Examining Ethylene Vinyl Acetate for Future Challenges
JUL 8, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
EVA Technology Background and Objectives
Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) has emerged as a versatile and widely used copolymer since its introduction in the 1950s. Initially developed as an alternative to polyethylene, EVA has evolved to become a crucial material in various industries due to its unique combination of properties. The technology behind EVA production has continuously advanced, driven by the growing demand for materials with enhanced flexibility, durability, and processability.
The evolution of EVA technology can be traced through several key milestones. Early developments focused on optimizing the copolymerization process to achieve desired vinyl acetate content, which significantly influences the material's properties. Subsequent advancements addressed challenges in melt processing, thermal stability, and adhesion characteristics. Recent innovations have centered on improving EVA's performance in specific applications, such as solar panel encapsulation and footwear manufacturing.
Current technological objectives in the EVA field are multifaceted, addressing both performance enhancements and sustainability concerns. One primary goal is to develop EVA formulations with improved weather resistance and UV stability, particularly for outdoor applications. Another objective is to increase the material's thermal conductivity without compromising its electrical insulation properties, which is crucial for its use in electronics and photovoltaics.
Sustainability has become a key driver in EVA technology development. Researchers are exploring bio-based alternatives to traditional petroleum-derived EVA, aiming to reduce the carbon footprint of production. Additionally, there is a growing focus on enhancing the recyclability and biodegradability of EVA products, aligning with global efforts to minimize plastic waste.
The future trajectory of EVA technology is likely to be shaped by emerging challenges and opportunities. One area of interest is the development of EVA-based composites with enhanced functional properties, such as self-healing capabilities or stimuli-responsive behavior. Another promising direction is the integration of nanotechnology to create EVA nanocomposites with superior mechanical and barrier properties.
As industries continue to demand materials with increasingly specialized characteristics, EVA technology is expected to evolve towards more tailored solutions. This may include the development of grade-specific EVA formulations optimized for particular applications, such as 3D printing filaments or advanced medical devices. The ongoing research in polymer science and materials engineering is likely to unlock new possibilities for EVA, potentially expanding its application range and addressing future technological challenges across various sectors.
The evolution of EVA technology can be traced through several key milestones. Early developments focused on optimizing the copolymerization process to achieve desired vinyl acetate content, which significantly influences the material's properties. Subsequent advancements addressed challenges in melt processing, thermal stability, and adhesion characteristics. Recent innovations have centered on improving EVA's performance in specific applications, such as solar panel encapsulation and footwear manufacturing.
Current technological objectives in the EVA field are multifaceted, addressing both performance enhancements and sustainability concerns. One primary goal is to develop EVA formulations with improved weather resistance and UV stability, particularly for outdoor applications. Another objective is to increase the material's thermal conductivity without compromising its electrical insulation properties, which is crucial for its use in electronics and photovoltaics.
Sustainability has become a key driver in EVA technology development. Researchers are exploring bio-based alternatives to traditional petroleum-derived EVA, aiming to reduce the carbon footprint of production. Additionally, there is a growing focus on enhancing the recyclability and biodegradability of EVA products, aligning with global efforts to minimize plastic waste.
The future trajectory of EVA technology is likely to be shaped by emerging challenges and opportunities. One area of interest is the development of EVA-based composites with enhanced functional properties, such as self-healing capabilities or stimuli-responsive behavior. Another promising direction is the integration of nanotechnology to create EVA nanocomposites with superior mechanical and barrier properties.
As industries continue to demand materials with increasingly specialized characteristics, EVA technology is expected to evolve towards more tailored solutions. This may include the development of grade-specific EVA formulations optimized for particular applications, such as 3D printing filaments or advanced medical devices. The ongoing research in polymer science and materials engineering is likely to unlock new possibilities for EVA, potentially expanding its application range and addressing future technological challenges across various sectors.
Market Demand Analysis for EVA Applications
The market demand for Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) applications has been steadily growing across various industries, driven by its versatile properties and cost-effectiveness. The global EVA market size was valued at USD 7.9 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach USD 11.4 billion by 2027, exhibiting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.3% during the forecast period.
The automotive sector represents a significant market for EVA applications, particularly in the production of solar cells for electric vehicles and as a component in automotive interiors. With the increasing adoption of electric vehicles worldwide, the demand for EVA in this sector is expected to surge. The construction industry also contributes substantially to EVA demand, utilizing the material in applications such as waterproofing membranes, adhesives, and sealants.
In the packaging industry, EVA finds extensive use in flexible packaging materials, shrink films, and lamination applications. The growing e-commerce sector and changing consumer preferences towards convenient packaging solutions are driving the demand for EVA in this segment. The footwear industry is another major consumer of EVA, employing it in the production of shoe soles, insoles, and midsoles due to its lightweight and cushioning properties.
The renewable energy sector, particularly the solar power industry, has emerged as a key growth driver for EVA demand. EVA is widely used as an encapsulant material in photovoltaic modules, providing protection and enhancing the efficiency of solar cells. As countries worldwide push for greater adoption of renewable energy sources, the demand for EVA in solar applications is expected to witness substantial growth.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific dominates the EVA market, accounting for the largest share of global consumption. This can be attributed to the rapid industrialization, growing construction activities, and increasing automotive production in countries like China and India. North America and Europe follow, with steady demand from established industries and ongoing technological advancements.
The market demand for EVA is also influenced by evolving regulatory landscapes and sustainability concerns. As environmental regulations become more stringent, there is a growing emphasis on developing bio-based and recyclable EVA alternatives. This trend is likely to shape the future of EVA applications and drive innovation in the industry.
In conclusion, the market demand for EVA applications remains robust across multiple sectors, with promising growth prospects in emerging applications and regions. However, manufacturers and industry players must address challenges related to raw material price volatility and environmental concerns to sustain long-term growth in the EVA market.
The automotive sector represents a significant market for EVA applications, particularly in the production of solar cells for electric vehicles and as a component in automotive interiors. With the increasing adoption of electric vehicles worldwide, the demand for EVA in this sector is expected to surge. The construction industry also contributes substantially to EVA demand, utilizing the material in applications such as waterproofing membranes, adhesives, and sealants.
In the packaging industry, EVA finds extensive use in flexible packaging materials, shrink films, and lamination applications. The growing e-commerce sector and changing consumer preferences towards convenient packaging solutions are driving the demand for EVA in this segment. The footwear industry is another major consumer of EVA, employing it in the production of shoe soles, insoles, and midsoles due to its lightweight and cushioning properties.
The renewable energy sector, particularly the solar power industry, has emerged as a key growth driver for EVA demand. EVA is widely used as an encapsulant material in photovoltaic modules, providing protection and enhancing the efficiency of solar cells. As countries worldwide push for greater adoption of renewable energy sources, the demand for EVA in solar applications is expected to witness substantial growth.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific dominates the EVA market, accounting for the largest share of global consumption. This can be attributed to the rapid industrialization, growing construction activities, and increasing automotive production in countries like China and India. North America and Europe follow, with steady demand from established industries and ongoing technological advancements.
The market demand for EVA is also influenced by evolving regulatory landscapes and sustainability concerns. As environmental regulations become more stringent, there is a growing emphasis on developing bio-based and recyclable EVA alternatives. This trend is likely to shape the future of EVA applications and drive innovation in the industry.
In conclusion, the market demand for EVA applications remains robust across multiple sectors, with promising growth prospects in emerging applications and regions. However, manufacturers and industry players must address challenges related to raw material price volatility and environmental concerns to sustain long-term growth in the EVA market.
EVA Current Status and Technical Challenges
Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) has gained significant traction in various industries due to its versatile properties. However, the current status and technical challenges associated with EVA present a complex landscape for researchers and manufacturers alike. The global EVA market has been experiencing steady growth, driven by increasing demand in sectors such as solar panel encapsulation, footwear, and packaging.
One of the primary challenges facing EVA production is the optimization of the copolymerization process. Achieving precise control over the vinyl acetate content in EVA remains a critical issue, as it directly influences the material's properties. Manufacturers are continually striving to develop more efficient catalysts and reaction conditions to enhance the consistency and quality of EVA copolymers.
The crosslinking process of EVA, crucial for many applications, presents another significant technical hurdle. Current methods often involve the use of peroxides or silane crosslinking agents, which can lead to inconsistencies in the final product's properties. Researchers are exploring alternative crosslinking techniques, such as radiation-induced crosslinking, to improve efficiency and reduce environmental impact.
EVA's thermal stability is an ongoing concern, particularly in high-temperature applications like solar panel encapsulation. The material's tendency to degrade and release acetic acid under prolonged heat exposure can compromise the performance and lifespan of end products. Developing heat-resistant EVA formulations without sacrificing other desirable properties remains a key focus area for material scientists.
The environmental impact of EVA production and disposal has come under scrutiny in recent years. While EVA is recyclable, the process is often complex and energy-intensive due to its crosslinked structure. Efforts are underway to develop more sustainable production methods and improve the recyclability of EVA-based products, aligning with global sustainability goals.
In the realm of EVA foam production, achieving uniform cell structure and density control continues to challenge manufacturers. The balance between foam expansion and crosslinking kinetics requires precise process control, which can be difficult to maintain consistently at industrial scales. Innovations in foaming agents and processing technologies are being pursued to address these issues.
The development of EVA-based composites and blends represents both an opportunity and a challenge. While combining EVA with other materials can lead to enhanced properties, ensuring compatibility and maintaining desired characteristics across different formulations remains complex. Research into novel compatibilizers and processing techniques is ongoing to expand the range of EVA-based composite materials.
As the demand for specialized EVA grades grows, particularly in emerging applications like 3D printing filaments and medical devices, tailoring the material's properties to meet specific requirements becomes increasingly challenging. This necessitates advancements in polymer science and processing technologies to create EVA variants with precisely controlled characteristics.
One of the primary challenges facing EVA production is the optimization of the copolymerization process. Achieving precise control over the vinyl acetate content in EVA remains a critical issue, as it directly influences the material's properties. Manufacturers are continually striving to develop more efficient catalysts and reaction conditions to enhance the consistency and quality of EVA copolymers.
The crosslinking process of EVA, crucial for many applications, presents another significant technical hurdle. Current methods often involve the use of peroxides or silane crosslinking agents, which can lead to inconsistencies in the final product's properties. Researchers are exploring alternative crosslinking techniques, such as radiation-induced crosslinking, to improve efficiency and reduce environmental impact.
EVA's thermal stability is an ongoing concern, particularly in high-temperature applications like solar panel encapsulation. The material's tendency to degrade and release acetic acid under prolonged heat exposure can compromise the performance and lifespan of end products. Developing heat-resistant EVA formulations without sacrificing other desirable properties remains a key focus area for material scientists.
The environmental impact of EVA production and disposal has come under scrutiny in recent years. While EVA is recyclable, the process is often complex and energy-intensive due to its crosslinked structure. Efforts are underway to develop more sustainable production methods and improve the recyclability of EVA-based products, aligning with global sustainability goals.
In the realm of EVA foam production, achieving uniform cell structure and density control continues to challenge manufacturers. The balance between foam expansion and crosslinking kinetics requires precise process control, which can be difficult to maintain consistently at industrial scales. Innovations in foaming agents and processing technologies are being pursued to address these issues.
The development of EVA-based composites and blends represents both an opportunity and a challenge. While combining EVA with other materials can lead to enhanced properties, ensuring compatibility and maintaining desired characteristics across different formulations remains complex. Research into novel compatibilizers and processing techniques is ongoing to expand the range of EVA-based composite materials.
As the demand for specialized EVA grades grows, particularly in emerging applications like 3D printing filaments and medical devices, tailoring the material's properties to meet specific requirements becomes increasingly challenging. This necessitates advancements in polymer science and processing technologies to create EVA variants with precisely controlled characteristics.
Current EVA Technical Solutions
01 Composition and properties of EVA
Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) is a copolymer of ethylene and vinyl acetate. It exhibits properties such as flexibility, toughness, and resistance to stress-cracking. The composition and ratio of ethylene to vinyl acetate can be adjusted to modify the properties of the resulting material, making it suitable for various applications.- Composition and properties of EVA: Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) is a copolymer of ethylene and vinyl acetate. It exhibits properties such as flexibility, toughness, and resistance to UV radiation and stress-cracking. The ratio of ethylene to vinyl acetate in the copolymer can be varied to achieve different characteristics, making it suitable for various applications.
- EVA in adhesive applications: EVA is widely used in adhesive formulations due to its excellent adhesion properties and compatibility with various substrates. It is particularly useful in hot melt adhesives, where it provides good thermal stability and flexibility. EVA-based adhesives find applications in packaging, bookbinding, and construction industries.
- EVA in foam and insulation materials: EVA is utilized in the production of foam and insulation materials. Its closed-cell structure and low thermal conductivity make it an excellent choice for applications requiring thermal insulation and shock absorption. EVA foams are used in footwear, sports equipment, and automotive components.
- EVA in solar panel encapsulation: EVA is a preferred material for encapsulating solar cells in photovoltaic modules. It provides excellent transparency, weather resistance, and electrical insulation properties. The use of EVA in solar panel encapsulation helps to protect the cells from environmental factors and enhance the overall performance and longevity of the modules.
- Modifications and blends of EVA: EVA can be modified or blended with other materials to enhance its properties for specific applications. This includes crosslinking, grafting, or blending with other polymers or additives. Such modifications can improve the material's mechanical strength, chemical resistance, or processability, expanding its range of applications in various industries.
02 EVA in adhesive applications
EVA is widely used in adhesive formulations due to its excellent adhesion properties and compatibility with various substrates. It can be used in hot melt adhesives, pressure-sensitive adhesives, and as a base polymer in adhesive blends. The adhesive strength and other properties can be tailored by adjusting the EVA composition and additives.Expand Specific Solutions03 EVA in foam and insulation materials
EVA is utilized in the production of foam and insulation materials due to its low density, good cushioning properties, and thermal insulation characteristics. It can be crosslinked or expanded to create closed-cell foams for applications such as footwear, sports equipment, and building insulation.Expand Specific Solutions04 EVA in solar panel encapsulation
EVA is commonly used as an encapsulant material in photovoltaic modules. It provides excellent transparency, weather resistance, and electrical insulation properties. The material helps protect solar cells from environmental factors and ensures long-term performance of the solar panels.Expand Specific Solutions05 Modification and blending of EVA
EVA can be modified or blended with other polymers and additives to enhance its properties or create new materials with specific characteristics. This includes crosslinking, grafting, and compounding with fillers or other polymers to improve mechanical properties, flame retardancy, or compatibility with other materials.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in EVA Industry
The ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) market is in a mature growth stage, characterized by steady demand across various industries. The global market size is substantial, driven by applications in packaging, solar panels, and footwear. Technologically, EVA production is well-established, with major players like China Petroleum & Chemical Corp., Celanese International Corp., and DuPont de Nemours, Inc. continuously refining their processes. Companies such as Kuraray Co., Ltd. and Bayer AG are focusing on developing specialized EVA grades for niche applications, indicating ongoing innovation in the field. The competitive landscape is diverse, with both large petrochemical corporations and specialized chemical companies vying for market share, suggesting a balanced market with opportunities for differentiation and growth.
China Petroleum & Chemical Corp.
Technical Solution: China Petroleum & Chemical Corp. (Sinopec) has developed advanced EVA production technologies, including a high-pressure tubular reactor process. Their method achieves precise control over VA content and molecular weight distribution, resulting in EVA with superior properties[1]. Sinopec has also implemented a proprietary catalyst system that enhances production efficiency and product quality. Their EVA grades are tailored for various applications, including photovoltaic encapsulants, which demonstrate excellent weatherability and low water absorption[2]. Additionally, Sinopec has invested in research to improve EVA's thermal stability and adhesion properties, addressing future challenges in high-performance applications[3].
Strengths: Large-scale production capabilities, advanced catalyst technology, and diverse product portfolio. Weaknesses: Potential environmental concerns associated with petrochemical processes and dependency on fossil fuel feedstocks.
Celanese International Corp.
Technical Solution: Celanese has developed a proprietary EVA production process that utilizes a unique combination of high-pressure polymerization and advanced catalyst systems. Their technology allows for precise control of VA content, ranging from 0% to 40%, enabling the production of tailored EVA grades for specific applications[4]. Celanese's EVA products, marketed under the brand name VitalDose®, are particularly notable for their use in drug delivery systems and medical devices. The company has invested in research to enhance EVA's biocompatibility and controlled release properties, addressing future challenges in the pharmaceutical and healthcare sectors[5]. Additionally, Celanese has developed EVA grades with improved thermal stability and processability for demanding industrial applications[6].
Strengths: Strong focus on high-value applications, particularly in healthcare and pharmaceuticals. Extensive R&D capabilities. Weaknesses: Potentially higher production costs due to specialized grades and applications.
Key EVA Innovations and Patents
Bio-based eva compositions and articles and methods thereof
PatentPendingUS20220185922A1
Innovation
- The development of bio-based ethylene vinyl acetate copolymers where ethylene is partially sourced from renewable carbon sources, such as plant materials, through fermentation and dehydration processes, combined with peroxide agents and blowing agents to create curable and expandable polymer compositions.
Method for preparing ethylene-vinyl acetate with low melt index
PatentWO2014181991A1
Innovation
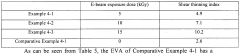
- Applying an electron beam with a defined exposure dose to an ethylene-vinyl acetate resin composition with a vinyl acetate content of 15 to 50 wt% to reduce the melt index to 10 g/10 min or less, thereby enhancing mechanical properties and processability without the need for additional modifiers like peroxides.
Environmental Impact of EVA Production
The production of Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) has significant environmental implications that warrant careful consideration. The manufacturing process involves the use of petrochemical feedstocks, which are derived from non-renewable resources and contribute to greenhouse gas emissions. The primary raw materials, ethylene and vinyl acetate, are produced through energy-intensive processes that often rely on fossil fuels, further exacerbating the carbon footprint of EVA production.
During the polymerization stage, various chemical additives and catalysts are employed, some of which may pose environmental risks if not properly managed. The release of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) during production can contribute to air pollution and potentially harm local ecosystems if not adequately controlled through emission reduction technologies.
Water usage and wastewater management are also critical environmental concerns in EVA production. The manufacturing process requires substantial amounts of water for cooling and cleaning purposes. Proper treatment and disposal of wastewater are essential to prevent contamination of local water bodies and groundwater resources.
The energy-intensive nature of EVA production contributes to its overall environmental impact. High temperatures and pressures are required throughout the manufacturing process, necessitating significant energy consumption. The source of this energy, whether from renewable or non-renewable sources, plays a crucial role in determining the carbon intensity of EVA production.
Waste generation is another environmental challenge associated with EVA manufacturing. Off-spec products, process residues, and packaging materials contribute to solid waste streams that require proper disposal or recycling. Implementing efficient waste management practices and exploring circular economy principles can help mitigate these impacts.
The end-of-life disposal of EVA products presents additional environmental concerns. While EVA is recyclable, the recycling infrastructure and processes for this material are not as well-established as those for other common plastics. Improper disposal can lead to long-term environmental persistence, as EVA does not readily biodegrade in natural environments.
To address these environmental challenges, the EVA industry is exploring various sustainability initiatives. These include improving energy efficiency in production processes, transitioning to renewable energy sources, developing bio-based feedstocks, and enhancing recycling technologies. Additionally, research into biodegradable alternatives and the optimization of product design for easier recycling are ongoing efforts to reduce the environmental footprint of EVA throughout its lifecycle.
During the polymerization stage, various chemical additives and catalysts are employed, some of which may pose environmental risks if not properly managed. The release of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) during production can contribute to air pollution and potentially harm local ecosystems if not adequately controlled through emission reduction technologies.
Water usage and wastewater management are also critical environmental concerns in EVA production. The manufacturing process requires substantial amounts of water for cooling and cleaning purposes. Proper treatment and disposal of wastewater are essential to prevent contamination of local water bodies and groundwater resources.
The energy-intensive nature of EVA production contributes to its overall environmental impact. High temperatures and pressures are required throughout the manufacturing process, necessitating significant energy consumption. The source of this energy, whether from renewable or non-renewable sources, plays a crucial role in determining the carbon intensity of EVA production.
Waste generation is another environmental challenge associated with EVA manufacturing. Off-spec products, process residues, and packaging materials contribute to solid waste streams that require proper disposal or recycling. Implementing efficient waste management practices and exploring circular economy principles can help mitigate these impacts.
The end-of-life disposal of EVA products presents additional environmental concerns. While EVA is recyclable, the recycling infrastructure and processes for this material are not as well-established as those for other common plastics. Improper disposal can lead to long-term environmental persistence, as EVA does not readily biodegrade in natural environments.
To address these environmental challenges, the EVA industry is exploring various sustainability initiatives. These include improving energy efficiency in production processes, transitioning to renewable energy sources, developing bio-based feedstocks, and enhancing recycling technologies. Additionally, research into biodegradable alternatives and the optimization of product design for easier recycling are ongoing efforts to reduce the environmental footprint of EVA throughout its lifecycle.
Regulatory Landscape for EVA Usage
The regulatory landscape for Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) usage is complex and multifaceted, reflecting the diverse applications of this versatile copolymer across various industries. As EVA continues to gain prominence in sectors such as solar panel manufacturing, packaging, and footwear production, regulatory bodies worldwide are increasingly scrutinizing its use and potential environmental impacts.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) plays a crucial role in regulating EVA usage, particularly in food contact applications. The FDA has established specific guidelines for EVA copolymers used in food packaging, ensuring that these materials meet stringent safety standards. Similarly, the European Union has implemented comprehensive regulations through the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA), which oversees the use of EVA in food contact materials.
Environmental regulations are becoming increasingly significant in shaping the EVA industry. The European Union's REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) regulation has placed additional requirements on manufacturers and importers of EVA, mandating thorough safety assessments and registration of substances. This has led to increased transparency in the supply chain and a greater focus on sustainable production practices.
In the renewable energy sector, particularly in solar panel manufacturing, regulations are evolving to address the end-of-life management of EVA-containing products. Countries like Japan and Germany have implemented extended producer responsibility (EPR) programs, requiring manufacturers to consider the entire lifecycle of their products, including recycling and disposal.
The automotive industry, another significant user of EVA, faces stringent regulations regarding vehicle emissions and fuel efficiency. This has led to increased demand for lightweight materials, including EVA-based components, to meet these regulatory requirements. However, this also necessitates compliance with safety standards set by organizations such as the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) in the United States.
Emerging markets, particularly in Asia, are rapidly developing their regulatory frameworks for EVA usage. China, for instance, has been updating its chemical management regulations, which will have significant implications for EVA manufacturers and users in the region. These evolving regulations are likely to align more closely with international standards, potentially facilitating global trade while ensuring product safety and environmental protection.
As concerns about plastic pollution grow, regulations targeting single-use plastics are indirectly affecting the EVA industry. While EVA is not typically used in single-use applications, these regulations are driving innovation in biodegradable and recyclable alternatives, which may compete with traditional EVA products in certain applications.
Looking ahead, the regulatory landscape for EVA usage is expected to continue evolving, with a greater emphasis on sustainability, circular economy principles, and lifecycle assessments. Manufacturers and users of EVA will need to stay abreast of these changes and adapt their practices accordingly to ensure compliance and maintain market competitiveness.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) plays a crucial role in regulating EVA usage, particularly in food contact applications. The FDA has established specific guidelines for EVA copolymers used in food packaging, ensuring that these materials meet stringent safety standards. Similarly, the European Union has implemented comprehensive regulations through the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA), which oversees the use of EVA in food contact materials.
Environmental regulations are becoming increasingly significant in shaping the EVA industry. The European Union's REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) regulation has placed additional requirements on manufacturers and importers of EVA, mandating thorough safety assessments and registration of substances. This has led to increased transparency in the supply chain and a greater focus on sustainable production practices.
In the renewable energy sector, particularly in solar panel manufacturing, regulations are evolving to address the end-of-life management of EVA-containing products. Countries like Japan and Germany have implemented extended producer responsibility (EPR) programs, requiring manufacturers to consider the entire lifecycle of their products, including recycling and disposal.
The automotive industry, another significant user of EVA, faces stringent regulations regarding vehicle emissions and fuel efficiency. This has led to increased demand for lightweight materials, including EVA-based components, to meet these regulatory requirements. However, this also necessitates compliance with safety standards set by organizations such as the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) in the United States.
Emerging markets, particularly in Asia, are rapidly developing their regulatory frameworks for EVA usage. China, for instance, has been updating its chemical management regulations, which will have significant implications for EVA manufacturers and users in the region. These evolving regulations are likely to align more closely with international standards, potentially facilitating global trade while ensuring product safety and environmental protection.
As concerns about plastic pollution grow, regulations targeting single-use plastics are indirectly affecting the EVA industry. While EVA is not typically used in single-use applications, these regulations are driving innovation in biodegradable and recyclable alternatives, which may compete with traditional EVA products in certain applications.
Looking ahead, the regulatory landscape for EVA usage is expected to continue evolving, with a greater emphasis on sustainability, circular economy principles, and lifecycle assessments. Manufacturers and users of EVA will need to stay abreast of these changes and adapt their practices accordingly to ensure compliance and maintain market competitiveness.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!