Dodecane in Photochemical Processes: A Research Perspective
JUL 29, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Dodecane Photochemistry Background and Objectives
Dodecane, a straight-chain alkane with twelve carbon atoms, has emerged as a significant compound in photochemical processes, attracting considerable attention from researchers and industry professionals alike. The study of dodecane in photochemistry has evolved over the past few decades, driven by its potential applications in various fields, including energy conversion, environmental remediation, and materials science.
The historical context of dodecane photochemistry can be traced back to the mid-20th century when scientists began exploring the photochemical behavior of hydrocarbons. Initially, research focused on simpler alkanes, but as analytical techniques advanced, more complex molecules like dodecane came under scrutiny. The 1970s and 1980s saw a surge in interest, particularly in the context of atmospheric chemistry and the formation of secondary organic aerosols.
As we entered the 21st century, the scope of dodecane photochemistry expanded significantly. Researchers began to explore its potential in solar energy harvesting, photocatalysis, and the development of novel photosensitive materials. The advent of advanced spectroscopic techniques and computational modeling has allowed for a more comprehensive understanding of the photochemical reactions involving dodecane.
The current technological landscape presents both opportunities and challenges in dodecane photochemistry. On one hand, there is growing interest in utilizing dodecane as a model compound for studying more complex photochemical systems. Its relatively simple structure, combined with its relevance to real-world applications, makes it an ideal candidate for fundamental research. On the other hand, the complexity of its photochemical behavior, particularly in multi-component systems, poses significant analytical and interpretative challenges.
Looking ahead, the objectives of research in dodecane photochemistry are multifaceted. One primary goal is to elucidate the detailed reaction mechanisms and kinetics of dodecane's photochemical transformations. This includes understanding the role of different excitation wavelengths, the influence of various reaction conditions, and the interplay between dodecane and other molecules in complex mixtures.
Another critical objective is to explore the potential applications of dodecane photochemistry in practical settings. This includes investigating its use in solar fuel production, where dodecane could serve as a hydrogen donor or a precursor for value-added chemicals. Additionally, there is growing interest in leveraging dodecane's photochemical properties for environmental applications, such as water purification and air quality improvement.
Researchers are also aiming to develop new photocatalytic systems that can efficiently utilize dodecane in chemical transformations. This involves designing novel photocatalysts, optimizing reaction conditions, and exploring the synergistic effects of combining dodecane with other compounds to enhance photochemical efficiency.
The historical context of dodecane photochemistry can be traced back to the mid-20th century when scientists began exploring the photochemical behavior of hydrocarbons. Initially, research focused on simpler alkanes, but as analytical techniques advanced, more complex molecules like dodecane came under scrutiny. The 1970s and 1980s saw a surge in interest, particularly in the context of atmospheric chemistry and the formation of secondary organic aerosols.
As we entered the 21st century, the scope of dodecane photochemistry expanded significantly. Researchers began to explore its potential in solar energy harvesting, photocatalysis, and the development of novel photosensitive materials. The advent of advanced spectroscopic techniques and computational modeling has allowed for a more comprehensive understanding of the photochemical reactions involving dodecane.
The current technological landscape presents both opportunities and challenges in dodecane photochemistry. On one hand, there is growing interest in utilizing dodecane as a model compound for studying more complex photochemical systems. Its relatively simple structure, combined with its relevance to real-world applications, makes it an ideal candidate for fundamental research. On the other hand, the complexity of its photochemical behavior, particularly in multi-component systems, poses significant analytical and interpretative challenges.
Looking ahead, the objectives of research in dodecane photochemistry are multifaceted. One primary goal is to elucidate the detailed reaction mechanisms and kinetics of dodecane's photochemical transformations. This includes understanding the role of different excitation wavelengths, the influence of various reaction conditions, and the interplay between dodecane and other molecules in complex mixtures.
Another critical objective is to explore the potential applications of dodecane photochemistry in practical settings. This includes investigating its use in solar fuel production, where dodecane could serve as a hydrogen donor or a precursor for value-added chemicals. Additionally, there is growing interest in leveraging dodecane's photochemical properties for environmental applications, such as water purification and air quality improvement.
Researchers are also aiming to develop new photocatalytic systems that can efficiently utilize dodecane in chemical transformations. This involves designing novel photocatalysts, optimizing reaction conditions, and exploring the synergistic effects of combining dodecane with other compounds to enhance photochemical efficiency.
Market Analysis for Dodecane-based Photochemical Products
The market for dodecane-based photochemical products is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing demand in various industrial sectors. Dodecane, a versatile hydrocarbon, plays a crucial role in photochemical processes, particularly in the production of specialty chemicals, pharmaceuticals, and advanced materials.
In the specialty chemicals sector, dodecane-based photochemical products are gaining traction due to their unique properties and applications. These products are extensively used in the manufacturing of high-performance coatings, adhesives, and sealants. The global specialty chemicals market, which includes these applications, is projected to grow steadily over the next five years, creating a favorable environment for dodecane-based photochemical products.
The pharmaceutical industry represents another key market for dodecane-based photochemical products. These compounds are utilized in the synthesis of complex drug molecules and intermediates, offering improved efficiency and selectivity in chemical reactions. As the pharmaceutical sector continues to expand, driven by factors such as aging populations and increasing healthcare expenditure, the demand for advanced synthesis methods incorporating dodecane-based photochemical processes is expected to rise.
In the field of advanced materials, dodecane-based photochemical products are finding applications in the development of novel polymers, composites, and functional materials. The growing emphasis on sustainable and high-performance materials in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and electronics is fueling the demand for these innovative solutions.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the market for dodecane-based photochemical products, owing to their well-established chemical and pharmaceutical industries. However, the Asia-Pacific region is emerging as a significant growth market, driven by rapid industrialization, increasing research and development activities, and growing demand for advanced materials in countries like China, Japan, and South Korea.
The market is characterized by intense competition among key players, including major chemical companies and specialty chemical manufacturers. These companies are investing heavily in research and development to expand their product portfolios and gain a competitive edge. Collaborations between industry and academia are also becoming more prevalent, fostering innovation in dodecane-based photochemical processes.
Despite the positive outlook, the market faces challenges such as stringent environmental regulations and the need for sustainable production methods. This has led to increased focus on developing green chemistry approaches and eco-friendly alternatives, which may impact the future trajectory of dodecane-based photochemical products.
In the specialty chemicals sector, dodecane-based photochemical products are gaining traction due to their unique properties and applications. These products are extensively used in the manufacturing of high-performance coatings, adhesives, and sealants. The global specialty chemicals market, which includes these applications, is projected to grow steadily over the next five years, creating a favorable environment for dodecane-based photochemical products.
The pharmaceutical industry represents another key market for dodecane-based photochemical products. These compounds are utilized in the synthesis of complex drug molecules and intermediates, offering improved efficiency and selectivity in chemical reactions. As the pharmaceutical sector continues to expand, driven by factors such as aging populations and increasing healthcare expenditure, the demand for advanced synthesis methods incorporating dodecane-based photochemical processes is expected to rise.
In the field of advanced materials, dodecane-based photochemical products are finding applications in the development of novel polymers, composites, and functional materials. The growing emphasis on sustainable and high-performance materials in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and electronics is fueling the demand for these innovative solutions.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the market for dodecane-based photochemical products, owing to their well-established chemical and pharmaceutical industries. However, the Asia-Pacific region is emerging as a significant growth market, driven by rapid industrialization, increasing research and development activities, and growing demand for advanced materials in countries like China, Japan, and South Korea.
The market is characterized by intense competition among key players, including major chemical companies and specialty chemical manufacturers. These companies are investing heavily in research and development to expand their product portfolios and gain a competitive edge. Collaborations between industry and academia are also becoming more prevalent, fostering innovation in dodecane-based photochemical processes.
Despite the positive outlook, the market faces challenges such as stringent environmental regulations and the need for sustainable production methods. This has led to increased focus on developing green chemistry approaches and eco-friendly alternatives, which may impact the future trajectory of dodecane-based photochemical products.
Current Challenges in Dodecane Photochemical Processes
The photochemical processes involving dodecane present several significant challenges that researchers and industry professionals are currently grappling with. One of the primary issues is the low reactivity of dodecane in photochemical reactions. As a saturated hydrocarbon, dodecane lacks the structural features that typically facilitate photochemical transformations, such as double bonds or easily excitable functional groups. This inherent stability makes it difficult to initiate and control photochemical reactions efficiently.
Another challenge lies in the selectivity of photochemical processes involving dodecane. When photochemical reactions do occur, they often result in a mixture of products, including various isomers and fragmentation products. Achieving high selectivity for desired products remains a significant hurdle, limiting the practical applications of dodecane in photochemical processes.
The energy requirements for dodecane photochemistry pose additional challenges. Due to the molecule's stability, high-energy ultraviolet light is typically necessary to induce reactions. This not only increases the energy costs associated with these processes but also raises safety concerns and may lead to unwanted side reactions or degradation of other components in the reaction system.
Scalability is another critical issue facing researchers in this field. While some photochemical processes involving dodecane may show promise on a laboratory scale, translating these reactions to industrial-scale production presents numerous engineering and economic challenges. The need for specialized photoreactors, light sources, and reaction conditions can make large-scale implementation prohibitively expensive or impractical.
Furthermore, the environmental impact of dodecane photochemistry is a growing concern. The potential formation of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and other environmentally harmful byproducts during these processes necessitates careful consideration of waste management and emission control strategies. Developing greener, more sustainable photochemical processes for dodecane remains an important goal for researchers in this field.
Lastly, the limited understanding of the fundamental photochemical mechanisms involving dodecane hinders progress in overcoming these challenges. While some reaction pathways have been elucidated, many aspects of dodecane photochemistry, particularly in complex reaction environments, remain poorly understood. This knowledge gap impedes the development of more efficient and selective photochemical processes for dodecane and related compounds.
Another challenge lies in the selectivity of photochemical processes involving dodecane. When photochemical reactions do occur, they often result in a mixture of products, including various isomers and fragmentation products. Achieving high selectivity for desired products remains a significant hurdle, limiting the practical applications of dodecane in photochemical processes.
The energy requirements for dodecane photochemistry pose additional challenges. Due to the molecule's stability, high-energy ultraviolet light is typically necessary to induce reactions. This not only increases the energy costs associated with these processes but also raises safety concerns and may lead to unwanted side reactions or degradation of other components in the reaction system.
Scalability is another critical issue facing researchers in this field. While some photochemical processes involving dodecane may show promise on a laboratory scale, translating these reactions to industrial-scale production presents numerous engineering and economic challenges. The need for specialized photoreactors, light sources, and reaction conditions can make large-scale implementation prohibitively expensive or impractical.
Furthermore, the environmental impact of dodecane photochemistry is a growing concern. The potential formation of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and other environmentally harmful byproducts during these processes necessitates careful consideration of waste management and emission control strategies. Developing greener, more sustainable photochemical processes for dodecane remains an important goal for researchers in this field.
Lastly, the limited understanding of the fundamental photochemical mechanisms involving dodecane hinders progress in overcoming these challenges. While some reaction pathways have been elucidated, many aspects of dodecane photochemistry, particularly in complex reaction environments, remain poorly understood. This knowledge gap impedes the development of more efficient and selective photochemical processes for dodecane and related compounds.
Existing Dodecane Photochemical Process Solutions
01 Synthesis and production of dodecane
Dodecane can be synthesized through various chemical processes, including the hydrogenation of long-chain alkenes or the reduction of fatty acids. It is also produced as a byproduct in petroleum refining. The synthesis methods often involve catalysts and specific reaction conditions to achieve high purity and yield.- Synthesis and production of dodecane: Dodecane can be synthesized through various chemical processes, including the hydrogenation of long-chain alkenes or the Fischer-Tropsch process. It can also be produced from renewable resources such as plant oils or biomass. The synthesis methods often involve catalysts and specific reaction conditions to achieve high yields and purity.
- Applications in cosmetics and personal care products: Dodecane is used in cosmetics and personal care products as an emollient, solvent, or carrier for active ingredients. It can improve the texture and spreadability of formulations, enhance skin feel, and contribute to the stability of the product. Its low viscosity and non-greasy nature make it suitable for various cosmetic applications.
- Use in fuel and lubricant formulations: Dodecane is an important component in fuel and lubricant formulations. It can be used as a fuel additive to improve combustion efficiency and reduce emissions. In lubricants, dodecane contributes to the overall performance by enhancing viscosity characteristics and thermal stability. It is also used in the development of synthetic lubricants.
- Applications in chemical and industrial processes: Dodecane finds applications in various chemical and industrial processes. It can be used as a solvent in organic synthesis, as a standard in chromatography, or as a phase change material for thermal energy storage. In industrial settings, it may be employed in heat transfer systems or as a component in specialty chemicals.
- Environmental and safety considerations: The use of dodecane in various applications requires consideration of environmental and safety aspects. This includes studying its biodegradability, potential environmental impact, and toxicological properties. Research is ongoing to develop more sustainable production methods and to assess the long-term effects of dodecane use in different industries.
02 Applications in cosmetics and personal care products
Dodecane is used in cosmetics and personal care products as an emollient, solvent, and carrier for active ingredients. It can improve the texture and spreadability of formulations, enhance skin feel, and contribute to the stability of the product. Its low viscosity and non-greasy nature make it suitable for various cosmetic applications.Expand Specific Solutions03 Use in industrial processes and lubricants
Dodecane finds applications in various industrial processes as a solvent, lubricant, and heat transfer fluid. It is used in the production of polymers, as a component in metalworking fluids, and in the formulation of specialty lubricants. Its properties, such as low volatility and good thermal stability, make it suitable for these applications.Expand Specific Solutions04 Role in fuel and energy applications
Dodecane is an important component in jet fuels and diesel fuels, contributing to their performance characteristics. It is also used as a reference compound in fuel research and testing. In energy applications, dodecane can serve as a phase change material for thermal energy storage systems.Expand Specific Solutions05 Environmental and safety considerations
The use of dodecane in various applications requires consideration of its environmental impact and safety profile. Research focuses on developing eco-friendly production methods, assessing biodegradability, and studying its potential effects on aquatic ecosystems. Safety measures for handling and storage are also important aspects of dodecane utilization.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Dodecane Photochemical Research
The research on dodecane in photochemical processes is in a nascent stage, with the market still developing. The global photochemical industry is experiencing steady growth, driven by increasing applications in various sectors. While the market size for dodecane-specific photochemical processes is not well-defined, the overall photochemistry market is expanding. Technologically, the field is evolving, with companies like BASF Corp., Arkema France SA, and The Chemours Co. leading research efforts. Academic institutions such as the Naval Research Laboratory and the Spanish National Research Council are also contributing significantly to advancing the understanding of dodecane's photochemical properties, indicating a collaborative approach between industry and academia in this emerging field.
BASF Corp.
Technical Solution: BASF Corp. has developed advanced photochemical processes utilizing dodecane as a key component. Their approach involves using dodecane as a solvent and reactant in photocatalytic reactions, particularly for the synthesis of fine chemicals and pharmaceuticals. BASF's technology employs specially designed photoreactors with optimized light penetration and mixing characteristics, enhancing the efficiency of dodecane-mediated photochemical transformations[1]. The company has also explored the use of dodecane in photooxidation processes, leveraging its stability and low volatility to improve reaction yields and selectivity[3].
Strengths: Extensive expertise in chemical processes, large-scale production capabilities, and a strong R&D foundation. Weaknesses: Potential environmental concerns associated with hydrocarbon-based processes and competition from greener alternatives.
Naval Research Laboratory
Technical Solution: The Naval Research Laboratory has conducted extensive research on dodecane in photochemical processes, focusing on its applications in fuel systems and energy storage. Their approach involves studying the photochemical degradation of dodecane under various conditions to understand its stability and potential for long-term storage in naval vessels[2]. The laboratory has developed advanced spectroscopic techniques to monitor dodecane's photochemical reactions in real-time, providing crucial insights into reaction kinetics and mechanisms[4]. Additionally, they have explored the use of dodecane as a model compound for investigating the photochemical behavior of more complex hydrocarbon fuels[6].
Strengths: Access to advanced research facilities, multidisciplinary expertise, and focus on practical applications for naval operations. Weaknesses: Limited commercial focus and potential restrictions on sharing research findings due to military affiliations.
Core Innovations in Dodecane Photochemistry
Light emitting display device, method for manufacturing the same, and tv set
PatentInactiveUS20070132377A1
Innovation
- The use of a droplet discharge method to form patterns for TFTs and light emitting display devices, including a conductive layer and insulating layer, using a photocatalytic substance to improve adhesion and reduce the number of photolithography steps, allowing for the formation of patterns on large area substrates with higher yield and lower costs.
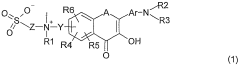
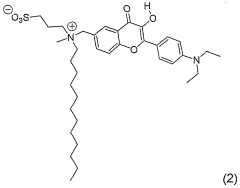
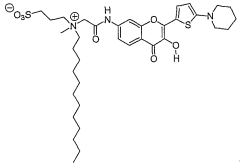
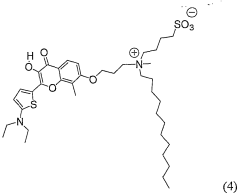
3 -hydroxyflavone derivatives for the detection and the quantification of cell apoptosis
PatentWO2007057782A2
Innovation
- Development of 3-hydroxyflavone derivatives with a zwitterionic group and long hydrocarbon chain, which selectively bind to the outer leaflet of the cell membrane, providing a two-color ratiometric response independent of Ca2+ ions and local probe concentration, allowing for precise apoptosis detection.
Environmental Impact of Dodecane Photochemical Processes
The environmental impact of dodecane photochemical processes is a critical consideration in the broader context of atmospheric chemistry and pollution. Dodecane, a common component in various industrial and consumer products, undergoes complex photochemical reactions when exposed to sunlight in the atmosphere. These reactions can lead to the formation of secondary organic aerosols (SOA), which have significant implications for air quality and climate change.
One of the primary environmental concerns associated with dodecane photochemistry is its contribution to the formation of tropospheric ozone. When dodecane reacts with nitrogen oxides in the presence of sunlight, it can lead to the production of ground-level ozone, a major component of smog. This process not only degrades air quality but also poses serious health risks to humans and ecosystems. The ozone formed through these reactions can cause respiratory issues in humans and damage vegetation, affecting crop yields and forest health.
Furthermore, the photochemical degradation of dodecane results in the production of various volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and particulate matter. These secondary pollutants can have far-reaching effects on the environment. VOCs contribute to the formation of photochemical smog and can react further to produce additional harmful compounds. Particulate matter, especially fine particles (PM2.5), can remain suspended in the air for extended periods, impacting visibility and potentially entering the respiratory system of living organisms.
The environmental impact of dodecane photochemistry extends to aquatic ecosystems as well. When these reaction products are deposited through wet or dry deposition, they can alter the chemical composition of water bodies. This can lead to acidification of lakes and streams, affecting aquatic life and disrupting ecosystem balance. Additionally, some of the byproducts may be persistent in the environment, potentially bioaccumulating in the food chain.
Climate change implications are another crucial aspect of dodecane photochemical processes. The formation of SOA from dodecane contributes to the overall aerosol burden in the atmosphere. These aerosols can influence the Earth's radiation balance by scattering or absorbing incoming solar radiation, thus affecting global climate patterns. Moreover, they can act as cloud condensation nuclei, altering cloud formation processes and precipitation patterns.
Understanding the environmental impact of dodecane photochemistry is essential for developing effective air quality management strategies and environmental policies. It highlights the need for continued research into the atmospheric fate of hydrocarbons and their role in complex atmospheric processes. This knowledge can inform the development of cleaner technologies and alternative products that minimize the release of dodecane and similar compounds into the environment, ultimately contributing to improved air quality and reduced environmental impact.
One of the primary environmental concerns associated with dodecane photochemistry is its contribution to the formation of tropospheric ozone. When dodecane reacts with nitrogen oxides in the presence of sunlight, it can lead to the production of ground-level ozone, a major component of smog. This process not only degrades air quality but also poses serious health risks to humans and ecosystems. The ozone formed through these reactions can cause respiratory issues in humans and damage vegetation, affecting crop yields and forest health.
Furthermore, the photochemical degradation of dodecane results in the production of various volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and particulate matter. These secondary pollutants can have far-reaching effects on the environment. VOCs contribute to the formation of photochemical smog and can react further to produce additional harmful compounds. Particulate matter, especially fine particles (PM2.5), can remain suspended in the air for extended periods, impacting visibility and potentially entering the respiratory system of living organisms.
The environmental impact of dodecane photochemistry extends to aquatic ecosystems as well. When these reaction products are deposited through wet or dry deposition, they can alter the chemical composition of water bodies. This can lead to acidification of lakes and streams, affecting aquatic life and disrupting ecosystem balance. Additionally, some of the byproducts may be persistent in the environment, potentially bioaccumulating in the food chain.
Climate change implications are another crucial aspect of dodecane photochemical processes. The formation of SOA from dodecane contributes to the overall aerosol burden in the atmosphere. These aerosols can influence the Earth's radiation balance by scattering or absorbing incoming solar radiation, thus affecting global climate patterns. Moreover, they can act as cloud condensation nuclei, altering cloud formation processes and precipitation patterns.
Understanding the environmental impact of dodecane photochemistry is essential for developing effective air quality management strategies and environmental policies. It highlights the need for continued research into the atmospheric fate of hydrocarbons and their role in complex atmospheric processes. This knowledge can inform the development of cleaner technologies and alternative products that minimize the release of dodecane and similar compounds into the environment, ultimately contributing to improved air quality and reduced environmental impact.
Safety Considerations in Dodecane Photochemistry
Safety considerations in dodecane photochemistry are paramount due to the compound's flammability and potential for generating hazardous byproducts during photochemical reactions. Dodecane, a long-chain hydrocarbon, is highly combustible and can form explosive mixtures with air, necessitating careful handling and storage practices. When used in photochemical processes, it is crucial to conduct operations in well-ventilated areas or under fume hoods to prevent the accumulation of vapors.
Researchers must be aware of the potential for dodecane to undergo photodegradation, which can lead to the formation of various reactive intermediates and byproducts. These may include aldehydes, ketones, and other oxygenated compounds, some of which could be irritants or pose health risks upon exposure. Proper personal protective equipment (PPE), including chemical-resistant gloves, safety goggles, and lab coats, should be worn at all times when handling dodecane and during photochemical experiments.
The choice of light sources for photochemical reactions involving dodecane requires careful consideration. UV light, often used in such processes, can be harmful to skin and eyes. Appropriate shielding and protective measures must be implemented to prevent accidental exposure. Additionally, the heat generated by light sources can increase the volatility of dodecane, potentially leading to higher concentrations of vapors in the work area.
Chemical incompatibilities must be taken into account when designing experimental setups. Dodecane should be kept away from strong oxidizing agents, as these can lead to violent reactions. The use of inert atmospheres, such as nitrogen or argon, may be necessary to prevent unwanted oxidation reactions and reduce fire risks.
Proper waste management is essential in dodecane photochemistry. Unreacted dodecane and reaction mixtures should be disposed of as hazardous waste according to institutional and regulatory guidelines. Spill control measures, including appropriate absorbents and containment strategies, should be readily available in case of accidental releases.
Researchers should be trained in emergency procedures specific to dodecane-related incidents, including fire response and first aid for chemical exposures. Regular safety audits and equipment checks are recommended to ensure the integrity of reaction vessels, light sources, and containment systems. By adhering to these safety considerations, researchers can minimize risks and conduct dodecane photochemistry experiments with greater confidence and security.
Researchers must be aware of the potential for dodecane to undergo photodegradation, which can lead to the formation of various reactive intermediates and byproducts. These may include aldehydes, ketones, and other oxygenated compounds, some of which could be irritants or pose health risks upon exposure. Proper personal protective equipment (PPE), including chemical-resistant gloves, safety goggles, and lab coats, should be worn at all times when handling dodecane and during photochemical experiments.
The choice of light sources for photochemical reactions involving dodecane requires careful consideration. UV light, often used in such processes, can be harmful to skin and eyes. Appropriate shielding and protective measures must be implemented to prevent accidental exposure. Additionally, the heat generated by light sources can increase the volatility of dodecane, potentially leading to higher concentrations of vapors in the work area.
Chemical incompatibilities must be taken into account when designing experimental setups. Dodecane should be kept away from strong oxidizing agents, as these can lead to violent reactions. The use of inert atmospheres, such as nitrogen or argon, may be necessary to prevent unwanted oxidation reactions and reduce fire risks.
Proper waste management is essential in dodecane photochemistry. Unreacted dodecane and reaction mixtures should be disposed of as hazardous waste according to institutional and regulatory guidelines. Spill control measures, including appropriate absorbents and containment strategies, should be readily available in case of accidental releases.
Researchers should be trained in emergency procedures specific to dodecane-related incidents, including fire response and first aid for chemical exposures. Regular safety audits and equipment checks are recommended to ensure the integrity of reaction vessels, light sources, and containment systems. By adhering to these safety considerations, researchers can minimize risks and conduct dodecane photochemistry experiments with greater confidence and security.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!