Examining user feedback integration in laryngoscope updates.
JUL 14, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Laryngoscope Evolution and User-Centric Goals
The evolution of laryngoscopes has been driven by a continuous pursuit of improved patient outcomes and enhanced user experience. From the early rigid designs to the modern video laryngoscopes, the technology has undergone significant transformations. The primary goal has always been to provide better visualization of the larynx and facilitate easier intubation, particularly in challenging airway scenarios.
User feedback has played a crucial role in shaping the development of laryngoscopes. As healthcare professionals encountered limitations with traditional designs, manufacturers began incorporating their insights into product updates. This user-centric approach has led to innovations such as ergonomic handles, adjustable blade angles, and integrated suction capabilities.
The integration of video technology marked a paradigm shift in laryngoscope design. By providing a clear, magnified view of the airway on an external screen, video laryngoscopes addressed many of the limitations associated with direct laryngoscopy. This advancement not only improved the success rate of intubations but also reduced the physical strain on practitioners during prolonged procedures.
Recent developments have focused on enhancing the portability and versatility of laryngoscopes. Compact, battery-powered devices with high-resolution displays have become increasingly popular, especially in emergency and pre-hospital settings. These innovations reflect the growing demand for tools that can be easily deployed in various clinical environments.
The emphasis on user feedback has extended beyond hardware improvements to include software enhancements. Modern laryngoscopes often feature intuitive user interfaces, customizable settings, and even augmented reality overlays to guide intubation. These features are direct responses to user requests for more informative and interactive tools.
As the field of airway management continues to evolve, the goals for laryngoscope development have expanded. Current objectives include reducing the learning curve for novice users, minimizing the risk of complications, and improving documentation capabilities. Manufacturers are exploring ways to integrate artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms to provide real-time guidance and performance feedback during intubation procedures.
The ongoing dialogue between end-users and manufacturers ensures that future laryngoscope updates will continue to address the practical needs of healthcare providers. This collaborative approach aims to create devices that not only meet clinical requirements but also enhance the overall efficiency and safety of airway management procedures.
User feedback has played a crucial role in shaping the development of laryngoscopes. As healthcare professionals encountered limitations with traditional designs, manufacturers began incorporating their insights into product updates. This user-centric approach has led to innovations such as ergonomic handles, adjustable blade angles, and integrated suction capabilities.
The integration of video technology marked a paradigm shift in laryngoscope design. By providing a clear, magnified view of the airway on an external screen, video laryngoscopes addressed many of the limitations associated with direct laryngoscopy. This advancement not only improved the success rate of intubations but also reduced the physical strain on practitioners during prolonged procedures.
Recent developments have focused on enhancing the portability and versatility of laryngoscopes. Compact, battery-powered devices with high-resolution displays have become increasingly popular, especially in emergency and pre-hospital settings. These innovations reflect the growing demand for tools that can be easily deployed in various clinical environments.
The emphasis on user feedback has extended beyond hardware improvements to include software enhancements. Modern laryngoscopes often feature intuitive user interfaces, customizable settings, and even augmented reality overlays to guide intubation. These features are direct responses to user requests for more informative and interactive tools.
As the field of airway management continues to evolve, the goals for laryngoscope development have expanded. Current objectives include reducing the learning curve for novice users, minimizing the risk of complications, and improving documentation capabilities. Manufacturers are exploring ways to integrate artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms to provide real-time guidance and performance feedback during intubation procedures.
The ongoing dialogue between end-users and manufacturers ensures that future laryngoscope updates will continue to address the practical needs of healthcare providers. This collaborative approach aims to create devices that not only meet clinical requirements but also enhance the overall efficiency and safety of airway management procedures.
Market Demand Analysis for Advanced Laryngoscopes
The market demand for advanced laryngoscopes has been steadily increasing, driven by several key factors in the healthcare industry. The global laryngoscope market is experiencing significant growth, with a particular emphasis on user-centric design and feedback integration. This trend is largely attributed to the rising prevalence of chronic respiratory diseases, the growing geriatric population, and the increasing number of surgical procedures requiring airway management.
Healthcare professionals are increasingly seeking laryngoscopes that offer improved ergonomics, enhanced visualization, and easier intubation processes. The integration of user feedback in laryngoscope updates has become a critical factor in meeting these demands. Hospitals and clinics are showing a strong preference for devices that incorporate practitioner insights, leading to more efficient and comfortable use during procedures.
The market is witnessing a shift towards video laryngoscopes, which offer superior visualization and recording capabilities. This trend is particularly pronounced in developed countries, where healthcare facilities are willing to invest in advanced technologies to improve patient outcomes and reduce procedure-related complications. The demand for these advanced devices is also growing in emerging markets as healthcare infrastructure improves and awareness of modern medical technologies increases.
Another significant market driver is the focus on reducing healthcare-associated infections. Laryngoscopes that offer disposable blades or easy-to-sterilize components are gaining traction, as they address concerns about cross-contamination between patients. This aspect of product design is heavily influenced by user feedback, highlighting the importance of integrating practitioner experiences into product updates.
The COVID-19 pandemic has further accelerated the demand for advanced laryngoscopes, particularly those designed to minimize the risk of virus transmission during intubation procedures. Healthcare providers are seeking devices that allow for quick and efficient intubation while maintaining a safe distance from the patient's airway, driving innovation in laryngoscope design and functionality.
In terms of market segmentation, there is a growing demand for specialized laryngoscopes tailored to different patient groups, such as pediatric and neonatal populations. This diversification is largely driven by user feedback, as healthcare professionals seek tools optimized for specific patient demographics and clinical scenarios.
The market is also seeing increased demand for training and simulation tools related to laryngoscope use. This trend is fueled by the need for healthcare professionals to gain proficiency with new devices and techniques, further emphasizing the importance of user feedback in both product development and training methodologies.
Healthcare professionals are increasingly seeking laryngoscopes that offer improved ergonomics, enhanced visualization, and easier intubation processes. The integration of user feedback in laryngoscope updates has become a critical factor in meeting these demands. Hospitals and clinics are showing a strong preference for devices that incorporate practitioner insights, leading to more efficient and comfortable use during procedures.
The market is witnessing a shift towards video laryngoscopes, which offer superior visualization and recording capabilities. This trend is particularly pronounced in developed countries, where healthcare facilities are willing to invest in advanced technologies to improve patient outcomes and reduce procedure-related complications. The demand for these advanced devices is also growing in emerging markets as healthcare infrastructure improves and awareness of modern medical technologies increases.
Another significant market driver is the focus on reducing healthcare-associated infections. Laryngoscopes that offer disposable blades or easy-to-sterilize components are gaining traction, as they address concerns about cross-contamination between patients. This aspect of product design is heavily influenced by user feedback, highlighting the importance of integrating practitioner experiences into product updates.
The COVID-19 pandemic has further accelerated the demand for advanced laryngoscopes, particularly those designed to minimize the risk of virus transmission during intubation procedures. Healthcare providers are seeking devices that allow for quick and efficient intubation while maintaining a safe distance from the patient's airway, driving innovation in laryngoscope design and functionality.
In terms of market segmentation, there is a growing demand for specialized laryngoscopes tailored to different patient groups, such as pediatric and neonatal populations. This diversification is largely driven by user feedback, as healthcare professionals seek tools optimized for specific patient demographics and clinical scenarios.
The market is also seeing increased demand for training and simulation tools related to laryngoscope use. This trend is fueled by the need for healthcare professionals to gain proficiency with new devices and techniques, further emphasizing the importance of user feedback in both product development and training methodologies.
Current Challenges in User Feedback Integration
Integrating user feedback into laryngoscope updates presents several significant challenges in the current landscape. One of the primary obstacles is the complexity of collecting and analyzing diverse user experiences across various medical settings. Laryngoscopes are utilized in a wide range of environments, from emergency rooms to operating theaters, each with unique requirements and constraints. This diversity makes it difficult to standardize feedback collection methods and prioritize improvements that benefit all users equally.
Another challenge lies in the interpretation and validation of user feedback. Medical professionals often have different preferences and techniques, which can lead to conflicting opinions on device improvements. Distinguishing between personal preferences and objectively beneficial enhancements requires careful analysis and sometimes additional clinical studies, which can be time-consuming and costly.
The regulatory environment in the medical device industry also poses a significant hurdle. Any changes to laryngoscopes based on user feedback must comply with strict safety and efficacy standards set by regulatory bodies such as the FDA. This often results in a lengthy and complex process of testing and approval before implementing even minor updates, potentially delaying the integration of valuable user-driven improvements.
Furthermore, there is a challenge in balancing user desires with technological feasibility and cost-effectiveness. While users may request certain features or improvements, these may not always align with current technological capabilities or may be prohibitively expensive to implement. Manufacturers must carefully weigh the potential benefits against development and production costs, as well as the impact on device pricing and market competitiveness.
The rapid pace of technological advancement in medical devices also complicates user feedback integration. By the time a particular user-suggested improvement is developed and implemented, new technologies or approaches may have emerged, potentially rendering the original feedback obsolete. This requires manufacturers to constantly reassess the relevance of collected feedback against evolving technological landscapes.
Lastly, there is the challenge of maintaining a continuous and effective feedback loop. Establishing systems for ongoing user feedback collection, analysis, and integration into product development cycles requires significant resources and organizational commitment. Many companies struggle to create and maintain such systems, leading to sporadic or inconsistent incorporation of user insights into product updates.
Another challenge lies in the interpretation and validation of user feedback. Medical professionals often have different preferences and techniques, which can lead to conflicting opinions on device improvements. Distinguishing between personal preferences and objectively beneficial enhancements requires careful analysis and sometimes additional clinical studies, which can be time-consuming and costly.
The regulatory environment in the medical device industry also poses a significant hurdle. Any changes to laryngoscopes based on user feedback must comply with strict safety and efficacy standards set by regulatory bodies such as the FDA. This often results in a lengthy and complex process of testing and approval before implementing even minor updates, potentially delaying the integration of valuable user-driven improvements.
Furthermore, there is a challenge in balancing user desires with technological feasibility and cost-effectiveness. While users may request certain features or improvements, these may not always align with current technological capabilities or may be prohibitively expensive to implement. Manufacturers must carefully weigh the potential benefits against development and production costs, as well as the impact on device pricing and market competitiveness.
The rapid pace of technological advancement in medical devices also complicates user feedback integration. By the time a particular user-suggested improvement is developed and implemented, new technologies or approaches may have emerged, potentially rendering the original feedback obsolete. This requires manufacturers to constantly reassess the relevance of collected feedback against evolving technological landscapes.
Lastly, there is the challenge of maintaining a continuous and effective feedback loop. Establishing systems for ongoing user feedback collection, analysis, and integration into product development cycles requires significant resources and organizational commitment. Many companies struggle to create and maintain such systems, leading to sporadic or inconsistent incorporation of user insights into product updates.
Existing User Feedback Collection Methods
01 User feedback integration in laryngoscope systems
Laryngoscope systems incorporate user feedback mechanisms to improve device usability and performance. These systems may include sensors to detect user actions, pressure applied, or positioning, and provide real-time feedback through visual, auditory, or haptic means. This integration allows for more precise and efficient intubation procedures, enhancing user experience and patient safety.- User feedback integration in laryngoscope systems: Laryngoscope systems are being developed with integrated user feedback mechanisms. These systems collect and analyze user input to improve device performance, enhance user experience, and optimize intubation procedures. The feedback may include tactile, visual, or auditory cues to guide users during laryngoscopy.
- Real-time data collection and analysis: Advanced laryngoscopes incorporate sensors and data processing capabilities to collect and analyze real-time information during intubation. This data can include pressure applied, angle of insertion, and duration of the procedure. The collected information is used to provide immediate feedback to the user and for post-procedure analysis to improve techniques.
- Integration of user interface and display technologies: Modern laryngoscopes are equipped with user-friendly interfaces and display technologies to present feedback and critical information. These may include touchscreens, LED indicators, or augmented reality displays that provide real-time guidance and visualizations to assist in proper laryngoscope use and placement.
- Adaptive learning and personalized feedback: Laryngoscope systems are being developed with machine learning capabilities to provide personalized feedback based on individual user patterns and preferences. These systems can adapt to the user's skill level, offering tailored suggestions for improvement and customized training programs.
- Remote monitoring and collaborative feedback: Some laryngoscope systems incorporate telemedicine features, allowing for remote monitoring and collaborative feedback. These systems enable experienced practitioners to provide real-time guidance to less experienced users, facilitating training and improving patient outcomes in various healthcare settings.
02 Data collection and analysis for laryngoscope usage
Advanced laryngoscope systems incorporate data collection and analysis features to gather information on device usage, user performance, and patient outcomes. This data can be used to generate reports, identify trends, and provide insights for improving intubation techniques and training programs. The collected information may be stored locally or transmitted to centralized databases for further analysis.Expand Specific Solutions03 Customizable user interfaces for laryngoscopes
Modern laryngoscopes feature customizable user interfaces that allow healthcare professionals to tailor the device settings and feedback mechanisms to their preferences. These interfaces may include adjustable display options, personalized alert settings, and configurable control layouts. The ability to customize the user experience enhances operator comfort and efficiency during intubation procedures.Expand Specific Solutions04 Integration of laryngoscope feedback with external systems
Laryngoscope systems are designed to integrate with external medical devices and hospital information systems. This integration allows for seamless data exchange, enabling real-time monitoring, recording of intubation procedures, and incorporation of patient data. The connected systems can provide comprehensive feedback to users and facilitate better decision-making during critical care situations.Expand Specific Solutions05 Augmented reality and visual guidance in laryngoscopes
Advanced laryngoscope systems incorporate augmented reality and visual guidance features to assist users during intubation procedures. These systems may overlay real-time imaging with anatomical markers, provide visual cues for optimal device positioning, or display vital patient information directly in the user's field of view. This technology enhances the accuracy and efficiency of intubation while reducing the learning curve for less experienced practitioners.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Laryngoscope Manufacturing
The integration of user feedback in laryngoscope updates represents a dynamic and competitive landscape within the medical device industry. Currently, the market is in a growth phase, with increasing demand for advanced airway management tools. The global laryngoscope market size is projected to expand significantly, driven by technological advancements and growing awareness of patient safety. Companies like Zhejiang Youyi Medical Equipment, Covidien, and Philips are at the forefront, leveraging user insights to enhance product features and usability. The technology's maturity is moderate, with ongoing innovations in video laryngoscopy and ergonomic designs. Key players are focusing on R&D to improve visualization, reduce complications, and streamline the intubation process, indicating a highly competitive environment with potential for further advancements.
Covidien Pte Ltd.
Technical Solution: Covidien has developed an advanced laryngoscope system that incorporates real-time user feedback integration. The system utilizes a combination of sensors and machine learning algorithms to analyze the pressure applied during intubation procedures. This data is then used to provide immediate guidance to the user, helping to optimize technique and reduce the risk of complications. The laryngoscope also features a cloud-connected platform that aggregates anonymized user data to continuously improve the device's performance and update its algorithms[1][3]. Additionally, Covidien has implemented a user-friendly interface that allows for easy customization of feedback settings based on individual preferences and skill levels[5].
Strengths: Real-time feedback, continuous improvement through data aggregation, customizable settings. Weaknesses: Potential reliance on internet connectivity, may require additional training for users to fully utilize advanced features.
Koninklijke Philips NV
Technical Solution: Philips has introduced a smart laryngoscope system that leverages user feedback for continuous improvement. The device incorporates haptic feedback technology to provide tactile cues to users during intubation procedures, enhancing precision and reducing the learning curve for new practitioners[2]. The system also features a built-in camera that records procedures, allowing for post-operation analysis and feedback. This visual data is processed using computer vision algorithms to identify areas for improvement and generate personalized training recommendations[4]. Philips has also developed a companion mobile app that allows users to review their performance metrics and access educational resources tailored to their specific needs based on the collected feedback data[6].
Strengths: Haptic feedback for improved precision, visual analysis for personalized training, mobile app integration. Weaknesses: Potential privacy concerns with video recording, may be more expensive than traditional laryngoscopes.
Innovative Approaches to Feedback Integration
Improved laryngoscope
PatentActiveUS20200170498A1
Innovation
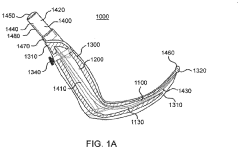
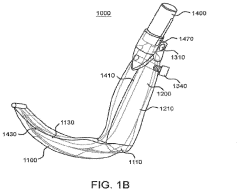
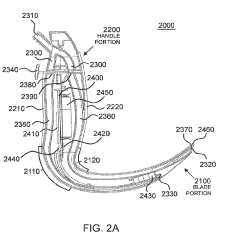
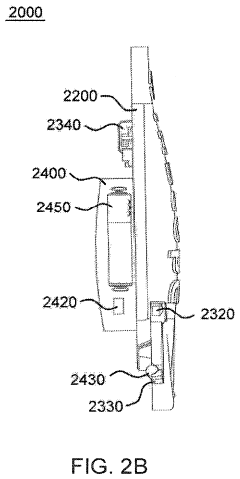
- A laryngoscope design featuring a blade portion with an inlet and handle portion with an outlet, incorporating an internal passageway for fluid communication, and an optional electronic component module providing sensing functionalities like pH, CO2, acoustic, and image sensing, along with wireless communication capabilities to aid in successful intubation.
Patient controlled medical system
PatentInactiveUS20220265160A1
Innovation
- A wearable patient device that enables wireless communication and control of medical examination or treatment apparatuses, allowing patients to send control commands and communicate with operators, featuring sensors for physiological monitoring and gesture recognition, and providing feedback through haptic, acoustic, and visual means.
Regulatory Framework for Medical Device Feedback
The regulatory framework for medical device feedback plays a crucial role in ensuring the safety and effectiveness of laryngoscopes and other medical devices. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) oversees the regulation of medical devices, including the integration of user feedback into product updates.
The FDA's Quality System Regulation (QSR) requires medical device manufacturers to establish and maintain procedures for receiving, reviewing, and evaluating complaints. This includes feedback from users, which can be invaluable in identifying potential safety issues or areas for improvement in laryngoscope design and functionality.
Under the Medical Device Reporting (MDR) regulation, manufacturers are obligated to report certain device-related adverse events and product problems to the FDA. This system helps to identify and address potential safety concerns quickly, ensuring that user feedback is not only collected but also acted upon when necessary.
The European Union's Medical Device Regulation (MDR) similarly emphasizes the importance of post-market surveillance and user feedback. Manufacturers are required to proactively collect and review user experiences with their devices, including laryngoscopes, as part of their ongoing risk management processes.
In both regulatory frameworks, there is a strong emphasis on the concept of a "closed-loop" feedback system. This means that manufacturers must not only collect user feedback but also demonstrate how this information is analyzed, evaluated, and incorporated into product improvements or updates.
For laryngoscope manufacturers, this regulatory environment necessitates robust systems for gathering user feedback from healthcare professionals. This may include surveys, focus groups, or direct reporting mechanisms. The feedback collected must be systematically reviewed and categorized to identify trends or recurring issues that may require design changes or updates to the device.
Moreover, the regulatory framework requires manufacturers to maintain detailed documentation of all feedback received and actions taken in response. This documentation serves as evidence of compliance with regulatory requirements and may be subject to inspection during audits.
The integration of user feedback into laryngoscope updates must also adhere to change control procedures as outlined in regulatory guidelines. Any significant changes to the device based on user feedback may require resubmission for regulatory approval, depending on the nature and extent of the modifications.
The FDA's Quality System Regulation (QSR) requires medical device manufacturers to establish and maintain procedures for receiving, reviewing, and evaluating complaints. This includes feedback from users, which can be invaluable in identifying potential safety issues or areas for improvement in laryngoscope design and functionality.
Under the Medical Device Reporting (MDR) regulation, manufacturers are obligated to report certain device-related adverse events and product problems to the FDA. This system helps to identify and address potential safety concerns quickly, ensuring that user feedback is not only collected but also acted upon when necessary.
The European Union's Medical Device Regulation (MDR) similarly emphasizes the importance of post-market surveillance and user feedback. Manufacturers are required to proactively collect and review user experiences with their devices, including laryngoscopes, as part of their ongoing risk management processes.
In both regulatory frameworks, there is a strong emphasis on the concept of a "closed-loop" feedback system. This means that manufacturers must not only collect user feedback but also demonstrate how this information is analyzed, evaluated, and incorporated into product improvements or updates.
For laryngoscope manufacturers, this regulatory environment necessitates robust systems for gathering user feedback from healthcare professionals. This may include surveys, focus groups, or direct reporting mechanisms. The feedback collected must be systematically reviewed and categorized to identify trends or recurring issues that may require design changes or updates to the device.
Moreover, the regulatory framework requires manufacturers to maintain detailed documentation of all feedback received and actions taken in response. This documentation serves as evidence of compliance with regulatory requirements and may be subject to inspection during audits.
The integration of user feedback into laryngoscope updates must also adhere to change control procedures as outlined in regulatory guidelines. Any significant changes to the device based on user feedback may require resubmission for regulatory approval, depending on the nature and extent of the modifications.
Ethical Considerations in User Data Utilization
The integration of user feedback in laryngoscope updates raises significant ethical considerations regarding the utilization of user data. As medical devices, laryngoscopes are subject to stringent regulatory requirements and ethical standards. The collection and use of user feedback must be conducted with utmost respect for patient privacy and data protection laws.
One primary ethical concern is the potential for inadvertent disclosure of sensitive patient information. Laryngoscopes are used in critical medical procedures, and user feedback may inadvertently contain identifiable patient data. Manufacturers must implement robust anonymization and data sanitization processes to ensure that any feedback used for product updates is completely devoid of personal health information.
Informed consent is another crucial ethical consideration. Users providing feedback should be fully aware of how their data will be used and have the option to opt-out of data collection. This transparency is essential for maintaining trust between manufacturers and healthcare professionals. Additionally, there should be clear guidelines on the ownership of the feedback data and the rights of users to access or delete their contributions.
The potential for bias in user feedback integration must also be addressed. Feedback from certain user groups or geographic regions may be overrepresented, leading to updates that do not reflect the needs of the broader user base. Manufacturers should implement strategies to ensure diverse and representative feedback collection.
There are also ethical implications related to the impact of updates on existing users. Changes based on feedback could potentially alter the functionality or user interface of laryngoscopes, which may require retraining or adaptation periods for current users. Manufacturers must carefully balance the benefits of updates against the potential disruption to established clinical practices.
Data security is paramount when handling user feedback. The storage, transmission, and processing of this data must adhere to the highest standards of cybersecurity to prevent unauthorized access or breaches. This is particularly critical given the sensitive nature of medical device information and its potential impact on patient care.
Lastly, there is an ethical obligation to act on critical feedback that may impact patient safety. Manufacturers must have clear protocols for addressing urgent issues identified through user feedback, ensuring that potentially life-saving improvements are implemented promptly and responsibly.
One primary ethical concern is the potential for inadvertent disclosure of sensitive patient information. Laryngoscopes are used in critical medical procedures, and user feedback may inadvertently contain identifiable patient data. Manufacturers must implement robust anonymization and data sanitization processes to ensure that any feedback used for product updates is completely devoid of personal health information.
Informed consent is another crucial ethical consideration. Users providing feedback should be fully aware of how their data will be used and have the option to opt-out of data collection. This transparency is essential for maintaining trust between manufacturers and healthcare professionals. Additionally, there should be clear guidelines on the ownership of the feedback data and the rights of users to access or delete their contributions.
The potential for bias in user feedback integration must also be addressed. Feedback from certain user groups or geographic regions may be overrepresented, leading to updates that do not reflect the needs of the broader user base. Manufacturers should implement strategies to ensure diverse and representative feedback collection.
There are also ethical implications related to the impact of updates on existing users. Changes based on feedback could potentially alter the functionality or user interface of laryngoscopes, which may require retraining or adaptation periods for current users. Manufacturers must carefully balance the benefits of updates against the potential disruption to established clinical practices.
Data security is paramount when handling user feedback. The storage, transmission, and processing of this data must adhere to the highest standards of cybersecurity to prevent unauthorized access or breaches. This is particularly critical given the sensitive nature of medical device information and its potential impact on patient care.
Lastly, there is an ethical obligation to act on critical feedback that may impact patient safety. Manufacturers must have clear protocols for addressing urgent issues identified through user feedback, ensuring that potentially life-saving improvements are implemented promptly and responsibly.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!