Dodecane's Application in Pharmaceutical Testing
JUL 29, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Dodecane in Pharma Testing: Background and Objectives
Dodecane, a straight-chain alkane hydrocarbon with the molecular formula C12H26, has emerged as a significant compound in pharmaceutical testing. Its application in this field has evolved over the years, driven by the increasing demand for more efficient and reliable testing methods in drug development and quality control processes.
The pharmaceutical industry has long sought effective solvents and reference standards for various analytical procedures. Dodecane's unique properties, including its low reactivity, stability, and ability to dissolve a wide range of organic compounds, have made it an attractive option for researchers and quality control specialists in the pharmaceutical sector.
The primary objective of utilizing dodecane in pharmaceutical testing is to enhance the accuracy, reproducibility, and efficiency of analytical methods. This aligns with the industry's broader goals of improving drug safety, efficacy, and quality while streamlining the development and manufacturing processes.
One of the key applications of dodecane in pharmaceutical testing is its use as a solvent in high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and gas chromatography (GC). These analytical techniques are crucial for the identification, quantification, and purity assessment of pharmaceutical compounds. Dodecane's low volatility and excellent solvating properties make it particularly suitable for these applications, especially when dealing with lipophilic drugs and their metabolites.
Furthermore, dodecane has found utility in dissolution testing, a critical step in evaluating the release characteristics of solid dosage forms. Its hydrophobic nature allows for the simulation of physiological conditions, particularly in the assessment of poorly water-soluble drugs. This application has become increasingly important as the pharmaceutical industry grapples with the challenge of improving the bioavailability of lipophilic drug candidates.
The use of dodecane in pharmaceutical testing also extends to stability studies, where it serves as a reference standard for assessing the degradation of certain drug formulations. Its chemical inertness and resistance to oxidation make it an ideal compound for long-term stability assessments, providing valuable insights into the shelf life and storage conditions of pharmaceutical products.
As the pharmaceutical industry continues to evolve, with a growing emphasis on personalized medicine and complex biopharmaceuticals, the role of dodecane in testing methodologies is expected to expand. Researchers are exploring novel applications, such as its potential use in microfluidic devices for drug screening and in the development of advanced drug delivery systems.
In conclusion, the background and objectives of dodecane's application in pharmaceutical testing reflect the industry's ongoing pursuit of more sophisticated, reliable, and versatile analytical tools. By leveraging the unique properties of this alkane, pharmaceutical researchers and quality control professionals aim to enhance the overall efficiency and accuracy of drug development and manufacturing processes, ultimately contributing to the production of safer and more effective medications.
The pharmaceutical industry has long sought effective solvents and reference standards for various analytical procedures. Dodecane's unique properties, including its low reactivity, stability, and ability to dissolve a wide range of organic compounds, have made it an attractive option for researchers and quality control specialists in the pharmaceutical sector.
The primary objective of utilizing dodecane in pharmaceutical testing is to enhance the accuracy, reproducibility, and efficiency of analytical methods. This aligns with the industry's broader goals of improving drug safety, efficacy, and quality while streamlining the development and manufacturing processes.
One of the key applications of dodecane in pharmaceutical testing is its use as a solvent in high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and gas chromatography (GC). These analytical techniques are crucial for the identification, quantification, and purity assessment of pharmaceutical compounds. Dodecane's low volatility and excellent solvating properties make it particularly suitable for these applications, especially when dealing with lipophilic drugs and their metabolites.
Furthermore, dodecane has found utility in dissolution testing, a critical step in evaluating the release characteristics of solid dosage forms. Its hydrophobic nature allows for the simulation of physiological conditions, particularly in the assessment of poorly water-soluble drugs. This application has become increasingly important as the pharmaceutical industry grapples with the challenge of improving the bioavailability of lipophilic drug candidates.
The use of dodecane in pharmaceutical testing also extends to stability studies, where it serves as a reference standard for assessing the degradation of certain drug formulations. Its chemical inertness and resistance to oxidation make it an ideal compound for long-term stability assessments, providing valuable insights into the shelf life and storage conditions of pharmaceutical products.
As the pharmaceutical industry continues to evolve, with a growing emphasis on personalized medicine and complex biopharmaceuticals, the role of dodecane in testing methodologies is expected to expand. Researchers are exploring novel applications, such as its potential use in microfluidic devices for drug screening and in the development of advanced drug delivery systems.
In conclusion, the background and objectives of dodecane's application in pharmaceutical testing reflect the industry's ongoing pursuit of more sophisticated, reliable, and versatile analytical tools. By leveraging the unique properties of this alkane, pharmaceutical researchers and quality control professionals aim to enhance the overall efficiency and accuracy of drug development and manufacturing processes, ultimately contributing to the production of safer and more effective medications.
Market Analysis for Dodecane in Pharmaceutical Industry
The pharmaceutical industry has shown a growing interest in dodecane as a crucial component in various testing and manufacturing processes. Market analysis reveals a steady increase in demand for dodecane within the pharmaceutical sector, driven by its versatile applications and unique properties. The global market for dodecane in pharmaceutical testing is projected to experience significant growth over the next five years, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) exceeding the overall pharmaceutical industry average.
One of the primary factors contributing to this market expansion is the rising number of drug development projects worldwide. As pharmaceutical companies intensify their research and development efforts, the need for reliable and efficient testing methods has become paramount. Dodecane's role in liquid-liquid extraction, solvent-based assays, and chromatography techniques has positioned it as an essential component in drug discovery and quality control processes.
The increasing adoption of high-throughput screening methods in pharmaceutical research has further bolstered the demand for dodecane. Its low volatility and excellent solvency properties make it an ideal choice for automated screening systems, allowing for more efficient and cost-effective drug candidate evaluation. This trend is particularly evident in developed markets such as North America and Europe, where investment in advanced pharmaceutical technologies remains robust.
Emerging markets, particularly in Asia-Pacific and Latin America, are also contributing to the growth of dodecane usage in pharmaceutical testing. As these regions expand their pharmaceutical manufacturing capabilities and research infrastructure, the demand for high-quality testing materials, including dodecane, is expected to rise substantially. This geographical expansion presents significant opportunities for dodecane suppliers to establish new market footholds and diversify their customer base.
The market analysis also highlights the increasing focus on sustainability and environmental regulations within the pharmaceutical industry. This trend has led to a growing interest in bio-based alternatives to traditional petroleum-derived dodecane. While the market share of bio-based dodecane remains relatively small, it is anticipated to grow as pharmaceutical companies seek to improve their environmental footprint and comply with stricter regulatory standards.
Pricing trends for dodecane in the pharmaceutical sector have remained relatively stable, with slight fluctuations primarily driven by changes in raw material costs and global supply chain dynamics. The market is characterized by a mix of large chemical manufacturers and specialized suppliers, with competition primarily based on product quality, consistency, and technical support services. As the pharmaceutical industry continues to evolve, suppliers who can offer high-purity dodecane tailored to specific pharmaceutical applications are likely to gain a competitive edge in this growing market segment.
One of the primary factors contributing to this market expansion is the rising number of drug development projects worldwide. As pharmaceutical companies intensify their research and development efforts, the need for reliable and efficient testing methods has become paramount. Dodecane's role in liquid-liquid extraction, solvent-based assays, and chromatography techniques has positioned it as an essential component in drug discovery and quality control processes.
The increasing adoption of high-throughput screening methods in pharmaceutical research has further bolstered the demand for dodecane. Its low volatility and excellent solvency properties make it an ideal choice for automated screening systems, allowing for more efficient and cost-effective drug candidate evaluation. This trend is particularly evident in developed markets such as North America and Europe, where investment in advanced pharmaceutical technologies remains robust.
Emerging markets, particularly in Asia-Pacific and Latin America, are also contributing to the growth of dodecane usage in pharmaceutical testing. As these regions expand their pharmaceutical manufacturing capabilities and research infrastructure, the demand for high-quality testing materials, including dodecane, is expected to rise substantially. This geographical expansion presents significant opportunities for dodecane suppliers to establish new market footholds and diversify their customer base.
The market analysis also highlights the increasing focus on sustainability and environmental regulations within the pharmaceutical industry. This trend has led to a growing interest in bio-based alternatives to traditional petroleum-derived dodecane. While the market share of bio-based dodecane remains relatively small, it is anticipated to grow as pharmaceutical companies seek to improve their environmental footprint and comply with stricter regulatory standards.
Pricing trends for dodecane in the pharmaceutical sector have remained relatively stable, with slight fluctuations primarily driven by changes in raw material costs and global supply chain dynamics. The market is characterized by a mix of large chemical manufacturers and specialized suppliers, with competition primarily based on product quality, consistency, and technical support services. As the pharmaceutical industry continues to evolve, suppliers who can offer high-purity dodecane tailored to specific pharmaceutical applications are likely to gain a competitive edge in this growing market segment.
Current Challenges in Dodecane-based Pharmaceutical Testing
Despite the widespread use of dodecane in pharmaceutical testing, several challenges persist in its application, hindering optimal performance and reliability. One of the primary issues is the variability in dodecane purity across different suppliers and batches. This inconsistency can lead to discrepancies in test results, potentially affecting the accuracy of drug formulation and stability assessments.
Another significant challenge is the limited solubility of certain pharmaceutical compounds in dodecane. While dodecane is an excellent solvent for many lipophilic substances, it may not effectively dissolve more polar or complex molecules. This limitation can restrict its applicability in testing a broader range of drug candidates, particularly those with diverse chemical structures or properties.
The volatility of dodecane at room temperature poses additional complications in long-term stability studies. Evaporation during extended testing periods can alter sample concentrations, potentially skewing results and compromising the integrity of pharmaceutical formulations under investigation. This issue becomes particularly pronounced in high-throughput screening environments where large numbers of samples are processed simultaneously.
Furthermore, the interaction between dodecane and certain packaging materials used in pharmaceutical testing can introduce unintended variables. Some plastics may leach compounds into dodecane-based solutions, potentially interfering with analytical results or altering the chemical composition of the test samples. This necessitates careful selection of container materials and additional validation steps to ensure the integrity of test outcomes.
The environmental impact of dodecane usage in pharmaceutical testing is also a growing concern. As regulatory bodies increasingly emphasize sustainable practices, the disposal of dodecane-containing waste presents challenges. Developing eco-friendly alternatives or implementing effective recycling methods for dodecane becomes crucial for maintaining compliance with environmental regulations while ensuring the continuity of testing protocols.
Lastly, the standardization of dodecane-based testing methods across different laboratories and regulatory jurisdictions remains a challenge. Variations in testing protocols, equipment calibration, and data interpretation can lead to inconsistencies in results between different facilities. This lack of harmonization complicates the comparison of test outcomes and may impede the global development and approval processes for pharmaceutical products.
Addressing these challenges requires a multifaceted approach, involving improvements in dodecane purification techniques, development of novel formulation strategies, and the establishment of robust standardization protocols. Collaborative efforts between pharmaceutical companies, regulatory bodies, and research institutions are essential to overcome these hurdles and enhance the reliability and applicability of dodecane-based pharmaceutical testing methods.
Another significant challenge is the limited solubility of certain pharmaceutical compounds in dodecane. While dodecane is an excellent solvent for many lipophilic substances, it may not effectively dissolve more polar or complex molecules. This limitation can restrict its applicability in testing a broader range of drug candidates, particularly those with diverse chemical structures or properties.
The volatility of dodecane at room temperature poses additional complications in long-term stability studies. Evaporation during extended testing periods can alter sample concentrations, potentially skewing results and compromising the integrity of pharmaceutical formulations under investigation. This issue becomes particularly pronounced in high-throughput screening environments where large numbers of samples are processed simultaneously.
Furthermore, the interaction between dodecane and certain packaging materials used in pharmaceutical testing can introduce unintended variables. Some plastics may leach compounds into dodecane-based solutions, potentially interfering with analytical results or altering the chemical composition of the test samples. This necessitates careful selection of container materials and additional validation steps to ensure the integrity of test outcomes.
The environmental impact of dodecane usage in pharmaceutical testing is also a growing concern. As regulatory bodies increasingly emphasize sustainable practices, the disposal of dodecane-containing waste presents challenges. Developing eco-friendly alternatives or implementing effective recycling methods for dodecane becomes crucial for maintaining compliance with environmental regulations while ensuring the continuity of testing protocols.
Lastly, the standardization of dodecane-based testing methods across different laboratories and regulatory jurisdictions remains a challenge. Variations in testing protocols, equipment calibration, and data interpretation can lead to inconsistencies in results between different facilities. This lack of harmonization complicates the comparison of test outcomes and may impede the global development and approval processes for pharmaceutical products.
Addressing these challenges requires a multifaceted approach, involving improvements in dodecane purification techniques, development of novel formulation strategies, and the establishment of robust standardization protocols. Collaborative efforts between pharmaceutical companies, regulatory bodies, and research institutions are essential to overcome these hurdles and enhance the reliability and applicability of dodecane-based pharmaceutical testing methods.
Existing Dodecane Applications in Drug Testing Protocols
01 Synthesis and production of dodecane
Dodecane can be synthesized through various chemical processes, including the hydrogenation of long-chain alkenes or the Fischer-Tropsch process. It is also produced as a byproduct in petroleum refining. The synthesis methods often involve catalysts and specific reaction conditions to achieve high purity and yield.- Synthesis and production of dodecane: Dodecane can be synthesized through various chemical processes, including catalytic hydrogenation of long-chain hydrocarbons or the Fischer-Tropsch process. It is also produced as a byproduct in petroleum refining. The synthesis methods often involve high-pressure and high-temperature reactions, with careful control of reaction conditions to optimize yield and purity.
- Applications in cosmetics and personal care products: Dodecane is widely used in cosmetics and personal care products due to its excellent solvent properties and low viscosity. It serves as a carrier for active ingredients, emollient, and texture enhancer in various formulations such as creams, lotions, and hair care products. Its non-greasy feel and quick-drying properties make it particularly suitable for leave-on products.
- Use in industrial lubricants and solvents: Dodecane finds extensive use as a component in industrial lubricants and solvents. Its low volatility and good thermal stability make it suitable for high-temperature applications. It is also used as a solvent in various industrial processes, including extraction, cleaning, and as a reaction medium in chemical synthesis.
- Role in fuel and energy applications: Dodecane is an important component in jet fuels and diesel fuels, contributing to their combustion properties and energy content. It is also used in the development of alternative fuels and as a model compound for studying combustion processes. Research is ongoing to optimize its use in various energy applications, including improving fuel efficiency and reducing emissions.
- Environmental and safety considerations: The use and handling of dodecane require careful consideration of environmental and safety aspects. Research focuses on developing environmentally friendly production methods, assessing its biodegradability, and studying its potential impact on ecosystems. Safety measures for storage, transportation, and handling are crucial due to its flammability and potential for environmental contamination.
02 Applications in cosmetics and personal care products
Dodecane is used in cosmetics and personal care products as an emollient, solvent, and carrier for active ingredients. It can improve the texture and spreadability of formulations, and enhance the delivery of other components. Its low viscosity and non-greasy feel make it suitable for various skincare and haircare applications.Expand Specific Solutions03 Use in fuel and lubricant formulations
Dodecane is an important component in fuel and lubricant formulations. It can be used as a fuel additive to improve combustion efficiency and reduce emissions. In lubricants, it serves as a base oil or additive to enhance performance characteristics such as viscosity and thermal stability.Expand Specific Solutions04 Role in chemical reactions and processes
Dodecane plays a significant role in various chemical reactions and processes. It can be used as a solvent, a starting material for the synthesis of other compounds, or as a standard in analytical chemistry. Its properties make it useful in extraction processes, chromatography, and as a reference compound in research.Expand Specific Solutions05 Environmental and safety considerations
The use and handling of dodecane require consideration of environmental and safety aspects. It is important to assess its potential environmental impact, biodegradability, and toxicity. Safety measures for storage, transportation, and disposal need to be implemented. Research is ongoing to develop more sustainable and eco-friendly alternatives or production methods for dodecane.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Dodecane Production and Pharmaceutical Testing
The application of dodecane in pharmaceutical testing is in an early stage of development, with a growing market potential as the pharmaceutical industry continues to seek innovative testing methods. The market size is relatively small but expanding, driven by the increasing demand for more efficient and accurate drug testing processes. Technologically, the field is still evolving, with companies like Novo Nordisk, Siemens Healthcare Diagnostics, and AbbVie leading research efforts. These firms are exploring dodecane's potential in various pharmaceutical applications, leveraging their expertise in drug development and diagnostic technologies. As the technology matures, we can expect to see more widespread adoption across the pharmaceutical sector, potentially revolutionizing certain aspects of drug testing and development.
Siemens Healthcare Diagnostics, Inc.
Technical Solution: Siemens Healthcare Diagnostics has incorporated dodecane in their development of advanced in vitro diagnostic assays. They utilize dodecane as a component in their proprietary sample preparation kits, particularly for lipid extraction and analysis in clinical chemistry tests[14]. The company has also developed automated systems that use dodecane-based reagents for sample pre-treatment in immunoassays, improving the detection of lipophilic biomarkers[15]. Siemens' researchers have implemented dodecane in their quality control materials, using it as a matrix for stabilizing calibrators and controls in lipid panel tests[16]. Furthermore, they have explored the use of dodecane in microfluidic devices for point-of-care diagnostics, leveraging its properties to create stable droplet-based assays[17].
Strengths: Improved lipid analysis in clinical diagnostics, enhanced automation capabilities. Weaknesses: Potential interference with certain analytes, limited to specific test types.
AbbVie, Inc.
Technical Solution: AbbVie has developed a novel approach using dodecane in pharmaceutical testing, particularly for lipid-based drug delivery systems. Their method involves using dodecane as a solvent in the preparation of self-emulsifying drug delivery systems (SEDDS) for poorly water-soluble drugs[1]. This technique enhances the solubility and bioavailability of hydrophobic compounds. AbbVie's researchers have also utilized dodecane in high-throughput screening assays to evaluate drug-excipient compatibility and stability[3]. The company has implemented automated liquid handling systems that use dodecane as a carrier solvent, allowing for rapid and efficient testing of multiple formulations simultaneously[5].
Strengths: Enhanced solubility for hydrophobic drugs, improved bioavailability, and high-throughput screening capabilities. Weaknesses: Potential toxicity concerns with residual dodecane, limited applicability to hydrophilic compounds.
Innovative Dodecane-based Testing Methodologies
(17-)-3-Oxoandrost-4-EN-17-YL Dodecanoate Compositions and Methods of Preparation and Use
PatentActiveUS20220332753A1
Innovation
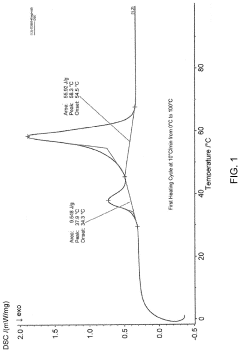
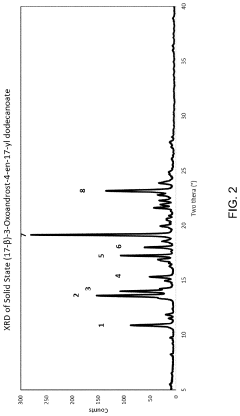
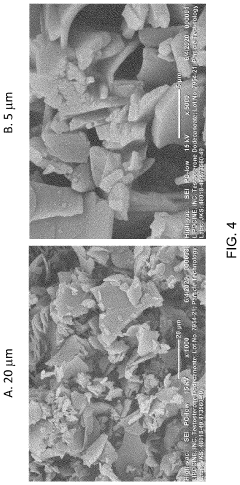
- A specific crystalline solid state form of (17-β)-3-Oxoandrost-4-en-17-yl dodecanoate with enhanced solubility and stability is developed, where at least 0.001% of the compound dissolves in an 8% Triton X100 aqueous solution within 30 minutes, and pharmaceutical compositions comprising this form are formulated for improved bioavailability.
Pharmaceutical composition containing 2,2-dichloro-12-(4-chlorophenyl)-dodecanoic acid
PatentInactiveUS20060051410A1
Innovation
- A pharmaceutical composition comprising a mixture of 2,2-dichloro-12-(4-chlorophenyl)-dodecanoic acid and croscarmellose sodium, with a preferred mixing ratio of 10:1 to 1:20, which improves the stability of the compound.
Regulatory Compliance for Dodecane in Pharmaceutical Testing
Regulatory compliance for dodecane in pharmaceutical testing is a critical aspect that ensures the safe and effective use of this compound in drug development and quality control processes. The regulatory landscape for dodecane is primarily governed by guidelines set forth by major health authorities such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), the European Medicines Agency (EMA), and the International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH).
One of the key regulatory considerations for dodecane in pharmaceutical testing is its classification as a residual solvent. The ICH Q3C guideline on residual solvents categorizes solvents based on their toxicity and provides limits for their use in pharmaceutical products. Dodecane, being a relatively non-toxic hydrocarbon, is generally classified as a Class 3 solvent, which has low toxic potential to human health. This classification allows for higher permitted daily exposure (PDE) limits compared to more toxic solvents.
Pharmaceutical companies must adhere to good manufacturing practices (GMP) when using dodecane in their testing procedures. This includes maintaining proper documentation of its use, implementing quality control measures, and ensuring that any residual dodecane in the final product falls within acceptable limits. Regular testing and validation of analytical methods for detecting and quantifying dodecane residues are essential components of regulatory compliance.
The FDA's guidance on residual solvents in drug products aligns with ICH Q3C and requires manufacturers to control and monitor the levels of residual solvents, including dodecane, in their products. This involves developing and validating analytical methods that can accurately detect and measure dodecane concentrations at the parts-per-million (ppm) level. These methods must be robust, reproducible, and capable of distinguishing dodecane from other similar hydrocarbons that may be present.
In the European Union, the EMA enforces similar regulations through its own guidelines on residual solvents. Manufacturers must demonstrate that their use of dodecane in pharmaceutical testing complies with these guidelines and that any residual amounts in the final product are below the specified limits. This often requires extensive documentation and may involve submitting data from stability studies and manufacturing process validations.
Regulatory bodies also require pharmaceutical companies to assess the potential impact of dodecane on drug product quality, safety, and efficacy. This includes evaluating the potential for dodecane to interact with active pharmaceutical ingredients or other excipients, as well as its impact on the stability and bioavailability of the drug product. Companies must provide scientific justification for the use of dodecane in their testing procedures and demonstrate that it does not adversely affect the quality or safety of the final product.
One of the key regulatory considerations for dodecane in pharmaceutical testing is its classification as a residual solvent. The ICH Q3C guideline on residual solvents categorizes solvents based on their toxicity and provides limits for their use in pharmaceutical products. Dodecane, being a relatively non-toxic hydrocarbon, is generally classified as a Class 3 solvent, which has low toxic potential to human health. This classification allows for higher permitted daily exposure (PDE) limits compared to more toxic solvents.
Pharmaceutical companies must adhere to good manufacturing practices (GMP) when using dodecane in their testing procedures. This includes maintaining proper documentation of its use, implementing quality control measures, and ensuring that any residual dodecane in the final product falls within acceptable limits. Regular testing and validation of analytical methods for detecting and quantifying dodecane residues are essential components of regulatory compliance.
The FDA's guidance on residual solvents in drug products aligns with ICH Q3C and requires manufacturers to control and monitor the levels of residual solvents, including dodecane, in their products. This involves developing and validating analytical methods that can accurately detect and measure dodecane concentrations at the parts-per-million (ppm) level. These methods must be robust, reproducible, and capable of distinguishing dodecane from other similar hydrocarbons that may be present.
In the European Union, the EMA enforces similar regulations through its own guidelines on residual solvents. Manufacturers must demonstrate that their use of dodecane in pharmaceutical testing complies with these guidelines and that any residual amounts in the final product are below the specified limits. This often requires extensive documentation and may involve submitting data from stability studies and manufacturing process validations.
Regulatory bodies also require pharmaceutical companies to assess the potential impact of dodecane on drug product quality, safety, and efficacy. This includes evaluating the potential for dodecane to interact with active pharmaceutical ingredients or other excipients, as well as its impact on the stability and bioavailability of the drug product. Companies must provide scientific justification for the use of dodecane in their testing procedures and demonstrate that it does not adversely affect the quality or safety of the final product.
Environmental Impact of Dodecane in Pharmaceutical Processes
The use of dodecane in pharmaceutical testing processes has raised concerns about its potential environmental impact. As a widely used solvent in drug development and quality control, dodecane's release into the environment through various pathways requires careful consideration.
One of the primary environmental concerns associated with dodecane is its potential for bioaccumulation in aquatic ecosystems. Due to its low water solubility and high lipophilicity, dodecane can accumulate in the fatty tissues of aquatic organisms, potentially leading to long-term ecological effects. This bioaccumulation may result in the transfer of dodecane through the food chain, affecting higher trophic levels and potentially impacting human health.
Atmospheric emissions of dodecane during pharmaceutical processes can contribute to the formation of ground-level ozone and photochemical smog. When released into the air, dodecane undergoes photochemical reactions with nitrogen oxides in the presence of sunlight, forming ozone and other secondary pollutants. These reactions can lead to reduced air quality and potential respiratory health issues in affected areas.
Soil contamination is another environmental concern associated with dodecane use in pharmaceutical testing. Accidental spills or improper disposal of dodecane-containing waste can result in soil pollution. Once in the soil, dodecane can persist due to its low biodegradability, potentially affecting soil microorganisms and plant growth. This persistence may lead to long-term impacts on soil ecosystems and agricultural productivity in affected areas.
Water pollution is a significant risk associated with dodecane use in pharmaceutical processes. Improper handling or disposal of dodecane-containing wastewater can lead to contamination of surface and groundwater resources. Due to its low water solubility, dodecane can form a separate phase on water surfaces, potentially impacting aquatic life and water quality. This contamination may also affect drinking water sources, posing risks to human health.
To mitigate the environmental impact of dodecane in pharmaceutical processes, several strategies can be implemented. These include improving containment and handling procedures to minimize accidental releases, implementing advanced wastewater treatment technologies to remove dodecane from effluents, and exploring alternative, more environmentally friendly solvents for pharmaceutical testing processes.
Furthermore, regulatory bodies and pharmaceutical companies are increasingly focusing on green chemistry principles to reduce the environmental footprint of drug development and testing processes. This includes the development of solvent selection guides that prioritize the use of less harmful alternatives to dodecane and other potentially hazardous solvents.
One of the primary environmental concerns associated with dodecane is its potential for bioaccumulation in aquatic ecosystems. Due to its low water solubility and high lipophilicity, dodecane can accumulate in the fatty tissues of aquatic organisms, potentially leading to long-term ecological effects. This bioaccumulation may result in the transfer of dodecane through the food chain, affecting higher trophic levels and potentially impacting human health.
Atmospheric emissions of dodecane during pharmaceutical processes can contribute to the formation of ground-level ozone and photochemical smog. When released into the air, dodecane undergoes photochemical reactions with nitrogen oxides in the presence of sunlight, forming ozone and other secondary pollutants. These reactions can lead to reduced air quality and potential respiratory health issues in affected areas.
Soil contamination is another environmental concern associated with dodecane use in pharmaceutical testing. Accidental spills or improper disposal of dodecane-containing waste can result in soil pollution. Once in the soil, dodecane can persist due to its low biodegradability, potentially affecting soil microorganisms and plant growth. This persistence may lead to long-term impacts on soil ecosystems and agricultural productivity in affected areas.
Water pollution is a significant risk associated with dodecane use in pharmaceutical processes. Improper handling or disposal of dodecane-containing wastewater can lead to contamination of surface and groundwater resources. Due to its low water solubility, dodecane can form a separate phase on water surfaces, potentially impacting aquatic life and water quality. This contamination may also affect drinking water sources, posing risks to human health.
To mitigate the environmental impact of dodecane in pharmaceutical processes, several strategies can be implemented. These include improving containment and handling procedures to minimize accidental releases, implementing advanced wastewater treatment technologies to remove dodecane from effluents, and exploring alternative, more environmentally friendly solvents for pharmaceutical testing processes.
Furthermore, regulatory bodies and pharmaceutical companies are increasingly focusing on green chemistry principles to reduce the environmental footprint of drug development and testing processes. This includes the development of solvent selection guides that prioritize the use of less harmful alternatives to dodecane and other potentially hazardous solvents.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!