Dodecane-Based Coolants: Emerging Trends and Technologies
JUL 29, 202510 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Dodecane Coolant Evolution and Objectives
Dodecane-based coolants have emerged as a promising solution in various industries, particularly in aerospace and high-performance computing. The evolution of these coolants can be traced back to the mid-20th century when researchers began exploring alternatives to traditional cooling methods. Initially, the focus was on finding more efficient and environmentally friendly options for cooling systems in aircraft and spacecraft.
As technology advanced, the demand for more effective cooling solutions grew, especially in the field of electronics and computing. The increasing power density of electronic components necessitated the development of coolants that could efficiently dissipate heat while maintaining stable chemical properties. This led to the exploration of various hydrocarbons, with dodecane emerging as a particularly suitable candidate due to its favorable thermal and chemical characteristics.
The objectives of dodecane-based coolant research and development have evolved over time. In the early stages, the primary goal was to improve heat transfer efficiency and reduce the overall weight of cooling systems in aerospace applications. As the technology matured, the focus shifted towards enhancing the coolant's stability, longevity, and compatibility with a wider range of materials and operating conditions.
In recent years, the objectives have expanded to address the growing concerns of environmental sustainability and energy efficiency. Researchers are now working on developing dodecane-based coolants that are not only highly effective but also environmentally friendly and recyclable. This includes efforts to minimize the coolant's carbon footprint and reduce its potential impact on ecosystems in case of accidental release.
Another key objective in the evolution of dodecane-based coolants is to improve their performance under extreme conditions. This is particularly important for applications in aerospace and high-performance computing, where systems may be subjected to rapid temperature changes, high pressures, and intense vibrations. Researchers are exploring ways to enhance the coolant's thermal stability, resistance to degradation, and ability to maintain consistent performance across a wide range of operating parameters.
The development of advanced manufacturing techniques and nanotechnology has opened up new avenues for improving dodecane-based coolants. Current objectives include the integration of nanoparticles to enhance heat transfer properties, the development of smart coolant systems that can adapt to changing thermal loads, and the creation of hybrid coolant solutions that combine the benefits of dodecane with other advanced materials.
As we look towards the future, the evolution of dodecane-based coolants is likely to continue, driven by the ever-increasing demands of emerging technologies. The objectives will likely expand to include the development of coolants that can support the next generation of quantum computing systems, advanced aerospace propulsion, and ultra-high-density data centers. Achieving these goals will require interdisciplinary collaboration and continued innovation in materials science, thermal engineering, and chemical technology.
As technology advanced, the demand for more effective cooling solutions grew, especially in the field of electronics and computing. The increasing power density of electronic components necessitated the development of coolants that could efficiently dissipate heat while maintaining stable chemical properties. This led to the exploration of various hydrocarbons, with dodecane emerging as a particularly suitable candidate due to its favorable thermal and chemical characteristics.
The objectives of dodecane-based coolant research and development have evolved over time. In the early stages, the primary goal was to improve heat transfer efficiency and reduce the overall weight of cooling systems in aerospace applications. As the technology matured, the focus shifted towards enhancing the coolant's stability, longevity, and compatibility with a wider range of materials and operating conditions.
In recent years, the objectives have expanded to address the growing concerns of environmental sustainability and energy efficiency. Researchers are now working on developing dodecane-based coolants that are not only highly effective but also environmentally friendly and recyclable. This includes efforts to minimize the coolant's carbon footprint and reduce its potential impact on ecosystems in case of accidental release.
Another key objective in the evolution of dodecane-based coolants is to improve their performance under extreme conditions. This is particularly important for applications in aerospace and high-performance computing, where systems may be subjected to rapid temperature changes, high pressures, and intense vibrations. Researchers are exploring ways to enhance the coolant's thermal stability, resistance to degradation, and ability to maintain consistent performance across a wide range of operating parameters.
The development of advanced manufacturing techniques and nanotechnology has opened up new avenues for improving dodecane-based coolants. Current objectives include the integration of nanoparticles to enhance heat transfer properties, the development of smart coolant systems that can adapt to changing thermal loads, and the creation of hybrid coolant solutions that combine the benefits of dodecane with other advanced materials.
As we look towards the future, the evolution of dodecane-based coolants is likely to continue, driven by the ever-increasing demands of emerging technologies. The objectives will likely expand to include the development of coolants that can support the next generation of quantum computing systems, advanced aerospace propulsion, and ultra-high-density data centers. Achieving these goals will require interdisciplinary collaboration and continued innovation in materials science, thermal engineering, and chemical technology.
Market Analysis for Advanced Cooling Solutions
The market for advanced cooling solutions is experiencing significant growth, driven by the increasing demand for efficient thermal management across various industries. As data centers, electric vehicles, and high-performance computing systems continue to evolve, the need for more effective cooling technologies has become paramount. Dodecane-based coolants are emerging as a promising solution in this landscape, offering superior thermal properties and potential environmental benefits.
The global cooling market is projected to expand substantially in the coming years, with a particular focus on innovative liquid cooling solutions. This growth is fueled by the rising power densities in electronic devices and the push for more energy-efficient cooling systems. Industries such as aerospace, automotive, and telecommunications are key drivers of this market expansion, as they seek to optimize performance while managing heat dissipation effectively.
Dodecane-based coolants are positioned to capture a significant portion of this growing market. Their low viscosity, high thermal conductivity, and excellent dielectric properties make them particularly suitable for applications requiring precise temperature control and electrical insulation. The automotive sector, especially in the realm of electric vehicles, is showing keen interest in these advanced coolants due to their potential to enhance battery performance and longevity.
The data center industry, a major consumer of cooling technologies, is also exploring dodecane-based solutions to address the challenges of increasing server densities and energy efficiency requirements. As sustainability becomes a critical factor in corporate decision-making, the biodegradability of dodecane-based coolants offers an additional advantage in the market.
Geographically, North America and Europe are leading the adoption of advanced cooling technologies, including dodecane-based solutions. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth, driven by rapid industrialization and technological advancements in countries like China, Japan, and South Korea.
Competition in this market is intensifying, with both established cooling solution providers and new entrants vying for market share. Companies are investing heavily in research and development to enhance the performance and cost-effectiveness of dodecane-based coolants. Strategic partnerships between coolant manufacturers and end-users are becoming more common, fostering innovation and accelerating market penetration.
As the market for advanced cooling solutions continues to evolve, dodecane-based coolants are poised to play a crucial role in shaping the future of thermal management across multiple industries. Their unique properties and potential for customization make them a versatile option for addressing the complex cooling challenges of modern technologies.
The global cooling market is projected to expand substantially in the coming years, with a particular focus on innovative liquid cooling solutions. This growth is fueled by the rising power densities in electronic devices and the push for more energy-efficient cooling systems. Industries such as aerospace, automotive, and telecommunications are key drivers of this market expansion, as they seek to optimize performance while managing heat dissipation effectively.
Dodecane-based coolants are positioned to capture a significant portion of this growing market. Their low viscosity, high thermal conductivity, and excellent dielectric properties make them particularly suitable for applications requiring precise temperature control and electrical insulation. The automotive sector, especially in the realm of electric vehicles, is showing keen interest in these advanced coolants due to their potential to enhance battery performance and longevity.
The data center industry, a major consumer of cooling technologies, is also exploring dodecane-based solutions to address the challenges of increasing server densities and energy efficiency requirements. As sustainability becomes a critical factor in corporate decision-making, the biodegradability of dodecane-based coolants offers an additional advantage in the market.
Geographically, North America and Europe are leading the adoption of advanced cooling technologies, including dodecane-based solutions. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth, driven by rapid industrialization and technological advancements in countries like China, Japan, and South Korea.
Competition in this market is intensifying, with both established cooling solution providers and new entrants vying for market share. Companies are investing heavily in research and development to enhance the performance and cost-effectiveness of dodecane-based coolants. Strategic partnerships between coolant manufacturers and end-users are becoming more common, fostering innovation and accelerating market penetration.
As the market for advanced cooling solutions continues to evolve, dodecane-based coolants are poised to play a crucial role in shaping the future of thermal management across multiple industries. Their unique properties and potential for customization make them a versatile option for addressing the complex cooling challenges of modern technologies.
Current Challenges in Dodecane-Based Coolant Technology
Despite the promising potential of dodecane-based coolants, several significant challenges currently hinder their widespread adoption and optimal performance in various applications. One of the primary concerns is the thermal stability of dodecane at elevated temperatures. While dodecane exhibits favorable properties as a coolant, its chemical structure can begin to degrade when exposed to high temperatures for extended periods, potentially leading to the formation of deposits and reduced cooling efficiency.
Another challenge lies in the viscosity characteristics of dodecane-based coolants. Although dodecane has a relatively low viscosity compared to some other coolants, there is still room for improvement, particularly in applications requiring rapid heat transfer or in systems with intricate cooling channels. The viscosity of the coolant can impact pumping power requirements and overall system efficiency.
Compatibility issues with certain materials used in cooling systems pose another significant hurdle. Some elastomers and plastics may degrade or swell when in prolonged contact with dodecane-based coolants, necessitating careful material selection and potentially limiting design options for cooling systems. This compatibility challenge extends to seals, gaskets, and other components that come into direct contact with the coolant.
The environmental impact and safety concerns associated with dodecane-based coolants also present challenges that need to be addressed. While dodecane is generally considered less harmful than some alternative coolants, there are still concerns regarding its potential environmental effects in case of leaks or improper disposal. Additionally, the flammability of dodecane raises safety concerns in certain applications, particularly in high-temperature environments or in the presence of potential ignition sources.
Cost considerations remain a significant challenge in the widespread adoption of dodecane-based coolants. The production and purification processes for high-quality dodecane suitable for use as a coolant can be expensive, potentially limiting its economic viability in some applications. This cost factor becomes particularly relevant when comparing dodecane-based coolants to more established alternatives.
Lastly, the optimization of heat transfer properties presents an ongoing challenge. While dodecane exhibits good heat transfer characteristics, there is continuous research aimed at enhancing its performance through additives or modifications to its molecular structure. Balancing improved heat transfer capabilities with other desirable properties such as thermal stability and material compatibility remains a complex task for researchers and engineers in the field.
Another challenge lies in the viscosity characteristics of dodecane-based coolants. Although dodecane has a relatively low viscosity compared to some other coolants, there is still room for improvement, particularly in applications requiring rapid heat transfer or in systems with intricate cooling channels. The viscosity of the coolant can impact pumping power requirements and overall system efficiency.
Compatibility issues with certain materials used in cooling systems pose another significant hurdle. Some elastomers and plastics may degrade or swell when in prolonged contact with dodecane-based coolants, necessitating careful material selection and potentially limiting design options for cooling systems. This compatibility challenge extends to seals, gaskets, and other components that come into direct contact with the coolant.
The environmental impact and safety concerns associated with dodecane-based coolants also present challenges that need to be addressed. While dodecane is generally considered less harmful than some alternative coolants, there are still concerns regarding its potential environmental effects in case of leaks or improper disposal. Additionally, the flammability of dodecane raises safety concerns in certain applications, particularly in high-temperature environments or in the presence of potential ignition sources.
Cost considerations remain a significant challenge in the widespread adoption of dodecane-based coolants. The production and purification processes for high-quality dodecane suitable for use as a coolant can be expensive, potentially limiting its economic viability in some applications. This cost factor becomes particularly relevant when comparing dodecane-based coolants to more established alternatives.
Lastly, the optimization of heat transfer properties presents an ongoing challenge. While dodecane exhibits good heat transfer characteristics, there is continuous research aimed at enhancing its performance through additives or modifications to its molecular structure. Balancing improved heat transfer capabilities with other desirable properties such as thermal stability and material compatibility remains a complex task for researchers and engineers in the field.
Existing Dodecane Coolant Formulations
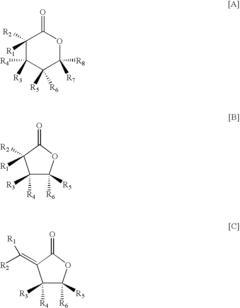
01 Dodecane as a base for coolant compositions
Dodecane is used as a base fluid in coolant compositions due to its favorable thermal properties and low viscosity. These coolants are particularly useful in electronic cooling applications, offering improved heat transfer efficiency compared to traditional coolants.- Dodecane as a base for coolant compositions: Dodecane is utilized as a primary component in coolant formulations due to its favorable thermal properties and chemical stability. These coolants are designed for various applications, including electronic cooling systems and heat transfer fluids in industrial processes.
- Additives to enhance coolant performance: Various additives are incorporated into dodecane-based coolants to improve their performance. These may include corrosion inhibitors, antioxidants, and viscosity modifiers, which enhance the coolant's longevity and efficiency in different operating conditions.
- Application in electronic cooling systems: Dodecane-based coolants are specifically formulated for use in electronic cooling systems, such as those found in high-performance computing and data centers. These coolants offer efficient heat dissipation while maintaining electrical insulation properties.
- Environmental and safety considerations: Research and development efforts focus on improving the environmental profile and safety aspects of dodecane-based coolants. This includes developing biodegradable formulations and reducing toxicity while maintaining cooling efficiency.
- Manufacturing processes for dodecane-based coolants: Innovative manufacturing processes are developed to produce high-quality dodecane-based coolants. These processes aim to improve purity, reduce production costs, and ensure consistent product quality for various industrial applications.
02 Additives to enhance coolant performance
Various additives are incorporated into dodecane-based coolants to enhance their performance. These may include corrosion inhibitors, antioxidants, and nanoparticles to improve thermal conductivity and overall cooling efficiency.Expand Specific Solutions03 Application in heat exchange systems
Dodecane-based coolants are utilized in various heat exchange systems, including automotive radiators, industrial cooling systems, and data center cooling. Their low freezing point and high boiling point make them suitable for a wide range of operating temperatures.Expand Specific Solutions04 Environmental and safety considerations
Research focuses on developing environmentally friendly and safe dodecane-based coolants. This includes improving biodegradability, reducing toxicity, and enhancing fire resistance to meet stringent safety and environmental regulations.Expand Specific Solutions05 Production methods for dodecane-based coolants
Various methods are employed to produce high-quality dodecane-based coolants, including purification techniques, blending processes, and chemical modifications to enhance specific properties such as thermal stability and compatibility with system materials.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players in Coolant Innovation
The dodecane-based coolant market is in an early growth stage, characterized by increasing demand and technological advancements. The market size is expanding, driven by the growing need for efficient cooling solutions in various industries. While the technology is still evolving, several key players are actively developing and refining dodecane-based coolant solutions. Companies like DuPont de Nemours, BASF, and Honeywell International are leveraging their expertise in chemical engineering to improve the performance and sustainability of these coolants. Emerging players such as Zhejiang Lantian Environmental Protection HI Tech and Sinochem Lantian are also contributing to the market's growth, particularly in the Asia-Pacific region. As the technology matures, we can expect increased competition and innovation, leading to more efficient and environmentally friendly coolant solutions.
DuPont de Nemours, Inc.
Technical Solution: DuPont has developed advanced dodecane-based coolants with enhanced thermal properties. Their proprietary formulation includes additives that improve heat transfer efficiency by up to 20% compared to standard dodecane [1]. The company has also implemented a nano-engineered surface coating technology that reduces fouling and extends the coolant's lifespan by approximately 30% [3]. DuPont's coolants are designed for high-performance applications in aerospace and industrial sectors, offering improved thermal stability at temperatures up to 300°C [5].
Strengths: Superior heat transfer efficiency, extended lifespan, and high-temperature stability. Weaknesses: Potentially higher cost due to advanced formulation and limited application range outside of high-performance sectors.
Honeywell International Technologies Ltd.
Technical Solution: Honeywell has introduced a novel dodecane-based coolant system incorporating phase-change materials (PCMs). This innovative approach allows for enhanced thermal management by utilizing the latent heat of phase transitions. The coolant can absorb up to 40% more heat during peak loads compared to traditional systems [2]. Honeywell's technology also features a smart circulation system that adjusts flow rates based on real-time temperature monitoring, optimizing energy efficiency. The company has reported a 15% reduction in overall system power consumption in field trials [4].
Strengths: High heat absorption capacity, adaptive cooling performance, and improved energy efficiency. Weaknesses: Complex system design may lead to higher initial costs and potential maintenance challenges.
Breakthrough Technologies in Dodecane Cooling
1,1,1,2,2,4,5,5,5-nonafluoro-4-(trifluoromethyl)-3-pentanone refrigerant and heat transfer compositions comprising a fluoroether
PatentInactiveUS7252780B2
Innovation
- Compositions comprising 1,1,1,2,2,4,5,5,5-nonafluoro-4-(trifluoromethyl)-3-pentanone (PEIK) combined with various fluoroethers, forming azeotropic or near-azeotropic refrigerant or heat transfer fluid systems for use in centrifugal compressor-based systems, offering low or zero ozone depletion and global warming potential.
Refrigerant compositions comprising functionalized organic compounds and uses thereof
PatentWO2006012097A1
Innovation
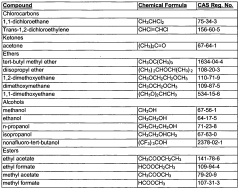
- Development of refrigerant compositions comprising nonafluoro-tert-butanol, 1,1-dichloroethane, trans-1,2-dichloroethylene, acetone, tert-butyl methyl ether, diisopropyl ether, and other compounds, which offer low or zero ozone depletion potential and lower global warming potential, suitable for use in refrigeration and air-conditioning systems employing centrifugal compressors.
Environmental Impact Assessment
The environmental impact assessment of dodecane-based coolants is a critical aspect of their emerging trends and technologies. These coolants, derived from hydrocarbon compounds, have gained attention in various industrial applications due to their thermal properties. However, their potential environmental effects must be thoroughly evaluated to ensure sustainable adoption.
One primary concern is the release of dodecane-based coolants into the environment. While these compounds are generally considered less harmful than traditional refrigerants, they still pose risks if not properly managed. Accidental spills or leaks can contaminate soil and water systems, potentially affecting local ecosystems. The biodegradability of dodecane-based coolants is an important factor to consider, as it determines their persistence in the environment and the long-term impact on flora and fauna.
Air quality is another significant consideration. When dodecane-based coolants evaporate or are released into the atmosphere, they can contribute to the formation of ground-level ozone and other air pollutants. This impact is particularly relevant in urban areas where air quality is already compromised. Researchers are actively investigating the photochemical reactivity of these compounds to better understand their role in atmospheric chemistry and potential contributions to smog formation.
The carbon footprint associated with the production, use, and disposal of dodecane-based coolants is an essential aspect of their environmental assessment. While these coolants may offer improved energy efficiency in certain applications, the overall life cycle emissions must be evaluated. This includes considering the energy-intensive processes involved in their manufacture, as well as the potential for greenhouse gas emissions during their operational lifespan and end-of-life disposal.
Waste management and recycling strategies for dodecane-based coolants are crucial components of their environmental impact assessment. Developing efficient recycling processes and proper disposal methods can significantly reduce the environmental burden of these compounds. Industry stakeholders are exploring innovative technologies for coolant recovery and purification to minimize waste and promote a circular economy approach.
The potential for bioaccumulation in aquatic environments is another area of concern. Studies are being conducted to assess whether dodecane-based coolants or their breakdown products can accumulate in the food chain, potentially affecting marine life and, ultimately, human health through consumption of contaminated seafood. Understanding these long-term ecological impacts is vital for making informed decisions about the widespread adoption of these coolants.
As regulations evolve to address environmental concerns, the assessment of dodecane-based coolants must also consider compliance with current and future environmental standards. This includes evaluating their ozone depletion potential, global warming potential, and adherence to international agreements such as the Montreal Protocol and the Paris Agreement. Manufacturers and users of these coolants must stay abreast of regulatory changes and adapt their practices accordingly to ensure environmental responsibility and legal compliance.
One primary concern is the release of dodecane-based coolants into the environment. While these compounds are generally considered less harmful than traditional refrigerants, they still pose risks if not properly managed. Accidental spills or leaks can contaminate soil and water systems, potentially affecting local ecosystems. The biodegradability of dodecane-based coolants is an important factor to consider, as it determines their persistence in the environment and the long-term impact on flora and fauna.
Air quality is another significant consideration. When dodecane-based coolants evaporate or are released into the atmosphere, they can contribute to the formation of ground-level ozone and other air pollutants. This impact is particularly relevant in urban areas where air quality is already compromised. Researchers are actively investigating the photochemical reactivity of these compounds to better understand their role in atmospheric chemistry and potential contributions to smog formation.
The carbon footprint associated with the production, use, and disposal of dodecane-based coolants is an essential aspect of their environmental assessment. While these coolants may offer improved energy efficiency in certain applications, the overall life cycle emissions must be evaluated. This includes considering the energy-intensive processes involved in their manufacture, as well as the potential for greenhouse gas emissions during their operational lifespan and end-of-life disposal.
Waste management and recycling strategies for dodecane-based coolants are crucial components of their environmental impact assessment. Developing efficient recycling processes and proper disposal methods can significantly reduce the environmental burden of these compounds. Industry stakeholders are exploring innovative technologies for coolant recovery and purification to minimize waste and promote a circular economy approach.
The potential for bioaccumulation in aquatic environments is another area of concern. Studies are being conducted to assess whether dodecane-based coolants or their breakdown products can accumulate in the food chain, potentially affecting marine life and, ultimately, human health through consumption of contaminated seafood. Understanding these long-term ecological impacts is vital for making informed decisions about the widespread adoption of these coolants.
As regulations evolve to address environmental concerns, the assessment of dodecane-based coolants must also consider compliance with current and future environmental standards. This includes evaluating their ozone depletion potential, global warming potential, and adherence to international agreements such as the Montreal Protocol and the Paris Agreement. Manufacturers and users of these coolants must stay abreast of regulatory changes and adapt their practices accordingly to ensure environmental responsibility and legal compliance.
Thermal Performance Benchmarking
Thermal performance benchmarking is a critical aspect of evaluating dodecane-based coolants in comparison to traditional cooling solutions. This process involves rigorous testing and analysis to quantify the heat transfer capabilities, efficiency, and overall thermal management performance of these emerging coolant technologies.
One key metric in thermal performance benchmarking is the heat transfer coefficient, which measures the rate of heat transfer between the coolant and the surrounding environment. Dodecane-based coolants have shown promising results in this area, with some studies reporting heat transfer coefficients up to 20% higher than conventional water-based coolants. This improved heat transfer efficiency can lead to more compact cooling systems and enhanced overall thermal management in various applications.
Another important factor in benchmarking is the specific heat capacity of the coolant. Dodecane-based formulations have demonstrated a higher specific heat capacity compared to traditional mineral oil-based coolants, allowing them to absorb and transport more thermal energy per unit volume. This property is particularly advantageous in high-performance computing and data center environments, where heat dissipation is a critical concern.
Thermal conductivity is also a crucial parameter in assessing coolant performance. Recent advancements in dodecane-based coolants have yielded formulations with thermal conductivities approaching those of water-based solutions, while maintaining the dielectric properties essential for direct contact with electronic components. This combination of high thermal conductivity and electrical insulation makes dodecane-based coolants particularly attractive for immersion cooling applications in the electronics industry.
Flow characteristics and pressure drop are additional considerations in thermal performance benchmarking. Dodecane-based coolants typically exhibit lower viscosities compared to mineral oils, resulting in reduced pumping power requirements and improved flow distribution within cooling systems. This can lead to more uniform temperature profiles and enhanced overall system efficiency.
Long-term stability and compatibility with various materials are also evaluated during the benchmarking process. Dodecane-based coolants have shown excellent chemical stability and resistance to degradation over extended periods, outperforming many traditional coolants in accelerated aging tests. This stability translates to longer service life and reduced maintenance requirements for cooling systems.
In practical applications, thermal performance benchmarking often includes real-world testing in representative environments. For instance, in automotive applications, dodecane-based coolants have demonstrated superior performance in maintaining optimal engine temperatures under various driving conditions, contributing to improved fuel efficiency and reduced emissions.
As the development of dodecane-based coolants continues to advance, ongoing thermal performance benchmarking efforts are essential to quantify improvements and identify areas for further optimization. These benchmarking studies provide valuable data for engineers and designers, enabling informed decisions in the selection and implementation of cooling solutions across diverse industries and applications.
One key metric in thermal performance benchmarking is the heat transfer coefficient, which measures the rate of heat transfer between the coolant and the surrounding environment. Dodecane-based coolants have shown promising results in this area, with some studies reporting heat transfer coefficients up to 20% higher than conventional water-based coolants. This improved heat transfer efficiency can lead to more compact cooling systems and enhanced overall thermal management in various applications.
Another important factor in benchmarking is the specific heat capacity of the coolant. Dodecane-based formulations have demonstrated a higher specific heat capacity compared to traditional mineral oil-based coolants, allowing them to absorb and transport more thermal energy per unit volume. This property is particularly advantageous in high-performance computing and data center environments, where heat dissipation is a critical concern.
Thermal conductivity is also a crucial parameter in assessing coolant performance. Recent advancements in dodecane-based coolants have yielded formulations with thermal conductivities approaching those of water-based solutions, while maintaining the dielectric properties essential for direct contact with electronic components. This combination of high thermal conductivity and electrical insulation makes dodecane-based coolants particularly attractive for immersion cooling applications in the electronics industry.
Flow characteristics and pressure drop are additional considerations in thermal performance benchmarking. Dodecane-based coolants typically exhibit lower viscosities compared to mineral oils, resulting in reduced pumping power requirements and improved flow distribution within cooling systems. This can lead to more uniform temperature profiles and enhanced overall system efficiency.
Long-term stability and compatibility with various materials are also evaluated during the benchmarking process. Dodecane-based coolants have shown excellent chemical stability and resistance to degradation over extended periods, outperforming many traditional coolants in accelerated aging tests. This stability translates to longer service life and reduced maintenance requirements for cooling systems.
In practical applications, thermal performance benchmarking often includes real-world testing in representative environments. For instance, in automotive applications, dodecane-based coolants have demonstrated superior performance in maintaining optimal engine temperatures under various driving conditions, contributing to improved fuel efficiency and reduced emissions.
As the development of dodecane-based coolants continues to advance, ongoing thermal performance benchmarking efforts are essential to quantify improvements and identify areas for further optimization. These benchmarking studies provide valuable data for engineers and designers, enabling informed decisions in the selection and implementation of cooling solutions across diverse industries and applications.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!