Cultural factors influencing global EREV adoption rates
AUG 14, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
EREV Adoption Background
Extended Range Electric Vehicles (EREVs) have emerged as a promising solution to address the growing concerns of environmental sustainability and energy efficiency in the automotive industry. The adoption of EREVs globally has been influenced by various cultural factors, which play a crucial role in shaping consumer attitudes and behaviors towards this innovative technology.
The concept of EREVs originated in the early 2000s as an evolution of hybrid electric vehicles, aiming to combine the benefits of both electric and conventional powertrains. These vehicles typically feature a battery-powered electric motor for primary propulsion and a small internal combustion engine that serves as a range extender. This configuration allows for longer driving ranges compared to pure electric vehicles while maintaining lower emissions and fuel consumption than traditional gasoline-powered vehicles.
Cultural factors have significantly impacted the adoption rates of EREVs across different regions worldwide. In countries with a strong environmental consciousness, such as Norway and the Netherlands, there has been a more rapid acceptance of EREVs due to cultural values that prioritize sustainability and eco-friendly practices. Conversely, in regions where car culture is deeply rooted in traditional combustion engines, such as the United States, the transition to EREVs has faced more resistance.
The perception of technological innovation also varies across cultures, influencing EREV adoption. Countries like Japan and South Korea, known for their technological advancements, have shown a greater willingness to embrace EREVs as part of their commitment to cutting-edge automotive technologies. In contrast, some developing nations may view EREVs as luxury items, limiting their widespread adoption due to economic and infrastructural constraints.
Government policies and incentives have played a crucial role in shaping cultural attitudes towards EREVs. Nations that have implemented strong support measures, such as tax breaks, subsidies, and infrastructure development, have generally seen higher adoption rates. These policies not only make EREVs more financially attractive but also signal a cultural shift towards prioritizing clean transportation options.
Urban planning and lifestyle preferences also contribute to the cultural factors affecting EREV adoption. In densely populated cities with limited parking spaces and stringent emission regulations, EREVs offer an appealing alternative to conventional vehicles. However, in cultures where long-distance travel is common or where there is a strong attachment to the freedom associated with traditional cars, the adoption of EREVs may face challenges.
As the global automotive landscape continues to evolve, understanding these cultural nuances becomes increasingly important for manufacturers, policymakers, and stakeholders in the EREV industry. By recognizing and addressing the diverse cultural factors influencing EREV adoption rates, stakeholders can develop targeted strategies to promote wider acceptance and integration of this technology across different regions and societies.
The concept of EREVs originated in the early 2000s as an evolution of hybrid electric vehicles, aiming to combine the benefits of both electric and conventional powertrains. These vehicles typically feature a battery-powered electric motor for primary propulsion and a small internal combustion engine that serves as a range extender. This configuration allows for longer driving ranges compared to pure electric vehicles while maintaining lower emissions and fuel consumption than traditional gasoline-powered vehicles.
Cultural factors have significantly impacted the adoption rates of EREVs across different regions worldwide. In countries with a strong environmental consciousness, such as Norway and the Netherlands, there has been a more rapid acceptance of EREVs due to cultural values that prioritize sustainability and eco-friendly practices. Conversely, in regions where car culture is deeply rooted in traditional combustion engines, such as the United States, the transition to EREVs has faced more resistance.
The perception of technological innovation also varies across cultures, influencing EREV adoption. Countries like Japan and South Korea, known for their technological advancements, have shown a greater willingness to embrace EREVs as part of their commitment to cutting-edge automotive technologies. In contrast, some developing nations may view EREVs as luxury items, limiting their widespread adoption due to economic and infrastructural constraints.
Government policies and incentives have played a crucial role in shaping cultural attitudes towards EREVs. Nations that have implemented strong support measures, such as tax breaks, subsidies, and infrastructure development, have generally seen higher adoption rates. These policies not only make EREVs more financially attractive but also signal a cultural shift towards prioritizing clean transportation options.
Urban planning and lifestyle preferences also contribute to the cultural factors affecting EREV adoption. In densely populated cities with limited parking spaces and stringent emission regulations, EREVs offer an appealing alternative to conventional vehicles. However, in cultures where long-distance travel is common or where there is a strong attachment to the freedom associated with traditional cars, the adoption of EREVs may face challenges.
As the global automotive landscape continues to evolve, understanding these cultural nuances becomes increasingly important for manufacturers, policymakers, and stakeholders in the EREV industry. By recognizing and addressing the diverse cultural factors influencing EREV adoption rates, stakeholders can develop targeted strategies to promote wider acceptance and integration of this technology across different regions and societies.
Global Market Analysis
The global market for Extended Range Electric Vehicles (EREVs) is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing environmental awareness and government incentives. However, cultural factors play a crucial role in shaping adoption rates across different regions, leading to varied market dynamics worldwide.
In North America, particularly the United States, there is a strong car-centric culture that has historically favored large, powerful vehicles. This cultural preference has posed challenges for EREV adoption, as consumers often associate electric vehicles with smaller, less powerful cars. However, recent shifts in consumer attitudes towards sustainability and the introduction of more robust EREV models have begun to change this perception, leading to gradual market growth.
European markets, especially in countries like Norway, the Netherlands, and Germany, have shown higher EREV adoption rates due to a more environmentally conscious culture and supportive government policies. The region's emphasis on reducing carbon emissions and promoting sustainable transportation aligns well with EREV technology, fostering a more receptive market environment.
In contrast, the Asian market presents a diverse landscape for EREV adoption. China, the world's largest automotive market, has seen rapid growth in electric vehicle sales, including EREVs, driven by government mandates and severe air pollution concerns in major cities. However, other Asian countries like Japan and South Korea, despite their technological prowess, have shown slower EREV adoption rates due to a cultural preference for hybrid vehicles and a well-established hydrogen fuel cell infrastructure.
Cultural factors also influence EREV adoption in emerging markets. In India, for example, the prevalence of two-wheelers and the cultural emphasis on affordability have led to a slower uptake of EREVs. Similarly, in parts of Africa and South America, where car ownership is less common and public transportation is more prevalent, EREV adoption faces unique challenges.
The global EREV market is further shaped by varying attitudes towards range anxiety across cultures. In countries with vast geographical expanses, such as Australia or Russia, concerns about long-distance travel capabilities have a more significant impact on EREV adoption compared to densely populated urban areas in Europe or Asia.
Additionally, cultural perceptions of technology and innovation play a role in EREV market dynamics. Regions with a strong culture of early technology adoption, like parts of East Asia and Scandinavia, tend to show higher acceptance of EREVs as cutting-edge transportation solutions.
Understanding these cultural nuances is crucial for automakers and policymakers aiming to increase global EREV adoption rates. Tailoring marketing strategies, vehicle designs, and policy incentives to align with local cultural values and preferences can significantly impact the success of EREV penetration in different markets worldwide.
In North America, particularly the United States, there is a strong car-centric culture that has historically favored large, powerful vehicles. This cultural preference has posed challenges for EREV adoption, as consumers often associate electric vehicles with smaller, less powerful cars. However, recent shifts in consumer attitudes towards sustainability and the introduction of more robust EREV models have begun to change this perception, leading to gradual market growth.
European markets, especially in countries like Norway, the Netherlands, and Germany, have shown higher EREV adoption rates due to a more environmentally conscious culture and supportive government policies. The region's emphasis on reducing carbon emissions and promoting sustainable transportation aligns well with EREV technology, fostering a more receptive market environment.
In contrast, the Asian market presents a diverse landscape for EREV adoption. China, the world's largest automotive market, has seen rapid growth in electric vehicle sales, including EREVs, driven by government mandates and severe air pollution concerns in major cities. However, other Asian countries like Japan and South Korea, despite their technological prowess, have shown slower EREV adoption rates due to a cultural preference for hybrid vehicles and a well-established hydrogen fuel cell infrastructure.
Cultural factors also influence EREV adoption in emerging markets. In India, for example, the prevalence of two-wheelers and the cultural emphasis on affordability have led to a slower uptake of EREVs. Similarly, in parts of Africa and South America, where car ownership is less common and public transportation is more prevalent, EREV adoption faces unique challenges.
The global EREV market is further shaped by varying attitudes towards range anxiety across cultures. In countries with vast geographical expanses, such as Australia or Russia, concerns about long-distance travel capabilities have a more significant impact on EREV adoption compared to densely populated urban areas in Europe or Asia.
Additionally, cultural perceptions of technology and innovation play a role in EREV market dynamics. Regions with a strong culture of early technology adoption, like parts of East Asia and Scandinavia, tend to show higher acceptance of EREVs as cutting-edge transportation solutions.
Understanding these cultural nuances is crucial for automakers and policymakers aiming to increase global EREV adoption rates. Tailoring marketing strategies, vehicle designs, and policy incentives to align with local cultural values and preferences can significantly impact the success of EREV penetration in different markets worldwide.
Cultural Barriers
Cultural barriers play a significant role in shaping the adoption rates of Extended Range Electric Vehicles (EREVs) across different global markets. These barriers stem from deeply ingrained societal norms, values, and perceptions that can either hinder or facilitate the acceptance of new automotive technologies.
One of the primary cultural barriers to EREV adoption is the varying levels of environmental consciousness across different societies. In some cultures, there is a strong emphasis on environmental protection and sustainability, which can drive the adoption of eco-friendly vehicles like EREVs. However, in other cultures where environmental concerns are not as prioritized, the motivation to switch to electric vehicles may be significantly lower.
The perception of automotive ownership as a status symbol also varies greatly between cultures. In some societies, traditional internal combustion engine vehicles, especially those from luxury brands, are seen as indicators of social status and success. This cultural association can make it challenging for EREVs to gain traction, particularly if they are perceived as less prestigious or powerful than conventional vehicles.
Cultural attitudes towards technological innovation and change also impact EREV adoption rates. Societies with a strong tradition of early technology adoption and openness to new ideas are more likely to embrace EREVs. Conversely, cultures that are more conservative or resistant to change may be slower to accept this new automotive technology.
The concept of "range anxiety" – the fear of running out of battery power during a journey – is another cultural barrier that affects EREV adoption. This anxiety is often more pronounced in cultures where long-distance travel is common or where there is a strong emphasis on personal mobility and independence. The perceived limitations of electric vehicles can be a significant deterrent in these societies.
Infrastructure expectations and urban planning norms also create cultural barriers. In some cultures, there is an expectation of widespread and easily accessible refueling stations for vehicles. The current limitations in charging infrastructure for electric vehicles can be a significant cultural hurdle in these societies. Additionally, urban planning norms that favor sprawling cities and long commutes can make EREVs less attractive in certain cultural contexts.
The role of government and public policy in shaping cultural attitudes towards EREVs cannot be overlooked. In cultures where there is a strong tradition of government intervention in consumer choices, policies promoting EREVs can significantly influence adoption rates. Conversely, in societies that value minimal government interference, such policies may be less effective or even face resistance.
Lastly, cultural differences in consumer behavior and purchasing patterns also affect EREV adoption. Some cultures prioritize long-term cost savings and efficiency, which can favor EREVs, while others may place more emphasis on upfront costs or immediate gratification, potentially hindering adoption.
One of the primary cultural barriers to EREV adoption is the varying levels of environmental consciousness across different societies. In some cultures, there is a strong emphasis on environmental protection and sustainability, which can drive the adoption of eco-friendly vehicles like EREVs. However, in other cultures where environmental concerns are not as prioritized, the motivation to switch to electric vehicles may be significantly lower.
The perception of automotive ownership as a status symbol also varies greatly between cultures. In some societies, traditional internal combustion engine vehicles, especially those from luxury brands, are seen as indicators of social status and success. This cultural association can make it challenging for EREVs to gain traction, particularly if they are perceived as less prestigious or powerful than conventional vehicles.
Cultural attitudes towards technological innovation and change also impact EREV adoption rates. Societies with a strong tradition of early technology adoption and openness to new ideas are more likely to embrace EREVs. Conversely, cultures that are more conservative or resistant to change may be slower to accept this new automotive technology.
The concept of "range anxiety" – the fear of running out of battery power during a journey – is another cultural barrier that affects EREV adoption. This anxiety is often more pronounced in cultures where long-distance travel is common or where there is a strong emphasis on personal mobility and independence. The perceived limitations of electric vehicles can be a significant deterrent in these societies.
Infrastructure expectations and urban planning norms also create cultural barriers. In some cultures, there is an expectation of widespread and easily accessible refueling stations for vehicles. The current limitations in charging infrastructure for electric vehicles can be a significant cultural hurdle in these societies. Additionally, urban planning norms that favor sprawling cities and long commutes can make EREVs less attractive in certain cultural contexts.
The role of government and public policy in shaping cultural attitudes towards EREVs cannot be overlooked. In cultures where there is a strong tradition of government intervention in consumer choices, policies promoting EREVs can significantly influence adoption rates. Conversely, in societies that value minimal government interference, such policies may be less effective or even face resistance.
Lastly, cultural differences in consumer behavior and purchasing patterns also affect EREV adoption. Some cultures prioritize long-term cost savings and efficiency, which can favor EREVs, while others may place more emphasis on upfront costs or immediate gratification, potentially hindering adoption.
Current Adoption Strategies
01 Market analysis and adoption prediction
Research on EREV adoption rates focuses on market analysis and prediction models. These studies examine factors influencing consumer acceptance, including infrastructure development, government policies, and technological advancements. Predictive models are used to forecast adoption trends and market penetration rates for EREVs in various regions and timeframes.- Market analysis and adoption trends of EREVs: This category focuses on analyzing market trends and adoption rates of Extended Range Electric Vehicles (EREVs). It includes studies on consumer preferences, market penetration, and factors influencing EREV adoption in different regions. The research also covers comparative analyses between EREVs and other electric vehicle types, as well as projections for future market growth.
- Technological advancements in EREV systems: This point covers the technological improvements in EREV systems, including battery technology, range extenders, and powertrain efficiency. It encompasses innovations in energy management systems, charging infrastructure, and integration of renewable energy sources. The advancements aim to enhance the overall performance, range, and reliability of EREVs.
- Policy and regulatory frameworks for EREV adoption: This category examines the impact of government policies, incentives, and regulations on EREV adoption rates. It includes analysis of subsidies, tax benefits, emission standards, and infrastructure development initiatives that influence the uptake of EREVs in various markets. The research also covers the effectiveness of different policy approaches in promoting EREV adoption.
- EREV charging infrastructure and network development: This point focuses on the development and expansion of charging infrastructure for EREVs. It covers the planning and implementation of charging networks, integration with existing power grids, and innovative charging solutions. The research also addresses challenges in infrastructure deployment and strategies to improve charging accessibility and convenience for EREV users.
- Environmental impact and sustainability of EREVs: This category examines the environmental benefits and sustainability aspects of EREV adoption. It includes life cycle assessments, carbon footprint analyses, and comparisons with conventional vehicles and other electric vehicle types. The research also covers the potential of EREVs in reducing greenhouse gas emissions and their role in achieving sustainable transportation goals.
02 Charging infrastructure and range anxiety mitigation
The development of charging infrastructure plays a crucial role in EREV adoption. Studies explore strategies to mitigate range anxiety through improved charging networks, fast-charging technologies, and intelligent route planning systems. These advancements aim to increase consumer confidence and accelerate EREV adoption rates.Expand Specific Solutions03 Government policies and incentives
Research examines the impact of government policies and incentives on EREV adoption rates. This includes studies on tax credits, subsidies, emissions regulations, and other policy measures designed to promote EREV sales. Analysis of policy effectiveness and its influence on consumer behavior is crucial for understanding adoption trends.Expand Specific Solutions04 Technological advancements and performance improvements
Studies focus on technological advancements in EREV design, battery technology, and powertrain efficiency. Improvements in vehicle range, charging speed, and overall performance are analyzed for their potential to drive adoption rates. Research also explores consumer perceptions of these technological advancements and their influence on purchasing decisions.Expand Specific Solutions05 Consumer behavior and market segmentation
Research investigates consumer behavior, preferences, and market segmentation related to EREV adoption. Studies analyze demographic factors, lifestyle choices, and environmental attitudes that influence EREV purchasing decisions. This information is used to develop targeted marketing strategies and product offerings to increase adoption rates across different consumer segments.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Stakeholders
The global adoption of Extended Range Electric Vehicles (EREVs) is influenced by a complex interplay of cultural factors, reflecting the technology's early stage of development. The market for EREVs is growing but remains relatively small, with adoption rates varying significantly across regions. Key players like Zhejiang Geely Holding Group, Chery Automobile, and Chaowei Power Group are driving innovation in this space, particularly in the Chinese market. However, the technology's maturity is still evolving, with companies such as Chery New Energy and established automakers investing in research and development to improve EREV performance and appeal. Cultural attitudes towards environmental sustainability, government policies, and local infrastructure development play crucial roles in shaping adoption patterns across different countries and regions.
Zhejiang Geely Holding Group Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Geely has been at the forefront of EREV (Extended Range Electric Vehicle) technology adoption, particularly in the Chinese market. Their approach involves integrating cultural preferences into vehicle design and marketing strategies. For instance, they have developed EREVs with larger interiors to cater to Chinese families' preference for spacious vehicles[1]. Geely has also implemented a "battery swapping" system in some models, addressing the cultural concern of long charging times in fast-paced urban environments[2]. Additionally, they have focused on incorporating advanced connectivity features, recognizing the high value placed on technology integration in Asian markets[3].
Strengths: Strong understanding of local market preferences, innovative battery solutions, and advanced connectivity features. Weaknesses: May face challenges in adapting strategies to Western markets with different cultural values.
Chery Automobile Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Chery has developed a unique approach to EREV adoption, focusing on affordability and practicality to appeal to a broader demographic in emerging markets. Their strategy includes producing compact EREVs that align with the urban lifestyle prevalent in many developing countries[4]. Chery has also invested in localized production facilities in key markets like Brazil and Egypt, allowing them to adapt their vehicles to local preferences and regulations more efficiently[5]. Furthermore, they have implemented a "shared mobility" program in some regions, addressing the cultural shift towards collaborative consumption in younger demographics[6].
Strengths: Cost-effective solutions, adaptability to emerging markets, and innovative shared mobility concepts. Weaknesses: Brand perception may be lower compared to more established global automakers.
Cultural Adaptation Innovations
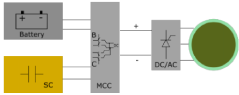
A power controlling device for electric vehicle with ultracapacitor storage and advanced regenerative braking
PatentPendingIN202311019018A
Innovation
- Integration of ultracapacitor storage with advanced regenerative braking system to improve energy recovery and extend EV range.
- Implementation of a power controlling device to manage energy flow between ultracapacitors, battery, and regenerative braking system.
- Utilization of ultracapacitors to handle high current spikes during acceleration and regenerative braking, reducing stress on the main battery.
Policy and Incentives
Policy and incentive structures play a crucial role in shaping the adoption rates of Extended Range Electric Vehicles (EREVs) across different cultures globally. These frameworks are often tailored to address specific cultural factors and local market conditions, resulting in varying levels of effectiveness in different regions.
In many Western countries, policies tend to focus on financial incentives such as tax credits, rebates, and grants to encourage EREV adoption. These measures align well with individualistic cultures that prioritize personal economic benefits. For instance, Norway's comprehensive incentive package, including tax exemptions and free parking for electric vehicles, has led to one of the highest EV adoption rates globally.
Conversely, in collectivist societies like Japan and South Korea, policies often emphasize the societal benefits of EREVs, such as reduced air pollution and energy independence. These countries frequently implement stricter emissions regulations and invest in public charging infrastructure to promote EREV adoption. This approach resonates with cultural values that prioritize community well-being over individual gain.
China, with its unique cultural and political landscape, has implemented a mix of top-down mandates and incentives. The government's strong push for new energy vehicles, including EREVs, through manufacturing quotas and city-level restrictions on conventional vehicles, reflects the cultural acceptance of centralized decision-making in driving technological adoption.
In developing economies, policies often focus on addressing infrastructure challenges and affordability issues. Countries like India and Brazil are exploring innovative approaches such as battery swapping stations and localized manufacturing to make EREVs more accessible and culturally relevant.
The effectiveness of policies and incentives is also influenced by cultural attitudes towards environmental issues. In countries with strong environmental consciousness, such as Germany and Sweden, policies that highlight the eco-friendly aspects of EREVs tend to be more impactful. These nations often combine financial incentives with strict emissions standards to drive EREV adoption.
Cultural perceptions of technology and innovation also play a role in shaping policy approaches. Tech-savvy cultures, like those in Silicon Valley or South Korea, may be more receptive to policies that promote cutting-edge EREV technologies and smart charging solutions. In contrast, more traditional societies might require policies that emphasize the reliability and practicality of EREVs to overcome cultural resistance to new technologies.
As global EREV adoption continues to evolve, policymakers must remain attuned to the nuanced interplay between cultural factors and policy effectiveness. Successful strategies will likely involve a combination of universal best practices and culturally tailored approaches to maximize EREV adoption rates across diverse global markets.
In many Western countries, policies tend to focus on financial incentives such as tax credits, rebates, and grants to encourage EREV adoption. These measures align well with individualistic cultures that prioritize personal economic benefits. For instance, Norway's comprehensive incentive package, including tax exemptions and free parking for electric vehicles, has led to one of the highest EV adoption rates globally.
Conversely, in collectivist societies like Japan and South Korea, policies often emphasize the societal benefits of EREVs, such as reduced air pollution and energy independence. These countries frequently implement stricter emissions regulations and invest in public charging infrastructure to promote EREV adoption. This approach resonates with cultural values that prioritize community well-being over individual gain.
China, with its unique cultural and political landscape, has implemented a mix of top-down mandates and incentives. The government's strong push for new energy vehicles, including EREVs, through manufacturing quotas and city-level restrictions on conventional vehicles, reflects the cultural acceptance of centralized decision-making in driving technological adoption.
In developing economies, policies often focus on addressing infrastructure challenges and affordability issues. Countries like India and Brazil are exploring innovative approaches such as battery swapping stations and localized manufacturing to make EREVs more accessible and culturally relevant.
The effectiveness of policies and incentives is also influenced by cultural attitudes towards environmental issues. In countries with strong environmental consciousness, such as Germany and Sweden, policies that highlight the eco-friendly aspects of EREVs tend to be more impactful. These nations often combine financial incentives with strict emissions standards to drive EREV adoption.
Cultural perceptions of technology and innovation also play a role in shaping policy approaches. Tech-savvy cultures, like those in Silicon Valley or South Korea, may be more receptive to policies that promote cutting-edge EREV technologies and smart charging solutions. In contrast, more traditional societies might require policies that emphasize the reliability and practicality of EREVs to overcome cultural resistance to new technologies.
As global EREV adoption continues to evolve, policymakers must remain attuned to the nuanced interplay between cultural factors and policy effectiveness. Successful strategies will likely involve a combination of universal best practices and culturally tailored approaches to maximize EREV adoption rates across diverse global markets.
Consumer Behavior Insights
Consumer behavior plays a crucial role in the adoption of Extended Range Electric Vehicles (EREVs) across different cultures. Understanding these behavioral patterns is essential for predicting and influencing global EREV adoption rates. Cultural factors significantly shape consumer attitudes, preferences, and decision-making processes when it comes to embracing new automotive technologies.
One of the primary cultural influences on EREV adoption is the varying levels of environmental consciousness across different societies. In cultures where environmental concerns are deeply ingrained, consumers are more likely to prioritize eco-friendly transportation options, leading to higher EREV adoption rates. Conversely, in cultures where environmental issues are less prominent, the transition to EREVs may face greater resistance.
The perception of social status associated with vehicle ownership also varies across cultures, impacting EREV adoption. In some societies, traditional combustion engine vehicles may be seen as status symbols, making the shift to EREVs more challenging. However, in cultures where innovation and sustainability are highly valued, EREVs could be perceived as prestigious, driving adoption rates upward.
Cultural attitudes towards risk and innovation play a significant role in EREV adoption. Societies with a higher tolerance for technological change and early adoption tendencies are more likely to embrace EREVs. In contrast, risk-averse cultures may exhibit slower adoption rates, preferring to wait for the technology to mature before making the switch.
The concept of "range anxiety" - the fear of running out of battery power during a journey - is influenced by cultural factors as well. In cultures with a strong emphasis on long-distance travel or where public charging infrastructure is perceived as inadequate, range anxiety may be more pronounced, potentially hindering EREV adoption.
Economic considerations, which are often culturally influenced, also impact consumer behavior towards EREVs. In cultures where frugality and long-term financial planning are valued, the potential long-term savings of EREVs may be more appealing. However, in societies focused on immediate gratification or where fossil fuels are heavily subsidized, the higher upfront costs of EREVs might deter adoption.
Cultural norms surrounding personal space and privacy can affect EREV adoption rates. In cultures where private vehicle ownership is seen as essential for maintaining personal freedom and independence, the perceived limitations of EREVs (such as charging time and range) may be viewed more negatively.
Understanding these cultural nuances in consumer behavior is crucial for automakers, policymakers, and marketers seeking to promote EREV adoption globally. Tailoring marketing strategies, policy incentives, and product features to align with local cultural values and preferences can significantly influence adoption rates across different regions.
One of the primary cultural influences on EREV adoption is the varying levels of environmental consciousness across different societies. In cultures where environmental concerns are deeply ingrained, consumers are more likely to prioritize eco-friendly transportation options, leading to higher EREV adoption rates. Conversely, in cultures where environmental issues are less prominent, the transition to EREVs may face greater resistance.
The perception of social status associated with vehicle ownership also varies across cultures, impacting EREV adoption. In some societies, traditional combustion engine vehicles may be seen as status symbols, making the shift to EREVs more challenging. However, in cultures where innovation and sustainability are highly valued, EREVs could be perceived as prestigious, driving adoption rates upward.
Cultural attitudes towards risk and innovation play a significant role in EREV adoption. Societies with a higher tolerance for technological change and early adoption tendencies are more likely to embrace EREVs. In contrast, risk-averse cultures may exhibit slower adoption rates, preferring to wait for the technology to mature before making the switch.
The concept of "range anxiety" - the fear of running out of battery power during a journey - is influenced by cultural factors as well. In cultures with a strong emphasis on long-distance travel or where public charging infrastructure is perceived as inadequate, range anxiety may be more pronounced, potentially hindering EREV adoption.
Economic considerations, which are often culturally influenced, also impact consumer behavior towards EREVs. In cultures where frugality and long-term financial planning are valued, the potential long-term savings of EREVs may be more appealing. However, in societies focused on immediate gratification or where fossil fuels are heavily subsidized, the higher upfront costs of EREVs might deter adoption.
Cultural norms surrounding personal space and privacy can affect EREV adoption rates. In cultures where private vehicle ownership is seen as essential for maintaining personal freedom and independence, the perceived limitations of EREVs (such as charging time and range) may be viewed more negatively.
Understanding these cultural nuances in consumer behavior is crucial for automakers, policymakers, and marketers seeking to promote EREV adoption globally. Tailoring marketing strategies, policy incentives, and product features to align with local cultural values and preferences can significantly influence adoption rates across different regions.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!