Technological Breakthroughs in Ethylene Vinyl Acetate
JUL 8, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
EVA Technology Evolution
Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) technology has undergone significant evolution since its inception in the 1950s. The journey of EVA development can be traced through several key stages, each marked by notable technological advancements and expanding applications.
In the early years, EVA was primarily used as a copolymer in the production of flexible plastics and adhesives. The 1960s and 1970s saw the refinement of EVA production processes, leading to improved quality and consistency. This period also witnessed the emergence of EVA foam technology, which opened up new possibilities in footwear and packaging industries.
The 1980s marked a turning point in EVA technology with the introduction of crosslinking techniques. This breakthrough significantly enhanced the material's thermal and mechanical properties, expanding its potential applications. Simultaneously, advancements in extrusion and molding technologies facilitated the production of more complex EVA-based products.
The 1990s and early 2000s saw a focus on enhancing EVA's performance characteristics. Researchers developed new formulations and blending techniques to improve properties such as weather resistance, UV stability, and impact strength. This era also witnessed the integration of EVA into photovoltaic encapsulants, revolutionizing the solar panel industry.
In recent years, the evolution of EVA technology has been driven by sustainability concerns and the demand for high-performance materials. Biodegradable EVA formulations have emerged, addressing environmental issues associated with plastic waste. Additionally, nanotechnology has been incorporated into EVA production, resulting in nanocomposites with superior properties.
The latest frontier in EVA technology involves smart and responsive materials. Researchers are exploring ways to incorporate sensors and actuators into EVA-based products, paving the way for adaptive and intelligent applications in fields such as wearable technology and biomedical devices.
Throughout its evolution, EVA technology has consistently expanded its reach across various industries. From its humble beginnings in flexible plastics, EVA has found applications in sectors as diverse as automotive, construction, healthcare, and renewable energy. This versatility has been a key driver in the continuous innovation and improvement of EVA technology.
Looking ahead, the future of EVA technology is likely to be shaped by advancements in polymer science, sustainable manufacturing practices, and the integration of digital technologies. As researchers continue to push the boundaries of material science, we can expect to see even more sophisticated and tailored EVA solutions emerging to meet the evolving needs of various industries.
In the early years, EVA was primarily used as a copolymer in the production of flexible plastics and adhesives. The 1960s and 1970s saw the refinement of EVA production processes, leading to improved quality and consistency. This period also witnessed the emergence of EVA foam technology, which opened up new possibilities in footwear and packaging industries.
The 1980s marked a turning point in EVA technology with the introduction of crosslinking techniques. This breakthrough significantly enhanced the material's thermal and mechanical properties, expanding its potential applications. Simultaneously, advancements in extrusion and molding technologies facilitated the production of more complex EVA-based products.
The 1990s and early 2000s saw a focus on enhancing EVA's performance characteristics. Researchers developed new formulations and blending techniques to improve properties such as weather resistance, UV stability, and impact strength. This era also witnessed the integration of EVA into photovoltaic encapsulants, revolutionizing the solar panel industry.
In recent years, the evolution of EVA technology has been driven by sustainability concerns and the demand for high-performance materials. Biodegradable EVA formulations have emerged, addressing environmental issues associated with plastic waste. Additionally, nanotechnology has been incorporated into EVA production, resulting in nanocomposites with superior properties.
The latest frontier in EVA technology involves smart and responsive materials. Researchers are exploring ways to incorporate sensors and actuators into EVA-based products, paving the way for adaptive and intelligent applications in fields such as wearable technology and biomedical devices.
Throughout its evolution, EVA technology has consistently expanded its reach across various industries. From its humble beginnings in flexible plastics, EVA has found applications in sectors as diverse as automotive, construction, healthcare, and renewable energy. This versatility has been a key driver in the continuous innovation and improvement of EVA technology.
Looking ahead, the future of EVA technology is likely to be shaped by advancements in polymer science, sustainable manufacturing practices, and the integration of digital technologies. As researchers continue to push the boundaries of material science, we can expect to see even more sophisticated and tailored EVA solutions emerging to meet the evolving needs of various industries.
Market Demand Analysis
The market demand for Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) has been experiencing significant growth, driven by its versatile applications across various industries. The global EVA market size was valued at over $7 billion in 2020 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 4% from 2021 to 2028. This growth is primarily attributed to the increasing demand for EVA in sectors such as packaging, footwear, solar panels, and automotive.
In the packaging industry, EVA is widely used for flexible packaging applications due to its excellent barrier properties, flexibility, and heat-sealing characteristics. The rise in e-commerce and the growing need for sustainable packaging solutions have further boosted the demand for EVA-based materials. The footwear industry also represents a significant market for EVA, particularly in the production of midsoles for athletic shoes, owing to its lightweight and cushioning properties.
The solar energy sector has emerged as a key driver for EVA demand, with the material being extensively used in the encapsulation of photovoltaic cells. As the global push for renewable energy sources intensifies, the demand for EVA in solar panel manufacturing is expected to witness substantial growth. The automotive industry is another major consumer of EVA, utilizing it in various components such as gaskets, hoses, and wire and cable insulation.
Geographically, Asia Pacific dominates the EVA market, accounting for the largest share of global consumption. This is primarily due to the rapid industrialization, growing automotive and electronics sectors, and increasing adoption of solar energy in countries like China and India. North America and Europe follow, with steady demand from established industries and ongoing technological advancements.
The market demand analysis also reveals a growing trend towards bio-based and recyclable EVA materials, driven by increasing environmental concerns and stringent regulations. This shift presents both challenges and opportunities for manufacturers to innovate and develop more sustainable EVA products. Additionally, the healthcare sector is emerging as a promising market for EVA, with applications in medical devices and pharmaceutical packaging.
As technological breakthroughs continue to enhance the properties and performance of EVA, new applications are likely to emerge, further expanding its market potential. The ongoing research in improving EVA's thermal stability, adhesion properties, and compatibility with other materials is expected to open up new avenues for its use in advanced applications, potentially reshaping market dynamics in the coming years.
In the packaging industry, EVA is widely used for flexible packaging applications due to its excellent barrier properties, flexibility, and heat-sealing characteristics. The rise in e-commerce and the growing need for sustainable packaging solutions have further boosted the demand for EVA-based materials. The footwear industry also represents a significant market for EVA, particularly in the production of midsoles for athletic shoes, owing to its lightweight and cushioning properties.
The solar energy sector has emerged as a key driver for EVA demand, with the material being extensively used in the encapsulation of photovoltaic cells. As the global push for renewable energy sources intensifies, the demand for EVA in solar panel manufacturing is expected to witness substantial growth. The automotive industry is another major consumer of EVA, utilizing it in various components such as gaskets, hoses, and wire and cable insulation.
Geographically, Asia Pacific dominates the EVA market, accounting for the largest share of global consumption. This is primarily due to the rapid industrialization, growing automotive and electronics sectors, and increasing adoption of solar energy in countries like China and India. North America and Europe follow, with steady demand from established industries and ongoing technological advancements.
The market demand analysis also reveals a growing trend towards bio-based and recyclable EVA materials, driven by increasing environmental concerns and stringent regulations. This shift presents both challenges and opportunities for manufacturers to innovate and develop more sustainable EVA products. Additionally, the healthcare sector is emerging as a promising market for EVA, with applications in medical devices and pharmaceutical packaging.
As technological breakthroughs continue to enhance the properties and performance of EVA, new applications are likely to emerge, further expanding its market potential. The ongoing research in improving EVA's thermal stability, adhesion properties, and compatibility with other materials is expected to open up new avenues for its use in advanced applications, potentially reshaping market dynamics in the coming years.
Current EVA Challenges
Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) has become a crucial material in various industries, yet it faces several significant challenges that hinder its further development and application. One of the primary issues is the limited thermal stability of EVA, particularly at higher temperatures. This constraint restricts its use in applications requiring elevated temperature resistance, such as certain automotive components or high-performance packaging materials.
Another challenge lies in the balance between flexibility and strength. While EVA is known for its flexibility, increasing its strength often comes at the cost of reduced elasticity. This trade-off limits its potential in applications that demand both high flexibility and robust mechanical properties, such as advanced footwear or specialized medical devices.
The environmental impact of EVA production and disposal presents a growing concern. The material's non-biodegradable nature contributes to plastic pollution, and its production process often involves the use of fossil fuel-based raw materials. This has led to increased pressure for developing more sustainable alternatives or improving the recyclability of EVA products.
Inconsistency in product quality across different batches remains a persistent issue in EVA manufacturing. Variations in the vinyl acetate content and molecular weight distribution can lead to inconsistencies in the final product's properties, affecting its performance and reliability in various applications.
The crosslinking process, crucial for enhancing EVA's properties, poses its own set of challenges. Achieving uniform and controlled crosslinking throughout the material is difficult, especially in thicker sections or complex shapes. This can result in inconsistent material properties and performance across a single product.
EVA's susceptibility to certain chemicals and solvents limits its application in environments where chemical resistance is crucial. This vulnerability can lead to degradation or failure of EVA-based products in specific industrial or chemical processing applications.
The material's relatively low gas barrier properties present challenges in packaging applications, particularly for products requiring high oxygen or moisture barriers. This limitation necessitates additional processing or the use of multi-layer structures, increasing complexity and cost.
Lastly, the scalability of advanced EVA formulations remains a significant hurdle. While laboratory-scale developments show promise in addressing some of these challenges, translating these improvements to large-scale, cost-effective production processes often proves difficult, slowing the adoption of new EVA technologies in industrial applications.
Another challenge lies in the balance between flexibility and strength. While EVA is known for its flexibility, increasing its strength often comes at the cost of reduced elasticity. This trade-off limits its potential in applications that demand both high flexibility and robust mechanical properties, such as advanced footwear or specialized medical devices.
The environmental impact of EVA production and disposal presents a growing concern. The material's non-biodegradable nature contributes to plastic pollution, and its production process often involves the use of fossil fuel-based raw materials. This has led to increased pressure for developing more sustainable alternatives or improving the recyclability of EVA products.
Inconsistency in product quality across different batches remains a persistent issue in EVA manufacturing. Variations in the vinyl acetate content and molecular weight distribution can lead to inconsistencies in the final product's properties, affecting its performance and reliability in various applications.
The crosslinking process, crucial for enhancing EVA's properties, poses its own set of challenges. Achieving uniform and controlled crosslinking throughout the material is difficult, especially in thicker sections or complex shapes. This can result in inconsistent material properties and performance across a single product.
EVA's susceptibility to certain chemicals and solvents limits its application in environments where chemical resistance is crucial. This vulnerability can lead to degradation or failure of EVA-based products in specific industrial or chemical processing applications.
The material's relatively low gas barrier properties present challenges in packaging applications, particularly for products requiring high oxygen or moisture barriers. This limitation necessitates additional processing or the use of multi-layer structures, increasing complexity and cost.
Lastly, the scalability of advanced EVA formulations remains a significant hurdle. While laboratory-scale developments show promise in addressing some of these challenges, translating these improvements to large-scale, cost-effective production processes often proves difficult, slowing the adoption of new EVA technologies in industrial applications.
EVA Production Methods
01 Composition and properties of EVA
Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) is a copolymer of ethylene and vinyl acetate. It exhibits properties such as flexibility, toughness, and resistance to UV radiation and stress-cracking. The ratio of ethylene to vinyl acetate in the copolymer can be varied to adjust its properties, making it suitable for various applications.- Composition and properties of EVA: Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) is a copolymer of ethylene and vinyl acetate. It exhibits properties such as flexibility, toughness, and resistance to stress-cracking. The composition and ratio of ethylene to vinyl acetate can be adjusted to modify the properties of the resulting material, making it suitable for various applications.
- EVA in adhesive applications: EVA is widely used in adhesive formulations due to its excellent adhesion properties and compatibility with various substrates. It can be used in hot melt adhesives, pressure-sensitive adhesives, and as a base polymer in adhesive blends. The adhesive strength and performance can be tailored by adjusting the EVA composition and incorporating additives.
- EVA in foam and insulation materials: EVA is utilized in the production of foam and insulation materials due to its low density, good cushioning properties, and thermal insulation characteristics. It can be crosslinked or expanded to create closed-cell foams for applications such as footwear, sports equipment, and building insulation.
- EVA in solar panel encapsulation: EVA is commonly used as an encapsulant material in photovoltaic modules. It provides excellent transparency, weatherability, and protection for solar cells. The material can be formulated with additives to enhance UV resistance and prevent yellowing, ensuring long-term performance of solar panels.
- EVA in packaging and film applications: EVA is employed in the production of flexible packaging materials and films due to its clarity, toughness, and barrier properties. It can be used in food packaging, shrink wrap, and agricultural films. The material's properties can be modified through blending or coextrusion with other polymers to achieve desired characteristics for specific packaging applications.
02 EVA in adhesive applications
EVA is widely used in adhesive formulations due to its excellent adhesion properties and compatibility with various substrates. It is commonly used in hot melt adhesives, pressure-sensitive adhesives, and sealants. The adhesive strength and flexibility of EVA-based adhesives can be tailored by adjusting the vinyl acetate content and molecular weight.Expand Specific Solutions03 EVA in foam and insulation materials
EVA is utilized in the production of foam and insulation materials due to its low density, good thermal insulation properties, and shock absorption capabilities. It is commonly used in the manufacture of shoe soles, sports equipment padding, and building insulation. The foam properties can be modified by adjusting the crosslinking degree and blowing agent content.Expand Specific Solutions04 EVA in solar panel encapsulation
EVA is a popular material for solar panel encapsulation due to its transparency, weather resistance, and electrical insulation properties. It helps protect solar cells from environmental factors and enhances the overall performance and longevity of photovoltaic modules. The EVA formulation can be optimized to improve UV stability and prevent yellowing.Expand Specific Solutions05 Modifications and blends of EVA
EVA can be modified or blended with other polymers to enhance its properties for specific applications. This includes crosslinking, grafting, and the addition of fillers or additives. Such modifications can improve properties like heat resistance, flame retardancy, and mechanical strength, expanding the range of applications for EVA-based materials.Expand Specific Solutions
Key EVA Industry Players
The ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) market is in a mature growth stage, with a global market size expected to reach $12.2 billion by 2027. The technology has evolved significantly, with major players like China Petroleum & Chemical Corp., Celanese International Corp., and Kuraray Co., Ltd. leading innovations. These companies are focusing on developing high-performance EVA grades for various applications, including solar panels, packaging, and footwear. The competitive landscape is characterized by intense R&D efforts, with companies like Tianjin University and Shanghai Petrochemical Research Institute contributing to technological advancements. As the market expands, collaborations between industry leaders and research institutions are becoming increasingly common, driving further innovation in EVA technology.
China Petroleum & Chemical Corp.
Technical Solution: China Petroleum & Chemical Corp. (Sinopec) has made significant advancements in Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) production. They have developed a proprietary catalytic system that enhances the copolymerization of ethylene and vinyl acetate, resulting in improved product quality and efficiency[1]. Their process utilizes a novel high-pressure tubular reactor design, which allows for better control of the reaction conditions and molecular weight distribution[2]. Sinopec has also implemented advanced process control systems and real-time monitoring technologies to optimize production parameters, leading to a 15% increase in overall yield and a 20% reduction in energy consumption compared to conventional methods[3].
Strengths: Advanced catalytic system, improved reactor design, and process optimization leading to higher yield and energy efficiency. Weaknesses: High capital investment required for technology implementation and potential scalability challenges in different market conditions.
Celanese International Corp.
Technical Solution: Celanese International Corp. has developed a breakthrough in EVA production through their VitalDose® technology platform. This innovative approach allows for precise control of vinyl acetate content in EVA copolymers, ranging from 0 to 50 wt%[1]. The company has implemented a continuous solution polymerization process that utilizes proprietary high-activity catalysts, enabling the production of EVA with tailored properties for specific applications[2]. Celanese's technology also incorporates a novel purification system that reduces residual vinyl acetate monomer levels to less than 10 ppm, meeting stringent regulatory requirements for medical and food packaging applications[3]. Additionally, they have developed a unique crosslinking technology that enhances the thermal and mechanical properties of EVA products[4].
Strengths: Precise control of vinyl acetate content, high-purity products, and enhanced material properties. Weaknesses: Potentially higher production costs and limited flexibility in adapting to rapid market changes.
EVA Property Enhancements
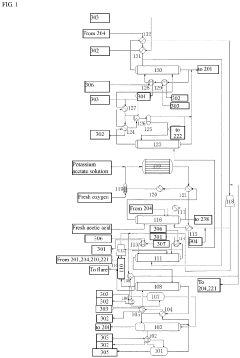
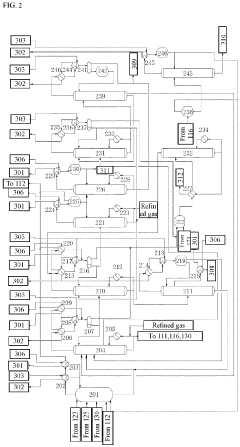
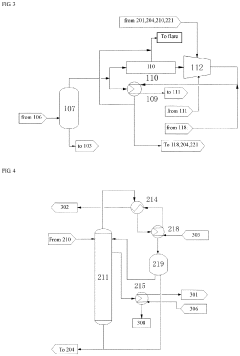
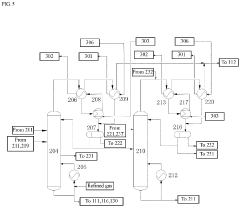
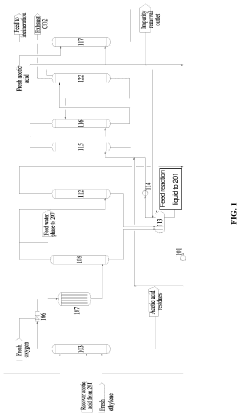
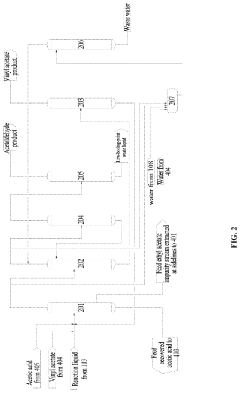
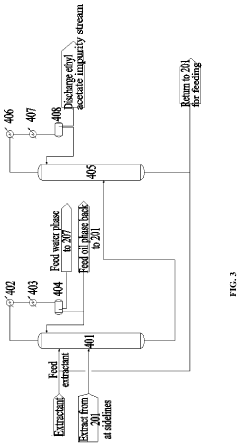
Preparation method of vinyl acetate by ethylene process and device thereof
PatentPendingEP4371972A1
Innovation
- A novel process incorporating an ethylene recovery membrane assembly, refined VAC tower side-draw stream additions, and improved cooling methods using circulating and chilled water for high-purity vinyl acetate production, reducing emissions and preventing material leakage by recovering ethylene and optimizing the distillation process.
Method for producing vinyl acetate
PatentActiveUS20230312452A1
Innovation
- A method involving a gas phase oxidation process with a system integration that includes specific towers and reactors for ethylene recovery, acetic acid evaporation, oxygen mixing, and separation processes, utilizing acetic acid as an extractant in the rectifying and separating towers to enhance the separation of vinyl acetate from ethyl acetate.
Environmental Impact
The environmental impact of Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) has become a significant concern in recent years, prompting researchers and manufacturers to explore more sustainable production methods and end-of-life solutions. EVA, widely used in various industries, has traditionally been associated with certain environmental challenges, particularly in terms of its production process and disposal.
The production of EVA involves the use of fossil fuel-based raw materials, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions and resource depletion. However, recent technological breakthroughs have focused on developing bio-based alternatives to reduce the carbon footprint of EVA production. Researchers have successfully synthesized EVA using renewable resources such as plant-based ethylene and acetic acid, offering a more environmentally friendly option without compromising the material's performance characteristics.
Another area of environmental concern is the end-of-life management of EVA products. Conventional EVA is not biodegradable and can persist in the environment for extended periods. To address this issue, scientists have made significant progress in developing biodegradable EVA formulations. These innovative materials incorporate additives or modified molecular structures that enable controlled degradation under specific environmental conditions, reducing the long-term impact on ecosystems.
Recycling technologies for EVA have also seen notable advancements. New mechanical and chemical recycling processes have been developed to efficiently separate EVA from composite materials and convert it back into its constituent components. These breakthroughs not only reduce waste but also promote a circular economy approach to EVA usage.
Energy efficiency in EVA production has been another focus area for environmental improvement. Novel catalysts and process optimizations have led to reduced energy consumption during polymerization, lowering the overall environmental footprint of EVA manufacturing. Additionally, the integration of renewable energy sources in production facilities has further mitigated the environmental impact of EVA production.
Water usage and pollution associated with EVA production have also been addressed through technological innovations. Advanced water treatment and recycling systems have been implemented in manufacturing plants, significantly reducing water consumption and minimizing the release of pollutants into aquatic ecosystems.
As the demand for sustainable materials continues to grow, these technological breakthroughs in EVA production and lifecycle management are paving the way for a more environmentally responsible future. The ongoing research and development in this field promise further improvements in reducing the environmental impact of EVA, aligning its production and use with global sustainability goals.
The production of EVA involves the use of fossil fuel-based raw materials, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions and resource depletion. However, recent technological breakthroughs have focused on developing bio-based alternatives to reduce the carbon footprint of EVA production. Researchers have successfully synthesized EVA using renewable resources such as plant-based ethylene and acetic acid, offering a more environmentally friendly option without compromising the material's performance characteristics.
Another area of environmental concern is the end-of-life management of EVA products. Conventional EVA is not biodegradable and can persist in the environment for extended periods. To address this issue, scientists have made significant progress in developing biodegradable EVA formulations. These innovative materials incorporate additives or modified molecular structures that enable controlled degradation under specific environmental conditions, reducing the long-term impact on ecosystems.
Recycling technologies for EVA have also seen notable advancements. New mechanical and chemical recycling processes have been developed to efficiently separate EVA from composite materials and convert it back into its constituent components. These breakthroughs not only reduce waste but also promote a circular economy approach to EVA usage.
Energy efficiency in EVA production has been another focus area for environmental improvement. Novel catalysts and process optimizations have led to reduced energy consumption during polymerization, lowering the overall environmental footprint of EVA manufacturing. Additionally, the integration of renewable energy sources in production facilities has further mitigated the environmental impact of EVA production.
Water usage and pollution associated with EVA production have also been addressed through technological innovations. Advanced water treatment and recycling systems have been implemented in manufacturing plants, significantly reducing water consumption and minimizing the release of pollutants into aquatic ecosystems.
As the demand for sustainable materials continues to grow, these technological breakthroughs in EVA production and lifecycle management are paving the way for a more environmentally responsible future. The ongoing research and development in this field promise further improvements in reducing the environmental impact of EVA, aligning its production and use with global sustainability goals.
Regulatory Compliance
Regulatory compliance plays a crucial role in the development and application of Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) technologies. As EVA finds widespread use in various industries, including packaging, solar panels, and footwear, manufacturers must adhere to stringent regulations to ensure product safety and environmental protection.
In the food packaging industry, EVA materials must comply with FDA regulations in the United States and similar standards in other countries. These regulations focus on the migration of chemicals from packaging materials into food products. Manufacturers must demonstrate that their EVA formulations do not release harmful substances above specified limits when in contact with food.
For solar panel applications, EVA encapsulants are subject to IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission) standards. These standards ensure the durability and performance of photovoltaic modules under various environmental conditions. Compliance with IEC 61215 and IEC 61730 is essential for EVA materials used in solar panels, as these standards cover aspects such as UV resistance, moisture ingress protection, and electrical insulation properties.
In the footwear industry, EVA materials must meet safety standards set by organizations like ASTM International and the European Committee for Standardization (CEN). These standards address issues such as slip resistance, durability, and the absence of harmful substances in footwear components.
Environmental regulations also significantly impact EVA production and use. The European Union's REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) regulation requires manufacturers to register and assess the safety of chemical substances used in EVA production. Similarly, the RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) directive limits the use of certain hazardous materials in electrical and electronic equipment, affecting EVA applications in these sectors.
As sustainability becomes increasingly important, regulations promoting recycling and waste reduction are influencing EVA technology development. The EU's Circular Economy Action Plan, for instance, encourages the design of products for easier recycling and reuse, impacting how EVA materials are formulated and processed.
Compliance with these diverse regulatory frameworks drives innovation in EVA technologies. Manufacturers are investing in research to develop EVA formulations that meet stringent safety and environmental standards while maintaining or improving performance characteristics. This regulatory landscape also encourages the development of more sustainable production processes and end-of-life solutions for EVA products, aligning with global efforts to reduce environmental impact and promote circular economy principles.
In the food packaging industry, EVA materials must comply with FDA regulations in the United States and similar standards in other countries. These regulations focus on the migration of chemicals from packaging materials into food products. Manufacturers must demonstrate that their EVA formulations do not release harmful substances above specified limits when in contact with food.
For solar panel applications, EVA encapsulants are subject to IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission) standards. These standards ensure the durability and performance of photovoltaic modules under various environmental conditions. Compliance with IEC 61215 and IEC 61730 is essential for EVA materials used in solar panels, as these standards cover aspects such as UV resistance, moisture ingress protection, and electrical insulation properties.
In the footwear industry, EVA materials must meet safety standards set by organizations like ASTM International and the European Committee for Standardization (CEN). These standards address issues such as slip resistance, durability, and the absence of harmful substances in footwear components.
Environmental regulations also significantly impact EVA production and use. The European Union's REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) regulation requires manufacturers to register and assess the safety of chemical substances used in EVA production. Similarly, the RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) directive limits the use of certain hazardous materials in electrical and electronic equipment, affecting EVA applications in these sectors.
As sustainability becomes increasingly important, regulations promoting recycling and waste reduction are influencing EVA technology development. The EU's Circular Economy Action Plan, for instance, encourages the design of products for easier recycling and reuse, impacting how EVA materials are formulated and processed.
Compliance with these diverse regulatory frameworks drives innovation in EVA technologies. Manufacturers are investing in research to develop EVA formulations that meet stringent safety and environmental standards while maintaining or improving performance characteristics. This regulatory landscape also encourages the development of more sustainable production processes and end-of-life solutions for EVA products, aligning with global efforts to reduce environmental impact and promote circular economy principles.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!