patient outcomes by leveraging advanced imaging technologies and robotic systems. These technologies offer enhanced visualization and control during the procedure, potentially leading to more accurate diagnoses and better-fitted laryngoscopes. Additionally, telesurgery seeks to reduce the risk of complications associated with traditional laryngoscope fittings by minimizing human error and optimizing surgical techniques.
The development of telesurgery for laryngoscopy also aims to address the growing demand for specialized care in an aging population. As the incidence of laryngeal disorders increases, telesurgery offers a scalable solution to meet the rising need for expert interventions without the constraints of physical proximity.
Furthermore, telesurgery in laryngoscope fittings has the potential to revolutionize medical education and training. By enabling real-time observation and participation in procedures performed by leading experts, it can facilitate knowledge transfer and skill development among medical professionals worldwide.
As we explore the impact of telesurgery on laryngoscope fittings, it is essential to consider the technological challenges, ethical implications, and regulatory frameworks that need to be addressed. The successful implementation of this technology requires overcoming issues related to network latency, data security, and the development of standardized protocols for remote surgical interventions.
In conclusion, the background and objectives of telesurgery in laryngoscopy represent a significant leap forward in medical care. By combining cutting-edge technology with surgical expertise, it holds the promise of improving patient outcomes, expanding access to specialized care, and advancing medical education on a global scale.
The evolution of telesurgery in laryngoscopy can be traced back to the early 2000s when robotic surgical systems were first introduced. Initially, these systems were primarily used for minimally invasive procedures in other medical fields. However, as technology advanced, researchers and medical professionals recognized the potential for applying telesurgery techniques to laryngoscope fittings.
The primary objective of implementing telesurgery in laryngoscope fittings is to enhance the precision and effectiveness of the procedure while overcoming geographical limitations. By allowing skilled surgeons to operate remotely, telesurgery aims to provide high-quality care to patients in remote or underserved areas who may not have access to specialized laryngology expertise.
Another crucial goal is to improve patient outcomes by leveraging advanced imaging technologies and robotic systems. These technologies offer enhanced visualization and control during the procedure, potentially leading to more accurate diagnoses and better-fitted laryngoscopes. Additionally, telesurgery seeks to reduce the risk of complications associated with traditional laryngoscope fittings by minimizing human error and optimizing surgical techniques.
The development of telesurgery for laryngoscopy also aims to address the growing demand for specialized care in an aging population. As the incidence of laryngeal disorders increases, telesurgery offers a scalable solution to meet the rising need for expert interventions without the constraints of physical proximity.
Furthermore, telesurgery in laryngoscope fittings has the potential to revolutionize medical education and training. By enabling real-time observation and participation in procedures performed by leading experts, it can facilitate knowledge transfer and skill development among medical professionals worldwide.
As we explore the impact of telesurgery on laryngoscope fittings, it is essential to consider the technological challenges, ethical implications, and regulatory frameworks that need to be addressed. The successful implementation of this technology requires overcoming issues related to network latency, data security, and the development of standardized protocols for remote surgical interventions.
In conclusion, the background and objectives of telesurgery in laryngoscopy represent a significant leap forward in medical care. By combining cutting-edge technology with surgical expertise, it holds the promise of improving patient outcomes, expanding access to specialized care, and advancing medical education on a global scale.
Market Analysis for Telesurgical Laryngoscope Fittings
The market for telesurgical laryngoscope fittings is experiencing significant growth, driven by advancements in telemedicine and the increasing demand for remote surgical procedures. This innovative technology allows surgeons to perform laryngoscope fittings from a distance, offering numerous benefits to both patients and healthcare providers.
The global telesurgery market, which encompasses telesurgical laryngoscope fittings, is projected to expand rapidly in the coming years. This growth is fueled by factors such as the rising prevalence of chronic diseases, the need for improved healthcare access in remote areas, and the ongoing development of robotic surgical systems.
Telesurgical laryngoscope fittings address several key market needs. Firstly, they help overcome geographical barriers, enabling patients in rural or underserved areas to access specialized care without the need for travel. This is particularly crucial for patients requiring urgent laryngoscopic procedures or those with limited mobility.
Furthermore, the COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated the adoption of telemedicine solutions, including telesurgical procedures. Healthcare providers are increasingly seeking ways to minimize physical contact while maintaining high-quality care, making telesurgical laryngoscope fittings an attractive option.
The market for this technology is also driven by the potential cost savings it offers to healthcare systems. By reducing the need for patient transportation and optimizing surgeon time, telesurgical laryngoscope fittings can lead to improved operational efficiency and reduced healthcare costs.
However, the market faces certain challenges. Concerns regarding the reliability of internet connections, especially in remote areas, may hinder widespread adoption. Additionally, regulatory hurdles and the need for standardization of telesurgical procedures across different regions pose obstacles to market growth.
Despite these challenges, the future outlook for telesurgical laryngoscope fittings remains promising. As technology continues to advance, particularly in areas such as 5G connectivity and haptic feedback systems, the precision and reliability of these procedures are expected to improve significantly.
The market is also likely to benefit from increasing investments in healthcare infrastructure and the growing emphasis on personalized medicine. As healthcare systems worldwide strive to provide more patient-centric care, telesurgical laryngoscope fittings align well with this trend by offering tailored solutions that can be adapted to individual patient needs.
The global telesurgery market, which encompasses telesurgical laryngoscope fittings, is projected to expand rapidly in the coming years. This growth is fueled by factors such as the rising prevalence of chronic diseases, the need for improved healthcare access in remote areas, and the ongoing development of robotic surgical systems.
Telesurgical laryngoscope fittings address several key market needs. Firstly, they help overcome geographical barriers, enabling patients in rural or underserved areas to access specialized care without the need for travel. This is particularly crucial for patients requiring urgent laryngoscopic procedures or those with limited mobility.
Furthermore, the COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated the adoption of telemedicine solutions, including telesurgical procedures. Healthcare providers are increasingly seeking ways to minimize physical contact while maintaining high-quality care, making telesurgical laryngoscope fittings an attractive option.
The market for this technology is also driven by the potential cost savings it offers to healthcare systems. By reducing the need for patient transportation and optimizing surgeon time, telesurgical laryngoscope fittings can lead to improved operational efficiency and reduced healthcare costs.
However, the market faces certain challenges. Concerns regarding the reliability of internet connections, especially in remote areas, may hinder widespread adoption. Additionally, regulatory hurdles and the need for standardization of telesurgical procedures across different regions pose obstacles to market growth.
Despite these challenges, the future outlook for telesurgical laryngoscope fittings remains promising. As technology continues to advance, particularly in areas such as 5G connectivity and haptic feedback systems, the precision and reliability of these procedures are expected to improve significantly.
The market is also likely to benefit from increasing investments in healthcare infrastructure and the growing emphasis on personalized medicine. As healthcare systems worldwide strive to provide more patient-centric care, telesurgical laryngoscope fittings align well with this trend by offering tailored solutions that can be adapted to individual patient needs.
Current Challenges in Telesurgical Laryngoscopy
Telesurgical laryngoscopy represents a significant advancement in medical technology, offering the potential for remote diagnosis and treatment of laryngeal conditions. However, the implementation of this technology faces several critical challenges that must be addressed to ensure its efficacy and widespread adoption.
One of the primary challenges is the need for high-precision control and real-time feedback. Laryngoscopy requires delicate manipulation of instruments within the confined space of the larynx. In a telesurgical setting, surgeons must rely on remote-controlled robotic systems to perform these intricate movements. Achieving the necessary level of precision and tactile feedback through teleoperation remains a significant technical hurdle.
Network latency and reliability pose another substantial challenge. Even minor delays or interruptions in data transmission can have severe consequences during a laryngoscopic procedure. Ensuring a stable, low-latency connection between the surgeon's control station and the remote robotic system is crucial for maintaining surgical accuracy and patient safety.
The integration of advanced imaging technologies with telesurgical systems presents both opportunities and challenges. While high-resolution cameras and 3D visualization can enhance the surgeon's view of the larynx, effectively transmitting and displaying this complex visual data in real-time requires substantial bandwidth and processing power.
Ergonomic considerations for remote surgeons also present challenges. Traditional laryngoscopy relies heavily on the surgeon's tactile senses and fine motor skills. Replicating these sensory inputs in a telesurgical environment, while maintaining surgeon comfort and preventing fatigue during extended procedures, remains an area of ongoing research and development.
Standardization and interoperability of telesurgical laryngoscopy systems are critical challenges that need to be addressed. As different manufacturers develop proprietary systems, ensuring compatibility and establishing universal protocols for telesurgical procedures becomes increasingly important for widespread adoption and seamless collaboration between medical institutions.
Lastly, regulatory and ethical considerations present significant hurdles. Ensuring patient safety, data security, and privacy in telesurgical settings requires the development of new guidelines and protocols. Additionally, addressing liability issues and obtaining informed consent for remote procedures adds complexity to the implementation of telesurgical laryngoscopy.
One of the primary challenges is the need for high-precision control and real-time feedback. Laryngoscopy requires delicate manipulation of instruments within the confined space of the larynx. In a telesurgical setting, surgeons must rely on remote-controlled robotic systems to perform these intricate movements. Achieving the necessary level of precision and tactile feedback through teleoperation remains a significant technical hurdle.
Network latency and reliability pose another substantial challenge. Even minor delays or interruptions in data transmission can have severe consequences during a laryngoscopic procedure. Ensuring a stable, low-latency connection between the surgeon's control station and the remote robotic system is crucial for maintaining surgical accuracy and patient safety.
The integration of advanced imaging technologies with telesurgical systems presents both opportunities and challenges. While high-resolution cameras and 3D visualization can enhance the surgeon's view of the larynx, effectively transmitting and displaying this complex visual data in real-time requires substantial bandwidth and processing power.
Ergonomic considerations for remote surgeons also present challenges. Traditional laryngoscopy relies heavily on the surgeon's tactile senses and fine motor skills. Replicating these sensory inputs in a telesurgical environment, while maintaining surgeon comfort and preventing fatigue during extended procedures, remains an area of ongoing research and development.
Standardization and interoperability of telesurgical laryngoscopy systems are critical challenges that need to be addressed. As different manufacturers develop proprietary systems, ensuring compatibility and establishing universal protocols for telesurgical procedures becomes increasingly important for widespread adoption and seamless collaboration between medical institutions.
Lastly, regulatory and ethical considerations present significant hurdles. Ensuring patient safety, data security, and privacy in telesurgical settings requires the development of new guidelines and protocols. Additionally, addressing liability issues and obtaining informed consent for remote procedures adds complexity to the implementation of telesurgical laryngoscopy.
Existing Telesurgical Laryngoscope Fitting Solutions
01 Blade design and attachments
Laryngoscope blades are designed with various fittings and attachments to improve functionality and ease of use. These may include adjustable blade angles, interchangeable blade types, and quick-release mechanisms for easy cleaning and sterilization. Some designs incorporate LED lighting systems directly into the blade for enhanced visibility.- Blade design and attachment mechanisms: Laryngoscope fittings include innovative blade designs and attachment mechanisms to improve visibility and ease of use during intubation procedures. These designs may feature adjustable angles, quick-release mechanisms, or interchangeable blades to accommodate different patient anatomies and clinical scenarios.
- Illumination systems: Advanced illumination systems are integrated into laryngoscope fittings to enhance visualization of the airway. These may include LED lights, fiber optic systems, or adjustable light intensity controls to provide optimal illumination during intubation procedures.
- Camera and video integration: Laryngoscope fittings incorporate camera and video technology to provide real-time imaging of the intubation process. These systems may include high-resolution cameras, wireless transmission capabilities, and display screens to assist in difficult intubations and for teaching purposes.
- Ergonomic handle designs: Ergonomic handle designs are developed to improve grip, control, and maneuverability during laryngoscopy. These designs may feature textured surfaces, contoured shapes, or adjustable grips to reduce hand fatigue and enhance overall performance.
- Disposable and sterile components: Laryngoscope fittings include disposable or easily sterilizable components to reduce the risk of cross-contamination between patients. These may include single-use blades, removable light sources, or protective covers that can be quickly replaced or sterilized between procedures.
02 Handle modifications and ergonomics
Laryngoscope handles are engineered with ergonomic considerations and modular designs. Features may include textured grips, adjustable length handles, and integrated power sources. Some handles are designed to accommodate various blade types and sizes, enhancing versatility and user comfort during procedures.Expand Specific Solutions03 Camera and imaging integration
Modern laryngoscopes often incorporate camera systems and imaging technologies. These may include high-resolution cameras, wireless video transmission capabilities, and integration with external display devices. Such features allow for real-time visualization, recording of procedures, and enhanced teaching capabilities.Expand Specific Solutions04 Disposable and sterile components
To address hygiene concerns and reduce cross-contamination risks, many laryngoscope designs now feature disposable or easily sterilizable components. This includes single-use blades, removable light sources, and protective sheaths. Some designs allow for quick disassembly to facilitate thorough cleaning and sterilization between uses.Expand Specific Solutions05 Advanced sensor and feedback systems
Laryngoscopes are being equipped with various sensors and feedback mechanisms to assist practitioners. These may include pressure sensors to monitor force applied during intubation, temperature sensors to detect tissue changes, and haptic feedback systems to guide proper placement. Some designs incorporate augmented reality overlays to provide real-time guidance during procedures.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Telesurgical Laryngoscopy Industry
The tele-surgery impact on laryngoscope fittings is in an early developmental stage, with a growing market potential as remote healthcare expands. The technology's maturity varies among key players. Companies like Intuitive Surgical Operations, Inc. and Verathon, Inc. are leading in surgical robotics and medical imaging, respectively. Zhejiang Youyi Medical Equipment Co Ltd and Aircraft Medical Ltd. are advancing visualized airway management tools. Research institutions such as the University of Maryland and Massachusetts Eye & Ear Infirmary are contributing to technological advancements. The competitive landscape is diverse, with both established medical device manufacturers and emerging specialized firms vying for market share in this evolving field.
Intuitive Surgical Operations, Inc.
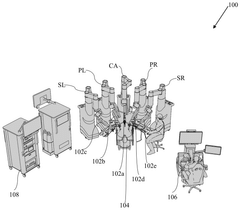
Technical Solution: Intuitive Surgical has developed advanced robotic-assisted surgical systems that can be applied to tele-surgery for laryngoscope fittings. Their da Vinci system, when adapted for laryngoscopy, allows for precise control and 3D visualization during remote procedures. The system incorporates high-definition cameras and articulating instruments, enabling surgeons to perform delicate manipulations with enhanced dexterity[1]. For laryngoscope fittings, this technology can provide real-time, high-resolution imaging of the larynx, allowing for accurate assessment and adjustment of the laryngoscope even from a distance[2]. The system also includes advanced haptic feedback mechanisms, giving surgeons a sense of touch and pressure during the remote fitting process[3].
Strengths: Unparalleled precision in remote surgical procedures, advanced 3D visualization, and haptic feedback. Weaknesses: High cost of implementation and maintenance, requires specialized training for operators.
Verathon, Inc.
Technical Solution: Verathon has developed the GlideScope video laryngoscope system, which can be adapted for tele-surgery applications in laryngoscope fittings. The system uses high-resolution cameras to provide clear, real-time images of the larynx, which can be transmitted to remote locations for expert assessment and guidance[4]. For tele-surgery, Verathon has integrated secure data transmission protocols to ensure patient privacy and data integrity during remote consultations[5]. The company has also developed AI-assisted image recognition software that can help identify optimal laryngoscope positioning, potentially improving the accuracy of remote fittings[6]. Their latest models incorporate wireless connectivity, allowing for seamless integration with telemedicine platforms.
Strengths: High-quality imaging, AI-assisted positioning, and secure data transmission. Weaknesses: Reliance on stable internet connectivity, potential for latency issues in real-time guidance.
Innovations in Remote Laryngoscope Manipulation
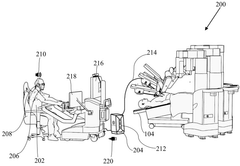
A portable mixed reality surgeon console for minimally invasive surgery
PatentPendingIN202311024625A
Innovation
- A mixed reality surgeon console system featuring a portable chair with hand gripper assemblies, a mixed reality headset, and a foot pedal tray, enabling two-way data communication and holographic UI elements for enhanced control and visualization, including electromagnetic wave-based sensors and a compact design for improved ergonomics and portability.
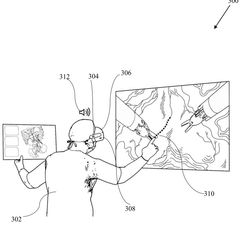
A system and method for mixed reality tele proctoring in minimally invasive surgery
PatentPendingSG11202500540YA
Innovation
- A mixed reality tele-proctoring system with a surgeon module and a proctor module, utilizing a webRTC architecture for low-latency communication, 3D stereoscopic display, and virtual annotation panel, enabling real-time 3D imagery and interactive guidance.
Regulatory Framework for Telesurgical Devices
The regulatory framework for telesurgical devices, including those used in laryngoscope fittings, is a complex and evolving landscape. As tele-surgery becomes more prevalent, regulatory bodies worldwide are adapting their guidelines to ensure patient safety and maintain high standards of care in remote surgical procedures.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) plays a crucial role in regulating telesurgical devices. These devices fall under the category of medical devices and are subject to the same rigorous approval processes as traditional surgical equipment. The FDA has established specific guidelines for telesurgery systems, focusing on aspects such as latency, reliability, and cybersecurity.
The European Union has implemented the Medical Device Regulation (MDR), which came into effect in May 2021. This regulation includes provisions for software as a medical device (SaMD), which is particularly relevant for telesurgery platforms. The MDR emphasizes the importance of risk management and post-market surveillance for telesurgical devices.
In Asia, countries like Japan and South Korea have also developed regulatory frameworks for telesurgical devices. The Japanese Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) has established guidelines for the evaluation of medical devices used in telemedicine, including those used in tele-surgery.
International standards organizations, such as the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), have developed standards specific to telesurgery. These include ISO 13485 for quality management systems and IEC 60601 for medical electrical equipment safety.
One of the key challenges in regulating telesurgical devices is addressing the unique risks associated with remote procedures. Regulatory bodies are increasingly focusing on cybersecurity requirements to protect patient data and prevent unauthorized access to telesurgery systems. Additionally, regulations are being developed to ensure the reliability of network connections and to establish protocols for handling potential disruptions during remote surgeries.
As the field of tele-surgery continues to advance, regulatory frameworks are likely to evolve. Future regulations may address emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence and machine learning in telesurgical applications. The goal of these regulations will be to balance innovation with patient safety, ensuring that the benefits of tele-surgery, including improved access to specialized care, can be realized while minimizing risks.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) plays a crucial role in regulating telesurgical devices. These devices fall under the category of medical devices and are subject to the same rigorous approval processes as traditional surgical equipment. The FDA has established specific guidelines for telesurgery systems, focusing on aspects such as latency, reliability, and cybersecurity.
The European Union has implemented the Medical Device Regulation (MDR), which came into effect in May 2021. This regulation includes provisions for software as a medical device (SaMD), which is particularly relevant for telesurgery platforms. The MDR emphasizes the importance of risk management and post-market surveillance for telesurgical devices.
In Asia, countries like Japan and South Korea have also developed regulatory frameworks for telesurgical devices. The Japanese Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) has established guidelines for the evaluation of medical devices used in telemedicine, including those used in tele-surgery.
International standards organizations, such as the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), have developed standards specific to telesurgery. These include ISO 13485 for quality management systems and IEC 60601 for medical electrical equipment safety.
One of the key challenges in regulating telesurgical devices is addressing the unique risks associated with remote procedures. Regulatory bodies are increasingly focusing on cybersecurity requirements to protect patient data and prevent unauthorized access to telesurgery systems. Additionally, regulations are being developed to ensure the reliability of network connections and to establish protocols for handling potential disruptions during remote surgeries.
As the field of tele-surgery continues to advance, regulatory frameworks are likely to evolve. Future regulations may address emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence and machine learning in telesurgical applications. The goal of these regulations will be to balance innovation with patient safety, ensuring that the benefits of tele-surgery, including improved access to specialized care, can be realized while minimizing risks.
Patient Safety and Data Security in Telesurgery
Patient safety and data security are paramount concerns in the implementation of telesurgery for laryngoscope fittings. As this innovative approach to surgical procedures gains traction, it is crucial to address the potential risks and establish robust safeguards to protect patients and their sensitive medical information.
One of the primary challenges in telesurgery is ensuring the safety of patients during remote procedures. The physical distance between the surgeon and the patient introduces new variables that must be carefully managed. Latency in data transmission, for instance, can lead to delays in the surgeon's actions, potentially compromising the precision of the laryngoscope fitting. To mitigate this risk, advanced network technologies and optimized data compression algorithms are being developed to minimize lag and maintain real-time responsiveness.
Furthermore, the reliability of the robotic systems used in telesurgery is critical. These systems must be designed with multiple fail-safes and redundancies to prevent malfunctions that could harm the patient. Regular maintenance, rigorous testing protocols, and continuous monitoring during procedures are essential to ensure the equipment's integrity and performance.
Data security in telesurgery presents another significant challenge. The transmission of sensitive patient information and real-time surgical data over networks exposes this data to potential breaches. Implementing end-to-end encryption, secure communication protocols, and robust authentication mechanisms is crucial to protect against unauthorized access and data interception.
Additionally, the storage and management of patient data collected during telesurgical procedures require stringent security measures. Healthcare institutions must comply with regulations such as HIPAA in the United States and GDPR in Europe, which mandate strict data protection standards. This includes secure data storage, access controls, and audit trails to track data usage and modifications.
The human factor in patient safety and data security cannot be overlooked. Comprehensive training programs for surgeons, technicians, and support staff are essential to ensure proper use of telesurgery systems and adherence to security protocols. This includes education on cybersecurity best practices, recognition of potential threats, and proper handling of patient data.
As telesurgery technology evolves, ongoing research and development efforts are focused on enhancing safety features and security measures. This includes the integration of artificial intelligence for real-time monitoring of surgical procedures, advanced error detection systems, and the development of more secure and resilient network infrastructures specifically designed for medical applications.
One of the primary challenges in telesurgery is ensuring the safety of patients during remote procedures. The physical distance between the surgeon and the patient introduces new variables that must be carefully managed. Latency in data transmission, for instance, can lead to delays in the surgeon's actions, potentially compromising the precision of the laryngoscope fitting. To mitigate this risk, advanced network technologies and optimized data compression algorithms are being developed to minimize lag and maintain real-time responsiveness.
Furthermore, the reliability of the robotic systems used in telesurgery is critical. These systems must be designed with multiple fail-safes and redundancies to prevent malfunctions that could harm the patient. Regular maintenance, rigorous testing protocols, and continuous monitoring during procedures are essential to ensure the equipment's integrity and performance.
Data security in telesurgery presents another significant challenge. The transmission of sensitive patient information and real-time surgical data over networks exposes this data to potential breaches. Implementing end-to-end encryption, secure communication protocols, and robust authentication mechanisms is crucial to protect against unauthorized access and data interception.
Additionally, the storage and management of patient data collected during telesurgical procedures require stringent security measures. Healthcare institutions must comply with regulations such as HIPAA in the United States and GDPR in Europe, which mandate strict data protection standards. This includes secure data storage, access controls, and audit trails to track data usage and modifications.
The human factor in patient safety and data security cannot be overlooked. Comprehensive training programs for surgeons, technicians, and support staff are essential to ensure proper use of telesurgery systems and adherence to security protocols. This includes education on cybersecurity best practices, recognition of potential threats, and proper handling of patient data.
As telesurgery technology evolves, ongoing research and development efforts are focused on enhancing safety features and security measures. This includes the integration of artificial intelligence for real-time monitoring of surgical procedures, advanced error detection systems, and the development of more secure and resilient network infrastructures specifically designed for medical applications.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!