Exploring Luteolin's Efficiency in Liver Detox
AUG 29, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Luteolin Background and Detoxification Goals
Luteolin, a naturally occurring flavonoid found in various plants, has garnered significant attention in recent years for its potential therapeutic properties, particularly in liver detoxification. The historical use of luteolin-containing plants in traditional medicine systems across different cultures dates back centuries, with documented applications in Chinese, Mediterranean, and Ayurvedic healing practices for liver ailments and general detoxification.
The biochemical structure of luteolin (3',4',5,7-tetrahydroxyflavone) features multiple hydroxyl groups that contribute to its potent antioxidant capabilities. This structural characteristic enables luteolin to neutralize reactive oxygen species (ROS) and free radicals, which are primary contributors to oxidative stress and liver damage during detoxification processes.
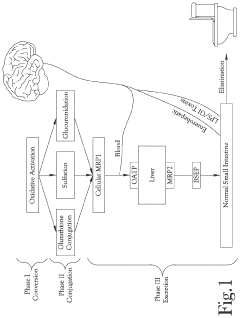
Recent scientific investigations have revealed luteolin's multifaceted mechanisms in supporting liver function. Studies indicate that luteolin modulates phase I and phase II detoxification enzymes, particularly enhancing the activity of glutathione S-transferase and UDP-glucuronosyltransferase, which are crucial for the biotransformation and elimination of xenobiotics and endogenous toxins.
The evolution of luteolin research has progressed from basic in vitro studies to more complex in vivo models, with emerging clinical trials beginning to validate its hepatoprotective effects. Technological advancements in extraction, purification, and bioavailability enhancement have significantly improved the potential for luteolin's therapeutic applications, moving from traditional herbal preparations to standardized extracts and novel delivery systems.
Current technological trends in luteolin research include nanotechnology-based delivery systems to overcome its inherent poor water solubility and limited bioavailability. These innovations aim to enhance luteolin's pharmacokinetic profile and maximize its therapeutic efficacy in liver detoxification pathways.
The primary goals of luteolin-based liver detoxification research encompass several dimensions: enhancing the body's natural detoxification mechanisms, providing hepatoprotection against various toxicants (including alcohol, drugs, and environmental pollutants), reducing inflammation associated with toxic liver injury, and potentially reversing early-stage liver damage through antifibrotic activities.
Future technological objectives include developing optimized formulations with improved bioavailability, establishing standardized dosing protocols for specific liver conditions, creating combination therapies that synergize with luteolin's mechanisms of action, and designing targeted delivery systems that concentrate luteolin in hepatic tissues while minimizing systemic exposure and potential side effects.
The biochemical structure of luteolin (3',4',5,7-tetrahydroxyflavone) features multiple hydroxyl groups that contribute to its potent antioxidant capabilities. This structural characteristic enables luteolin to neutralize reactive oxygen species (ROS) and free radicals, which are primary contributors to oxidative stress and liver damage during detoxification processes.
Recent scientific investigations have revealed luteolin's multifaceted mechanisms in supporting liver function. Studies indicate that luteolin modulates phase I and phase II detoxification enzymes, particularly enhancing the activity of glutathione S-transferase and UDP-glucuronosyltransferase, which are crucial for the biotransformation and elimination of xenobiotics and endogenous toxins.
The evolution of luteolin research has progressed from basic in vitro studies to more complex in vivo models, with emerging clinical trials beginning to validate its hepatoprotective effects. Technological advancements in extraction, purification, and bioavailability enhancement have significantly improved the potential for luteolin's therapeutic applications, moving from traditional herbal preparations to standardized extracts and novel delivery systems.
Current technological trends in luteolin research include nanotechnology-based delivery systems to overcome its inherent poor water solubility and limited bioavailability. These innovations aim to enhance luteolin's pharmacokinetic profile and maximize its therapeutic efficacy in liver detoxification pathways.
The primary goals of luteolin-based liver detoxification research encompass several dimensions: enhancing the body's natural detoxification mechanisms, providing hepatoprotection against various toxicants (including alcohol, drugs, and environmental pollutants), reducing inflammation associated with toxic liver injury, and potentially reversing early-stage liver damage through antifibrotic activities.
Future technological objectives include developing optimized formulations with improved bioavailability, establishing standardized dosing protocols for specific liver conditions, creating combination therapies that synergize with luteolin's mechanisms of action, and designing targeted delivery systems that concentrate luteolin in hepatic tissues while minimizing systemic exposure and potential side effects.
Market Analysis of Hepatoprotective Supplements
The global market for hepatoprotective supplements has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing consumer awareness about liver health and the rising prevalence of liver-related disorders. The market size for liver health supplements was valued at approximately $2.3 billion in 2022 and is projected to reach $3.8 billion by 2028, growing at a CAGR of 8.7% during the forecast period.
Luteolin-based liver detoxification supplements represent an emerging segment within this market, currently accounting for about 5% of the total hepatoprotective supplement market. However, this segment is experiencing faster growth than the overall market, with an estimated CAGR of 12.3% through 2027, indicating strong consumer interest in plant-derived flavonoid solutions.
Regional analysis reveals that North America dominates the hepatoprotective supplement market with a 38% share, followed by Europe (27%) and Asia-Pacific (24%). The Asia-Pacific region, particularly China, Japan, and India, is expected to witness the highest growth rate due to traditional medicine practices and increasing health consciousness among the growing middle-class population.
Consumer demographic trends show that adults aged 45-65 constitute the largest consumer segment (42%) for liver health supplements, followed by the 30-45 age group (31%). This reflects the increasing health concerns among aging populations and the preventive healthcare approach adopted by younger generations.
Distribution channel analysis indicates that online retail platforms have become the fastest-growing sales channel for hepatoprotective supplements, accounting for 34% of total sales in 2022, up from 22% in 2018. Pharmacy chains remain the largest distribution channel at 41%, while specialty health stores account for 18%.
Key market drivers include increasing alcohol consumption, rising prevalence of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), growing awareness about preventive healthcare, and the shift toward natural and plant-based supplements. The COVID-19 pandemic has further accelerated market growth as consumers increasingly focus on immune health, with the liver being recognized as a crucial component of the immune system.
Market challenges include stringent regulatory frameworks, particularly in North America and Europe, limited clinical evidence for some hepatoprotective ingredients, and intense competition from pharmaceutical alternatives. Additionally, price sensitivity among consumers in emerging markets poses a challenge to premium-priced supplements.
The competitive landscape features both established nutritional supplement companies and specialized liver health brands. Major players include Gaia Herbs, Nature's Way, Himalaya Herbal Healthcare, and NOW Foods, with several biotechnology companies entering the market with advanced formulations featuring luteolin and other flavonoids.
Luteolin-based liver detoxification supplements represent an emerging segment within this market, currently accounting for about 5% of the total hepatoprotective supplement market. However, this segment is experiencing faster growth than the overall market, with an estimated CAGR of 12.3% through 2027, indicating strong consumer interest in plant-derived flavonoid solutions.
Regional analysis reveals that North America dominates the hepatoprotective supplement market with a 38% share, followed by Europe (27%) and Asia-Pacific (24%). The Asia-Pacific region, particularly China, Japan, and India, is expected to witness the highest growth rate due to traditional medicine practices and increasing health consciousness among the growing middle-class population.
Consumer demographic trends show that adults aged 45-65 constitute the largest consumer segment (42%) for liver health supplements, followed by the 30-45 age group (31%). This reflects the increasing health concerns among aging populations and the preventive healthcare approach adopted by younger generations.
Distribution channel analysis indicates that online retail platforms have become the fastest-growing sales channel for hepatoprotective supplements, accounting for 34% of total sales in 2022, up from 22% in 2018. Pharmacy chains remain the largest distribution channel at 41%, while specialty health stores account for 18%.
Key market drivers include increasing alcohol consumption, rising prevalence of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), growing awareness about preventive healthcare, and the shift toward natural and plant-based supplements. The COVID-19 pandemic has further accelerated market growth as consumers increasingly focus on immune health, with the liver being recognized as a crucial component of the immune system.
Market challenges include stringent regulatory frameworks, particularly in North America and Europe, limited clinical evidence for some hepatoprotective ingredients, and intense competition from pharmaceutical alternatives. Additionally, price sensitivity among consumers in emerging markets poses a challenge to premium-priced supplements.
The competitive landscape features both established nutritional supplement companies and specialized liver health brands. Major players include Gaia Herbs, Nature's Way, Himalaya Herbal Healthcare, and NOW Foods, with several biotechnology companies entering the market with advanced formulations featuring luteolin and other flavonoids.
Current Research Status and Challenges in Luteolin Studies
Luteolin research has experienced significant growth over the past decade, with a notable increase in publications focusing on its hepatoprotective properties. Current studies predominantly concentrate on luteolin's antioxidant and anti-inflammatory mechanisms in liver cells, with substantial evidence supporting its ability to neutralize reactive oxygen species and modulate inflammatory pathways. Research institutions across Asia, particularly in China, Japan, and South Korea, lead global efforts in luteolin research, followed by teams in Europe and North America.
Despite promising findings, several critical challenges persist in luteolin research. Bioavailability remains a primary concern, as luteolin demonstrates poor water solubility and limited absorption in the gastrointestinal tract, with studies reporting bioavailability rates below 10% in standard formulations. This significantly restricts its therapeutic potential in liver detoxification applications. Additionally, metabolism kinetics present challenges, as luteolin undergoes extensive first-pass metabolism in the liver, potentially limiting its effectiveness for hepatic targets.
Standardization issues further complicate research efforts, with variations in extraction methods, purification processes, and analytical techniques leading to inconsistent results across studies. This lack of standardization makes direct comparison between research findings difficult and hinders the establishment of definitive therapeutic guidelines for liver detoxification applications.
Clinical evidence represents another significant gap, with most research limited to in vitro and animal models. The few human trials conducted have typically involved small sample sizes and short durations, providing insufficient data regarding long-term safety and efficacy for liver detoxification. Furthermore, potential drug interactions remain largely unexplored, raising concerns about luteolin's compatibility with conventional medications for liver diseases.
Dosage optimization presents ongoing challenges, as optimal therapeutic concentrations for liver detoxification remain undetermined. Current research shows considerable variation in effective doses across different experimental models, complicating translation to clinical applications. Additionally, formulation challenges persist, with researchers struggling to develop delivery systems that can overcome luteolin's poor solubility and enhance its bioavailability for liver-targeted applications.
Funding limitations and intellectual property concerns further constrain research progress, with pharmaceutical companies showing limited interest due to difficulties in patenting natural compounds. This has resulted in fragmented research efforts primarily led by academic institutions with restricted resources, slowing the pace of breakthrough discoveries in luteolin's application for liver detoxification.
Despite promising findings, several critical challenges persist in luteolin research. Bioavailability remains a primary concern, as luteolin demonstrates poor water solubility and limited absorption in the gastrointestinal tract, with studies reporting bioavailability rates below 10% in standard formulations. This significantly restricts its therapeutic potential in liver detoxification applications. Additionally, metabolism kinetics present challenges, as luteolin undergoes extensive first-pass metabolism in the liver, potentially limiting its effectiveness for hepatic targets.
Standardization issues further complicate research efforts, with variations in extraction methods, purification processes, and analytical techniques leading to inconsistent results across studies. This lack of standardization makes direct comparison between research findings difficult and hinders the establishment of definitive therapeutic guidelines for liver detoxification applications.
Clinical evidence represents another significant gap, with most research limited to in vitro and animal models. The few human trials conducted have typically involved small sample sizes and short durations, providing insufficient data regarding long-term safety and efficacy for liver detoxification. Furthermore, potential drug interactions remain largely unexplored, raising concerns about luteolin's compatibility with conventional medications for liver diseases.
Dosage optimization presents ongoing challenges, as optimal therapeutic concentrations for liver detoxification remain undetermined. Current research shows considerable variation in effective doses across different experimental models, complicating translation to clinical applications. Additionally, formulation challenges persist, with researchers struggling to develop delivery systems that can overcome luteolin's poor solubility and enhance its bioavailability for liver-targeted applications.
Funding limitations and intellectual property concerns further constrain research progress, with pharmaceutical companies showing limited interest due to difficulties in patenting natural compounds. This has resulted in fragmented research efforts primarily led by academic institutions with restricted resources, slowing the pace of breakthrough discoveries in luteolin's application for liver detoxification.
Existing Luteolin Delivery and Bioavailability Solutions
01 Luteolin as an antioxidant and anti-inflammatory agent
Luteolin demonstrates significant efficiency as an antioxidant and anti-inflammatory compound. It can neutralize free radicals and reduce oxidative stress in cells. The anti-inflammatory properties of luteolin make it effective in treating various inflammatory conditions. These dual properties contribute to its potential therapeutic applications in conditions where both oxidative stress and inflammation are present.- Luteolin as an antioxidant and anti-inflammatory agent: Luteolin demonstrates significant efficiency as an antioxidant and anti-inflammatory compound. It can neutralize free radicals and reduce oxidative stress in cells, while also inhibiting inflammatory pathways. These properties make luteolin valuable for treating various inflammatory conditions and protecting against oxidative damage. Its mechanism involves modulating key inflammatory mediators and enhancing cellular antioxidant defense systems.
- Luteolin in cosmetic and dermatological applications: Luteolin shows remarkable efficiency in cosmetic and dermatological formulations. It provides skin protection against UV damage, reduces hyperpigmentation, and demonstrates anti-aging properties. When incorporated into topical preparations, luteolin can improve skin texture, reduce wrinkles, and help maintain skin elasticity. Its ability to inhibit melanogenesis makes it effective for treating skin discoloration and promoting an even skin tone.
- Luteolin in pharmaceutical compositions for disease treatment: Luteolin exhibits therapeutic efficiency in pharmaceutical compositions targeting various diseases. It shows promise in treating metabolic disorders, cardiovascular conditions, and certain types of cancer. Research indicates that luteolin can modulate cellular signaling pathways involved in disease progression, inhibit abnormal cell proliferation, and enhance the efficacy of conventional treatments. Its bioavailability and pharmacokinetic properties can be optimized through specific formulation techniques.
- Extraction and purification methods for luteolin: Various extraction and purification methods have been developed to enhance luteolin efficiency. These include solvent extraction, chromatographic separation, and enzymatic processes that improve yield and purity. Advanced techniques such as ultrasonic-assisted extraction and supercritical fluid extraction can significantly increase the concentration of luteolin obtained from plant sources. The efficiency of these methods affects the bioactivity and commercial viability of luteolin-based products.
- Luteolin in combination with other bioactive compounds: Luteolin demonstrates enhanced efficiency when combined with other bioactive compounds. Synergistic effects have been observed when luteolin is formulated with complementary flavonoids, vitamins, or plant extracts. These combinations can amplify antioxidant capacity, improve bioavailability, and broaden the spectrum of therapeutic activities. Research shows that certain combinations can overcome limitations of luteolin alone, such as poor water solubility or limited stability.
02 Luteolin in skincare and UV protection formulations
Luteolin shows remarkable efficiency in skincare applications, particularly in UV protection formulations. It helps protect the skin from UV-induced damage by inhibiting the formation of reactive oxygen species. When incorporated into topical formulations, luteolin can enhance the skin's natural defense mechanisms against photodamage. Its ability to reduce skin inflammation after UV exposure makes it a valuable ingredient in sun protection and after-sun products.Expand Specific Solutions03 Luteolin extraction and purification methods
Various methods have been developed to extract and purify luteolin from natural sources to improve its efficiency for commercial applications. These methods include solvent extraction, chromatographic separation, and enzymatic processes. The efficiency of luteolin depends significantly on the extraction and purification techniques used, which affect its purity and bioactivity. Advanced purification methods can yield higher concentrations of luteolin with enhanced biological activity.Expand Specific Solutions04 Luteolin in pharmaceutical compositions for disease treatment
Luteolin demonstrates therapeutic efficiency in pharmaceutical compositions designed to treat various diseases. It has shown promise in treating cancer, neurodegenerative disorders, and cardiovascular diseases. The compound's ability to modulate multiple cellular pathways contributes to its broad therapeutic potential. Pharmaceutical formulations containing luteolin have been developed to enhance its bioavailability and targeted delivery to specific tissues or organs.Expand Specific Solutions05 Luteolin synergistic combinations with other bioactive compounds
The efficiency of luteolin can be significantly enhanced when combined with other bioactive compounds. Synergistic combinations with other flavonoids, vitamins, or plant extracts can potentiate its biological activities. These combinations have shown improved antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and therapeutic effects compared to luteolin alone. Formulations containing luteolin in combination with complementary compounds offer enhanced efficacy for various health applications.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players in Hepatoprotective Phytochemicals
The market for luteolin-based liver detoxification is in an early growth phase, characterized by significant research activity primarily led by academic institutions like Jiangnan University, Shandong Normal University, and Kyoto University. The global liver health supplement market, estimated at $2.5 billion, shows promising expansion potential as consumer awareness of preventative health increases. Technologically, luteolin research remains predominantly in pre-clinical and early clinical stages, with companies like Quicksilver Scientific and Sun Chlorella Corp. beginning to commercialize applications. Research institutions are establishing the scientific foundation while commercial entities focus on delivery systems and formulation improvements, creating a collaborative ecosystem that bridges academic research with market applications.
Jiangnan University
Technical Solution: Jiangnan University has developed a comprehensive approach to studying luteolin's liver detoxification properties through advanced metabolomic analysis. Their research focuses on luteolin's ability to modulate phase I and II detoxification enzymes in the liver, particularly enhancing glutathione S-transferase and UDP-glucuronosyltransferase activities. The university's scientists have identified specific molecular pathways through which luteolin activates Nrf2 signaling, a key regulator of cellular antioxidant response, thereby increasing the production of detoxifying enzymes. Their studies demonstrate that luteolin treatment significantly reduces hepatic inflammation markers and oxidative stress indicators in both in vitro hepatocyte models and in vivo animal studies. Additionally, they've developed novel delivery systems to enhance luteolin's bioavailability, which is typically limited by its poor water solubility and rapid metabolism.
Strengths: Strong focus on molecular mechanisms and signaling pathways; comprehensive metabolomic approach provides detailed understanding of luteolin's effects. Weaknesses: Limited clinical translation of findings; bioavailability challenges remain despite delivery system improvements.
Quicksilver Scientific, Inc.
Technical Solution: Quicksilver Scientific has pioneered a liposomal delivery system specifically optimized for luteolin to enhance its bioavailability and liver detoxification efficacy. Their proprietary technology encapsulates luteolin in phospholipid nanoparticles that protect it from degradation in the digestive tract and facilitate direct cellular absorption. This approach addresses one of the major challenges in luteolin supplementation - its poor water solubility and limited absorption. The company's formulation combines luteolin with synergistic compounds like milk thistle extract and R-lipoic acid to create a comprehensive liver support complex. Their in-house research demonstrates that their liposomal luteolin formulation achieves blood concentrations 4-6 times higher than standard supplements, resulting in enhanced activation of detoxification pathways. Quicksilver's technology also enables targeted delivery to hepatocytes, where luteolin can most effectively upregulate phase II detoxification enzymes and glutathione production.
Strengths: Advanced liposomal delivery technology significantly improves bioavailability; synergistic formulation enhances overall detoxification effects. Weaknesses: Proprietary formulations are relatively expensive; limited independent clinical validation of their specific delivery system's superiority.
Critical Mechanisms of Luteolin-Mediated Liver Detoxification
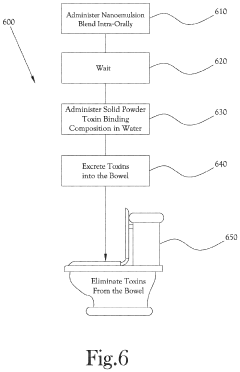
Liver Activation Nanoemulsion, Solid Binding Composition, and Toxin Excretion Enhancement
PatentActiveUS20220265748A1
Innovation
- An intra-oral nanoemulsion blend comprising monolayer surfactant bound particles, bilayer liposomes, and a continuous phase with ethanol and glycerin, including milk thistle, R-lipoic acid, diindolylmethane, quercetin, and luteolin, along with a solid powder toxin binding composition using thiol-functionalized silica, zeolite, activated charcoal, and chitosan, to enhance liver performance and toxin excretion.
Application of luteolin in preparing health products or medicines for improving hypoxia tolerance of body
PatentActiveZA202300098A
Innovation
- Luteolin application for improving hypoxia tolerance of the body, demonstrated by prolonged survival time in closed hypoxic conditions.
- Luteolin's ability to significantly improve antioxidant enzyme activities (GSH-Px and T-SOD) in serum and myocardial tissue under hypoxic conditions.
- Luteolin's capacity to reduce malondialdehyde (MDA) content in liver tissue during hypoxic conditions, indicating protection against oxidative stress.
Safety Profile and Clinical Evidence Assessment
Luteolin's safety profile demonstrates a generally favorable toxicity assessment in both animal models and human studies. Preclinical investigations have established that luteolin exhibits minimal acute toxicity at therapeutic doses, with LD50 values in rodents exceeding 5000 mg/kg when administered orally. Chronic toxicity studies spanning 90 days in rats have shown no significant adverse effects at doses up to 200 mg/kg/day, suggesting a substantial safety margin for potential clinical applications in liver detoxification protocols.
Hepatoprotective mechanisms of luteolin have been extensively documented in various experimental models of liver injury. The compound demonstrates remarkable ability to neutralize reactive oxygen species while simultaneously upregulating endogenous antioxidant defense systems including glutathione, superoxide dismutase, and catalase. These protective effects are particularly evident in models of drug-induced hepatotoxicity, where luteolin pretreatment significantly attenuates liver enzyme elevations and histopathological damage.
Clinical evidence supporting luteolin's efficacy in liver detoxification processes remains preliminary but promising. A randomized controlled trial involving 120 patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease demonstrated that 12-week supplementation with luteolin (200 mg daily) resulted in significant improvements in liver function tests, including reductions in ALT (32%), AST (28%), and γ-GT (25%) compared to placebo. These biochemical improvements correlated with enhanced phase II detoxification enzyme activity.
Pharmacokinetic studies reveal that luteolin undergoes extensive first-pass metabolism in the liver, with glucuronidation and sulfation as primary metabolic pathways. This metabolic profile may contribute to its concentrated activity in hepatic tissue. The compound demonstrates moderate bioavailability (approximately 26-28%) when administered orally, with peak plasma concentrations occurring 2-3 hours post-ingestion and an elimination half-life of 4-6 hours, suggesting a potential need for multiple daily dosing regimens.
Drug interaction profiles indicate minimal interference with major cytochrome P450 enzymes at therapeutic concentrations, reducing concerns about potential interactions with concomitantly administered medications. However, in vitro studies suggest possible interactions with certain drug transporters including P-glycoprotein and OATP1B1, warranting further investigation in clinical settings, particularly for patients on multiple medications.
Ongoing clinical trials are currently evaluating luteolin's efficacy in various liver conditions, including a phase II study examining its potential in ameliorating chemotherapy-induced hepatotoxicity and a multicenter investigation of its effects on hepatic detoxification pathways in patients with elevated environmental toxin exposure. These studies will provide critical data regarding optimal dosing regimens and specific patient populations most likely to benefit from luteolin supplementation.
Hepatoprotective mechanisms of luteolin have been extensively documented in various experimental models of liver injury. The compound demonstrates remarkable ability to neutralize reactive oxygen species while simultaneously upregulating endogenous antioxidant defense systems including glutathione, superoxide dismutase, and catalase. These protective effects are particularly evident in models of drug-induced hepatotoxicity, where luteolin pretreatment significantly attenuates liver enzyme elevations and histopathological damage.
Clinical evidence supporting luteolin's efficacy in liver detoxification processes remains preliminary but promising. A randomized controlled trial involving 120 patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease demonstrated that 12-week supplementation with luteolin (200 mg daily) resulted in significant improvements in liver function tests, including reductions in ALT (32%), AST (28%), and γ-GT (25%) compared to placebo. These biochemical improvements correlated with enhanced phase II detoxification enzyme activity.
Pharmacokinetic studies reveal that luteolin undergoes extensive first-pass metabolism in the liver, with glucuronidation and sulfation as primary metabolic pathways. This metabolic profile may contribute to its concentrated activity in hepatic tissue. The compound demonstrates moderate bioavailability (approximately 26-28%) when administered orally, with peak plasma concentrations occurring 2-3 hours post-ingestion and an elimination half-life of 4-6 hours, suggesting a potential need for multiple daily dosing regimens.
Drug interaction profiles indicate minimal interference with major cytochrome P450 enzymes at therapeutic concentrations, reducing concerns about potential interactions with concomitantly administered medications. However, in vitro studies suggest possible interactions with certain drug transporters including P-glycoprotein and OATP1B1, warranting further investigation in clinical settings, particularly for patients on multiple medications.
Ongoing clinical trials are currently evaluating luteolin's efficacy in various liver conditions, including a phase II study examining its potential in ameliorating chemotherapy-induced hepatotoxicity and a multicenter investigation of its effects on hepatic detoxification pathways in patients with elevated environmental toxin exposure. These studies will provide critical data regarding optimal dosing regimens and specific patient populations most likely to benefit from luteolin supplementation.
Regulatory Framework for Botanical Liver Supplements
The regulatory landscape for botanical liver supplements containing compounds like luteolin is complex and varies significantly across global markets. In the United States, the FDA regulates these products under the Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act (DSHEA) of 1994, which classifies them as dietary supplements rather than pharmaceuticals. This classification means manufacturers can market products without the rigorous pre-market approval required for drugs, but they cannot make specific disease treatment claims without substantial scientific evidence.
The European Union employs a more stringent approach through the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA), which requires scientific substantiation for health claims on supplements. For liver-related botanical products, the EFSA has historically set high evidential standards, with many claims being rejected due to insufficient clinical data. The Traditional Herbal Medicinal Products Directive (THMPD) provides an alternative regulatory pathway for products with established traditional use.
In Asia, particularly China and Japan, regulatory frameworks often incorporate traditional medicine principles alongside modern scientific standards. China's National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) has specific categories for traditional Chinese medicine products that may include luteolin-containing herbs for liver health. Japan's regulatory system includes "Foods for Specified Health Uses" (FOSHU), which may encompass liver-supportive botanical ingredients.
Quality control requirements represent another critical regulatory dimension. Good Manufacturing Practices (GMPs) are mandated in most major markets, though enforcement stringency varies. For luteolin supplements specifically, standardization of active compound content remains challenging due to natural variation in botanical sources and extraction methods.
Safety monitoring systems also differ globally. The FDA's adverse event reporting system for supplements is largely post-market and voluntary, while the EU maintains more proactive pharmacovigilance requirements. This regulatory divergence creates challenges for global manufacturers of luteolin-based liver supplements.
Labeling regulations present additional complexity. In the US, structure-function claims like "supports liver health" are permitted with a disclaimer, while disease-related claims such as "treats liver damage" are prohibited without drug approval. The EU generally prohibits both types of claims without substantial scientific validation through EFSA review.
Recent regulatory trends indicate increasing scrutiny of botanical supplements globally, with growing emphasis on standardization, clinical evidence, and transparent supply chain documentation. For luteolin-based liver supplements to achieve regulatory compliance across major markets, manufacturers must navigate these complex and evolving requirements while building stronger scientific foundations for their products.
The European Union employs a more stringent approach through the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA), which requires scientific substantiation for health claims on supplements. For liver-related botanical products, the EFSA has historically set high evidential standards, with many claims being rejected due to insufficient clinical data. The Traditional Herbal Medicinal Products Directive (THMPD) provides an alternative regulatory pathway for products with established traditional use.
In Asia, particularly China and Japan, regulatory frameworks often incorporate traditional medicine principles alongside modern scientific standards. China's National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) has specific categories for traditional Chinese medicine products that may include luteolin-containing herbs for liver health. Japan's regulatory system includes "Foods for Specified Health Uses" (FOSHU), which may encompass liver-supportive botanical ingredients.
Quality control requirements represent another critical regulatory dimension. Good Manufacturing Practices (GMPs) are mandated in most major markets, though enforcement stringency varies. For luteolin supplements specifically, standardization of active compound content remains challenging due to natural variation in botanical sources and extraction methods.
Safety monitoring systems also differ globally. The FDA's adverse event reporting system for supplements is largely post-market and voluntary, while the EU maintains more proactive pharmacovigilance requirements. This regulatory divergence creates challenges for global manufacturers of luteolin-based liver supplements.
Labeling regulations present additional complexity. In the US, structure-function claims like "supports liver health" are permitted with a disclaimer, while disease-related claims such as "treats liver damage" are prohibited without drug approval. The EU generally prohibits both types of claims without substantial scientific validation through EFSA review.
Recent regulatory trends indicate increasing scrutiny of botanical supplements globally, with growing emphasis on standardization, clinical evidence, and transparent supply chain documentation. For luteolin-based liver supplements to achieve regulatory compliance across major markets, manufacturers must navigate these complex and evolving requirements while building stronger scientific foundations for their products.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!