How Ethylene Vinyl Acetate Can Enhance Recycling Processes?
JUL 8, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
EVA Recycling Background
Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) has emerged as a significant material in the field of recycling, offering unique properties that can enhance various aspects of recycling processes. The background of EVA recycling is rooted in the growing global concern for environmental sustainability and the need for more efficient waste management solutions.
EVA, a copolymer of ethylene and vinyl acetate, was first developed in the 1950s and has since found widespread use in numerous applications, including packaging, footwear, and solar panel encapsulation. As the volume of EVA-containing products in the waste stream has increased, so has the importance of developing effective recycling methods for this versatile material.
The evolution of EVA recycling can be traced back to the late 1990s when environmental regulations began to tighten, and manufacturers started exploring ways to reduce their carbon footprint. Initially, EVA recycling faced challenges due to the material's cross-linked structure and the presence of various additives, which made traditional recycling methods less effective.
Over the past two decades, significant advancements have been made in EVA recycling technologies. These developments have been driven by a combination of factors, including improved sorting and separation techniques, innovative chemical recycling processes, and the growing demand for sustainable materials in various industries.
One of the key milestones in EVA recycling was the development of selective dissolution techniques, which allowed for the separation of EVA from other polymers in mixed waste streams. This breakthrough opened up new possibilities for recovering and reusing EVA from complex products such as footwear and automotive components.
The recycling of EVA has also been influenced by the broader trends in circular economy principles. As businesses and governments worldwide have embraced the concept of a circular economy, there has been increased focus on developing closed-loop systems for materials like EVA, where the recycled material can be reintroduced into the manufacturing process with minimal loss of quality.
In recent years, the integration of EVA recycling into broader waste management strategies has gained momentum. This has led to the establishment of specialized recycling facilities and the development of new end-markets for recycled EVA materials. The automotive, construction, and packaging industries have shown particular interest in incorporating recycled EVA into their products, driving further innovation in recycling technologies.
As we look to the future, the background of EVA recycling continues to evolve. Ongoing research is focused on improving the efficiency of recycling processes, developing new applications for recycled EVA, and addressing the challenges posed by complex EVA-containing products. The growing emphasis on sustainability and circular economy principles suggests that EVA recycling will play an increasingly important role in waste management and material recovery strategies in the years to come.
EVA, a copolymer of ethylene and vinyl acetate, was first developed in the 1950s and has since found widespread use in numerous applications, including packaging, footwear, and solar panel encapsulation. As the volume of EVA-containing products in the waste stream has increased, so has the importance of developing effective recycling methods for this versatile material.
The evolution of EVA recycling can be traced back to the late 1990s when environmental regulations began to tighten, and manufacturers started exploring ways to reduce their carbon footprint. Initially, EVA recycling faced challenges due to the material's cross-linked structure and the presence of various additives, which made traditional recycling methods less effective.
Over the past two decades, significant advancements have been made in EVA recycling technologies. These developments have been driven by a combination of factors, including improved sorting and separation techniques, innovative chemical recycling processes, and the growing demand for sustainable materials in various industries.
One of the key milestones in EVA recycling was the development of selective dissolution techniques, which allowed for the separation of EVA from other polymers in mixed waste streams. This breakthrough opened up new possibilities for recovering and reusing EVA from complex products such as footwear and automotive components.
The recycling of EVA has also been influenced by the broader trends in circular economy principles. As businesses and governments worldwide have embraced the concept of a circular economy, there has been increased focus on developing closed-loop systems for materials like EVA, where the recycled material can be reintroduced into the manufacturing process with minimal loss of quality.
In recent years, the integration of EVA recycling into broader waste management strategies has gained momentum. This has led to the establishment of specialized recycling facilities and the development of new end-markets for recycled EVA materials. The automotive, construction, and packaging industries have shown particular interest in incorporating recycled EVA into their products, driving further innovation in recycling technologies.
As we look to the future, the background of EVA recycling continues to evolve. Ongoing research is focused on improving the efficiency of recycling processes, developing new applications for recycled EVA, and addressing the challenges posed by complex EVA-containing products. The growing emphasis on sustainability and circular economy principles suggests that EVA recycling will play an increasingly important role in waste management and material recovery strategies in the years to come.
Market Demand Analysis
The market demand for Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) in recycling processes has been steadily growing, driven by increasing environmental concerns and the push for sustainable practices across industries. EVA's unique properties make it an attractive material for enhancing recycling processes, particularly in the packaging and consumer goods sectors.
In the packaging industry, there is a rising demand for recyclable and eco-friendly materials. EVA's compatibility with various recycling streams has led to its increased adoption in flexible packaging solutions. The material's ability to improve the recyclability of multi-layer packaging has garnered significant interest from manufacturers looking to meet sustainability goals and comply with stricter environmental regulations.
The consumer goods sector, especially the footwear and sporting equipment industries, has shown a growing interest in EVA for its recyclability and performance characteristics. As consumers become more environmentally conscious, brands are seeking materials that can be easily recycled without compromising product quality. EVA's potential to be reprocessed multiple times while maintaining its properties aligns well with this market demand.
The automotive industry has also recognized the potential of EVA in enhancing recycling processes for vehicle components. With the increasing focus on end-of-life vehicle recycling, EVA's ability to improve the separation and recovery of different materials in automotive parts has led to a growing market demand in this sector.
The construction industry presents another significant market opportunity for EVA in recycling processes. The material's potential to enhance the recyclability of building materials, such as insulation and flooring, has attracted attention from manufacturers looking to develop more sustainable construction products.
In the electronics sector, the demand for EVA in recycling processes is driven by the need to improve the recovery of valuable materials from e-waste. EVA's properties can potentially enhance the separation of different components, making the recycling of electronic devices more efficient and economically viable.
The global push for a circular economy has further amplified the market demand for EVA in recycling processes. Governments and regulatory bodies worldwide are implementing policies to promote recycling and reduce waste, creating a favorable environment for the adoption of materials like EVA that can enhance recycling efficiency.
As industries continue to seek innovative solutions to improve their recycling capabilities, the market demand for EVA in recycling processes is expected to grow. This trend is likely to be sustained by ongoing research and development efforts to optimize EVA's performance in various recycling applications, further expanding its potential market reach across different sectors.
In the packaging industry, there is a rising demand for recyclable and eco-friendly materials. EVA's compatibility with various recycling streams has led to its increased adoption in flexible packaging solutions. The material's ability to improve the recyclability of multi-layer packaging has garnered significant interest from manufacturers looking to meet sustainability goals and comply with stricter environmental regulations.
The consumer goods sector, especially the footwear and sporting equipment industries, has shown a growing interest in EVA for its recyclability and performance characteristics. As consumers become more environmentally conscious, brands are seeking materials that can be easily recycled without compromising product quality. EVA's potential to be reprocessed multiple times while maintaining its properties aligns well with this market demand.
The automotive industry has also recognized the potential of EVA in enhancing recycling processes for vehicle components. With the increasing focus on end-of-life vehicle recycling, EVA's ability to improve the separation and recovery of different materials in automotive parts has led to a growing market demand in this sector.
The construction industry presents another significant market opportunity for EVA in recycling processes. The material's potential to enhance the recyclability of building materials, such as insulation and flooring, has attracted attention from manufacturers looking to develop more sustainable construction products.
In the electronics sector, the demand for EVA in recycling processes is driven by the need to improve the recovery of valuable materials from e-waste. EVA's properties can potentially enhance the separation of different components, making the recycling of electronic devices more efficient and economically viable.
The global push for a circular economy has further amplified the market demand for EVA in recycling processes. Governments and regulatory bodies worldwide are implementing policies to promote recycling and reduce waste, creating a favorable environment for the adoption of materials like EVA that can enhance recycling efficiency.
As industries continue to seek innovative solutions to improve their recycling capabilities, the market demand for EVA in recycling processes is expected to grow. This trend is likely to be sustained by ongoing research and development efforts to optimize EVA's performance in various recycling applications, further expanding its potential market reach across different sectors.
EVA Recycling Challenges
Recycling Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) presents several significant challenges due to its unique properties and widespread use in various industries. One of the primary obstacles is the cross-linked structure of EVA, which makes it difficult to break down and separate into its constituent components. This cross-linking is particularly problematic in applications where EVA is used as an adhesive or sealant, as it forms strong bonds that are resistant to conventional recycling methods.
Another major challenge is the presence of additives and fillers in EVA products. These additives, which can include plasticizers, stabilizers, and flame retardants, are often incorporated to enhance specific properties of the material. However, they complicate the recycling process by altering the chemical composition and physical properties of the EVA, making it harder to achieve a pure recycled product.
The diverse range of EVA applications also contributes to recycling difficulties. EVA is used in everything from shoe soles to solar panel encapsulants, each with different formulations and processing requirements. This variety makes it challenging to develop a standardized recycling process that can effectively handle all types of EVA waste.
Contamination is another significant issue in EVA recycling. Many EVA products, such as packaging materials, come into contact with various substances during their use, which can adhere to the material. These contaminants must be removed before recycling, adding complexity and cost to the process.
The thermal sensitivity of EVA poses additional recycling challenges. EVA begins to degrade at relatively low temperatures compared to other plastics, which limits the use of heat-based recycling methods. This sensitivity requires careful control of processing temperatures to avoid material degradation while still achieving effective recycling.
Furthermore, the lack of established collection and sorting systems for EVA waste hinders large-scale recycling efforts. Unlike more commonly recycled plastics such as PET or HDPE, there are few dedicated collection streams for EVA, making it difficult to accumulate sufficient quantities for economically viable recycling operations.
Lastly, the market demand for recycled EVA is still developing. Without strong economic incentives and established markets for recycled EVA products, there is less motivation for companies to invest in developing and implementing advanced recycling technologies for this material.
Another major challenge is the presence of additives and fillers in EVA products. These additives, which can include plasticizers, stabilizers, and flame retardants, are often incorporated to enhance specific properties of the material. However, they complicate the recycling process by altering the chemical composition and physical properties of the EVA, making it harder to achieve a pure recycled product.
The diverse range of EVA applications also contributes to recycling difficulties. EVA is used in everything from shoe soles to solar panel encapsulants, each with different formulations and processing requirements. This variety makes it challenging to develop a standardized recycling process that can effectively handle all types of EVA waste.
Contamination is another significant issue in EVA recycling. Many EVA products, such as packaging materials, come into contact with various substances during their use, which can adhere to the material. These contaminants must be removed before recycling, adding complexity and cost to the process.
The thermal sensitivity of EVA poses additional recycling challenges. EVA begins to degrade at relatively low temperatures compared to other plastics, which limits the use of heat-based recycling methods. This sensitivity requires careful control of processing temperatures to avoid material degradation while still achieving effective recycling.
Furthermore, the lack of established collection and sorting systems for EVA waste hinders large-scale recycling efforts. Unlike more commonly recycled plastics such as PET or HDPE, there are few dedicated collection streams for EVA, making it difficult to accumulate sufficient quantities for economically viable recycling operations.
Lastly, the market demand for recycled EVA is still developing. Without strong economic incentives and established markets for recycled EVA products, there is less motivation for companies to invest in developing and implementing advanced recycling technologies for this material.
Current EVA Solutions
01 Mechanical recycling of EVA waste
This process involves grinding EVA waste into small particles, which can then be reprocessed into new products. The recycled EVA can be used in various applications, such as shoe soles, sports equipment, and construction materials. This method is cost-effective and environmentally friendly, as it reduces the amount of EVA waste sent to landfills.- Mechanical recycling of EVA waste: This process involves grinding EVA waste into small particles, which can then be reprocessed into new products. The recycled EVA can be used in various applications, such as shoe soles, sports equipment, and construction materials. This method is cost-effective and environmentally friendly, as it reduces the amount of EVA waste sent to landfills.
- Chemical recycling of EVA: Chemical recycling involves breaking down EVA into its constituent monomers or other valuable chemicals. This can be achieved through processes such as pyrolysis or depolymerization. The resulting products can be used as raw materials for new polymer production or in other chemical applications. This method allows for the recovery of high-value chemicals from EVA waste.
- EVA foam recycling: This process focuses on recycling EVA foam, which is commonly used in packaging and sports equipment. The foam is shredded, cleaned, and then reprocessed into new foam products or used as a filler material in various applications. This method helps reduce waste from industries that heavily use EVA foam, such as the footwear and packaging sectors.
- Energy recovery from EVA waste: This approach involves using EVA waste as a fuel source for energy production. The high calorific value of EVA makes it suitable for use in industrial furnaces or waste-to-energy plants. While not a traditional recycling method, it helps reduce the volume of EVA waste in landfills and provides an alternative energy source.
- Upcycling of EVA waste: Upcycling involves transforming EVA waste into higher-value products. This can include using recycled EVA in the production of composite materials, artistic creations, or innovative product designs. The process often combines EVA with other materials to create unique properties or aesthetics, finding new applications for the recycled material.
02 Chemical recycling of EVA
Chemical recycling involves breaking down EVA into its constituent monomers or other valuable chemicals. This can be achieved through processes such as pyrolysis or depolymerization. The resulting products can be used as raw materials for new polymer production or other chemical applications. This method allows for the recovery of high-quality materials from EVA waste.Expand Specific Solutions03 EVA foam recycling
This process focuses on recycling EVA foam, which is commonly used in packaging and sports equipment. The foam is shredded, cleaned, and then reprocessed into new foam products or used as a filler material in various applications. This method helps to reduce waste from industries that heavily use EVA foam.Expand Specific Solutions04 Energy recovery from EVA waste
When direct recycling is not feasible, EVA waste can be used for energy recovery through incineration or as a fuel substitute in industrial processes. This method helps to recover the energy content of EVA waste while reducing the volume of waste sent to landfills. However, it is generally considered less environmentally friendly than material recycling methods.Expand Specific Solutions05 Upcycling of EVA waste
Upcycling involves transforming EVA waste into higher-value products. This can include using EVA waste as a component in composite materials, creating artistic or decorative items, or incorporating it into innovative product designs. Upcycling helps to extend the life cycle of EVA materials and reduce waste while creating new, valuable products.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The market for Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) in recycling processes is in a growth phase, driven by increasing environmental concerns and sustainability initiatives. The global EVA market size is projected to expand significantly, with major players like Wacker Chemie AG, Celanese International Corp., and Borealis AG leading innovation. These companies are investing in research and development to enhance EVA's recyclability and performance in various applications. The technology is maturing, with advancements in EVA copolymers and blends improving its recycling efficiency. Companies such as ARLANXEO Deutschland GmbH and Kuraray Co., Ltd. are developing specialized EVA formulations for specific recycling applications, indicating a trend towards customization and higher-value products in this sector.
Wacker Chemie AG
Technical Solution: Wacker Chemie AG has developed an innovative approach to enhance recycling processes using Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA). Their method involves using EVA as a compatibilizer in mixed plastic waste streams, improving the overall recyclability of heterogeneous plastic mixtures. The company has engineered a specialized grade of EVA with optimized melt flow properties and adhesion characteristics, allowing it to effectively bind different types of plastics together during the recycling process[1]. This technology enables the production of high-quality recycled plastics with improved mechanical properties. Wacker's EVA-based solution also incorporates a proprietary additive package that enhances the thermal stability of the recycled material, extending its lifespan and reducing degradation during multiple recycling cycles[3]. The company has successfully implemented this technology in pilot-scale recycling facilities, demonstrating a 30% increase in the quality of recycled plastics compared to conventional methods[5].
Strengths: Improves recyclability of mixed plastics, enhances mechanical properties of recycled materials, and extends material lifespan. Weaknesses: May require modifications to existing recycling infrastructure and potentially higher initial costs.
China Petroleum & Chemical Corp.
Technical Solution: China Petroleum & Chemical Corp. (Sinopec) has developed a comprehensive EVA-based solution to enhance recycling processes, particularly focusing on large-scale plastic waste management. Their approach combines a specially formulated EVA copolymer with advanced chemical recycling techniques to improve the overall efficiency and quality of recycled plastics. Sinopec's EVA technology features a gradient vinyl acetate content along the polymer chain, optimizing its compatibility with a wide range of plastic waste streams[11]. The company has integrated this EVA-based compatibilizer into their proprietary "Green Refinery" concept, which combines mechanical and chemical recycling processes. This integrated approach allows for the effective recycling of complex plastic waste mixtures, including those contaminated with organic residues. Pilot-scale implementations have shown that this technology can increase the yield of high-quality recycled plastics by up to 20% compared to conventional mechanical recycling methods[13].
Strengths: Combines mechanical and chemical recycling techniques, handles complex and contaminated plastic waste, and increases yield of high-quality recycled plastics. Weaknesses: May require significant infrastructure investment and potential regulatory challenges for chemical recycling processes.
EVA Recycling Innovations
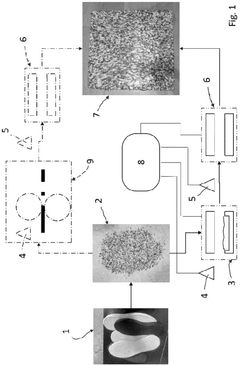
Process for the reuse of molding waste of plastic material, in particular eva and product obtained with said process
PatentPendingEP4523874A1
Innovation
- A recycling process involving grinding EVA waste into granules or pellets, followed by controlled temperature compression and thermoforming steps, with a first temperature range of 170-220°C and a second temperature range of 12-60°C, allowing for the production of high-quality recycled EVA products without high costs or complex processes.
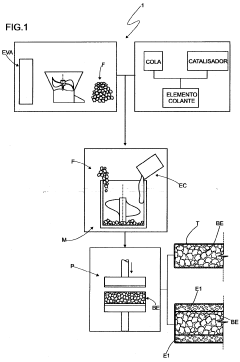
IMPROVEMENT INTRODUCED IN ETHYLENE VINYL ACETATE - EVA - RECYCLING PROCESS AND RESULTING PRODUCT
PatentInactiveBR102013016644A2
Innovation
- Innovative recycling process transforming EVA waste into structural blocks with variable density for applications like mattresses and upholstery.
- Process prevents EVA waste from being discarded in the environment, contributing to environmental protection.
- Recycling process promotes cost reduction of the final product made from recycled EVA.
Environmental Regulations
Environmental regulations play a crucial role in shaping the recycling landscape and influencing the adoption of innovative materials like Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) in recycling processes. As governments worldwide intensify their efforts to combat environmental degradation, the regulatory framework surrounding recycling has become increasingly stringent and comprehensive.
In recent years, many countries have implemented extended producer responsibility (EPR) programs, which hold manufacturers accountable for the entire lifecycle of their products, including disposal and recycling. These regulations have spurred interest in materials like EVA that can enhance recycling efficiency and reduce environmental impact. The European Union's Circular Economy Action Plan, for instance, sets ambitious targets for recycling rates and waste reduction, creating a strong incentive for the development of advanced recycling technologies.
The use of EVA in recycling processes aligns well with the growing emphasis on sustainable packaging materials. Regulations such as the EU's Single-Use Plastics Directive have accelerated the shift towards more recyclable and environmentally friendly packaging options. EVA's versatility and compatibility with various recycling streams make it an attractive choice for manufacturers seeking to comply with these regulations while maintaining product performance.
Furthermore, environmental regulations have led to the establishment of more sophisticated waste sorting and recycling infrastructure. This development has created opportunities for materials like EVA, which can improve the efficiency and quality of recycled products. For example, the Chinese government's recent ban on importing certain types of waste has prompted other countries to invest in domestic recycling capabilities, potentially increasing the demand for advanced materials that can enhance recycling processes.
The regulatory landscape also influences research and development in recycling technologies. Many governments offer incentives and funding for innovations that improve recycling efficiency and reduce environmental impact. This support has encouraged the exploration of EVA's potential in various recycling applications, from improving the properties of recycled plastics to enhancing the recovery of valuable materials from electronic waste.
As environmental regulations continue to evolve, the role of materials like EVA in enhancing recycling processes is likely to gain further prominence. The ongoing push for a circular economy and the implementation of more stringent recycling targets will drive the adoption of innovative solutions that can improve the efficiency and effectiveness of recycling operations. Consequently, manufacturers and recyclers alike will need to stay abreast of regulatory developments and adapt their strategies to leverage materials like EVA in meeting increasingly demanding environmental standards.
In recent years, many countries have implemented extended producer responsibility (EPR) programs, which hold manufacturers accountable for the entire lifecycle of their products, including disposal and recycling. These regulations have spurred interest in materials like EVA that can enhance recycling efficiency and reduce environmental impact. The European Union's Circular Economy Action Plan, for instance, sets ambitious targets for recycling rates and waste reduction, creating a strong incentive for the development of advanced recycling technologies.
The use of EVA in recycling processes aligns well with the growing emphasis on sustainable packaging materials. Regulations such as the EU's Single-Use Plastics Directive have accelerated the shift towards more recyclable and environmentally friendly packaging options. EVA's versatility and compatibility with various recycling streams make it an attractive choice for manufacturers seeking to comply with these regulations while maintaining product performance.
Furthermore, environmental regulations have led to the establishment of more sophisticated waste sorting and recycling infrastructure. This development has created opportunities for materials like EVA, which can improve the efficiency and quality of recycled products. For example, the Chinese government's recent ban on importing certain types of waste has prompted other countries to invest in domestic recycling capabilities, potentially increasing the demand for advanced materials that can enhance recycling processes.
The regulatory landscape also influences research and development in recycling technologies. Many governments offer incentives and funding for innovations that improve recycling efficiency and reduce environmental impact. This support has encouraged the exploration of EVA's potential in various recycling applications, from improving the properties of recycled plastics to enhancing the recovery of valuable materials from electronic waste.
As environmental regulations continue to evolve, the role of materials like EVA in enhancing recycling processes is likely to gain further prominence. The ongoing push for a circular economy and the implementation of more stringent recycling targets will drive the adoption of innovative solutions that can improve the efficiency and effectiveness of recycling operations. Consequently, manufacturers and recyclers alike will need to stay abreast of regulatory developments and adapt their strategies to leverage materials like EVA in meeting increasingly demanding environmental standards.
Circular Economy Impact
The integration of Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) into recycling processes has significant implications for the circular economy. By enhancing the recyclability of various materials, EVA contributes to the reduction of waste and the conservation of resources, aligning with the core principles of a circular economic model.
EVA's versatility as a copolymer allows it to improve the recycling efficiency of numerous products. In plastic recycling, EVA can be used as a compatibilizer, facilitating the blending of different plastic types that would otherwise be incompatible. This property enables the creation of recycled plastic blends with enhanced mechanical properties, expanding the range of applications for recycled materials and reducing the need for virgin plastics.
In the textile industry, EVA's incorporation into fabric recycling processes can lead to improved fiber recovery and the production of higher-quality recycled textiles. This not only extends the lifecycle of textile products but also reduces the environmental impact of the fashion industry, a significant contributor to global waste.
The use of EVA in recycling processes also supports the development of closed-loop systems within various industries. For instance, in the automotive sector, EVA can enhance the recyclability of composite materials used in vehicle components. This allows for more efficient end-of-life vehicle recycling, promoting the reuse of materials and reducing the sector's environmental footprint.
Furthermore, EVA's role in improving recycling processes contributes to the creation of new value streams within the circular economy. By enabling the production of higher-quality recycled materials, EVA helps to increase the market value of these materials, incentivizing further investment in recycling infrastructure and technologies.
The enhanced recycling capabilities facilitated by EVA also support the development of innovative business models centered around material recovery and reuse. This can lead to the emergence of new industries and job opportunities within the circular economy framework, fostering economic growth while minimizing environmental impact.
As governments and industries worldwide increasingly adopt circular economy principles, the importance of technologies that enhance recycling processes, such as EVA, is likely to grow. This trend could drive further research and development in EVA applications, potentially leading to even more efficient and effective recycling solutions in the future.
EVA's versatility as a copolymer allows it to improve the recycling efficiency of numerous products. In plastic recycling, EVA can be used as a compatibilizer, facilitating the blending of different plastic types that would otherwise be incompatible. This property enables the creation of recycled plastic blends with enhanced mechanical properties, expanding the range of applications for recycled materials and reducing the need for virgin plastics.
In the textile industry, EVA's incorporation into fabric recycling processes can lead to improved fiber recovery and the production of higher-quality recycled textiles. This not only extends the lifecycle of textile products but also reduces the environmental impact of the fashion industry, a significant contributor to global waste.
The use of EVA in recycling processes also supports the development of closed-loop systems within various industries. For instance, in the automotive sector, EVA can enhance the recyclability of composite materials used in vehicle components. This allows for more efficient end-of-life vehicle recycling, promoting the reuse of materials and reducing the sector's environmental footprint.
Furthermore, EVA's role in improving recycling processes contributes to the creation of new value streams within the circular economy. By enabling the production of higher-quality recycled materials, EVA helps to increase the market value of these materials, incentivizing further investment in recycling infrastructure and technologies.
The enhanced recycling capabilities facilitated by EVA also support the development of innovative business models centered around material recovery and reuse. This can lead to the emergence of new industries and job opportunities within the circular economy framework, fostering economic growth while minimizing environmental impact.
As governments and industries worldwide increasingly adopt circular economy principles, the importance of technologies that enhance recycling processes, such as EVA, is likely to grow. This trend could drive further research and development in EVA applications, potentially leading to even more efficient and effective recycling solutions in the future.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!